

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (1): 75-86.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.01.010
• Cultivation Physiology·Physiology and Biochemistry·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Genetics·Soil Fertilizer • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Zijian1( ), LI Liulong2, ZHAO Yanhui1, XU Linfeng1, QIU Zhizhong1, LI Zhaofeng1, LEI Junjie3, WANG Xiao2, WAN Wenliang1(
), LI Liulong2, ZHAO Yanhui1, XU Linfeng1, QIU Zhizhong1, LI Zhaofeng1, LEI Junjie3, WANG Xiao2, WAN Wenliang1( ), JIANG Dong1,2(
), JIANG Dong1,2( )
)
Received:2024-07-21
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-03-11
Correspondence author:
WAN Wenliang, JIANG Dong
Supported by:
王子健1( ), 李刘龙2, 赵焰辉1, 徐林峰1, 邱治中1, 李召锋1, 雷钧杰3, 王笑2, 万文亮1(
), 李刘龙2, 赵焰辉1, 徐林峰1, 邱治中1, 李召锋1, 雷钧杰3, 王笑2, 万文亮1( ), 姜东1,2(
), 姜东1,2( )
)
通讯作者:
万文亮,姜东
作者简介:王子健(1999-),男,安徽巢湖人,硕士研究生,研究方向为作物栽培,(E-mail)1281459828@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
WANG Zijian, LI Liulong, ZHAO Yanhui, XU Linfeng, QIU Zhizhong, LI Zhaofeng, LEI Junjie, WANG Xiao, WAN Wenliang, JIANG Dong. Effects of water and nitrogen coupling on canopy structure and photosynthetic rate of slope drip irrigated spring wheat[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 75-86.
王子健, 李刘龙, 赵焰辉, 徐林峰, 邱治中, 李召锋, 雷钧杰, 王笑, 万文亮, 姜东. 水氮耦合对斜坡滴灌春小麦冠层结构及光合速率的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 75-86.
| 处理 Treatments | 3叶1心 Three-leaf stage(%) | 拔节期 Jointing stage(%) | 孕穗期 Booting stage(%) | 开花期 Anthesis(%) | 乳熟期 Early milk stage(%) | 乳熟末期 Late milk stage(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌水Irrigation | 15 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 15 | 10 |
| 施氮Nitrogen | 15 | 35 | 25 | 15 | 10 | 0 |
Tab.1 Irrigation and nitrogen fertilization strategies at different growth stages
| 处理 Treatments | 3叶1心 Three-leaf stage(%) | 拔节期 Jointing stage(%) | 孕穗期 Booting stage(%) | 开花期 Anthesis(%) | 乳熟期 Early milk stage(%) | 乳熟末期 Late milk stage(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌水Irrigation | 15 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 15 | 10 |
| 施氮Nitrogen | 15 | 35 | 25 | 15 | 10 | 0 |
| 处理 Treatments | TR6H | TR8H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | ||
| W3 | N3 | 87.7a | 85.2a | 91a | 81.3a | 74.8a | 84.2a |
| N2 | 88.3a | 84.9a | 92.4a | 79.3a | 75.1a | 84.1a | |
| N1 | 84.5bc | 83.7ab | 86.7b | 76.6b | 71.3b | 82.4b | |
| N0 | 74.2d | 76.2d | 62.6e | 69.3d | |||
| W2 | N3 | 87.4a | 83.5ab | 92.4a | 80.8a | 70.9b | 84.5a |
| N2 | 85.2b | 83.6ab | 91a | 76.6b | 71.8b | 81.1b | |
| N1 | 83.1cd | 82.1bc | 84.4c | 73.3cd | 69c | 81.4b | |
| N0 | 71.7e | 73.6e | 61f | 68.8d | |||
| W1 | N3 | 84bc | 82.2bc | 87.6b | 75.6bc | 68.4c | 82b |
| N2 | 83.9bc | 82.8b | 88.2b | 72.3d | 69c | 78.6c | |
| N1 | 82d | 80.7c | 83.5c | 69e | 66.2d | 77.2c | |
| N0 | 67.1f | 71f | 58g | 65e | |||
| F | 灌水量(W) | 47.7** | 41** | 39.4** | 47.6** | 186.5** | 63.2** |
| 施氮量(N) | 42.4** | 323.2** | 442.5** | 38.8** | 505.8** | 486.1** | |
| W×N | 3.9* | 3.9** | 2.6* | 0.7 | 1.9 | 2.6* | |
Tab.2 Changes of plant height of wheat at flowering stage under different water and nitrogen treatments(cm)
| 处理 Treatments | TR6H | TR8H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | ||
| W3 | N3 | 87.7a | 85.2a | 91a | 81.3a | 74.8a | 84.2a |
| N2 | 88.3a | 84.9a | 92.4a | 79.3a | 75.1a | 84.1a | |
| N1 | 84.5bc | 83.7ab | 86.7b | 76.6b | 71.3b | 82.4b | |
| N0 | 74.2d | 76.2d | 62.6e | 69.3d | |||
| W2 | N3 | 87.4a | 83.5ab | 92.4a | 80.8a | 70.9b | 84.5a |
| N2 | 85.2b | 83.6ab | 91a | 76.6b | 71.8b | 81.1b | |
| N1 | 83.1cd | 82.1bc | 84.4c | 73.3cd | 69c | 81.4b | |
| N0 | 71.7e | 73.6e | 61f | 68.8d | |||
| W1 | N3 | 84bc | 82.2bc | 87.6b | 75.6bc | 68.4c | 82b |
| N2 | 83.9bc | 82.8b | 88.2b | 72.3d | 69c | 78.6c | |
| N1 | 82d | 80.7c | 83.5c | 69e | 66.2d | 77.2c | |
| N0 | 67.1f | 71f | 58g | 65e | |||
| F | 灌水量(W) | 47.7** | 41** | 39.4** | 47.6** | 186.5** | 63.2** |
| 施氮量(N) | 42.4** | 323.2** | 442.5** | 38.8** | 505.8** | 486.1** | |
| W×N | 3.9* | 3.9** | 2.6* | 0.7 | 1.9 | 2.6* | |
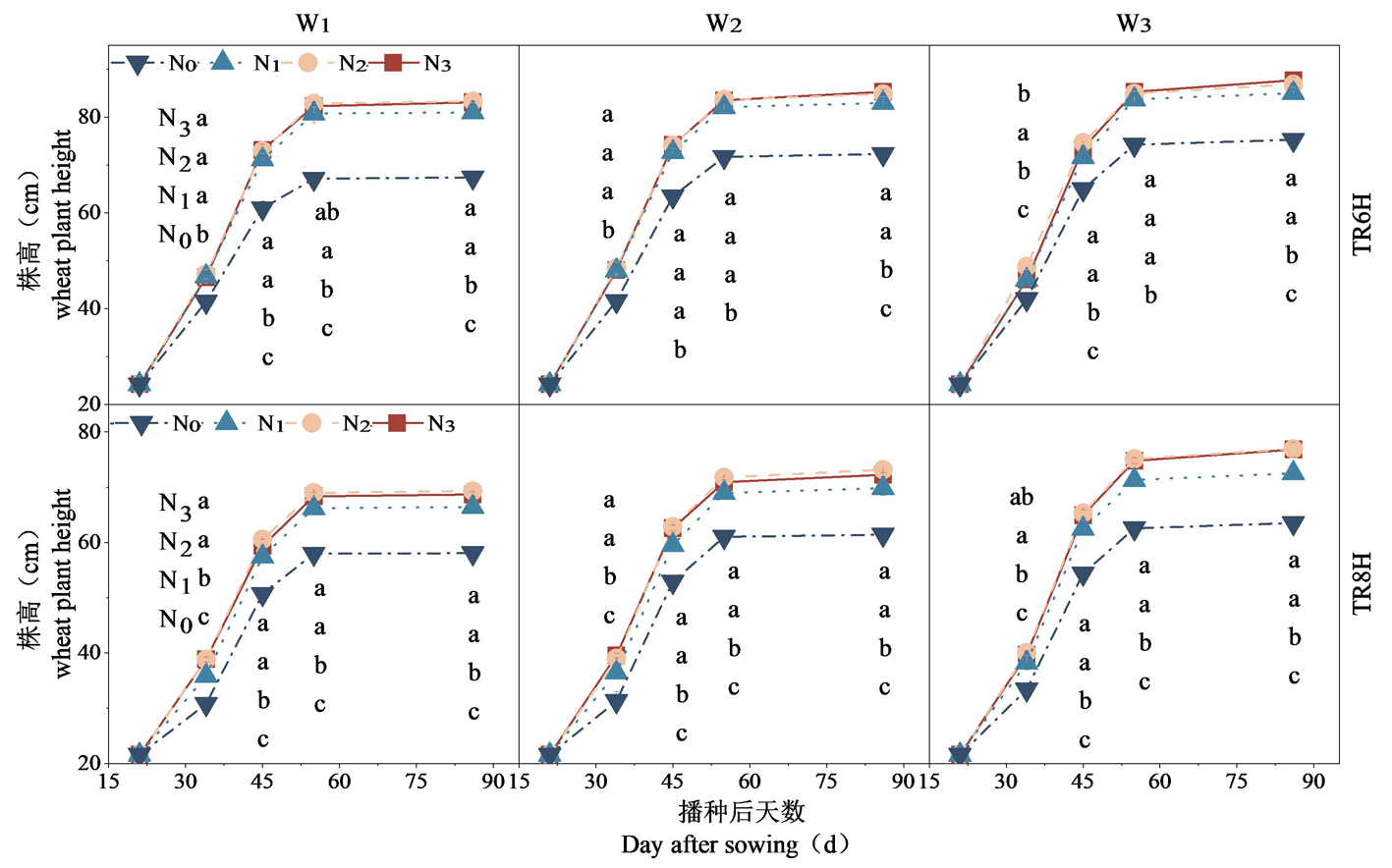
Fig.2 Changes of plant height dynamics of wheat during whole growth period under different water and nitrogen treatments Notes: The picture shows the plant height during the whole growth period in 2022, and the corresponding growth periods at each point from left to right are seedling stage, jointing stage, booting stage, flowering stage and maturity stage.Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different nitrogen treatments under the same mode and the same irrigation treatment at the same time (P<0.05), corresponding to N3, N2, N1 and N0 treatments from top to bottom, respectively
| 处理 Treatments | TR6H | TR8H | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 2023 | 2022 | 2023 | ||
| W3 | N3 | 25.4fg | 30de | 27.7e | 31.8e |
| N2 | 25.9fg | 28.5e | 25.1f | 29.4f | |
| N1 | 31.3de | 32.3cd | 28.4e | 33.8d | |
| N0 | 37.6b | 34.2bc | 34.2ab | 35.2cd | |
| W2 | N3 | 26.8f | 27.9e | 30.8cd | 30.5ef |
| N2 | 24.5g | 29.2e | 28.5e | 27.3g | |
| N1 | 32.2de | 30.2de | 29.2de | 34.2cd | |
| N0 | 37.6b | 34.9ab | 35.1a | 37.7ab | |
| W1 | N3 | 33.2cd | 32.7bc | 30.8cd | 31.6e |
| N2 | 30.9e | 32.1cd | 31.6c | 36.2bc | |
| N1 | 34.5c | 32.2cd | 32.4bc | 35.1cd | |
| N0 | 41.1a | 36.6a | 35.3a | 39.4a | |
| F | 灌水量(W) | 62** | 21.8** | 30.5** | 30.7** |
| 施氮量(N) | 170.5** | 41** | 53** | 68.7** | |
| W×N | 3.4* | 3.3* | 3.8** | 11.6** | |
Tab.3 Changes of flag leaf angles of wheat at flowering stage under different water and nitrogen treatments
| 处理 Treatments | TR6H | TR8H | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 2023 | 2022 | 2023 | ||
| W3 | N3 | 25.4fg | 30de | 27.7e | 31.8e |
| N2 | 25.9fg | 28.5e | 25.1f | 29.4f | |
| N1 | 31.3de | 32.3cd | 28.4e | 33.8d | |
| N0 | 37.6b | 34.2bc | 34.2ab | 35.2cd | |
| W2 | N3 | 26.8f | 27.9e | 30.8cd | 30.5ef |
| N2 | 24.5g | 29.2e | 28.5e | 27.3g | |
| N1 | 32.2de | 30.2de | 29.2de | 34.2cd | |
| N0 | 37.6b | 34.9ab | 35.1a | 37.7ab | |
| W1 | N3 | 33.2cd | 32.7bc | 30.8cd | 31.6e |
| N2 | 30.9e | 32.1cd | 31.6c | 36.2bc | |
| N1 | 34.5c | 32.2cd | 32.4bc | 35.1cd | |
| N0 | 41.1a | 36.6a | 35.3a | 39.4a | |
| F | 灌水量(W) | 62** | 21.8** | 30.5** | 30.7** |
| 施氮量(N) | 170.5** | 41** | 53** | 68.7** | |
| W×N | 3.4* | 3.3* | 3.8** | 11.6** | |
| 处理 Treatments | TR6H | TR8H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | ||
| W3 | N3 | 568.3bc | 585.8a | 585bc | 554.7b | 552a | 545.3b |
| N2 | 599.2a | 570.8bc | 592.5ab | 572a | 548a | 571.3a | |
| N1 | 554.2d | 561.7cd | 567.5d | 549.3c | 531.3b | 540b | |
| N0 | 543.3e | 545.8f | 500ef | 537.3b | |||
| W2 | N3 | 595a | 590.8a | 597.5a | 540d | 526.7b | 577.3a |
| N2 | 580.8b | 595.8a | 583.3c | 546.7c | 518.7c | 570a | |
| N1 | 560.8cd | 575b | 565de | 510.7f | 502.7def | 522.7cd | |
| N0 | 539.2e | 527.5g | 495.3fg | 516.7d | |||
| W1 | N3 | 552.5d | 565.8bcd | 577.5c | 510.7f | 509.3d | 538.7b |
| N2 | 557.5cd | 562.5cd | 568.3d | 518e | 505.3de | 527.3c | |
| N1 | 534.2e | 555.8d | 559.2e | 507.3f | 497.3efg | 505.3e | |
| N0 | 527.5f | 510h | 490g | 507.3e | |||
| F | 灌水量(W) | 45.2** | 45.8** | 54.8** | 600.3** | 150.5** | 144.6** |
| 施氮量(N) | 38.9** | 108.5** | 295.3** | 147** | 96.9** | 155.9** | |
| W×N | 7.4** | 4.3** | 9.1** | 24.7** | 9.4** | 25.3** | |
Tab.4 Changes of number of stem tillers at flowering stage of wheat under different water and nitrogen treatments(104/hm2)
| 处理 Treatments | TR6H | TR8H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | ||
| W3 | N3 | 568.3bc | 585.8a | 585bc | 554.7b | 552a | 545.3b |
| N2 | 599.2a | 570.8bc | 592.5ab | 572a | 548a | 571.3a | |
| N1 | 554.2d | 561.7cd | 567.5d | 549.3c | 531.3b | 540b | |
| N0 | 543.3e | 545.8f | 500ef | 537.3b | |||
| W2 | N3 | 595a | 590.8a | 597.5a | 540d | 526.7b | 577.3a |
| N2 | 580.8b | 595.8a | 583.3c | 546.7c | 518.7c | 570a | |
| N1 | 560.8cd | 575b | 565de | 510.7f | 502.7def | 522.7cd | |
| N0 | 539.2e | 527.5g | 495.3fg | 516.7d | |||
| W1 | N3 | 552.5d | 565.8bcd | 577.5c | 510.7f | 509.3d | 538.7b |
| N2 | 557.5cd | 562.5cd | 568.3d | 518e | 505.3de | 527.3c | |
| N1 | 534.2e | 555.8d | 559.2e | 507.3f | 497.3efg | 505.3e | |
| N0 | 527.5f | 510h | 490g | 507.3e | |||
| F | 灌水量(W) | 45.2** | 45.8** | 54.8** | 600.3** | 150.5** | 144.6** |
| 施氮量(N) | 38.9** | 108.5** | 295.3** | 147** | 96.9** | 155.9** | |
| W×N | 7.4** | 4.3** | 9.1** | 24.7** | 9.4** | 25.3** | |
| [1] |
高新, 汪烨霖, 朱泰武, 等. 不同施氮量对春小麦灌浆速率和产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 310-317.
DOI |
|
GAO Xin, WANG Yelin, ZHU Taiwu, et al. Influence of different nitrogen application levels on the grain filling rate and yields of spring wheat[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(2): 310-317.
DOI |
|
| [2] |
张宁, 汪子晨, 杨肖, 等. 新疆水资源与农业种植系统耦合协调及时空差异研究——以粮食和棉花种植系统为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(3): 349-359.
DOI |
|
ZHANG Ning, WANG Zichen, YANG Xiao, et al. Coupling coordination and spatiotemporal differences between water resources and agriculture cropping system in Xinjiang: a case of grain and cotton cropping systems[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2023, 46(3): 349-359.
DOI |
|
| [3] | Yu S B, Khan S, Mo F, et al. Determining optimal nitrogen input rate on the base of fallow season precipitation to achieve higher crop water productivity and yield[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2021, 246: 106689. |
| [4] | 吕广德, 亓晓蕾, 张继波, 等. 中、高产型小麦干物质和氮素累积转运对水氮的响应[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(9): 1534-1547. |
| LYU Guangde, QI Xiaolei, ZHANG Jibo, et al. Response of nitrogen and dry matter accumulation in middle and high yield wheat cultivars to water and nitrogen supply[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(9): 1534-1547. | |
| [5] | 韩东伟, 何建宁, 李浩然, 等. 灌水时期对冬小麦个体、群体结构和冠层光合作用的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2022, 38(3): 577-586. |
| HAN Dongwei, HE Jianning, LI Haoran, et al. Effects of irrigation period on individual structure, population structure and canopy photosynthesis of winter wheat[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 38(3): 577-586. | |
| [6] | Zhu X G, Long S P, Ort D R. Improving photosynthetic efficiency for greater yield[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2010, 61: 235-261. |
| [7] | Kumar Jha S, Ramatshaba T S, Wang G S, et al. Response of growth, yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat to different irrigation methods and scheduling in North China Plain[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2019, 217: 292-302. |
| [8] |
王海琪, 王荣荣, 蒋桂英, 等. 施氮量对滴灌春小麦叶片光合生理性状的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2023, 49(1): 211-224.
DOI |
|
WANG Haiqi, WANG Rongrong, JIANG Guiying, et al. Effect of amount of nitrogen fertilizer applied on photosynthetic physiological characteristics of drip irrigated spring wheat leaves[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2023, 49(1): 211-224.
DOI |
|
| [9] | Lv Z Y, Diao M, Li W H, et al. Impacts of lateral spacing on the spatial variations in water use and grain yield of spring wheat plants within different rows in the drip irrigation system[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2019, 212: 252-261. |
| [10] | 吕钊彦. 不同行管比滴灌模式对新疆春小麦产量及品质行间差异形成的影响及其生理机理[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2017. |
| LYU Zhaoyan. Effects of drip irrigation modes with different row-to-tube ratios on the formation of inter-row differences in yield and quality of spring wheat in Xinjiang and its physiological mechanism[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| [11] | Wan W L, Li L L, Jing J G, et al. Narrowing row space improves productivity and profit of enlarged lateral space drip irrigated spring wheat system in Xinjiang, China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2022, 280: 108474. |
| [12] | 肖治林, 吴昊, 顾汉柱, 等. 不同栽培措施集成对稻茬小麦产量、农艺及光合特性的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2022, 42(8): 988-1000. |
| XIAO Zhilin, WU Hao, GU Hanzhu, et al. Effect of different integrated cultivation modes on yield, agronomic and photosynthetic characteristics of wheat following rice stubble[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2022, 42(8): 988-1000. | |
| [13] | 郭培武, 赵俊晔, 石玉, 等. 水肥一体化条件下施氮量对小麦冠层光截获特性和产量的影响[J]. 山东农业科学, 2018, 50(8): 81-85. |
| GUO Peiwu, ZHAO Junye, SHI Yu, et al. Effects of nitrogen application rate on canopy photosynthetic active radiation interception and yield of wheat under integration of water and fertilizer[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 50(8): 81-85. | |
| [14] | 杨建平, 吕钊彦, 刁明, 等. 滴灌春小麦植株干物质积累与分配特性及对产量的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2021, 30(1): 50-59. |
| YANG Jianping, LYU Zhaoyan, DIAO Ming, et al. Accumulation and distribution of dry matter in plants and their contribution to grain yield in drip-irrigated spring wheat[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 50-59. | |
| [15] | Wan W L, Zhao Y H, Wang Z J, et al. Mitigation fluctuations of inter-row water use efficiency of spring wheat via narrowing row space in enlarged lateral space drip irrigation systems[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2022, 274: 107958. |
| [16] | Guo Y J, Zhang L, Qin Y H, et al. Exploring the vertical distribution of structural parameters and light radiation in rice canopies by the coupling model and remote sensing[J]. Remote Sensing, 2015, 7(5): 5203-5221. |
| [17] |
王立红, 张宏芝, 李剑峰, 等. 新疆冬小麦不同产量群体冠层光截获与干物质分布特性分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(1): 275-282.
DOI |
|
WANG Lihong, ZHANG Hongzhi, LI Jianfeng, et al. Analysis of canopy light interception and dry matter distribution characteristics of different winter wheat yield groups in Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(1): 275-282.
DOI |
|
| [18] | 刘兆晔, 于经川, 辛庆国. 小麦株高问题的探讨[J]. 山东农业科学, 2014, 46(3): 130-134. |
| LIU Zhaoye, YU Jingchuan, XIN Qingguo. Study on plant height of wheat[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 46(3): 130-134. | |
| [19] | 杨旸, 王金龙, 刘双禄, 等. 水氮耦合对河套灌区春小麦生长发育及产量的影响[J]. 耕作与栽培, 2020, 40(4): 28-30, 33. |
| YANG Yang, WANG Jinlong, LIU Shuanglu, et al. Influence of water-nitrogen coupling on growthand yield of spring wheat of Hetao irrigation areas[J]. Tillage and Cultivation, 2020, 40(4): 28-30, 33. | |
| [20] | Mantilla-Perez M B, Salas Fernandez M G. Differential manipulation of leaf angle throughout the canopy: current status and prospects[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2017, 68(21/22): 5699-5717. |
| [21] | Liu Y K, Li M J, Li J Y, et al. Dynamic changes in flag leaf angle contribute to high photosynthetic capacity[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54(17): 3045-3052. |
| [22] | 胡语妍, 万文亮, 王江丽, 等. 不同水氮处理对滴灌春小麦氮素积累转运及产量的影响[J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 36(4): 448-456. |
| HU Yuyan, WAN Wenliang, WANG Jiangli, et al. Effects of different water and nitrogen application rates on the accumulation and translocation of nitrogen and yield of spring wheat under drip irrigation[J]. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science), 2018, 36(4): 448-456. | |
| [23] | 刘其, 刁明, 王江丽, 等. 施氮对滴灌春小麦干物质、氮素积累和产量的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2013, 33(4): 722-726. |
| LIU Qi, DIAO Ming, WANG Jiangli, et al. Effect of nitrogen application on accumulation of dry matter and nitrogen, yield of spring wheat under drip irrigation[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2013, 33(4): 722-726. | |
| [24] | 欧阳雪莹, 蒋桂英, 冉辉, 等. 水氮运筹对新疆滴灌春小麦群体质量和产量的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2020, 40(5): 585-593. |
| OUYANG Xueying, JIANG Guiying, RAN Hui, et al. Effect of water and nitrogen application on population quality and yield of spring wheat under drip irrigation in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2020, 40(5): 585-593. | |
| [25] | Zhao D D, Shen J Y, Lang K, et al. Effects of irrigation and wide-precision planting on water use, radiation interception, and grain yield of winter wheat in the North China Plain[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2013, 118: 87-92. |
| [26] | 闻磊, 张富仓, 邹海洋, 等. 水分亏缺和施氮对春小麦生长和水氮利用的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2019, 39(4): 478-486. |
| WEN Lei, ZHANG Fucang, ZOU Haiyang, et al. Effect of water deficit and nitrogen rate on the growth, water and nitrogen use of spring wheat[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2019, 39(4): 478-486. | |
| [27] | 李艳大, 汤亮, 张玉屏, 等. 水稻冠层光截获与叶面积和产量的关系[J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(16): 3296-3305. |
| LI Yanda, TANG Liang, ZHANG Yuping, et al. Relationship of PAR interception of canopy to leaf area and yield in rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(16): 3296-3305. | |
| [28] | Salvagiotti F, Miralles D J. Radiation interception, biomass production and grain yield as affected by the interaction of nitrogen and sulfur fertilization in wheat[J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 2008, 28(3): 282-290. |
| [29] | Zhang Z, Wang Y F, Chen Y Y, et al. Effects of different fertilization methods on grain yield, photosynthetic characteristics and nitrogen synthetase enzymatic activities of direct-seeded rice in South China[J]. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2022, 41(4): 1642-1653. |
| [30] |
刘国宏, 付彦博, 扁青永, 等. 水氮耦合对滴灌小麦生理生长及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(7): 1582-1589.
DOI |
|
LIU Guohong, FU Yanbo, BIAN Qingyong, et al. Effects of water and nitrogen coupling on physiological growth and yield of wheat under drip irrigation[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(7): 1582-1589.
DOI |
| [1] | CHEN Hui, ZHANG Yongqiang, BI Haiyan, TANJun , CHEN Chuanxin, XU Qijiang, NIE Shihui, YU Jianxin, LU Dong, LEI Junjie. Yield formation characteristics of different spring wheat varieties in dryland farming area of Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 13-20. |
| [2] | LI Na, LYU Caixia, Xin Huinan, LI Yongfu, LAI Ning, GENG Qinglong, CHEN Shuhuang. Effects of different nitrogen application rates on the characteristics and root zone soil nutrients of drip irrigation wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 87-94. |
| [3] | WANG Chunsheng, LI Jianfeng, ZHANG Yueqiang, FAN Zheru, WANG Zhong, GAO Xin, SHI Jia, ZHANG Hongzhi, WANG Lihong, XIA Jianqiang, WANG Fangping, ZHAO Qi. Study on genotypic differences of anther culture ability in mainly cultivated spring wheat varieties in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2081-2086. |
| [4] | YUAN Yingying, ZHAO Jinghua, Dilimulati Simayi, YANG Tingrui. Study on physiological indexes and yield analysis of spring wheat in pots based on apriori algorithm [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1861-1871. |
| [5] | YUAN Yilin, YAN An, ZUO Xiaoxiao, HOU Zhengqing, ZHANG Zhenfei, XIAO Shuting, SUN Zhe, MA Mengqian, ZHAO Yuhang. Impact of reduced nitrogen fertilization combined with bio-organic fertilizer on spring wheat yield enhancement and soil enrichment [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1872-1882. |
| [6] | LIU Xuhuan, YU Shan, LIU Yue, SHI Shubing. Comparative on the vigor differences of spring wheat seeds of different sizes [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1883-1887. |
| [7] | YANG Mei, ZHAO Hongmei, Dilireba Xiamixiding, YANG Weijun, ZHANG Jinshan, HUI Chao. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer reduction and biochar application on population structure, photosynthetic characteristics and yield of spring wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1582-1589. |
| [8] |
WANG Yizhao, YANG Qizhi, LIU Yuxiu, Alayi Nurkamali, Vladimir Shvidchenko, ZHANG Zhengmao.
Evaluation of drought resistance of different spring wheat germplasm introduced from Kazakhstan during seedling stage under 20% PEG stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1352-1360. |
| [9] | ZHANG Hongzhi, WANG Lihong, SHI Jia, KONG Depeng, WANG Zhong, GAO Xin, LI Jianfeng, WANG Chunsheng, XIA Jianqiang, FAN Zheru, ZHANG Yueqiang. Effects of soil moisture on leaf protective enzyme activities and yield of spring wheat cultivars with different drought resistance [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(5): 1041-1047. |
| [10] | Gulinigaer Tuerhong, ZHANG Jinshan, LI Dandan, ZHANG Lulu, WANG Runqi, SHI Shubing. Effects of different priming treatments on seed vigor and physiological characteristics of spring wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 869-877. |
| [11] | DONG Yanxue, JIA Yonghong, ZHANG Jinshan, LI Dandan, WANG Kai, LUO Siwei, WANG Runqi, SHI Shubing. Effects of different ecological conditions on dry matter accumulation and yield of spring wheat varieties [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1848-1857. |
| [12] | LI Huaisheng, AI Hongyu, MENG Ling, WANG Heya, ZHANG Lei, AI Haifeng. Effects of chasing rate during peak nutrient uptake of transport under n Reduction on spring wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1866-1872. |
| [13] | ZHANG Chao, BAI Yungang, ZHENG Ming, XIAO Jun, DING Ping. Synergistic effect of water and fertilizer on grape in extreme arid area [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1931-1939. |
| [14] | MA Xinchao, XUAN Zhengying, MIN Haozhe, QI Zhiwen, CHENG Hongyu, TAN Zhanming, WANG Xufeng. Effects of water and nitrogen coupling on diurnal changes of photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of cucumber in sandy culture [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1966-1974. |
| [15] | WANG Xingzhou, SHI Xiaolei, ZHANG Heng, QU Kejia, GENG Hongwei, DING Sunlei, ZHANG Jinbo, YAN Yongliang. Identification and evaluation of salt tolerance at germination stage of introduced spring wheat varieties [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1353-1362. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 24
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 85
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||