

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (4): 823-831.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.04.005
• Crop Genetics and Breeding·Cultivation Physiology·Germplasm Resources • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Chen( ), LIANG Yue, YIN Hao, ZHANG Yingrong, CHEN Bolang(
), LIANG Yue, YIN Hao, ZHANG Yingrong, CHEN Bolang( )
)
Received:2022-08-20
Online:2023-04-20
Published:2023-05-06
Correspondence author:
CHEN Bolang(1979-), male, native place:Hunan. professor, research field: High-efficiency nutrient resource utilization, (E-mail)Supported by:通讯作者:
陈波浪(1979-),男,湖南汨罗人,教授,硕士生导师,研究方向为养分资源高效利用,(E-mail)作者简介:张宸(1994-),男,四川富顺人,硕士研究生,研究方向为养分资源高效利用,(E-mail)624147418@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHANG Chen, LIANG Yue, YIN Hao, ZHANG Yingrong, CHEN Bolang. Effects of nitrogen forms and varieties on root morphology and nitrogen accumulation of cotton[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(4): 823-831.
张宸, 梁悦, 殷昊, 张应榕, 陈波浪. 氮肥形态和品种对棉花根系形态与氮素积累的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(4): 823-831.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.xjnykx.com/EN/10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.04.005
| 因子 Factor | 根系干物质重量 Root dry matter weight (g/plant) | 根系总长度 Total root length (cm/plant) | 根系体积 Root volume (cm3/plant) | 根系表面积 Root surface area (cm2/plant) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F值 | P值 | F值 | P值 | F值 | P值 | F值 | P值 | |
| V | 1.15 | >0.05 | 17.06 | <0.01 | 15.08 | <0.01 | 1.40 | >0.05 |
| N | 3.65 | <0.05 | 48.49 | <0.01 | 60.62 | <0.01 | 25.87 | <0.01 |
| V×N | 1.41 | >0.05 | 3.84 | <0.05 | 0.80 | >0.05 | 0.44 | >0.05 |
Tab.1 The variance analysis and interaction effect of cotton variety and nitrogen fertilizer form on root morphology
| 因子 Factor | 根系干物质重量 Root dry matter weight (g/plant) | 根系总长度 Total root length (cm/plant) | 根系体积 Root volume (cm3/plant) | 根系表面积 Root surface area (cm2/plant) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F值 | P值 | F值 | P值 | F值 | P值 | F值 | P值 | |
| V | 1.15 | >0.05 | 17.06 | <0.01 | 15.08 | <0.01 | 1.40 | >0.05 |
| N | 3.65 | <0.05 | 48.49 | <0.01 | 60.62 | <0.01 | 25.87 | <0.01 |
| V×N | 1.41 | >0.05 | 3.84 | <0.05 | 0.80 | >0.05 | 0.44 | >0.05 |
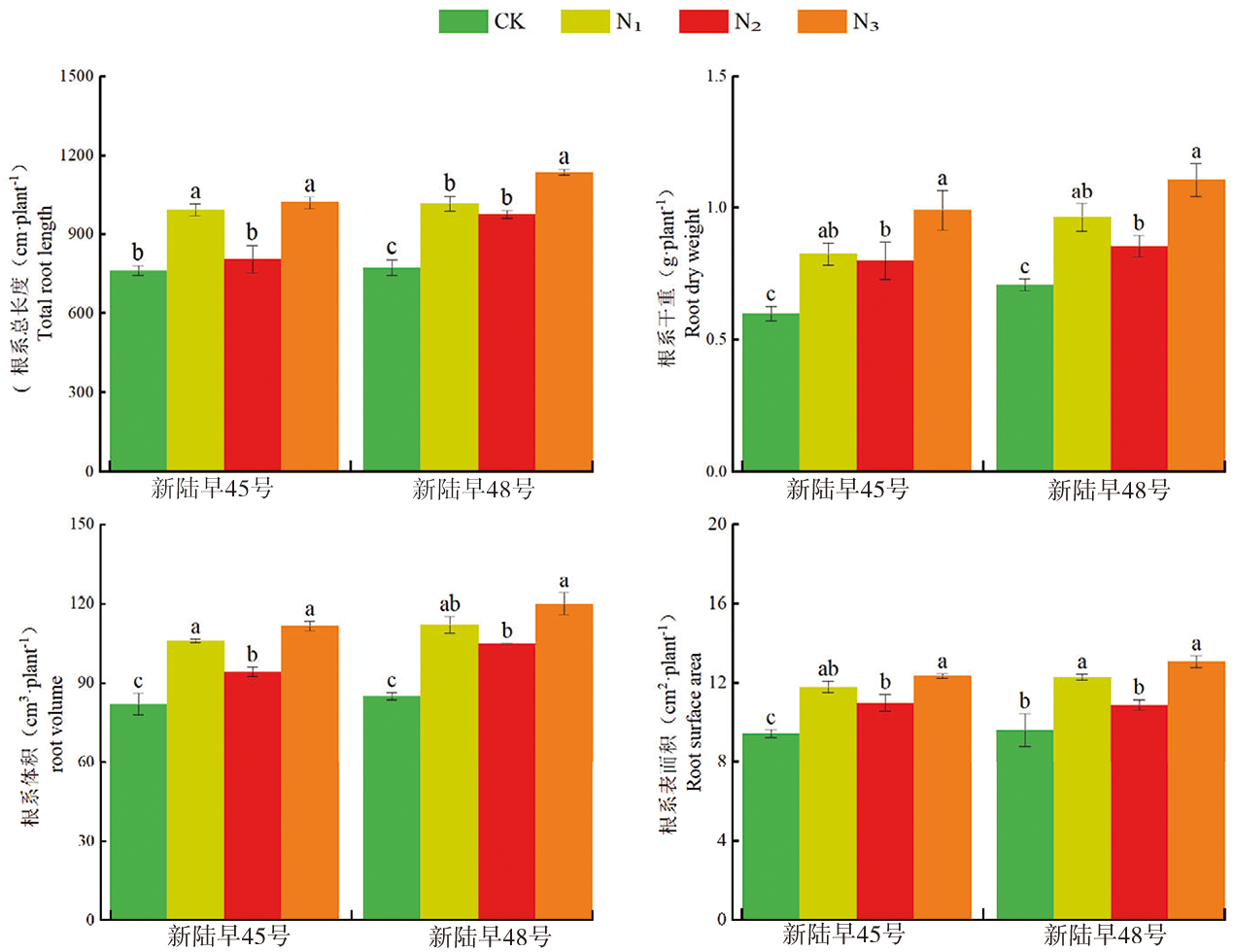
Fig.1 Root morphological indexes measured in different nitrogen fertilizer forms Note: Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at P<0.05 level
| 因子 Factor | 根冠比 Root:Shoot ratio | 比根长 Specific root length(m/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F值 | P值 | F值 | P值 | |
| V | 2.178 | >0.05 | 0.455 | >0.05 |
| N | 3.685 | <0.05 | 1.592 | >0.05 |
| V×N | 0.943 | >0.05 | 2.924 | >0.05 |
Tab.2 Variance analysis and interaction effects of cotton types and nitrogen fertilizerforms on cotton root-shoot ratio and specific root length
| 因子 Factor | 根冠比 Root:Shoot ratio | 比根长 Specific root length(m/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F值 | P值 | F值 | P值 | |
| V | 2.178 | >0.05 | 0.455 | >0.05 |
| N | 3.685 | <0.05 | 1.592 | >0.05 |
| V×N | 0.943 | >0.05 | 2.924 | >0.05 |
| 因子 Factor | 根系氮积累量 Root N accumulation (mg/plant) | 茎部氮素积累量 Accumulation in stem (mg/plant) | 叶部氮素积累量 Accumulation in leaves (mg/plant) | 植株氮素积累量 Plant N accumulation (mg/plant) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F值 | P值 | F值 | P值 | F值 | P值 | F值 | P值 | |
| V | 8.93 | <0.01 | 4.36 | <0.05 | 10.89 | <0.01 | 19.58 | <0.01 |
| N | 14.97 | <0.01 | 12.84 | <0.01 | 4.58 | <0.05 | 19.18 | <0.01 |
| V×N | 0.60 | >0.05 | 0.24 | >0.05 | 0.15 | >0.05 | 0.44 | >0.05 |
Tab.3 Analysis of variance and interaction effects of cotton types and nitrogen fertilizer forms on nitrogen accumulation
| 因子 Factor | 根系氮积累量 Root N accumulation (mg/plant) | 茎部氮素积累量 Accumulation in stem (mg/plant) | 叶部氮素积累量 Accumulation in leaves (mg/plant) | 植株氮素积累量 Plant N accumulation (mg/plant) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F值 | P值 | F值 | P值 | F值 | P值 | F值 | P值 | |
| V | 8.93 | <0.01 | 4.36 | <0.05 | 10.89 | <0.01 | 19.58 | <0.01 |
| N | 14.97 | <0.01 | 12.84 | <0.01 | 4.58 | <0.05 | 19.18 | <0.01 |
| V×N | 0.60 | >0.05 | 0.24 | >0.05 | 0.15 | >0.05 | 0.44 | >0.05 |
| [1] | 陈求柱, 杨国正, 张献龙, 等. 棉花氮素营养特性研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2012, 28(18):15-19. |
| CHEN Qiuzhu, YANG Guozheng, ZHANG Xianlong, et al. Review on Nitrogen Nutriti-on Characteristic of Cotton[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2012, 28(18):15-19. | |
| [2] | Snider J, Harris G, Roberts P, et al. Cotton physiological and agronomic response to nitrogen application rate[J]. Field Crops Research, 2021,(270):108-194. |
| [3] | 周伟, 吕腾飞, 杨志平, 等. 氮肥种类及运筹技术调控土壤氮素损失的研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(9):3051-3058. |
| ZHOU Wei, LU Tengfei, YANG Zhiping, et al. Research advances on regulating soil nitrogen loss by the type of nitrogen fertilizer and its application strategy[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(9):3051-3058. | |
| [4] | 李鹏程, 郑苍松, 孙淼, 等. 不同形态氮肥对棉花15N回收率和产量的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021,(5):53-57. |
| LI Pengcheng, ZHENG Cangsong, SUN Miao, et al. Effects of different nitrogen forms on15N recovery and yield of cotton[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021,(5):53-57. | |
| [5] |
Dai J, Duan L, Dong H. Comparative Effect of Nitrogen Forms on Nitrogen Uptake a-nd Cotton Growth Under Salinity Stress[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2015, 38(10) :1530-1543.
DOI URL |
| [6] | 罗新宁, 陈冰, 张巨松, 等. 氮肥对不同质地土壤棉花生物量与氮素积累的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2009, 18(4):160-166. |
| LUO Xinning, CHEN Bing, ZHANG Judong, et al. Effect of Nitrogen Applied Levels on the Dynamics of Biomass, Nitrogen Accumulation of Cotton Plant on Different Soil Textures[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalia Sinica, 2009, 18(4) :160-166. | |
| [7] | 孙思敏, 韩贝, 陈林, 等. 棉花苗期根系分型及根系性状的关联分析[J/OL]. 作物学报:1-27 [2021-11-19]. |
| SUN Simin, HAN Bei, CHEN Lin, et al. System architecture analysis and genome wide association study of root system architecture related traits in cotton[J/OL]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2021, 1-27 [2021-11-19]. | |
| [8] |
Uga Y, Sugimoto K, Ogawa S, et al. Control of root system architecture by DEEPER ROOTING 1 increases rice yield under drought conditions[J]. Nature Genetics, 2013, 45(9) :1097.
DOI |
| [9] | 李嘉, 吕慎强, 杨泽宇, 等. 氮肥运筹对黄土塬区春玉米产量、效益和氮肥利用率的综合效应[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(1):32-41. |
| LI Jia, LÜ Shenqiang, YANG Zeyu, et al. Comprehensive effects of nitrogen fertilizer management on yield, economic performance and nitrogen use efficiency of spring maize in Loess Plateau, China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(1):32-41. | |
| [10] |
郭小琰, 孙桂兰, 熊世武, 等. 施氮量对棉花养分吸收利用及产量和品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(7):1246-1254.
DOI |
| GUO Xiaoya, SUN Guilan, XIONG Shiwu, et al. Effects of Nitrogen Application Ra-tes on Nutrition Uptake and Utilization,Yield and Fiber Quality of Cotton[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 201, 58(7):1246-1254. | |
| [11] |
张宏, 曾雄, 王爱莲, 等. 不同施氮量对棉花产量、养分吸收及氮素利用的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(9):1656-1664.
DOI |
|
ZHANG Hong, ZENG Xiong, WANG Ailian, et al. Effects of Different Nitrogen Application Rates on Yield,Nutrient Uptake and Nitrogen Utilization of Cotton in Southern Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(9):1656-1664.
DOI |
|
| [12] | 李乌日吉木斯, 高欣梅, 徐兴健, 等. 氮肥种类及用量对旱地玉米肥料利用率和产量的影响[J]. 土壤与作物, 2019, 8(4):415-426. |
| LI Wurijimus, GAO Xinmei, XU Xingjian, et al. Effects of N fertilizer type and rate on maize fertilizer utilization efficiency and yield in arid farmland[J]. Soils and Crops, 2019, 8(4):415-426. | |
| [13] | 齐欣, 司玉坤, 赵亚南, 等. 不同氮肥在不同土壤中对小麦氮素利用及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7):172-181. |
|
QI Xin, SI Yukun, ZHAO Yanan, et al. Impacts of Nitrogen Forms on Nitrogen Utilization and Yield of Wheat in different Types of Soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(7):172-181.
DOI |
|
| [14] | 董海荣, 李存东, 李金才. 不同形态氮素比例对棉花苗期生长及物质积累的影响[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2003,(1):9-12. |
| DONG Hairong, LI Cundong, LI Jincai. Effect of different $NH^{+}_{4}$/$NO^{-}_{3}$ ratios on youngcotton growth and material accumulation[J]. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei, 2003,(1):9-12. | |
| [15] | 刘爱忠, 洪德成, 董合林, 等. 不同供钾水平和氮素形态对棉花功能叶质体色素、碳氮代谢及钾含量的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 2018, 47(4):31-37. |
| LIU Aizhong, HONG Decheng, DONG Helin, et al. Effects of Potassium Level and Nitrogen Forms on Plastid Pigment, Carbon Nitrogen Metabolism and Potassium Content of Cotton Functional Leaves[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 47(4):31-37. | |
| [16] | 汤清秋, 罗剑洪, 徐永峰, 等. 不同施肥方式对棉花生长与产量的影响[J]. 新疆农垦科技, 2019, 42(1):30-33. |
| TANG Qingqiu, LUO Jianhong, XU Yongfeng, et al. Effects of different fertilization methods on cotton growth and yield[J]. Xinjiang Farm Research of Science and Technology, 2019, 42(1) :30-33. | |
| [17] | 束孝海. 棉花施肥误区与科学施肥[J]. 现代农业科技, 2008,(3):171. |
| SHU Xiaohai. Misunderstanding of cotton fertilization and scientific fertilization[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2008,(3):171. | |
| [18] | 刘爱忠, 董合林, 裴亮只, 等. 氮素形态对不同钾效率基因型棉花钾素吸收利用及根系形态的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2017, 54(6):998-1007. |
| LIU Aizhong, DONG Helin, PEI Liangji, et al. Effects of Nitrogen Forms for Different Cotton Genotypes on the Potassium Absorption and Utilization and Root Morphology[J]. Xinjiang agricultural sciences, 2017, 54(6):998-1007. | |
| [19] | 李洪亮, 孙玉友, 曲金玲, 等. 施氮量对东北粳稻根系形态生理特征的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(6):723-730. |
|
LI Hongliang, SUN Yuyou, QU Jinling, et al. Influence of Nitrogen Levels on Morphological and Physiological Characteristics of Root System in japonica Rice in Northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2012, 26(6):723-730.
DOI |
|
| [20] |
王士红, 杨中旭, 史加亮, 等. 增密减氮对棉花干物质和氮素积累分配及产量的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(3):395-407.
DOI |
| WANG Shihong, YANG Zhongxu, SHI Jialiang, et al. Effects of increasing planting density and decreasing nitrogen rate on dry matter, nitrogen accumulation and distribution, and yield of cotton[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 46(3):395-407. | |
| [21] |
Zotarelli L, DukesM D, Scholberg J M S, et al. Tomato nitrogen accumulation and fertilizer use efficiency on a sandy soil, as affected by nitrogen rate and irrigation scheduling[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2009, 96(8): 1247-1258.
DOI URL |
| [22] | 沈宏, 施卫明, 王校常, 等. 不同作物对低磷胁迫的适应机理研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2001,(2):172-177, 210. |
| SHEN Hong, SHI Weiming, WANG Xiaochang, et al. Study on adaptation mechanisms of different crops to low phosphorus stress[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2001,(2):172-177, 210. | |
| [23] | 杨振安, 宋双飞, 李靖, 等. 不同林龄华北落叶松人工林根系特征和氮磷养分研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 2014, 34(7):1432-1442. |
| YANG Zhenan, SONG Shuangfei, LI Jing, et al. A Study on Root Characteristics and N utrients of DifferentAged Larix princi pis rupprechtiiMayr. Plantations[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2014, 34(7):1432-1442. | |
| [24] | Mehrabi F, Sepaskhah A R, Ahmadi S H. Winter wheat root distribution with irrigation, planting methods, and nitrogen application[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 2021, 199(2):231-245. |
| [25] | 张建波, 白史且, 张新全, 等. 紫花苜蓿根系与土壤物理性质的关系[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2006,(14):3424-3425, 3427. |
| ZHANG Jianbo, BAI Shiqi, ZHANG Xinquan, et al. Relation of Alfalfa Root System and Soil Physical Property[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2006,(14):3424-3425, 3427. | |
| [26] | 王峻, 宋科, 潘剑君, 等. 氮磷养分胁迫下小麦幼苗期生物学响应研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2019,(2):152-158,164. |
| WANG Jun, SONG Ke, PAN Jianjun, et al. Study of biologic response of wheat seedling to low nitrogen and phosphorus stress[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2019,(2):152-158, 164. | |
| [27] |
程乙, 王洪章, 刘鹏, 等. 品种和氮素供应对玉米根系特征及氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(12):2259-2269.
DOI |
|
CHENG Yi, WANG Hongzhang, LIU Peng, et al. Effect of Different Maize Varieties and Nitrogen Supply on Root Characteristics and Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization Efficiency[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(12):2259-2269.
DOI |
|
| [28] |
录亚丹, 郭丽琢, 李春春, 等. 干旱胁迫和氮素形态对豌豆根系生长的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(3):19-25.
DOI |
|
LU Yadan, GUO Lizhuo, LI Chunchun, et al. Effect of Drought Stress and Nitrogen Forms on Root Morphology of Pea[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2018, 34(3):19-25.
DOI |
|
| [29] | 康佳惠, 梁秀芝, 郑敏娜, 等. 不同外源氮素形态对紫花苜蓿根系的影响[J]. 山西农业科学, 2021, 49(4):467-471. |
| KANG Jiahui, LIANG Xiuzhi, ZHENG Minna, et al. Effects of Exogenous Nitrogen Forms on the Root of Alfalfa[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 201, 49(4):467-471. | |
| [30] | 薛艳芳, 张慧, 夏海勇, 等. 不同氮素形态供应对玉米幼苗生物量和氮素累积的影响[J]. 玉米科学, 2016, 24(6):126-130. |
| XUE Yanfang, ZHANG Hui, XIA Haiyong, et al. Effect of Different N Forms on the Dry Weight and N Accumulation of Maize Seedlings[J]. Journal of Maize Science, 2016, 24(6):126-130. | |
| [31] | 刘文涛, 王玉强, 孙盛楠, 等. 氮素形态对不同茬次紫花苜蓿氮素积累及利用的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2021, 38(4):716-725. |
| LIU Wentao, WANG Yuqiang, SUN Shengnan, et al. Effects of nitrogen forms on nitrogen accumulation and utilization of alfalfa in different stubbles[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(4):716-725. | |
| [32] |
郝凤, 于铁峰, 刘晓静, 等. 不同氮效率型苜蓿氮素吸收差异与根系形态的关系及其对氮的响应[J]. 草地学报, 2021, 29(11):2428-2434.
DOI |
| HAO Feng, YU Tiefeng, LIU Xiaojing, et al. Relationship between Nitrogen Uptake a-nd Root Morphology of Alfalfa with Different Nitrogen Efficiency and Its Response to Nitrogen[J]. Chinese Journal Of Grassland, 201, 29(11):2428-2434. |
| [1] | LIU Haijun, ZHANG Hao, WANG Yifan, CHEN Maoguang, WU Fengquan, LIN Tao, TANG Qiuxiang. Effects of different mulching materials and irrigation on yield formation and effective accumulated temperature production efficiency of machine-picked cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2091-2100. |
| [2] | CHEN Maoguang, LIN Tao, ZHANG Hao, LIU Haijun, WANG Yifan, TANG Qiuxiang. Effects of mulch film types on cotton growth and analysis of self-degradation recycling characteristics [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2101-2108. |
| [3] | WANG Hui, GUO Jincheng, SONG Jia, ZHANG Tingjun, He Liangrong. Physiological and biochemical analysis of transgenic offspring of upland cotton GhCIPK6 under high temperature Stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2109-2119. |
| [4] | YANG Chuan, ZHANG Kai, CHEN Bing, ZHANG Hui, LIU Ping, CHANG Song, SHENG Jiandong. Responses of morphological characteristics of cotton to different water conditions [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2120-2127. |
| [5] | ZHU Yujie, LIN Ling, TANG Guangmu, ZHANG Yunshu, XU Wanli. Effect of modified cotton straw charcoal on ammonia volatilization characteristics of nitrogen fertilizer in grey desert soils of Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2128-2137. |
| [6] | YANG Guojiang, CHEN Yun, LIN Xiangqun, HE Jiangyong, LIU Shenglin, QU Yongqing. Effects of organic fertilizer replacement on the yield and nutrient absorption of cotton and nitrate nitrogen under chemical fertilizer reduction [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2138-2145. |
| [7] | WANG Xin, LIN Tao, CUI Jianping, WU Fengquan, TANG Zhixuan, CUI Laiyuan, GUO Rensong, WANG Liang, ZHENG Zipiao. Effects of planting mode and irrigation quota on yield and fiber quality of machine-picked long-staple cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1821-1829. |
| [8] | LI Xueling, GUO Junxian, CHEN Li, SONG Heling, ZHANG Zhong. Effects of Different Film Mulching Width on Cotton Farmland Environment [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1840-1847. |
| [9] | DONG Yanxue, JIA Yonghong, ZHANG Jinshan, LI Dandan, WANG Kai, LUO Siwei, WANG Runqi, SHI Shubing. Effects of different ecological conditions on dry matter accumulation and yield of spring wheat varieties [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1848-1857. |
| [10] | YANG Ni, Mayila Yusuyin, YANG Yanlong, LI Chunping, ZHANG Dawei, XU Haijiang, LAI Chengxia. Comparative analysis of plant volatiles from the Verticillium-Infected withered spot and etiolated leaves in cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1975-1986. |
| [11] | Mierzhati Mutalifu, SHI Xiunan, BO Junbing, Zubaidai Abudukerimu, Wulejialehasi Azhati, SHI Shubing. Effects of different delinting modes on seed vigor and seedling characteristics of cotton under PEG stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(7): 1561-1568. |
| [12] | DUAN Songjiang, PENG Zengying, SHEN Yingying, Mulidier Baibolati, WU Yifan, CUI jianping, ZHANG Jusong. Responses of seed cotton yield and fiber quality of different sea island cotton varieties to nitrogen fertilizer [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(7): 1569-1579. |
| [13] | LIN Ling, ZHU Yujie, FENG Lei, TANG Guangmu, ZHANG Yunshu, XU Wanli. Features of aged cotton stalk charcoal and its effect on ammonia volatilization from sand soil [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(7): 1580-1588. |
| [14] | XUE Zhengxuan, CAI Zhiping, ZHANG Zhijian, PENG Tianxiang, HUANG Zhiwei, HUANG Enze, WANG Peiling, LU Yanhui. Transfer of Hippodamia variegate between licorice and cotton fields based on rubidium marker technology [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(7): 1741-1747. |
| [15] | LU Yantian, SANG Zhiqin, XU Can, ZHANG Li, XIA Chunlan, WANG Youde, LI Wei, CHEN Shubin. Evolution of main characters of maize varieties approved in Xinjiang and Ningxia over the years and analysis of the current situation of variety approval [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1379-1388. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||