

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (10): 2351-2357.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.10.002
• Crop Genetics and Breeding · Germplasm Resources · Molecular Genetics · Cultivation Physiology · Physiology and Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Kang1( ), CHENG Rongrong2, PANG Bo1, ZHANG Mengyuan1, ZHANG Ru1, WANG Yongpan1, YANG Zhining1, WANG Zhi3, WANG Honggang1, GAO Wenwei1(
), CHENG Rongrong2, PANG Bo1, ZHANG Mengyuan1, ZHANG Ru1, WANG Yongpan1, YANG Zhining1, WANG Zhi3, WANG Honggang1, GAO Wenwei1( )
)
Received:2024-04-06
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-11-07
Correspondence author:
GAO Wenwei
Supported by:
赵康1( ), 程蓉蓉2, 庞博1, 张梦媛1, 张茹1, 王勇攀1, 杨志宁1, 王志3, 王红刚1, 高文伟1(
), 程蓉蓉2, 庞博1, 张梦媛1, 张茹1, 王勇攀1, 杨志宁1, 王志3, 王红刚1, 高文伟1( )
)
通讯作者:
高文伟
作者简介:赵康(1998-),男,新疆人,硕士研究生,研究方向为作物遗传育种,(E-mail)zhaokang07@yeah.net
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHAO Kang, CHENG Rongrong, PANG Bo, ZHANG Mengyuan, ZHANG Ru, WANG Yongpan, YANG Zhining, WANG Zhi, WANG Honggang, GAO Wenwei. Effects of salt stress and re-watering on the physiology, biochemistry and microstructure of cotton leaf structure[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(10): 2351-2357.
赵康, 程蓉蓉, 庞博, 张梦媛, 张茹, 王勇攀, 杨志宁, 王志, 王红刚, 高文伟. 盐胁迫及复水对棉花叶片生理生化和显微结构的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(10): 2351-2357.
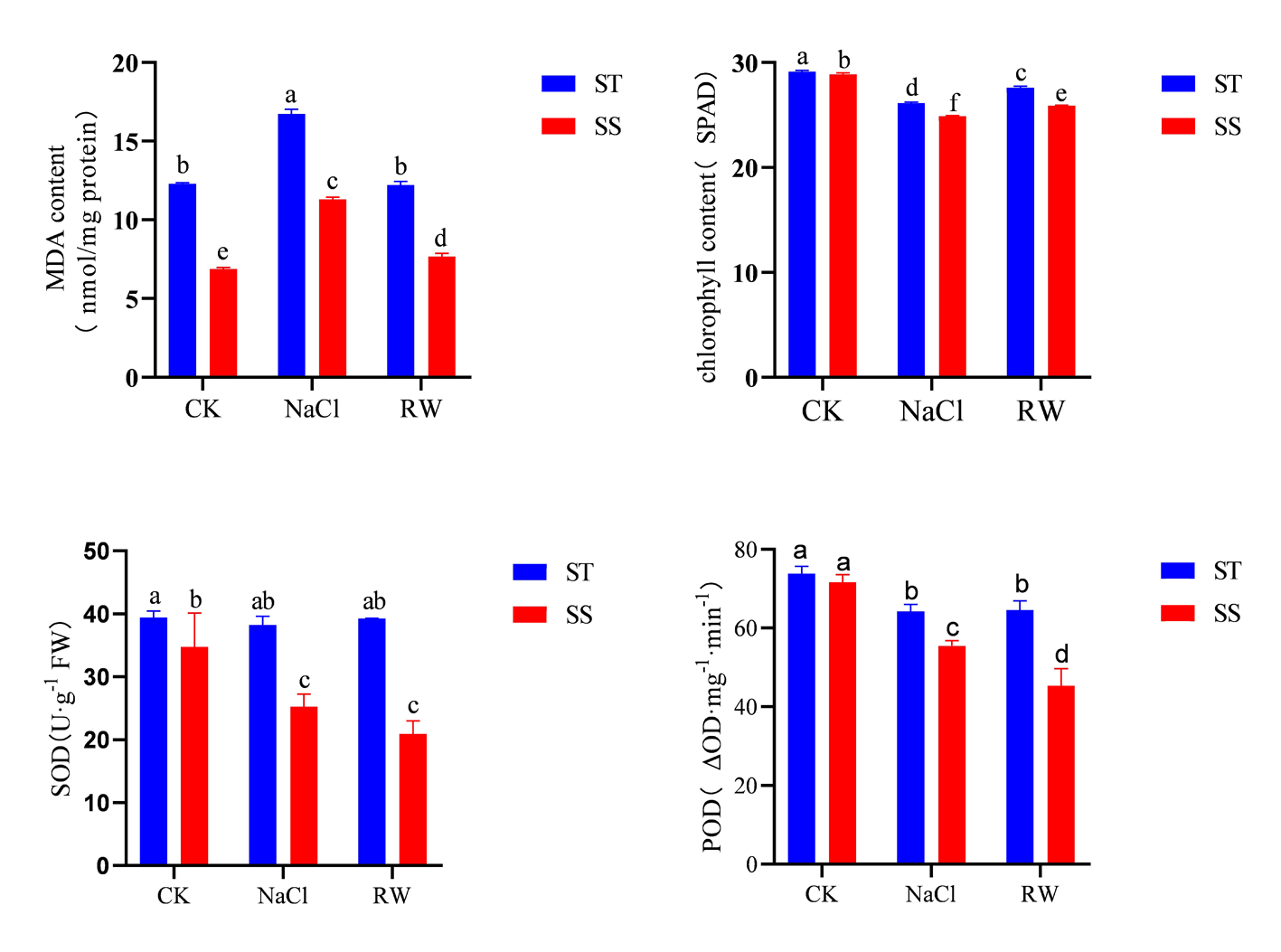
Fig.2 Physiological response of cotton seedlings to salt stress and re-watering Note: The same letter means no significant difference between treatments, and the same letter means significant difference (P< 0.05, LSD method)
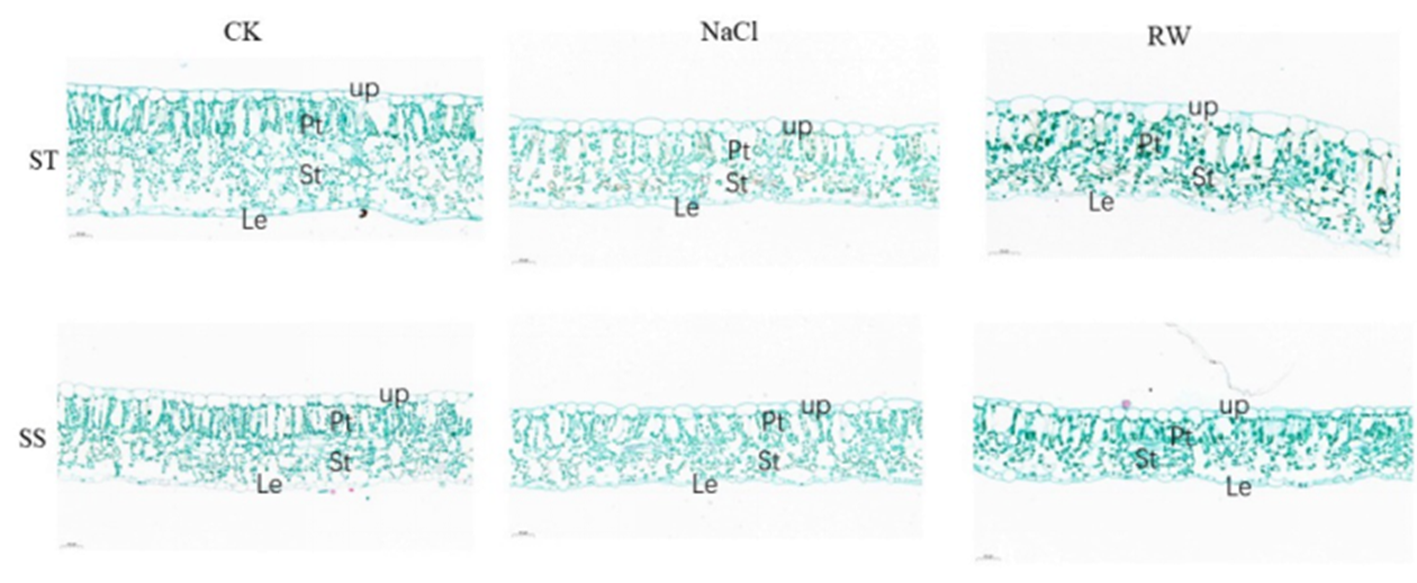
Fig.3 Cotton leaf micro structure after salt stress and re-watering Notes:Up: Upper epidermis; Pt: Palisade tissue; st: Spongy tissue; Le: Lower epidermis
| 品种 Varieties | 处理 Treatments | 叶片厚度 Thickness of leaf (μm) | 栅栏组织厚度 Thickness of palisade tissue (μm) | 海绵组织厚度 Thickness of spongy tissue (μm) | 上表皮厚度 Thickness of upper epidermis (μm) | 下表皮厚度 Thickness of lower epidermis (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST型 ST Type | CK | 246.38±4.07a | 86.00±2.94a | 108.99±2.94ab | 28.54±4.06ab | 21.87±2.71a |
| NaCl | 206.54±25.05ab | 88.87±12.92ab | 88.87±12.92abc | 25.77±2.18a | 18.62±1.74abc | |
| RW | 248.67±56.35a | 112.71±37.92a | 112.71±37.92a | 29.19±2.04a | 16.21±2.90c | |
| SS型 SS Type | CK | 247.17±23.64a | 111.30±15.61a | 111.30±15.61a | 25.19±4.31b | 20.66±1.24ab |
| NaCl | 167.01±31.27b | 65.55±11.22b | 65.55±11.22bc | 25.58±1.06ab | 18.27±2.12abc | |
| RW | 176.47±11.23b | 75.09±6.78b | 75.09±6.78c | 25.60±7,77ab | 16.66±1.94bc |
Tab.1 Changes of leaf epidermis structure of cotton seedlings under salt stress and after re-watering
| 品种 Varieties | 处理 Treatments | 叶片厚度 Thickness of leaf (μm) | 栅栏组织厚度 Thickness of palisade tissue (μm) | 海绵组织厚度 Thickness of spongy tissue (μm) | 上表皮厚度 Thickness of upper epidermis (μm) | 下表皮厚度 Thickness of lower epidermis (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST型 ST Type | CK | 246.38±4.07a | 86.00±2.94a | 108.99±2.94ab | 28.54±4.06ab | 21.87±2.71a |
| NaCl | 206.54±25.05ab | 88.87±12.92ab | 88.87±12.92abc | 25.77±2.18a | 18.62±1.74abc | |
| RW | 248.67±56.35a | 112.71±37.92a | 112.71±37.92a | 29.19±2.04a | 16.21±2.90c | |
| SS型 SS Type | CK | 247.17±23.64a | 111.30±15.61a | 111.30±15.61a | 25.19±4.31b | 20.66±1.24ab |
| NaCl | 167.01±31.27b | 65.55±11.22b | 65.55±11.22bc | 25.58±1.06ab | 18.27±2.12abc | |
| RW | 176.47±11.23b | 75.09±6.78b | 75.09±6.78c | 25.60±7,77ab | 16.66±1.94bc |
| [1] | Li Q, Song J. Analysis of widely targeted metabolites of the euhalophyte Suaeda salsa under saline conditions provides new insights into salt tolerance and nutritional value in halophytic species[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 388. |
| [2] |
Wang J, Jiang X, Zhao C F, et al. Transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis reveals the role of CoA in the salt tolerance of Zygophyllum spp[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2020, 20(1): 9.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Li X W, Zheng H L, Wu W S, et al. QTL mapping and candidate gene analysis for alkali tolerance in japonica rice at the bud stage based on linkage mapping and genome-wide association study[J]. Rice, 2020, 13(1): 48.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | 赵起越, 夏夜, 邹本东. 土壤盐渍化成因危害及恢复[J]. 农业与技术, 2022, 42(11): 115-119. |
| ZHAO Qiyue, XIA Ye, ZOU Bendong. Causes, harm and recovery of soil salinization[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2022, 42(11): 115-119. | |
| [5] | 努尔沙吾列·哈斯木汉. 新疆土壤盐渍化成因及其防治对策[J]. 科学技术创新, 2020, (9): 52-53. |
| Nuershawulie Hasimuhan. Causes of soil salinization in Xinjiang and its control countermeasures[J]. Scientific and Technological Innovation, 2020, (9): 52-53. | |
| [6] | Zhao H X, Gu B J, Chen D C, et al. Physicochemical properties and salinization characteristics of soils in coastal land reclamation areas: a case study of China-Singapore Tianjin Eco-City[J]. Heliyon, 2022, 8(12): e12629. |
| [7] | Rogers P P, Llamas M R, Martínez-Cortina L. Water Crisis: Myth Or Reality[M]. Taylor and Francis, CRC Press. |
| [8] |
van Zelm E, Zhang Y X, Testerink C. Salt tolerance mechanisms of plants[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2020, 71: 403-433.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Zhang B L, Chen X G, Lu X K, et al. Transcriptome analysis of Gossypium hirsutum L. reveals different mechanisms among NaCl, NaOH and Na2CO3 stress tolerance[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 13527. |
| [10] | Chen W C, Cui P J, Sun H Y, et al. Comparative effects of salt and alkali stresses on organic acid accumulation and ionic balance of seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.)[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2009, 30(3): 351-358. |
| [11] |
Byrt C S, Munns R, Burton R A, et al. Root cell wall solutions for crop plants in saline soils[J]. Plant Science, 2018, 269: 47-55.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Geng G, Li R R, Stevanato P, et al. Physiological and transcriptome analysis of sugar beet reveals different mechanisms of response to neutral salt and alkaline salt stresses[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 571864. |
| [13] |
卢秀茹, 贾肖月, 牛佳慧. 中国棉花产业发展现状及展望[J]. 中国农业科学, 2018, 51(1): 26-36.
DOI |
|
LU Xiuru, JIA Xiaoyue, NIU Jiahui. The present situation and prospects of cotton industry development in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2018, 51(1): 26-36.
DOI |
|
| [14] | 史晓玲. 国家、生态、技术、市场——棉花与鲁西北社会变迁(1906-2006)[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2020. |
| SHI Xiaoling. Country, Ecology, Technology and Market: Cotton and Social changes in Northwest Shandong(1906-2006)[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2020. | |
| [15] | 吴方卫, 张锦华. 丝绸之路经济带农牧业合作的空间、潜力与中国农业“走出去” 策略[J]. 科学发展, 2016, (4): 76-81. |
| WU Fangwei, ZHANG Jinhua. Space and potential for husbandry cooperation in silk road economic belt and “going out” strategy of Chinese agriculture[J]. Scientific Development, 2016, (4): 76-81. | |
| [16] | 苏莹, 郭安慧, 华金平. 棉花耐盐性鉴定方法探讨[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2021, 26(12): 11-19. |
| SU Ying, GUO Anhui, HUA Jinping. Strategies for evaluation the salt tolerance in cotton[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2021, 26(12): 11-19. | |
| [17] | 孙小芳, 刘友良, 陈沁. 棉花耐盐性研究进展[J]. 棉花学报, 1998, 10(3): 118-124. |
| SUN Xiaofang, LIU Youliang, CHEN Qin. Recent progresses in studies on salinity tolerence in cotton[J]. Cotton Science, 1998, 10(3): 118-124. | |
| [18] | Maryum Zahra, Luqman Tahira, Nadeem Sahar, et al. An overview of salinity stress, mechanism of salinity tolerance and strategies for its management in cotton [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13. |
| [19] | Fu H Q, Yang Y Q. How Plants Tolerate Salt Stress[J], 2023, 45(7):.5914-5934. |
| [20] | 毛桂莲, 许兴, 徐兆桢. 植物耐盐生理生化研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2004, 12(1): 43-46. |
| MAO Guilian, XU Xing, XU Zhaozhen. Advances in physiological and biochemical research of salt tolerance in plant[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2004, 12(1): 43-46. | |
| [21] | Hasanuzzaman M, Oku H, Nahar K, et al. Nitric oxide-induced saltstress tolerance in plants: ROS metabolism, signaling, and molecular interactions[J]. Plant Biotechnology Reports, 2018, 12(2): 77-92. |
| [22] |
段慧荣, 周学辉, 胡静, 等. 高等植物K+吸收及转运的分子机制研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 174-191.
DOI |
|
DUAN Huirong, ZHOU Xuehui, HU Jing, et al. Advances in understanding molecular mechanisms of K+ uptake and transport in higher plants[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(9): 174-191.
DOI |
|
| [23] | Hauser F, Horie T. A conserved primary salt tolerance mechanism mediated by HKT transporters: a mechanism for sodium exclusion and maintenance of high K(+)/Na(+) ratio in leaves during salinity stress[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2010, 33(4): 552-565. |
| [24] |
李瑞强, 王玉祥, 孙玉兰, 等. 盐胁迫对无芒雀麦幼苗叶片形态及解剖结构的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2022, 30(6): 1450-1459.
DOI |
|
LI Ruiqiang, WANG Yuxiang, SUN Yulan, et al. Effects of salt stress on leaf morphology and anatomical structure of Bromus inermis seedlings[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(6): 1450-1459.
DOI |
|
| [25] |
李双男, 郭慧娟, 侯振安. 不同盐碱胁迫对棉花离子组稳态及Na+相关基因表达影响[J]. 棉花学报, 2019, 31(6): 515-528.
DOI |
| LI Shuangnan, GUO Huijuan, HOU Zhen’an. Ionic homeostasis and expression of Na+ related genes of cotton under different salt and alkali stresses[J]. Cotton Science, 2019, 31(6): 515-528. | |
| [26] | Hameed M, Ashraf M, Naz N. Anatomical adaptations to salinity in cogon grass[Imperata cylindrica (L.) Raeuschel]from the Salt Range, Pakistan[J]. Plant and Soil, 2009, 322(1): 229-238. |
| [27] |
赵海燕, 王建设, 刘林强, 等. 海岛棉苗期盐胁迫下形态学和生理学指标变化[J]. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(18): 3494-3505.
DOI |
| ZHAO Haiyan, WANG Jianshe, LIU Linqiang, et al. Morphological and physiological mechanism of salt tolerance in Gossypium barbadense to salt stress at seedling stage[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(18): 3494-3505. | |
| [28] | Azeem A, Wu Y Y, Xing D K, et al. Photosynthetic response of two okra cultivars under salt stress and re-watering[J]. Journal of Plant Interactions, 2017, 12(1): 67-77. |
| [29] | Du L, Cai C P, Wu S, et al. Evaluation and exploration of favorable QTL alleles for salt stress related traits in cotton cultivars (G. hirsutum L.)[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(3): e0151076. |
| [30] | 范蓉. 基于生理指标与基因表达量评价棉花抗旱耐盐性[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2020. |
| FAN Rong. Evaluation of Cotton Drought and Salt Tolerance Based on Physiological Indexes and Gene Expression[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| [31] | 李娜. 不同基因型大白菜对盐碱胁迫的响应特性[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2022. |
| LI Na. Response Characteristics of Different Genotype Chinese Cabbages to Salt and Alkali Stress[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2022. | |
| [32] | 叶武威. 棉花种质的耐盐性及其耐盐基因表达的研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2007. |
| YE Wuwei. Study on the Salinity Resistance and Resistance Gene Expression in Cotton Germplasm[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2007. | |
| [33] | 王德龙. 盐胁迫下棉花细胞壁重塑相关基因GhEXLB1与GhGRP1功能研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2021. |
| WANG Delong. Study on the Function of GhEXLB1 and GhGRP1 Genes Related to Cell Wall Remodeling in Cotton under Salt Stress[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| [34] | 袁雨豪. 盐胁迫下糜子的生理响应及适应机制研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2022. |
| YUAN Yuhao. Study on Physiological Response and Adaptive Mechanism of Broomcorn Millet(Panicum Miliaceum L.)Under Salt Stress[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2022. | |
| [35] | 石亚飞, 闵炜芳, 摆小蓉, 等. 外源物调节碱胁迫水稻生理特性及相关基因表达的效应[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(5): 813-825. |
| SHI Yafei, MIN Weifang, BAI Xiaorong, et al. Effects of exogenous regulatory substances on physiological characteristics and gene expression of rice seedlings under alkali stress[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(5): 813-825. | |
| [36] |
Zhao B Q, Liu Q Y, Wang B S, et al. Roles of phytohormones and their signaling pathways in leaf development and stress responses[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2021, 69(12): 3566-3584.
DOI PMID |
| [37] | 彭振. 棉花苗期耐盐和耐热的生理机制及其基因转录调控分析[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2016. |
| PENG Zhen. The Gene Transcriptional Regulation Analysis and Physiology Mechanism of Salt Tolerance and Thermotolerance at Seedling Stage in Upland Cotton[D]. Yaan: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2016. |
| [1] | ZHOU Xin, LIU Xuanfeng, JIANG Yuhan, ZHANG Haichun, YANG Yuxin, Yeerbdati Tiemuer, JIANG Yongxin, ZHANG Li. Current situation and development proposal of mechanized recovery and resource utilization of used mulch film in cotton fields in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 131-141. |
| [2] | MIAO Hongping, WANG Xiaowei, TIAN Conghua, LI Zhi, ZHANG Yuxin, DAI Junsheng. Evolution characteristics and driving factors of cotton production and distribution in Tarim River basin [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 217-226. |
| [3] | WANG Junduo, CUI Yujiang, LIANG Yajun, GONG Zhaolong, ZHENG Junyun, LI Xueyuan. Xinjiang cotton production advantageous regional layout scheme [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 60-69. |
| [4] | ZHENG Juyun, GONG Zhaolong, LIANG Yajun, GENG Shiwei, SUN Fenglei, YANG ni, LI Xueyuan, WANG Junduo. Key technology model of machine-picked cotton production in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 70-74. |
| [5] | LI Jie, LIU Jia, WANG Liang, ZHANG Na, YANG Yanlong, ZHENG Zipiao, WEI Xin, WANG Meng, ZHOU Zixin, YANG Ni, GONG Zhaolong, HOU Xianfei, HUANG Qixiu, Abudukadier kuerban, ZHANG Jipeng, CHANG Pengzhong. Current situation of transformation and application of scientific and technological achievements of "cotton, oil and sugar" [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 89-94. |
| [6] | BIAN Qingyong, FU Yanbo, QI Tong, HUANG Jian, PU Shenghai, MENG Ajing, Halihashi Yibati. Study on influencing factors of cotton emergence and protection measures in saline-alkali land in southern Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 95-100. |
| [7] | LI Yongtai, GAO Axiang, LI Yanjun, ZHANG Xinyu. Effects of defoliants on the physiological characteristics of cotton varieties with different sensitivities [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2094-2102. |
| [8] | ZHANG Zehua, YE Hanchun, WANG Zhenhua, LI Wenhao, LI Haiqiang, LIU Jian. Effects of equal nitrogen applied with urease inhibitor on cotton growth, yield, and quality under mulched drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2103-2111. |
| [9] | CHEN Ruijie, LUO Linyi, RUAN Xiangyang, YE Jun. Effects of humic acid on soil nutrients, cotton yield and quality in cotton fields under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2112-2121. |
| [10] | HUANG Boxuan, LI Pengcheng, ZHENG Cangsong, SUN Miao, SHAO Jingjing, FENG Weina, PANG Chaoyou, XU Wenxiu, DONG Helin. Effects of different nitrogen inhibitors on growth, nitrogen utilization and yield of cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2122-2131. |
| [11] | WANG Chao, XU Wenxiu, LI Pengcheng, ZHENG Cangsong, SUN Miao, FENG Weina, SHAO Jingjing, DONG Helin. Response of cotton seedling growth and development to soil available potassium levels [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2132-2139. |
| [12] | ZHANG Fan, CHEN Xiaolu, WANG Jie, HOU Xianfei, JIA Donghai, GU Yuanguo, MIAO Haocui, LI Qiang. Effects of mixed salt stress on seed germination and seedling growth of peanut seed [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2168-2182. |
| [13] | ZHANG Tingjun, LI Zihui, CUI Yujiang, SUN Xiaogui, CHEN Fang. Effects of microbial agents on cotton growth and soil physico-chemical properties [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2269-2276. |
| [14] | LI Jinyao, XU Guiqing, WANG Lisheng, LU Ping, SHI Dongfang, ZHENG Weihua. Study on the effect of N fertilization on drought resistance of Calligonum caput-medusae seedlings [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2330-2340. |
| [15] | DONG Zhiduo, XU Fei, FU Qiuping, HUANG Jian, QI Tong, MENG Ajing, FU Yanbo, Kaisaier Kuerban. Effects of different types of salt and alkali stress on cotton seed germination [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1831-1844. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 87
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 189
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||