

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (11): 2687-2693.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.11.011
• Crop Genetics and Breeding · Germplasm Resources·Molecular Genetics·Soil Fertilizer • Previous Articles Next Articles
TANG Huaijun( ), XIE Xiaoqing, ZHANG Lei, SUN Baocheng, YANG Jie, LIU Cheng(
), XIE Xiaoqing, ZHANG Lei, SUN Baocheng, YANG Jie, LIU Cheng( )
)
Received:2023-02-20
Online:2023-11-20
Published:2023-12-07
Correspondence author:
LIU Cheng (1968-), female, from Jiuquan, Gansu province, Ph.D., researcher, master supervisor, research direction: Grain crop stress resistance research, (E-mail)liuchengxj@126.com
Supported by:通讯作者:
刘成(1968-), 女, 甘肃酒泉人, 研究员, 博士, 硕士生导师, 研究方向为粮食作物抗逆, (E-mail)liuchengxj@126.com
作者简介:唐怀君(1983-),男, 安徽砀山人, 副研究员, 硕士, 研究方向为粮食作物抗逆, (E-mail)tanghuaijun83@sina.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
TANG Huaijun, XIE Xiaoqing, ZHANG Lei, SUN Baocheng, YANG Jie, LIU Cheng. Drought resistance identification and screening of 283 maize[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(11): 2687-2693.
唐怀君, 谢小清, 张磊, 孙宝成, 杨杰, 刘成. 283份玉米田间抗旱性鉴定与筛选[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(11): 2687-2693.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.xjnykx.com/EN/10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.11.011
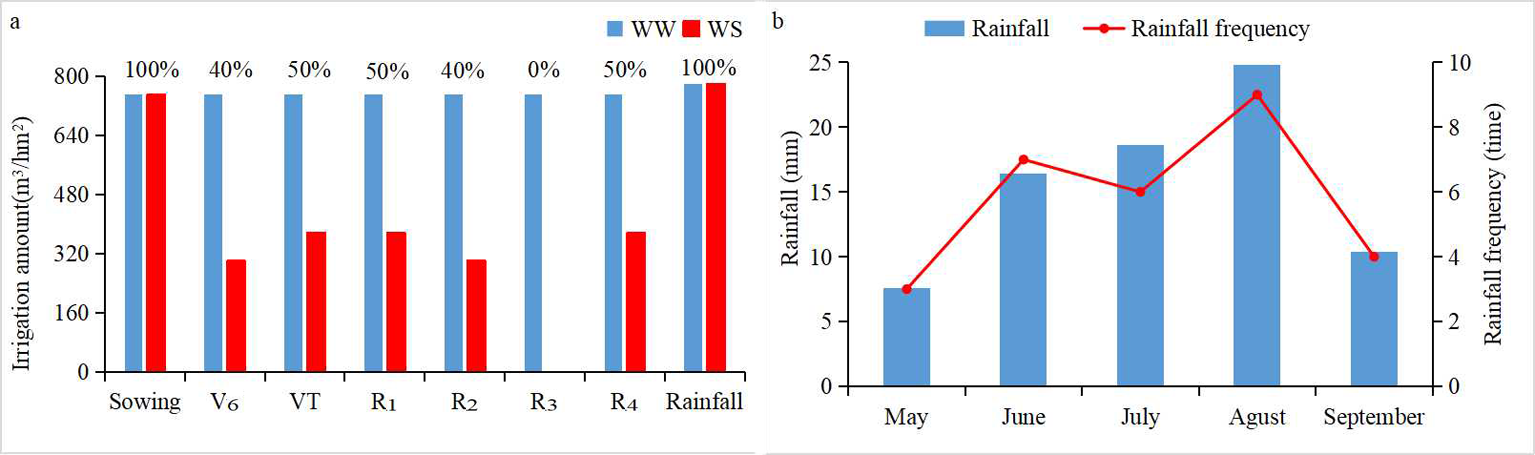
Fig.1 Irrigation amount(a) and rainfall of different treatments(b) Note: (a) The amount and period of irrigation for the different treatments.WW, well-watered.WS, water-stressed.V6, sixth leaf; VT, tasseling; R1, silking, R2, blister, R3, milk, R4, dough.(b) The rainfall frequency and amount during the maize growth stage (from May to September)
| 类型 Type | 材料编号 No. | 吐丝天数 Days to Silking (day) | 株高 Plant Height (cm) | 穗位高 Ear Height (cm) | 穗粒数 Grain Number Per Ear (粒/穗) | 百粒重 Hundred Grain Weight (g) | 单株粒重 YieldPer Plant (g) | 抗旱系数 Drought Resistance Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自交系 Inbred lines | 21NHL018 | 65.0 | 166.4 | 53.3 | 392.0 | 28.6 | 64.2 | 0.86 |
| 21NHL033 | 67.5 | 191.1 | 77.5 | 354.0 | 36.0 | 76.0 | 0.88 | |
| 21NHL034 | 70.0 | 188.5 | 56.3 | 448.0 | 35.1 | 79.3 | 0.88 | |
| 21NHL037 | 69.0 | 208.1 | 61.9 | 414.0 | 33.9 | 85.4 | 0.84 | |
| 21NHL038 | 71.0 | 177.8 | 65.5 | 465.0 | 34.3 | 84.9 | 0.83 | |
| 21NHL040 | 68.0 | 183.1 | 60.8 | 392.0 | 29.6 | 64.6 | 0.93 | |
| 21NHL049 | 59.0 | 175.4 | 65.6 | 502.0 | 22.0 | 87.8 | 0.85 | |
| 21NHL064 | 64.0 | 150.0 | 44.6 | 338.0 | 24.4 | 60.4 | 0.81 | |
| 21NHL101 | 68.0 | 180.0 | 47.4 | 405.0 | 34.9 | 61.9 | 0.99 | |
| 21NHL104 | 68.5 | 199.6 | 67.5 | 455.0 | 29.2 | 89.6 | 0.92 | |
| 21NHL105 | 71.0 | 206.8 | 76.0 | 397.0 | 32.4 | 82.3 | 0.82 | |
| 21NHL106 | 68.5 | 200.1 | 64.4 | 470.0 | 34.1 | 90.5 | 0.81 | |
| 21NHL112 | 69.5 | 168.0 | 61.0 | 295.0 | 32.7 | 61.5 | 0.84 | |
| 21NHL147 | 69.0 | 183.9 | 71.6 | 452.0 | 31.2 | 76.7 | 0.84 | |
| 21NHL202 | 58.5 | 164.4 | 61.1 | 371.0 | 16.5 | 61.5 | 1.00 | |
| 所有自交 系平均值 | 66.2 | 174.1 | 60.4 | 342.9 | 26.1 | 58.9 | 0.61 | |
| 杂交种 Hybrid | 21VNH23 | 62.5 | 287.8 | 106.8 | 692.0 | 38.6 | 186.8 | 0.80 |
| 21VNH24 | 63.0 | 307.6 | 115.0 | 634.0 | 34.9 | 183.0 | 0.80 | |
| 21VNH25 | 61.5 | 275.6 | 103.8 | 538.0 | 38.9 | 165.7 | 0.80 | |
| 所有杂交 种平均值 | 60.6 | 254.3 | 95.6 | 594.7 | 32.6 | 159.1 | 0.67 |
Tab.1 Characteristics of 15 inbred lines and 3 hybrids screened for drought resistance in 2021 under well-watered
| 类型 Type | 材料编号 No. | 吐丝天数 Days to Silking (day) | 株高 Plant Height (cm) | 穗位高 Ear Height (cm) | 穗粒数 Grain Number Per Ear (粒/穗) | 百粒重 Hundred Grain Weight (g) | 单株粒重 YieldPer Plant (g) | 抗旱系数 Drought Resistance Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自交系 Inbred lines | 21NHL018 | 65.0 | 166.4 | 53.3 | 392.0 | 28.6 | 64.2 | 0.86 |
| 21NHL033 | 67.5 | 191.1 | 77.5 | 354.0 | 36.0 | 76.0 | 0.88 | |
| 21NHL034 | 70.0 | 188.5 | 56.3 | 448.0 | 35.1 | 79.3 | 0.88 | |
| 21NHL037 | 69.0 | 208.1 | 61.9 | 414.0 | 33.9 | 85.4 | 0.84 | |
| 21NHL038 | 71.0 | 177.8 | 65.5 | 465.0 | 34.3 | 84.9 | 0.83 | |
| 21NHL040 | 68.0 | 183.1 | 60.8 | 392.0 | 29.6 | 64.6 | 0.93 | |
| 21NHL049 | 59.0 | 175.4 | 65.6 | 502.0 | 22.0 | 87.8 | 0.85 | |
| 21NHL064 | 64.0 | 150.0 | 44.6 | 338.0 | 24.4 | 60.4 | 0.81 | |
| 21NHL101 | 68.0 | 180.0 | 47.4 | 405.0 | 34.9 | 61.9 | 0.99 | |
| 21NHL104 | 68.5 | 199.6 | 67.5 | 455.0 | 29.2 | 89.6 | 0.92 | |
| 21NHL105 | 71.0 | 206.8 | 76.0 | 397.0 | 32.4 | 82.3 | 0.82 | |
| 21NHL106 | 68.5 | 200.1 | 64.4 | 470.0 | 34.1 | 90.5 | 0.81 | |
| 21NHL112 | 69.5 | 168.0 | 61.0 | 295.0 | 32.7 | 61.5 | 0.84 | |
| 21NHL147 | 69.0 | 183.9 | 71.6 | 452.0 | 31.2 | 76.7 | 0.84 | |
| 21NHL202 | 58.5 | 164.4 | 61.1 | 371.0 | 16.5 | 61.5 | 1.00 | |
| 所有自交 系平均值 | 66.2 | 174.1 | 60.4 | 342.9 | 26.1 | 58.9 | 0.61 | |
| 杂交种 Hybrid | 21VNH23 | 62.5 | 287.8 | 106.8 | 692.0 | 38.6 | 186.8 | 0.80 |
| 21VNH24 | 63.0 | 307.6 | 115.0 | 634.0 | 34.9 | 183.0 | 0.80 | |
| 21VNH25 | 61.5 | 275.6 | 103.8 | 538.0 | 38.9 | 165.7 | 0.80 | |
| 所有杂交 种平均值 | 60.6 | 254.3 | 95.6 | 594.7 | 32.6 | 159.1 | 0.67 |
| [1] | Liu S, Qin F. Genetic dissection of maize drought tolerance for trait improvement[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2021, 41(2). |
| [2] |
Lobell, D B, Roberts M J, Schlenker W, et al. Greater sensitivity to drought accompanies maize yield increase in the U.S. Midwest[J]. Science, 2014, 344: 516-519.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | 梁晓玲, 刘文欣, 阿不来提阿布拉, 等. 干旱胁迫对玉米杂交种产量及穗部性状的影响[J]. 玉米科学, 2021, 29(2): 75-80. |
| LIANG Xiaoling, LIU Wenxin, Abulaiti Abra, et al. Influence of drought stress on yield and ear traits of maize hybrids[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2021, 29(2): 75-80. | |
| [4] | 任志强, 王晓清, 卜华虎, 等. 玉米抗旱育种研究进展[J]. 山西农业科学, 2019, 47(7): 1291-1294. |
| REN Zhiqiang, WANG Xiaoqing, BU Huahu, et al. Research progress in drought resistance breeding of maize[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(7): 1291-1294. | |
| [5] | 周玉乾, 杨彦忠, 周文期, 等. 干旱胁迫下玉米自交抗旱性评价及筛选[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2020, 38(5): 211-217. |
| ZHOU Yuqian, YANG Yanzhong, ZHOU Wenqi, et al. Evaluation and selection of drought resistance inbred lines of maize under drought stress[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2020, 38(5): 211-217. | |
| [6] | 崔静宇, 关小康, 杨明达, 等. 基于主成分分析的玉米萌发期抗旱性综合评定[J]. 玉米科学, 2019, 27(5): 62-72. |
| CUI Jingyu, GUAN Xiaokang, YANG Mingda, et al. Integrative evaluation of maize drought tolerance in germination period by PCA method[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2019, 27(5): 62-72. | |
| [7] | 刘化涛, 黄学芳, 黄明镜, 等. 拔节期干旱对春玉米产量性状及抗旱性的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2016, (2) : 89-94. |
| LIU Huatao, HUANG Xuefang, HUANG Mingjing, et al. Effects of drought stress at jointing stage on yield and drought resistance in spring Maize[J]. Crops, 2016,(2): 89-94. | |
| [8] | 邹成林, 谭华, 郑德波, 等. 广西玉米品种开花期抗旱性鉴定与评价[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2019, 37(2): 136-143. |
| ZOU Chenglin, TAN Hua, ZHENG Debo, et al. Identification and evaluation of drought tolerance of different maize varieties during flowering stage in Guangxi[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2019, 37(2): 136-143. | |
| [9] | 李娇, 韩鹏, 穆云森, 等. 玉米灌浆期干旱胁迫对产量性状及生理生化的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48 (18): 107-110. |
| LI Jiao, HAN Peng, MU Yunsen, et al. Effects of drought stress on yield characters, physiological and biochemical characteristics in maize at the filling stage[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48 (18): 107-110. | |
| [10] | 唐怀君, 谢小清, 赵连佳, 等. 欠量灌水方法用于玉米抗旱性鉴定和评价研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2017, 54(5): 804-810. |
| TANG Huaijun, XIE Xiaoqing, ZHAO Lianjia, et al. Study on the evaluation and identification of maize drought resistance by using the method of water shortage irrigation[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 54(5): 804-810. | |
| [11] | 高志勇, 谢恒星, 王志平, 等. 玉米抗旱性功能基因研究进展[J]. 作物研究, 2016, 30(6): 732-735,740. |
| GAO Zhiyong, XIE Hengxing, WANG Zhiping, et al. Advances in research on functional genes of drought resistance in Maize[J]. Crop Research, 2016, 30(6): 732-735,740. | |
| [12] |
Cheng L, Xiao Hong Y, Jian Sheng L I, et al. Simple nonlinear' model for the relationship between maize yield and cumulative water amount[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2017, 16(4):858-866.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
唐怀君, 谢小清, 张磊, 等. 应用缺次灌溉和半产需水量模型鉴定玉米杂交种的抗旱性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(11): 1994-2001.
DOI |
|
TANG Huaijun, XIE Xiaoqing, ZHANG Lei, et al. Drought resistance of Maize Hybrid was identified by the model of water shortage irrigation and half-yield water requirement demand[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(11): 1994-2001.
DOI |
|
| [14] | 杨瑞晗, 许海涛, 王文文. 玉米抗旱性指标研究进展[J]. 大麦与谷类科学, 2021, 38(2): 1-7. |
| YANG Ruihan, XU Haitao, WANG Wenwen. Research advances in drought tolerance in Maize[J]. Barley and Cereal Sciences, 2021, 38(2): 1-7. | |
| [15] | 王秋兰, 靳鲲鹏, 刘永忠, 等. 玉米苗期抗旱性鉴定指标及综合评价[J]. 山西农业科学, 2019, 47(3): 319-322, 365. |
| WANG Qiulan, JIN Kunpeng, LIU Yongzhong, et al. Identification index and comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance in Maize seedling stage[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(3): 319-322, 365. |
| [1] | CHEN Maoguang, LIN Tao, ZHANG Hao, LIU Haijun, WANG Yifan, TANG Qiuxiang. Effects of mulch film types on cotton growth and analysis of self-degradation recycling characteristics [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2101-2108. |
| [2] | YANG Guojiang, CHEN Yun, LIN Xiangqun, HE Jiangyong, LIU Shenglin, QU Yongqing. Effects of organic fertilizer replacement on the yield and nutrient absorption of cotton and nitrate nitrogen under chemical fertilizer reduction [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2138-2145. |
| [3] | CHEN Chuanxin, ZHNAG Yongqiang, NIE Shihui, KONG Depeng, Sailihan Sai, XU Qijiang, LEI Junjie. Effects of biomass charcoal application rate on the growth, development, and yield of winter wheat under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2146-2151. |
| [4] | WANG Lihong, ZHANG Hongzhi, ZHANG Yueqiang, LI Jianfeng, WANG Zhong, GAO Xin, SHI Jia, WANG Chunsheng, XIA Jianqiang, FAN Zheru. Analysis of dry matter production, transport and nitrogen fertilizer utilization caused by yield Gap at different yield levels of winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2152-2162. |
| [5] | WANG Xiaoyu, WANG Xiaoping, SHI Wenyu, LIU Meiyan, MA Jian, GUO Yunpeng, SONG Ruixin, WANG Qingtao. Responses of photosynthetic characteristics, dry matter accumulation and yield to drought stress in winter wheat at jointing stage [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2163-2172. |
| [6] | XIANG Li, WANG Xian, DONG Yusheng, GUO Xiaoling, FANG Furong, CHEN Zhijun, MA Yanming, MIAO Yu. Effects of exogenous butyric acid on yield and quality of barley under drought stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2173-2181. |
| [7] | YANG Hongmei, ZHANG Yueqiang, SHI Yingwu, Omarjan Kurban, LIN Qing, WANG Ning, CHU Min, ZENG Jun. Effects of different types of foliar fertilizers on grain yield and 1uality of winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2182-2188. |
| [8] | WANG Xin, LIN Tao, CUI Jianping, WU Fengquan, TANG Zhixuan, CUI Laiyuan, GUO Rensong, WANG Liang, ZHENG Zipiao. Effects of planting mode and irrigation quota on yield and fiber quality of machine-picked long-staple cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1821-1829. |
| [9] | DONG Yanxue, JIA Yonghong, ZHANG Jinshan, LI Dandan, WANG Kai, LUO Siwei, WANG Runqi, SHI Shubing. Effects of different ecological conditions on dry matter accumulation and yield of spring wheat varieties [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1848-1857. |
| [10] | LI Huaisheng, AI Hongyu, MENG Ling, WANG Heya, ZHANG Lei, AI Haifeng. Effects of chasing rate during peak nutrient uptake of transport under n Reduction on spring wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1866-1872. |
| [11] | ZHANG Chao, BAI Yungang, ZHENG Ming, XIAO Jun, DING Ping. Synergistic effect of water and fertilizer on grape in extreme arid area [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1931-1939. |
| [12] | WANG Ting, ZHANG Li, ZHANG Fanfan, HUANG Rongzheng, LI Xiao, ZHANG Yulin, CHEN Yongcheng, ZHAO Jiantao, MA Chunhui. Poduction performance screening and nutritional value evaluation of corn varieties suitable for silage [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(7): 1596-1605. |
| [13] | CHEN Zhanhui, SUN Qiang, REN Jiaojiao, HUANG Bowen, XU Jiabo, YANG Jie, WU Penghao. QTL mapping and genomic selection of maize leaf width [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(7): 1606-1613. |
| [14] | LIANG Zhiguo, WANG Zepeng, JIA Songnan, FAN Fengcui, LIU Shengyao, ZHANG Zhe, DU Fenghuan, QIN Yong. Effects of different soil moisture on growth, yield, quality and water use efficiency of greenhouse eggplant [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(7): 1713-1721. |
| [15] | LAI Ning, GENG Qinglong, LI Yongfu, LI Na, XIN Huinan, BU Shengbing, CHEN Shuhuang. Effects of organic manure application combined with chemical fertilizer on yield, nitrogen, phosphorus uptake and utilization, and soil fertility of the extremely-late winter sown wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1335-1343. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||