

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (2): 261-269.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.02.001
• Crop Genetics and Breeding·Cultivation Physiology·Physiology and Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Yongpan1,2( ), MA Jun3, LI Chenyu1,2, YAO Mengyao1,2, WANG Zixuan1,2, HUANG Lingzhi1, ZHU Haiyan1, LIU Wanrong2, LI Bo2, YANG Yang2(
), MA Jun3, LI Chenyu1,2, YAO Mengyao1,2, WANG Zixuan1,2, HUANG Lingzhi1, ZHU Haiyan1, LIU Wanrong2, LI Bo2, YANG Yang2( ), GAO Wenwei1(
), GAO Wenwei1( )
)
Received:2024-08-28
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-04-17
Correspondence author:
YANG Yang, GAO Wenwei
Supported by:
王勇攀1,2( ), 马君3, 李晨宇1,2, 姚梦瑶1,2, 王子轩1,2, 黄灵芝1, 朱海艳1, 刘皖蓉2, 李波2, 杨洋2(
), 马君3, 李晨宇1,2, 姚梦瑶1,2, 王子轩1,2, 黄灵芝1, 朱海艳1, 刘皖蓉2, 李波2, 杨洋2( ), 高文伟1(
), 高文伟1( )
)
通讯作者:
杨洋,高文伟
作者简介:王勇攀(1998-),男,河南商丘人,硕士研究生,研究方向为棉花遗传育种,(E-mail)wyp620917@163.com
基金资助:WANG Yongpan, MA Jun, LI Chenyu, YAO Mengyao, WANG Zixuan, HUANG Lingzhi, ZHU Haiyan, LIU Wanrong, LI Bo, YANG Yang, GAO Wenwei. Salt tolerance in germination period of cotton seeds based on convolutional neural network and synthetic dataset[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(2): 261-269.
王勇攀, 马君, 李晨宇, 姚梦瑶, 王子轩, 黄灵芝, 朱海艳, 刘皖蓉, 李波, 杨洋, 高文伟. 基于卷积神经网络和合成数据集训练鉴定棉花种子萌发期的耐盐性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(2): 261-269.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.xjnykx.com/EN/10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.02.001
| 材料 编号 Material number | 材料名称 Name of material | 材料 编号 Material number | 材料名称 Name of material | 材料 编号 Material number | 材料名称 Name of material |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MC-1 | 21 | MC-21 | 41 | MC-41 |
| 2 | MC-2 | 22 | N718 | 42 | N20 |
| 3 | MC-3 | 23 | MC-23 | 43 | MC-43 |
| 4 | 新陆中9号 | 24 | 珂字棉4号 | 44 | MC-44 |
| 5 | N701 | 25 | 新陆早1号 | 45 | N5 |
| 6 | 新中棉49号 | 26 | MC-26 | 46 | MC-46 |
| 7 | N719—1 | 27 | 晋棉2号 | 47 | MC-47 |
| 8 | 陆8早 | 28 | MC-28 | 48 | 斯字棉 |
| 9 | MC-9 | 29 | MC-29 | 49 | TM-1 |
| 10 | MC-10 | 30 | MC-30 | 50 | MC-50 |
| 11 | N19 | 31 | 石大 | 51 | MC-51 |
| 12 | MC-12 | 32 | MC-32 | 52 | K8 |
| 13 | MC-13 | 33 | B3-9 | 53 | MC-53 |
| 14 | MC-14 | 34 | MC-34 | 54 | 中棉所50号 |
| 15 | MC-15 | 35 | MC-35 | 55 | MC-55 |
| 16 | N2 | 36 | MC-36 | 56 | 萨可不 |
| 17 | MC-17 | 37 | MC-37 | 57 | MC-57 |
| 18 | MC-18 | 38 | MC-38 | 58 | MC-58 |
| 19 | MC-19 | 39 | MC-39 | 59 | 塔吉克斯坦 |
| 20 | MC-20 | 40 | N708 | 60 | N638 |
Tab.1 60 land cotton germplasm resource materials
| 材料 编号 Material number | 材料名称 Name of material | 材料 编号 Material number | 材料名称 Name of material | 材料 编号 Material number | 材料名称 Name of material |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MC-1 | 21 | MC-21 | 41 | MC-41 |
| 2 | MC-2 | 22 | N718 | 42 | N20 |
| 3 | MC-3 | 23 | MC-23 | 43 | MC-43 |
| 4 | 新陆中9号 | 24 | 珂字棉4号 | 44 | MC-44 |
| 5 | N701 | 25 | 新陆早1号 | 45 | N5 |
| 6 | 新中棉49号 | 26 | MC-26 | 46 | MC-46 |
| 7 | N719—1 | 27 | 晋棉2号 | 47 | MC-47 |
| 8 | 陆8早 | 28 | MC-28 | 48 | 斯字棉 |
| 9 | MC-9 | 29 | MC-29 | 49 | TM-1 |
| 10 | MC-10 | 30 | MC-30 | 50 | MC-50 |
| 11 | N19 | 31 | 石大 | 51 | MC-51 |
| 12 | MC-12 | 32 | MC-32 | 52 | K8 |
| 13 | MC-13 | 33 | B3-9 | 53 | MC-53 |
| 14 | MC-14 | 34 | MC-34 | 54 | 中棉所50号 |
| 15 | MC-15 | 35 | MC-35 | 55 | MC-55 |
| 16 | N2 | 36 | MC-36 | 56 | 萨可不 |
| 17 | MC-17 | 37 | MC-37 | 57 | MC-57 |
| 18 | MC-18 | 38 | MC-38 | 58 | MC-58 |
| 19 | MC-19 | 39 | MC-39 | 59 | 塔吉克斯坦 |
| 20 | MC-20 | 40 | N708 | 60 | N638 |
| 项目 Items | 合成图像 Synthetic image | 真实图像 Real-world image | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 精度 Precision (%) | 召回率 Recall (%) | F1 (%) | 精度 Pression (%) | 召回率 Recall (%) | F2 (%) | |
| 种壳 Shell planting | 98.55 | 97.68 | 98.11 | 97.71 | 96.12 | 96.91 |
| 胚芽 Gemmule | 97.81 | 97.25 | 97.53 | 95.33 | 94.56 | 94.94 |
| 平均 Average | 98.18 | 97.47 | 97.82 | 96.52 | 95.34 | 95.93 |
Tab.2 Segmentation accuracy of the trained Mask R-CNN model for real-world image
| 项目 Items | 合成图像 Synthetic image | 真实图像 Real-world image | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 精度 Precision (%) | 召回率 Recall (%) | F1 (%) | 精度 Pression (%) | 召回率 Recall (%) | F2 (%) | |
| 种壳 Shell planting | 98.55 | 97.68 | 98.11 | 97.71 | 96.12 | 96.91 |
| 胚芽 Gemmule | 97.81 | 97.25 | 97.53 | 95.33 | 94.56 | 94.94 |
| 平均 Average | 98.18 | 97.47 | 97.82 | 96.52 | 95.34 | 95.93 |
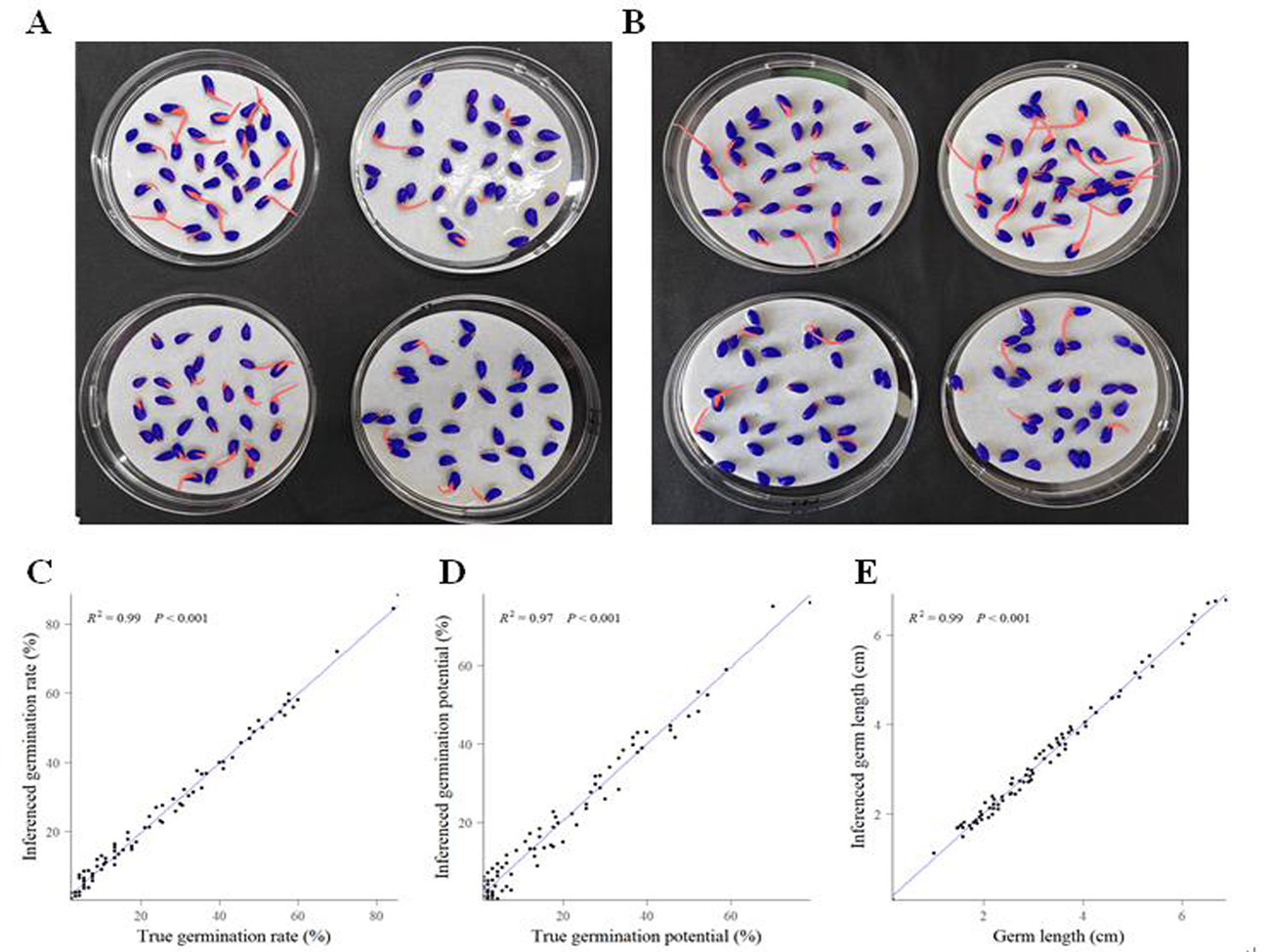
Fig 2 The accuracy of the trained Mask R-CNN model Notes: A,B:Visual result of the trained Mask R-CNN model on real-world image of cotton seed germination images.Blue and red colors indicate the segmented region of seed shell and germ, respectively.C-E: The linear correlation of the seed germination traits that was measured by the Mask-R CNN model and by manual operation
| 性状 Traits | 变异来源Source of variation | 平方和 SS | 自由度 DF | 均方 MS | F值 F value | P值 P value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 品种 Assortment(%) | 处理 Process(%) | 相互作用 Interplay(%) | ||||||
| RGR | 43.59 | 19.74 | 21.92 | 115 534.882 | 179 | 1 953.452 | 833.607 | P<0.0001 |
| RGP | 38.25 | 19.64 | 22.89 | 130 895.351 | 179 | 2 213.383 | 868.638 | P<0.0001 |
| RGI | 40.24 | 21.78 | 21.99 | 119 574.866 | 179 | 2 021.512 | 793.528 | P<0.0001 |
| RVI | 42.24 | 24.20 | 22.52 | 63 551.556 | 179 | 1 072.463 | 465.876 | P<0.0001 |
Tab.3 Analysis of variance for germination traits of test materials
| 性状 Traits | 变异来源Source of variation | 平方和 SS | 自由度 DF | 均方 MS | F值 F value | P值 P value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 品种 Assortment(%) | 处理 Process(%) | 相互作用 Interplay(%) | ||||||
| RGR | 43.59 | 19.74 | 21.92 | 115 534.882 | 179 | 1 953.452 | 833.607 | P<0.0001 |
| RGP | 38.25 | 19.64 | 22.89 | 130 895.351 | 179 | 2 213.383 | 868.638 | P<0.0001 |
| RGI | 40.24 | 21.78 | 21.99 | 119 574.866 | 179 | 2 021.512 | 793.528 | P<0.0001 |
| RVI | 42.24 | 24.20 | 22.52 | 63 551.556 | 179 | 1 072.463 | 465.876 | P<0.0001 |
| 性状Traits | RGP | RGR | RGI | RVI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGP | 1.000 | |||
| RGR | 0.777** | 1.000 | ||
| RGI | 0.859** | 0.957** | 1.000 | |
| RVI | 0.778** | 0.835** | 0.872** | 1.000 |
Tab.4 Correlation analysis between salt tolerance coefficients of seed germination traits under salt stress
| 性状Traits | RGP | RGR | RGI | RVI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGP | 1.000 | |||
| RGR | 0.777** | 1.000 | ||
| RGI | 0.859** | 0.957** | 1.000 | |
| RVI | 0.778** | 0.835** | 0.872** | 1.000 |
| 耐盐水平 Salt tolerance level | 品种数 Number of varieties | D值 D value | 频率 Frequency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 8 | 0.84±0.07 | 13.33 |
| Ⅱ | 17 | 0.61±0.08 | 28.33 |
| Ⅲ | 16 | 0.39±0.06 | 26.67 |
| Ⅳ | 19 | 0.21±0.02 | 31.67 |
| 总计Total | 60 | 100 |
Tab.5 Frequency distribution of salt tolerance types of test materials based on cluster analysis
| 耐盐水平 Salt tolerance level | 品种数 Number of varieties | D值 D value | 频率 Frequency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 8 | 0.84±0.07 | 13.33 |
| Ⅱ | 17 | 0.61±0.08 | 28.33 |
| Ⅲ | 16 | 0.39±0.06 | 26.67 |
| Ⅳ | 19 | 0.21±0.02 | 31.67 |
| 总计Total | 60 | 100 |
| 材料名称 Varieties name | D值 D value | 聚类号 Cluster number | 材料名称 Varieties name | D值 D value | 聚类号 Cluster number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC-2 | 0.86 | Ⅰ | 新陆早1号 | 0.40 | Ⅲ |
| 陆8早 | 0.81 | Ⅰ | N718 | 0.42 | Ⅲ |
| MC-19 | 0.88 | Ⅰ | 中棉所50号 | 0.33 | Ⅲ |
| 珂字棉4号 | 0.95 | Ⅰ | MC-43 | 0.30 | Ⅲ |
| MC-30 | 0.88 | Ⅰ | 石大 | 0.31 | Ⅲ |
| K8 | 0.62 | Ⅱ | MC-46 | 0.18 | Ⅳ |
| N701 | 0.54 | Ⅱ | MC-47 | 0.19 | Ⅳ |
| N719-1 | 0.69 | Ⅱ | TM-1 | 0.18 | Ⅳ |
| N19 | 0.70 | Ⅱ | MC-50 | 0.25 | Ⅳ |
| 斯字棉 | 0.66 | Ⅱ | MC-55 | 0.24 | Ⅳ |
Tab.6 Results of comprehensive evaluation of some land cotton germplasm materials for testing
| 材料名称 Varieties name | D值 D value | 聚类号 Cluster number | 材料名称 Varieties name | D值 D value | 聚类号 Cluster number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC-2 | 0.86 | Ⅰ | 新陆早1号 | 0.40 | Ⅲ |
| 陆8早 | 0.81 | Ⅰ | N718 | 0.42 | Ⅲ |
| MC-19 | 0.88 | Ⅰ | 中棉所50号 | 0.33 | Ⅲ |
| 珂字棉4号 | 0.95 | Ⅰ | MC-43 | 0.30 | Ⅲ |
| MC-30 | 0.88 | Ⅰ | 石大 | 0.31 | Ⅲ |
| K8 | 0.62 | Ⅱ | MC-46 | 0.18 | Ⅳ |
| N701 | 0.54 | Ⅱ | MC-47 | 0.19 | Ⅳ |
| N719-1 | 0.69 | Ⅱ | TM-1 | 0.18 | Ⅳ |
| N19 | 0.70 | Ⅱ | MC-50 | 0.25 | Ⅳ |
| 斯字棉 | 0.66 | Ⅱ | MC-55 | 0.24 | Ⅳ |
| [1] |
刘星宏, 张青青, 张鹏, 等. 北疆盐碱地空间分布特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(8): 141-148.
DOI |
| LIU Xinghong, ZHANG Qingqing, ZHANG Peng, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and analysis of saline-alkali land in northern Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(8): 141-148. | |
| [2] | 杨淑萍, 危常州, 梁永超. 盐胁迫对海岛棉不同基因型幼苗生长及生理生态特征的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(9): 2322-2331. |
| YANG Shuping, WEI Changzhou, LIANG Yongchao. Effects of NaCl stress on growth and eco-physiological characteristics of different in sea island cotton genotypes in seedlings[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(9): 2322-2331. | |
| [3] | 王雷, 郭岩, 杨淑华. 非生物胁迫与环境适应性育种的现状及对策[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2021, 51(10): 1424-1434. |
| WANG Lei, GUO Yan, YANG Shuhua. Designed breeding for adaptation of crops to environmental abiotic stresses[J]. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 2021, 51(10): 1424-1434. | |
| [4] |
Rocha-Munive M G, Soberón M, Castañeda S, et al. Evaluation of the impact of genetically modified cotton after 20 years of cultivation in Mexico[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2018, 6: 82.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | 杨真, 王宝山. 中国盐渍土资源现状及改良利用对策[J]. 山东农业科学, 2015, 47(4): 125-130. |
| YANG Zhen, WANG Baoshan. Present status of saline soil resources and countermeasures for improvement and utilization in China[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 47(4): 125-130. | |
| [6] | 孟超敏, 蔡彩平, 郭旺珍. 棉花抗逆育种研究进展[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2012, 35(5): 25-34. |
| MENG Chaomin, CAI Caiping, GUO Wangzhen. Advances in cotton stress resistance breeding[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2012, 35(5): 25-34. | |
| [7] | 李忠旺, 陈玉梁, 罗俊杰, 等. 棉花抗旱品种筛选鉴定及抗旱性综合评价方法[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2017, 35(1): 240-247. |
| LI Zhongwang, CHEN Yuliang, LUO Junjie, et al. Screening and evaluation for drought resistance of cotton varieties[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2017, 35(1): 240-247. | |
| [8] | 张国伟, 路海玲, 张雷, 等. 棉花萌发期和苗期耐盐性评价及耐盐指标筛选[J]. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(8): 2045-2053. |
|
ZHANG Guowei, LU Hailing, ZHANG Lei, et al. Salt tolerance evaluation of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) at its germinating and seedling stages and selection of related indices[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011, 22(8): 2045-2053.
PMID |
|
| [9] | Ahmad S, Khan N U I, Iqba M Z, et al. Salt tolerance of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)[J]. Asian Journal of Plant Sciences, 2002, 1(6): 715-719. |
| [10] |
Sharif I, Aleem S, Farooq J, et al. Salinity stress in cotton: effects, mechanism of tolerance and its management strategies[J]. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2019, 25(4): 807-820.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | 蒋玉蓉, 吕有军, 祝水金. 棉花耐盐机理与盐害控制研究进展[J]. 棉花学报, 2006, 18(4): 248-254. |
| JIANG Yurong, LYU Youjun, ZHU Shuijin. Advance in studies of the mechanism of salt tolerance and controlling of salt damage in upland cotton[J]. Cotton Science, 2006, 18(4): 248-254. | |
| [12] | 师恭曜. 对比根系转录组研究棉花盐胁迫应答及耐受机理[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2015. |
| SHI Gongyao. Comparative study on salt stress response and tolerance mechanism of cotton by root transcriptome[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2015. | |
| [13] |
Deinlein U, Stephan A B, Horie T, et al. Plant salt-tolerance mechanisms[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2014, 19(6): 371-379.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Ye X X, Wang H, Cao X L, et al. Transcriptome profiling of Puccinellia tenuiflora during seed germination under a long-term saline-alkali stress[J]. BMC Genomics, 2019, 20(1): 589. |
| [15] |
苏秀娟, 徐海江, 邓晓娟, 等. 盐胁迫对海岛棉种子活力的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(9): 1604-1614.
DOI |
|
SU Xiujuan, XU Haijiang, DENG Xiaojuan, et al. Effects of salt stress on seed vigor of Gossypium barbadense L[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(9): 1604-1614.
DOI |
|
| [16] | 李佩茹. 棉花转录因子GhRAV和GhMYB功能分析[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2013. |
| LI Peiru. Functional analysis of cotton transcription factors GhRAV and GhMYB[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2013. | |
| [17] | 郭文琦, 张培通, 李春宏, 等. 蕾期土壤盐度降低后棉花生长发育的补偿效应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(1): 162-168. |
|
GUO Wenqi, ZHANG Peitong, LI Chunhong, et al. Compensation effect of cotton growth and development after soil salt content reduction at bud stage[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(1): 162-168.
PMID |
|
| [18] |
Singh A, Ganapathysubramanian B, Singh A K, et al. Machine learning for high-throughput stress phenotyping in plants[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2016, 21(2): 110-124.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Ghosal S, Blystone D, Singh A K, et al. An explainable deep machine vision framework for plant stress phenotyping[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(18): 4613-4618.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Giuffrida M V, Scharr H, Tsaftaris S A. ARIGAN: synthetic Arabidopsis plants using generative adversarial network[C]// 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), 2017 |
| [21] | Arsenovic M, Karanovic M, Sladojevic S, et al. Solving current limitations of deep learning based approaches for plant disease detection[J]. Symmetry, 2019, 11(7): 939. |
| [22] |
Toda Y, Okura F, Ito J, et al. Training instance segmentation neural network with synthetic datasets for crop seed phenotyping[J]. Communications Biology, 2020, 3(1): 173.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
王宁, 霍飞超, 张逸彬, 等. 棉花种子萌发期耐盐机理初探[J]. 中国棉花, 2023, 50(5): 7-11.
DOI |
| WANG Ning, HUO Feichao, ZHANG Yibin, et al. A preliminary exploration on the mechanism of salt tolerance in cotton cultivars during seed germination[J]. China Cotton, 2023, 50(5): 7-11. | |
| [24] | 杨涛. 海岛棉耐盐性评价及关联分析[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2020. |
| YANG Tao. Evaluation and correlation analysis of salt tolerance of island cotton[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| [25] |
魏俊梅. 24个棉花种质资源耐盐性差异比较[J]. 中国棉花, 2014, 41(5): 14-16.
DOI |
|
WEI Junmei. Comparison on salt tolerance of 24 cotton germplasm resources[J]. China Cotton, 2014, 41(5): 14-16.
DOI |
|
| [26] | Wang N, Wang X R, Qi Q, et al. Analysis of the effects of mepiquat chloride priming on the seedling growth-promoting in cotton under salt stress by multi-omics[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2022, 186: 115296. |
| [27] |
Zhang N, Zhang H J, Sun Q Q, et al. Proteomic analysis reveals a role of melatonin in promoting cucumber seed germination under high salinity by regulating energy production[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 503.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
戴海芳, 武辉, 阿曼古丽·买买提阿力, 等. 不同基因型棉花苗期耐盐性分析及其鉴定指标筛选[J]. 中国农业科学, 2014, 47(7): 1290-1300.
DOI |
| DAI Haifang, WU Hui, Amanguli Maimaitiali, et al. Analysis of salt-tolerance and determination of salt-tolerant evaluation indicators in cotton seedlings of different genotypes[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2014, 47(7): 1290-1300. |
| [1] | HU Shasha, SHAO Liping, CHEN Lihua, SONG Weiping, ZHAO Hai, ZHANG Xinyu, SUN Jie. Effect of defoliant on boll development and fiber quality of machine-picked cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(2): 270-277. |
| [2] | LU Mingkun, LI Junhong, Nilupaier Yusufujiang, PAN Xipeng, LIU Xiaocheng, ZHANG Zhenggui, PAN Zhanlei, ZHAI Menghua, ZHANG Yaopeng, ZHAO Wenqi, WANG Lihong, WANG Zhanbiao. Effect of silic on fertiliser application on the growth and development of cotton and its yield and quality [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(2): 286-293. |
| [3] | WANG Yiding, ZHANG Kai, ZHANG Lingjian, ZHANG Hui, GUO Xiaomeng, CHEN Guoyue. Effects of drip irrigation on the growth and development, yield formation, and water use efficiency of cotton in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(2): 294-301. |
| [4] | WANG Xiaoyan, BAI Yungang, CHAI Zhongping, LU Zhenlin, LIU Hongbo, XIAO Jun, Amannisa . Effect of "dry sowing and wet emergence" on cotton growth and yield under the control of winter drip irrigation in off-cropping period [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(2): 302-313. |
| [5] | SUN Caiqin, WU Jia, HUANG Hai, GUO Jiaxin, MIN Wei, GUO Huijuan. Effects of different saline and alkaline stress on the proteome of cotton root system [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 146-160. |
| [6] | LAI Chengxia, YANG Yanlong, WANG Penglong, ZHU Mengyu, YANG Dong, LI Chunping, GE Fengwei, Mayila Yusuyin, YANG Ni, MA Jun. Pathogen colony’s morphological characteristics and pathogenicity identification of defioating cotton Verticillium wilt in some areas in northern Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 174-181. |
| [7] | WANG Wei, ZHANG Renfu, LIU Haiyang, LI Xiaowei, YAO Ju. Occurrence dynamics and spatial distribution pattern of Frankliniella intonsa in cotton fields in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 202-209. |
| [8] | WEN Fang, LIAO Na, WANG Na, JIN Jing, YAO Yiqiang. Adsorption and immobilization of Cd2+ by cotton straw biochar [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 225-233. |
| [9] | ZHOU Xin, LIU Xuanfeng, JIANG Yuhan, ZHANG Haichun, YANG Yuxin, Yeerbdati Tiemuer, JIANG Yongxin, ZHANG Li. Current situation and development proposal of mechanized recovery and resource utilization of used mulch film in cotton fields in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 131-141. |
| [10] | MIAO Hongping, WANG Xiaowei, TIAN Conghua, LI Zhi, ZHANG Yuxin, DAI Junsheng. Evolution characteristics and driving factors of cotton production and distribution in Tarim River basin [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 217-226. |
| [11] | GONG Xuehua, WANG Xiaowu, FU Kaiyun, JIA Zunzun, TURSUN Ahmat, QIAO Xiaoyan, YE Xiaoqin, GUO Wenchao, DING Xinhua. Effects of weed seeds bank and environmental factors on weed seeds germination in oasis irrigation areas of Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 49-59. |
| [12] | WANG Junduo, CUI Yujiang, LIANG Yajun, GONG Zhaolong, ZHENG Junyun, LI Xueyuan. Xinjiang cotton production advantageous regional layout scheme [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 60-69. |
| [13] | ZHENG Juyun, GONG Zhaolong, LIANG Yajun, GENG Shiwei, SUN Fenglei, YANG ni, LI Xueyuan, WANG Junduo. Key technology model of machine-picked cotton production in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 70-74. |
| [14] | LI Jie, LIU Jia, WANG Liang, ZHANG Na, YANG Yanlong, ZHENG Zipiao, WEI Xin, WANG Meng, ZHOU Zixin, YANG Ni, GONG Zhaolong, HOU Xianfei, HUANG Qixiu, Abudukadier kuerban, ZHANG Jipeng, CHANG Pengzhong. Current situation of transformation and application of scientific and technological achievements of "cotton, oil and sugar" [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 89-94. |
| [15] | BIAN Qingyong, FU Yanbo, QI Tong, HUANG Jian, PU Shenghai, MENG Ajing, Halihashi Yibati. Study on influencing factors of cotton emergence and protection measures in saline-alkali land in southern Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 95-100. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||