

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (1): 174-181.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.01.020
• Plant Protection·Horticultural Special Local Products • Previous Articles Next Articles
LAI Chengxia1( ), YANG Yanlong1, WANG Penglong1, ZHU Mengyu2, YANG Dong3, LI Chunping1, GE Fengwei4, Mayila Yusuyin1, YANG Ni1, MA Jun1(
), YANG Yanlong1, WANG Penglong1, ZHU Mengyu2, YANG Dong3, LI Chunping1, GE Fengwei4, Mayila Yusuyin1, YANG Ni1, MA Jun1( )
)
Received:2024-07-27
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-03-11
Correspondence author:
MA Jun
Supported by:
赖成霞1( ), 杨延龙1, 汪鹏龙1, 朱梦宇2, 杨栋3, 李春平1, 葛风伟4, 玛依拉·玉素音1, 阳妮1, 马君1(
), 杨延龙1, 汪鹏龙1, 朱梦宇2, 杨栋3, 李春平1, 葛风伟4, 玛依拉·玉素音1, 阳妮1, 马君1( )
)
通讯作者:
马君
作者简介:赖成霞(1972-),女,新疆乌鲁木齐人,副研究员,研究方向为棉花抗逆分子育种,(E-mail)lchxia2001@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LAI Chengxia, YANG Yanlong, WANG Penglong, ZHU Mengyu, YANG Dong, LI Chunping, GE Fengwei, Mayila Yusuyin, YANG Ni, MA Jun. Pathogen colony’s morphological characteristics and pathogenicity identification of defioating cotton Verticillium wilt in some areas in northern Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 174-181.
赖成霞, 杨延龙, 汪鹏龙, 朱梦宇, 杨栋, 李春平, 葛风伟, 玛依拉·玉素音, 阳妮, 马君. 新疆北疆部分棉区落叶型棉花黄萎病菌落形态特征及致病力鉴定[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 174-181.
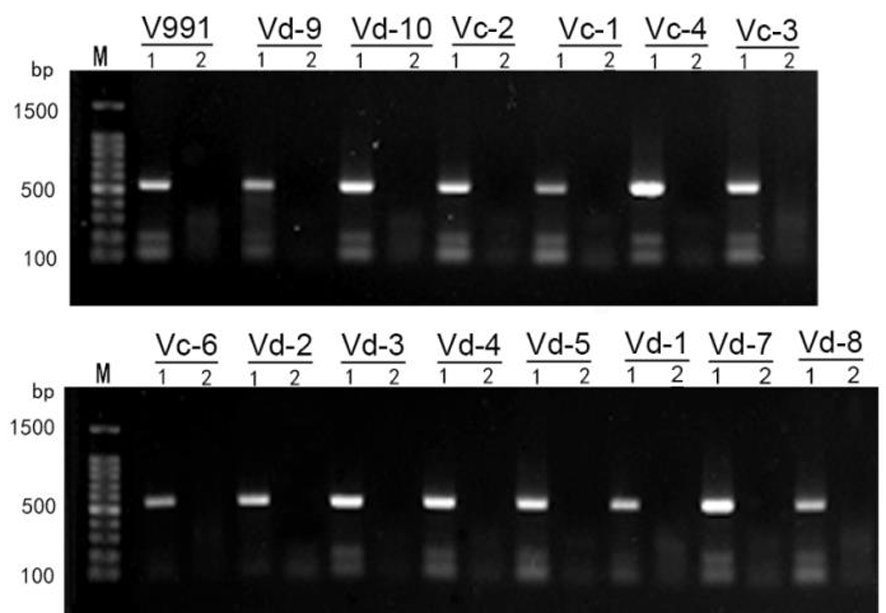
Fig.1 Electrophoretic map of the molecular identification for cotton Verticillium wilt Notes:M:DNA Mark 1 defoliating primer pairs DB19f/DB22r, 2: non-defoliating primer pairsINTND2f/INTND2r
| 序号 ID | 名称 Name | 轮枝数 Number of round branches | 孢子颜色 Conidia color | 孢子形状 Conidia shape | 孢子大小 Conidiasize (μm) | 菌落颜色 Colony color | 菌落形状 Colony shape |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vc-1 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (1.81-5.22)×(4.29-11.95) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 2 | Vc-2 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (2.05-6.36)×(4.42-11.15) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 3 | Vc-3 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (1.76-5.63)×(4.48-8.97) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 4 | Vc-4 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (2.25-5.79)×(3.56-9.32) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 5 | Vd-1 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (1.27-5.24)×(3.26-10.34) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 6 | Vd-2 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (2.48-5.12)×(4.23-9.46) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 7 | Vd-3 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (2.36-5.47)×(4.35-9.49) | 黑色 | 圆 |
| 8 | Vd-4 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (2-5.51)×(4.73-9.1) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 9 | Vd-5 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (2.29-8.51)×(1.45-9.66) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 10 | Vd-6 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (1.94-5.71)×(3.89-9.76) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 11 | Vd-7 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (1.94-6.5)×(5.36-9.93) | 黑色 | 圆 |
| 12 | Vd-8 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (1.76-4.39)×(4.57-9.44) | 黑色 | 圆 |
| 13 | Vd-9 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (2.29-5.59)×(4.46-10.34) | 黑色 | 圆 |
| 14 | Vd-10 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (1.59-5.49)×(4.48-9.19) | 黑色 | 圆 |
| 15 | V991 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (2-6.25)×(5.03-10.45) | 白色 | 圆 |
Tab.1 The morphology and microstructure of different colony
| 序号 ID | 名称 Name | 轮枝数 Number of round branches | 孢子颜色 Conidia color | 孢子形状 Conidia shape | 孢子大小 Conidiasize (μm) | 菌落颜色 Colony color | 菌落形状 Colony shape |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vc-1 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (1.81-5.22)×(4.29-11.95) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 2 | Vc-2 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (2.05-6.36)×(4.42-11.15) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 3 | Vc-3 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (1.76-5.63)×(4.48-8.97) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 4 | Vc-4 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (2.25-5.79)×(3.56-9.32) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 5 | Vd-1 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (1.27-5.24)×(3.26-10.34) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 6 | Vd-2 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (2.48-5.12)×(4.23-9.46) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 7 | Vd-3 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (2.36-5.47)×(4.35-9.49) | 黑色 | 圆 |
| 8 | Vd-4 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (2-5.51)×(4.73-9.1) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 9 | Vd-5 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (2.29-8.51)×(1.45-9.66) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 10 | Vd-6 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (1.94-5.71)×(3.89-9.76) | 白色 | 圆 |
| 11 | Vd-7 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (1.94-6.5)×(5.36-9.93) | 黑色 | 圆 |
| 12 | Vd-8 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (1.76-4.39)×(4.57-9.44) | 黑色 | 圆 |
| 13 | Vd-9 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (2.29-5.59)×(4.46-10.34) | 黑色 | 圆 |
| 14 | Vd-10 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (1.59-5.49)×(4.48-9.19) | 黑色 | 圆 |
| 15 | V991 | 2 | 无色 | 卵圆形 | (2-6.25)×(5.03-10.45) | 白色 | 圆 |
| [1] | 张绪振, 张树琴, 陈吉棣, 等. 我国棉花黄萎病菌“种” 的鉴定[J]. 植物病理学报, 1981, 11(3): 15-20, 67-68. |
| ZHANG Xuzhen, ZHANG Shuqin, CHEN Jidi, et al. Identification of Verticillium wilt pathogen of cotton in China[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 1981, 11(3): 15-20, 67-68. | |
| [2] | Zhu Y T, Zhao M, Li T T, et al. Interactions between Verticillium dahliae and cotton: pathogenic mechanism and cotton resistance mechanism to Verticillium wilt[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14: 1174281. |
| [3] | 赖成霞, 阳妮, 玛依拉·玉素音, 等. 基于孢内毒素浸泡叶盘联合叶绿素荧光测定技术鉴定棉花抗黄萎病[J]. 西北农业学报, 2022, 31(12): 1654-1664. |
| LAI Chengxia, YANG Ni, Mayila Yusuyin, et al. Identification of cotton resistant to Verticillium wilt based on endotoxin soaked leaf discs combined with chlorophyll fluorescence technology[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2022, 31(12): 1654-1664. | |
| [4] | Gkizi D, Lehmann S, L’Haridon F, et al. The innate immune signaling system as a regulator of disease resistance and induced systemic resistance activity against Verticillium dahliae[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2016, 29(4): 313-323. |
| [5] |
Li C, Yang W, Liu H H, et al. Crystal structures and antifungal activities of fluorine-containing thioureido complexes with nickel(II)[J]. Molecules, 2013, 18(12): 15737-15749.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Shaban M, Miao Y H, Ullah A, et al. Physiological and molecular mechanism of defense in cotton against Verticillium dahliae[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2018, 125: 193-204. |
| [7] |
Cooper R M, Williams J S. Elemental sulphur as an induced antifungal substance in plant defence[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2004, 55(404): 1947-1953.
PMID |
| [8] | 侯丽娟, 李卫, 刘燕霞, 等. 棉花黄萎病菌毒素对棉花生化代谢的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2010, 19(12): 63-67. |
| HOU Lijuan, LI Wei, LIU Yanxia, et al. Effect of V. dahliae toxin on biochemical metabolism of cotton seedlings[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2010, 19(12): 63-67. | |
| [9] | Xiong X P, Sun S C, Zhang X Y, et al. GhWRKY70D13 regulates resistance to Verticillium dahliae in cotton through the ethylene and jasmonic acid signaling pathways[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 69. |
| [10] | 刘海洋, 王伟, 张仁福, 等. 北疆棉花黄萎病发病率调查及土壤中黄萎病菌微菌核数量与种群类型分析[J]. 植物保护, 2023, 49(4): 276-283, 292. |
| LIU Haiyang, WANG Wei, ZHANG Renfu, et al. Investigation on the incidence rate of Verticillium wilt and analysis on the number of microsclerotia and the population type of Verticillium dahliae in soil of Northern Xinjiang[J]. Plant Protection, 2023, 49(4): 276-283, 292. | |
| [11] | 段维军, 李国英, 张莉, 等. 新疆棉花黄萎病菌致病性分化监测研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2004, (5): 324-328. |
| DUAN Weijun, LI Guoying, ZHANG Li, et al. The Monitor of Pathogenic Differentiation of VerticilliumDahliae fromCotton in Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2004 (5): 324-328. | |
| [12] | 张莉, 马慧宁, 陈文霞, 等. 石河子地区棉花黄萎病菌致病型监测研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2007, 35(16): 4879-4880, 4882. |
| ZHANG Li, MA Huining, CHEN Wenxia, et al. Monitoring study on pathotype of Verticillium dahliae of cotton in Shihezi Region[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 35(16): 4879-4880, 4882. | |
| [13] |
刘廷利, 惠慧, 阚家亮, 等. 新疆北部棉花黄萎病菌培养特性、致病型、致病性分化及ISSR遗传变异研究[J]. 棉花学报, 2017, 29(6): 541-549.
DOI |
| LIU Tingli, HUI Hui, KAN Jialiang, et al. The monitoring of cultural characteristics, pathotype, pathogenicity differentiation and ISSR genetic variation of Verticillium dahliae isolates from cotton in northern Xinjiang[J]. Cotton Science, 2017, 29(6): 541-549. | |
| [14] | 韩宏伟, 刘培源, 高峰, 等. 新疆北部棉区黄萎病菌种群致病性分化及变异[J]. 植物保护学报, 2011, 38(2): 121-126. |
| HAN Hongwei, LIU Peiyuan, GAO Feng, et al. The pathogenicity differentiation and variability of Verticillium dahliae from cotton in northern Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2011, 38(2): 121-126. | |
| [15] |
袁洪波, 艾尼江, 赵建军, 等. 棉花黄萎病菌致病力分化与ISSR遗传变异分析[J]. 华北农学报, 2013, 28(5): 84-89.
DOI |
| YUAN Hongbo, AI Nijiang, ZHAO Jianjun, et al. Pathogenicity differentiation and ISSR genetic variation analysis of Verticillium dahliae isolates from cotton in Shihezi, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2013, 28(5): 84-89. | |
| [16] | 刘培源. 棉花黄萎病菌致病类型快速检测技术的研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2010. |
| LIU Peiyuan. Study on rapid detection technology of pathogenic types of Verticillium dahliae in cotton[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2010. | |
| [17] | Mercado-Blanco J, Rodríguez-Jurado D, Pérez-Artés E, et al. Detection of the defoliating pathotype of Verticillium dahliae in infected olive plants by nested PCR[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2002, 108(1): 1-13. |
| [18] |
赖成霞, 玛依拉·玉素音, 石必显, 等. 助剂激健在防治棉花黄萎病中的效果[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(12): 2220-2227.
DOI |
|
LAI Chengxia, Mayila Yusuyin, SHI Bixian, et al. Application study on the adjuvant jijian as synergist for cotton Verticillium disease control[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(12): 2220-2227.
DOI |
|
| [19] | 龙希洋, 肖新力, 张启辉, 等. 大豆种荚应答镰刀菌侵染的叶绿素荧光成像规律[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2020, 37(3): 540-546. |
| LONG Xiyang, XIAO Xinli, ZHANG Qihui, et al. Imaging rules in chlorophyll fluorescence of soybean pods in response to[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 2020, 37(3): 540-546. | |
| [20] |
许培磊, 范书田, 刘迎雪, 等. 山葡萄应答霜霉病侵染过程中叶绿素荧光成像的变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2015, 42(7): 1378-1384.
DOI |
|
XU Peilei, FAN Shutian, LIU Yingxue, et al. Image changes in chlorophyll fluorescence of Vitis amurensis in response to downy mildew[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2015, 42(7): 1378-1384.
DOI |
|
| [21] | 王迎旭, 孙晔, 李玉花, 等. 基于叶绿素荧光成像的温室黄瓜植株病害分类与病情监测[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2020, 43(4): 770-780. |
| WANG Yingxu, SUN Ye, LI Yuhua, et al. Classification and monitoring of disease cucumber plants in greenhouse based on chlorophyll fluorescence imaging technology[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2020, 43(4): 770-780. | |
| [22] | 李钦夫, 李征明, 纪建伟, 等. 叶绿素荧光动力学及在植物抗逆生理研究中的应用[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2013, 52(22): 5399-5402. |
| LI Qinfu, LI Zhengming, JI Jianwei, et al. Applications of chlorophyll fluorescence kinetics in the physiological resistance studies of plant[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 52(22): 5399-5402. |
| [1] | ZHAI Yawei, CHEN Hongjin, SUN Hongtao, CHEN Shuaikang, LIU Chuli, MA Rong. Study on pathogenicity of Cytospora on Poplus and Salix in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(5): 1227-1235. |
| [2] | LUO Wenfang, Zhou Junhui, HE Wei, XU Jianjun. Isolation and identification of the Passalora nattrassii HR-1 from aubergine in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(2): 455-460. |
| [3] | TANG Li, LI Chunyan, JIA Wenhao, LIU Zhenya, LI Yapeng, DAN Hongxia, ZHANG Wangbin. Identification of the pathogen of Prunus davidiana canker in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(12): 3089-3096. |
| [4] | YU Lyujian, YANG Jin, DING Yu, LI Xiaoman, LIU Fengjuan, FAN Yingying, LIANG Hongyu, JIAO Ziwei, WANG Cheng. Isolation,identification and pathogenicity of fungi on the surface of pomegranate fruit [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(1): 148-155. |
| [5] | YANG Ni, Mayila Yusuyin, YANG Yanlong, LI Chunping, ZHANG Dawei, XU Haijiang, LAI Chengxia. Comparative analysis of plant volatiles from the Verticillium-Infected withered spot and etiolated leaves in cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1975-1986. |
| [6] | CHEN Cheng, HOU Xinqiang, ZHAN Faqiang, YANG Rong, BAO Huifang, WANG Ning, SHI Yingwu, LONG Xuanqi. Study on abiotic stress tolerance of three entomopathogenic nematodes and its bacteriostasis of symbiotic bacteria [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(12): 3072-3079. |
| [7] | GAO Yonggang, GAO Haifeng, LÜ Zhuo, XU lijuan, , TANG Qiyong, GU Meiying, ZHANG Lijuan, ZHU Jinquan, SONG Suqin. Investigation into the Diseases of the Potato in Different Producing Areas in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(1): 170-178. |
| [8] | LIU Haiyang, WANG Wei, ZHANG Renfu, Wenqiemu Abulizi, YAO Ju. A Brief Analysis of the Factors Restricting the Effectiveness of Controlling Cotton Verticillium wilt by Using Biocontrol Bacteria in the Field [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(1): 155-161. |
| [9] | LAI Chengxia, Mayila Yusuyin, SHI Bixian, LI Chunping, JIANG Mengzhu, ZHENG Zipiao, YANG Dong. Application Study on the Adjuvant Jijian as Synergist for Cotton Verticillium Disease Control [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(12): 2220-2227. |
| [10] | SHI Zhiyu, PEI Yakun, ZHU Yutao, JIA Yujiao, HU Xiaoqian, HOU Shicong, HOU Yuxia. Study on Remote Monitoring of Cotton Verticillium wilt Diagnosis and Control Management Based on Digital Image [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(6): 1166-1174. |
| [11] | CAI Meng-hang, XU Can, LIU Qi, YU Yan, HUANG Jia-feng. Cultural Characteristics and Pathogenicity Differentiation among Strains of Verticillium dahliae from Cottons in Northern Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(1): 93-103. |
| [12] | YU Yan, CAI Meng-hang, XU Can, HUANG Jia-feng. Effects of Different C / N Ratio on the Main Biological Characteristics and Pathogenicity of Verticillium dahliae in Cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(1): 84-92. |
| [13] | ZHANG Li-juan;WANG Wei;XIE Yu-qing;ZHANG Zhi-dong;GU Mei-ying;ZHU Jing;TANG Qi-yong;WANG Bo;SONG Su-qin. Isolation and Identification of the Pathogens Causing Garlic Root Rot in Jimsar [J]. , 2017, 54(4): 725-734. |
| [14] | ZHOU Yang;WU Qiong;LIU Meng-li;BAI Jian-yu;LI Jin;LEI Bin;GUO Qing-yuan. Pathogenicity Comparison between Rhizoctonia solani and Fusarium moniliforme with Their Respective Isolate Pathogens in Cotton Belt in the South of Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang [J]. , 2017, 54(3): 489-496. |
| [15] | LI Guo-ying;DU Shu-chun;LI Zi;YUE Yong-liang;REN Yu-zhong;ZHANG Li. Occurrence Trend, Resistance Status and Proposal on Cotton Verticillium wilt in Southern Xinjiang [J]. , 2015, 52(9): 1640-1647. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 19
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 67
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||