

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (3): 584-592.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.03.007
• Crop Genetics and Breeding·Cultivation Physiology·Physiology and Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
NIE Lingfan1( ), ZHANG Jinshan1, TIAN Wenqiang1, SUN Ganggang2, WANG Hongyi1, ZHANG Jun1, ZHANG Qiangbin1, GUO Fei3, WU Li3, SHI Shubing1(
), ZHANG Jinshan1, TIAN Wenqiang1, SUN Ganggang2, WANG Hongyi1, ZHANG Jun1, ZHANG Qiangbin1, GUO Fei3, WU Li3, SHI Shubing1( )
)
Received:2024-08-12
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-05-14
Correspondence author:
SHI Shubing
Supported by:
聂凌帆1( ), 张金汕1, 田文强1, 孙刚刚2, 王泓懿1, 张君1, 张强斌1, 郭飞3, 吴利3, 石书兵1(
), 张金汕1, 田文强1, 孙刚刚2, 王泓懿1, 张君1, 张强斌1, 郭飞3, 吴利3, 石书兵1( )
)
通讯作者:
石书兵
作者简介:聂凌帆(1998-),男,新疆库尔勒人,硕士研究生,研究方向为作物栽培,(E-mail) 614985262@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
NIE Lingfan, ZHANG Jinshan, TIAN Wenqiang, SUN Ganggang, WANG Hongyi, ZHANG Jun, ZHANG Qiangbin, GUO Fei, WU Li, SHI Shubing. Effects of different water and nitrogen treatments on the growth, water and nitrogen use efficiency and yield of ultra-late sowing winter wheat[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(3): 584-592.
聂凌帆, 张金汕, 田文强, 孙刚刚, 王泓懿, 张君, 张强斌, 郭飞, 吴利, 石书兵. 不同水氮处理对超晚播冬麦生长、水氮利用及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(3): 584-592.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.xjnykx.com/EN/10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.03.007
| 处理 Treatments | 起身期灌水量 Seedling stage | 拔节期灌水量 Jointing stage | 孕穗期灌水量 Booting stage | 开花期灌水量 Anthesis | 灌浆期灌水量 Filling stage | 总量 Total capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 250 | 750 | 750 | 500 | 500 | 2 750 |
| W2 | 350 | 1 000 | 1 000 | 700 | 700 | 3 750 |
| W3 | 450 | 1 250 | 1 250 | 900 | 900 | 4 750 |
Tab.1 Different treatments of each birth period of winter wheat irrigation water quantity(m3/hm2)
| 处理 Treatments | 起身期灌水量 Seedling stage | 拔节期灌水量 Jointing stage | 孕穗期灌水量 Booting stage | 开花期灌水量 Anthesis | 灌浆期灌水量 Filling stage | 总量 Total capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 250 | 750 | 750 | 500 | 500 | 2 750 |
| W2 | 350 | 1 000 | 1 000 | 700 | 700 | 3 750 |
| W3 | 450 | 1 250 | 1 250 | 900 | 900 | 4 750 |
| 处理 Treat- ments | 起身期 施用量 Seedling stage | 拔节期 施用量 Jointing stage | 孕穗期 施用量 Booting stage | 总量 Total capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| N1 | 30 | 90 | 60 | 180 |
| N2 | 90 | 150 | 120 | 360 |
| N3 | 120 | 240 | 180 | 540 |
Tab.2 The amount of winter wheat urea was applied in different treatments periods(kg/hm2)
| 处理 Treat- ments | 起身期 施用量 Seedling stage | 拔节期 施用量 Jointing stage | 孕穗期 施用量 Booting stage | 总量 Total capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| N1 | 30 | 90 | 60 | 180 |
| N2 | 90 | 150 | 120 | 360 |
| N3 | 120 | 240 | 180 | 540 |
| 处理 Treatments | 生育进程(月/日)Growth process(M/D) | 生育期 Growth period(d) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苗期 Seedling | 拔节期 Jointing | 孕穗期 Booting | 开花期 Flowing | 成熟期 Maturity | |||
| W1 | N0 | 3/12 | 5/3 | 5/12 | 5/24 | 7/4 | 113 |
| N1 | 3/12 | 5/3 | 5/13 | 5/26 | 7/4 | 113 | |
| N2 | 3/12 | 5/3 | 5/13 | 5/27 | 7/6 | 115 | |
| N3 | 3/12 | 5/3 | 5/14 | 5/27 | 7/6 | 115 | |
| W2 | N0 | 3/12 | 5/1 | 5/12 | 5/26 | 7/6 | 115 |
| N1 | 3/12 | 5/1 | 5/14 | 5/29 | 7/6 | 115 | |
| N2 | 3/12 | 4/30 | 5/15 | 5/31 | 7/10 | 119 | |
| N3 | 3/12 | 4/30 | 5/15 | 6/1 | 7/10 | 119 | |
| W3 | N0 | 3/12 | 4/28 | 5/14 | 5/26 | 7/6 | 115 |
| N1 | 3/12 | 4/28 | 5/14 | 5/31 | 7/8 | 117 | |
| N2 | 3/12 | 4/27 | 5/16 | 6/2 | 7/12 | 121 | |
| N3 | 3/12 | 4/27 | 5/16 | 6/3 | 7/13 | 122 | |
Tab.3 Different growth periods of winter wheat under different water and nitrogen conditions
| 处理 Treatments | 生育进程(月/日)Growth process(M/D) | 生育期 Growth period(d) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苗期 Seedling | 拔节期 Jointing | 孕穗期 Booting | 开花期 Flowing | 成熟期 Maturity | |||
| W1 | N0 | 3/12 | 5/3 | 5/12 | 5/24 | 7/4 | 113 |
| N1 | 3/12 | 5/3 | 5/13 | 5/26 | 7/4 | 113 | |
| N2 | 3/12 | 5/3 | 5/13 | 5/27 | 7/6 | 115 | |
| N3 | 3/12 | 5/3 | 5/14 | 5/27 | 7/6 | 115 | |
| W2 | N0 | 3/12 | 5/1 | 5/12 | 5/26 | 7/6 | 115 |
| N1 | 3/12 | 5/1 | 5/14 | 5/29 | 7/6 | 115 | |
| N2 | 3/12 | 4/30 | 5/15 | 5/31 | 7/10 | 119 | |
| N3 | 3/12 | 4/30 | 5/15 | 6/1 | 7/10 | 119 | |
| W3 | N0 | 3/12 | 4/28 | 5/14 | 5/26 | 7/6 | 115 |
| N1 | 3/12 | 4/28 | 5/14 | 5/31 | 7/8 | 117 | |
| N2 | 3/12 | 4/27 | 5/16 | 6/2 | 7/12 | 121 | |
| N3 | 3/12 | 4/27 | 5/16 | 6/3 | 7/13 | 122 | |
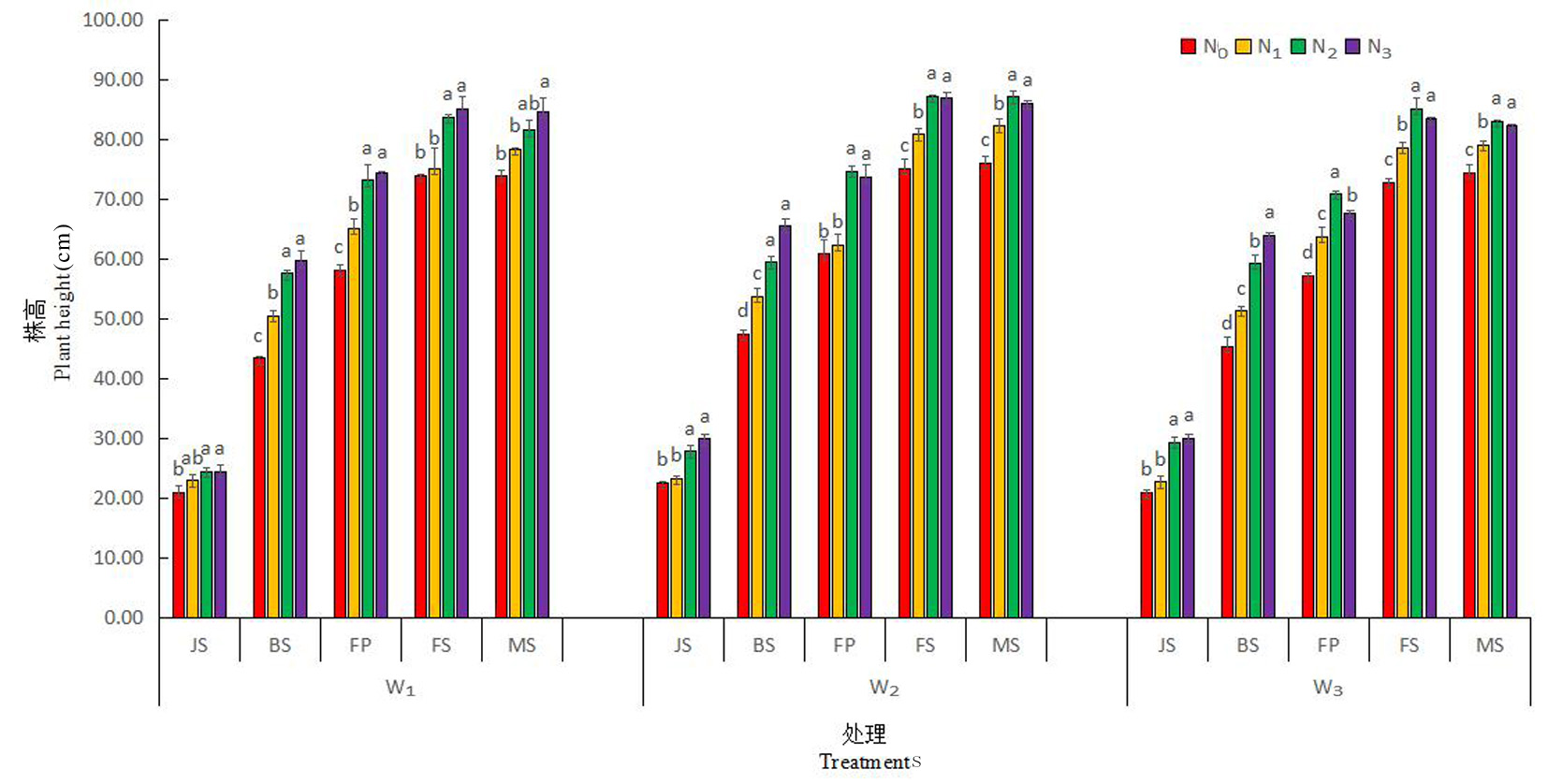
Fig.1 Changes of dynamic changes of plant height in different water and nitrogen treatments during winter wheat growth period Notes: JS: Jionting stage; BS: Booting stage; FP: Flowering stage; FS: Filling stages;MS:Full ripe stage
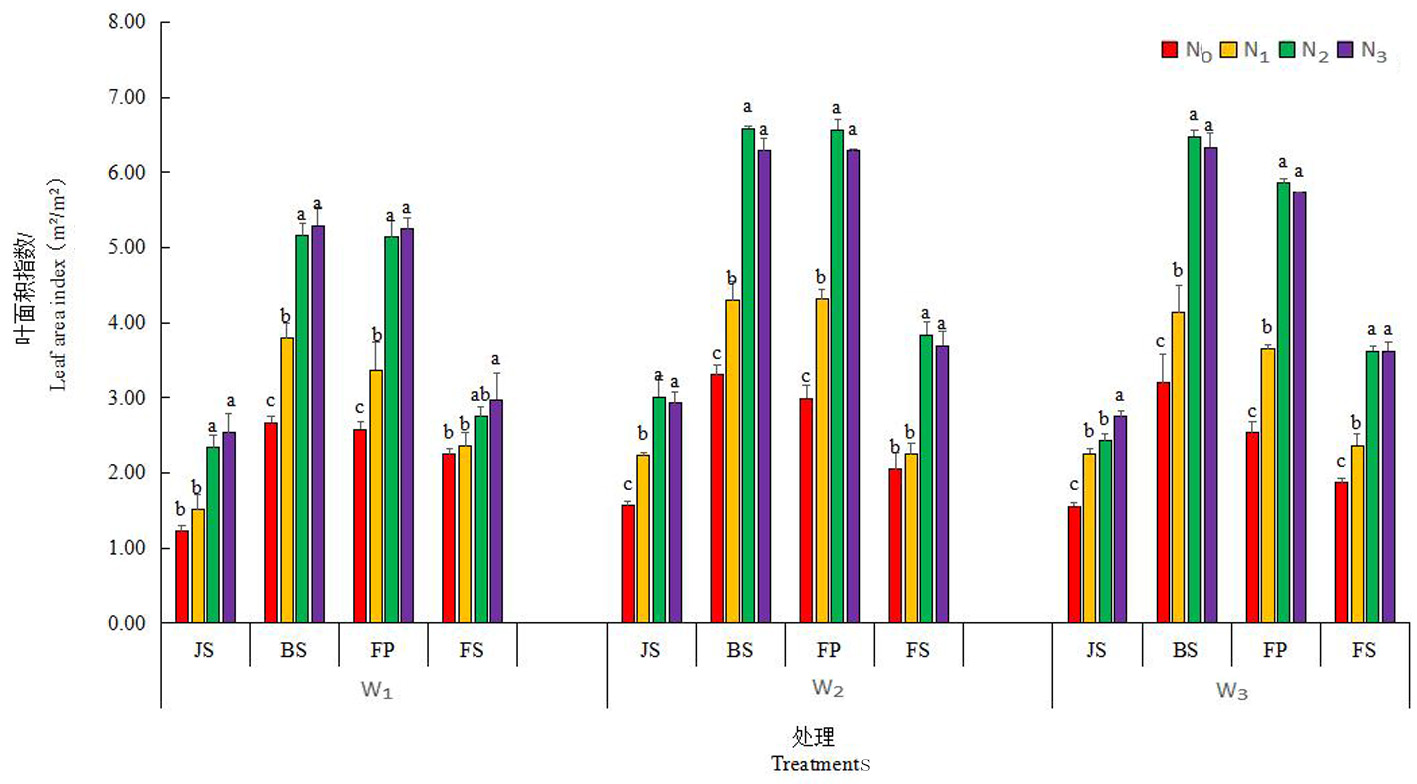
Fig.2 Changes of dynamic change of leaf area index in different water and nitrogen treatment during winter wheat growth period Notes: JS: Jionting stage; BS: Booting stage; FP: Flowering stage; FS: Filling stages
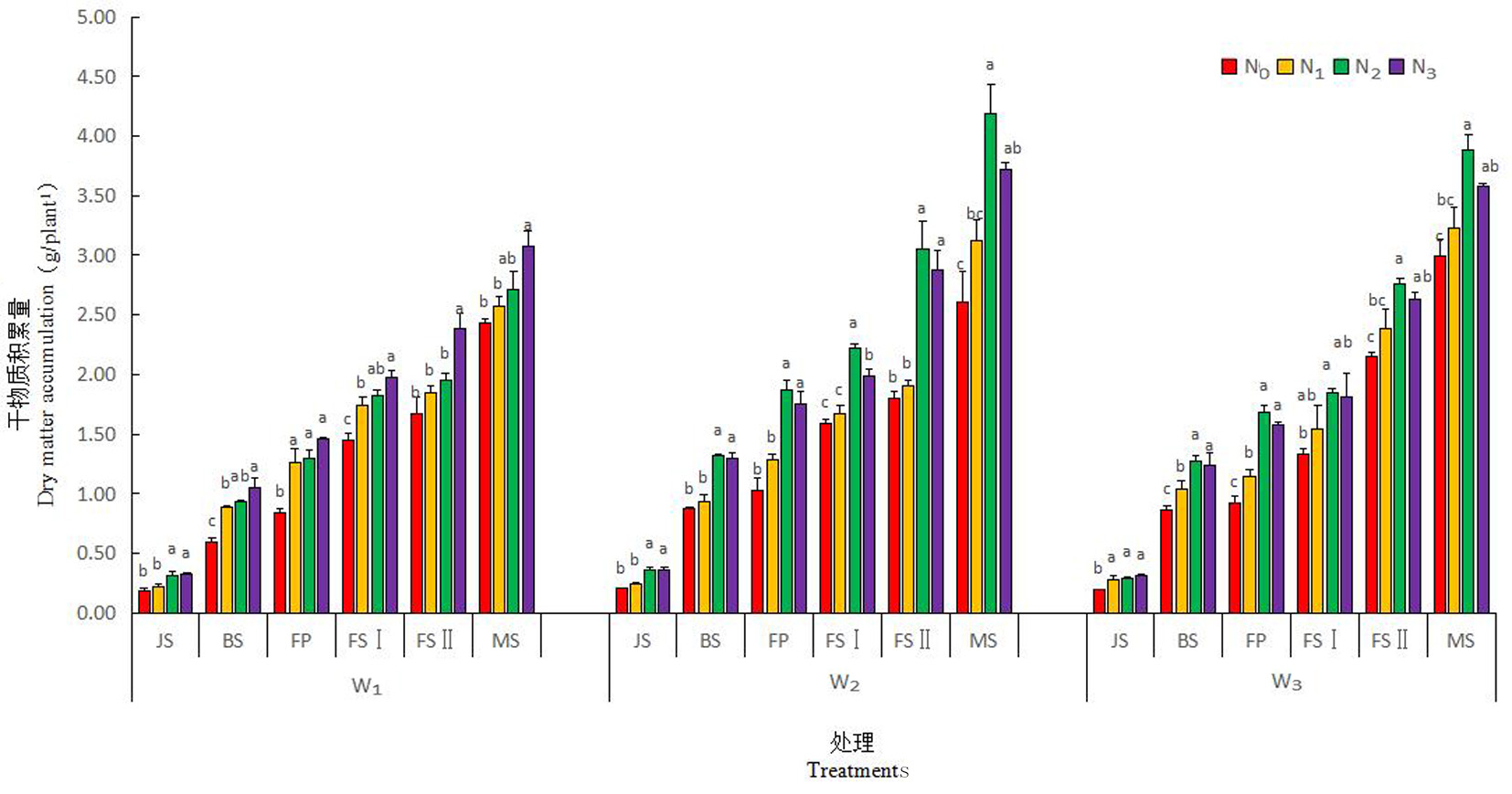
Fig.3 Changes of dry matter accumulation in different water and nitrogen treatment during winter wheat growth period Notes: JS: Jionting stage; BS: Booting stage; FP: Flowering stage; FSⅠ: Early grain filling stage; FSⅡ: Mid grain Filling stage; MS:Full ripe stage
| 处理 Treat- ments | 总灌水量 Total irrigation (m3/hm2) | 降水量 Precipitation (m3/hm2) | 土壤耗水量 Soil water consumption (m3/hm2) | 总耗水量 Toal water consumption (m3/hm2) | 水分利用效率 Water use efficiency (kg/m3) | 氮肥农学 利用效率 Agronomic nitrogen useefficiency (kg/kg) | 氮肥偏生产力 Nitrogen Partial productivity (kg/kg) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | N0 | 2 750 | 627 | 1 930.00b | 5 307.00f | 10.00g | / | / | ||||||||
| N1 | 2 750 | 627 | 1 920.99b | 5 297.99e | 10.56g | 3.62e | 67.55c | |||||||||
| N2 | 2 750 | 627 | 2 170.12a | 5 547.12f | 12.03e | 8.25d | 40.21f | |||||||||
| N3 | 2 750 | 627 | 2 210.28a | 5 587.28de | 14.03b | 10.23cd | 31.62g | |||||||||
| W2 | N0 | 3 750 | 627 | 1 230.24d | 5 607.24de | 9.61h | / | / | ||||||||
| N1 | 3 750 | 627 | 1 310.60cd | 5 687.60cde | 12.00e | 17.70b | 82.32a | |||||||||
| N2 | 3 750 | 627 | 1 420.35c | 5 797.35c | 16.80a | 26.38a | 58.69d | |||||||||
| N3 | 3 750 | 627 | 1 330.62cd | 5 707.62cd | 14.38b | 11.50c | 33.13g | |||||||||
| W3 | N0 | 4 750 | 627 | 830.48e | 6 207.48a | 9.06i | / | / | ||||||||
| N1 | 4 750 | 627 | 580.73f | 5 957.73b | 10.61f | 8.38d | 76.21b | |||||||||
| N2 | 4 750 | 627 | 720.06ef | 6 097.06ab | 13.68c | 16.34b | 50.25e | |||||||||
| N3 | 4 750 | 627 | 610.25f | 5 987.25b | 13.32d | 9.46cd | 32.16g | |||||||||
Tab.4 Changes of water consumption characteristics and water utilization rate of wheat under different winter water and nitrogen conditions
| 处理 Treat- ments | 总灌水量 Total irrigation (m3/hm2) | 降水量 Precipitation (m3/hm2) | 土壤耗水量 Soil water consumption (m3/hm2) | 总耗水量 Toal water consumption (m3/hm2) | 水分利用效率 Water use efficiency (kg/m3) | 氮肥农学 利用效率 Agronomic nitrogen useefficiency (kg/kg) | 氮肥偏生产力 Nitrogen Partial productivity (kg/kg) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | N0 | 2 750 | 627 | 1 930.00b | 5 307.00f | 10.00g | / | / | ||||||||
| N1 | 2 750 | 627 | 1 920.99b | 5 297.99e | 10.56g | 3.62e | 67.55c | |||||||||
| N2 | 2 750 | 627 | 2 170.12a | 5 547.12f | 12.03e | 8.25d | 40.21f | |||||||||
| N3 | 2 750 | 627 | 2 210.28a | 5 587.28de | 14.03b | 10.23cd | 31.62g | |||||||||
| W2 | N0 | 3 750 | 627 | 1 230.24d | 5 607.24de | 9.61h | / | / | ||||||||
| N1 | 3 750 | 627 | 1 310.60cd | 5 687.60cde | 12.00e | 17.70b | 82.32a | |||||||||
| N2 | 3 750 | 627 | 1 420.35c | 5 797.35c | 16.80a | 26.38a | 58.69d | |||||||||
| N3 | 3 750 | 627 | 1 330.62cd | 5 707.62cd | 14.38b | 11.50c | 33.13g | |||||||||
| W3 | N0 | 4 750 | 627 | 830.48e | 6 207.48a | 9.06i | / | / | ||||||||
| N1 | 4 750 | 627 | 580.73f | 5 957.73b | 10.61f | 8.38d | 76.21b | |||||||||
| N2 | 4 750 | 627 | 720.06ef | 6 097.06ab | 13.68c | 16.34b | 50.25e | |||||||||
| N3 | 4 750 | 627 | 610.25f | 5 987.25b | 13.32d | 9.46cd | 32.16g | |||||||||
| 处理 Treat- ments | 穗数 Spike (104/hm2) | 穗粒数 Grains per spike | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Yield (kg/hm2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | N0 | 601.24d | 28.67e | 41.93cde | 5 306.44d | |
| N1 | 606.24cd | 33.67cd | 41.07de | 5 606.66d | ||
| N2 | 636.62bcd | 35.33bc | 40.69de | 6 675.33c | ||
| N3 | 677.35ab | 38.53b | 40.51e | 7 842.79b | ||
| W2 | N0 | 610.92cd | 29.93de | 44.03a | 5 364.13d | |
| N1 | 679.02ab | 37.80b | 43.91a | 6 833.14c | ||
| N2 | 688.37a | 46.27a | 43.61ab | 9 743.01a | ||
| N3 | 684.70a | 44.20a | 42.96abc | 8 216.85b | ||
| W3 | N0 | 605.58cd | 32.13cd | 44.15a | 5 629.79d | |
| N1 | 608.25cd | 38.73b | 42.92abc | 6 325.64c | ||
| N2 | 672.01ab | 46.27a | 42.80abc | 8 342.04b | ||
| N3 | 649.98abc | 45.47a | 42.28bcd | 7 976.05b | ||
Tab.5 Yield index of winter wheat under different water and nitrogen treatments
| 处理 Treat- ments | 穗数 Spike (104/hm2) | 穗粒数 Grains per spike | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Yield (kg/hm2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | N0 | 601.24d | 28.67e | 41.93cde | 5 306.44d | |
| N1 | 606.24cd | 33.67cd | 41.07de | 5 606.66d | ||
| N2 | 636.62bcd | 35.33bc | 40.69de | 6 675.33c | ||
| N3 | 677.35ab | 38.53b | 40.51e | 7 842.79b | ||
| W2 | N0 | 610.92cd | 29.93de | 44.03a | 5 364.13d | |
| N1 | 679.02ab | 37.80b | 43.91a | 6 833.14c | ||
| N2 | 688.37a | 46.27a | 43.61ab | 9 743.01a | ||
| N3 | 684.70a | 44.20a | 42.96abc | 8 216.85b | ||
| W3 | N0 | 605.58cd | 32.13cd | 44.15a | 5 629.79d | |
| N1 | 608.25cd | 38.73b | 42.92abc | 6 325.64c | ||
| N2 | 672.01ab | 46.27a | 42.80abc | 8 342.04b | ||
| N3 | 649.98abc | 45.47a | 42.28bcd | 7 976.05b | ||
| [1] | 王明杰. 新疆小麦生产发展现状及存在的问题分析[J]. 种子科技, 2023, 41(19): 142-144. |
| WANG Mingjie. Analysis on the present situation and existing problems of wheat production in Xinjiang[J]. Seed Science & Technology, 2023, 41(19): 142-144. | |
| [2] |
田文强, 郭飞, 聂凌帆, 等. 超晚播对冬小麦光合特性、干物质积累及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(5): 1059-1066.
DOI |
|
TIAN Wenqiang, NIE Lingfan, et al. Effects of super late sowing on photosynthetic characteristics, dry matter accumulation and yield of winter wheat[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(5): 1059-1066.
DOI |
|
| [3] | 李磊, 王铜, 汪晓东, 等. 北疆超晚播小麦品种生育特性及产量比较[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2020, 40(7): 826-831. |
| LI Lei, WANG Tong, WANG Xiaodong, et al. Comparison of growth characteristics and yield of wheat varieties under super late sowing in north Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2020, 40(7): 826-831. | |
| [4] | 李灿云, 谢学林. 在北疆种植包蛋春麦是解决棉粮倒茬的一条新途径[J]. 新疆农垦科技, 1996, 19(1): 16-18. |
| LI Canyun, XIE Xuelin. Planting egg-coated spring wheat in northern Xinjiang is a new way to solve the problem of cotton and grain stubble[J]. Xinjiang Farm Research of Science and Technology, 1996, 19(1): 16-18. | |
| [5] | 薛丽华, 王铜, 李磊, 等. 北疆超晚冬播小麦高产生育规律及干物质积累研究[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2019, 37(6): 153-159, 165. |
| XUE Lihua, WANG Tong, LI Lei, et al. Study on the growth regularity of high yield and dry matter accumulation of the extremely-late winter sown wheat in Northern Xinjiang[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2019, 37(6): 153-159, 165. | |
| [6] |
王彬, 张萌, 陈景天, 等. 超晚播节水栽培冬小麦品种花后光合与灌浆特性[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(18): 86-91.
DOI |
| WANG Bin, ZHANG Meng, CHEN Jingtian, et al. Characteristics of photosynthesis and grain-filling of various winter wheat cultivars under extremely-late sown and water-saving cultivation conditions[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2017, 35(18): 86-91. | |
| [7] |
田文强, 董艳雪, 史永清, 等. 播期对超晚冬麦茎秆性状及群体动态的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1301-1307.
DOI |
|
TIAN Wenqiang, DONG Yanxue, SHI Yongqing, et al. Effects of sowing date on stem traits and population dynamics of ultra late winter wheat[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1301-1307.
DOI |
|
| [8] | 肖自添, 蒋卫杰, 余宏军. 作物水肥耦合效应研究进展[J]. 作物杂志, 2007,(6): 18-22. |
| XIAO Zitian, JIANG Weijie, YU Hongjun. Research progress on coupling effect of water and fertilizer on crops[J]. Crops, 2007,(6): 18-22. | |
| [9] | 姚战军, 杨玉锋, 陈若英, 等. 限水灌溉与施氮方式对小麦群体动态及产量的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 2011, 40(8): 63-66. |
| YAO Zhanjun, YANG Yufeng, CHEN Ruoying, et al. Effects of limited irrigation and nitrogen application on population development and grain yields of wheat[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 40(8): 63-66. | |
| [10] | Plaut Z, Butow B J, Blumenthal C S, et al. Transport of dry matter into developing wheat kernels and its contribution to grain yield under post-anthesis water deficit and elevated temperature[J]. Field Crops Research, 2004, 86(2/3): 185-198. |
| [11] | 谢小清, 章建新, 段丽娜, 等. 滴灌量对冬小麦根系时空分布及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2015, 35(7): 971-979. |
| XIE Xiaoqing, ZHANG Jianxin, DUAN Lina, et al. Effect of drip irrigation amount on temporal spatial distribution of root and water use efficiency of winter wheat[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2015, 35(7): 971-979. | |
| [12] |
郭亚宁, 周建朝, 王秋红, 等. 作物水氮耦合效应的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(15): 1-5.
DOI |
|
GUO Yaning, ZHOU Jianchao, WANG Qiuhong, et al. Research progress on coupling effect of water and nitrogen in crops[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2019, 35(15): 1-5.
DOI |
|
| [13] | 王铜, 李磊, 汪晓东, 等. 播期对冬播春麦品种生育进程及产量品质的影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2021, 26(10): 28-40. |
| WANG Tong, LI Lei, WANG Xiaodong, et al. Effect of sowing date on growth characteristics and yield and quality of spring wheat varieties sowing in winter[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2021, 26(10): 28-40. | |
| [14] | Fang Q, Ma L, Yu Q, et al. Irrigation strategies to improve the water use efficiency of wheat-maize double cropping systems in North China Plain[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2010, 97(8): 1165-1174. |
| [15] | Karrou M, Oweis T. Water and land productivities of wheat and food legumes with deficit supplemental irrigation in a Mediterranean environment[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2012, 107: 94-103. |
| [16] | 王敏, 张胜全, 方保停, 等. 氮肥运筹对限水灌溉冬小麦产量及氮素利用的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2007, 23(7): 349-353. |
| WANG Min, ZHANG Shengquan, FANG Baoting, et al. Effect of nitrogen applications on grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of winter wheat in limited water supply[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2007, 23(7): 349-353. | |
| [17] | 王成雨, 代兴龙, 石玉华, 等. 花后小麦叶面积指数与光合和产量关系的研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(1): 27-34. |
| WANG Chengyu, DAI Xinglong, SHI Yuhua, et al. Effects of leaf area index on photosynthesis and yield of winter wheat after anthesis[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2012, 18(1): 27-34. | |
| [18] | 高亚军, 李生秀. 北方旱区农田水肥效应分析[J]. 中国工程科学, 2002, 4(7): 74-79. |
| GAO Yajun, LI Shengxiu. Analysis of the effect of water and fertilizer on crop production in farmland of arid zone in northern China[J]. Engineering Science, 2002, 4(7): 74-79. | |
| [19] | 崔月. 水氮运筹对滴灌冬小麦光合物质生产及产量的影响[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2018. |
| CUI Yue. Effects of water and nitrogen management on photosynthetic matter production and yield of winter wheat under drip irrigation[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| [20] | 许振柱, 李长荣, 陈平, 等. 土壤干旱对冬小麦生理特性和干物质积累的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2000, 18(1): 113-118, 123. |
| XU Zhenzhu, LI Changrong, CHEN Ping, et al. Effect of soil drought on physiological characteristics and dry matter accumulation in winter wheat[J]. Agricultural Reseach in the Arid Areas, 2000, 18(1): 113-118, 123. | |
| [21] | 任巍, 姚克敏, 于强, 等. 水分调控对冬小麦同化物分配与水分利用效率的影响研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2003, 11(4): 92-94. |
| REN Wei, YAO Kemin, YU Qiang, et al. Effect of water control in combination of depth and amount on dry mat ter partition and water use efficiency of winter wheat[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2003, 11(4): 92-94. | |
| [22] | 冉文星. 滴灌小麦水氮耦合的生理调控效应研究[D]. 阿拉尔: 塔里木大学, 2016. |
| RAN Wenxing. Study on physiological regulation effect of water and nitrogen coupling in drip irrigation wheat[D]. Aral: Tarim University, 2016. | |
| [23] | 曹宏鑫, 王世敬, 戴晓华. 土壤基础肥力和肥水运筹对春小麦产量和品质及植株氮素状况的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2003, 23(2): 52-56. |
| CAO Hongxin, WANG Shijing, DAI Xiaohua. Effects of soil basic fertility and fertilizer and water on yield and quality and nitrogen content and nitrate reductase in leaf in spring wheat[J]. Acta Tritical Crops, 2003, 23(2): 52-56. | |
| [24] | 谢伟, 黄璜, 沈建凯. 植物水肥耦合研究进展[J]. 作物研究, 2007, 21(S1): 541-546. |
| XIE Wei, HUANG Huang, SHEN Jiankai. Research progress on coupling of water and fertilizer in plants[J]. Crop Research, 2007, 21(S1): 541-546. | |
| [25] | 刘小刚, 张富仓, 田育丰, 等. 水氮互作对石羊河流域春小麦群体产量和水氮利用的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 37(3): 107-113. |
| LIU Xiaogang, ZHANG Fucang, TIAN Yufeng, et al. Interactive impact of water and nitrogen on group yield of spring wheat and use of water and nitrogen in Shiyang River Basin[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 37(3): 107-113. | |
| [26] | 张永丽, 于振文. 灌水量对小麦氮素吸收、分配、利用及产量与品质的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2008, 34(5): 870-878. |
| ZHANG Yongli, YU Zhenwen. Effects of irrigation amount on nitrogen uptake, distribution, use, and grain yield and quality in wheat[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2008, 34(5): 870-878. | |
| [27] | 雷钧杰. 新疆滴灌小麦带型配置及水氮供给对产量品质形成的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2017. |
| LEI Junjie. Effects of belt configuration and water and nitrogen supply on yield and quality formation of drip irrigation wheat in Xinjiang[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2017. |
| [1] | JIAO Runxing, BU Dongsheng, SHAO Yanhui, ZHANG Tao, CHEN Ling, ZHANG Dongdong. Effects of “dry sowing and wet emergence” on water and salt distribution, nutrients and cotton yield in different salinized soils [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(3): 572-583. |
| [2] | SUN Ganggang, GUO Fei, NIE Lingfan, TIAN Wenqiang, WANG Hongyi, SHI Yongqing, WU Li, AI Hongyu, ZHANG Jinshan, SHI Shubing. Effects of seed fertilizer separation on photosynthesis, dry matter accumulation and yield formation of winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(3): 593-599. |
| [3] | LEI Jiacheng, ZHANG Jingjing, HAN Bo, LU Ziao. Research on virtual wheat growth simulation and visualization system based on PyOpenGL [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(3): 609-618. |
| [4] | HAO Xiyu, LIU Tingting, WANG Hui, LENG Jingwen, GONG Shihang, LIU Wei. Selection and comprehensive evaluation of nitrogen-efficient foxtail millet varieties based on principal component analysis [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(3): 619-626. |
| [5] | LIU Limeng, MA Wenbin, LI Lingui, YUAN Cen, SHI Zhihai, LIU Yanfeng, QIN Rongyan, WANG Wenqi. Effects of fermented Chinese herbal medicines on growth performance, serum biochemistry and growth hormone in lamb [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(3): 754-765. |
| [6] | LIU Yue, LIAN Shihao, LI Jiahao, WANG Hongyi, TIAN Wenqiang, NIE Lingfan, SUN Ganggang, JIA Yonghong, SHI Shubing, YU Yuehua, ZHANG Jinshan. Effects of sowing dates and planting density on yield formation and quality of peanut [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(2): 278-285. |
| [7] | LU Mingkun, LI Junhong, Nilupaier Yusufujiang, PAN Xipeng, LIU Xiaocheng, ZHANG Zhenggui, PAN Zhanlei, ZHAI Menghua, ZHANG Yaopeng, ZHAO Wenqi, WANG Lihong, WANG Zhanbiao. Effect of silic on fertiliser application on the growth and development of cotton and its yield and quality [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(2): 286-293. |
| [8] | WANG Yiding, ZHANG Kai, ZHANG Lingjian, ZHANG Hui, GUO Xiaomeng, CHEN Guoyue. Effects of drip irrigation on the growth and development, yield formation, and water use efficiency of cotton in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(2): 294-301. |
| [9] | WANG Xiaoyan, BAI Yungang, CHAI Zhongping, LU Zhenlin, LIU Hongbo, XIAO Jun, Amannisa . Effect of "dry sowing and wet emergence" on cotton growth and yield under the control of winter drip irrigation in off-cropping period [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(2): 302-313. |
| [10] | LI Tianle, BAI Xinlu, AN Shijie, ZHENG Qiangqing, TANG Zhihui, ZHI Jinhu. Effects of water and fertilizer coupling on the growth, fruit quality and yield of Korla Fragrant Pear [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(2): 335-342. |
| [11] | HAN Xiqing, ZHANG Xianhua, YUAN Hui, XIONG Hui, SA Chenghui. Analysis and evaluation of morphological characteristics and yield of 10 Phleum pratense (L. ) plants [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(2): 454-462. |
| [12] | SUN Na, MA Lin, ZOU Hui, ZHANG Zhihui, ZHANG Shengjun, HUANG Qiannan, YANG Hui, Dengsilamu Tuerxunbai, LI Zhibin, CAO Junmei, LEI Junjie. Analysis of combined application of NPK fertilizers on yield and quality of winter wheat and the fertilizer effect [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 1-12. |
| [13] | GONG Zhaoxing, HAN Pengcheng, LI Zesen, LI Guizhen, WANG Yuxiang, ZHANG Bo. The physiological effects of inoculation with AM fungi under salt stress on wild smooth [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 129-136. |
| [14] | DU Yalong, FU Qiuping, AI Pengrui, MA Yingjie, QI Tong, PAN Yang. Comprehensive evaluation of irrigation treatment based on the growth and yield of drip-irrigated Gossypium barbadense [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 161-173. |
| [15] | XIE Xiurong, ZHANG Yongqiang, HAI Feng, LEI Junjie, LYU Xiaoqing, CHEN Chuanxin, XU Qijiang, NIE Shihui, WANG Jichuan. Effects of uniform sowing and densification on population structure and yield of late sowing winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 21-28. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||