

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (11): 2684-2692.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.11.009
• Germplasm Resources·Molecular Genetics·Physiology and Biochemistry·Microbes • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHENG Yunxia1( ), TAN Zhanming1(
), TAN Zhanming1( ), GUO Ling1, LI Wenwen2, DU Jiageng1
), GUO Ling1, LI Wenwen2, DU Jiageng1
Received:2024-05-15
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2025-01-08
Correspondence author:
TAN Zhanming
Supported by:
程云霞1( ), 谭占明1(
), 谭占明1( ), 郭玲1, 李雯雯2, 杜佳庚1
), 郭玲1, 李雯雯2, 杜佳庚1
通讯作者:
谭占明
作者简介:程云霞(1996-),女,新疆石河子人,讲师,研究方向为设施园艺植物栽培与生理生态,(E-mail)chengyunxia2018@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
CHENG Yunxia, TAN Zhanming, GUO Ling, LI Wenwen, DU Jiageng. Effects of different drought stresses on anatomical structure of roots, stems and leaves of two apricot varieties[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2684-2692.
程云霞, 谭占明, 郭玲, 李雯雯, 杜佳庚. 不同干旱胁迫对野生山杏和人工栽培山杏品种根茎叶解剖结构的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2684-2692.
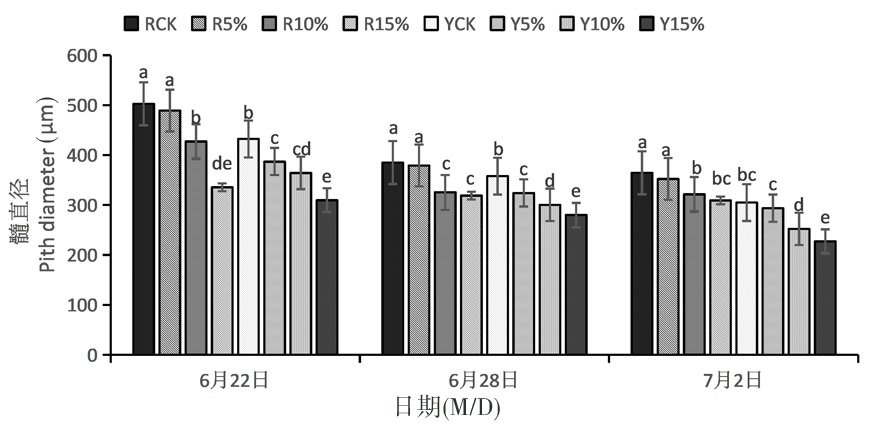
Fig.1 Changes of drought stress on pith diameter of two apricot cultivars Notes:The different letters above the error line show significant differences,the same as below
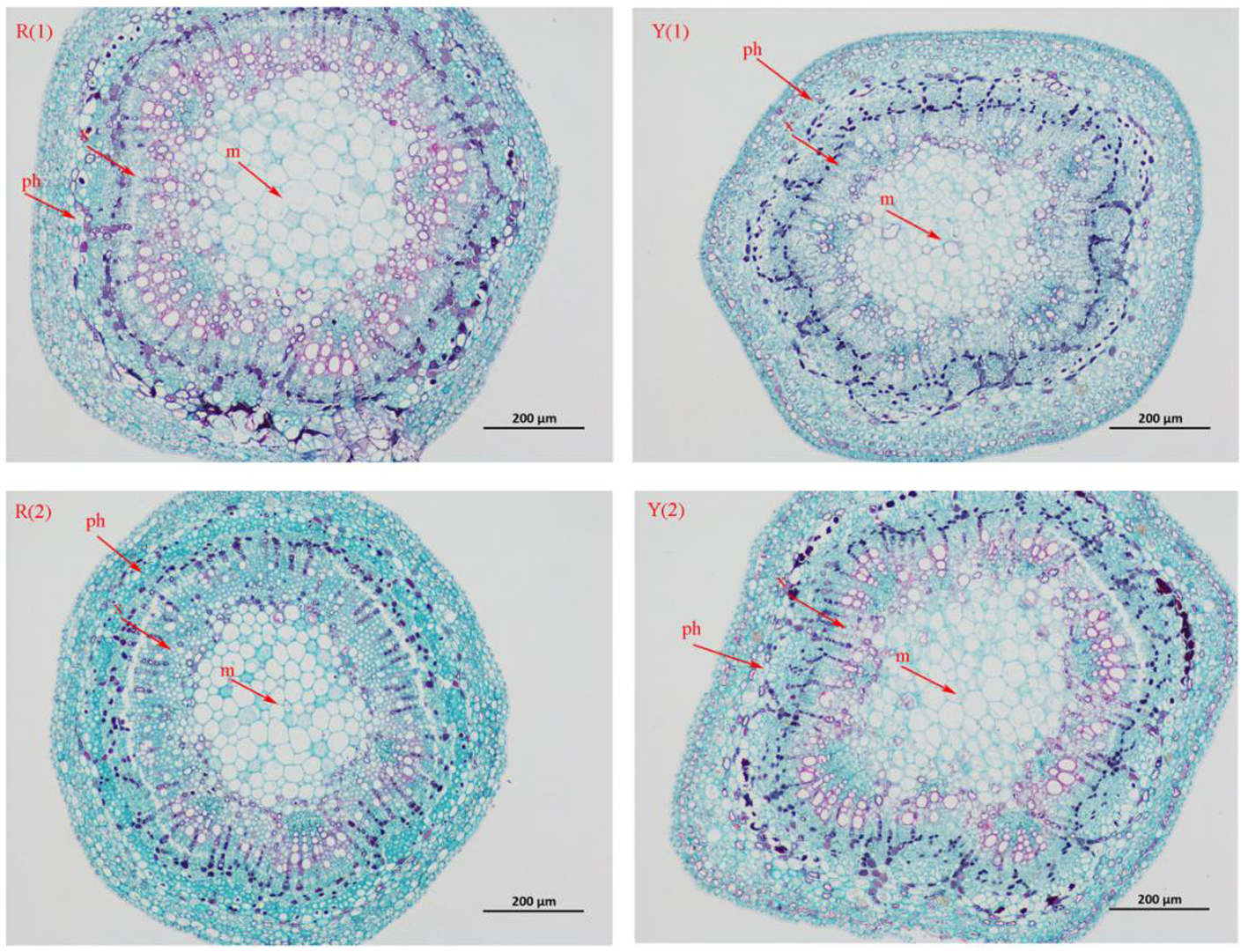
Fig.9 Changes of stem anatomy of two apricot cultivars under drought stress Notes:R(1)The cultivated varieties grew normally;R(2) The cultivated varieties grew under drought stress;Y(1) The wild variety grows normally;Y(2) Wild varieties grow under drought stress;x-Xylem;ph-Phloem;m-Marrow,the same as below
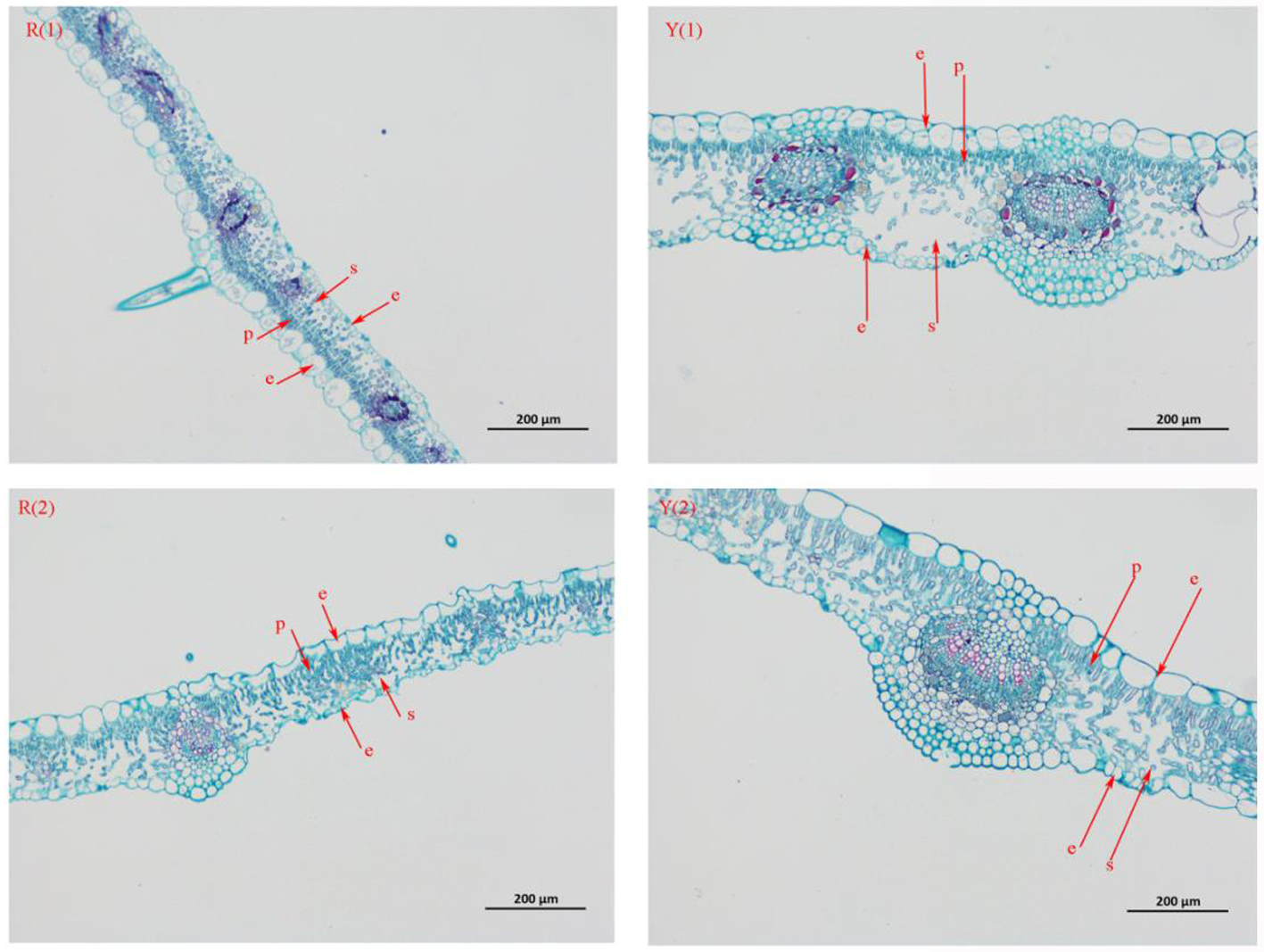
Fig.10 Changes of stem anatomy of two apricot varieties under drought stress Notes:R(1)The cultivated varieties grew normally;R(2) The cultivated varieties grew under drought stress;Y(1) The wild variety grows normally;Y(2) Wild varieties grow under drought stress;e-Epidermic structure;p-Palisade;cell;s-Spongy tissue;the same as below,the same as below
| 种类 Type | 第一 主成分 得分 First principal component score | 第二 主成分 得分 Second principal component score | 第三 主成分 得分 Third principal component score | 综合 得分 Compre- hensive score | 综合 排名 Compre- hensive ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCK | -7.86 | -1.13 | 1.29 | -5.28 | 8 |
| R5% | -2.83 | 1.25 | 0.76 | -1.61 | 6 |
| R10% | 0.66 | 0.2 | 0.66 | 0.56 | 4 |
| R15% | 4.21 | 2.11 | 0.23 | 3.18 | 2 |
| YCK | -4.99 | 0.17 | -2.11 | -3.6 | 7 |
| Y5% | -0.98 | -0.15 | -0.73 | -0.78 | 5 |
| Y10% | 3.78 | -1.46 | -0.07 | 2.31 | 3 |
| Y15% | 8.02 | -0.99 | -0.04 | 5.23 | 1 |
Tab.1 Comprehensive scores and comprehensive ranking of drought resistance of two apricot varieties with different treatments
| 种类 Type | 第一 主成分 得分 First principal component score | 第二 主成分 得分 Second principal component score | 第三 主成分 得分 Third principal component score | 综合 得分 Compre- hensive score | 综合 排名 Compre- hensive ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCK | -7.86 | -1.13 | 1.29 | -5.28 | 8 |
| R5% | -2.83 | 1.25 | 0.76 | -1.61 | 6 |
| R10% | 0.66 | 0.2 | 0.66 | 0.56 | 4 |
| R15% | 4.21 | 2.11 | 0.23 | 3.18 | 2 |
| YCK | -4.99 | 0.17 | -2.11 | -3.6 | 7 |
| Y5% | -0.98 | -0.15 | -0.73 | -0.78 | 5 |
| Y10% | 3.78 | -1.46 | -0.07 | 2.31 | 3 |
| Y15% | 8.02 | -0.99 | -0.04 | 5.23 | 1 |
| [1] | 谭占明, 张朋朋, 吴翠云, 等. 干旱胁迫对两个杏品种的生长和生理指标的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2020,(8): 50-54. |
| TAN Zhanming, ZHANG Pengpeng, WU Cuiyun, et al. Effects of drought stress on growth and physiological indicators of two apricot varieties[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2020,(8): 50-54. | |
| [2] | 丁龙, 赵慧敏, 曾文静, 等. 五种西北旱区植物对干旱胁迫的生理响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(5): 1455-1463. |
| DING Long, ZHAO Huimin, ZENG Wenjing, et al. Physiological responses of five plants in Northwest China arid area under drought stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(5): 1455-1463. | |
| [3] |
Borrell A K, Mullet J E, George-Jaeggli B, et al. Drought adaptation of stay-green sorghum is associated with canopy development, leaf anatomy, root growth, and water uptake[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2014, 65(21): 6251-6263.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
刘玉冰, 李新荣, 李蒙蒙, 等. 中国干旱半干旱区荒漠植物叶片(或同化枝)表皮微形态特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2016, 40(11): 1189-1207.
DOI |
|
LIU Yubing, LI Xinrong, LI Mengmeng, et al. Leaf(or assimilation branch) epidermal micromorphology of desert plant in arid and semiarid areas of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2016, 40(11): 1189-1207.
DOI |
|
| [5] | 杜华栋, 焦菊英, 寇萌, 等. 黄土高原先锋种猪毛蒿叶片形态解剖与生理特征对立地的适应性[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(10): 2914-2925. |
| DU Huadong, JIAO Juying, KOU Meng, et al. Adaptability of foliar morphological, anatomical, and physiological characteristics of the pioneer species Artemisia scoparia growing in a hilly-gully Loess Region at different slope sites[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(10): 2914-2925. | |
| [6] | 马亚丽, 王璐, 刘艳霞, 等. 荒漠植物几种主要附属结构的抗逆功能及其协同调控的研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2015, 51(11): 1821-1836. |
| MA Yali, WANG Lu, LIU Yanxia, et al. Uptates on stress tolerance of main accessory structures and their synergetic interaction in desert plants[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2015, 51(11): 1821-1836. | |
| [7] | 卓仁英, 陈益泰. 木本植物抗涝性研究进展[J]. 林业科学研究, 2001, 14(2): 215-222. |
| ZHUO Renying, CHEN Yitai. Advances in waterlogging-resistance of woody plants[J]. Forest Research, 2001, 14(2): 215-222. | |
| [8] | 杨赵平, 贾露. 塔里木盆地碱蓬属6种植物叶的解剖学研究[J]. 西部林业科学, 2011, 40(2): 36-39. |
| YANG Zhaoping, JIA Lu. Anatomy of leaves from 6 types of Suaeda in Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2011, 40(2): 36-39. | |
| [9] | 赵金花, 李青丰. 内蒙古荒漠草原三种野生葱属植物解剖结构的抗旱性分析[J]. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 41(2): 201-205, 241-242. |
| ZHAO Jinhua, LI Qingfeng. Drought resistance analysis based on anatomical structures of three Wild Allium in Inner Mongolia arid grassland[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia University, 2010, 41(2): 201-205, 241-242. | |
| [10] | 任尚福. 南疆蒺藜科三种植物叶解剖结构及生态适应性[J]. 喀什师范学院学报, 2010, 31(3): 52-55. |
| REN Shangfu. Study on anatomical structure of leaf o three zygophyllaceaes of South Xinjiang and ecology adaptability[J]. Journal of Kashgar Teachers College, 2010, 31(3): 52-55. | |
| [11] | 杜华栋, 徐翠红, 刘萍, 等. 陕北黄土高原优势植物叶片解剖结构的生态适应性[J]. 西北植物学报, 2010, 30(2): 293-300. |
| DU Huadong, XU Cuihong, LIU Ping, et al. Foliar anatomical structures and ecological adaptabilities of dominant plants in the North Shaanxi Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2010, 30(2): 293-300. | |
| [12] | 廖声熙, 刘娟, 和菊, 等. 印楝叶解剖结构与抗旱性关系初步研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 2001, 14(4): 435-440. |
| LIAO Shengxi, LIU Juan, HE Ju, et al. A study on the relationship between anatomical structure of leaves and resistance drought of neem (Azadirachta indica)[J]. Forest Research, 2001, 14(4): 435-440. | |
| [13] | 杨赵平, 刘琴, 李志军. 胡杨雌雄株叶片的比较解剖学研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 2011, 31(1): 79-83. |
| YANG Zhaoping, LIU Qin, LI Zhijun. Leaf blade comparative anatomy between the female and the male of Populus euphratica oliv[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2011, 31(1): 79-83. | |
| [14] | 白重炎, 高巨营, 张朝. 13种核桃茎的解剖结构与其抗寒抗旱性研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2011, 39(27): 16496-16498,16502. |
| BAI Zhongyan, GAO Juying, ZHANG Zhao. Study on the anatomical structure and cold and drought resistance of 13 varieties of walnut caudices[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 39(27): 16496-16498, 16502. | |
| [15] | 丁菲, 杨帆, 李德龙, 等. 构树解剖结构特征与抗旱性研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(36): 20949-20952. |
| DING Fei, YANG Fan, LI Delong, et al. Studies on the anatomical structure characteristics and drought resistance of Broussonetia papyrifera[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(36): 20949-20952. | |
| [16] | 孟庆辉, 潘青华, 鲁韧强, 等. 4个品种扶芳藤茎叶解剖结构及其与抗旱性的关系[J]. 中国农学通报, 2006, 22(4): 138-142. |
| MENG Qinghui, PAN Qinghua, LU Renqiang, et al. The study on anatomical structure and drought-resistant of stem and leaves of four Euonymus fortunei[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2006, 22(4): 138-142. | |
| [17] | 胡云, 燕玲, 李红. 14种荒漠植物茎的解剖结构特征分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2006, 20(1): 202-208. |
| HU Yun,YAN Ling, LI Hong. Studies on the anatomical characteristics of the stems of 14 desert plants[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2006, 20(1): 202-208. | |
| [18] | Kulkarni M, Deshpande U. Comparative studies in stem anatomy and morphology in relation to drought resistance in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum)[J]. American Journal of Plant Physiology, 2005, 1(1): 82-88. |
| [19] |
任媛媛, 刘艳萍, 王念, 等. 9种屋顶绿化阔叶植物叶片解剖结构与抗旱性的关系[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 38(4): 64-68.
DOI |
| REN Yuanyuan, LIU Yanping, WANG Nian, et al. The relationship between leaf anatomic structure and drought resistance of nine broadleaf plants[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2014, 38(4): 64-68. | |
| [20] | 陈燕, 刘锴栋, 黎海利, 等. 5种红树植物的叶片结构及其抗逆性比较[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2014, 42(7): 27-31, 68. |
| CHEN Yan, LIU Kaidong, LI Haili, et al. Leaf stuctures and stress resistance in five mangrove species[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2014, 42(7): 27-31, 68. | |
| [21] | 胡亦民, 胡奕文, 宋朝辉, 等. 太行山区常见绿化树种叶片栅栏组织与植物耐旱性的相关性分析[J]. 北方园艺, 2012,(14): 68-69. |
| HU Yimin, HU Yiwen, SONG Zhaohui, et al. Correlation analysis between the palisade tissue of common greening species leaves in Taihang moutain and the drought tolerance of plants[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2012,(14): 68-69. | |
| [22] | 潘存娥, 田丽萍, 李贞贞, 等. 5种杨树无性系叶片解剖结构的抗旱性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(2): 21-25. |
|
PAN Cune, TIAN Liping, LI Zhenzhen, et al. Studies on drought resistance on anatomical structure of leaves of 5 poplar clones[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(2): 21-25.
DOI |
|
| [23] | 王贝贝, 孙虹豆, 江文, 等. 两种地被植物生长、叶片解剖结构及光合特性对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 天津农业科学, 2017, 23(3): 1-5. |
| WANG Beibei, SUN Hongdou, JIANG Wen, et al. Responses of growth, leaf anatomical structure and photosynthetic characteristics of two ground cover plants to drought stress[J]. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 23(3): 1-5. | |
| [24] | 张敏娟, 李昭良, 焦锋, 等. 8个桑品种的植株茎叶解剖结构及与耐旱性的关联分析[J]. 蚕业科学, 2018, 44(4): 516-522. |
| ZHANG Minjuan, LI Zhaoliang, JIAO Feng, et al. Anatomical structures of stem and leaf from eight mulberry varieties and their correlationship with drought tolerance[J]. Science of Sericulture, 2018, 44(4): 516-522. | |
| [25] | 缪丽华, 王莹莹, 乔东东, 等. 香菇草匍匐茎及叶结构对不同水湿生境的生态适应性[J]. 湿地科学与管理, 2018, 14(3): 45-49. |
| MIAO Lihua, WANG Yingying, QIAO Dongdong, et al. Ecological adaptability of stolon and leaf anatomical structure of Hydrocotyle vulgaris to various water conditions[J]. Wetland Science & Management, 2018, 14(3): 45-49. |
| [1] | ZHANG Shuai, GAO Guowen, WU Lili, ZHAO Haiyan, WANG Xiaowu, FU Kaiyun, JIA Zunzun, Tuerxun Ahemaiti, DING Xinhua, LI Kemei, GUO Wenchao. Evaluation of the synergistic application of seed coating agents, synergists, and micro fertilizers for the prevention and control of corn stem rot disease [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 19-27. |
| [2] | ZENG Wanying, GENG Hongwei, CHENG Yukun, LI Sizhong, QIAN Songting, GAO Weishi, ZHANG Liming. Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance during the rapid growth stage of sugar beet cultivars [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2140-2151. |
| [3] | Areziguli Tuxun, GAO Jie. Effects of drought stress and planting density on physiological characteristics and yield of onion bulblets [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2211-2222. |
| [4] | LUO Hao, JIAN Zhengbo, SUN Tingting, WANG Yuelin, SHAN Nana, YANG Zhiying. Study on the trade-off and synergy of ecosystem services in extreme arid areas under multi scenario land use changes [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2245-2256. |
| [5] | YAO Shiyu, WANG Jie, HUANG Wenjuan, JIAO Peipei, PENG Chengzhi, XIONG Dan, CHEN Yue, WANG Xin. Effects of different saline environments on anatomical structure and ion content of Populus euphratica leaves [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 2004-2013. |
| [6] | ZHANG Yiran, Yeerjiang Baiketuerhan, Baihetiguli Kayier, QI Zhiying. Spatial distribution pattern and prediction of Rhus typhina L. roots sucker in urban green space system [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 2023-2033. |
| [7] | JU Le, QI Juncang, NIU Yinting, SHI Peichun, SONG Ruijiao, SONG Lingyu, YIN Zhigang, CHEN Peiyu, QIANG Xuelan. RNA-seq-based mining and analysis of drought-related genes in barley seedlings [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(5): 1077-1084. |
| [8] | ZHANG Yijia, CHENG Ping, WANG Lei, WU Sheng li. Effects of different irrigation rates on physiological characteristics, yield and quality of dwarfed close-planted apple trees [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(5): 1140-1150. |
| [9] | LIU Junqing, LIANG Guocheng, ZHANG Xin, WANG Qingyong, ZHAO Jinghua. Study on spatial distribution characteristics of walnut root system under regulated deficit drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(5): 1160-1171. |
| [10] | YAN Rong, ZHOU Xiaoyun, ZHANG Jungao, WANG Li, LI Jin, LIANG Jing, GONG Jingyun, DU Yu, LI Kemei, LEI Bin. Identification and biological characterization of the root rot pathogen of wheat in Xinjiang caused by Bipolaris sorokiniana [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(5): 1209-1217. |
| [11] | DONG Zhaosen, ZHANG Jiaxi, ZHOU Xin, LUO Wenjie, JIANG Yongxin, GUO Gang. Design and experiment of stress and strain monitoring system for soil loosening device based on wireless communication technology [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 1029-1040. |
| [12] | QIAN Tao, WU Lili, LI Lei, Anniwaer Kuerban, DING Ruifeng. Control effect of pyroxasulfone mixed with pendimethalin on broadleaf weeds in cotton filed and its safety evaluation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 861-868. |
| [13] | YANG Wenli, XU Lirong, LIU Bin, LING Yueming, LI Meihua, YANG Yong, FAN Rong, LI Yushun, ZHANG Yongbin, ZHANG Xuejun. Effects of salt stress on ion balance, membrane lipid peroxidation, and osmotic regulation substance accumulation in thin skin muskmelon ‘Huishu’ [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 900-907. |
| [14] | Mahemuti Abulaiti, Muhetaer zhare, Mireguli Waili, Hadier Yishake. Correlation and regression analysis between leaf margin scorch diseases and leaf nutrient content of walnut [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 945-953. |
| [15] | ZHANG Wei, YANG Guohui, YU Hui. Effects of 2,4-epibrassinolide on growth and related genes expression of watermelon seedlings under drought Stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(3): 615-622. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 17
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 87
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||