

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (1): 68-74.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.01.009
• Special volume for green,yield increasing,quality improving and efficiency improving technologies for major grain crops in Xinjing • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Chuanxin( ), ZHANG Yongqiang, NIE Shihui, XU Qijiang, LEI Junjie(
), ZHANG Yongqiang, NIE Shihui, XU Qijiang, LEI Junjie( )
)
Received:2024-05-21
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-03-11
Correspondence author:
LEI Junjie
Supported by:通讯作者:
雷钧杰
作者简介:陈传信(1988-),男,河南商丘人,助理研究员,硕士,研究方向为作物高产栽培生理,(E-mail)lixp618@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
CHEN Chuanxin, ZHANG Yongqiang, NIE Shihui, XU Qijiang, LEI Junjie. Effect of microbial agents combined with nitrogen fertilizer on the photosynthetic characteristics and yield of winter wheat[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 68-74.
陈传信, 张永强, 聂石辉, 徐其江, 雷钧杰. 微生物菌剂与氮肥配施对冬小麦光合特性和产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 68-74.
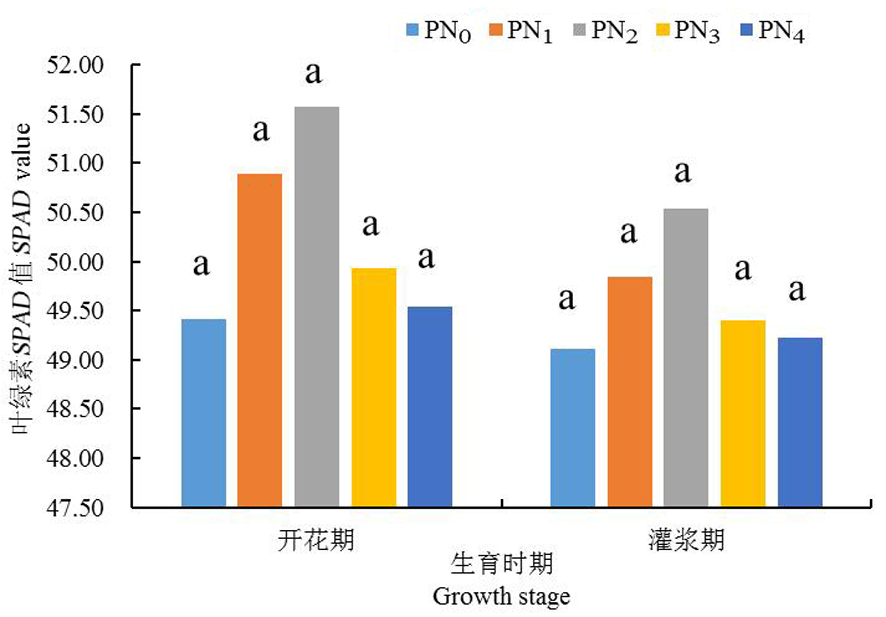
Fig.1 Changes of different treatments on SPAD value of winter wheat Notes:The letters on the column indicate the differences between different treatments during the same period (P<0.05),the same as below
| 处理 Treat- ments | 穗数 Spike number (104穗/hm2) | 穗粒数 (个) Grains per spike (piece) | 千粒重 1000- grain weight (g) | 产量 Yield (kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PN0 | 654.80c | 37.67b | 38.04c | 8 116.90d |
| PN1 | 710.90ab | 42.00a | 44.87ab | 10 496.31b |
| PN2 | 745.95a | 43.33a | 46.34a | 11 496.31a |
| PN3 | 697.40bc | 40.00ab | 43.23ab | 9 528.57c |
| PN4 | 676.60bc | 39.33ab | 42.14b | 9 369.76c |
Tab.1 Changes of different treatments on winter wheat yield and yield components
| 处理 Treat- ments | 穗数 Spike number (104穗/hm2) | 穗粒数 (个) Grains per spike (piece) | 千粒重 1000- grain weight (g) | 产量 Yield (kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PN0 | 654.80c | 37.67b | 38.04c | 8 116.90d |
| PN1 | 710.90ab | 42.00a | 44.87ab | 10 496.31b |
| PN2 | 745.95a | 43.33a | 46.34a | 11 496.31a |
| PN3 | 697.40bc | 40.00ab | 43.23ab | 9 528.57c |
| PN4 | 676.60bc | 39.33ab | 42.14b | 9 369.76c |
| [1] | 赵广才, 常旭虹, 王德梅, 等. 小麦生产概况及其发展[J]. 作物杂志, 2018,(4): 1-7. |
| ZHAO Guangcai, CHANG Xuhong, WANG Demei, et al. General situation and development of wheat production[J]. Crops, 2018,(4): 1-7. | |
| [2] | 张玲, 曹环, 刘平. 有机肥等氮量替代尿素对小麦产量及氮肥利用效率的影响[J]. 现代农业科技, 2023,(20): 1-3, 7. |
| ZHANG Ling, CAO Huan, LIU Ping. Effects of replacing urea with organic fertilizer and other nitrogen amounts on wheat yield and nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023,(20): 1-3, 7. | |
| [3] |
德木其格, 刘志萍, 王磊, 等. 不同施氮水平对大麦光合性能及氮素积累和转运的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2020, 35(3): 126-135.
DOI |
| Demuqige, LIU Zhiping, WANG Lei, et al. Effects of different nitrogen levels on photosynthetic performance, nitrogen accumulation and translocation of barley[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2020, 35(3): 126-135. | |
| [4] |
刘笑鸣, 顾万荣, 李从锋, 等. 化学调控和氮肥对高密度下春玉米光热水利用效率和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2020, 53(15): 3083-3094.
DOI |
|
LIU Xiaoming, GU Wanrong, LI Congfeng, et al. Effects of chemical regulation and nitrogen fertilizer on radiation, heat and water utilization efficiency and yield of spring maize under dense planting condition[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2020, 53(15): 3083-3094.
DOI |
|
| [5] | 杨雯玉, 贺明荣, 王远军, 等. 控释尿素与普通尿素配施对冬小麦氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2005, 11(5): 627-633. |
| YANG Wenyu, HE Mingrong, WANG Yuanjun, et al. Effect of controlled-release urea combined application with urea on nitrogen utilization efficiency of winter wheat[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizing Science, 2005, 11(5): 627-633. | |
| [6] | 张福锁, 王激清, 张卫峰, 等. 中国主要粮食作物肥料利用率现状与提高途径[J]. 土壤学报, 2008, 45(5): 915-924. |
| ZHANG Fusuo, WANG Jiqing, ZHANG Weifeng, et al. Nutrient use efficiencies of major cereal crops in China and measures for improvement[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2008, 45(5): 915-924. | |
| [7] | 邵秀丽, 王吉庆, 张慎璞, 等. 微生物菌剂与尿素配施对大蒜氮吸收及产量的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2013,(16): 199-202. |
| SHAO Xiuli, WANG Jiqing, ZHANG Shenpu, et al. Effects of complex bacteria with urea combined application on the yield and nitrogen uptake of garlic[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2013,(16): 199-202. | |
| [8] |
钱海燕, 杨滨娟, 黄国勤, 等. 秸秆还田配施化肥及微生物菌剂对水田土壤酶活性和微生物数量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2012, 21(3): 440-445.
DOI |
| QIAN Haiyan, YANG Binjuan, HUANG Guoqin, et al. Effects of returning rice straw to fields with fertilizers and microorganism liquids on soil enzyme activities and microorganisms in paddy fields[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2012, 21(3): 440-445. | |
| [9] | 王涛, 乔卫花, 李玉奇, 等. 轮作和微生物菌肥对黄瓜连作土壤理化性状及生物活性的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2011, 42(3): 578-583. |
| WANG Tao, QIAO Weihua, LI Yuqi, et al. Effects of rotation and microbial fertilizers on the properties of continuous cucumber cropping soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2011, 42(3): 578-583. | |
| [10] | 方成, 岳明灿, 王东升, 等. 化肥减施配施微生物菌剂对鲜食玉米生长和土壤肥力的影响[J]. 土壤, 2020, 52(4): 743-749. |
| FANG Cheng, YUE Mingcan, WANG Dongsheng, et al. Effects of fertilizer reduction combined with microbial agent application on growth and soil fertility of fresh corn[J]. Soils, 2020, 52(4): 743-749. | |
| [11] |
高雁, 张永强, 张志东, 等. 功能性微生物菌剂对小麦生长和根际土壤生态的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(1): 115-124.
DOI |
|
GAO Yan, ZHANG Yongqiang, ZHANG Zhidong, et al. Effects of functional microbial agents on wheat growth and rhizosphere soil micro-ecology[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(1): 115-124.
DOI |
|
| [12] | 张雅楠, 汤婧, 燕香梅, 等. 氮肥减量配施菌剂对水稻土养分及水稻产量的影响[J]. 辽宁农业科学, 2019,(3): 1-6. |
| ZHANG Yanan, TANG Jing, YAN Xiangmei, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer reduction combined with bacterial ingredients on paddy soil nutrients and rice yield[J]. Liaoning Agricultural Sciences, 2019,(3): 1-6. | |
| [13] | 肖让, 张永玲, 赵芸晨, 等. 不同抗旱措施配施菌肥对河西绿洲土壤改良和制种玉米产量的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2021, 35(3): 341-349. |
| XIAO Rang, ZHANG Yongling, ZHAO Yunchen, et al. Effects of different drought resistance measures combined with microbial fertilizer on soil amelioration and yield of seed maize in Hexi Corridor[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 35(3): 341-349. | |
| [14] |
张永强, 张璐, 陈传信, 等. 拔节期氮肥运筹对不同滴灌量下冬小麦光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(16): 1-6.
DOI |
|
ZHANG Yongqiang, ZHANG Lu, CHEN Chuanxin, et al. Nitrogen application at jointing stage under different drip irrigation amount: effects on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of winter wheat[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(16): 1-6.
DOI |
|
| [15] | 王琦, 李俊, 李润发. 微生物菌剂对小白菜营养生长及产量效应的研究[J]. 基层农技推广, 2017, 5(7): 35-36. |
| WANG Qi, LI Jun, LI Runfa. Effects of microbial agents on vegetative growth and yield of Chinese cabbage[J]. Primary Agricultural Technology Extension, 2017, 5(7): 35-36. | |
| [16] |
方辉, 范贵强, 高永红, 等. 施氮对不同小麦品种光合荧光特性及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(1): 55-62.
DOI |
|
FANG Hui, FAN Guiqiang, GAO Yonghong, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on photosynthetic fluorescence and yield of different wheat varieties[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(1): 55-62.
DOI |
|
| [17] | 肖明纲, 杨贤莉, 孙兵, 等. 减肥配施微生物菌剂对五优稻四号抗倒性和产量的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2020, 48(21): 156-158. |
| XIAO Minggang, YANG Xianli, SUN Bing, et al. Effect of reduced fertilizer and utilization of microbial inoculant on lodging resistance and yield of wuyoudao 4[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(21): 156-158. | |
| [18] | 李红宇, 周雪松, 杨锡铜, 等. 减氮施肥对寒地水稻产量品质及抗倒性的影响[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报, 2019, 31(5): 1-8. |
| LI Hongyu, ZHOU Xuesong, YANG Xitong, et al. Effects of decrease fertilizer nitrogen on yield, quality and lodging resistance traits of rice in cold region[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2019, 31(5): 1-8. | |
| [19] | 常会庆, 李兆君. 腐植酸尿素与复合微生物菌剂配施对番茄产量和品质的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 2016, 45(4): 113-116. |
| CHANG Huiqing, LI Zhaojun. Effects of combined application of humic acid urea and compound microbial agents on yield and quality of tomato[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 45(4): 113-116. | |
| [20] | 范秀勤, 黄文祥. 微生物菌剂对番茄生长的影响[J]. 上海蔬菜, 2017,(2): 70-71. |
| FAN Xiuqin, HUANG Wenxiang. Effects of microbial agents on tomato growth[J]. Shanghai Vegetables, 2017,(2): 70-71. | |
| [21] | 李丽, 韩周, 张昀, 等. 减氮配施菌剂对水稻土酶活性及水稻根系生长的影响[J]. 辽宁农业科学, 2019,(2): 1-7. |
| LI Li, HAN Zhou, ZHANG Yun, et al. Effects of application of reducing nitrogen combined with microbial agents on paddy soil enzyme activity and rice root growth[J]. Liaoning Agricultural Sciences, 2019,(2): 1-7. |
| [1] | SUN Na, MA Lin, ZOU Hui, ZHANG Zhihui, ZHANG Shengjun, HUANG Qiannan, YANG Hui, Dengsilamu Tuerxunbai, LI Zhibin, CAO Junmei, LEI Junjie. Analysis of combined application of NPK fertilizers on yield and quality of winter wheat and the fertilizer effect [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 1-12. |
| [2] | CHEN Hui, ZHANG Yongqiang, BI Haiyan, TANJun , CHEN Chuanxin, XU Qijiang, NIE Shihui, YU Jianxin, LU Dong, LEI Junjie. Yield formation characteristics of different spring wheat varieties in dryland farming area of Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 13-20. |
| [3] | DU Yalong, FU Qiuping, AI Pengrui, MA Yingjie, QI Tong, PAN Yang. Comprehensive evaluation of irrigation treatment based on the growth and yield of drip-irrigated Gossypium barbadense [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 161-173. |
| [4] | XIE Xiurong, ZHANG Yongqiang, HAI Feng, LEI Junjie, LYU Xiaoqing, CHEN Chuanxin, XU Qijiang, NIE Shihui, WANG Jichuan. Effects of uniform sowing and densification on population structure and yield of late sowing winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 21-28. |
| [5] | HU Mengting, LIU Shengyao, JIA Songnan, FAN Fengcui, DU Fenghuan, LI Jingsong, QIN Yong. Effects of different planting row spacings on yield and water use efficiency of spinach [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 217-224. |
| [6] | ZHANG Yanting, ZHANG Yongqiang, LEI Junjie, CHEN Hui, CHEN Chuanxin, XU Qijiang, NIE Shihui, XU Wenxiu. Effects of different phosphorus application modes on photosynthetic physiological characteristics and yield of Dry-Seeded and Wet-Emerged winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 29-36. |
| [7] | ZHANG Jingcan, XU Qijiang, ZHANG Yongqiang, LEI Junjie, LYU Xiaoqing, CHEN Chuanxin, NIE Shihui, XU Wenxiu. Effects of different growth regulator and its application times on stem characteristics and lodging resistance of winter wheat under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 37-44. |
| [8] | HAI Feng, ZHANG Yongqiang, XIE Xiurong, LYU Xiaoqing, CHEN Chuanxin, XU Qijiang, NIE Shihui, WANG Jichuan, LEI Junjie. Effects of different drip irrigation rates on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of drip irrigated winter wheat under limited irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 45-52. |
| [9] | LI Jie, XU Qijiang, ZHANG Yongqiang, XU Wenxiu, LYU Xiaoqing, CHEN Chuanxin, NIE Shihui, LEI Junjie. Effects of different urea and application methods on photosynthetic characteristics, yield formation and nitrogen use efficiency of winter wheat under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 53-59. |
| [10] | MA Lin, HUANG Qiannan, YANG Hui, Dengsilamu Tuerxunbai, ZOU Hui, SUN Na, LEI Junjie. Effects of different nitrogen fertilizers with humic acid strategies on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 60-67. |
| [11] | WANG Zijian, LI Liulong, ZHAO Yanhui, XU Linfeng, QIU Zhizhong, LI Zhaofeng, LEI Junjie, WANG Xiao, WAN Wenliang, JIANG Dong. Effects of water and nitrogen coupling on canopy structure and photosynthetic rate of slope drip irrigated spring wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 75-86. |
| [12] | LI Na, LYU Caixia, Xin Huinan, LI Yongfu, LAI Ning, GENG Qinglong, CHEN Shuhuang. Effects of different nitrogen application rates on the characteristics and root zone soil nutrients of drip irrigation wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 87-94. |
| [13] | LI Jin, SHEN Yuyang, DENG Feifei, CHEN Jianghua, SUN Jingjing, LI Guangkuo, GAO Haifeng. Analysis of Occurrence Status and Control Strategies of Wheat Harmful Organisms in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 122-126. |
| [14] | FANG Hui, DING Yindeng, FAN Guiqiang, GAO Yonghong, HUANG Tianrong. Research report on the development status of wheat industry in southern Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 75-80. |
| [15] | WANG Chunsheng, LI Jianfeng, ZHANG Yueqiang, FAN Zheru, WANG Zhong, GAO Xin, SHI Jia, ZHANG Hongzhi, WANG Lihong, XIA Jianqiang, WANG Fangping, ZHAO Qi. Study on genotypic differences of anther culture ability in mainly cultivated spring wheat varieties in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2081-2086. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||