

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (1): 146-160.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.01.018
• Cultivation Physiology·Physiology and Biochemistry·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Genetics·Soil Fertilizer • Previous Articles Next Articles
SUN Caiqin( ), WU Jia, HUANG Hai, GUO Jiaxin, MIN Wei, GUO Huijuan(
), WU Jia, HUANG Hai, GUO Jiaxin, MIN Wei, GUO Huijuan( )
)
Received:2024-07-25
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-03-11
Correspondence author:
GUO Huijuan
Supported by:通讯作者:
郭慧娟
作者简介:孙彩琴(2001-),女,甘肃通渭人,本科生,研究方向为土壤肥力与调控,(E-mail)scaiq0927@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
SUN Caiqin, WU Jia, HUANG Hai, GUO Jiaxin, MIN Wei, GUO Huijuan. Effects of different saline and alkaline stress on the proteome of cotton root system[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 146-160.
孙彩琴, 吴佳, 黄海, 郭家鑫, 闵伟, 郭慧娟. 不同盐碱胁迫对棉花根系蛋白质组的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 146-160.
| 处理 Treat- ments | 盐碱类型及 盐碱化程度 Saline and alkaline | 含盐量 Salt content (g/kg) | 电导率 EC1∶5 (dS/m) | pH值 pH value (1∶2.5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 对照-非盐(碱)化 | 0.53 | 0.17 | 8.16 |
| CS | NaCl-中度盐化 | 4.43 | 1.39 | 8.43 |
| AS | Na2CO3+NaHCO3- 中度碱化 | 2.03 | 0.63 | 9.92 |
Tab.1 Type and degree of salinity and alkalinity in soil under different treatments
| 处理 Treat- ments | 盐碱类型及 盐碱化程度 Saline and alkaline | 含盐量 Salt content (g/kg) | 电导率 EC1∶5 (dS/m) | pH值 pH value (1∶2.5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 对照-非盐(碱)化 | 0.53 | 0.17 | 8.16 |
| CS | NaCl-中度盐化 | 4.43 | 1.39 | 8.43 |
| AS | Na2CO3+NaHCO3- 中度碱化 | 2.03 | 0.63 | 9.92 |
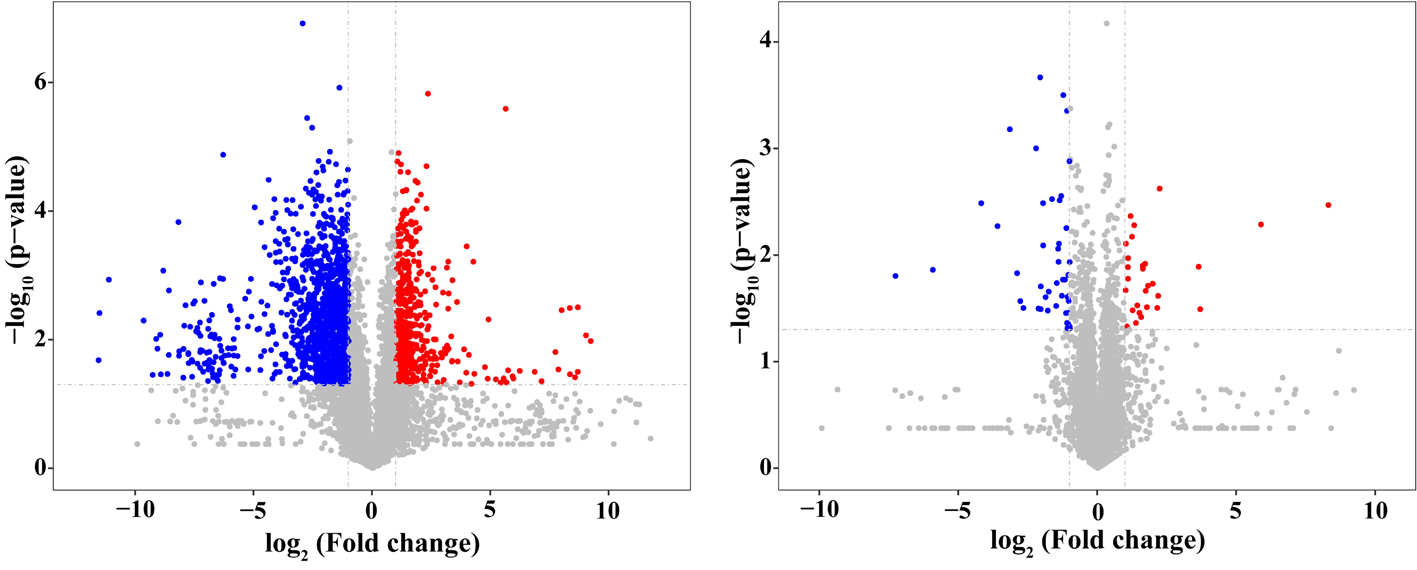
Fig.2 Volcanic map of proteins expressed in cotton roots Notes: Scatter color: protein that are significantly up-regulated are shown in red, protein that are significantly down-regulated are shown in blue, and protein that are not significantly different are shown in gray
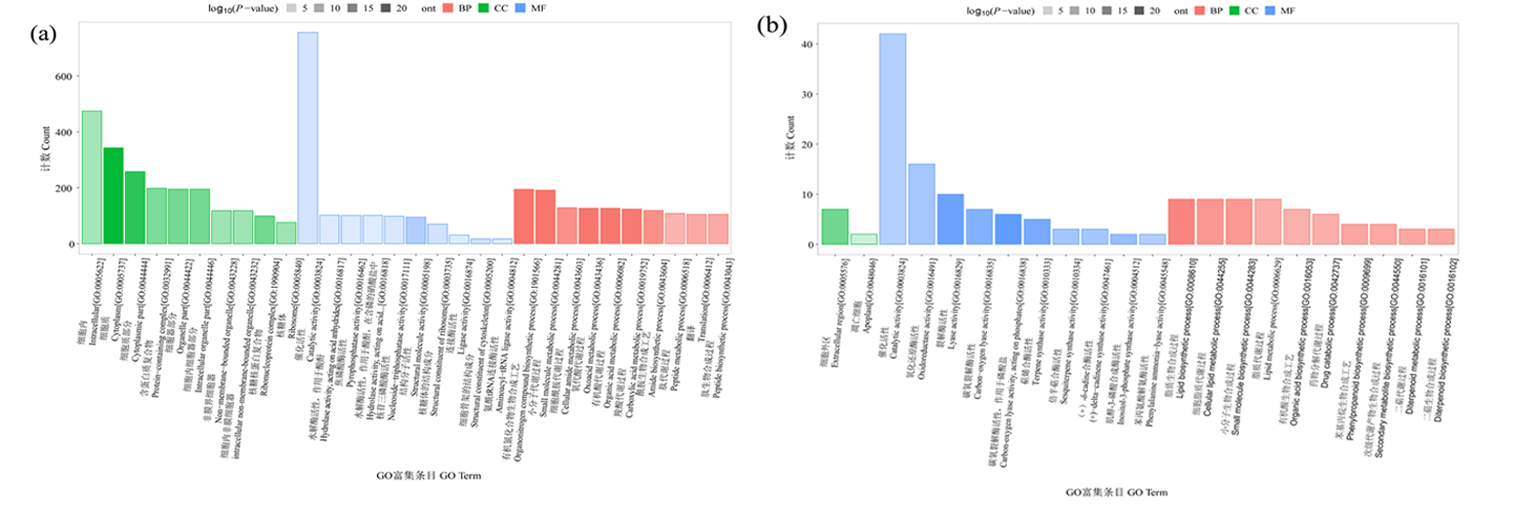
Fig.4 GO enrichment analysis of differential protein in cotton roots Notes: Number of enrichment terms less than top 10, the ordinate is the number of mapped differential expression proteins.BP: Biological Process, CC: Cellular Component, MF: Molecular Function;(a) salt stress, (b) alkali stress
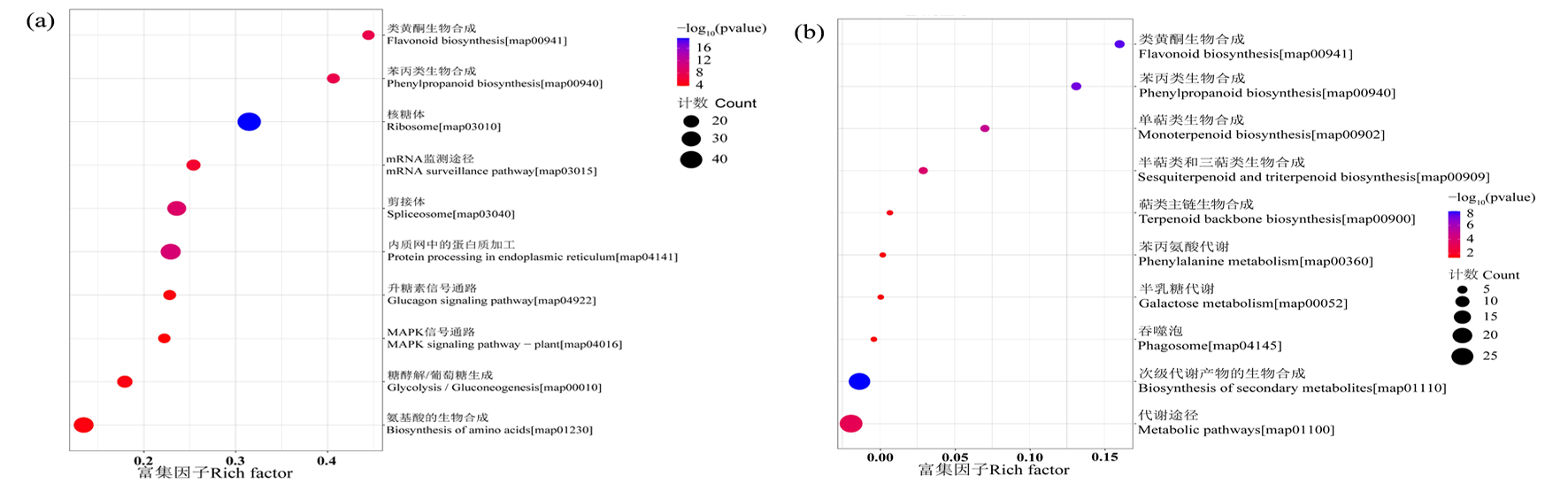
Fig.5 Enrichment analysis of top ten KEGG metabolic pathways of differentially expressed proteins in cotton roots Notes: The abscissa in the figure is the rich factor value of the enrichment degree, and the ordinate is the KEGG Pathway information.The size of the circle indicates the number of differentially expressed proteins in the mapping pathway.The larger the circle, the more the number; The color of the circle indicates the size of the P value.The redder the color, the smaller the P value;(a) salt stress, (b) alkali stress
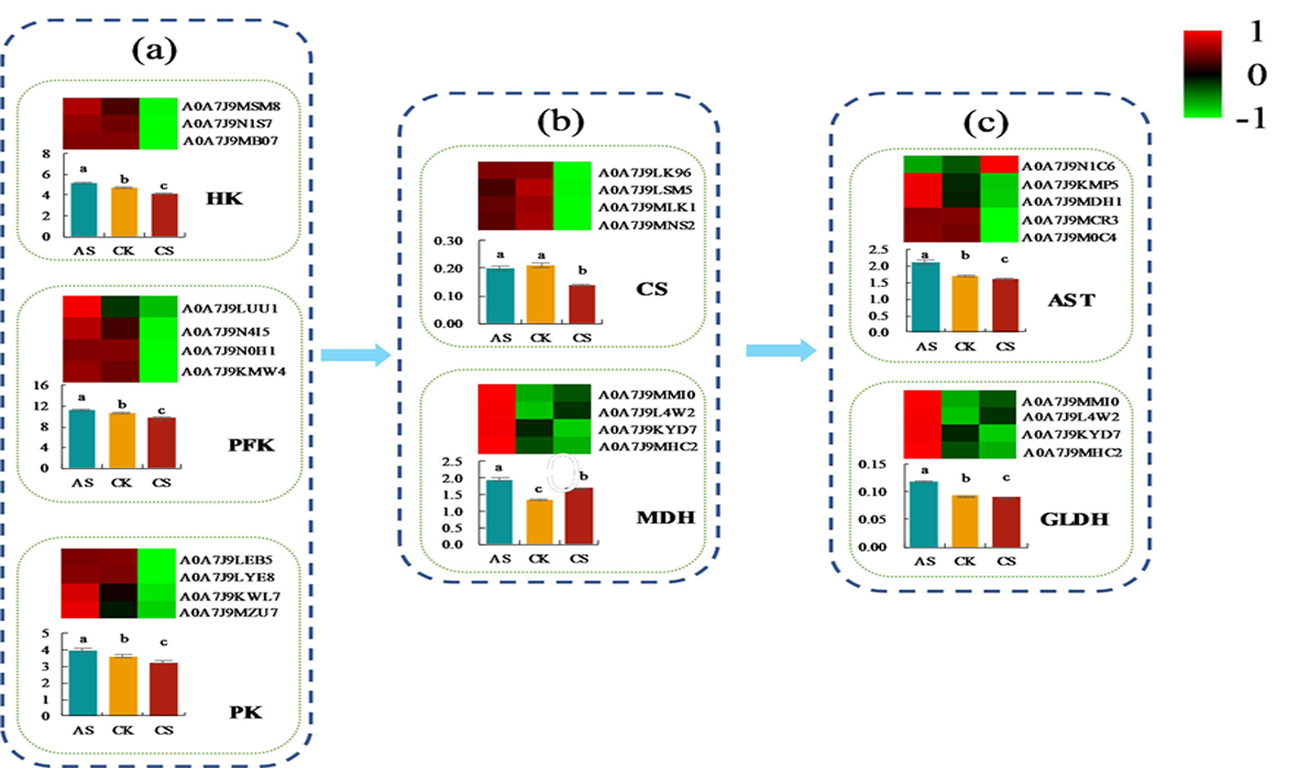
Fig.6 Changes of different salt and alkali stress on carbon transforming protein in cotton roots Notes: A: Glycolysis, B: Citric acid cycle, C: Amino acid conversion; different lowercase letters above the bars indicate significant differences among different treatments at the 0.05 probability level
| 代谢通路 Pathway name | 序列号 Accession | 功能描述 Description | 变化倍数 Flod change CS/CK |
|---|---|---|---|
| 光合生物中的碳固定 Carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms | A0A7J9MMV1 | 苹果酸脱氢酶(脱羧) | 0.44 |
| A0A7J9KKP5 | 苹果酸脱氢酶 | 0.28 | |
| A0A7J9LT88 | 转酮酶 | 0.4 | |
| A0A7J9MIN9 | 丙酮酸,正磷酸二激酶 | 2.48 | |
| A0A7J9LQW1 | 二磷酸核糖羧化酶大链 | 0.22 | |
| A0A7J9LWV8 | 果糖二磷酸醛缩酶 | 0.29 | |
| A0A7J9L8J1 | 谷氨酸乙醛酸氨基转移酶 | 0.38 | |
| 脂肪酸代谢 Fatty acid metabolism | A0A7J9LXK4 | 酰基CoA氧化酶 | 0.36 |
| A0A7J9LGP8 | 3-氧代酰基-[酰基载体蛋白]合成酶III | 0.32 | |
| A0A7J9MDP4 | 长链酰基辅酶A合成酶 | 0.03 | |
| A0A7J9MNJ9 | 乙酰辅酶A羧化酶羧基转移酶亚基α | 0.3 | |
| A0A7J9LQW1 | 乙酰辅酶A羧化酶羧基转移酶亚基β | 0.22 | |
| A0A7J9N2P9 | 酰基-[酰基载体蛋白]去饱和酶 | 0.45 | |
| A0A7J9MI46 | 乙酰辅酶A酰基转移酶1 | 0.48 | |
| A0A7J9MBT9 | 3-氧代酰基-[酰基载体蛋白]合成酶II | 0.156 | |
| A0A7J9MML8 | 极长链烯酰辅酶A还原酶 | 0.08 | |
| 2-氧代羧酸代谢 2-Oxocarboxylic acid metabolism | A0A7J9MHQ1 | 酮酸还原酶 | 0.42 |
| A0A7J9MCR3 | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 | 0.45 | |
| A0A7J9LR84 | 支链氨基酸氨基转移酶 | 0.45 | |
| A0A7J9MF79 | 乙酰乳酸合成酶I/II/III大亚基 | 0.33 | |
| A0A7J9M5F7 | 乌头酸水合酶 | 0.3 | |
| A0A7J9LFB5 | 3-异丙基苹果酸/(R)-2-甲基苹果酸脱水酶大亚基 | 0.22 | |
| A0A7J9L8J1 | 谷氨酸乙醛酸氨基转移酶 | 0.38 | |
| A0A7J9MLD0 | 氨基酸N-乙酰转移酶 | 0.3 | |
| 氧化磷酸化 Oxidative phosphorylation | A0A7J9M3S6 | 无机焦磷酸酶 | 0.33 |
| A0A7J9KSN1 | ATP酶亚基δ | 3.34 | |
| A0A7J9LU75 | ATP酶亚基δ | 4.01 | |
| A0A7J9LUR9 | ATP酶亚单位γ | 0.49 | |
| A0A7J9MXH6 | ATP酶亚基d | 2.56 | |
| A0A7J9M8P5 | V型H+转运ATP酶亚基A | 0.38 | |
| A0A7J9NCI0 | V型H+转运ATP酶亚基G | 2.15 | |
| A0A7J9LE84 | V型H+转运ATP酶亚基a | 0.29 | |
| A0A7J9MAN9 | V型H+转运ATP酶16kDa蛋白脂质亚基 | 0.36 | |
| A0A7J9N9Y3 | 细胞色素c氧化酶亚基5b | 2.64 | |
| A0A7J9M160 | 细胞色素c氧化酶亚基6b | 3.09 | |
| A0A7J9MBK5 | NADH脱氢酶(泛醌)Fe-S蛋白7 | 0.44 | |
| A0A7J9LX02 | NADH脱氢酶(泛醌)黄素蛋白1 | 0.21 | |
| 氧化磷酸化 Oxidative phosphorylation | A0A7J9MRV1 | NADH脱氢酶(泛醌)1α亚基2 | 2.48 |
| A0A7J9MJS6 | NADH脱氢酶(泛醌)1α亚基8 | 3.94 | |
| A0A7J9L0N9 | NADH脱氢酶(泛醌)1β亚基10 | 2.29 | |
| 氮代谢 Nitrogen metabolism | A0A7J9LWX4 | 谷氨酸脱氢酶(NAD(P)+) | 0.48 |
| A0A7J9KIX3 | 腈化酶 | 0.36 | |
| A0A7J9L9B3 | 硝酸还原酶(NAD(P)H) | 0.01 | |
| 甲烷代谢 Methane metabolism | A0A7J9LUW0 | 2-氧戊二酸还原酶 | 0.27 |
| A0A7J9MLG9 | 甘氨酸羟甲基转移酶 | 0.36 | |
| A0A7J9N9M4 | 6-磷酸果糖激酶1 | 0.5 | |
| A0A7J9LWV8 | 果糖二磷酸醛缩酶 | 0.29 | |
| A0A7J9KZF9 | 烯醇化酶 Enolase | 0.25 | |
| A0A7J9MAZ1 | 2,3-双磷酸甘油酸依赖性磷酸甘油酸变位酶 | 0.22 | |
| A0A7J9M9E5 | 乙酰辅酶A合成酶 Acetyl-CoA synthetase | 0.35 | |
| 硫代谢 Sulfur metabolism | A0A7J9MWP2 | 丝氨酸O-乙酰转移酶 | 0.38 |
| A0A7J9MMD9 | 胱硫苷γ合酶 | 0.38 | |
| A0A7J9M7E2 | 腺嘌呤基硫酸还原酶(谷胱甘肽) | 0.32 |
Tab.2 Changes of salt stress on energy metabolism of cotton roots
| 代谢通路 Pathway name | 序列号 Accession | 功能描述 Description | 变化倍数 Flod change CS/CK |
|---|---|---|---|
| 光合生物中的碳固定 Carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms | A0A7J9MMV1 | 苹果酸脱氢酶(脱羧) | 0.44 |
| A0A7J9KKP5 | 苹果酸脱氢酶 | 0.28 | |
| A0A7J9LT88 | 转酮酶 | 0.4 | |
| A0A7J9MIN9 | 丙酮酸,正磷酸二激酶 | 2.48 | |
| A0A7J9LQW1 | 二磷酸核糖羧化酶大链 | 0.22 | |
| A0A7J9LWV8 | 果糖二磷酸醛缩酶 | 0.29 | |
| A0A7J9L8J1 | 谷氨酸乙醛酸氨基转移酶 | 0.38 | |
| 脂肪酸代谢 Fatty acid metabolism | A0A7J9LXK4 | 酰基CoA氧化酶 | 0.36 |
| A0A7J9LGP8 | 3-氧代酰基-[酰基载体蛋白]合成酶III | 0.32 | |
| A0A7J9MDP4 | 长链酰基辅酶A合成酶 | 0.03 | |
| A0A7J9MNJ9 | 乙酰辅酶A羧化酶羧基转移酶亚基α | 0.3 | |
| A0A7J9LQW1 | 乙酰辅酶A羧化酶羧基转移酶亚基β | 0.22 | |
| A0A7J9N2P9 | 酰基-[酰基载体蛋白]去饱和酶 | 0.45 | |
| A0A7J9MI46 | 乙酰辅酶A酰基转移酶1 | 0.48 | |
| A0A7J9MBT9 | 3-氧代酰基-[酰基载体蛋白]合成酶II | 0.156 | |
| A0A7J9MML8 | 极长链烯酰辅酶A还原酶 | 0.08 | |
| 2-氧代羧酸代谢 2-Oxocarboxylic acid metabolism | A0A7J9MHQ1 | 酮酸还原酶 | 0.42 |
| A0A7J9MCR3 | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 | 0.45 | |
| A0A7J9LR84 | 支链氨基酸氨基转移酶 | 0.45 | |
| A0A7J9MF79 | 乙酰乳酸合成酶I/II/III大亚基 | 0.33 | |
| A0A7J9M5F7 | 乌头酸水合酶 | 0.3 | |
| A0A7J9LFB5 | 3-异丙基苹果酸/(R)-2-甲基苹果酸脱水酶大亚基 | 0.22 | |
| A0A7J9L8J1 | 谷氨酸乙醛酸氨基转移酶 | 0.38 | |
| A0A7J9MLD0 | 氨基酸N-乙酰转移酶 | 0.3 | |
| 氧化磷酸化 Oxidative phosphorylation | A0A7J9M3S6 | 无机焦磷酸酶 | 0.33 |
| A0A7J9KSN1 | ATP酶亚基δ | 3.34 | |
| A0A7J9LU75 | ATP酶亚基δ | 4.01 | |
| A0A7J9LUR9 | ATP酶亚单位γ | 0.49 | |
| A0A7J9MXH6 | ATP酶亚基d | 2.56 | |
| A0A7J9M8P5 | V型H+转运ATP酶亚基A | 0.38 | |
| A0A7J9NCI0 | V型H+转运ATP酶亚基G | 2.15 | |
| A0A7J9LE84 | V型H+转运ATP酶亚基a | 0.29 | |
| A0A7J9MAN9 | V型H+转运ATP酶16kDa蛋白脂质亚基 | 0.36 | |
| A0A7J9N9Y3 | 细胞色素c氧化酶亚基5b | 2.64 | |
| A0A7J9M160 | 细胞色素c氧化酶亚基6b | 3.09 | |
| A0A7J9MBK5 | NADH脱氢酶(泛醌)Fe-S蛋白7 | 0.44 | |
| A0A7J9LX02 | NADH脱氢酶(泛醌)黄素蛋白1 | 0.21 | |
| 氧化磷酸化 Oxidative phosphorylation | A0A7J9MRV1 | NADH脱氢酶(泛醌)1α亚基2 | 2.48 |
| A0A7J9MJS6 | NADH脱氢酶(泛醌)1α亚基8 | 3.94 | |
| A0A7J9L0N9 | NADH脱氢酶(泛醌)1β亚基10 | 2.29 | |
| 氮代谢 Nitrogen metabolism | A0A7J9LWX4 | 谷氨酸脱氢酶(NAD(P)+) | 0.48 |
| A0A7J9KIX3 | 腈化酶 | 0.36 | |
| A0A7J9L9B3 | 硝酸还原酶(NAD(P)H) | 0.01 | |
| 甲烷代谢 Methane metabolism | A0A7J9LUW0 | 2-氧戊二酸还原酶 | 0.27 |
| A0A7J9MLG9 | 甘氨酸羟甲基转移酶 | 0.36 | |
| A0A7J9N9M4 | 6-磷酸果糖激酶1 | 0.5 | |
| A0A7J9LWV8 | 果糖二磷酸醛缩酶 | 0.29 | |
| A0A7J9KZF9 | 烯醇化酶 Enolase | 0.25 | |
| A0A7J9MAZ1 | 2,3-双磷酸甘油酸依赖性磷酸甘油酸变位酶 | 0.22 | |
| A0A7J9M9E5 | 乙酰辅酶A合成酶 Acetyl-CoA synthetase | 0.35 | |
| 硫代谢 Sulfur metabolism | A0A7J9MWP2 | 丝氨酸O-乙酰转移酶 | 0.38 |
| A0A7J9MMD9 | 胱硫苷γ合酶 | 0.38 | |
| A0A7J9M7E2 | 腺嘌呤基硫酸还原酶(谷胱甘肽) | 0.32 |
| 代谢通路 Pathway name | 序列号 Accession | 功能描述 Description | 变化倍数 Flod change AS/CK |
|---|---|---|---|
| 半乳糖代谢 Galactose metabolism | A0A7J9L4C2 | 拉菲糖合酶 | 0.49 |
| A0A7J9LKB1 | 肌醇3-α-半乳糖基转移酶 | 0.48 |
Tab.3 Changes of alkali stress on energy metabolism of cotton roots
| 代谢通路 Pathway name | 序列号 Accession | 功能描述 Description | 变化倍数 Flod change AS/CK |
|---|---|---|---|
| 半乳糖代谢 Galactose metabolism | A0A7J9L4C2 | 拉菲糖合酶 | 0.49 |
| A0A7J9LKB1 | 肌醇3-α-半乳糖基转移酶 | 0.48 |
| 代谢通路 Pathway name | 序列号 Accession | 功能描述 Description | 变化倍数 Flod change CS/CK | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甘氨酸、丝氨酸和苏氨酸代谢 Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | A0A7J9LUW0 | 2-氧戊二酸还原酶 | 0.27 | |
| A0A7J9KN24 | 甜菜碱醛脱氢酶 | 0.44 | ||
| A0A7J9LXZ1 | 伯胺氧化酶 | 37 | ||
| A0A7J9MER7 | 甘氨酸脱氢酶 | 0.26 | ||
| A0A7J9MLG9 | 甘氨酸羟甲基转移酶 | 0.36 | ||
| A0A7J9N6E1 | 丙氨酸乙醛酸转氨酶 | 0.2 | ||
| A0A7J9LL52 | 苏氨酸醛缩酶 | 0.267 | ||
| A0A7J9MGE3 | 苏氨酸合酶 | 0.11 | ||
| A0A7J9MAZ1 | 2,3-双磷酸甘油酸依赖性磷酸甘油酸变位酶 | 0.22 | ||
| A0A7J9MAZ1 | 丝氨酸外消旋酶 | 0.22 | ||
| A0A7J9L1Q8 | 双功能天冬氨酸激酶 | 0.27 | ||
| A0A7J9L8J1 | 谷氨酸乙醛酸氨基转移酶 | 0.38 | ||
| 半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢 Cysteine and methionine metabolism | A0A7J9M5W1 | L-乳酸脱氢酶 | 0.44 | |
| A0A7J9LUW0 | 2-氧戊二酸还原酶 | 0.27 | ||
| A0A7J9NEL2 | 5-甲基四氢蝶酰三谷氨酸--同型半胱氨酸甲基转移酶 | 0.1 | ||
| A0A7J9MWP2 | 丝氨酸O-乙酰转移酶 | 0.38 | ||
| A0A7J9LLZ2 | 腺苷甲硫氨酸合成酶 | 0.4 | ||
| A0A7J9MCR3 | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9LR84 | 支链氨基酸氨基转移酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9N6E1 | 丙氨酸乙醛酸转氨酶 | 0.2 | ||
| A0A7J9MYF0 | 5-甲基硫核糖激酶 | 0.47 | ||
| A0A7J9MJW3 | 腺苷同型半胱氨酸酶 | 0.12 | ||
| A0A7J9MMD9 | 胱硫苷γ合酶 | 0.38 | ||
| A0A7J9N309 | 氨基环丙烷羧酸氧化酶 | 0.13 | ||
| A0A7J9L1Q8 | 双功能天冬氨酸激酶 | 0.27 | ||
| A0A7J9M1U3 | DNA(胞嘧啶-5)-甲基转移酶3A | 0.21 | ||
| 缬氨酸、亮氨酸和 异亮氨酸生物合成 Valine, leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis | A0A7J9MBQ9 | 酮酸还原酶 | 0.44 | |
| A0A7J9LR84 | 支链氨基酸氨基转移酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9MF79 | 乙酰乳酸合成酶I/II/III大亚基 | 0.33 | ||
| A0A7J9LFB5 | 3-苹果酸异丙酯 | 0.22 | ||
| 酪氨酸代谢 Tyrosine metabolism | A0A7J9L2C9 | 乙醇脱氢酶 | 253 | |
| A0A7J9LXZ1 | 伯胺氧化酶 | 36.9 | ||
| A0A7J9KSA0 | 均龙胆酸1,2-双加氧酶 | 0.38 | ||
| A0A7J9MCR3 | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9LHK9 | 组氨酸磷酸氨基转移酶 | 0.37 | ||
| A0A7J9MDP1 | 富马酸酯酶 | 0.39 | ||
| A0A7J9KS17 | 酰基丙酮酸水解酶 | 3.11 | ||
| A0A7J9MFQ6 | 马来酰乙酰乙酸异构酶 | 2.22 | ||
| A0A7J9N0H0 | 苯丙酮酸互变异构酶 | 3.84 | ||
| 缬氨酸、亮氨酸和异亮氨酸降解 Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation | A0A7J9MA01 | 乙醛脱氢酶(NAD+) | 0.26 | |
| A0A7J9LIW6 | 二氢硫酰胺脱氢酶 | 0.32 | ||
| A0A7J9LR84 | 支链氨基酸氨基转移酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9N6E1 | 丙氨酸乙醛酸转氨酶 | 0.2 | ||
| A0A7J9LT94 | 羟甲基戊二酰辅酶A合酶 | 0.21 | ||
| A0A7J9L5M5 | 3-甲基巴豆酰基-CoA羧化酶α亚基 | 0.36 | ||
| A0A7J9MI46 | 乙酰辅酶A酰基转移酶1 | 0.48 | ||
| 丙氨酸、天冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢 Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | A0A7J9LWX4 | 谷氨酸脱氢酶(NAD(P)+) | 0.48 | |
| A0A7J9MCR3 | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9N6E1 | 丙氨酸乙醛酸转氨酶 | 0.2 | ||
| A0A7J9LXM7 | 谷氨酸脱羧酶 | 0.22 | ||
| A0A7J9MSM4 | 天门冬氨酸合成酶(谷氨酰胺水解) | 0.17 | ||
| A0A7J9M2E1 | L-天冬酰胺酶 | 0.44 | ||
| A0A7J9L8J1 | 谷氨酸乙醛酸氨基转移酶 | 0.38 | ||
| 苯丙氨酸、酪氨酸和 色氨酸生物合成 Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis | A0A7J9LV97 | 3-磷基木酸1-羧基乙烯基转移酶 | 0.17 | |
| A0A7J9MCR3 | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9LHK9 | 组氨酸磷酸氨基转移酶 | 0.37 | ||
| A0A7J9M6S3 | 3-脱氧-7-磷庚烯酸合酶 | 0.24 | ||
| A0A7J9KNK6 | 蒽合酶组分I | 0.48 | ||
| A0A7J9MH57 | 绒毛膜酸合成酶 | 124 | ||
| A0A7J9MCV6 | 芳香烃 | 2.52 | ||
| 苯丙氨酸代谢 Phenylalanine metabolism | A0A7J9LXZ1 | 伯胺氧化酶 | 37 | |
| A0A7J9MCR3 | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9LHK9 | 组氨酸磷酸氨基转移酶 | 0.37 | ||
| A0A7J9LRP4 | 酰胺酶 | 2.53 | ||
| A0A7J9N0H0 | 苯丙酮酸互变异构酶 | 3.84 | ||
| A0A7J9MHY7 | 苯丙氨酸解氨酶 | 0.17 | ||
| A0A7J9LEH2 | 苯丙氨酸 | 0.35 | ||
| 色氨酸代谢 Tryptophan metabolism | A0A7J9MA01 | 乙醛脱氢酶(NAD+) | 0.26 | |
| A0A7J9LIW6 | 二氢硫酰胺脱氢酶 | 0.32 | ||
| A0A7J9LRP4 | 酰胺酶 | 2.53 | ||
| A0A7J9KIX3 | 腈化酶 | 0.36 | ||
| A0A7J9M4T6 | 过氧化氢酶 | 0.35 | ||
| A0A7J9NEG8 | 细胞色素P450家族1亚家族A1 | 0.37 | ||
| A0A7J9NEG8 | 吲哚乙酰肟脱水酶 | 0.37 | ||
| 精氨酸生物合成 Arginine biosynthesis | A0A7J9LWX4 | 谷氨酸脱氢酶(NAD(P)+) | 0.48 | |
| A0A7J9MCR3 | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9L8J1 | 谷氨酸乙醛酸氨基转移酶 | 0.38 | ||
| A0A7J9MLD0 | 氨基酸N-乙酰转移酶 | 0.3 | ||
| 组氨酸代谢 Histidine metabolism | A0A7J9MA01 | 乙醛脱氢酶(NAD+) | 0.26 | |
| A0A7J9LHK9 | 组氨酸磷酸氨基转移酶 | 0.37 | ||
| 赖氨酸生物合成 Lysine biosynthesis | A0A7J9N056 | 4-羟基-四氢二磷胆碱还原酶 | 4.67 | |
| A0A7J9L1Q8 | 双功能天冬氨酸激酶 | 0.27 | ||
| 精氨酸和脯氨酸代谢 Arginine and proline metabolism | A0A7J9MA01 | 乙醛脱氢酶(NAD+) | 0.26 | |
| A0A7J9N8G8 | 脯氨酰4-羟化酶 | 0.22 | ||
| A0A7J9MCR3 | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9LRP4 | 酰胺酶 | 2.53 | ||
| A0A7J9M6K7 | 精胺氧化酶 | 0.27 | ||
| 赖氨酸降解 Lysine degradation | A0A7J9MA01 | 乙醛脱氢酶(NAD+) | 0.26 | |
| A0A7J9LIW6 | 二氢硫酰胺脱氢酶 | 0.32 | ||
| A0A7J9KTK0 | N-三甲基转移酶 | 0.09 | ||
Tab.4 Changes of salt stress on amino acid metabolism in cotton roots
| 代谢通路 Pathway name | 序列号 Accession | 功能描述 Description | 变化倍数 Flod change CS/CK | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甘氨酸、丝氨酸和苏氨酸代谢 Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | A0A7J9LUW0 | 2-氧戊二酸还原酶 | 0.27 | |
| A0A7J9KN24 | 甜菜碱醛脱氢酶 | 0.44 | ||
| A0A7J9LXZ1 | 伯胺氧化酶 | 37 | ||
| A0A7J9MER7 | 甘氨酸脱氢酶 | 0.26 | ||
| A0A7J9MLG9 | 甘氨酸羟甲基转移酶 | 0.36 | ||
| A0A7J9N6E1 | 丙氨酸乙醛酸转氨酶 | 0.2 | ||
| A0A7J9LL52 | 苏氨酸醛缩酶 | 0.267 | ||
| A0A7J9MGE3 | 苏氨酸合酶 | 0.11 | ||
| A0A7J9MAZ1 | 2,3-双磷酸甘油酸依赖性磷酸甘油酸变位酶 | 0.22 | ||
| A0A7J9MAZ1 | 丝氨酸外消旋酶 | 0.22 | ||
| A0A7J9L1Q8 | 双功能天冬氨酸激酶 | 0.27 | ||
| A0A7J9L8J1 | 谷氨酸乙醛酸氨基转移酶 | 0.38 | ||
| 半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢 Cysteine and methionine metabolism | A0A7J9M5W1 | L-乳酸脱氢酶 | 0.44 | |
| A0A7J9LUW0 | 2-氧戊二酸还原酶 | 0.27 | ||
| A0A7J9NEL2 | 5-甲基四氢蝶酰三谷氨酸--同型半胱氨酸甲基转移酶 | 0.1 | ||
| A0A7J9MWP2 | 丝氨酸O-乙酰转移酶 | 0.38 | ||
| A0A7J9LLZ2 | 腺苷甲硫氨酸合成酶 | 0.4 | ||
| A0A7J9MCR3 | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9LR84 | 支链氨基酸氨基转移酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9N6E1 | 丙氨酸乙醛酸转氨酶 | 0.2 | ||
| A0A7J9MYF0 | 5-甲基硫核糖激酶 | 0.47 | ||
| A0A7J9MJW3 | 腺苷同型半胱氨酸酶 | 0.12 | ||
| A0A7J9MMD9 | 胱硫苷γ合酶 | 0.38 | ||
| A0A7J9N309 | 氨基环丙烷羧酸氧化酶 | 0.13 | ||
| A0A7J9L1Q8 | 双功能天冬氨酸激酶 | 0.27 | ||
| A0A7J9M1U3 | DNA(胞嘧啶-5)-甲基转移酶3A | 0.21 | ||
| 缬氨酸、亮氨酸和 异亮氨酸生物合成 Valine, leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis | A0A7J9MBQ9 | 酮酸还原酶 | 0.44 | |
| A0A7J9LR84 | 支链氨基酸氨基转移酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9MF79 | 乙酰乳酸合成酶I/II/III大亚基 | 0.33 | ||
| A0A7J9LFB5 | 3-苹果酸异丙酯 | 0.22 | ||
| 酪氨酸代谢 Tyrosine metabolism | A0A7J9L2C9 | 乙醇脱氢酶 | 253 | |
| A0A7J9LXZ1 | 伯胺氧化酶 | 36.9 | ||
| A0A7J9KSA0 | 均龙胆酸1,2-双加氧酶 | 0.38 | ||
| A0A7J9MCR3 | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9LHK9 | 组氨酸磷酸氨基转移酶 | 0.37 | ||
| A0A7J9MDP1 | 富马酸酯酶 | 0.39 | ||
| A0A7J9KS17 | 酰基丙酮酸水解酶 | 3.11 | ||
| A0A7J9MFQ6 | 马来酰乙酰乙酸异构酶 | 2.22 | ||
| A0A7J9N0H0 | 苯丙酮酸互变异构酶 | 3.84 | ||
| 缬氨酸、亮氨酸和异亮氨酸降解 Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation | A0A7J9MA01 | 乙醛脱氢酶(NAD+) | 0.26 | |
| A0A7J9LIW6 | 二氢硫酰胺脱氢酶 | 0.32 | ||
| A0A7J9LR84 | 支链氨基酸氨基转移酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9N6E1 | 丙氨酸乙醛酸转氨酶 | 0.2 | ||
| A0A7J9LT94 | 羟甲基戊二酰辅酶A合酶 | 0.21 | ||
| A0A7J9L5M5 | 3-甲基巴豆酰基-CoA羧化酶α亚基 | 0.36 | ||
| A0A7J9MI46 | 乙酰辅酶A酰基转移酶1 | 0.48 | ||
| 丙氨酸、天冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢 Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | A0A7J9LWX4 | 谷氨酸脱氢酶(NAD(P)+) | 0.48 | |
| A0A7J9MCR3 | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9N6E1 | 丙氨酸乙醛酸转氨酶 | 0.2 | ||
| A0A7J9LXM7 | 谷氨酸脱羧酶 | 0.22 | ||
| A0A7J9MSM4 | 天门冬氨酸合成酶(谷氨酰胺水解) | 0.17 | ||
| A0A7J9M2E1 | L-天冬酰胺酶 | 0.44 | ||
| A0A7J9L8J1 | 谷氨酸乙醛酸氨基转移酶 | 0.38 | ||
| 苯丙氨酸、酪氨酸和 色氨酸生物合成 Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis | A0A7J9LV97 | 3-磷基木酸1-羧基乙烯基转移酶 | 0.17 | |
| A0A7J9MCR3 | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9LHK9 | 组氨酸磷酸氨基转移酶 | 0.37 | ||
| A0A7J9M6S3 | 3-脱氧-7-磷庚烯酸合酶 | 0.24 | ||
| A0A7J9KNK6 | 蒽合酶组分I | 0.48 | ||
| A0A7J9MH57 | 绒毛膜酸合成酶 | 124 | ||
| A0A7J9MCV6 | 芳香烃 | 2.52 | ||
| 苯丙氨酸代谢 Phenylalanine metabolism | A0A7J9LXZ1 | 伯胺氧化酶 | 37 | |
| A0A7J9MCR3 | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9LHK9 | 组氨酸磷酸氨基转移酶 | 0.37 | ||
| A0A7J9LRP4 | 酰胺酶 | 2.53 | ||
| A0A7J9N0H0 | 苯丙酮酸互变异构酶 | 3.84 | ||
| A0A7J9MHY7 | 苯丙氨酸解氨酶 | 0.17 | ||
| A0A7J9LEH2 | 苯丙氨酸 | 0.35 | ||
| 色氨酸代谢 Tryptophan metabolism | A0A7J9MA01 | 乙醛脱氢酶(NAD+) | 0.26 | |
| A0A7J9LIW6 | 二氢硫酰胺脱氢酶 | 0.32 | ||
| A0A7J9LRP4 | 酰胺酶 | 2.53 | ||
| A0A7J9KIX3 | 腈化酶 | 0.36 | ||
| A0A7J9M4T6 | 过氧化氢酶 | 0.35 | ||
| A0A7J9NEG8 | 细胞色素P450家族1亚家族A1 | 0.37 | ||
| A0A7J9NEG8 | 吲哚乙酰肟脱水酶 | 0.37 | ||
| 精氨酸生物合成 Arginine biosynthesis | A0A7J9LWX4 | 谷氨酸脱氢酶(NAD(P)+) | 0.48 | |
| A0A7J9MCR3 | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9L8J1 | 谷氨酸乙醛酸氨基转移酶 | 0.38 | ||
| A0A7J9MLD0 | 氨基酸N-乙酰转移酶 | 0.3 | ||
| 组氨酸代谢 Histidine metabolism | A0A7J9MA01 | 乙醛脱氢酶(NAD+) | 0.26 | |
| A0A7J9LHK9 | 组氨酸磷酸氨基转移酶 | 0.37 | ||
| 赖氨酸生物合成 Lysine biosynthesis | A0A7J9N056 | 4-羟基-四氢二磷胆碱还原酶 | 4.67 | |
| A0A7J9L1Q8 | 双功能天冬氨酸激酶 | 0.27 | ||
| 精氨酸和脯氨酸代谢 Arginine and proline metabolism | A0A7J9MA01 | 乙醛脱氢酶(NAD+) | 0.26 | |
| A0A7J9N8G8 | 脯氨酰4-羟化酶 | 0.22 | ||
| A0A7J9MCR3 | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9LRP4 | 酰胺酶 | 2.53 | ||
| A0A7J9M6K7 | 精胺氧化酶 | 0.27 | ||
| 赖氨酸降解 Lysine degradation | A0A7J9MA01 | 乙醛脱氢酶(NAD+) | 0.26 | |
| A0A7J9LIW6 | 二氢硫酰胺脱氢酶 | 0.32 | ||
| A0A7J9KTK0 | N-三甲基转移酶 | 0.09 | ||
| 代谢通路 Pathway name | 序列号 Accession | 功能描述 Description | 变化倍数 Flod change AS/CK |
|---|---|---|---|
| 苯丙氨酸代谢 Phenylalanine metabolism | A0A7J9KVJ8 | 苯丙氨酸解氨酶 | 0.423 |
| A0A7J9LEH2 | 苯丙氨酸 | 0.46 | |
| 氨基酸的生物合成 Biosynthesis of amino acids | A0A7J9MGE3 | 苏氨酸合酶 | 2.13 |
| A0A7J9NAH1 | 3-脱氢奎尼酸脱水酶 | 0.47 |
Tab.5 Changes of alkali stress on amino acid metabolism in cotton roots
| 代谢通路 Pathway name | 序列号 Accession | 功能描述 Description | 变化倍数 Flod change AS/CK |
|---|---|---|---|
| 苯丙氨酸代谢 Phenylalanine metabolism | A0A7J9KVJ8 | 苯丙氨酸解氨酶 | 0.423 |
| A0A7J9LEH2 | 苯丙氨酸 | 0.46 | |
| 氨基酸的生物合成 Biosynthesis of amino acids | A0A7J9MGE3 | 苏氨酸合酶 | 2.13 |
| A0A7J9NAH1 | 3-脱氢奎尼酸脱水酶 | 0.47 |

Fig.7 Changes of salt stress on genetic information processing of cotton roots Notes:(a) Translation, (b) Folding, sorting and degradation, (c) Transcription, (d) Replication and repair
| 代谢通路 Pathway name | 序列号Accession | 功能描述 Description | 变化倍数 Flod change CS/CK | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK信号通路-植物 MAPK signaling pathway - plant | A0A7J9KZD8 | 钙调素 | 3.68 | |
| A0A7J9LX47 | 过氧化氢酶 Catalase | 4.04 | ||
| A0A7J9L9T9 | Brassinoseroid不敏感1-相关受体激酶1 | 2.06 | ||
| A0A7J9LW53 | 转录因子MYC2 | 0.11 | ||
| A0A7J9LK24 | 脱落酸受体PYR/PYL家族 | 2.30 | ||
| A0A7J9NCH4 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶SRK2 | 0.33 | ||
| A0A7J9LCC9 | 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶6 | 0.39 | ||
| A0A7J9NE39 | 乙烯不敏感蛋白2 | 0.47 | ||
| A0A7J9LMQ1 | 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶8 | 0.30 | ||
| A0A7J9KVE0 | 碱性内几丁质酶B | 6.72 | ||
| A0A7J9KME4 | 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶4 | 0.48 | ||
| A0A7J9LTC8 | MAP激酶底物1 | 4.19 | ||
| 植物激素信号转导 Plant hormone signal transduction | A0A7J9L9T9 | Brassinoseroid不敏感1-相关受体激酶1 | 2.06 | |
| A0A7J9LW53 | 转录因子MYC2 | 0.11 | ||
| A0A7J9LX96 | ABA响应元件结合因子 | 2.05 | ||
| A0A7J9LNX1 | 含组氨酸磷酸转移蛋白 | 3.29 | ||
| A0A7J9MPP5 | 双组分响应调节器ARR-A系列 | 0.25 | ||
| A0A7J9LK24 | 脱落酸受体PYR/PYL家族 | 2.30 | ||
| A0A7J9NCH4 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶SRK2 | 0.33 | ||
| A0A7J9N499 | BR信号激酶 | 0.49 | ||
| A0A7J9LCC9 | 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶6 | 0.39 | ||
| A0A7J9NE39 | 乙烯不敏感蛋白2 | 0.47 | ||
| AMPK信号通路 AMPK signaling pathway | A0A7J9NAK5 | 羟甲基戊二酰辅酶A还原酶(NADPH) | 0.13 | |
| A0A7J9N9M4 | 6-磷酸果糖激酶1 | 0.50 | ||
| A0A7J9LZM7 | 延伸因子2 | 0.18 | ||
| A0A7J9L2G8 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白磷酸酶2A调节亚单位A | 0.47 | ||
| A0A7J9LEN1 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白磷酸酶2A调节亚基B | 0.35 | ||
| A0A7J9MQN1 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白磷酸酶2A催化亚单位 | 0.01 | ||
| A0A7J9LHR5 | 5'-AMP活化蛋白激酶,催化α亚基 | 0.49 | ||
| A0A7J9MA19 | 5'-AMP激活蛋白激酶,调节β亚基 | 0.41 | ||
| A0A7J9KN49 | Ras相关蛋白Rab-11B | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9LM96 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白磷酸酶2A调节亚基B | 0.25 | ||
| A0A7J9LX47 | 钙调素 | 4.04 | ||
| A0A7J9M7L8 | 磷脂酰肌醇磷脂酶C,δ | 0.50 | ||
| A0A7J9L4M6 | 溶质载体系列25 | 0.23 | ||
| A0A7J9LIH2 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白磷酸酶2B调节亚单位 | 2.36 | ||
| A0A7J9LBI6 | 电压依赖性阴离子通道蛋白2 | 0.24 | ||
| cAMP信号通路 cAMP signaling pathway | A0A7J9LXK4 | 酰基CoA氧化酶 | 0.36 | |
| A0A7J9MF74 | 磷脂酶D1/2 | 0.35 | ||
| A0A7J9LX47 | 钙调素 | 4.04 | ||
| A0A7J9KME4 | 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶1/3 | 0.48 | ||
| A0A7J9LSA1 | Ras相关C3肉毒素底物1 | 0.30 | ||
Tab.6 Changes of salt stress on signal transduction in cotton roots
| 代谢通路 Pathway name | 序列号Accession | 功能描述 Description | 变化倍数 Flod change CS/CK | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK信号通路-植物 MAPK signaling pathway - plant | A0A7J9KZD8 | 钙调素 | 3.68 | |
| A0A7J9LX47 | 过氧化氢酶 Catalase | 4.04 | ||
| A0A7J9L9T9 | Brassinoseroid不敏感1-相关受体激酶1 | 2.06 | ||
| A0A7J9LW53 | 转录因子MYC2 | 0.11 | ||
| A0A7J9LK24 | 脱落酸受体PYR/PYL家族 | 2.30 | ||
| A0A7J9NCH4 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶SRK2 | 0.33 | ||
| A0A7J9LCC9 | 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶6 | 0.39 | ||
| A0A7J9NE39 | 乙烯不敏感蛋白2 | 0.47 | ||
| A0A7J9LMQ1 | 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶8 | 0.30 | ||
| A0A7J9KVE0 | 碱性内几丁质酶B | 6.72 | ||
| A0A7J9KME4 | 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶4 | 0.48 | ||
| A0A7J9LTC8 | MAP激酶底物1 | 4.19 | ||
| 植物激素信号转导 Plant hormone signal transduction | A0A7J9L9T9 | Brassinoseroid不敏感1-相关受体激酶1 | 2.06 | |
| A0A7J9LW53 | 转录因子MYC2 | 0.11 | ||
| A0A7J9LX96 | ABA响应元件结合因子 | 2.05 | ||
| A0A7J9LNX1 | 含组氨酸磷酸转移蛋白 | 3.29 | ||
| A0A7J9MPP5 | 双组分响应调节器ARR-A系列 | 0.25 | ||
| A0A7J9LK24 | 脱落酸受体PYR/PYL家族 | 2.30 | ||
| A0A7J9NCH4 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶SRK2 | 0.33 | ||
| A0A7J9N499 | BR信号激酶 | 0.49 | ||
| A0A7J9LCC9 | 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶6 | 0.39 | ||
| A0A7J9NE39 | 乙烯不敏感蛋白2 | 0.47 | ||
| AMPK信号通路 AMPK signaling pathway | A0A7J9NAK5 | 羟甲基戊二酰辅酶A还原酶(NADPH) | 0.13 | |
| A0A7J9N9M4 | 6-磷酸果糖激酶1 | 0.50 | ||
| A0A7J9LZM7 | 延伸因子2 | 0.18 | ||
| A0A7J9L2G8 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白磷酸酶2A调节亚单位A | 0.47 | ||
| A0A7J9LEN1 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白磷酸酶2A调节亚基B | 0.35 | ||
| A0A7J9MQN1 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白磷酸酶2A催化亚单位 | 0.01 | ||
| A0A7J9LHR5 | 5'-AMP活化蛋白激酶,催化α亚基 | 0.49 | ||
| A0A7J9MA19 | 5'-AMP激活蛋白激酶,调节β亚基 | 0.41 | ||
| A0A7J9KN49 | Ras相关蛋白Rab-11B | 0.45 | ||
| A0A7J9LM96 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白磷酸酶2A调节亚基B | 0.25 | ||
| A0A7J9LX47 | 钙调素 | 4.04 | ||
| A0A7J9M7L8 | 磷脂酰肌醇磷脂酶C,δ | 0.50 | ||
| A0A7J9L4M6 | 溶质载体系列25 | 0.23 | ||
| A0A7J9LIH2 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白磷酸酶2B调节亚单位 | 2.36 | ||
| A0A7J9LBI6 | 电压依赖性阴离子通道蛋白2 | 0.24 | ||
| cAMP信号通路 cAMP signaling pathway | A0A7J9LXK4 | 酰基CoA氧化酶 | 0.36 | |
| A0A7J9MF74 | 磷脂酶D1/2 | 0.35 | ||
| A0A7J9LX47 | 钙调素 | 4.04 | ||
| A0A7J9KME4 | 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶1/3 | 0.48 | ||
| A0A7J9LSA1 | Ras相关C3肉毒素底物1 | 0.30 | ||
| [1] | Mbarki S, Sytar O, Cerda A, et al. Strategies to mitigate the salt stress effects on photosynthetic apparatus and productivity of crop plants[M]// Salinity Responses and Tolerance in Plants, Volume 1. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018: 85-136. |
| [2] |
董心久, 沙红, 高燕, 等. 盐碱胁迫对甜菜光合物质积累及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(4): 642-651.
DOI |
|
DONG Xinjiu, SHA Hong, GAO Yan, et al. Effects of saline alkali stress on photosynthesis and dry matter accumulation and yield of sugar beet[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(4): 642-651.
DOI |
|
| [3] | 李双男, 郭慧娟, 王晶, 等. 不同盐碱胁迫对棉花种子萌发的影响[J]. 种子, 2018, 37(1): 38-45. |
| LI Shuangnan, GUO Huijuan, WANG Jing, et al. Effects of different saline and alkaline stress on seed[J]. Seed, 2018, 37(1): 38-45. | |
| [4] |
Yang H C, Wang J Y, Zhang F H. Soil aggregation and aggregate-associated carbon under four typical halophyte communities in an arid area[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2016, 23(23): 23920-23929.
PMID |
| [5] |
Munns R, Tester M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2008, 59: 651-681.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Passamani L Z, Barbosa R R, Reis R S, et al. Salt stress induces changes in the proteomic profile of micropropagated sugarcane shoots[J]. Plos One, 2017, 12(4): e0176076. |
| [7] | 罗光宇, 肖敏敏, 刘爱玲, 等. 蛋白质组学在水稻作物非生物胁迫研究中的应用[J]. 分子植物育种, 2018, 16(2): 423-426. |
| LUO Guangyu, XIAO Minmin, LIU Ailing, et al. Application of proteomics in the study of abiotic stress in rice[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2018, 16(2): 423-426. | |
| [8] | 王占旗. 水稻应答铝毒害的根蛋白质组学研究及OsTCTP功能分析[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2014. |
| WANG Zhanqi. Proteomics Study of the Response of Rice Root to Aluminum Stress and Functional Analysis of OsTCTP[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2014. | |
| [9] | 马洪雨. 高低耐盐性大豆幼苗根叶和黄麻幼苗根响应盐胁迫的蛋白质组学研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2011. |
| MA Hongyu. Proteomic Analysis of Salttolerant Andsensitive Soybean Seedling Root and Leaf and Just Seeding Root to Salt Stress[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2011. | |
| [10] | 张黛静, 王多多, 董文, 等. 铜胁迫下小麦幼根转录组学及蛋白质组学研究[J]. 河南农业科学, 2015, 44(4): 31-35. |
| ZHANG Daijing, WANG Duoduo, DONG Wen, et al. Transcriptomics and proteomics analysis in root of wheat under copper stress[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 44(4): 31-35. | |
| [11] |
李兵娟, 郑璐, 沈仁芳, 等. 拟南芥RPP1A参与幼苗生长的蛋白质组学分析[J]. 生物技术通报, 2022, 38(2): 10-20.
DOI |
|
LI Bingjuan, ZHENG Lu, SHEN Renfang, et al. Proteomic analysis of RPP1A involved in the seedling growth of Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2022, 38(2): 10-20.
DOI |
|
| [12] | 高飞, 王彦平, 周宜君, 等. 植物应答非生物胁迫的蛋白质组学研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2008, 10(6): 9-15. |
| GAO Fei, WANG Yanping, ZHOU Yijun, et al. Research progress on proteomics to uncover abiotic stress tolerance mechanisms in plant[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2008, 10(6): 9-15. | |
| [13] | 李雪梅, 李玥莹, 马莲菊, 等. 逆境胁迫下水稻蛋白质组学研究进展[J]. 沈阳师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 27(3): 257-263. |
| LI Xuemei, LI Yueying, MA Lianju, et al. Progress research in on rice proteomics under stress[J]. Journal of Shenyang Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 27(3): 257-263. | |
| [14] | Wang J C, Li B C, Meng Y X, et al. Transcriptomic profiling of the salt-stress response in the halophyte Halogeton glomeratus[J]. BMC Genomics, 2015, 16(1): 169. |
| [15] |
Zhang Z, Mao C Y, Shi Z, et al. The amino acid metabolic and carbohydrate metabolic pathway play important roles during salt-stress response in tomato[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1231.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Zhang J, Yang D S, Li M X, et al. Metabolic profiles reveal changes in wild and cultivated soybean seedling leaves under salt stress[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(7): e0159622. |
| [17] | Guo J X, Lu X Y, Tao Y F, et al. Comparative ionomics and metabolic responses and adaptive strategies of cotton to salt and alkali stress[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 871387. |
| [18] | Abbas G, Saqib M, Akhtar J, et al. Interactive effects of salinity and iron deficiency on different rice genotypes[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 2015, 178(2): 306-311. |
| [19] |
廖欢, 侯振安. 盐碱胁迫对不同棉花品种生长及离子组含量分布的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(2): 219-232.
DOI |
|
LIAO Huan, HOU Zhenan. Effects of saline-alkali stress on growth and ion group content distribution of different cotton varieties[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(2): 219-232.
DOI |
|
| [20] | 焦德志, 赵泽龙. 盐碱胁迫对植物形态和生理生化影响及植物响应的研究进展[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(20): 1-4. |
| JIAO Dezhi, ZHAO Zelong. Research progress on influences of saline-alkali stress on plant morphology, physiology and biochemistry and response of plants to saline-alkali stress[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(20): 1-4. | |
| [21] | Berkowitz O, De Clercq I, Van Breusegem F, et al. Interaction between hormonal and mitochondrial signalling during growth, development and in plant defence responses[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2016, 39(5): 1127-1139. |
| [22] |
Meyer E H, Welchen E, Carrie C. Assembly of the complexes of the oxidative phosphorylation system in land plant mitochondria[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2019, 70: 23-50.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | 姜维, 张庆威, 陈三雄, 等. 基于TMT的长果桑根部盐胁迫蛋白质组学研究[J]. 仲恺农业工程学院学报, 2023, 36(1): 26-35. |
| JIANG Wei, ZHANG Qingwei, CHEN Sanxiong, et al. Proteomics of Morus root under salt stress based on TMT[J]. Journal of Zhongkai University of Agriculture and Engineering, 2023, 36(1): 26-35. | |
| [24] | Xiang G Q, Ma W Y, Gao S W, et al. Transcriptomic and phosphoproteomic profiling and metabolite analyses reveal the mechanism of NaHCO3-induced organic acid secretion in grapevine roots[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 383.. |
| [25] | 陈国林, 吴建国, 石春海. 作物种子氨基酸性状的遗传效应研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2009, 21(5): 524-528. |
| CHEN Guolin, WU Jianguo, SHI Chunhai. Analysis of the genetic effects on the trait of seed amino acid content in crops[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2009, 21(5): 524-528. | |
| [26] | Li J K, Essemine J, Shang C, et al. Combined proteomics and metabolism analysis unravels prominent roles of antioxidant system in the prevention of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) against salt stress[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(3): 909. |
| [27] |
Hardie D G, Ross F A, Hawley S A. AMPK: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2012, 13(4): 251-262.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | GONG Zhaoxing, HAN Pengcheng, LI Zesen, LI Guizhen, WANG Yuxiang, ZHANG Bo. The physiological effects of inoculation with AM fungi under salt stress on wild smooth [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 129-136. |
| [2] | LAI Chengxia, YANG Yanlong, WANG Penglong, ZHU Mengyu, YANG Dong, LI Chunping, GE Fengwei, Mayila Yusuyin, YANG Ni, MA Jun. Pathogen colony’s morphological characteristics and pathogenicity identification of defioating cotton Verticillium wilt in some areas in northern Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 174-181. |
| [3] | WANG Wei, ZHANG Renfu, LIU Haiyang, LI Xiaowei, YAO Ju. Occurrence dynamics and spatial distribution pattern of Frankliniella intonsa in cotton fields in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 202-209. |
| [4] | WEN Fang, LIAO Na, WANG Na, JIN Jing, YAO Yiqiang. Adsorption and immobilization of Cd2+ by cotton straw biochar [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 225-233. |
| [5] | ZHOU Xin, LIU Xuanfeng, JIANG Yuhan, ZHANG Haichun, YANG Yuxin, Yeerbdati Tiemuer, JIANG Yongxin, ZHANG Li. Current situation and development proposal of mechanized recovery and resource utilization of used mulch film in cotton fields in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 131-141. |
| [6] | MIAO Hongping, WANG Xiaowei, TIAN Conghua, LI Zhi, ZHANG Yuxin, DAI Junsheng. Evolution characteristics and driving factors of cotton production and distribution in Tarim River basin [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 217-226. |
| [7] | WANG Junduo, CUI Yujiang, LIANG Yajun, GONG Zhaolong, ZHENG Junyun, LI Xueyuan. Xinjiang cotton production advantageous regional layout scheme [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 60-69. |
| [8] | ZHENG Juyun, GONG Zhaolong, LIANG Yajun, GENG Shiwei, SUN Fenglei, YANG ni, LI Xueyuan, WANG Junduo. Key technology model of machine-picked cotton production in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 70-74. |
| [9] | LI Jie, LIU Jia, WANG Liang, ZHANG Na, YANG Yanlong, ZHENG Zipiao, WEI Xin, WANG Meng, ZHOU Zixin, YANG Ni, GONG Zhaolong, HOU Xianfei, HUANG Qixiu, Abudukadier kuerban, ZHANG Jipeng, CHANG Pengzhong. Current situation of transformation and application of scientific and technological achievements of "cotton, oil and sugar" [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 89-94. |
| [10] | BIAN Qingyong, FU Yanbo, QI Tong, HUANG Jian, PU Shenghai, MENG Ajing, Halihashi Yibati. Study on influencing factors of cotton emergence and protection measures in saline-alkali land in southern Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 95-100. |
| [11] | LI Yongtai, GAO Axiang, LI Yanjun, ZHANG Xinyu. Effects of defoliants on the physiological characteristics of cotton varieties with different sensitivities [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2094-2102. |
| [12] | ZHANG Zehua, YE Hanchun, WANG Zhenhua, LI Wenhao, LI Haiqiang, LIU Jian. Effects of equal nitrogen applied with urease inhibitor on cotton growth, yield, and quality under mulched drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2103-2111. |
| [13] | CHEN Ruijie, LUO Linyi, RUAN Xiangyang, YE Jun. Effects of humic acid on soil nutrients, cotton yield and quality in cotton fields under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2112-2121. |
| [14] | HUANG Boxuan, LI Pengcheng, ZHENG Cangsong, SUN Miao, SHAO Jingjing, FENG Weina, PANG Chaoyou, XU Wenxiu, DONG Helin. Effects of different nitrogen inhibitors on growth, nitrogen utilization and yield of cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2122-2131. |
| [15] | WANG Chao, XU Wenxiu, LI Pengcheng, ZHENG Cangsong, SUN Miao, FENG Weina, SHAO Jingjing, DONG Helin. Response of cotton seedling growth and development to soil available potassium levels [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2132-2139. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 20
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 64
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||