

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (12): 2921-2933.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.12.007
• Germplasm Resources · Molecular Genetics. Cultivation Physiology · Physiology and Biochemistry Microbes • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Xiangbo1( ), CHEN Liangyu2, YANG Songnan2, CHEN Xifeng2, XING Weiming3, LI Xueying2, CONG Weixuan2, ZANG Zhenyuan2, ZANG Yuanbo4, ZHANG Jun2(
), CHEN Liangyu2, YANG Songnan2, CHEN Xifeng2, XING Weiming3, LI Xueying2, CONG Weixuan2, ZANG Zhenyuan2, ZANG Yuanbo4, ZHANG Jun2( )
)
Received:2024-03-30
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2025-01-16
Correspondence author:
ZHANG Jun
Supported by:
杨祥波1( ), 陈亮宇2, 杨松楠2, 陈喜凤2, 邢伟明3, 李雪莹2, 丛炜轩2, 臧振原2, 臧远波4, 张君2(
), 陈亮宇2, 杨松楠2, 陈喜凤2, 邢伟明3, 李雪莹2, 丛炜轩2, 臧振原2, 臧远波4, 张君2( )
)
通讯作者:
张君
作者简介:杨祥波(1980-),男,吉林人,副教授,博士,研究方向为作物遗传育种,(E-mail)yangxiangbo1980@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
YANG Xiangbo, CHEN Liangyu, YANG Songnan, CHEN Xifeng, XING Weiming, LI Xueying, CONG Weixuan, ZANG Zhenyuan, ZANG Yuanbo, ZHANG Jun. Phenotype analysis and comprehensive evaluation of spring soybean germplasm resources from northeast China[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(12): 2921-2933.
杨祥波, 陈亮宇, 杨松楠, 陈喜凤, 邢伟明, 李雪莹, 丛炜轩, 臧振原, 臧远波, 张君. 东北春大豆种质资源表型分析及综合性评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(12): 2921-2933.
| 性状 Traits | 平均值 Average | 标准差 SD | 最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 变异系数 CV(%) | 多样性指数 H' | 基因型 Genotype | 年份 Years | 基因型与 年份互作 G × Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高PH | 84.61 | 19.96 | 35.64 | 160.82 | 23.59 | 1.98 | ** | ** | ** |
| 节数BNN | 16.55 | 2.27 | 11.11 | 23.22 | 13.74 | 2.04 | ** | ** | ** |
| 分枝数BN | 2.53 | 1.69 | 0.22 | 7.57 | 66.65 | 1.92 | ** | ** | ** |
| 茎粗ST | 9.79 | 1.32 | 6.58 | 15.16 | 13.48 | 2.05 | ** | ** | ** |
| 单株荚数PNP | 71.08 | 21.05 | 35.78 | 132.29 | 29.62 | 1.94 | ** | ** | ** |
| 单株粒数SNP | 146.59 | 43.37 | 68 | 319.17 | 29.59 | 1.95 | ** | ** | ** |
| 单数粒重SWP | 24.13 | 6.8 | 12.19 | 50.82 | 28.17 | 1.97 | ** | ** | ** |
| 百粒重HSW | 17.07 | 2.77 | 6.65 | 25.26 | 16.25 | 1.96 | ** | ** | ** |
| 虫食粒数SDI | 8.69 | 4.01 | 1.43 | 28 | 46.09 | 1.98 | ** | ** | ** |
| 虫食粒重SWI | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 1 | 49.87 | 1.95 | ** | ** | ** |
| 虫食粒率PDS | 6.71 | 2.92 | 1.69 | 17.26 | 43.54 | 2.01 | ** | ** | ** |
| 虫食重比PWI | 1.73 | 0.93 | 0.36 | 7.44 | 53.57 | 1.86 | ** | ** | ** |
Tab.1 Compares of statistics analysis of agronomic traits in soybean germplasm
| 性状 Traits | 平均值 Average | 标准差 SD | 最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 变异系数 CV(%) | 多样性指数 H' | 基因型 Genotype | 年份 Years | 基因型与 年份互作 G × Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高PH | 84.61 | 19.96 | 35.64 | 160.82 | 23.59 | 1.98 | ** | ** | ** |
| 节数BNN | 16.55 | 2.27 | 11.11 | 23.22 | 13.74 | 2.04 | ** | ** | ** |
| 分枝数BN | 2.53 | 1.69 | 0.22 | 7.57 | 66.65 | 1.92 | ** | ** | ** |
| 茎粗ST | 9.79 | 1.32 | 6.58 | 15.16 | 13.48 | 2.05 | ** | ** | ** |
| 单株荚数PNP | 71.08 | 21.05 | 35.78 | 132.29 | 29.62 | 1.94 | ** | ** | ** |
| 单株粒数SNP | 146.59 | 43.37 | 68 | 319.17 | 29.59 | 1.95 | ** | ** | ** |
| 单数粒重SWP | 24.13 | 6.8 | 12.19 | 50.82 | 28.17 | 1.97 | ** | ** | ** |
| 百粒重HSW | 17.07 | 2.77 | 6.65 | 25.26 | 16.25 | 1.96 | ** | ** | ** |
| 虫食粒数SDI | 8.69 | 4.01 | 1.43 | 28 | 46.09 | 1.98 | ** | ** | ** |
| 虫食粒重SWI | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 1 | 49.87 | 1.95 | ** | ** | ** |
| 虫食粒率PDS | 6.71 | 2.92 | 1.69 | 17.26 | 43.54 | 2.01 | ** | ** | ** |
| 虫食重比PWI | 1.73 | 0.93 | 0.36 | 7.44 | 53.57 | 1.86 | ** | ** | ** |
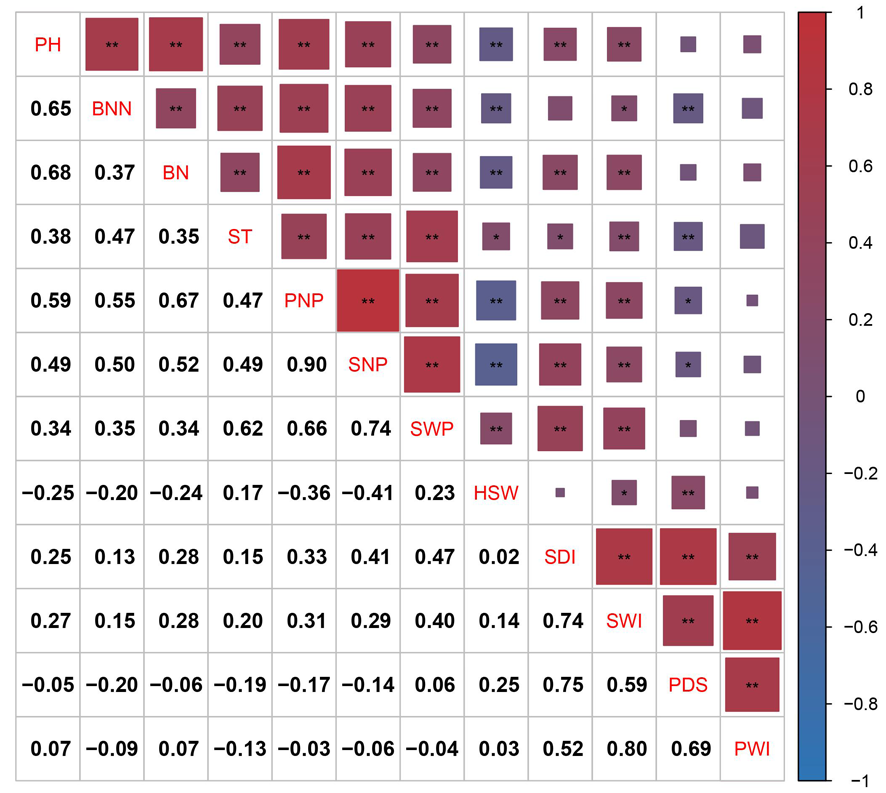
Fig.1 Correlation analysis of differential triats in soybean Notes:The correlation between colors is positive when they are close to red and negative when they are close to blue.* indicates a significant correlation between traits (P < 0.05), while ** indicates a highly significant correlation between traits (P < 0.01)
| 性状 Traits | 类群Cluster | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | |
| 株高PH | 83.18 | 67.67 | 103.22 | 93.27 |
| 节数BNN | 17.10 | 14.72 | 18.26 | 16.38 |
| 分枝数BN | 2.15 | 1.24 | 4.32 | 3.28 |
| 茎粗ST | 10.13 | 8.70 | 10.70 | 9.82 |
| 单株荚数PNP | 67.80 | 52.75 | 102.30 | 68.32 |
| 单株粒数SNP | 142.15 | 108.84 | 208.47 | 139.30 |
| 单数粒重SWP | 24.08 | 18.55 | 31.98 | 23.60 |
| 百粒重HSW | 17.37 | 17.45 | 15.97 | 17.29 |
| 虫食粒数SDI | 7.20 | 6.51 | 10.80 | 13.08 |
| 虫食粒重SWI | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.43 | 0.56 |
| 虫食粒率PDS | 5.39 | 6.86 | 6.02 | 10.29 |
| 虫食重比PWI | 1.30 | 1.65 | 1.58 | 3.02 |
Tab.2 Average performance of each trait in different class
| 性状 Traits | 类群Cluster | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | |
| 株高PH | 83.18 | 67.67 | 103.22 | 93.27 |
| 节数BNN | 17.10 | 14.72 | 18.26 | 16.38 |
| 分枝数BN | 2.15 | 1.24 | 4.32 | 3.28 |
| 茎粗ST | 10.13 | 8.70 | 10.70 | 9.82 |
| 单株荚数PNP | 67.80 | 52.75 | 102.30 | 68.32 |
| 单株粒数SNP | 142.15 | 108.84 | 208.47 | 139.30 |
| 单数粒重SWP | 24.08 | 18.55 | 31.98 | 23.60 |
| 百粒重HSW | 17.37 | 17.45 | 15.97 | 17.29 |
| 虫食粒数SDI | 7.20 | 6.51 | 10.80 | 13.08 |
| 虫食粒重SWI | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.43 | 0.56 |
| 虫食粒率PDS | 5.39 | 6.86 | 6.02 | 10.29 |
| 虫食重比PWI | 1.30 | 1.65 | 1.58 | 3.02 |
| 性状 Traits | 主成分特征向量 Principal component eigenvector | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 株高PH | 0.73 | -0.16 | -0.24 | 0.47 |
| 节数BNN | 0.65 | -0.32 | -0.04 | 0.39 |
| 分枝数BN | 0.71 | -0.13 | -0.24 | 0.22 |
| 茎粗ST | 0.62 | -0.22 | 0.54 | 0.18 |
| 单株荚数PNP | 0.89 | -0.24 | -0.10 | -0.22 |
| 单株粒数SNP | 0.86 | -0.22 | -0.04 | -0.41 |
| 单数粒重SWP | 0.75 | 0.02 | 0.53 | -0.27 |
| 百粒重HSW | -0.21 | 0.33 | 0.82 | 0.29 |
| 虫食粒数SDI | 0.57 | 0.69 | -0.02 | -0.21 |
| 虫食粒重SWI | 0.55 | 0.74 | 0.00 | 0.08 |
| 虫食粒率PDS | 0.07 | 0.91 | -0.03 | -0.01 |
| 虫食重比PWI | 0.17 | 0.83 | -0.28 | 0.16 |
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 4.65 | 2.97 | 1.45 | 0.90 |
| 贡献率 PV(%) | 38.94 | 24.84 | 12.17 | 7.53 |
| 累积贡献率 CPV(%) | 38.94 | 63.77 | 75.94 | 83.47 |
Tab.3 Principal components analysis of phenotype of soybean germplasm
| 性状 Traits | 主成分特征向量 Principal component eigenvector | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 株高PH | 0.73 | -0.16 | -0.24 | 0.47 |
| 节数BNN | 0.65 | -0.32 | -0.04 | 0.39 |
| 分枝数BN | 0.71 | -0.13 | -0.24 | 0.22 |
| 茎粗ST | 0.62 | -0.22 | 0.54 | 0.18 |
| 单株荚数PNP | 0.89 | -0.24 | -0.10 | -0.22 |
| 单株粒数SNP | 0.86 | -0.22 | -0.04 | -0.41 |
| 单数粒重SWP | 0.75 | 0.02 | 0.53 | -0.27 |
| 百粒重HSW | -0.21 | 0.33 | 0.82 | 0.29 |
| 虫食粒数SDI | 0.57 | 0.69 | -0.02 | -0.21 |
| 虫食粒重SWI | 0.55 | 0.74 | 0.00 | 0.08 |
| 虫食粒率PDS | 0.07 | 0.91 | -0.03 | -0.01 |
| 虫食重比PWI | 0.17 | 0.83 | -0.28 | 0.16 |
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 4.65 | 2.97 | 1.45 | 0.90 |
| 贡献率 PV(%) | 38.94 | 24.84 | 12.17 | 7.53 |
| 累积贡献率 CPV(%) | 38.94 | 63.77 | 75.94 | 83.47 |
| 自变量 Independent variable | 分界点 Change point | 第1段函数 First segment function | 第2段函数 Second segment function |
|---|---|---|---|
| 株高PH | 102.03 | Y= 0.22X + 6.29 | Y= -0.12X + 41.22 |
| 节数BNN | 19.93 | Y= 1.26X + 3.55 | Y= -1.13X + 51.11 |
| 分枝数BN | 3.50 | Y= 2.31X + 19.19 | Y= -0.14X + 27.78 |
| 茎粗ST | 11.69 | Y= 3.70X - 11.79 | Y= -0.67X + 39.18 |
| 单株荚数PNP | 99.73 | Y= 0.27X + 5.41 | Y= -0.04X + 36.18 |
| 单株粒数SNP | 286.09 | Y= 0.13X + 5.79 | |
| 百粒重HSW | 10.30 | Y= 0.60X + 13.77 | |
| 虫食粒数SDI | 8.88 | Y= 1.07X + 15.52 | Y= 0.63X + 19.39 |
| 虫食粒重SWI | 0.39 | Y= 28.49X + 15.37 | Y= 5.69X + 24.28 |
| 虫食粒率PDS | 9.95 | Y= 0.43X + 21.58 | Y= -0.94X + 35.21 |
| 虫食重比PWI | 1.17 | Y= 6.89X + 17.31 | Y= -1.04X + 26.57 |
Tab.4 Piecewise linear regression between variable phenotype and SWP
| 自变量 Independent variable | 分界点 Change point | 第1段函数 First segment function | 第2段函数 Second segment function |
|---|---|---|---|
| 株高PH | 102.03 | Y= 0.22X + 6.29 | Y= -0.12X + 41.22 |
| 节数BNN | 19.93 | Y= 1.26X + 3.55 | Y= -1.13X + 51.11 |
| 分枝数BN | 3.50 | Y= 2.31X + 19.19 | Y= -0.14X + 27.78 |
| 茎粗ST | 11.69 | Y= 3.70X - 11.79 | Y= -0.67X + 39.18 |
| 单株荚数PNP | 99.73 | Y= 0.27X + 5.41 | Y= -0.04X + 36.18 |
| 单株粒数SNP | 286.09 | Y= 0.13X + 5.79 | |
| 百粒重HSW | 10.30 | Y= 0.60X + 13.77 | |
| 虫食粒数SDI | 8.88 | Y= 1.07X + 15.52 | Y= 0.63X + 19.39 |
| 虫食粒重SWI | 0.39 | Y= 28.49X + 15.37 | Y= 5.69X + 24.28 |
| 虫食粒率PDS | 9.95 | Y= 0.43X + 21.58 | Y= -0.94X + 35.21 |
| 虫食重比PWI | 1.17 | Y= 6.89X + 17.31 | Y= -1.04X + 26.57 |

Fig.3 Piecewise linear regression between SWP and different traits Notes: Red line is fitted line for the first segment function, blue line is fitted line for the second segment function, and dashed brown line is demarcation point between the two segments function
| 种质 编号 | 综合评价 得分 | 排名 | 类型 | 类群 | 种质 编号 | 综合评价 得分 | 排名 | 类型 | 类群 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | D score | Rank | Type | Cluster | Number | D score | Rank | Type | Cluster | |
| Soy194 | 0.59 | 1 | 地方 | III | Soy157 | 0.13 | 106 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy209 | 0.55 | 2 | 地方 | III | Soy170 | 0.13 | 107 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy015 | 0.52 | 3 | 地方 | III | Soy096 | 0.13 | 108 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy052 | 0.50 | 4 | 选育 | III | Soy094 | 0.13 | 109 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy152 | 0.50 | 5 | 地方 | III | Soy175 | 0.13 | 110 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy205 | 0.48 | 6 | 地方 | III | Soy125 | 0.13 | 111 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy196 | 0.44 | 7 | 选育 | III | Soy056 | 0.13 | 112 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy166 | 0.41 | 8 | 地方 | III | Soy191 | 0.13 | 113 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy158 | 0.40 | 9 | 地方 | III | Soy182 | 0.12 | 114 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy105 | 0.39 | 10 | 选育 | III | Soy204 | 0.12 | 115 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy075 | 0.39 | 11 | 地方 | III | Soy130 | 0.12 | 116 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy027 | 0.39 | 12 | 选育 | III | Soy087 | 0.12 | 117 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy167 | 0.38 | 13 | 选育 | III | Soy113 | 0.12 | 118 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy050 | 0.38 | 14 | 选育 | III | Soy032 | 0.12 | 119 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy198 | 0.38 | 15 | 选育 | III | Soy001 | 0.11 | 120 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy072 | 0.38 | 16 | 选育 | III | Soy189 | 0.11 | 121 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy163 | 0.38 | 17 | 选育 | III | Soy081 | 0.11 | 122 | 选育 | III | |
| Soy190 | 0.38 | 18 | 地方 | III | Soy095 | 0.11 | 123 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy065 | 0.37 | 19 | 选育 | III | Soy019 | 0.11 | 124 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy099 | 0.36 | 20 | 选育 | III | Soy131 | 0.11 | 125 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy156 | 0.36 | 21 | 地方 | III | Soy148 | 0.11 | 126 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy069 | 0.35 | 22 | 地方 | III | Soy121 | 0.11 | 127 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy076 | 0.34 | 23 | 地方 | I | Soy203 | 0.10 | 128 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy202 | 0.34 | 24 | 地方 | I | Soy134 | 0.10 | 129 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy118 | 0.33 | 25 | 选育 | III | Soy098 | 0.10 | 130 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy043 | 0.33 | 26 | 选育 | III | Soy003 | 0.10 | 131 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy077 | 0.32 | 27 | 选育 | III | Soy084 | 0.10 | 132 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy151 | 0.32 | 28 | 地方 | III | Soy122 | 0.09 | 133 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy074 | 0.32 | 29 | 地方 | III | Soy109 | 0.09 | 134 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy180 | 0.31 | 30 | 选育 | I | Soy049 | 0.09 | 135 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy023 | 0.31 | 31 | 地方 | III | Soy132 | 0.09 | 136 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy035 | 0.31 | 32 | 选育 | III | Soy048 | 0.09 | 137 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy133 | 0.31 | 33 | 选育 | III | Soy068 | 0.09 | 138 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy177 | 0.30 | 34 | 选育 | III | Soy036 | 0.09 | 139 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy149 | 0.29 | 35 | 地方 | III | Soy140 | 0.09 | 140 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy147 | 0.29 | 36 | 地方 | III | Soy143 | 0.08 | 141 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy101 | 0.28 | 37 | 选育 | I | Soy059 | 0.08 | 142 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy172 | 0.28 | 38 | 选育 | I | Soy008 | 0.08 | 143 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy034 | 0.27 | 39 | 选育 | I | Soy089 | 0.08 | 144 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy085 | 0.27 | 40 | 选育 | I | Soy057 | 0.08 | 145 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy024 | 0.27 | 41 | 地方 | III | Soy110 | 0.08 | 146 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy022 | 0.27 | 42 | 选育 | I | Soy114 | 0.08 | 147 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy070 | 0.27 | 43 | 地方 | III | Soy045 | 0.08 | 148 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy159 | 0.26 | 44 | 地方 | IV | Soy144 | 0.08 | 149 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy004 | 0.25 | 45 | 地方 | III | Soy188 | 0.07 | 150 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy020 | 0.25 | 46 | 地方 | III | Soy083 | 0.07 | 151 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy111 | 0.25 | 47 | 选育 | III | Soy047 | 0.07 | 152 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy090 | 0.25 | 48 | 选育 | I | Soy097 | 0.07 | 153 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy006 | 0.25 | 49 | 地方 | I | Soy014 | 0.07 | 154 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy183 | 0.24 | 50 | 地方 | I | Soy129 | 0.07 | 155 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy193 | 0.24 | 51 | 选育 | III | Soy106 | 0.07 | 156 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy042 | 0.23 | 52 | 选育 | III | Soy092 | 0.07 | 157 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy013 | 0.23 | 53 | 地方 | I | Soy153 | 0.06 | 158 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy108 | 0.23 | 54 | 选育 | I | Soy046 | 0.06 | 159 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy178 | 0.23 | 55 | 选育 | I | Soy067 | 0.06 | 160 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy127 | 0.23 | 56 | 选育 | I | Soy060 | 0.06 | 161 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy005 | 0.23 | 57 | 地方 | I | Soy119 | 0.05 | 162 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy082 | 0.23 | 58 | 选育 | I | Soy201 | 0.05 | 163 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy088 | 0.23 | 59 | 选育 | III | Soy010 | 0.05 | 164 | 地方 | II | |
| Soy161 | 0.22 | 60 | 地方 | III | Soy086 | 0.05 | 165 | 地方 | II | |
| Soy011 | 0.22 | 61 | 地方 | III | Soy053 | 0.05 | 166 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy104 | 0.22 | 62 | 选育 | I | Soy185 | 0.05 | 167 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy160 | 0.22 | 63 | 地方 | III | Soy093 | 0.05 | 168 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy179 | 0.22 | 64 | 选育 | I | Soy155 | 0.05 | 169 | 地方 | II | |
| Soy026 | 0.21 | 65 | 选育 | I | Soy124 | 0.04 | 170 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy164 | 0.21 | 66 | 选育 | I | Soy112 | 0.04 | 171 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy181 | 0.21 | 67 | 选育 | I | Soy078 | 0.04 | 172 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy007 | 0.20 | 68 | 地方 | I | Soy173 | 0.03 | 173 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy025 | 0.20 | 69 | 选育 | I | Soy107 | 0.03 | 174 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy018 | 0.19 | 70 | 地方 | I | Soy030 | 0.03 | 175 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy017 | 0.19 | 71 | 地方 | I | Soy033 | 0.03 | 176 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy063 | 0.19 | 72 | 选育 | IV | Soy080 | 0.02 | 177 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy071 | 0.18 | 73 | 选育 | III | Soy009 | 0.02 | 178 | 地方 | II | |
| Soy145 | 0.18 | 74 | 选育 | I | Soy137 | 0.02 | 179 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy176 | 0.18 | 75 | 选育 | I | Soy192 | 0.01 | 180 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy012 | 0.18 | 76 | 地方 | I | Soy128 | 0.01 | 181 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy061 | 0.18 | 77 | 选育 | I | Soy206 | 0.01 | 182 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy028 | 0.17 | 78 | 选育 | I | Soy123 | 0.01 | 183 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy091 | 0.17 | 79 | 选育 | II | Soy142 | 0.01 | 184 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy136 | 0.17 | 80 | 选育 | I | Soy102 | 0.01 | 185 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy044 | 0.17 | 81 | 选育 | I | Soy041 | 0.01 | 186 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy139 | 0.16 | 82 | 选育 | I | Soy186 | 0.00 | 187 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy126 | 0.16 | 83 | 选育 | I | Soy195 | 0.00 | 188 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy055 | 0.16 | 84 | 选育 | II | Soy038 | 0.00 | 189 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy103 | 0.16 | 85 | 选育 | I | Soy162 | 0.00 | 190 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy115 | 0.16 | 86 | 选育 | I | Soy079 | -0.01 | 191 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy100 | 0.16 | 87 | 选育 | I | Soy117 | -0.01 | 192 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy208 | 0.16 | 88 | 选育 | I | Soy073 | -0.01 | 193 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy002 | 0.15 | 89 | 选育 | I | Soy200 | -0.01 | 194 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy174 | 0.15 | 90 | 选育 | I | Soy154 | -0.02 | 195 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy120 | 0.15 | 91 | 选育 | I | Soy064 | -0.02 | 196 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy187 | 0.15 | 92 | 选育 | I | Soy171 | -0.02 | 197 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy138 | 0.15 | 93 | 选育 | I | Soy197 | -0.02 | 198 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy116 | 0.15 | 94 | 选育 | I | Soy021 | -0.03 | 199 | 地方 | II | |
| Soy058 | 0.15 | 95 | 选育 | I | Soy146 | -0.03 | 200 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy066 | 0.15 | 96 | 选育 | I | Soy016 | -0.03 | 201 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy062 | 0.15 | 97 | 选育 | I | Soy165 | -0.06 | 202 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy207 | 0.14 | 98 | 选育 | II | Soy199 | -0.06 | 203 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy184 | 0.14 | 99 | 地方 | IV | Soy040 | -0.06 | 204 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy169 | 0.14 | 100 | 选育 | I | Soy150 | -0.07 | 205 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy029 | 0.14 | 101 | 选育 | IV | Soy168 | -0.07 | 206 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy054 | 0.14 | 102 | 选育 | I | Soy031 | -0.09 | 207 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy051 | 0.14 | 103 | 选育 | IV | Soy039 | -0.14 | 208 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy141 | 0.14 | 104 | 选育 | I | Soy037 | -0.25 | 209 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy135 | 0.13 | 105 | 选育 | II |
Tab.5 Comprehensive evaluation scores and ranking of 209 soybean germplasm
| 种质 编号 | 综合评价 得分 | 排名 | 类型 | 类群 | 种质 编号 | 综合评价 得分 | 排名 | 类型 | 类群 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | D score | Rank | Type | Cluster | Number | D score | Rank | Type | Cluster | |
| Soy194 | 0.59 | 1 | 地方 | III | Soy157 | 0.13 | 106 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy209 | 0.55 | 2 | 地方 | III | Soy170 | 0.13 | 107 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy015 | 0.52 | 3 | 地方 | III | Soy096 | 0.13 | 108 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy052 | 0.50 | 4 | 选育 | III | Soy094 | 0.13 | 109 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy152 | 0.50 | 5 | 地方 | III | Soy175 | 0.13 | 110 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy205 | 0.48 | 6 | 地方 | III | Soy125 | 0.13 | 111 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy196 | 0.44 | 7 | 选育 | III | Soy056 | 0.13 | 112 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy166 | 0.41 | 8 | 地方 | III | Soy191 | 0.13 | 113 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy158 | 0.40 | 9 | 地方 | III | Soy182 | 0.12 | 114 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy105 | 0.39 | 10 | 选育 | III | Soy204 | 0.12 | 115 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy075 | 0.39 | 11 | 地方 | III | Soy130 | 0.12 | 116 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy027 | 0.39 | 12 | 选育 | III | Soy087 | 0.12 | 117 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy167 | 0.38 | 13 | 选育 | III | Soy113 | 0.12 | 118 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy050 | 0.38 | 14 | 选育 | III | Soy032 | 0.12 | 119 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy198 | 0.38 | 15 | 选育 | III | Soy001 | 0.11 | 120 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy072 | 0.38 | 16 | 选育 | III | Soy189 | 0.11 | 121 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy163 | 0.38 | 17 | 选育 | III | Soy081 | 0.11 | 122 | 选育 | III | |
| Soy190 | 0.38 | 18 | 地方 | III | Soy095 | 0.11 | 123 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy065 | 0.37 | 19 | 选育 | III | Soy019 | 0.11 | 124 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy099 | 0.36 | 20 | 选育 | III | Soy131 | 0.11 | 125 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy156 | 0.36 | 21 | 地方 | III | Soy148 | 0.11 | 126 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy069 | 0.35 | 22 | 地方 | III | Soy121 | 0.11 | 127 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy076 | 0.34 | 23 | 地方 | I | Soy203 | 0.10 | 128 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy202 | 0.34 | 24 | 地方 | I | Soy134 | 0.10 | 129 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy118 | 0.33 | 25 | 选育 | III | Soy098 | 0.10 | 130 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy043 | 0.33 | 26 | 选育 | III | Soy003 | 0.10 | 131 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy077 | 0.32 | 27 | 选育 | III | Soy084 | 0.10 | 132 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy151 | 0.32 | 28 | 地方 | III | Soy122 | 0.09 | 133 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy074 | 0.32 | 29 | 地方 | III | Soy109 | 0.09 | 134 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy180 | 0.31 | 30 | 选育 | I | Soy049 | 0.09 | 135 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy023 | 0.31 | 31 | 地方 | III | Soy132 | 0.09 | 136 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy035 | 0.31 | 32 | 选育 | III | Soy048 | 0.09 | 137 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy133 | 0.31 | 33 | 选育 | III | Soy068 | 0.09 | 138 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy177 | 0.30 | 34 | 选育 | III | Soy036 | 0.09 | 139 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy149 | 0.29 | 35 | 地方 | III | Soy140 | 0.09 | 140 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy147 | 0.29 | 36 | 地方 | III | Soy143 | 0.08 | 141 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy101 | 0.28 | 37 | 选育 | I | Soy059 | 0.08 | 142 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy172 | 0.28 | 38 | 选育 | I | Soy008 | 0.08 | 143 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy034 | 0.27 | 39 | 选育 | I | Soy089 | 0.08 | 144 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy085 | 0.27 | 40 | 选育 | I | Soy057 | 0.08 | 145 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy024 | 0.27 | 41 | 地方 | III | Soy110 | 0.08 | 146 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy022 | 0.27 | 42 | 选育 | I | Soy114 | 0.08 | 147 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy070 | 0.27 | 43 | 地方 | III | Soy045 | 0.08 | 148 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy159 | 0.26 | 44 | 地方 | IV | Soy144 | 0.08 | 149 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy004 | 0.25 | 45 | 地方 | III | Soy188 | 0.07 | 150 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy020 | 0.25 | 46 | 地方 | III | Soy083 | 0.07 | 151 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy111 | 0.25 | 47 | 选育 | III | Soy047 | 0.07 | 152 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy090 | 0.25 | 48 | 选育 | I | Soy097 | 0.07 | 153 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy006 | 0.25 | 49 | 地方 | I | Soy014 | 0.07 | 154 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy183 | 0.24 | 50 | 地方 | I | Soy129 | 0.07 | 155 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy193 | 0.24 | 51 | 选育 | III | Soy106 | 0.07 | 156 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy042 | 0.23 | 52 | 选育 | III | Soy092 | 0.07 | 157 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy013 | 0.23 | 53 | 地方 | I | Soy153 | 0.06 | 158 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy108 | 0.23 | 54 | 选育 | I | Soy046 | 0.06 | 159 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy178 | 0.23 | 55 | 选育 | I | Soy067 | 0.06 | 160 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy127 | 0.23 | 56 | 选育 | I | Soy060 | 0.06 | 161 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy005 | 0.23 | 57 | 地方 | I | Soy119 | 0.05 | 162 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy082 | 0.23 | 58 | 选育 | I | Soy201 | 0.05 | 163 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy088 | 0.23 | 59 | 选育 | III | Soy010 | 0.05 | 164 | 地方 | II | |
| Soy161 | 0.22 | 60 | 地方 | III | Soy086 | 0.05 | 165 | 地方 | II | |
| Soy011 | 0.22 | 61 | 地方 | III | Soy053 | 0.05 | 166 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy104 | 0.22 | 62 | 选育 | I | Soy185 | 0.05 | 167 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy160 | 0.22 | 63 | 地方 | III | Soy093 | 0.05 | 168 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy179 | 0.22 | 64 | 选育 | I | Soy155 | 0.05 | 169 | 地方 | II | |
| Soy026 | 0.21 | 65 | 选育 | I | Soy124 | 0.04 | 170 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy164 | 0.21 | 66 | 选育 | I | Soy112 | 0.04 | 171 | 选育 | I | |
| Soy181 | 0.21 | 67 | 选育 | I | Soy078 | 0.04 | 172 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy007 | 0.20 | 68 | 地方 | I | Soy173 | 0.03 | 173 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy025 | 0.20 | 69 | 选育 | I | Soy107 | 0.03 | 174 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy018 | 0.19 | 70 | 地方 | I | Soy030 | 0.03 | 175 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy017 | 0.19 | 71 | 地方 | I | Soy033 | 0.03 | 176 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy063 | 0.19 | 72 | 选育 | IV | Soy080 | 0.02 | 177 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy071 | 0.18 | 73 | 选育 | III | Soy009 | 0.02 | 178 | 地方 | II | |
| Soy145 | 0.18 | 74 | 选育 | I | Soy137 | 0.02 | 179 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy176 | 0.18 | 75 | 选育 | I | Soy192 | 0.01 | 180 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy012 | 0.18 | 76 | 地方 | I | Soy128 | 0.01 | 181 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy061 | 0.18 | 77 | 选育 | I | Soy206 | 0.01 | 182 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy028 | 0.17 | 78 | 选育 | I | Soy123 | 0.01 | 183 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy091 | 0.17 | 79 | 选育 | II | Soy142 | 0.01 | 184 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy136 | 0.17 | 80 | 选育 | I | Soy102 | 0.01 | 185 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy044 | 0.17 | 81 | 选育 | I | Soy041 | 0.01 | 186 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy139 | 0.16 | 82 | 选育 | I | Soy186 | 0.00 | 187 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy126 | 0.16 | 83 | 选育 | I | Soy195 | 0.00 | 188 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy055 | 0.16 | 84 | 选育 | II | Soy038 | 0.00 | 189 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy103 | 0.16 | 85 | 选育 | I | Soy162 | 0.00 | 190 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy115 | 0.16 | 86 | 选育 | I | Soy079 | -0.01 | 191 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy100 | 0.16 | 87 | 选育 | I | Soy117 | -0.01 | 192 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy208 | 0.16 | 88 | 选育 | I | Soy073 | -0.01 | 193 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy002 | 0.15 | 89 | 选育 | I | Soy200 | -0.01 | 194 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy174 | 0.15 | 90 | 选育 | I | Soy154 | -0.02 | 195 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy120 | 0.15 | 91 | 选育 | I | Soy064 | -0.02 | 196 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy187 | 0.15 | 92 | 选育 | I | Soy171 | -0.02 | 197 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy138 | 0.15 | 93 | 选育 | I | Soy197 | -0.02 | 198 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy116 | 0.15 | 94 | 选育 | I | Soy021 | -0.03 | 199 | 地方 | II | |
| Soy058 | 0.15 | 95 | 选育 | I | Soy146 | -0.03 | 200 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy066 | 0.15 | 96 | 选育 | I | Soy016 | -0.03 | 201 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy062 | 0.15 | 97 | 选育 | I | Soy165 | -0.06 | 202 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy207 | 0.14 | 98 | 选育 | II | Soy199 | -0.06 | 203 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy184 | 0.14 | 99 | 地方 | IV | Soy040 | -0.06 | 204 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy169 | 0.14 | 100 | 选育 | I | Soy150 | -0.07 | 205 | 地方 | IV | |
| Soy029 | 0.14 | 101 | 选育 | IV | Soy168 | -0.07 | 206 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy054 | 0.14 | 102 | 选育 | I | Soy031 | -0.09 | 207 | 选育 | II | |
| Soy051 | 0.14 | 103 | 选育 | IV | Soy039 | -0.14 | 208 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy141 | 0.14 | 104 | 选育 | I | Soy037 | -0.25 | 209 | 选育 | IV | |
| Soy135 | 0.13 | 105 | 选育 | II |
| 性状 Traits | 综合评价得分 D score |
|---|---|
| 株高PH | 0.55** |
| 节数BNN | 0.59** |
| 分枝数BN | 0.60** |
| 茎粗ST | 0.56** |
| 单株荚数PNP | 0.86** |
| 单株粒数SNP | 0.83** |
| 单数粒重SWP | 0.64** |
| 百粒重HSW | -0.30** |
| 虫食粒数SDI | -0.03 |
| 虫食粒重SWI | -0.10 |
| 虫食粒率PDS | -0.54** |
| 虫食重比PWI | -0.45** |
Tab.6 Correlation analysis between phenotypes and comprehensive evaluation scores
| 性状 Traits | 综合评价得分 D score |
|---|---|
| 株高PH | 0.55** |
| 节数BNN | 0.59** |
| 分枝数BN | 0.60** |
| 茎粗ST | 0.56** |
| 单株荚数PNP | 0.86** |
| 单株粒数SNP | 0.83** |
| 单数粒重SWP | 0.64** |
| 百粒重HSW | -0.30** |
| 虫食粒数SDI | -0.03 |
| 虫食粒重SWI | -0.10 |
| 虫食粒率PDS | -0.54** |
| 虫食重比PWI | -0.45** |
| [1] | 查霆, 钟宣伯, 周启政, 等. 我国大豆产业发展现状及振兴策略[J]. 大豆科学, 2018, 37(3): 458-463. |
| ZHA Ting, ZHONG Xuanbo, ZHOU Qizheng, et al. Development status of China’s soybean industry and strategies of revitalizing[J]. Soybean Science, 2018, 37(3): 458-463. | |
| [2] |
徐瑶, 冷苏凤, 张玉明, 等. 1982-2021年江苏省审定大豆品种主要农艺性状、产量、品质及抗性演变分析[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2022, 44(4): 780-789.
DOI |
|
XU Yao, LENG Sufeng, ZHANG Yuming, et al. Evolution analysis of main agronomic traits, yield, quality and resistance of soybean varieties released in Jiangsu Province from 1982 to 2021[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2022, 44(4): 780-789.
DOI |
|
| [3] |
聂波涛, 刘德泉, 陈健, 等. 北方春大豆品种农艺和品质性状分析与综合评价[J]. 作物学报, 2024, 50(9): 2248-2266.
DOI |
|
NIE Botao, LIU Dequan, CHEN Jian, et al. Analysis and comprehensive evaluation of agronomic and quality traits of spring soybean varieties in Northern China[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2024, 50(9): 2248-2266.
DOI |
|
| [4] | 邱丽娟, 李英慧, 关荣霞, 等. 大豆核心种质和微核心种质的构建、验证与研究进展[J]. 作物学报, 2009, 35(4): 571-579. |
|
QIU Lijuan, LI Yinghui, GUAN Rongxia, et al. Establishment, representative testing and research progress of soybean core collection and mini core collection[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2009, 35(4): 571-579.
DOI |
|
| [5] | 常汝镇, 孙建英, 陈一舞. 中国大豆种质创新的内容与方法[J]. 作物品种资源, 1995, (1): 2-4. |
| CHANG Ruzhen, SUN Jianying, CHEN Yiwu. Content and Methods of Soybean Germplasm Innovation in China[J]. China Seed Industry, 1995, (1): 2-4. | |
| [6] | 赵朝森, 王瑞珍, 李英慧, 等. 江西大豆种质资源表型及品质性状综合分析与评价[J]. 大豆科学, 2019, 38(5): 686-693. |
| ZHAO Chaosen, WANG Ruizhen, LI Yinghui, et al. Comprehensive analysis and evaluation of the phenotype and quality traits of Jiangxi soybean germplasm resources[J]. Soybean Science, 2019, 38(5): 686-693. | |
| [7] |
徐泽俊, 齐玉军, 邢兴华, 等. 黄淮海大豆种质农艺与品质性状分析及综合评价[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2022, 23(2): 468-480.
DOI |
|
XU Zejun, QI Yujun, XING Xinghua, et al. Analysis and evaluation of agronomic and quality traits in soybean germplasms from Huang-Huai-Hai Region[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2022, 23(2): 468-480.
DOI |
|
| [8] | 曾维英, 赖振光, 谭玉荣, 等. 广西地方大豆种质资源的收集与评价鉴定筛选[J]. 大豆科学, 2021, 40(3): 354-361. |
| ZENG Weiying, LAI Zhenguang, TAN Yurong, et al. Collection, evaluation and screening of local soybean germplasm in Guangxi[J]. Soybean Science, 2021, 40(3): 354-361. | |
| [9] | 盖钧镒, 崔章林. 我国南方大豆地方品种群体特点和特异种质的发掘与遗传基础研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 1993, 9(2): 1-5. |
| GAI Junyi, CUI Zhanglin. Studies on the properties of soybean Landrace population from Southern China and on the germpiasm with specific target traits and their genetic background[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 1993, 9(2): 1-5. | |
| [10] | 常汝镇, 孙建英, 邱丽娟. 中国大豆种质资源研究进展[J]. 作物杂志, 1998, (3): 7-9. |
| CHANG Ruzhen, SUN Jianying, QIU Lijuan. Research progress on soybean germplasm resources in China[J]. Crops, 1998,(3): 7-9. | |
| [11] |
王继亮, 宗春美, 王德亮, 等. 东北大豆种质群体在佳木斯的表型鉴定及利用探析[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2021, 43(6): 996-1005.
DOI |
|
WANG Jiliang, ZONG Chunmei, WANG Deliang, et al. Identification, evaluation and improvement utilization of Northeast China Soybean Germplasm Population in Jiamusi[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2021, 43(6): 996-1005.
DOI |
|
| [12] | Zhao G Y, Jiang Z F, Li D M, et al. Molecular loci associated with seed isoflavone content may underlie resistance to soybean pod borer (Leguminivora glycinivorella)[J]. Plant Breeding, 2015, 134(1): 78-84. |
| [13] | 孟珊, 徐婷婷, 朱小品, 等. 江苏大豆地方种质资源表型多样性分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2023, 24(2): 419-436. |
|
MENG Shan, XU Tingting, ZHU Xiaopin, et al. Diversity analysis of soybean landraces collected from Jiangsu Province using phenotypic traits[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2023, 24(2): 419-436.
DOI |
|
| [14] |
李艳花, 杜成章, 陈红, 等. 重庆大豆地方资源多样性评价及群体表型特点研究[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2013, 14(6): 1025-1030.
DOI |
| LI Yanhua, DU Chengzhang, CHEN Hong, et al. Study of genetic diversity and population morphological characteristics of soybean landraces in Chongqing[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2013, 14(6): 1025-1030. | |
| [15] | 齐建双, 夏来坤, 黄保, 等. 基于熵权的DTOPSIS法和灰色局势决策法在玉米品种区域试验中的应用探讨[J]. 作物杂志, 2021, (1): 60-67. |
| QI Jianshuang, XIA Laikun, HUANG Bao, et al. Discussion on the application in the regional experiment of maize varieties by entropy DTOPSIS mode and grey situation decision methods[J]. Crops, 2021, (1): 60-67. | |
| [16] | 宋慧, 郭岩, 邢璐, 等. 基于灰色关联度、DTOPSIS与灰色局势决策法的谷子品种综合评价[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2023, 28(11): 42-56. |
| SONG Hui, GUO Yan, XING Lu, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of foxtail millet varieties based on grey correlation degree, DTOPSIS and situational decision-making method[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2023, 28(11): 42-56. | |
| [17] |
高山, 闫程铭, 万畅, 等. 基于灰色关联度法和DTOPSIS法对羊草种质资源综合评价[J]. 草地学报, 2024, 32(2): 599-609.
DOI |
|
GAO Shan, YAN Chengming, WAN Chang, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of germplasm resources of Leymus chinensis based on grey correlation method and DTOPSIS method[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(2): 599-609.
DOI |
|
| [18] | 段会军, 张彩英, 王省芬, 等. 河北省大豆品种主要农艺性状及聚类分析[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2003, 26(2): 5-9. |
| DUAN Huijun, ZHANG Caiying, WANG Xingfen, et al. The main agronomic traits and cluster analysis of soybean varieties in Hebei[J]. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei, 2003, 26(2): 5-9. | |
| [19] | 黎松松, 赖建军, 张红梅, 等. 江苏鲜食春大豆种质资源表型鉴定及综合评价[J]. 大豆科学, 2022, 41(4): 385-396. |
| LI Songsong, LAI Jianjun, ZHANG Hongmei, et al. Phenotyping identification and comprehensive evaluation of fresh spring soybean germplasms in Jiangsu Province[J]. Soybean Science, 2022, 41(4): 385-396. | |
| [20] | Charrad M, Ghazzali N, Boiteau V, et al. NbClust: AnRPackage for determining the relevant number of clusters in a data set[J]. Journal of Statistical Software, 2014, 61(6): 1-36. |
| [21] | Shannon C E, Weaver W. The mathematical theory of communication[M]. Champaign, IL, US: University of Illinois Press, 1949: 117. |
| [22] |
孙东雷, 卞能飞, 陈志德, 等. 花生种质资源表型性状的综合评价及指标筛选[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2018, 19(5): 865-874.
DOI |
|
SUN Donglei, BIAN Nengfei, CHEN Zhide, et al. Comprehensive evaluation and index screening of phenotypic traits in peanut germplasm resources[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2018, 19(5): 865-874.
DOI |
|
| [23] | 苏江顺, 齐玉鑫, 杨君, 等. 东北大豆种质群体在吉林省白城市的表现及其潜在的育种意义[J]. 土壤与作物, 2019, 8(1): 1-10. |
| SU Jiangshun, QI Yuxin, YANG Jun, et al. Performance and genetic potential of Northeast China soybean germplasm population in Baicheng City of Jilin Province[J]. Soils and Crops, 2019, 8(1): 1-10. | |
| [24] | 张君, 蔡立楠, 姚丹, 等. 大豆抗食心虫主基因+多基因遗传效应分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2012, 28(36): 227-230. |
|
ZHANG Jun, CAI Linan, YAO Dan, et al. Analysis of major gene plus polygene inheritance effects on soybean pod borer resistance[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2012, 28(36): 227-230.
DOI |
|
| [25] |
崔娟, 乔方, 秦贝华, 等. 大豆食心虫成虫对大豆品种的产卵选择性和幼虫适生性分析[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2023, 45(3): 592-599.
DOI |
|
CUI Juan, QIAO Fang, QIN Beihua, et al. Oviposition selectivity and larval fitness of soybean pod borer, Leguminivora glycinivorella(Lepidoptera: Olethreutidae)to different soybean varieties[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2023, 45(3): 592-599.
DOI |
|
| [26] | 林凡云, 邱丽娟, 常汝镇, 等. 山西省大豆地方品种与选育品种农艺性状及SSR标记遗传多样性比较分析[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2003, 25(3): 26-31. |
| LIN Fanyun, QIU Lijuan, CHANG Ruzhen, et al. Genetic diversity of Landrace and bred varieties of soybean in Shanxi[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Scieves, 2003, 25(3): 26-31. | |
| [27] | 昝凯, 陈亚光, 申为民, 等. 黄淮海夏大豆(南片)品种(系)农艺性状的综合分析及评价模型构建[J]. 大豆科学, 2023, 42(2): 129-137. |
| ZAN Kai, CHEN Yaguang, SHEN Weimin, et al. Comprehensive analysis of agronomic characters of summer sowing soybean varieties(lines) in Huang-Huai-Hai Region(south) and constructing A comprehensive evaluation model[J]. Soybean Science, 2023, 42(2): 129-137. | |
| [28] | 昝凯, 周青, 张志民, 等. 灰色关联度和DTOPSIS法综合分析河南区域试验中大豆新品种(系)的农艺性状表现[J]. 大豆科学, 2018, 37(5): 664-671. |
| ZAN Kai, ZHOU Qing, ZHANG Zhimin, et al. Gray correlation analysis and DTOPSIS method for comprehensive agronomic performance analysis of new soybean varieties(lines) in Henan regional test[J]. Soybean Science, 2018, 37(5): 664-671. |
| [1] | LIU Jing, DU Mingchuan, ZHANG Wenting, BAO Haijuan, JING Meiling, DU Wenhua. Screening of triticale germplasm in different areas of Qinghai [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2183-2190. |
| [2] | CHEN Yong, ZHOU Lei, SUI Chun, LIN Caixia. The characteristics of 32 cultivated germplasms of Isatis tinctoria Linnaeus in Xinjiang production area [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2307-2314. |
| [3] | MIAO Yu, CHEN Cuixia, MA Yanming, XING Guofang, DONG Yusheng, CHEN Zhijun, WANG Xian, XIANG Li. Genetic diversity analysis of phenotypic traits of 276 Central Asian barley germplasm resources [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1888-1895. |
| [4] | LIU Huijie, WANG Junhao, GONG Zhaolong, LIANG Yajun, WANG Junduo, LI Xueyuan, ZHENG Juyun, WANG Jichuan. Identification of salt tolerance of 197 upland cotton varieties at germination stage [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1574-1581. |
| [5] | YE Pingyi, LONG Yilei, TANG Yanping, DU Xiao, AN Mengjie, TAO Zhixin, LIANG Farui, AI Xiantao, HU Shoulin. Identification and evaluation of fruit branch angle and machine-picked agronomic traits in Gossypium hirsutum L. [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1318-1327. |
| [6] | LIU Yue, JIA Yonghong, ZHANG Jinshan, YU Yuehua, WANG Runqi, LI Dandan, SHI Shubing. Comparison of peanut varieties with different high oleic acid under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1361-1367. |
| [7] | Abudukadier Kurban, PAN Jinghai, CHEN Youqiang, LIU Huajun, DONG Xinjiu, BAI Xiaoshan, LI Sizhong, GAO Weishi, LI Xiaohui. Comprehensive evaluation of adaptability of late sowing sugar-beet varieties based on yield correlation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1368-1377. |
| [8] | YANG Junyan, YAN Miao, WU Haibo, YANG Wenli, WANG Haojie, MAO Jiancai, ZHAI Wenqiang, LI Junhua. The impact of high temperature on different thick -skinned melon varieties and comprehensive evaluation of its heat resistance [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1386-1396. |
| [9] | YANG Lu, WANG Na, FAN Shaoli, CHENG Ping, LI Hong, WANG Yangdong. Analysis of phenotypic trait variation characteristics of Morus nigra L.germplasm resources [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(5): 1172-1181. |
| [10] | ZHU Tao, Lei Qingyuan, MA Liang. Effects of water and nitrogen on growth, yield and water and nitrogen utilization efficiency of resown Maize and verification of scheme optimization model [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 835-844. |
| [11] | GAO Mutian, XIAO Yanmei, LIAO Zhijie, HUANG Cheng. Comprehensive evaluation of kernel and quality traits in maize-teosinte introgression line population [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 885-891. |
| [12] | YANG Minghua, LIAO Biyong, LIU Qiang, FENG Guorui, Dawulai Jiekeshan, Buayixiamu Namanti, LIU Qi, Aierjuma Tuluhan, PENG Yuncheng. Comprehensive evaluation of dehydration of maize hybrid combinations based on principal component analysis [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(2): 318-325. |
| [13] | OU Yuan, LUO Shasha, WANG Ruyue, SUN Yali, HU Haifang. Effects of salt stress on the growth and physiological characteristics of american black walnut seedlings [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(2): 393-401. |
| [14] | HAO Xiyu, LIU Tingting, WANG Hui, LENG Jingwen, GONG Shihang, LIU Wei, LIANG Jie. Comprehensive evaluation of foxtail millet varieties based on entropy weight method and grey relational analysis [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(12): 2902-2912. |
| [15] | XU Bin, WANG Zheng, SONG Zhanteng, Merhaba Paerhati, ZHU Jingrong, CHE Fengbin, LI Yonghai, WU Fengyan, MIAO Fuhong. Analysis and comprehensive evaluation of the fruit quality of 11 wild seabuckthorn germplasm resources [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(12): 3020-3031. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 34
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 97
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||