

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (9): 2094-2102.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.09.003
• Crop Genetics and Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Genetics·Cultivation Physiology·Physiology and Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Yongtai( ), GAO Axiang, LI Yanjun, ZHANG Xinyu(
), GAO Axiang, LI Yanjun, ZHANG Xinyu( )
)
Received:2024-02-19
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-10-09
Correspondence author:
ZHANG Xinyu
Supported by:通讯作者:
张新宇
作者简介:李永泰(2000-),男,甘肃人,硕士研究生,研究方向为棉花分子育种,(E-mail)2049706098@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LI Yongtai, GAO Axiang, LI Yanjun, ZHANG Xinyu. Effects of defoliants on the physiological characteristics of cotton varieties with different sensitivities[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2094-2102.
李永泰, 高阿香, 李艳军, 张新宇. 脱叶剂对不同敏感性棉花品种生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2094-2102.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.xjnykx.com/EN/10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.09.003
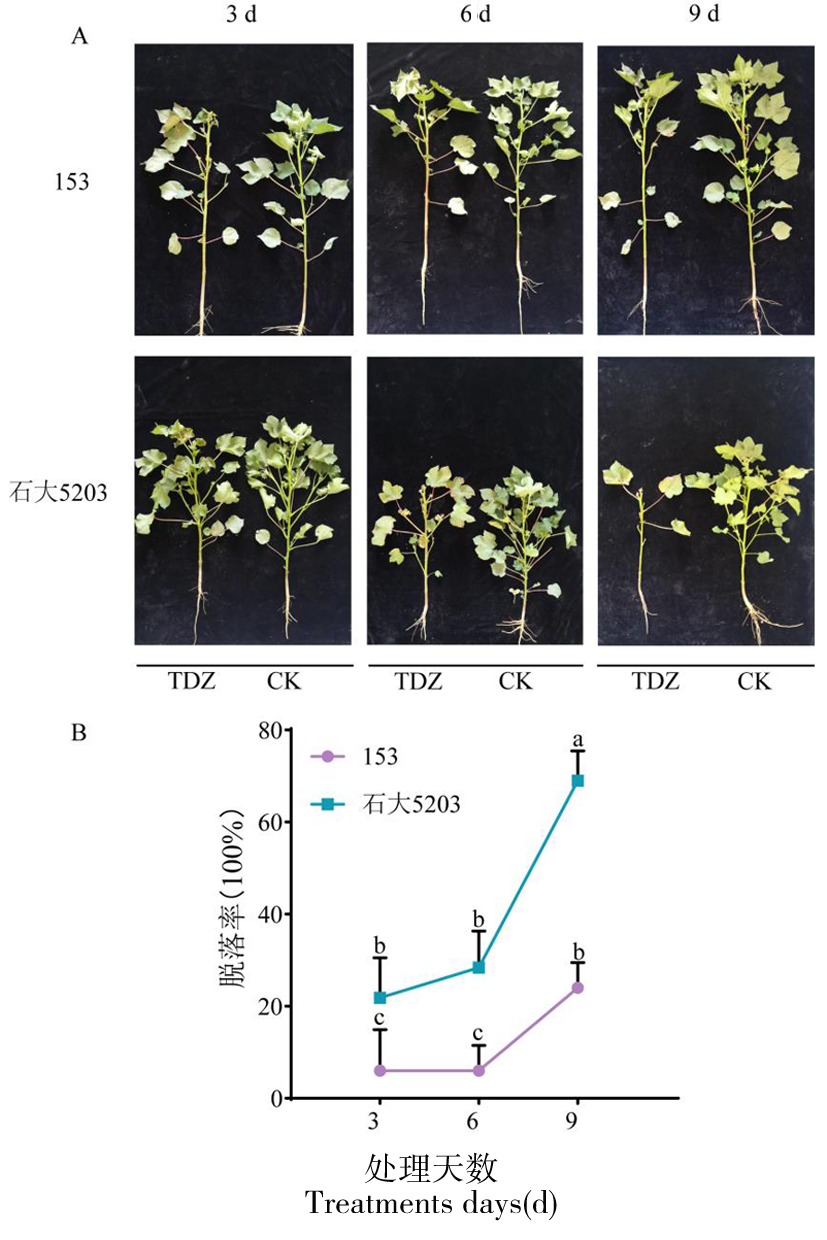
Fig.1 Comparisons of sensitivity of different cotton varieties to defoliants at seedling stage Note: Figure 1A shows representative images of leaf abscission after 3, 6, and 9 days of defoliation treatment. TDZ represents the defoliation treatment, while CK represents the water-treated control. Figure 1B presents the statistical analysis of leaf abscission rates after 3, 6, and 9 days of defoliation treatment. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in the changes of photosynthetic rate among cotton varieties with different sensitivity at the same time (P<0.05), the data in the figure are presented as mean ± standard error
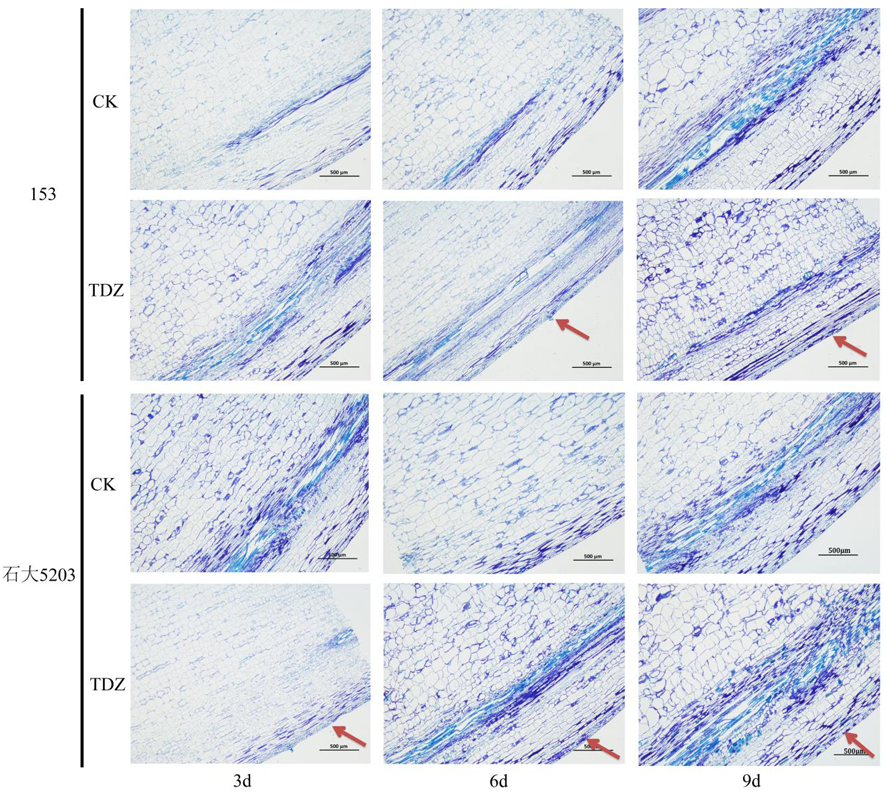
Fig.2 Changes of longitudinal section of petiole of cotton varieties with different sensitivity to defoliants after defoliation treatment at seedling stage Note: Abscission layer is indicated by the arrows. The sections were stained with toluidine blue. Scale bars are 500 μm
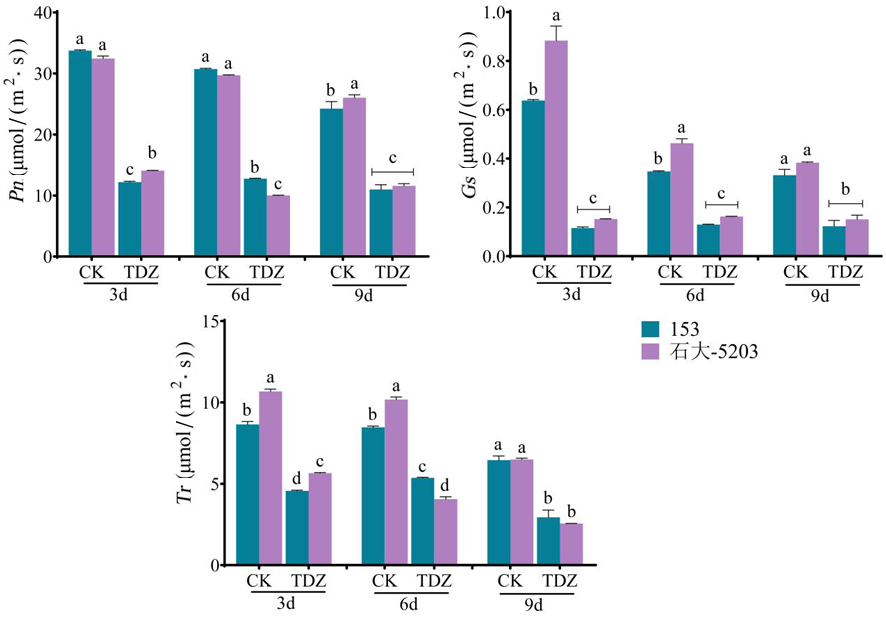
Fig.3 Changes of hotosynthetic rate leaves of cotton varieties with different sensitivity to defoliants after defoliation treatment at seedling stage Note: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in the changes of photosynthetic rate among cotton varieties with different sensitivity at the same time (P<0.05),The data in the figure are presented as mean ± standard error,the same as below
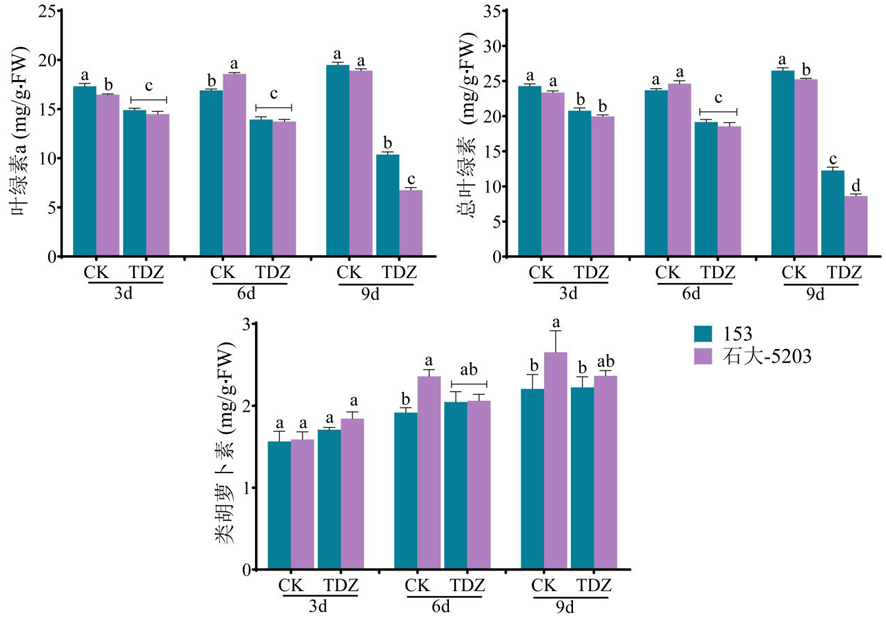
Fig.4 Changes of chlorophyll and carotenoid content in leaves of cotton varieties with different sensitivity to defoliants after defoliation treatment at seedling stage Note: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in the changes of chlorophyll and carotenoid content among cotton varieties with different sensitivity at the same time (P<0.05)
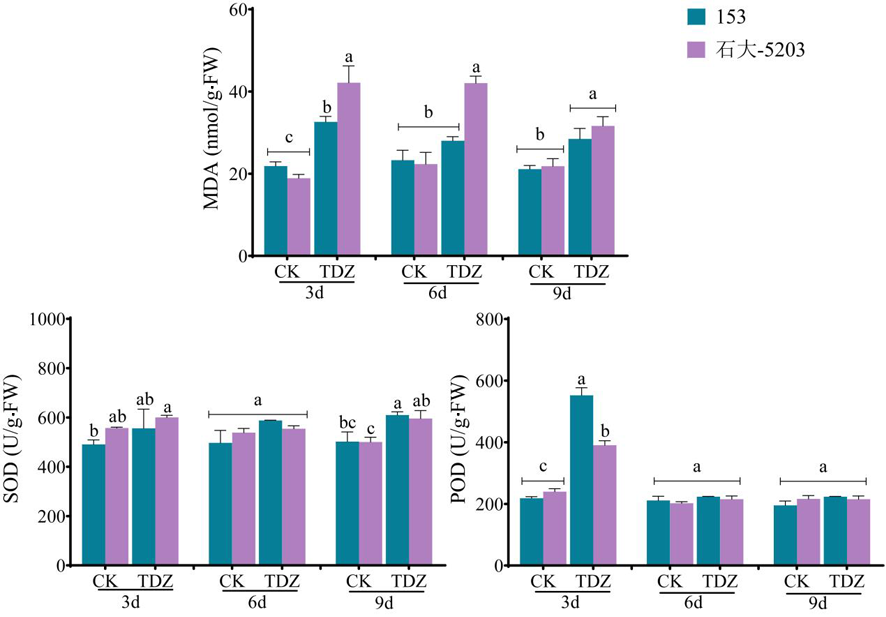
Fig.5 Changes of antioxidant enzyme activities and malondialdehyde content in leaves of cotton varieties with different sensitivity to defoliants after defoliation treatment at seedling stage Note: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in the changes of antioxidant enzyme activity and malondialdehyde (MDA) content among varieties with different sensitivity at the same time (P<0.05)
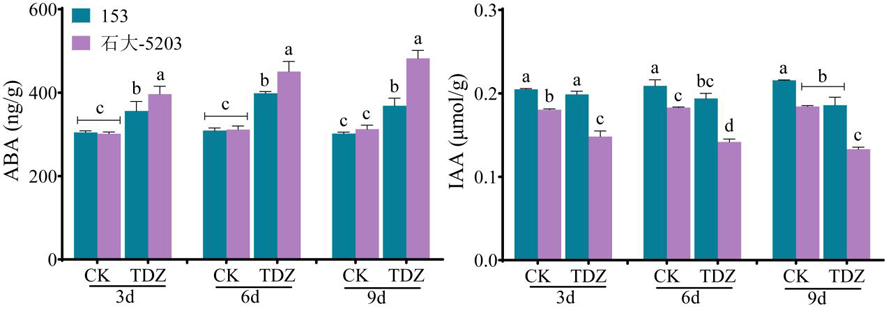
Fig.6 Changes of endogenous hormones content in leaves of cotton varieties with different sensitivity to defoliants after defoliation treatment at seedlings stage Note: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in the changes of endogenous hormone content among varieties with different sensitivity at the same time (P<0.05)
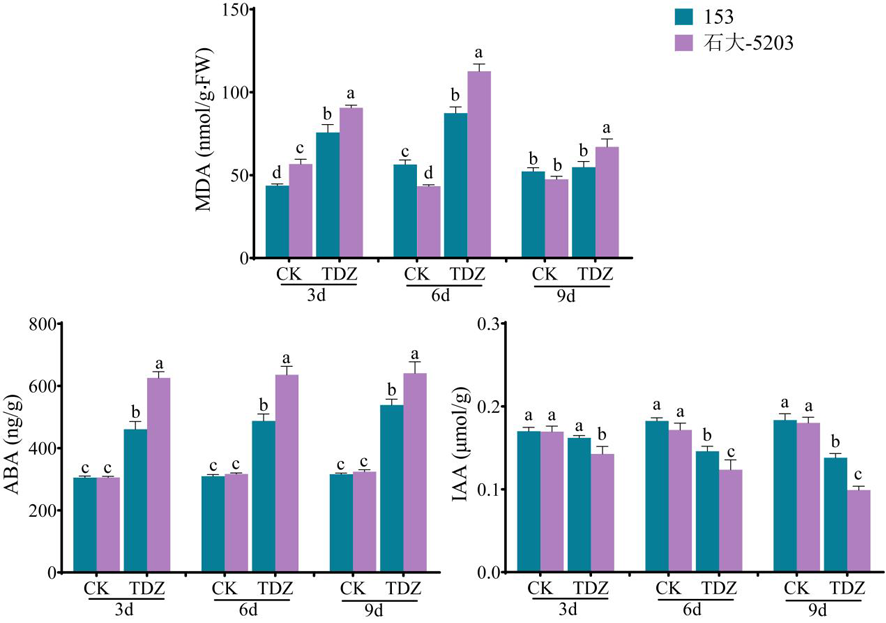
Fig.7 Changes of malondialdehyde content and endogenous hormone levels in leaves of cotton varieties with different sensitivity to defoliants after defoliation treatment at boll opening stage Note: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in the impact of cotton leaf malondialdehyde (MDA) content among varieties with different sensitivity at the same time (P<0.05)
| [1] | 李双江. 阿拉尔垦区棉花主栽品种脱叶剂敏感性研究[D]. 塔里木大学, 2022. |
| LI Shuangjiang. Study on defoliation sensitivity of main cotton varieties in Alaer Reclamation area[D]. Tarim University, 2022. | |
| [2] | 朱继杰, 赵红霞, 王士杰, 等. 不同棉花品种对脱叶剂敏感性研究[J]. 中国棉花, 2018, 45(4): 15-18, 33. |
| ZHU Jijie, ZHAO Hongxia, WANG Shijie, et al. Study on the sensitivity of different cotton cultivars to defoliant[J]. China Cotton, 2018, 45(4): 15-18, 33. | |
| [3] | 马怡茹, 吕新, 张泽, 等. 基于无人机数码图像的机采棉脱叶率监测模型构建[J]. 棉花学报, 2021, 33 (4): 347-359 |
| MA Yiru, LYU Xin, ZHANG Ze, et al. Estimation of the defoliation rate of cotton based on unmanned aerial vehicle digital images[J]. Cotton Science, 2021, 33 (4):347-359. | |
| [4] | 樊翠芹, 王贵启, 苏立军, 等. 50%噻苯隆在棉田的应用效果及气候因素的影响[J]. 河北农业科学, 2007, 11(1): 51-54. |
| FAN Cuiqin, WANG Guiqi, SU Lijun, et al. Studies on 50% thidiazuron on leaves shedding and boll open percentage of cotton and influence of climatic factor[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 11(1): 51-54. | |
| [5] | 马龙. 不同脱叶剂脱叶效果及对棉花产量品质的影响[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2017. |
| MA Long. Different Defoliants Spraying on Cotton Influences of Defoliant Effects, Yield and Quality[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2017. | |
| [6] | 雷斌, 张云生, 李忠华, 等. 棉花脱叶剂的田间效果筛选[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2011, 48(12): 2321-2324. |
| LEI Bin, ZHANG Yunsheng, LI Zhonghua, et al. Screening test of different disleave agents for accelerating effect[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 48(12): 2321-2324. | |
| [7] | 吴凤鸣. 三种不同脱叶剂对棉花产量的影响[J]. 农村科技, 2013, (2): 19-20. |
| WU Fengming. Effects of three different defoliants on cotton yield[J]. Rural Science & Technology, 2013, (2): 19-20. | |
| [8] | 刘勇, 杨明凤, 白书军, 等. 石河子地区机采棉不同时期喷施化学脱叶剂的效果[J]. 棉花科学, 2020, 42(6): 28-31. |
| LIU Yong, YANG Mingfeng, BAI Shujun, et al. Effects of spraying chemical defoliats in different period of machine picked cotton in Shihezi district[J]. Cotton Sciences, 2020, 42(6): 28-31. | |
| [9] | 李思嘉. 温度影响棉花化学脱叶的生理机制及其应用研究[D]. 扬州大学, 2020. |
| LI Sijia. Physiology Mechanism of Temperature Affecting Chemical Defoliation and Its Application in Cotton[D]. Yangzhou University, 2020. | |
| [10] | 徐新洲, 聂新富, 张学辉, 等. 北疆机采棉化学脱叶试验初探[J]. 新疆农机化, 2001, (2): 26-27, 37. |
| XU Xinzhou, NIE Xinfu, ZHANG Xuehui, et al. Preliminary study on chemical defoliation test of machine-picked cotton in northern Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Mechanization, 2001, (2): 26-27, 37. | |
| [11] | 张大伟, 魏鑫, 徐海江, 等. 不同棉花品种对脱叶剂的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(1): 146-153. |
| ZHANG Dawei, WEI Xin, XU Haijiang, et al. Study on the response of cotton varieties with different genotypes to defoliants[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(1): 146-153. | |
| [12] | 樊庆鲁, 陈云, 陈冠文, 等. 不同配方棉花脱叶与催熟应用技术研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2010, 47(12): 2390-2396. |
| FAN Qinglu, CHEN Yun, CHEN Guanwen, et al. Study on and venli technology of maturation and defoliation of contton under different formulations[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 47(12): 2390-2396. | |
| [13] | 曹阳, 严玉萍, 冯振秀, 等. 棉花机械采收脱叶剂应用试验及提高脱叶效果途径分析[J]. 作物杂志, 2012, (4): 144-147. |
| CAO Yang, YAN Yuping, FENG Zhenxiu, et al. Application test of defoliant for cotton mechanical harvesting and analysis of ways to improve defoliant effect[J]. Crops, 2012, (4): 144-147. | |
| [14] | 王天友, 周燕, 刘春艳, 等. 筛选对脱叶剂敏感的南疆陆地棉种质资源[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(12): 2189-2198. |
| WANG Tianyou, ZHOU Yan, LIU Chunyan, et al. Screening of Defoliant-Sensitive Upland Cotton Germplasm Resources in Southern Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(12), 2189-2198. | |
| [15] | 徐向红, 刘月娥. 喷施不同脱叶剂对棉叶中脱落酸及乙烯含量的影响[J]. 中国棉花, 2004, 31(5): 9-11. |
| XU Xianghong, LIU Yue’e. Effects of spraying different defoliants on abscisic acid and ethylene content in cotton leaves[J]. China Cotton, 2004, 31(5): 9-11. | |
| [16] | 惠基运, 肖伟, 陈春燕, 等. 喷施脱叶剂对设施桃树光合特性和果实品质的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 2019, 55(5): 676-684. |
| HUI Jiyun, XIAO Wei, CHEN Chunyan, et al. Effects of spraying defoliants on photosynthetic characteristics and fruit quality in greenhouse peach[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2019, 55(5): 676-684. | |
| [17] | 靳丁沙. 噻苯隆调控棉花叶片脱落的机制研究[D]. 华中农业大学, 2021. |
| JIN Dingsha. The Mechanism of Thidiazuron Regulating Cotton Leaf Abscission[D]. Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| [18] | 高丽丽, 李淦, 康正华, 等. 脱叶剂对棉花抗氧化酶及内源激素的影响[J]. 农药学学报, 2016, 18(4): 439-446. |
| GAO Lili, LI Gan, KANG Zhenghua, et al. Effect of defoliants on antioxidative enzyme activity and endogenous hormone contents of cotton[J]. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science, 2016, 18(4): 439-446. | |
| [19] | 高丽丽, 李淦, 康正华, 等. 脱叶剂对棉花叶片叶绿素荧光动力学参数的影响[J]. 棉花学报, 2016, 28(4): 345-352. |
| GAO Lili, LI Gan, KANG Zhenghua, et al. Effect of defoliants on chlorophyll fluorescence of cotton leaves[J]. Cotton Science, 2016, 28(4): 345-352. | |
| [20] | 常璟. 棉花离层相关基因GhBOP1的分离及功能鉴定[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2015. |
| CHANG Jing. Isolation And Function Identification of Abscission Zone Related Gene GhBOP1 of Gossypium Hirsutum L.[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2015. | |
| [21] | Giannopolitis C N, Ries S K. Superoxide dismutases[J]. Plant Physiology, 1977, 59(2): 309-314. |
| [22] | Cakmak I, Marschner H. Magnesium deficiency and high light intensity enhance activities of superoxide dismutase, ascorbate peroxidase, and glutathione reductase in bean leaves[J]. Plant Physiology, 1992, 98(4): 1222-1227. |
| [23] | 赵世杰, 许长成, 邹琦, 等. 植物组织中丙二醛测定方法的改进[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 1994, 30(3): 207-210. |
| ZHAO Shijie, XU Changcheng, ZOU Qi, et al. Improvement of determination method of malondialdehyde in plant tissues[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 1994, 30(3): 207-210. | |
| [24] | 张世英, 刘易超, 李泳潭, 等. 干旱胁迫对中华金叶榆盆栽苗内源激素的影响[J]. 西部林业科学, 2021, 50(6): 40-45. |
| ZHANG Shiying, LIU Yichao, LI Yongtan, et al. Effects of drought stress on endogenous hormones in potted seedlings of Ulmus pumila ‘jinye’[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2021, 50(6): 40-45. | |
| [25] | 马辉, 戴路, 阿布都艾尼·阿布都维力, 等. 不同脱叶剂对长绒棉性状的影响及模糊综合评价模型构建[J]. 中国棉花, 2020, 47(3): 21-24. |
| Ma Hui, Dai Lu, Abuduaini Abuduweili, et al. Effects of different defoliants on the traits of sea-island cottons and construction of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model[J]. China Cotton, 2020, 47(3): 21-24. | |
| [26] | 王灵燕, 王学军, 李锦辉, 等. 南疆棉区棉花脱叶剂的筛选[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2004, (5): 392-394. |
| WANG Lingyan, WANG Xuejun, LI Jinhui, et al. Screening of Cotton Fisleave Agent of Cotton Area in the South of Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2004,(5) : 392-394. | |
| [27] | 刘康永, 焦玚, 赵福相, 等. TDZ处理对棉花叶片脱落率及酶活性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(6): 981-991. |
| LIU Kangyong, JIAO Chang|Yang, ZHAO Fuxiang, et al. Effects of spraying TDZ on leaf loss rate and leaf enzyme activity of cotton[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(6): 981-991. | |
| [28] | 胡根海, 王清连, 张金宝, 等. 早熟棉花新材料叶绿素含量的变化规律[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2009, 48(12): 2970-2972. |
| HU Genhai, WANG Qinglian, ZHANG Jinbao, et al. Changes of chlorophyll content in new cotton varieties with short growth period[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 48(12): 2970-2972. | |
| [29] | Q Zhou, Li Y, Wang X, et al. Effects of Different Drought Degrees on Physiological Characteristics and Endogenous Hormones of Soybean[J]. Plants (Basel), 2022, 11(17). |
| [30] | 田晓莉, 段留生, 李召虎, 等. 棉花化学催熟与脱叶的生理基础[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2004, (6): 758-762. |
| TIAN Xiaoli, DUAN Liusheng, LI Zhaohu, et al. Physiological Basis of Chemical Accelerated Boll Maturation and Defoliation in Cotton[J]. Plant Physiology Newsletter, 2004, (6) : 758-762. |
| [1] | ZHOU Xin, LIU Xuanfeng, JIANG Yuhan, ZHANG Haichun, YANG Yuxin, Yeerbdati Tiemuer, JIANG Yongxin, ZHANG Li. Current situation and development proposal of mechanized recovery and resource utilization of used mulch film in cotton fields in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 131-141. |
| [2] | MIAO Hongping, WANG Xiaowei, TIAN Conghua, LI Zhi, ZHANG Yuxin, DAI Junsheng. Evolution characteristics and driving factors of cotton production and distribution in Tarim River basin [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 217-226. |
| [3] | WANG Junduo, CUI Yujiang, LIANG Yajun, GONG Zhaolong, ZHENG Junyun, LI Xueyuan. Xinjiang cotton production advantageous regional layout scheme [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 60-69. |
| [4] | ZHENG Juyun, GONG Zhaolong, LIANG Yajun, GENG Shiwei, SUN Fenglei, YANG ni, LI Xueyuan, WANG Junduo. Key technology model of machine-picked cotton production in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 70-74. |
| [5] | LI Jie, LIU Jia, WANG Liang, ZHANG Na, YANG Yanlong, ZHENG Zipiao, WEI Xin, WANG Meng, ZHOU Zixin, YANG Ni, GONG Zhaolong, HOU Xianfei, HUANG Qixiu, Abudukadier kuerban, ZHANG Jipeng, CHANG Pengzhong. Current situation of transformation and application of scientific and technological achievements of "cotton, oil and sugar" [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 89-94. |
| [6] | BIAN Qingyong, FU Yanbo, QI Tong, HUANG Jian, PU Shenghai, MENG Ajing, Halihashi Yibati. Study on influencing factors of cotton emergence and protection measures in saline-alkali land in southern Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 95-100. |
| [7] | ZHANG Zehua, YE Hanchun, WANG Zhenhua, LI Wenhao, LI Haiqiang, LIU Jian. Effects of equal nitrogen applied with urease inhibitor on cotton growth, yield, and quality under mulched drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2103-2111. |
| [8] | CHEN Ruijie, LUO Linyi, RUAN Xiangyang, YE Jun. Effects of humic acid on soil nutrients, cotton yield and quality in cotton fields under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2112-2121. |
| [9] | HUANG Boxuan, LI Pengcheng, ZHENG Cangsong, SUN Miao, SHAO Jingjing, FENG Weina, PANG Chaoyou, XU Wenxiu, DONG Helin. Effects of different nitrogen inhibitors on growth, nitrogen utilization and yield of cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2122-2131. |
| [10] | WANG Chao, XU Wenxiu, LI Pengcheng, ZHENG Cangsong, SUN Miao, FENG Weina, SHAO Jingjing, DONG Helin. Response of cotton seedling growth and development to soil available potassium levels [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2132-2139. |
| [11] | ZHANG Tingjun, LI Zihui, CUI Yujiang, SUN Xiaogui, CHEN Fang. Effects of microbial agents on cotton growth and soil physico-chemical properties [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2269-2276. |
| [12] | Paziliye Ahemati, WANG Xinyong, ZHOU Yan, SONG Bin, Yusuf Abulitifu. Effects of microbial inoculants on physiological and photosynthetic characteristics of walnut leaves [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2299-2306. |
| [13] | DONG Zhiduo, XU Fei, FU Qiuping, HUANG Jian, QI Tong, MENG Ajing, FU Yanbo, Kaisaier Kuerban. Effects of different types of salt and alkali stress on cotton seed germination [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1831-1844. |
| [14] | LI Suocheng, LIU Yantao, DONG Hongye, SUN Zhenbo, LI Ziwei, ZHANG Chunyuan, WANG Kaiyong, LI Qiang, YANG Mingfeng. Effects of potassium nutrition on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of peanut [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1926-1936. |
| [15] | LI Ying, GUO Wenwen, LI Jiangbo, QU Yanying, CHEN Quanjia, ZHENG Kai. Evaluation of adaptability of 90 BT transgenic insectresistant cotton varieties (lines) in early cotton areas of Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1561-1573. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||