

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (4): 897-907.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.04.014
• Horticultural Special Local Products·Forestry·Facility Agriculture • Previous Articles Next Articles
TANG Xixi1,2( ), Mubarek Ayup2(
), Mubarek Ayup2( ), XU Panyun2, YU Qiuhong3, GUO Chunmiao2, ZHANG Ping1(
), XU Panyun2, YU Qiuhong3, GUO Chunmiao2, ZHANG Ping1( ), GONG Peng2
), GONG Peng2
Received:2022-06-03
Online:2023-04-20
Published:2023-05-06
Correspondence author:
ZHANG Ping(1980-),femail,Shandong native,associate professor,main research direction:forest genetic improvement,(E-mail)Supported by:
唐茜茜1,2( ), 木巴热克·阿尤普2(
), 木巴热克·阿尤普2( ), 许盼云2, 于秋红3, 郭春苗2, 张萍1(
), 许盼云2, 于秋红3, 郭春苗2, 张萍1( ), 龚鹏2
), 龚鹏2
通讯作者:
张萍(1980-),女,山东人,副教授,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为林木遗传改良,(E-mail)作者简介:唐茜茜(1996-),女,江苏南通人,硕士研究生,研究方向为林木遗传与良种选育,(E-mail)1778923221@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
TANG Xixi, Mubarek Ayup, XU Panyun, YU Qiuhong, GUO Chunmiao, ZHANG Ping, GONG Peng. Response of root anatomical structure of different rootstock resources of almond to drought stress[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(4): 897-907.
唐茜茜, 木巴热克·阿尤普, 许盼云, 于秋红, 郭春苗, 张萍, 龚鹏. 扁桃不同砧木资源根系解剖结构对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(4): 897-907.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.xjnykx.com/EN/10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.04.014
| 指标 Target | 缩写 Ablorevia- tion | 测量倍数 Measurement multiple | 备注 Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 木质部面积 Xylem area | XA | 10×4 | |
| 韧皮部面积 Phloem area | PHA | 10×4 | |
| 维管束面积 Vascular bundle area | VBA | 10×4 | |
| 木质部占比 Proportion of xylem | X(%) | 10×4 | 木质部面积占 总根面积的占比 |
| 韧皮部占比 Proportion of phloem | PH(%) | 10×4 | 韧皮部面积占 总根面积的占比 |
| 维管束占比 Proportion of vascular bundles | VB(%) | 10×4 | 维管束面积占 总根面积的占比 |
| 木栓层厚度 Cork layer thickness | CL | 10×40 | |
| 木栓层层数 Number of cork layers | CLN | 10×40 | |
| 导管直径 vessel diameter | D | 10×40 | |
| 导管壁厚度 Vessel wall thickness | DWT | 10×40 | |
| 导管密度 Vessel density | VD | 10×40 | 单位木质部面积内的 导管数占比 |
Tab.1 Chinese and English names, abbreviations of root anatomical structure indexes
| 指标 Target | 缩写 Ablorevia- tion | 测量倍数 Measurement multiple | 备注 Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 木质部面积 Xylem area | XA | 10×4 | |
| 韧皮部面积 Phloem area | PHA | 10×4 | |
| 维管束面积 Vascular bundle area | VBA | 10×4 | |
| 木质部占比 Proportion of xylem | X(%) | 10×4 | 木质部面积占 总根面积的占比 |
| 韧皮部占比 Proportion of phloem | PH(%) | 10×4 | 韧皮部面积占 总根面积的占比 |
| 维管束占比 Proportion of vascular bundles | VB(%) | 10×4 | 维管束面积占 总根面积的占比 |
| 木栓层厚度 Cork layer thickness | CL | 10×40 | |
| 木栓层层数 Number of cork layers | CLN | 10×40 | |
| 导管直径 vessel diameter | D | 10×40 | |
| 导管壁厚度 Vessel wall thickness | DWT | 10×40 | |
| 导管密度 Vessel density | VD | 10×40 | 单位木质部面积内的 导管数占比 |
| 指标 Indexes | 处理组 Treatment grcap | 砧木资源Rootstock resources | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 桃×扁桃天然杂交Peach×Almond | 桃Peach | 扁桃Almond | |||||
| 桃巴旦1号 Peach × Almond 1 varity | 桃巴旦2号 Peach × Almond 2 varity | 毛桃 Peach | 石头扁桃 Stone almond | 大巴旦 Big almond | 苦扁桃 Ku almond | ||
| XAT (mm2) | 对照 CK | 1.47±0.32bc | 4.71±0.502a | 1.16±0.52c | 2.52±0.50bc | 4.18±1.74ab | 2.75±0.36b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 2.08±0.20b | 3.53±0.36a | 1.62±0.54b | 3.78±1.20a | 3.18±1.21ab | 4.04±0.75a | |
| PHAT (mm2) | 对照 CK | 4.07±1.38ab | 2.98±0.20b | 4.89±1.59a | 1.60±0.30b | 2.43±0.54b | 1.83±0.16b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 3.80±0.96a | 3.28±0.43ab | 4.27±0.47a | 2.31±0.61b | 2.03±0.50b | 2.44±0.91b | |
| VBAT (mm2) | 对照 CK | 5.54±1.59ab | 7.68±0.31a | 6.05±1.47ab | 4.12±0.75b | 6.61±2.27ab | 4.59±0.50b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 5.88±1.16a | 6.82±0.79a | 5.90±0.84a | 6.09±1.74a | 5.13±1.70a | 6.48±0.97a | |
| XAT (%) | 对照 CK | 24.46±4.85b | 53.60±5.70a | 17.49±9.16b | 53.51±2.00a | 57.89±8.28a | 52.64±2.09a |
| 干旱胁迫 | 32.52±3.54c | 47.85±2.56b | 22.80±4.70d | 54.19±4.11ab | 60.70±3.33a | 52.92±6.96ab | |
| PHAT (%) | 对照 CK | 65.85±5.52a | 34.00±4.23b | 70.82±10.99a | 34.05±4.20b | 34.902.93b | 35.13±1.51b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 58.23±4.79a | 44.42±3.37b | 61.56±6.36a | 33.72±4.16c | 39.68±3.29bc | 31.79±9.74c | |
| VBAT (%) | 对照 CK | 90.31±2.53a | 87.60±6.75a | 88.30±2.00a | 87.56±3.84a | 92.79±7.65a | 87.77±1.25a |
| 干旱胁迫 | 90.75±5.36bc | 92.27±5.70b | 84.36±1.81c | 87.91±0.05bc | 98.58±2.61a | 84.72±3.26c | |
| CLT | 对照 CK | 14.74±2.05ab* | 14.54±2.96ab | 15.24±5.00ab | 13.50±4.64b | 18.94±3.75a | 17.34±2.83ab |
| 干旱胁迫 | 10.84±1.67b* | 14.97±1.94b | 13.25±9.03b | 17.96±2.48ab | 22.28±6.58a | 18.58±2.73ab | |
Tab.2 Root anatomical structure comparison and analysis of 6 different Almond roots resources under normal and drought stress conditions
| 指标 Indexes | 处理组 Treatment grcap | 砧木资源Rootstock resources | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 桃×扁桃天然杂交Peach×Almond | 桃Peach | 扁桃Almond | |||||
| 桃巴旦1号 Peach × Almond 1 varity | 桃巴旦2号 Peach × Almond 2 varity | 毛桃 Peach | 石头扁桃 Stone almond | 大巴旦 Big almond | 苦扁桃 Ku almond | ||
| XAT (mm2) | 对照 CK | 1.47±0.32bc | 4.71±0.502a | 1.16±0.52c | 2.52±0.50bc | 4.18±1.74ab | 2.75±0.36b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 2.08±0.20b | 3.53±0.36a | 1.62±0.54b | 3.78±1.20a | 3.18±1.21ab | 4.04±0.75a | |
| PHAT (mm2) | 对照 CK | 4.07±1.38ab | 2.98±0.20b | 4.89±1.59a | 1.60±0.30b | 2.43±0.54b | 1.83±0.16b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 3.80±0.96a | 3.28±0.43ab | 4.27±0.47a | 2.31±0.61b | 2.03±0.50b | 2.44±0.91b | |
| VBAT (mm2) | 对照 CK | 5.54±1.59ab | 7.68±0.31a | 6.05±1.47ab | 4.12±0.75b | 6.61±2.27ab | 4.59±0.50b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 5.88±1.16a | 6.82±0.79a | 5.90±0.84a | 6.09±1.74a | 5.13±1.70a | 6.48±0.97a | |
| XAT (%) | 对照 CK | 24.46±4.85b | 53.60±5.70a | 17.49±9.16b | 53.51±2.00a | 57.89±8.28a | 52.64±2.09a |
| 干旱胁迫 | 32.52±3.54c | 47.85±2.56b | 22.80±4.70d | 54.19±4.11ab | 60.70±3.33a | 52.92±6.96ab | |
| PHAT (%) | 对照 CK | 65.85±5.52a | 34.00±4.23b | 70.82±10.99a | 34.05±4.20b | 34.902.93b | 35.13±1.51b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 58.23±4.79a | 44.42±3.37b | 61.56±6.36a | 33.72±4.16c | 39.68±3.29bc | 31.79±9.74c | |
| VBAT (%) | 对照 CK | 90.31±2.53a | 87.60±6.75a | 88.30±2.00a | 87.56±3.84a | 92.79±7.65a | 87.77±1.25a |
| 干旱胁迫 | 90.75±5.36bc | 92.27±5.70b | 84.36±1.81c | 87.91±0.05bc | 98.58±2.61a | 84.72±3.26c | |
| CLT | 对照 CK | 14.74±2.05ab* | 14.54±2.96ab | 15.24±5.00ab | 13.50±4.64b | 18.94±3.75a | 17.34±2.83ab |
| 干旱胁迫 | 10.84±1.67b* | 14.97±1.94b | 13.25±9.03b | 17.96±2.48ab | 22.28±6.58a | 18.58±2.73ab | |
| 指标 Indexes | 处理组 Treatment grcap | 砧木资源Rootstock resources | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 桃×扁桃天然杂交Peach×Almond | 桃Peach | 扁桃Almond | |||||
| 桃巴旦1号 Peach × Almond 1 varity | 桃巴旦2号 Peach ×Almond 2 varity | 毛桃 Peach | 石头扁桃 Stone almond | 大巴旦 Big almond | 苦扁桃 Ku almond | ||
| XAl (mm2) | 对照 CK | 0.92±0.12b | 1.45±0.22a | 0.55±0.16c | 1.12±0.15ab | 0.82±0.35bc | 0.98±0.36b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 0.87±0.07b | 1.34±0.13a | 0.61±0.35b | 0.82±0.05b | 0.89±0.28b | 0.66±0.32b | |
| PHAL (mm2) | 对照 CK | 0.87±0.17a | 0.55±0.09b | 0.47±0.16b | 0.34±0.06b | 0.38±0.08b | 0.41±0.22b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 0.57±0.09ab | 0.45±0.05ab | 0.60±0.40a | 0.29±0.07b | 0.41±0.11ab | 0.20±0.04b | |
| VBAL (mm2) | 对照 CK | 1.79±0.29a | 2.00±0.13a | 1.03±0.32b | 1.46±0.21ab | 1.21±0.39b | 1.39±0.58ab |
| 干旱胁迫 | 1.44±0.12ab | 1.79±0.12a | 1.22±0.74b | 1.11±0.11b | 1.30±0.26ab | 0.86±0.36b | |
| XAL (%) | 对照 CK | 29.51±1.46c | 43.78±10.70ab | 19.43±1.96d | 53.73±1.50a | 38.90±8.37b | 41.23±1.87b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 28.11±3.01b | 43.67±2.63a | 19.18±4.99c | 47.11±4.15a | 39.93±8.73a | 40.50±9.54a | |
| PHAL (%) | 对照 CK | 27.66±1.31a | 16.50±1.08b | 16.46±2.62b | 23.14±0.50ab | 18.46±2.56b | 16.47±4.30b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 18.67±3.07a | 14.73±1.66a | 18.50±4.81a | 16.27±1.54a | 18.95±4.60a | 13.42±2.67a | |
| VBAL (%) | 对照 CK | 57.17±1.10b | 60.28±9.62ab | 35.88±4.45c | 69.91±2.41a | 57.36±6.00b | 57.71±3.88b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 46.77±4.32b | 58.40±1.36a | 37.68±8.78c | 63.38±3.51a | 58.88±4.20a | 53.92±7.77ab | |
| CLL | 对照 CK | 22.52±3.77b* | 26.07±5.11b | 35.63±6.34ab | 44.05±0.02a | 35.95±6.18ab | 35.36±11.95ab |
| 干旱胁迫 | 33.01±4.52bc* | 29.97±2.49c | 37.48±1.43b | 45.07±5.67a | 43.75±8.58ab | 39.58±1.29ab | |
| CLNL | 对照CK | 6.09±0.59b* | 7.42±1.06b | 5.88±1.51b | 10.80±0.28a | 8.43±1.18ab | 8.16±2.46ab |
| 干旱胁迫 | 7.15±0.74b* | 7.53±0.38b | 7.88±0.22b | 11.24±1.51a | 10.42±3.76ab | 8.17±0.81b | |
Tab.3 Root anatomical structure comparison and analysis of 6 different Almond roots resources (2<D<4mm) under normal and drought stress conditions
| 指标 Indexes | 处理组 Treatment grcap | 砧木资源Rootstock resources | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 桃×扁桃天然杂交Peach×Almond | 桃Peach | 扁桃Almond | |||||
| 桃巴旦1号 Peach × Almond 1 varity | 桃巴旦2号 Peach ×Almond 2 varity | 毛桃 Peach | 石头扁桃 Stone almond | 大巴旦 Big almond | 苦扁桃 Ku almond | ||
| XAl (mm2) | 对照 CK | 0.92±0.12b | 1.45±0.22a | 0.55±0.16c | 1.12±0.15ab | 0.82±0.35bc | 0.98±0.36b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 0.87±0.07b | 1.34±0.13a | 0.61±0.35b | 0.82±0.05b | 0.89±0.28b | 0.66±0.32b | |
| PHAL (mm2) | 对照 CK | 0.87±0.17a | 0.55±0.09b | 0.47±0.16b | 0.34±0.06b | 0.38±0.08b | 0.41±0.22b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 0.57±0.09ab | 0.45±0.05ab | 0.60±0.40a | 0.29±0.07b | 0.41±0.11ab | 0.20±0.04b | |
| VBAL (mm2) | 对照 CK | 1.79±0.29a | 2.00±0.13a | 1.03±0.32b | 1.46±0.21ab | 1.21±0.39b | 1.39±0.58ab |
| 干旱胁迫 | 1.44±0.12ab | 1.79±0.12a | 1.22±0.74b | 1.11±0.11b | 1.30±0.26ab | 0.86±0.36b | |
| XAL (%) | 对照 CK | 29.51±1.46c | 43.78±10.70ab | 19.43±1.96d | 53.73±1.50a | 38.90±8.37b | 41.23±1.87b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 28.11±3.01b | 43.67±2.63a | 19.18±4.99c | 47.11±4.15a | 39.93±8.73a | 40.50±9.54a | |
| PHAL (%) | 对照 CK | 27.66±1.31a | 16.50±1.08b | 16.46±2.62b | 23.14±0.50ab | 18.46±2.56b | 16.47±4.30b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 18.67±3.07a | 14.73±1.66a | 18.50±4.81a | 16.27±1.54a | 18.95±4.60a | 13.42±2.67a | |
| VBAL (%) | 对照 CK | 57.17±1.10b | 60.28±9.62ab | 35.88±4.45c | 69.91±2.41a | 57.36±6.00b | 57.71±3.88b |
| 干旱胁迫 | 46.77±4.32b | 58.40±1.36a | 37.68±8.78c | 63.38±3.51a | 58.88±4.20a | 53.92±7.77ab | |
| CLL | 对照 CK | 22.52±3.77b* | 26.07±5.11b | 35.63±6.34ab | 44.05±0.02a | 35.95±6.18ab | 35.36±11.95ab |
| 干旱胁迫 | 33.01±4.52bc* | 29.97±2.49c | 37.48±1.43b | 45.07±5.67a | 43.75±8.58ab | 39.58±1.29ab | |
| CLNL | 对照CK | 6.09±0.59b* | 7.42±1.06b | 5.88±1.51b | 10.80±0.28a | 8.43±1.18ab | 8.16±2.46ab |
| 干旱胁迫 | 7.15±0.74b* | 7.53±0.38b | 7.88±0.22b | 11.24±1.51a | 10.42±3.76ab | 8.17±0.81b | |
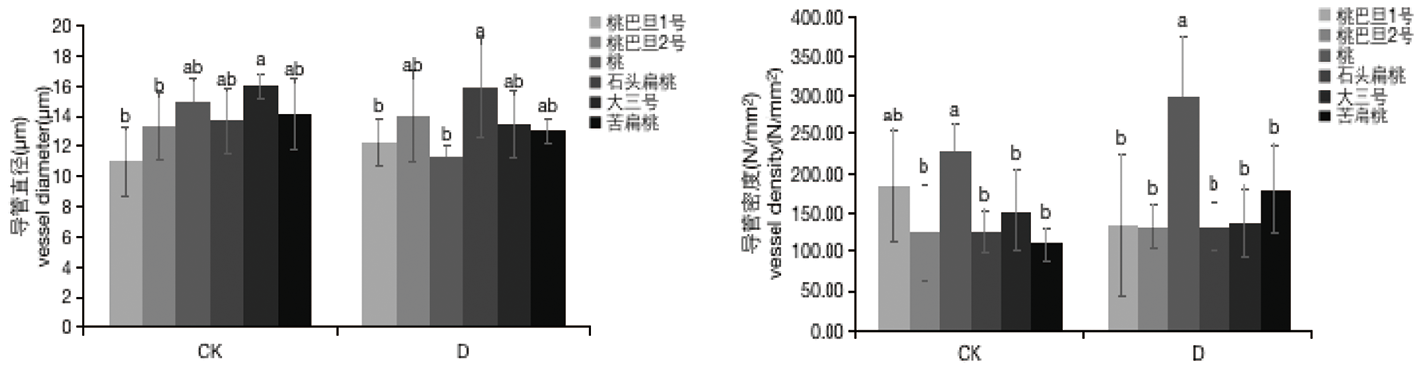
Fig.2 Effects of drought stress on xylem vessel density and vessel diameter of six Almond rootstock resources Note:Different lowercase letters represent significant differences in the same treatment group of different varieties,“*”Represents the significant difference in different treatment groups of the same species(P< 0.05),the same as below
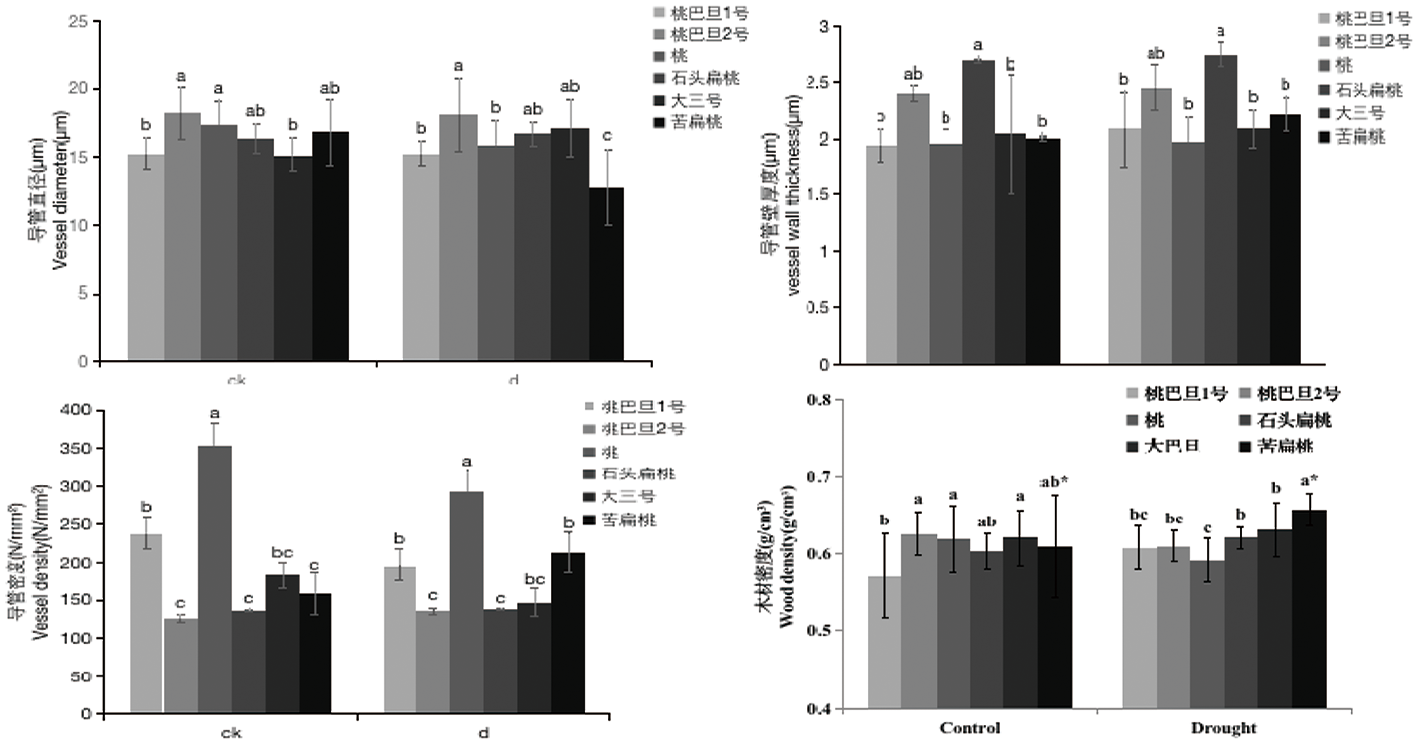
Fig.4 Effects of drought stress on xylem vessel diameter, vessel wall thickness, vessel density and wood density of 6 different Almond rootstock resources
| 成分 Comp- onent | 初始特征值 Initial eigenvalue | 提取平方和载入 Extract the sum of squares and load | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 合计 Total | 方差的% Variance of % | 累积 Accum- ulation (%) | 合计 Total | 方差的% Variance of % | 累积 Accum- ulation (%) | |
| 1 | 3.802 | 34.566 | 34.566 | 3.802 | 34.566 | 34.566 |
| 2 | 2.219 | 20.17 | 54.736 | 2.219 | 20.17 | 54.736 |
| 3 | 1.606 | 14.601 | 69.336 | 1.606 | 14.601 | 69.336 |
| 4 | 1.093 | 9.94 | 79.277 | 1.093 | 9.94 | 79.277 |
| 5 | 0.819 | 7.45 | 86.726 | |||
| 6 | 0.535 | 4.864 | 91.59 | |||
| 7 | 0.364 | 3.306 | 94.897 | |||
| 8 | 0.239 | 2.176 | 97.073 | |||
| 9 | 0.171 | 1.551 | 98.624 | |||
| 10 | 0.11 | 1.004 | 99.628 | |||
| 11 | 0.041 | 0.372 | 100 | |||
Tab.4 Every component proportion
| 成分 Comp- onent | 初始特征值 Initial eigenvalue | 提取平方和载入 Extract the sum of squares and load | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 合计 Total | 方差的% Variance of % | 累积 Accum- ulation (%) | 合计 Total | 方差的% Variance of % | 累积 Accum- ulation (%) | |
| 1 | 3.802 | 34.566 | 34.566 | 3.802 | 34.566 | 34.566 |
| 2 | 2.219 | 20.17 | 54.736 | 2.219 | 20.17 | 54.736 |
| 3 | 1.606 | 14.601 | 69.336 | 1.606 | 14.601 | 69.336 |
| 4 | 1.093 | 9.94 | 79.277 | 1.093 | 9.94 | 79.277 |
| 5 | 0.819 | 7.45 | 86.726 | |||
| 6 | 0.535 | 4.864 | 91.59 | |||
| 7 | 0.364 | 3.306 | 94.897 | |||
| 8 | 0.239 | 2.176 | 97.073 | |||
| 9 | 0.171 | 1.551 | 98.624 | |||
| 10 | 0.11 | 1.004 | 99.628 | |||
| 11 | 0.041 | 0.372 | 100 | |||
| 指标 Indexes | 成份 Principal components | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| VBAT (%) | 0.797 | 0.067 | -0.093 | -0.427 |
| CLL | 0.461 | -0.367 | 0.712 | 0.054 |
| CLNL | 0.621 | -0.467 | 0.511 | 0.178 |
| DL | 0.348 | 0.573 | -0.164 | 0.59 |
| DWTL | 0.654 | 0.531 | 0.216 | 0.023 |
| VDT | 0.769 | -0.055 | -0.017 | -0.073 |
| CLT | 0.277 | -0.766 | -0.244 | 0.402 |
| XAT (%) | 0.906 | -0.096 | -0.175 | -0.088 |
| VBAT (%) | 0.401 | -0.165 | -0.61 | 0.392 |
| XAL | 0.608 | 0.41 | -0.302 | -0.259 |
| WD | 0.026 | 0.676 | 0.449 | 0.366 |
Tab.5 Principal components matrix
| 指标 Indexes | 成份 Principal components | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| VBAT (%) | 0.797 | 0.067 | -0.093 | -0.427 |
| CLL | 0.461 | -0.367 | 0.712 | 0.054 |
| CLNL | 0.621 | -0.467 | 0.511 | 0.178 |
| DL | 0.348 | 0.573 | -0.164 | 0.59 |
| DWTL | 0.654 | 0.531 | 0.216 | 0.023 |
| VDT | 0.769 | -0.055 | -0.017 | -0.073 |
| CLT | 0.277 | -0.766 | -0.244 | 0.402 |
| XAT (%) | 0.906 | -0.096 | -0.175 | -0.088 |
| VBAT (%) | 0.401 | -0.165 | -0.61 | 0.392 |
| XAL | 0.608 | 0.41 | -0.302 | -0.259 |
| WD | 0.026 | 0.676 | 0.449 | 0.366 |
| 砧木资源 Rootstock resources | 指标 Indexes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLT | XAT (%) | DL | CLL | 平均值 Average value | 抗旱性排序 Drought resistance ranking | ||
| 桃×扁桃天然杂交 Natural hybrid of peach × almond | 桃巴旦1号 | 0.279 5 | 0.315 8 | 0.538 4 | 0.295 7 | 0.357 4 | 5 |
| 桃巴旦2号 | 0.341 9 | 0.741 2 | 0.506 8 | 0.305 8 | 0.473 9 | 4 | |
| 桃 Peach | 毛桃 | 0.322 3 | 0.156 1 | 0.314 6 | 0.557 5 | 0.337 6 | 6 |
| 扁桃 Almond | 石头扁桃 | 0.363 8 | 0.801 0 | 0.389 5 | 0.823 1 | 0.594 3 | 2 |
| 大巴旦 | 0.594 6 | 0.905 1 | 0.813 6 | 0.649 4 | 0.740 7 | 1 | |
| 苦扁桃 | 0.471 3 | 0.780 5 | 0.309 7 | 0.590 5 | 0.538 0 | 3 | |
Tab.6 Comprehensive score and ranking of root anatomical structure and drought resistance of 6 Almond rootstock varieties based on membership function
| 砧木资源 Rootstock resources | 指标 Indexes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLT | XAT (%) | DL | CLL | 平均值 Average value | 抗旱性排序 Drought resistance ranking | ||
| 桃×扁桃天然杂交 Natural hybrid of peach × almond | 桃巴旦1号 | 0.279 5 | 0.315 8 | 0.538 4 | 0.295 7 | 0.357 4 | 5 |
| 桃巴旦2号 | 0.341 9 | 0.741 2 | 0.506 8 | 0.305 8 | 0.473 9 | 4 | |
| 桃 Peach | 毛桃 | 0.322 3 | 0.156 1 | 0.314 6 | 0.557 5 | 0.337 6 | 6 |
| 扁桃 Almond | 石头扁桃 | 0.363 8 | 0.801 0 | 0.389 5 | 0.823 1 | 0.594 3 | 2 |
| 大巴旦 | 0.594 6 | 0.905 1 | 0.813 6 | 0.649 4 | 0.740 7 | 1 | |
| 苦扁桃 | 0.471 3 | 0.780 5 | 0.309 7 | 0.590 5 | 0.538 0 | 3 | |
| [1] |
Cattivelli L, Rizza F, Badeck F W, et al. Drought tolerance improvement in crop plants: An integrated view from breeding to genomics[J]. Field Crops Research, 2008, 105(1-2): 1-14.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Gainza F, Opazo I, Guajardo V, et al. Rootstock breeding in Prunus species: Ongoing efforts and new challenges[J]. Chilean Journal of Agricultural Research, 2015, 75: 6-16.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Arzani K, Yadollahi A, Ebadi A, et al. The relationship between bitterness and drought resistance of almond (Prunus dulcis Mill.)[J]. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 2010, 5(9): 861-866. |
| [4] |
Yadollahi A, Arzani K, Ebadi A, et al. The response of different almond genotypes to moderate and severe water stress in order to screen for drought tolerance[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2011, 129(3): 403-413.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 郭玉. 四倍体苹果砧木形态特征、生理生化特性及其对接穗品种的影响[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2012. |
| GUO Yu. Morphological characteristics, physiological and biochemical characteristics of tetraploid apple rootstocks and their effects on scion varieties[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2012. | |
| [6] |
刘飞, 王金花, 张洪毅, 等. 四种苹果砧木幼苗对锌胁迫的耐性差异[J]. 中国农业科学, 2012, 45(18): 3801-3811.
DOI |
|
LIU Fei, WANG Jinhua, ZhANG Hongyi, et al. Differences in tolerance of four apple rootstock seedlings to zinc stress[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012, 45(18): 3801-3811.
DOI |
|
| [7] | 赵秀明, 王飞, 韩明玉, 等. 新引进苹果矮化砧木的叶片解剖结构及抗旱性[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2012,(5): 136-142. |
| ZHAO Xiuming, WANG Fei, HAN Mingyu, et al. Leaf anatomical structure and drought resistance of newly introduced apple dwarf rootstocks[J]. Journal of Northwest Sci-Tech University of Agriculture and Forestry (Natural Science Ed.), 2012,(5): 136-142. | |
| [8] | 王延秀, 贾旭梅, 石晓昀, 等. 三种苹果砧木应对干旱胁迫的超微及解剖结构响应特性[J]. 植物生理学报, 2018, 54(4): 594-606. |
| WANG Yanxiu, JIA Xumei, SHI Xiaoyun, et al. Response characteristics of ultramicro and anatomical structures of three apple rootstocks to drought stress[J]. Acta Phytophysiology, 2018, 54(4): 594-606. | |
| [9] |
Marcinska I, Czyczyo -Mysza I, Skrzypek E, et al. Impact of osmotic stress on physiological and biochemical characteristics in rought-susceptible and drought-resistant wheat genotypes[J]. Acta Physiol Plant, 2013, 35: 451-461.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Tuberosa R, Salvo S. Genomics-based approaches to improve drought tolerance of crops[J]. Trends Plant Science, 2006, 11(8): 405-412.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 田建保, 何勇, 称恩明. 中国扁桃[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2008: 255. |
| TIAN Jianbao, HE Yong, CHEN E M. Chinese Almond[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2008: 255. | |
| [12] |
Herralde F D, Biel C, R Savé. Leaf Photosynthesis in Eight Almond Tree Cultivars[J]. Biologia Plantarum, 2003, 46(4): 557-561.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Castel J R, Fereres E. Responses of Young Almond Trees to Two Drought Periods in the Field[J]. Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology, 1982, 57(2): 175-187. |
| [14] |
Torrecillas A, Ruiz-Sanchez M C, Leon A, et al. Stomatal response to leaf water potential in almond trees under drip irrigated and non irrigated conditions[J]. Plant and Soil, 1988, 112(1): 151-153.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Torrecillas A, Domingo R, Planes J, et al. Strategies for drought resistance in leaves of two almond cultivars[J]. Plant Science, 1996, 118(2): 135-143.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Akbarpour E, Imani A, Yeganeh S F. Physiological and Morphological Responses of Almond Cultivars under In Vitro Drought Stress. 2017. |
| [17] | Micke W C, Freeman M W, Beede R H, et al. Almond trees grown on peach rootstock initially more productive[J]. California Agriculture, 1996, 50(4): 29-31. |
| [18] | 郭改改, 封斌, 麻保林, 等. 不同区域长柄扁桃叶片解剖结构及其抗旱性分析[J]. 西北植物学报, 2013, 33(4): 720-728. |
| GUO Gaigai, FENG Bing, Ma B L, et al. Anatomical structure of Amygdalus amygdalus in different regions and its drought resistance analysis[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2013, 33(4): 720-728. | |
| [19] |
Wang J, Zheng R, Bai S, Gao X, Liu M, Yan W. Mongolian Almond(Prunus mongolica Maxim): The Morpho-Physio-logical, Biochemical and Transcriptomic Response to Drought Stress[J]. Plos One, 2015, 10(4): e0124442.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 王丽娜, 克热木·伊力, 侯江涛. 水分胁迫对扁桃砧木叶片脯氨酸、可溶性蛋白质、质膜透性、相对含水量的影响[J]. 新疆农业大学学报, 2006, 29(3): 53-58. |
| WANG Lina, Keremu Yili, HOU Jiangtao. Effects of water stress on proline, soluble protein, membrane permeability, relative water content of Almond rootstock[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2006, 29(3): 53-58. | |
| [21] | 克热木·伊力, 王丽娜, 侯江涛. 水分胁迫对扁桃砧木干物质和叶绿素含量的影响[J]. 经济林研究, 2007, 25(4): 1-5. |
| YILI Keremu, WANG Lina, HOU Jiangtao. Effects of Water Stress on Contents of Dry Matters and Chlorophyll in Almond Rootstock[J]. Nonwood Forest Research, 2007, 25(4): 1-5. | |
| [22] | Zhang J, Poudel B, Kenworthy K, et al. Drought responses of above-ground and below‐ground characteristics in warm‐season turfgrass[J]. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 2019. |
| [23] | 乔胜. 玉米根系性状多样性及其对干旱胁迫的响应[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2018. |
| QIAO Sheng. Diversity of Maize Root Traits and its response to drought stress[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University. 2018. | |
| [24] | Boyrahm ad i, Mozhgan, Raiesi, et al. Plant roots and species moderate the salinity effect on microbial respiration, biomass, and enzyme activities in a sandy clay soil[J]. Biology & Fertility of Soils Cooperating Journal of the International Society of Soil Science, 2018. |
| [25] | 何广志, 陈亚宁, 陈亚鹏, 等. 柽柳根系构型对干旱的适应策略[J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(3):6. |
| HE Guangzhi, CHEN Yaning, CHEN Yapeng, et al. Adaptation strategy of Tamarix root architecture to drought[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science Ed.), 2016, 52(3): 6. | |
| [26] |
Zhao J, Bodner, Gernot, et al. Root architecture simulation improves the inference from seedling root phenotyping towards mature root systems[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2017, 68(5):965-982.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Pande P K, Ghyldiyal J C, Gautam P. Secondary Xylem Anatomy of Root and Stem of Alstonia scholais, Bischhiofia javanica and Trewia nudiflora: The Characteristic Plant Species of Manu Fresh Water Swamp, Rishikesh, Dehradun (India)[J]. Indian Forester, 2013, 139(8). |
| [28] | 汪攀, 陈奶莲, 邹显花, 等. 植物根系解剖结构对逆境胁迫响应的研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(2):7. |
| WANG Pan, CHEN Nailian, ZOU Xianhua, et al. Research progress on the response of plant root anatomical structure to stress[J]. Journal Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34 (2): 7. | |
| [29] | 潘晓迪, 张颖, 邵萌, 等. 作物根系结构对干旱胁迫的适应性研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(2):8. |
| PAN Xiaodi, ZHANG Ying, SHAO Meng, et al. Research progress on Adaptability of crop root structure to drought stress[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19 (2): 8. | |
| [30] | 刘捷平. 植物形态解剖学[M]. 北京: 北京师范学院出版社, 1991: 310-311. |
| LIU Jieping. Plant morphological anatomy[M]. Beijing: Beijing Normal University Press, 1991: 310-311. | |
| [31] | 李正理, 李荣敖. 我国甘肃九种旱生植物同化枝的解剖观察[J]. 植物学报, 1981, 23(3): 181-185. |
| LI Zhengli, LI Rongao. Anatomical observation of assimilating branches of nine xerophytes in Gansu, China[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 1981, 23(3): 181-185. | |
| [32] | 陈小红, 徐扬, 刘韩, 等. 川西高原4种高山海棠的根茎解剖结构特征及其抗旱响应策略分析[J]. 西北植物学报, 2017, 37(7):7. |
| CHEN Xiaohong, XU Yang, LIU Han, et al. Analysis of rhizome anatomical characteristics and drought resistance response strategies of four alpine begonias in Western Sichuan Plateau[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2017, 37(7): 7. | |
| [33] | 赵祥, 董宽虎, 张土垚, 等. 达乌里胡枝子根解剖结构与其抗旱性的关系[J]. 草地学报, 2011, 19(1):7. |
| ZHAO Xiang, DONG Kuanhu, ZHANG Tuyao, et al. Relationship between root anatomical structure and drought resistance of Lespedeza davurica[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2011, 19(1): 7. | |
| [34] | 潘学燕, 苗芳. 小麦维管组织结构研究概况[J]. 中国农学通报, 2006, 21(9): 121-123. |
| PAN Xueyan, MIAO Fang. Overview of vascular tissue structure of wheat[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2006, 21(9): 121-123. | |
| [35] |
Thangthong N, Jogloy S, Punjansing T, et al. Changes in Root Anatomy of Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) under Different Durations of Early Season Drought[J]. Agronomy, 2019, 9(5):215.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 黄振英, 吴鸿. 30种新疆沙生植物的结构及其对沙漠环境的适应[J]. 植物生态学报, 1997, 21(6): 521-530. |
| HUANG Zhengying, WU Hong. Structure of 30 species of desert plants in Xinjiang and their adaptation to desert environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 1997, 21(6): 521-530. | |
| [37] | 张翠梅, 师尚礼, 刘珍, 等. 干旱胁迫对不同抗旱性苜蓿品种根系形态及解剖结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(5):11. |
| ZHANG Cuimei, SHI Shangli, LIU Zhen, et al. Effects of drought stress on root morphology and anatomical structure of Alfalfa Varieties with different drought resistance[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(5): 11. | |
| [38] | 金芳玉. 绵刺的营养器官解剖结构与抗旱适应性的关系[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2014. |
| JIN Fangyu. Relationship between anatomical structure of vegetative organs and drought resistance adaptability of cotton thorn[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2014. | |
| [39] | 王静, 黄薇. 初生根的形态解剖结构与春小麦的抗旱性的关系初探[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 1998, 34(4): 154-156. |
| WANG Jing, HUANG Wei. Relationship between morphological and anatomical structure of primary roots and drought resistance of spring wheat[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Science Ed.), 1998, 34(4): 154-156. | |
| [40] | 李鲁华, 李世清, 翟军海. 小麦根系与土壤水分胁迫关系的研究进展[J]. 西北植物学报, 2001, 21(1): 1-7 |
| LI Luhua, LI Shiqing, ZHAI Junhai. Research progress on the relationship between wheat roots and soil water stress[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2001, 21(1): 1-7. | |
| [41] | Audus L J, Garrard A. How does water get through roots[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 1998, 49(322):775-788. |
| [42] | 彭伟秀, 王文全, 梁海永, 等. 水分胁迫对甘草营养器官解剖构造的影响[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2003, 26(3): 46-48. |
| PENG Weixiu, WANG Wenquan, LIANG Haiyong, et al. Effect of water stress on anatomical structure of vegetative organs of Glycyrrhiza uralensis[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University, 2003, 26(3): 46-48. | |
| [43] | 王法宏, 郑丕尧, 王树安, 等. 大豆不同抗旱性品种根系性状的比较研究Ⅰ、形态特征及解剖组织结构[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 1989, (1): 32-38. |
| WANG Fahong, ZHENG Piyao, WANG Shuan, et al. Comparative study on Root Traits of soybean varieties with different drought resistanceⅠMorphological characteristics and anatomical structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 1989,(1): 32-38. | |
| [44] | 木巴热克·阿尤普, 杨波, 艾沙江·买买提, 等. 基于当年生枝木质部解剖结构的扁桃品种栓塞抗性分析[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2021, 36(5): 99-105. |
| AYUP Mubareke, YANR Bo, AISHAJIANG Maimaiti, et al. Analysis of embolic resistance of Almond Varieties Based on the anatomical structure of xylem of current year branches[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2021, 36(5): 99-105. | |
| [45] |
AYUP Mubarek, YANG Bo, GONG Peng, GUO Chunmiao. Evaluation of drought resistance of native almond-rootstock varieties in Xinjiang, China[J]. DOI: 10.1080/01140671.2021.1925709.
DOI |
| [1] | BAI Ling, FENG Guojun, HU Xiangwei, ZHAO Yun, SHI Shubing. Drought resistance identification and physiological changes of different millet varieties during germination [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(7): 1630-1640. |
| [2] | LIU Min, JIN Juan, Abudoukayoumu Ayimaiti, FAN Dingyu, HAO Qing, YANG Lei, ZHAO Xiaomei, GENG Wenjuan. Evaluation of cold resistance of three fresh edible jujube cultivars in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(4): 916-924. |
| [3] | JIA Yonghong, WEI Haipeng, HOU Dianliang, ZENG Chaowu, Nasirula Keremu, LIANG Xiaodong. Evaluation of correlation between drought resistance and agronomic traits of self-breeding spring wheat varieties in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(12): 2940-2948. |
| [4] | SHAN Ying, LI Yue, XU Min, LIU Yanzhen, LI Ran, CHEN Jieyin, WANG Zisheng, ZHU He. Drought resistance evaluation of liaomian cotton varieties at germination stage under PEG simulated drought stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(11): 2653-2660. |
| [5] | TANG Huaijun, XIE Xiaoqing, ZHANG Lei, SUN Baocheng, YANG Jie, LIU Cheng. Drought resistance identification and screening of 283 maize [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(11): 2687-2693. |
| [6] | SUN Fenglei, REN Jiaojiao, LEI Bin, GAO Wenwei, QU Yanying. QTL mapping and genomic selection of maize leaf width [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(10): 2341-2351. |
| [7] | XIE Xiaoqing, TANG Huaijun, ZHANG Lei, SUN Baocheng, LIU Cheng. Changes of maize ear traits and drought resistance with irrigation amount [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(10): 2412-2418. |
| [8] | NIE Shihui, WANG Xian, PENG Lin, JI Liang. Preliminary Construction of Chickpea Drought Resistance Core Germplasm Based on Agronomic Traits [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(4): 847-854. |
| [9] | FU Dongqing, WANG Yanchao, MAO Jiaxiang, YANG Fan, SONG Lei, ZHANG Fanfan, MA Chunhui. Comprehensive Quality Analysis and Evaluation Oat Varieties under Dry Farming Conditions in Balluk Mountain [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(2): 344-352. |
| [10] | YANG Long, ZHAO Fuxiang, DUAN Yajie, CAI Yongsheng, ZHENG Kai, CHEN Qin, CHEN Quanjia, QU Yanying. Evaluation on Drought Resistance of Recombinant Inbred Lines of Gossypium barbadense L. at Flowering and Boll Stages [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(12): 2861-2869. |
| [11] | ZOU Chenglin, TAN Hua, HUANG Kaijian, HUANG Aihua, ZHAI Ruining, MO Runxiu. Drought Resistance Identification of 28 Maize Lines [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(10): 2411-2420. |
| [12] | LIAO Niu, DIAO Ming, CUI Hongxin, NIU Ning, LIU Huiying. Effect of Drip Irrigation with Saltwater during Flowering on Main Characters of 10 Tomato Germplasm and Evaluation of Salt Tolerance [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(10): 2486-2494. |
| [13] | XIE Xiaoqing, TANG Huaijun, ZHANG Lei, SUN Baocheng, LIU Cheng. Study on the Theoretical Model of Watering Ratio and Drought Resistance under Proportional Irrigation of Maize [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(1): 70-78. |
| [14] | XU Panyun, LI Chunlan, SONG Jindi, WANG Xi, CHENG Jiabao, WU Yuxia, HE Tianming. Physiological Responses of Seedlings of Different Apple Rootstocks to Salt-Alkali Complex Stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(9): 1694-1703. |
| [15] | SUN Yali, CHU Fenfei, Gulimirei Kakeshi, Baharguli Ayupu, Gulijiang Xukuerhan. Comparative Analysis of Photosynthetic Physiological Responses of Different Gooseberry Varieties to Salt Stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(5): 829-837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||