

新疆农业科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (2): 302-313.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.02.006
王晓艳1,2( ), 白云岗2(
), 白云岗2( ), 柴仲平1(
), 柴仲平1( ), 卢震林2, 刘洪波2, 肖军2, 阿曼尼萨1
), 卢震林2, 刘洪波2, 肖军2, 阿曼尼萨1
收稿日期:2024-08-11
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2025-04-17
通信作者:
白云岗(1974-),男,新疆奇台人,教授级高级工程师,博士,研究方向为农业水土工程,(E-mail)xjbaiyg@sina.com;作者简介:王晓艳(1998-),女,新疆霍城人,硕士研究生,研究方向为节水灌溉,(E-mail)2770046616@qq.com
基金资助:
WANG Xiaoyan1,2( ), BAI Yungang2(
), BAI Yungang2( ), CHAI Zhongping1(
), CHAI Zhongping1( ), LU Zhenlin2, LIU Hongbo2, XIAO Jun2, Amannisa 1
), LU Zhenlin2, LIU Hongbo2, XIAO Jun2, Amannisa 1
Received:2024-08-11
Published:2025-02-20
Online:2025-04-17
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】研究不同滴水冬灌定额对“干播湿出”播种质量、棉花生理、生长特性及产量的影响,确定节水增效的休作期棉田墒情调控策略。【方法】采用在棉田休作期少量灌水调控墒情,春季开播后“干播湿出”的灌水方式,共设计9个处理,冬灌滴灌定额设4个梯度:休作期冬灌滴灌(W1S0~W4S0):600、900、1 200和1 500 m3/hm2;春季播种后采用非“干播湿出”和“干播湿出”2种方案,“干播湿出”定额为225 m3/hm2(W1S1~W4S4),常规冬灌2 250 m3/hm2为对照处理。【结果】滴灌冬灌+“干播湿出”对比仅冬灌处理能够促进苗期棉花生长(株高茎粗显著高于非“干播湿出”及常规冬灌),W1S1~W4S4处理可在棉花营养生长转生殖生长期间在一定程度上可控制株高过度增长,其中处理W3S3及W4S4最为显著;滴灌冬灌+“干播湿出”可提高苗期及蕾期叶面积指数,花铃期后期W1S0~W4S0处理叶面积指数稍高于CK及W1S1~W4S4处理;W1S1~W4S4处理干物质总积累量显著大于W1S0~W4S0处理,可促进生殖器官干物质积累,W3S3、W4S4处理生殖器官干物质积累量比例可占50%以上;花铃期后期叶面积指数与产量呈显著负相关关系,干物质积累总量与产量呈极显著正相关关系,滴灌冬灌+“干播湿出”产量高于仅滴灌冬灌处理及常规冬灌,其中处理W4S4的产量比冬季滴灌的W4S0处理高出18.8%、比CK高出13.5%左右。【结论】休作期滴灌冬灌调控下“干播湿出”灌水模式可再节约灌溉用水24%~36%情况下显著提高棉花产量3.5%~13.5%。
中图分类号:
王晓艳, 白云岗, 柴仲平, 卢震林, 刘洪波, 肖军, 阿曼尼萨. 休作期冬灌滴灌调控下“干播湿出”对棉花生长及产量影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(2): 302-313.
WANG Xiaoyan, BAI Yungang, CHAI Zhongping, LU Zhenlin, LIU Hongbo, XIAO Jun, Amannisa . Effect of "dry sowing and wet emergence" on cotton growth and yield under the control of winter drip irrigation in off-cropping period[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(2): 302-313.
| 项目 Items | 深度Depth(cm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 | 10~20 | 20~30 | 30~40 | 40~60 | 60~80 | 80~100 | |
| 初始含水率 Initial moisture content(%) | 10.60 | 13.22 | 20.01 | 21.11 | 25.95 | 20.47 | 6.95 |
| 田间持水量 Field holding capacity(%) | 29.41 | 27.43 | 28.35 | 28.19 | 35.27 | 29.01 | 10.55 |
| 容重 Bulk density(g/cm3) | 1.49 | 1.62 | 1.64 | 1.65 | 1.63 | 1.53 | 1.49 |
| 土壤质地 Soil texture | 沙壤土 | 沙壤土 | 壤土 | 壤土 | 沙壤土 | 沙壤土 | 沙壤土 |
表1 试验地相关土壤理化性状
Tab.1 Related soil physicochemical traits
| 项目 Items | 深度Depth(cm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 | 10~20 | 20~30 | 30~40 | 40~60 | 60~80 | 80~100 | |
| 初始含水率 Initial moisture content(%) | 10.60 | 13.22 | 20.01 | 21.11 | 25.95 | 20.47 | 6.95 |
| 田间持水量 Field holding capacity(%) | 29.41 | 27.43 | 28.35 | 28.19 | 35.27 | 29.01 | 10.55 |
| 容重 Bulk density(g/cm3) | 1.49 | 1.62 | 1.64 | 1.65 | 1.63 | 1.53 | 1.49 |
| 土壤质地 Soil texture | 沙壤土 | 沙壤土 | 壤土 | 壤土 | 沙壤土 | 沙壤土 | 沙壤土 |
| 处理 Treat- ments | 灌水日期 (年.月.日) Irrigation Date (Year.month. day) | 冬灌滴 灌定额 Winter irrigation drip irrigation quota (m3/hm2) | “干播湿出” 灌溉定额 “Dry sowing and wet out” irrigation quota (m3/hm2) | 灌溉总额 Total amount of irrigation (m3/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1S0 | 2021.11.15 | 600 | 0 | 600 |
| W2S0 | 900 | 0 | 900 | |
| W3S0 | 1 200 | 0 | 1 200 | |
| W4S0 | 1 500 | 0 | 1 500 | |
| W1S1 | 2021.11.15 2022.04.15 2022.05.07 | 600 | 45+180 | 825 |
| W2S2 | 900 | 45+180 | 1 125 | |
| W3S3 | 1 200 | 45+180 | 1 425 | |
| W4S4 | 1 500 | 45+180 | 1725 | |
| CK | 2021.11.15 | 2 250 | 0 | 2 250 |
表2 棉花灌水试验方案
Tab.2 Cotton irrigation test scheme
| 处理 Treat- ments | 灌水日期 (年.月.日) Irrigation Date (Year.month. day) | 冬灌滴 灌定额 Winter irrigation drip irrigation quota (m3/hm2) | “干播湿出” 灌溉定额 “Dry sowing and wet out” irrigation quota (m3/hm2) | 灌溉总额 Total amount of irrigation (m3/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1S0 | 2021.11.15 | 600 | 0 | 600 |
| W2S0 | 900 | 0 | 900 | |
| W3S0 | 1 200 | 0 | 1 200 | |
| W4S0 | 1 500 | 0 | 1 500 | |
| W1S1 | 2021.11.15 2022.04.15 2022.05.07 | 600 | 45+180 | 825 |
| W2S2 | 900 | 45+180 | 1 125 | |
| W3S3 | 1 200 | 45+180 | 1 425 | |
| W4S4 | 1 500 | 45+180 | 1725 | |
| CK | 2021.11.15 | 2 250 | 0 | 2 250 |
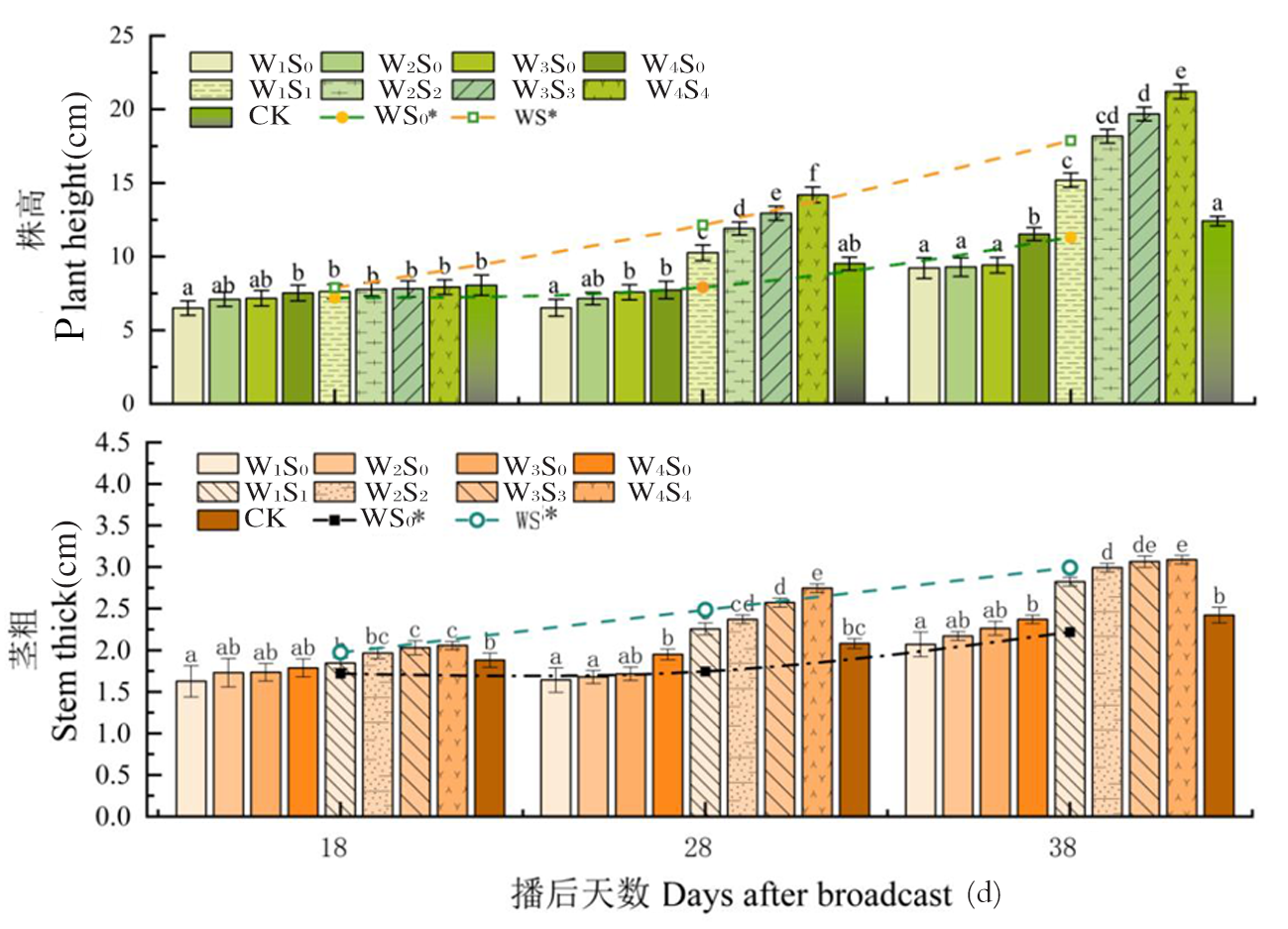
图2 棉花苗期各阶段株高及茎粗的变化 注: W S 0 *为休作期滴灌冬灌处理株高及茎粗平均值;WS*为休作期滴灌冬灌调控下“干播湿出”处理株高及茎粗平均值,下同
Fig.2 Changes of plant height and stem thickness in each stage of cotton seedling stage Notes: W S 0 * is the average value of plants treated with winter irrigation during the fallow period; WS* is the average value of "dry sowing wet out" under the control of drip irrigation during the fallow period,similarly hereinafter,the same as below
| 处理 Treatments | 5月3日 | 5月13日 | 5月23日 |
|---|---|---|---|
| W1S0 | 0.23±0.03a | 0.47±0.03a | 0.56±0.05a |
| W2S0 | 0.36±0.04b | 0.51±0.04b | 0.58±0.04b |
| W3S0 | 0.41±0.03c | 0.55±0.04c | 0.60±0.04b |
| W4S0 | 0.45±0.02d | 0.67±0.05d | 0.71±0.03c |
| W1S1 | 0.48±0.03e | 0.69±0.03e | 1.01±0.04d |
| W2S2 | 0.50±0.03e | 0.82±0.03f | 1.18±0.03e |
| W3S3 | 0.69±0.04f | 0.98±0.02g | 1.20±0.04f |
| W4S4 | 0.714±0.026g | 1.06±0.03h | 1.25±0.03g |
| CK | 0.451±0.044d | 0.68±0.05d | 0.71±0.04c |
表3 棉花苗期不同水分处理下LAI指数对比
Tab.3 Comparison of LAI index in different moisture treatment periods in cotton seedling stage
| 处理 Treatments | 5月3日 | 5月13日 | 5月23日 |
|---|---|---|---|
| W1S0 | 0.23±0.03a | 0.47±0.03a | 0.56±0.05a |
| W2S0 | 0.36±0.04b | 0.51±0.04b | 0.58±0.04b |
| W3S0 | 0.41±0.03c | 0.55±0.04c | 0.60±0.04b |
| W4S0 | 0.45±0.02d | 0.67±0.05d | 0.71±0.03c |
| W1S1 | 0.48±0.03e | 0.69±0.03e | 1.01±0.04d |
| W2S2 | 0.50±0.03e | 0.82±0.03f | 1.18±0.03e |
| W3S3 | 0.69±0.04f | 0.98±0.02g | 1.20±0.04f |
| W4S4 | 0.714±0.026g | 1.06±0.03h | 1.25±0.03g |
| CK | 0.451±0.044d | 0.68±0.05d | 0.71±0.04c |
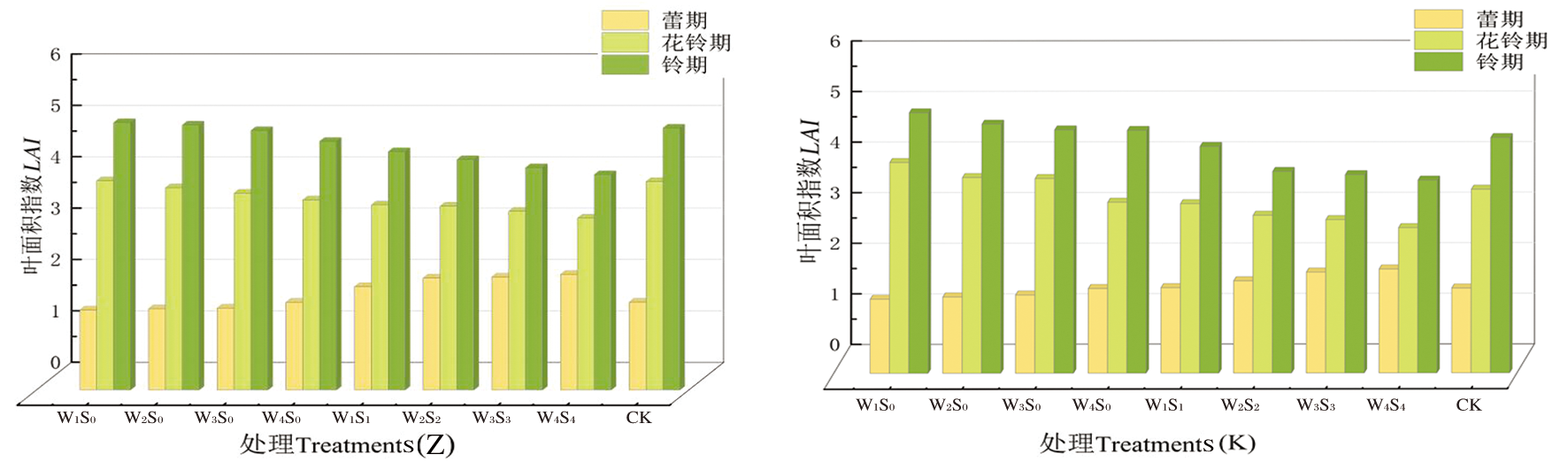
图4 棉花生育期不同水分处理下叶面积指数的变化 注:图中分别为棉花窄行(Z),间行(J)及宽行(K)位置叶面积指数
Fig.4 Changes of leaf area under different moisture treatments in other growth periods of cotton Notes:The figure shows the leaf area index of cotton narrow (Z), inter (J) and wide (K) positions, respectively
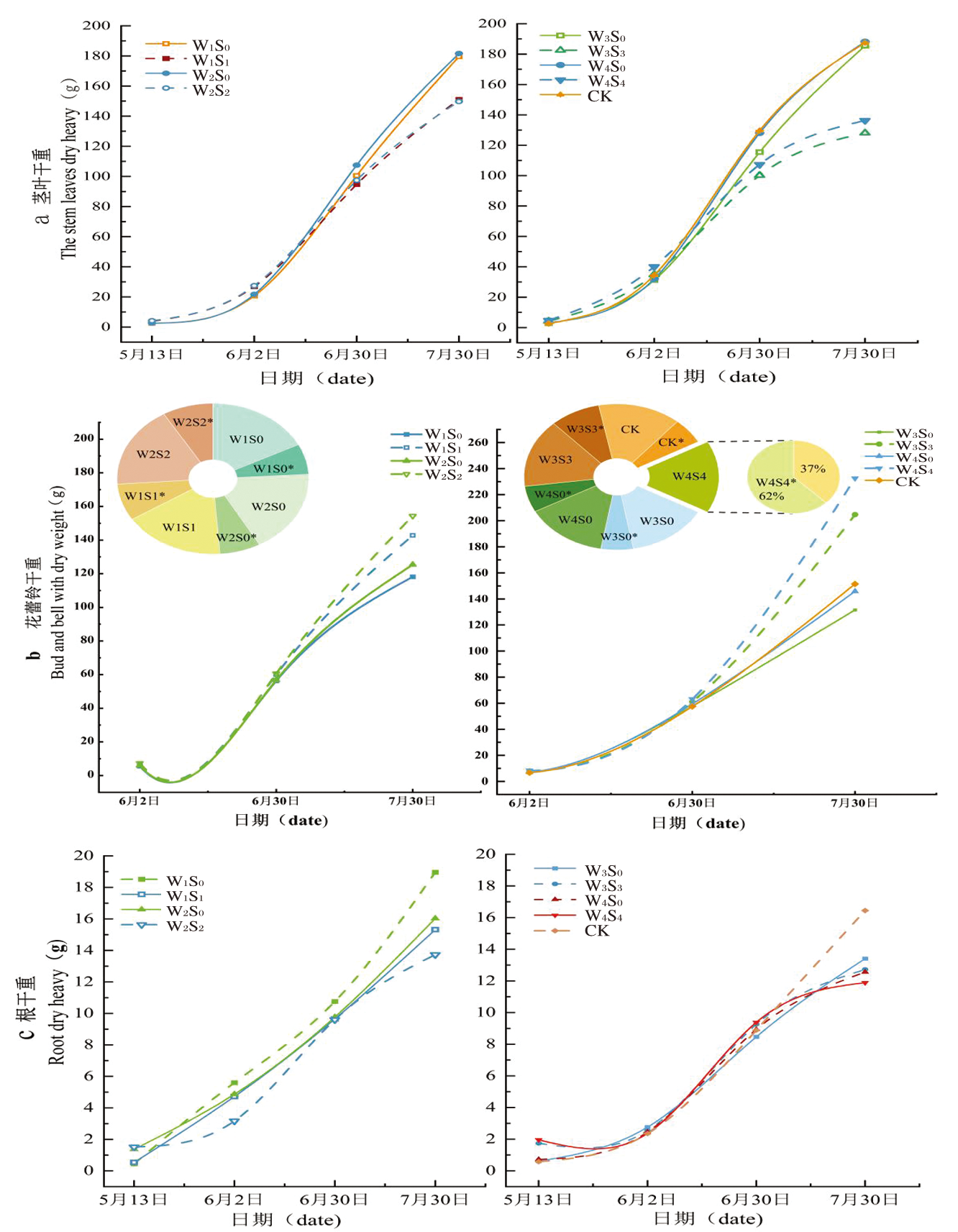
图5 棉花生长过程中各处理不同器官干物质量及分配的变化 注:a图为茎叶干物质量,b图为花蕾铃干物质积累量(饼图为吐絮期棉株总干物质量与生殖器官干物质量占比:W1S0 *、W2S0 *、W3S0 *、W4S0 *、W1S1 *、W1S1 *、W1S1 *、W1S1 *为生殖器官干物质量),c图为根部干物质量
Fig.5 Quality changes of dry matter and distribution of different organs in the process of cotton growth Notes:The figure a is the mass of dry stem and leaf, and b shows the accumulation of dry substance of flower buds (pie chart shows the ratio of total dry mass of cotton plants: W1S0 *, W2S0 *, W3S0 *, W4S0 *, W1S1 *, W1S1 *, W1S1 *, W1S1 *, W 1 S 1 * is the dry mass of reproductive organs), and c shows the dry mass of the root
| 处理 Treatments | 单株成铃数 Number of bells per plant (个) | 单铃质量 Single bell quality (g) | 衣分 Ginning outturn (%) | 产量 Yield (Kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1S0 | 6±0.654d | 5.47±0.35d | 40%±0.012d | 4 543.79±90.12g |
| W2S0 | 6.56±0.57c | 5.64±0.32bc | 40%±0.011d | 4 755.79±95.37f |
| W3S0 | 6.63±0.66c | 5.66±0.33b | 41%±0.012c | 4 955.83±87.95e |
| W4S0 | 7±0.47b | 5.76±0.42ab | 42%±0.022b | 5 040.3±88.46d |
| W1S1 | 6.21±0.47d | 5.58±0.25c | 40.50±0.098cd | 4731.24±78.99fg |
| W2S2 | 6.86±0.45bc | 5.72±0.26ab | 41%±0.012c | 5 009.14±77.36de |
| W3S3 | 8.21±0.45a | 5.78±0.24ab | 43%±0.098b | 5 460.08±76.73b |
| W4S4 | 8.76±0.3a | 5.85±0.23a | 44%±0.072a | 5 988.92±78.36a |
| CK | 6.77±0.54bc | 5.69±0.35ab | 40.5%±0.011cd | 5 276.44±90.48c |
表4 不同灌溉方式下棉花产量构成的变化
Tab.4 Changes of different irrigation methods on cotton yield composition
| 处理 Treatments | 单株成铃数 Number of bells per plant (个) | 单铃质量 Single bell quality (g) | 衣分 Ginning outturn (%) | 产量 Yield (Kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1S0 | 6±0.654d | 5.47±0.35d | 40%±0.012d | 4 543.79±90.12g |
| W2S0 | 6.56±0.57c | 5.64±0.32bc | 40%±0.011d | 4 755.79±95.37f |
| W3S0 | 6.63±0.66c | 5.66±0.33b | 41%±0.012c | 4 955.83±87.95e |
| W4S0 | 7±0.47b | 5.76±0.42ab | 42%±0.022b | 5 040.3±88.46d |
| W1S1 | 6.21±0.47d | 5.58±0.25c | 40.50±0.098cd | 4731.24±78.99fg |
| W2S2 | 6.86±0.45bc | 5.72±0.26ab | 41%±0.012c | 5 009.14±77.36de |
| W3S3 | 8.21±0.45a | 5.78±0.24ab | 43%±0.098b | 5 460.08±76.73b |
| W4S4 | 8.76±0.3a | 5.85±0.23a | 44%±0.072a | 5 988.92±78.36a |
| CK | 6.77±0.54bc | 5.69±0.35ab | 40.5%±0.011cd | 5 276.44±90.48c |
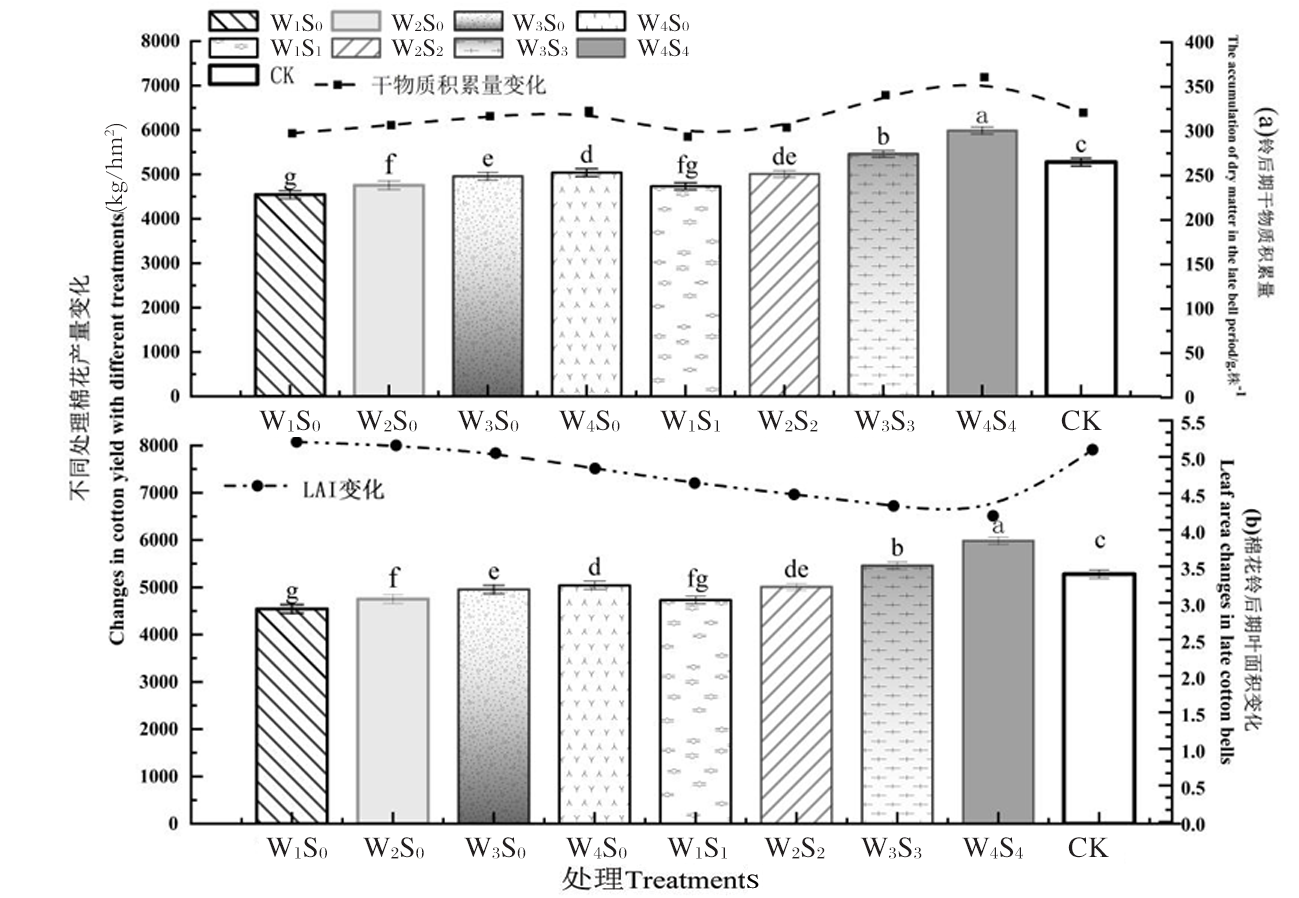
图6 棉花铃后期叶面积、干物质积累及产量变化 注:a:不同处理铃后期叶面积指数变化,b:不同处理干物质积累量变化,c:为不同灌水处理棉花产量变化
Fig.6 Changes of leaf area, dry matter accumulation and yield change Notes:a:shows the index change of leaf area in the late period of different treatments, b:shows the change of dry matter accumulation in different treatments, and c:shows the change of cotton yield in different irrigation treatments
| 棉花生理指标 Physiological indicators of cotton | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | 回归方程 Regression equation | 决定系数R2 Coefficient of determination R2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干物质积累量 Accumulation of dry matter | 0.778** | Y=81.92+0.05X | 0.879 | <0.01 |
| 叶面积指数leaf area index | -556* | Y=7.94+-6.21E-4X | 0.356 | <0.05 |
表5 产量与铃后期叶面积指数、干物质积累量相关性
Tab.5 Correlation between yield and leaf area index and dry matter accumulation
| 棉花生理指标 Physiological indicators of cotton | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | 回归方程 Regression equation | 决定系数R2 Coefficient of determination R2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干物质积累量 Accumulation of dry matter | 0.778** | Y=81.92+0.05X | 0.879 | <0.01 |
| 叶面积指数leaf area index | -556* | Y=7.94+-6.21E-4X | 0.356 | <0.05 |
| [1] | 喻树迅, 魏晓文. 中国棉花生产与科技发展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2000, 2(2): 39-42. |
| YU Shuxun, WEI Xiaowen. Cotton production and technological development in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2000, 2(2): 39-42. | |
| [2] |
邢晋, 张思平, 赵新华, 等. 种植密度和缩节胺互作对棉花株型及产量的调控效应[J]. 棉花学报, 2018, 30(1): 53-61.
DOI |
| XING Jin, ZHANG Siping, ZHAO Xinhua, et al. Interaction of plant density with mepiquat chloride affects plant architecture and yield in cotton[J]. Cotton Science, 2018, 30(1): 53-61. | |
| [3] | 刘磊, 陈元翰, 雷紫翔. 新疆棉花产业高质量发展研究[J]. 宏观经济管理, 2021,(10): 77-83, 90. |
| LIU Lei, CHEN Yuanhan, LEI Zixiang. A study on high-quality development of the cotton industry of Xinjiang[J]. Macroeconomic Management, 2021,(10): 77-83, 90. | |
| [4] | 郑媛芳. 新疆水资源分布及脆弱性评价[J]. 陕西水利, 2018,(S1):39-41. |
| ZHENG Yuanfang. Evaluation of the distribution and vulnerability of water resources in Xinjiang[J]. Shaanxi Water, 2018,(S1): 39-41. | |
| [5] | 热依汗. 新疆水资源可持续发展问题研究[J]. 地下水, 2022, 44(4): 235-237. |
| RE Yihan. Research on the sustainable Development of water Resources in Xinjiang[J]. Ground Water, 2022, 44(4): 235-237. | |
| [6] | 姚宝林. 南疆免冬春灌棉田土壤水热盐时空迁移规律与调控研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2017. |
| YAO Baolin. Study on the law and regulation of hydroheat and salt in winter and spring cotton fields in southern Xinjiang[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| [7] | 李明思, 刘洪光, 郑旭荣. 长期膜下滴灌农田土壤盐分时空变化[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(22): 82-87. |
| LI Mingsi, LIU Hongguang, ZHENG Xurong. Spatiotemporal variation for soil salinity of field land under long-term mulched drip irrigation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28(22): 82-87. | |
| [8] | 赵波, 王振华, 李文昊. 滴灌方式及定额对北疆冬灌棉田土壤水盐分布及次年棉花生长的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(6): 139-148. |
| ZHAO Bo, WANG Zhenhua, LI Wenhao. Effects of winter drip irrigation mode and quota on water and salt distribution in cotton field soil and cotton growth next year in northern Xinjiang[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(6): 139-148. | |
| [9] | 陈小芹, 王振华, 何新林, 等. 北疆棉田不同冬灌方式对土壤水分、盐分和温度分布的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2014, 28(2): 132-137. |
| CHEN Xiaoqin, WANG Zhenhua, HE Xinlin, et al. Effects of winter irrigation method on soil moisture, salt and temperature distribution in cotton fields of North Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 28(2): 132-137. | |
| [10] | 蔡焕杰, 邵光成, 张振华. 荒漠气候区膜下滴灌棉花需水量和灌溉制度的试验研究[J]. 水利学报, 2002, 33(11): 119-123. |
| CAI Huanjie, SHAO Guangcheng, ZHANG Zhenhua. Water demand and irrigation scheduling of drip irrigation for cotton under plastic mulch[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2002, 33(11): 119-123. | |
| [11] | 刘梅先, 杨劲松, 李晓明, 等. 膜下滴灌条件下滴水量和滴水频率对棉田土壤水分分布及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(12): 3203-3210. |
|
LIU Meixian, YANG Jinsong, LI Xiaoming, et al. Effects of irrigation amount and frequency on soil water distribution and water use efficiency in a cotton field under mulched drip irrigation[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011, 22(12): 3203-3210.
PMID |
|
| [12] | 周国信. 干播湿出苗齐苗壮[J]. 中国棉花, 2007, 34(6): 18. |
| ZHOU Guoxin. Dry sowing wet seedlings[J]. China Cotton, 2007, 34(6): 18. | |
| [13] | 邢小宁, 姚宝林, 孙三民. 不同灌溉制度对南疆绿洲区膜下滴灌棉花生长及产量的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2016, 25(2): 227-236. |
| XING Xiaoning, YAO Baolin, SUN Sanmin. Effects of different irrigation regimes on cotton growth and yield with drip irrigation under plastic film in oasis region of South Xinjiang[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2016, 25(2): 227-236. | |
| [14] | 李玉环, 何新林, 杨丽莉, 等. 不同残膜量对土壤水盐运移及棉花生长发育的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2022, 40(3): 154-161. |
| LI Yuhuan, HE Xinlin, YANG Lili, et al. Effects of different amount of residual film on soil water and salt transport and cotton growth and development[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2022, 40(3): 154-161. | |
| [15] | 弋鹏飞, 虎胆·吐马尔白, 王一民, 等. 干旱区棉花膜下滴灌优化灌溉制度的试验研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 2011, 31(1): 53-57. |
| YI Pengfei, Hudan Tumaerbai, WANG Yimin, et al. Schedule optimization of under-plastic-mulch drip irrigation for cotton in arid areas[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011, 31(1): 53-57. | |
| [16] |
王峰, 孙景生, 刘祖贵, 等. 灌溉制度对机采棉生长、产量及品质的影响[J]. 棉花学报, 2014, 26(1): 41-48.
DOI |
| WANG Feng, SUN Jingsheng, LIU Zugui, et al. Effects of irrigation scheduling on growth, yield and fiber quality of cotton under mechanical harvest cropping model[J]. Cotton Science, 2014, 26(1): 41-48. | |
| [17] | Wang R S, Kang Y H, Wan S Q, et al. Influence of different amounts of irrigation water on salt leaching and cotton growth under drip irrigation in an arid and saline area[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2012, 110: 109-117. |
| [18] | 罗雪园, 周宏飞, 柴晨好, 等. 不同淋洗模式下干旱区盐渍土改良效果分析[J]. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(2): 322-326. |
| LUO Xueyuan, ZHOU Hongfei, CHAI Chenhao, et al. Analysis of improvement effects on different leaching modes of saline soil in arid areas[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 31(2): 322-326. | |
| [19] | 申孝军, 张寄阳, 刘祖贵, 等. 膜下滴灌条件下不同水分处理对棉花产量和水分利用效率的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2012, 30(2): 118-124. |
| SHEN Xiaojun, ZHANG Jiyang, LIU Zugui, et al. Effects of different water treatments on yield and water use efficiency of cotton with drip irrigation under film mulch[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2012, 30(2): 118-124. | |
| [20] | 张永玲, 王兴鹏, 肖让, 等. 干播湿出棉田土壤温度及水分对出苗率的影响[J]. 节水灌溉, 2013,(10): 11-13. |
| ZHANG Yongling, WANG Xingpeng, XIAO Rang, et al. Impacts of drip irrigation under mulch with dry sowing and wet seedling on soil temperature, water content and seedling emergence rate of cotton[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2013,(10): 11-13. | |
| [21] |
陈绪兰, 孙春梅, 刘萍. 棉花“干播湿出” 技术在新疆库尔勒推广实践[J]. 中国棉花, 2021, 48(5): 41-42, 45.
DOI |
|
CHEN Xulan, SUN Chunmei, LIU Ping. The practice of cotton “sowing drily and emerging wet” technology in Korla, Xinjiang[J]. China Cotton, 2021, 48(5): 41-42, 45.
DOI |
|
| [22] | 马丽, 王潭刚, 李克富, 等. 南疆第三师棉花干播湿出技术推广情况调查及建议[J]. 新疆农垦科技, 2020, 43(10): 13-14. |
| MA Li, WANG Tangang, LI Kefu, et al. Investigation and suggestions on the promotion of cotton dry sowing wet out technology of the third Division of Southern Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Farm Research of Science and Technology, 2020, 43(10): 13-14. | |
| [23] |
王晓艳, 白云岗, 柴仲平, 等. 南疆休作期棉田墒情调控及播种前适宜灌水阈值研究[J]. 节水灌溉, 2023,(8): 89-94, 101.
DOI |
|
WANG Xiaoyan, BAI Yungang, CHAI Zhongping, et al. Study on soil moisture control and suitable irrigation threshold before planting in cotton field during off cropping period[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2023,(8): 89-94, 101.
DOI |
|
| [24] | 李志军, 王海东, 张富仓, 等. 新疆滴灌施肥棉花生长和产量的水肥耦合效应[J]. 排灌机械工程学报, 2015, 33(12): 1069-1077. |
| LI Zhijun, WANG Haidong, ZHANG Fucang, et al. Effects of water- fertilizer coupling on field cotton growth and yield under fertigation in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 2015, 33(12): 1069-1077. | |
| [25] |
杜刚锋, 汪江涛, 孙雪冰, 等. 不同灌溉方式和灌水量对棉花冠层叶铃配置的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(7): 1177-1186.
DOI |
|
DU Gangfeng, WANG Jiangtao, SUN Xuebing, et al. Effects of irrigation method and irrigation amount on cotton crown leaf boll configuration[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(7): 1177-1186.
DOI |
|
| [26] | 刘雪艳, 丁邦新, 白云岗, 等. 微咸水膜下滴灌对棉花生长及产量的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(6): 1627-1634. |
| LIU Xueyan, DING Bangxin, BAI Yungang, et al. Effect of drip irrigation under brackish water film on cotton growth and yield[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(6): 1627-1634. |
| [1] | 王勇攀, 马君, 李晨宇, 姚梦瑶, 王子轩, 黄灵芝, 朱海艳, 刘皖蓉, 李波, 杨洋, 高文伟. 基于卷积神经网络和合成数据集训练鉴定棉花种子萌发期的耐盐性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(2): 261-269. |
| [2] | 胡莎莎, 邵丽萍, 陈丽华, 宋卫平, 赵海, 张新宇, 孙杰. 脱叶剂对机采棉棉铃发育及纤维品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(2): 270-277. |
| [3] | 刘跃, 连世昊, 李家豪, 王泓懿, 田文强, 聂凌帆, 孙刚刚, 贾永红, 石书兵, 于月华, 张金汕. 播期和密度对花生产量形成及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(2): 278-285. |
| [4] | 陆明昆, 李军宏, 尼陆排尔·于苏甫江, 潘喜鹏, 刘晓成, 张正贵, 潘占磊, 翟梦华, 张要朋, 赵文琪, 王丽宏, 王占彪. 追施硅肥对棉花生长发育及产量品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(2): 286-293. |
| [5] | 王奕丁, 张凯, 张凌健, 张慧, 郭小梦, 陈国悦. 滴灌量对新疆棉花生长发育、产量形成和水分利用效率的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(2): 294-301. |
| [6] | 李天乐, 白新禄, 安世杰, 郑强卿, 汤智辉, 支金虎. 水肥耦合对库尔勒香梨生长、果实品质及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(2): 335-342. |
| [7] | 韩禧卿, 张鲜花, 袁惠, 熊辉, 撒成辉. 10份梯牧草植株形态特征与产量分析及评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(2): 454-462. |
| [8] | 孙娜, 马林, 邹辉, 张志辉, 张胜军, 黄倩楠, 杨蕙, 登斯拉木·吐尔逊拜, 李志彬, 曹俊梅, 雷钧杰. 氮磷钾配施对冬小麦产量和品质的影响及其肥效分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 1-12. |
| [9] | 孙彩琴, 吴佳, 黄海, 郭家鑫, 闵伟, 郭慧娟. 不同盐碱胁迫对棉花根系蛋白质组的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 146-160. |
| [10] | 杜亚隆, 付秋萍, 艾鹏睿, 马英杰, 祁通, 潘洋. 综合评价不同灌溉处理对长绒棉生长及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 161-173. |
| [11] | 赖成霞, 杨延龙, 汪鹏龙, 朱梦宇, 杨栋, 李春平, 葛风伟, 玛依拉·玉素音, 阳妮, 马君. 新疆北疆部分棉区落叶型棉花黄萎病菌落形态特征及致病力鉴定[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 174-181. |
| [12] | 王伟, 张仁福, 刘海洋, 李晓维, 姚举. 新疆棉田花蓟马消长规律及空间分布[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 202-209. |
| [13] | 谢秀荣, 张永强, 海峰, 雷钧杰, 吕晓庆, 陈传信, 徐其江, 聂石辉, 王冀川. 匀播增密对适期晚播冬小麦群体结构及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 21-28. |
| [14] | 胡梦婷, 刘胜尧, 贾宋楠, 范凤翠, 杜凤焕, 李劲松, 秦勇. 不同种植行距对菠菜产量和水分利用效率的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 217-224. |
| [15] | 张妍婷, 张永强, 雷钧杰, 陈慧, 陈传信, 徐其江, 聂石辉, 徐文修. 不同施磷方式对干播湿出冬小麦光合生理特性及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 29-36. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 24
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 44
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||