

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (1): 60-67.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.01.008
• Special volume for green,yield increasing,quality improving and efficiency improving technologies for major grain crops in Xinjing • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Lin1( ), HUANG Qiannan1, YANG Hui1, Dengsilamu Tuerxunbai1, ZOU Hui1, SUN Na1(
), HUANG Qiannan1, YANG Hui1, Dengsilamu Tuerxunbai1, ZOU Hui1, SUN Na1( ), LEI Junjie2(
), LEI Junjie2( )
)
Received:2024-08-11
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-03-11
Correspondence author:
SUN Na, LEI Junjie
Supported by:
马林1( ), 黄倩楠1, 杨蕙1, 登斯拉木·吐尔逊拜1, 邹辉1, 孙娜1(
), 黄倩楠1, 杨蕙1, 登斯拉木·吐尔逊拜1, 邹辉1, 孙娜1( ), 雷钧杰2(
), 雷钧杰2( )
)
通讯作者:
孙娜,雷钧杰
作者简介:马林(1993-),男,甘肃人,助理研究员,研究方向为小麦遗传育种与栽培,(E-mail)1330846112@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
MA Lin, HUANG Qiannan, YANG Hui, Dengsilamu Tuerxunbai, ZOU Hui, SUN Na, LEI Junjie. Effects of different nitrogen fertilizers with humic acid strategies on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of winter wheat[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 60-67.
马林, 黄倩楠, 杨蕙, 登斯拉木·吐尔逊拜, 邹辉, 孙娜, 雷钧杰. 不同氮肥配施腐殖酸策略对冬小麦光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 60-67.
| 处理 Treat- ments | 基施 Basal application (kg/667 m2) | 追施 Dressing (kg/667 m2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18-磷 酸二铵 18-DAP | 16-磷 酸二铵 16-DAP | 尿素 Urea | 腐殖酸尿素 Humic acid urea | |
| CK | - | - | - | - |
| T1 | 25.00 | - | 20.29 | - |
| T2 | - | 25.00 | 20.29 | - |
| T3 | 25.00 | - | - | 20.29 |
| T4 | - | 25.00 | - | 20.29 |
Tab. 1 Experiment treatments
| 处理 Treat- ments | 基施 Basal application (kg/667 m2) | 追施 Dressing (kg/667 m2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18-磷 酸二铵 18-DAP | 16-磷 酸二铵 16-DAP | 尿素 Urea | 腐殖酸尿素 Humic acid urea | |
| CK | - | - | - | - |
| T1 | 25.00 | - | 20.29 | - |
| T2 | - | 25.00 | 20.29 | - |
| T3 | 25.00 | - | - | 20.29 |
| T4 | - | 25.00 | - | 20.29 |

Fig.1 Changes of winter wheat leaf area index under different fertilization strategies Notes: CK: No nitrogen treatment; T1: basal application of 18-DAP+topdressing of urea; T2: Base application of 16-DAP+topdressing of urea; T3: basal application of 18-DAP+topdressing of humic acid urea; T4: Base application of 16-DAP+topdressing of humic acid urea. The shaded areas in the figure represent standard errors in processing, while non overlapping shadows indicate significant differences in processing during the same period (P<0.05),the same as below
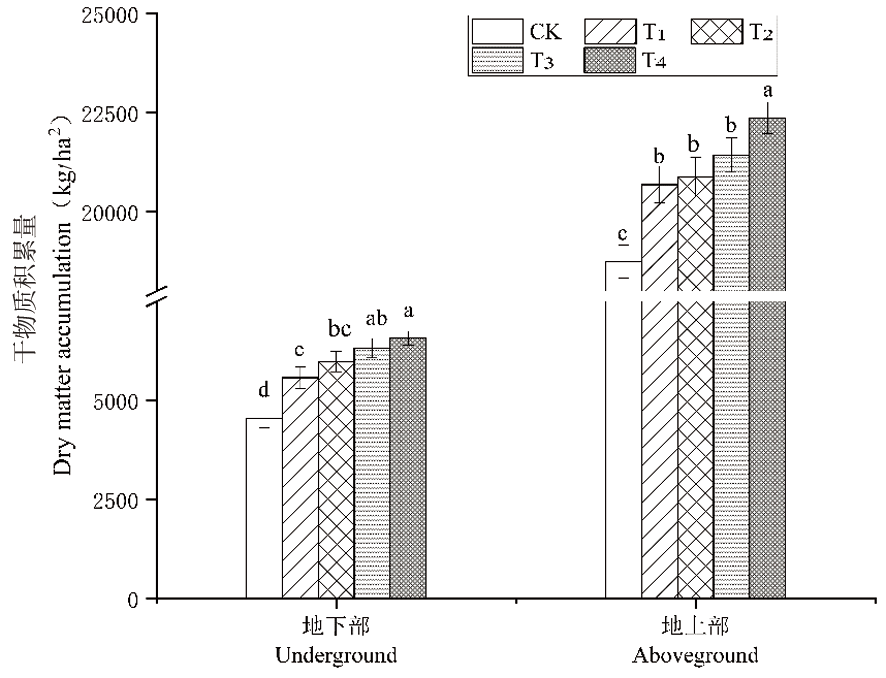
Fig.4 Changes of winter wheat aboveground and underground biomass under different fertilization strategies Notes: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in different treatments during the same period (P<0.05),the same as below
| 处理 Treatments | 穗数 Number (104株/ 667 m2) | 穗粒数 Number (粒) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Yield (kg/667 m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 22.13c | 37.42c | 43.78b | 455.37c |
| T1 | 27.44b | 41.22b | 45.51a | 526.25b |
| T2 | 28.81ab | 41.62b | 45.83a | 520.51b |
| T3 | 28.67ab | 42.47ab | 46.08a | 535.63ab |
| T4 | 29.22a | 43.14a | 46.25a | 550.84a |
Tab.2 Winter wheat yield and yield composition under different fertilization strategies
| 处理 Treatments | 穗数 Number (104株/ 667 m2) | 穗粒数 Number (粒) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Yield (kg/667 m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 22.13c | 37.42c | 43.78b | 455.37c |
| T1 | 27.44b | 41.22b | 45.51a | 526.25b |
| T2 | 28.81ab | 41.62b | 45.83a | 520.51b |
| T3 | 28.67ab | 42.47ab | 46.08a | 535.63ab |
| T4 | 29.22a | 43.14a | 46.25a | 550.84a |
| [1] | Du Y, Niu W, Zhang Q, et al. A synthetic analysis of the effect of water and nitrogen inputs on wheat yield and water-and nitrogen-use efficiencies in China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2021, 265: 108105. |
| [2] | Zhang Pengyan, Wang Maodong, Yu Lianyu, et al. Optimization of water and nitrogen management in wheat cultivation affected by biochar application-insights into resource utilization and economic benefits[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2024, 304: 109093. |
| [3] | 裴雪霞, 党建友, 张定一, 等. 化肥减量配施有机肥对旱地小麦产量, 品质和水分利用率的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2021, 35(4): 250-258. |
| PEI Xuexia, DANG Jianyou, ZHANG Dingyi, et al. Effects of chemical fertilizer reduction combined with or ganie fertilizer on the yield, quality, and water use efficiency of dryland wheat[J] Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 202l, 35(4):250. | |
| [4] | 殷永娴, 刘鸿雁. 设施栽培下土壤中硝化、反硝化作用的研究[J]. 生态学报, 1996, 16(3):248. |
| YIN Yongxian, LIU Hongyan. Investigation on nitrification and denitrification of soil under installing cultivation conditions[J]. Acta EcologicaSinica, 1996, 16(3): 248. | |
| [5] |
Mehmood F, Wang, Gao Y, et al. Nitrous oxide emission from winter wheat field as responded to irrigation scheduling and irrigation methods in the North China Plain[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2019, 222: 367-374.
DOI |
| [6] | Kong Lingan, Xie Yan, Hu Ling, et al. Remobilization of vegetative nitrogen to developing grain in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)[J]. Field Crops Research, 2016, 196: 134-144. |
| [7] | 李书田, 刘晓永, 何萍. 当前我国农业生产中的养分需求分析[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(6): 1417. |
| LI Shutian, LIU Xiaoyong, HE Ping. Analyses on nutrient requirements incurrent agriculture production in China[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2017, 23(6): 1417. | |
| [8] | Liu Xuejing, Yin Baozhong, Bao Xiaoyuan, et al. Optimization of irrigation period improves wheat yield by regulating source-sink relationship under water deficit[J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 2024, 156: 127164. |
| [9] |
刘盛林, 董晓霞, 孙泽强, 等. 尿素中添加腐植酸提升冬小麦产量和氮吸收效率[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(14):16-21.
DOI |
|
LIU Shenglin, DONG Xiaoxia, SUN Zeqiang, et al. Humic Acid Added in Urea proves Yield and Nitrogen Uptake of Winter Wheat[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(14):16-21.
DOI |
|
| [10] | 袁晶晶, 同延安, 卢绍辉, 等. 生物炭与氮肥配施改善土壤团聚体结构提高红枣产量[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34: 159-165. |
| YUAN Jingjing, TONG Yanan, LU Shaohui, et al. Biochar and nitrogen amendments improving soil aggregate structure and jujube yields[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 201834:159-165 | |
| [11] | 张贺, 杨静, 周吉祥, 等. 连续施用土壤改良剂对砂质潮土团聚体及作物产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27: 791-801. |
| ZHANG He, YANG Jing, ZHOU Jixiang, et al. Effects of organic and inorganic amendments on aggregation and crop yields in sandy fluvo-aguic soil[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2021,27: 791-801. | |
| [12] | Aghajani S D, Alavifazel M, Nurmohammadi G, et al. Soil respiration, root traits and dry matter yield of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) as affected by biochar application under different cropping patterns and irrigation method[J]. International Agrophysics, 2020, 34(4): 495-502. |
| [13] | 宋世龙, 杨卫君, 陈雨欣, 等. 氮肥减量配施生物炭对北疆灌区春小麦光合和干物质转运特性及产量的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2023, 43: 311-320. |
| SONG Shilong, YANG Weijun, CHEN Yuxin, et al. Effect of reduced nitrogen fertilizer combined with biochar on photosynthetic characteristics, dry matter accumulation and distribution, and yield of spring wheat in irrigated area of Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Crops, 2023, 43: 311-320. | |
| [14] | Li Weiwei, Ahmad Sajjad, Liu Dun, et al. Subsurface banding of blended controlled-release urea can optimize rice yields while minimizing yield-scaled greenhouse gas emissions[J]. The Crop Journal, 2023, 11(3): 914-921. |
| [15] | Liu Tingna, Su Yongzhong, Niu Ziru, et al. Attapulgite application improves maize yield, water, and fertilizer utilization efficiency in newly cultivated sandy farmland in northwestern China[J]. Arid Land Research and Management, 2023, 37(3): 408-426. |
| [16] | Liu Xiaoyuan, Yang Jingsong, Tao Jianyu, et al. Integrated application of inorganic fertilizer with fulvic acid for improving soil nutrient supply and nutrient use efficiency of winter wheat in a salt-affected soil[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2022, 170: 104255. |
| [17] | 王艳哲, 刘秀位, 孙宏勇, 等. 水氮调控对冬小麦根冠比和水分利用效率的影响研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(3): 283. |
| WANG Yanzhe, LIU Xiuwei, SUN Hongyong, et al. Effects of water and nitrogen on root/shoot ratio and water use efficiency of winter wheat[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2013, 21(3):283. | |
| [18] | 王丽芳, 康娟, 马耕, 等. 农田施氮对冬小麦产量, 根-冠氮素积累及其利用效率的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2021, 41(11): 1403-1408. |
| WANG Lifang, KANG Juan, MA Geng, et al. Effect of Nitrogen Application on Yield, Nitrogen Accumulation and Use Efficiency in Root-Shoot of Winter Wheat[J]. Journal of Triticeas Crops, 2021, 41(11): 1403-1408. | |
| [19] | 缑培欣, 陈智勇, 张阳阳, 等. 不同类型肥料对潮土冬小麦产量和品质及氮肥利用效率的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2021, 41(8): 1023-1032. |
| HOU Peixin, CHEN Zhiyong, ZHANG Yangyang, et al. Effect of Different Types of Fertilizers on Yield, Quality and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Winter Wheat in Alluvial Soil Farmland[J]. Journal of Triticeas Crops, 2021, 41(8): 1023-1032. | |
| [20] | 涂攀峰, 陈小娟, 杨依彬, 等. 不同含铵磷源在石灰性土壤中氮磷元素的有效性及对玉米生长的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2019, 47(23): 170-173. |
| TU Panfeng, CHEN Xiaojuan, YANG Yibin, et al. Effectiveness of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Calcareous Soil from Different Sources of Ammonium and Phosphorus and Their Effects on Maize Growth[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(23): 170-173. | |
| [21] | 康飞, 孟凡乔. 基于文献分析的北方冬麦田氨挥发特性[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(1): 228-234. |
| KANG Fei, MENG Fanqiao. Ammonia volatilization from winter wheat cropland in Norther China based on a literature analysis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(1): 228-234. | |
| [22] | 邢素丽, 李孝兰, 杨军芳, 等. 新型尿素对小麦产量和氮肥利用率的应用效果研究[J]. 河北农业科学, 2017, 21(6): 40-43. |
| XING Suli, LI Xiaolan, YANG Junfang, et al. Application effect of new urea on wheat yield and utilization rate of nitrogen fertilizer[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural Science, 2017, (6):40-43. | |
| [23] | 刘红恩, 张胜男, 刘世亮, 等. 腐植酸尿素对冬小麦产量, 养分吸收利用和土壤养分的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2018, 27(7): 944. |
| LIU Hongen, ZHANG Shengnan, LIU Shiliang, et al. Effects of humic acid urea onwinter wheat yield, nutrient absorption and utilization,and soil nutrients[J]. Acta AgriculturaeBoreali-OccidentalisSinica, 2018, 27(7):944-952. | |
| [24] | 于正国, 袁亮, 赵秉强, 等. 腐植酸与尿素结合工艺对尿素在潮土中转化的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022, (1): 206-212. |
| YU Zhengguo, YUAN Liang, ZHAO Bingqiang, et al. Effect of the combination of humic acid and urea on the conversion of urea in fluvo-aquic soil[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2022, (1): 206-212. | |
| [25] |
Campitelli P A, Velasco M I, Ceppi S B. Chemical and physicochemical characteristics of humic acids extracted from compost, soil and amended soil[J]. Talanta, 2006, 69(5): 1234-1239.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Shen Yuwen, Lin Haitao, Gao Wensheng, et al. The effects of humic acid urea and poly aspartic acid urea on reducing nitrogen loss compared with urea[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2020, 100(12): 4425-4432.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | 王欢, 苏文平, 赵鑫琳. 不同水氮处理对冬播春小麦产量和水氮利用效率的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2022, 42(11): 1381-1390. |
| WANG Huan, SU Wenping, ZHAO Xinlin. Effect of Different Irrigation and Nitrogen Application on Yield, Waterand Nitrogen UseEfficiency of Spring Wheat Sown in Winter[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2022, 42(11): 1381-1390. | |
| [28] |
聂峥睿, 坚天才, 张战胜, 等. 施氮量对花后高温春小麦源库特征及关系的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2024, 38(12): 2421-2431.
DOI |
| NIE Zhengrui, JIAN Tiancai, ZHANG Zhansheng, et al. Effects of Nitrogen Rates on Source-Sink Characteristics and Relationship of Spring Wheat after Anthesis under High Temperature[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2024, 38(12): 2421-2431. | |
| [29] | MA Zhentao, ZHANG Zhen, WANG Xizhi, et al. Effect of Nitrogen Management Practices on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Grain Yield of Wheat in High-Fertility Soil[J]. Agronomy, 2024, 14(10): 2197. |
| [30] | 曲文凯, 徐学欣, 赵金科, 等. 施氮对滴灌冬小麦花后光合生理, 灌浆特性及产量品质的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2022, 36(5): 327-336. |
| QU Wenkai, XU Xuexin, ZHAO Jinke, et al. Effect of Nitrogen Application on Photosynthetic Physiology, Grain-Filling Characteristics and Yield and Quality After Anthesis of Winter Wheat Under Drip Irrigation[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 36(5): 327-336. | |
| [31] | 郝水源, 李林虎, 闫素珍, 等. 不同施肥方式对河套灌区春小麦光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 内蒙古农业大学学报, 2018,(1): 10-16. |
| HAO Shuiyuan, LI Linhu, YAN Suzhen, et al. Effect of different fertilization systems on spring wheat and photosynthesis characteristic and yield in HETAO irrigation district[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2018,(1): 10-16. | |
| [32] | Mora V, Baigorri R, Bacaicoa E, et al. The humic acid-induced changes in the root concentration of nitric oxide, IAA and ethylene do not explain the changes in root architecture caused by humic acid in cucumber[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2012, 76: 24-32. |
| [33] |
Mora V, Bacaicoa E, Zamarreno A M, et al. Action of humic acid on promotion of cucumber shoot growth involves nitrate-related changes associated with the root-to-shoot distribution of cytokinins, polyamines and mineral nutrients[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2010, 167(8): 633-642.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | SUN Na, MA Lin, ZOU Hui, ZHANG Zhihui, ZHANG Shengjun, HUANG Qiannan, YANG Hui, Dengsilamu Tuerxunbai, LI Zhibin, CAO Junmei, LEI Junjie. Analysis of combined application of NPK fertilizers on yield and quality of winter wheat and the fertilizer effect [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 1-12. |
| [2] | DU Yalong, FU Qiuping, AI Pengrui, MA Yingjie, QI Tong, PAN Yang. Comprehensive evaluation of irrigation treatment based on the growth and yield of drip-irrigated Gossypium barbadense [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 161-173. |
| [3] | XIE Xiurong, ZHANG Yongqiang, HAI Feng, LEI Junjie, LYU Xiaoqing, CHEN Chuanxin, XU Qijiang, NIE Shihui, WANG Jichuan. Effects of uniform sowing and densification on population structure and yield of late sowing winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 21-28. |
| [4] | HU Mengting, LIU Shengyao, JIA Songnan, FAN Fengcui, DU Fenghuan, LI Jingsong, QIN Yong. Effects of different planting row spacings on yield and water use efficiency of spinach [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 217-224. |
| [5] | ZHANG Yanting, ZHANG Yongqiang, LEI Junjie, CHEN Hui, CHEN Chuanxin, XU Qijiang, NIE Shihui, XU Wenxiu. Effects of different phosphorus application modes on photosynthetic physiological characteristics and yield of Dry-Seeded and Wet-Emerged winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 29-36. |
| [6] | ZHANG Jingcan, XU Qijiang, ZHANG Yongqiang, LEI Junjie, LYU Xiaoqing, CHEN Chuanxin, NIE Shihui, XU Wenxiu. Effects of different growth regulator and its application times on stem characteristics and lodging resistance of winter wheat under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 37-44. |
| [7] | HAI Feng, ZHANG Yongqiang, XIE Xiurong, LYU Xiaoqing, CHEN Chuanxin, XU Qijiang, NIE Shihui, WANG Jichuan, LEI Junjie. Effects of different drip irrigation rates on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of drip irrigated winter wheat under limited irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 45-52. |
| [8] | LI Jie, XU Qijiang, ZHANG Yongqiang, XU Wenxiu, LYU Xiaoqing, CHEN Chuanxin, NIE Shihui, LEI Junjie. Effects of different urea and application methods on photosynthetic characteristics, yield formation and nitrogen use efficiency of winter wheat under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 53-59. |
| [9] | CHEN Chuanxin, ZHANG Yongqiang, NIE Shihui, XU Qijiang, LEI Junjie. Effect of microbial agents combined with nitrogen fertilizer on the photosynthetic characteristics and yield of winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 68-74. |
| [10] | LI Na, LYU Caixia, Xin Huinan, LI Yongfu, LAI Ning, GENG Qinglong, CHEN Shuhuang. Effects of different nitrogen application rates on the characteristics and root zone soil nutrients of drip irrigation wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 87-94. |
| [11] | FANG Hui, DING Yindeng, FAN Guiqiang, GAO Yonghong, HUANG Tianrong. Research report on the development status of wheat industry in southern Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 75-80. |
| [12] | ZHANG Zehua, YE Hanchun, WANG Zhenhua, LI Wenhao, LI Haiqiang, LIU Jian. Effects of equal nitrogen applied with urease inhibitor on cotton growth, yield, and quality under mulched drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2103-2111. |
| [13] | CHEN Ruijie, LUO Linyi, RUAN Xiangyang, YE Jun. Effects of humic acid on soil nutrients, cotton yield and quality in cotton fields under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2112-2121. |
| [14] | HUANG Boxuan, LI Pengcheng, ZHENG Cangsong, SUN Miao, SHAO Jingjing, FENG Weina, PANG Chaoyou, XU Wenxiu, DONG Helin. Effects of different nitrogen inhibitors on growth, nitrogen utilization and yield of cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2122-2131. |
| [15] | CHEN Fang, LI Zihui, SUNXiaogui , ZHANG Tingjun. Different dosage of microbial agents on the yield and quality of processed tomatoes [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2285-2289. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 26
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||