

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (6): 1328-1335.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.06.004
• Crop Genetics and Breeding • Germplasm Resources?Molecular Genetics • Cultivation Physiology • Physiology and Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHAO Yajie1( ), LI Ke1, DING Wenhao1, LIN Tao2(
), LI Ke1, DING Wenhao1, LIN Tao2( ), CUI Jianping2, GUO Rensong2, WANG Liang2, WU Fengquan1, WANG Xin1, TANG Qiuxiang1(
), CUI Jianping2, GUO Rensong2, WANG Liang2, WU Fengquan1, WANG Xin1, TANG Qiuxiang1( )
)
Received:2023-10-24
Online:2024-06-20
Published:2024-08-08
Correspondence author:
LIN Tao, TANG Qiuxiang
Supported by:
邵亚杰1( ), 李珂1, 丁文浩1, 林涛2(
), 李珂1, 丁文浩1, 林涛2( ), 崔建平2, 郭仁松2, 王亮2, 吴凤全1, 王心1, 汤秋香1(
), 崔建平2, 郭仁松2, 王亮2, 吴凤全1, 王心1, 汤秋香1( )
)
通讯作者:
林涛,汤秋香
作者简介:邵亚杰(1996-),男,新疆博乐人,硕士研究生,研究方向为棉花生长信息快速诊断,(E-mail)1519858040@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
SHAO Yajie, LI Ke, DING Wenhao, LIN Tao, CUI Jianping, GUO Rensong, WANG Liang, WU Fengquan, WANG Xin, TANG Qiuxiang. Study on cotton biomass estimation based on multi-spectral imaging features of unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1328-1335.
邵亚杰, 李珂, 丁文浩, 林涛, 崔建平, 郭仁松, 王亮, 吴凤全, 王心, 汤秋香. 基于无人机多光谱影像特征估算棉花生物量[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1328-1335.
| 植被指数 Vegetation index | 计算公式 Calculation formula | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|
| DVI | 夏天等[ | |
| GNDVI | Camille et.al[ | |
| TCRI | Shao et.al[ | |
| EVI | Liu et.al[ | |
| NDREI | Shao et.al[ | |
| EXG | Liu et.al[ | |
| EXGR | Fu et.al[ | |
| NGBDI | Sulik et.al[ |
Tab.1 The vegetation indexs in this study
| 植被指数 Vegetation index | 计算公式 Calculation formula | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|
| DVI | 夏天等[ | |
| GNDVI | Camille et.al[ | |
| TCRI | Shao et.al[ | |
| EVI | Liu et.al[ | |
| NDREI | Shao et.al[ | |
| EXG | Liu et.al[ | |
| EXGR | Fu et.al[ | |
| NGBDI | Sulik et.al[ |
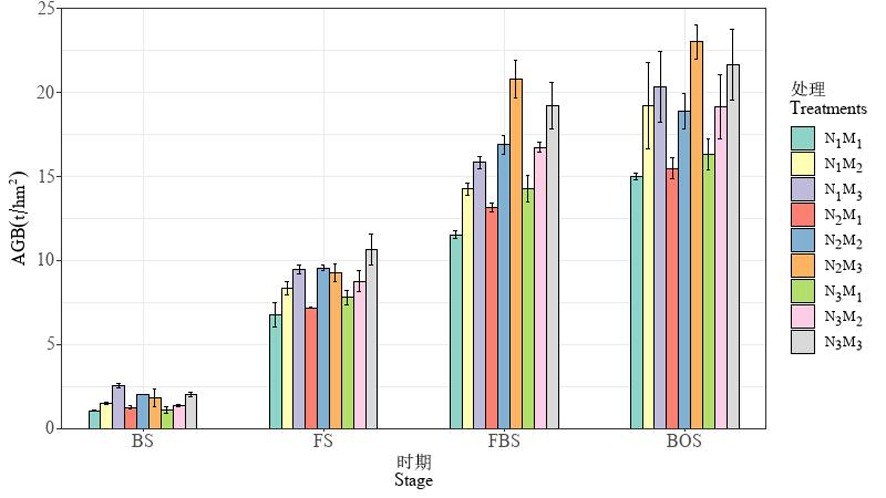
Fig.1 Changes of cotton AGB under Different Nitrogen Rates and plant Densities Note: BS : bud stage, FS : flowering stage, FBS : full bolling stage, BOS : boll opening stage
| 模型 Model | 建模集 Training set | 验证集 Testing set | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | rRMSE | R2 | RMSE | rRMSE | |
| SVR | 0.89 | 2.23 | 0.20 | 0.89 | 2.30 | 0.20 |
| PLSR | 0.86 | 2.55 | 0.23 | 0.81 | 3.01 | 0.27 |
| DNN | 0.87 | 2.47 | 0.22 | 0.84 | 2.79 | 0.25 |
Tab.2 Evaluation of AGB estimation results of cotton based on vegetation index
| 模型 Model | 建模集 Training set | 验证集 Testing set | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | rRMSE | R2 | RMSE | rRMSE | |
| SVR | 0.89 | 2.23 | 0.20 | 0.89 | 2.30 | 0.20 |
| PLSR | 0.86 | 2.55 | 0.23 | 0.81 | 3.01 | 0.27 |
| DNN | 0.87 | 2.47 | 0.22 | 0.84 | 2.79 | 0.25 |
| [1] | 刘杨, 孙乾, 黄珏, 等. 无人机多光谱影像的马铃薯地上生物量估算[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2021, 41(8): 2549-2555. |
| LIU Yang, SUN Qian, HUANG Jue, et al. Estimation of potato above ground biomass based on UAV multispectral images[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2021, 41(8): 2549-2555. | |
| [2] | 樊鸿叶, 李姚姚, 卢宪菊, 等. 基于无人机多光谱遥感的春玉米叶面积指数和地上部生物量估算模型比较研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 112-120. |
| FAN Hongye, LI Yaoyao, LU Xianju, et al. Comparative analysis of LAI and above-ground biomass estimation models based on UAV multispectral remote sensing[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(9): 112-120. | |
| [3] | 黄春燕, 王登伟, 曹连莆, 等. 棉花地上鲜生物量的高光谱估算模型研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2007, 23(3): 131-135. |
| HUANG Chunyan, WANG Dengwei, CAO Lianpu, et al. Models for estimating cotton aboveground fresh biomass using hyperspectral data[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2007, 23(3): 131-135. | |
| [4] | 李岚涛, 郭宇龙, 韩鹏, 等. 基于高光谱的冬小麦不同生育时期地上部生物量监测[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2021, 41(7): 904-913. |
| LI Lantao, GUO Yulong, HAN Peng, et al. Estimation of shoot biomass at different growth stages of winter wheat based on hyperspectral reflectance[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2021, 41(7): 904-913. | |
| [5] |
卜灵心, 来全, 刘心怡. 不同机器学习算法在草原草地生物量估算上的适应性研究[J]. 草地学报, 2022, 30(11): 3156-3164.
DOI |
|
BU Lingxin, LAI Quan, LIU Xinyi. Adaptation of different machine learning algorithms for grassland biomass estimation[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(11): 3156-3164.
DOI |
|
| [6] | Ballesteros R, Ortega J F, Hernandez D, et al. Onion biomass monitoring using UAV-based RGB imaging[J]. Precision Agriculture, 2018, 19(5): 840-857. |
| [7] | 张正健, 李爱农, 边金虎, 等. 基于无人机影像可见光植被指数的若尔盖草地地上生物量估算研究[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2016, 31(1): 51-62. |
| ZHANG Zhengjian, LI Ainong, BIAN Jinhu, et al. Estimating aboveground biomass of grassland in zoige by visible vegetation index derived from unmanned aerial vehicle image[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2016, 31(1): 51-62. | |
| [8] | 陆国政, 杨贵军, 赵晓庆, 等. 基于多载荷无人机遥感的大豆地上鲜生物量反演[J]. 大豆科学, 2017, 36(1): 41-50. |
| LU Guozheng, YANG Guijun, ZHAO Xiaoqing, et al. Inversion of soybean fresh biomass based on multi-payload unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)[J]. Soybean Science, 2017, 36(1): 41-50. | |
| [9] | 孙世泽, 汪传建, 尹小君, 等. 无人机多光谱影像的天然草地生物量估算[J]. 遥感学报, 2018, 22(5): 848-856. |
| SUN Shize, WANG Chuanjian, YIN Xiaojun, et al. Estimating aboveground biomass of natural grassland based on multispectral images of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2018, 22(5): 848-856. | |
| [10] | Wang D L, Xin X P, Shao Q Q, et al. Modeling aboveground biomass in Hulunber grassland ecosystem by using unmanned aerial vehicle discrete lidar[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(12): 180. |
| [11] |
张雨欣, 黄健熙, 金云翔, 等. 草地地上生物量估算模型研究进展[J]. 草地学报, 2022, 30(4): 850-858.
DOI |
|
ZHANG Yuxin, HUANG Jianxi, JIN Yunxiang, et al. Estimation of grasslands aboveground biomass: a review[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(4): 850-858.
DOI |
|
| [12] | Deo R C, Şahin M. Forecasting long-term global solar radiation with an ANN algorithm coupled with satellite-derived (MODIS) land surface temperature (LST) for regional locations in Queensland[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 72: 828-848. |
| [13] | Safari A, Sohrabi H, Powell S, et al. A comparative assessment of multi-temporal Landsat 8 and machine learning algorithms for estimating aboveground carbon stock in coppice oak forests[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2017, 38(22): 6407-6432. |
| [14] | 王玉娜, 李粉玲, 王伟东, 等. 基于连续投影算法和光谱变换的冬小麦生物量高光谱遥感估算[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2020, 40(11): 1389-1398. |
| WANG Yuna, LI Fenling, WANG Weidong, et al. Hyper-spectral remote sensing stimation of shoot biomass of winter wheat based on SPA and transformation spectra[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2020, 40(11): 1389-1398. | |
| [15] | 纪伟帅. 基于无人机多光谱的棉花冠层叶片叶绿素相对含量、叶面积指数反演[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2021: 56. |
| JI Weishuai. Inversion of SPAD and LAI in Cotton Canopy Leaves Based on UAV Multispectral[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2021: 56. | |
| [16] | 王士红. 增密减氮对棉花产量品质的影响及氮高效生理基础研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2019: 124. |
| WANG Shihong. Effects of Increasing Plant Density and Decreasing Nitrogen Rate on Yield and Quality of Cotton, and Physiological Mechanisms of Nitrogen Efficient Utilization[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2019: 124. | |
| [17] | 李春艳. 密度与氮肥对机采棉产量及氮肥利用影响的研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2018: 61. |
| LI Chunyan. Effects of Density and Nitrogen Fertilizer on Cotton Production and Nitrogen Utilization[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2018: 61. | |
| [18] | 夏天, 周清波, 陈仲新, 等. 基于HJ-1卫星的冬小麦叶片SPAD遥感监测研究[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2012, 33(6): 38-44. |
| XIA Tian, ZHOU Qingbo, CHEN Zhongxin, et al. Monitoring winter wheat spad based on hj-1 ccd[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2012, 33(6): 38-44. | |
| [19] |
Lelong C, Burger P, Jubelin G, et al. Assessment of unmanned aerial vehicles imagery for quantitative monitoring of wheat crop in small plots[J]. Sensors, 2008, 8(5): 3557-3585.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Shao G M, Han W T, Zhang H H, et al. Estimation of transpiration coefficient and aboveground biomass in maize using time-series UAV multispectral imagery[J]. The Crop Journal, 2022, 10(5): 1376-1385. |
| [21] |
Liu S B, Jin X L, Nie C W, et al. Estimating leaf area index using unmanned aerial vehicle data: shallow vs. deep machine learning algorithms[J]. Plant Physiology, 2021, 187(3): 1551-1576.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Liu Y, Feng H K, Yue J B, et al. Remote-sensing estimation of potato above-ground biomass based on spectral and spatial features extracted from high-definition digital camera images[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2022, 198: 107089. |
| [23] | Fu Y Y, Yang G J, Li Z H, et al. Winter wheat nitrogen status estimation using UAV-based RGB imagery and Gaussian processes regression[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(22): 3778. |
| [24] | Sulik J J, Long D S. Spectral considerations for modeling yield of canola[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2016, 184: 161-174. |
| [25] | 贾学勤, 冯美臣, 杨武德, 等. 基于多植被指数组合的冬小麦地上干生物量高光谱估测[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(2): 424-429. |
| JIA Xueqin, FENG Meichen, YANG Wude, et al. Hyperspectral estimation of aboveground dry biomass of winter wheat based on the combination of vegetation indices[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(2): 424-429. | |
| [26] | 尚珂. 基于支持向量机回归的草地地上生物量遥感估测研究[D]. 昆明: 西南林业大学, 2015: 67. |
| SHANG Ke. The Study of Grassland above Ground Biomass Inversion Based on Support Vector Machine Regression[D]. Kunming: Southwest Forestry University, 2015: 67. | |
| [27] | 兰仕浩, 李映雪, 吴芳, 等. 基于卫星光谱尺度反射率的冬小麦生物量估算[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(24): 118-128. |
| LAN Shihao, LI Yingxue, WU Fang, et al. Winter wheat biomass estimation based on satellite spectral-scale reflectance[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(24): 118-128. | |
| [28] | 张子慧, 吴世新, 赵子飞, 等. 基于机器学习算法的草地地上生物量估测——以祁连山草地为例[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(22): 8953-8963. |
| ZHANG Zihui, WU Shixin, ZHAO Zifei, et al. Estimation of grassland biomass using machine learning methods: a case study of grassland in Qilian Mountains[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(22): 8953-8963. | |
| [29] | 孙全. 基于无人机可见光-近红外图像的小麦关键生长指标监测研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2021: 92. |
| SUN Quan. Key Wheat Growth Indicators Monitoring Based on UAV Visible-NIR Imagery[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2021: 92. | |
| [30] | 吴芳, 李映雪, 张缘园, 等. 基于机器学习算法的冬小麦不同生育时期生物量高光谱估算[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2019, 39(2): 217-224. |
| WU Fang, LI Yingxue, ZHANG Yuanyuan, et al. Hyperspectral estimation of biomass of winter wheat at different growth stages based on machine learning algorithms[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2019, 39(2): 217-224. | |
| [31] | 李鹏程, 董合林, 刘爱忠, 等. 施氮量对棉花功能叶片生理特性、氮素利用效率及产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(1): 81-91. |
| LI Pengcheng, DONG Helin, LIU Aizhong, et al. Effects of nitrogen application rates on physiological characteristics of functional leaves, nitrogen use efficiency and yield of cotton[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2015, 21(1): 81-91. | |
| [32] |
李飞, 郭莉莉, 赵瑞元, 等. 氮肥减量深施对油后直播棉花干物质与氮素积累、分配及产量的影响[J]. 棉花学报, 2022, 34(3): 198-214.
DOI |
| LI Fei, GUO Lili, ZHAO Ruiyuan, et al. Effects of increasing application depth and decreasing nitrogen rate on dry matter, nitrogen accumulation and distribution, and yield of direct seeding cotton after rape harvest[J]. Cotton Science, 2022, 34(3): 198-214. | |
| [33] | 辛明华, 王占彪, 李小飞, 等. 南疆棉区机采种植模式下棉花种植密度研究[J]. 山东农业科学, 2020, 52(1): 46-52. |
| XIN Minghua, WANG Zhanbiao, LI Xiaofei, et al. Study on suitable planting density of cotton under machine-picked planting mode in South Xinjiang[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 52(1): 46-52. | |
| [34] |
支晓宇, 韩迎春, 王国平, 等. 不同密度下棉花群体光辐射空间分布及生物量和纤维品质的变化[J]. 棉花学报, 2017, 29(4): 365-373.
DOI |
| ZHI Xiaoyu, HAN Yingchun, WANG Guoping, et al. Changes to the PAR spatial distribution, biomass, and fiber quality in response to plant densities[J]. Cotton Science, 2017, 29(4): 365-373. | |
| [35] |
牛玉萍, 陈宗奎, 杨林川, 等. 干旱区滴灌模式和种植密度对棉花生长和产量性能的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(10): 1506-1515.
DOI |
|
NIU Yuping, CHEN Zongkui, YANG Linchuan, et al. Effect of drip irrigation pattern and planting density on growth and yield performance of cotton in arid area[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(10): 1506-1515.
DOI |
|
| [36] |
王士红, 杨中旭, 史加亮, 等. 增密减氮对棉花干物质和氮素积累分配及产量的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(3): 395-407.
DOI |
|
WANG Shihong, YANG Zhongxu, SHI Jialiang, et al. Effects of increasing planting density and decreasing nitrogen rate on dry matter, nitrogen accumulation and distribution, and yield of cotton[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(3): 395-407.
DOI |
|
| [37] | Sankaran S, Zhou J F, Khot L R, et al. High-throughput field phenotyping in dry bean using small unmanned aerial vehicle based multispectral imagery[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2018, 151: 84-92. |
| [38] | Hunt E R Jr, Hively W D, Fujikawa S, et al. Acquisition of NIR-green-blue digital photographs from unmanned aircraft for crop monitoring[J]. Remote Sensing, 2010, 2(1): 290-305. |
| [39] | 岳继博, 杨贵军, 冯海宽. 基于随机森林算法的冬小麦生物量遥感估算模型对比[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(18): 175-182. |
| YUE Jibo, YANG Guijun, FENG Haikuan. Comparative of remote sensing estimation models of winter wheat biomass based on random forest algorithm[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(18): 175-182. | |
| [40] | 肖武, 陈佳乐, 笪宏志, 等. 基于无人机影像的采煤沉陷区玉米生物量反演与分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(8): 169-180. |
| XIAO Wu, CHEN Jiale, DA Hongzhi, et al. Inversion and analysis of maize biomass in coal mining subsidence area based on UAV images[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(8): 169-180. |
| [1] | ZHOU Xin, LIU Xuanfeng, JIANG Yuhan, ZHANG Haichun, YANG Yuxin, Yeerbdati Tiemuer, JIANG Yongxin, ZHANG Li. Current situation and development proposal of mechanized recovery and resource utilization of used mulch film in cotton fields in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 131-141. |
| [2] | MIAO Hongping, WANG Xiaowei, TIAN Conghua, LI Zhi, ZHANG Yuxin, DAI Junsheng. Evolution characteristics and driving factors of cotton production and distribution in Tarim River basin [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 217-226. |
| [3] | WANG Junduo, CUI Yujiang, LIANG Yajun, GONG Zhaolong, ZHENG Junyun, LI Xueyuan. Xinjiang cotton production advantageous regional layout scheme [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 60-69. |
| [4] | ZHENG Juyun, GONG Zhaolong, LIANG Yajun, GENG Shiwei, SUN Fenglei, YANG ni, LI Xueyuan, WANG Junduo. Key technology model of machine-picked cotton production in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 70-74. |
| [5] | LI Jie, LIU Jia, WANG Liang, ZHANG Na, YANG Yanlong, ZHENG Zipiao, WEI Xin, WANG Meng, ZHOU Zixin, YANG Ni, GONG Zhaolong, HOU Xianfei, HUANG Qixiu, Abudukadier kuerban, ZHANG Jipeng, CHANG Pengzhong. Current situation of transformation and application of scientific and technological achievements of "cotton, oil and sugar" [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 89-94. |
| [6] | BIAN Qingyong, FU Yanbo, QI Tong, HUANG Jian, PU Shenghai, MENG Ajing, Halihashi Yibati. Study on influencing factors of cotton emergence and protection measures in saline-alkali land in southern Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 95-100. |
| [7] | LI Yongtai, GAO Axiang, LI Yanjun, ZHANG Xinyu. Effects of defoliants on the physiological characteristics of cotton varieties with different sensitivities [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2094-2102. |
| [8] | ZHANG Zehua, YE Hanchun, WANG Zhenhua, LI Wenhao, LI Haiqiang, LIU Jian. Effects of equal nitrogen applied with urease inhibitor on cotton growth, yield, and quality under mulched drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2103-2111. |
| [9] | CHEN Ruijie, LUO Linyi, RUAN Xiangyang, YE Jun. Effects of humic acid on soil nutrients, cotton yield and quality in cotton fields under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2112-2121. |
| [10] | HUANG Boxuan, LI Pengcheng, ZHENG Cangsong, SUN Miao, SHAO Jingjing, FENG Weina, PANG Chaoyou, XU Wenxiu, DONG Helin. Effects of different nitrogen inhibitors on growth, nitrogen utilization and yield of cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2122-2131. |
| [11] | WANG Chao, XU Wenxiu, LI Pengcheng, ZHENG Cangsong, SUN Miao, FENG Weina, SHAO Jingjing, DONG Helin. Response of cotton seedling growth and development to soil available potassium levels [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2132-2139. |
| [12] | XIAO Shuting, YAN An, WANG Weixia, ZHANG Qingqing, HOU Zhengqing, MA Mengqian, SUN Zhe. Analysis of spatial and temporal variations of aboveground biomass and the factors affecting it in a typical forest area in the central Tianshan Mountains [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2237-2244. |
| [13] | ZHANG Tingjun, LI Zihui, CUI Yujiang, SUN Xiaogui, CHEN Fang. Effects of microbial agents on cotton growth and soil physico-chemical properties [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2269-2276. |
| [14] | DONG Zhiduo, XU Fei, FU Qiuping, HUANG Jian, QI Tong, MENG Ajing, FU Yanbo, Kaisaier Kuerban. Effects of different types of salt and alkali stress on cotton seed germination [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1831-1844. |
| [15] | LI Ruyong, REN Jiuming, LEI Ting, WANG Kelin, LIU Pengcheng, LI Jiangtao. Differences in carbon sink estimation between photosynthetic and biomass methods in the Tarim Desert Highway shelterbelt [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 2014-2022. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 53
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 237
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||