

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (11): 2693-2704.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.11.010
• Crop Genetics and Breeding·Cultivation Physiology • Previous Articles Next Articles
YU Qiuhong1( ), XU Panyun2, GUO Chunmiao2, Dilixiati Hasimu1, Mubareke Ayoupu1(
), XU Panyun2, GUO Chunmiao2, Dilixiati Hasimu1, Mubareke Ayoupu1( )
)
Received:2024-04-19
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2025-01-08
Correspondence author:
Mubareke Ayoupu
Supported by:
于秋红1( ), 许盼云2, 郭春苗2, 迪利夏提·哈斯木1, 木巴热克·阿尤普1(
), 许盼云2, 郭春苗2, 迪利夏提·哈斯木1, 木巴热克·阿尤普1( )
)
通讯作者:
木巴热克·阿尤普
作者简介:于秋红(1998-),女,河北沧州人,硕士研究生,研究方向为植物逆境生理,(E-mail)2074276722@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
YU Qiuhong, XU Panyun, GUO Chunmiao, Dilixiati Hasimu, Mubareke Ayoupu. Relationship between the anatomical structure of xylem and embolization characteristics of drought tolerant rootstocks of almond[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2693-2704.
于秋红, 许盼云, 郭春苗, 迪利夏提·哈斯木, 木巴热克·阿尤普. 扁桃耐旱砧木木质部解剖结构与栓塞特性的关系分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2693-2704.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.xjnykx.com/EN/10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.11.010
| 项目Items | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height(cm) | 43.69±1.19bc | 53.60±1.52a | 49.80±3.93ab | 49.90±3.49ab | 52.82±3.59a |
| 基径 Stem diameter(mm) | 6.21±0.35b | 5.00±0.25de | 4.80±0.62de | 3.94±0.14e | 5.43±0.37cd |
| 侧枝长度 Lateral branch length(cm) | 14.01±0.66b | 25.66±2.89a | 18.62±3.40b | 29.41±3.65a | 18.58±1.21b |
| 侧枝直径 Lateral branch diameter(mm) | 2.15±0.06a | 2.26±0.17a | 1.97±0.21a | 1.99±0.16a | 2.11±0.47a |
| 单株叶片数 Leaf number per plant | 282±22ab | 156±28bc | 127±36bc | 98±11c | 180±39bc |
| 平均叶长 Average leaf length(cm) | 3.88±0.05c | 5.74±0.15b | 7.03±0.26a | 7.37±0.16a | 7.69±0.16a |
| 平均叶宽 Average leaf width(cm) | 1.21±0.02c | 1.92±0.09a | 1.75±0.04b | 2.04±0.05a | 1.71±0.03b |
| 平均叶柄长 Average petiole length(cm) | 0.59±0.01c | 0.78±0.06ab | 0.56±0.03cd | 0.76±0.05b | 0.30±0.03e |
Tab.1 Basic situation of samplings of almond rootstock seedlings (Mean ± SE)
| 项目Items | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height(cm) | 43.69±1.19bc | 53.60±1.52a | 49.80±3.93ab | 49.90±3.49ab | 52.82±3.59a |
| 基径 Stem diameter(mm) | 6.21±0.35b | 5.00±0.25de | 4.80±0.62de | 3.94±0.14e | 5.43±0.37cd |
| 侧枝长度 Lateral branch length(cm) | 14.01±0.66b | 25.66±2.89a | 18.62±3.40b | 29.41±3.65a | 18.58±1.21b |
| 侧枝直径 Lateral branch diameter(mm) | 2.15±0.06a | 2.26±0.17a | 1.97±0.21a | 1.99±0.16a | 2.11±0.47a |
| 单株叶片数 Leaf number per plant | 282±22ab | 156±28bc | 127±36bc | 98±11c | 180±39bc |
| 平均叶长 Average leaf length(cm) | 3.88±0.05c | 5.74±0.15b | 7.03±0.26a | 7.37±0.16a | 7.69±0.16a |
| 平均叶宽 Average leaf width(cm) | 1.21±0.02c | 1.92±0.09a | 1.75±0.04b | 2.04±0.05a | 1.71±0.03b |
| 平均叶柄长 Average petiole length(cm) | 0.59±0.01c | 0.78±0.06ab | 0.56±0.03cd | 0.76±0.05b | 0.30±0.03e |
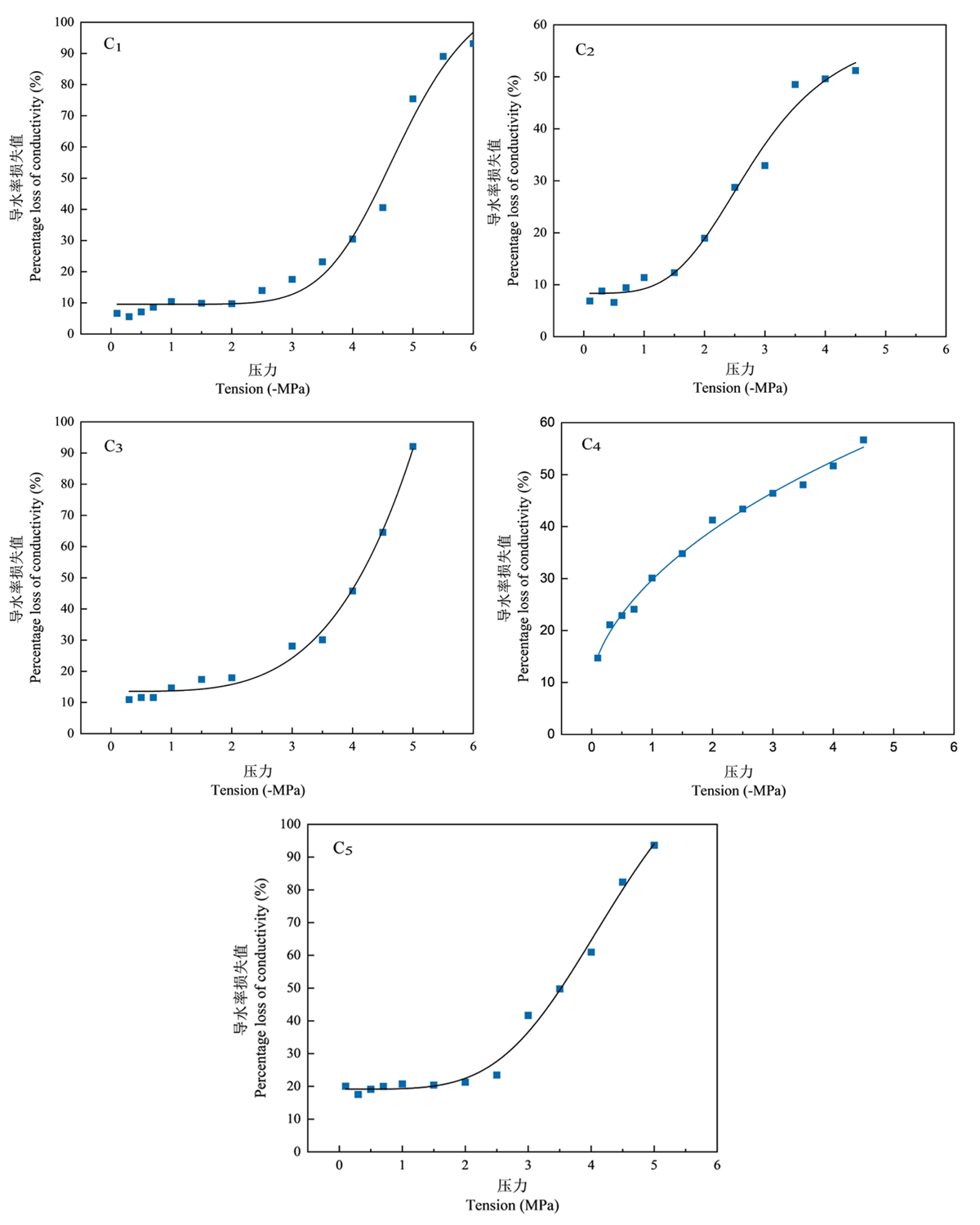
Fig.1 Stem xylem embolism vulnerability curves of different germplasm resources of almond Notes: C1: Dabadan; C2: Kubadan; C3:Tianrentaobadan; C4: Kurentaobadan; C5:Peach
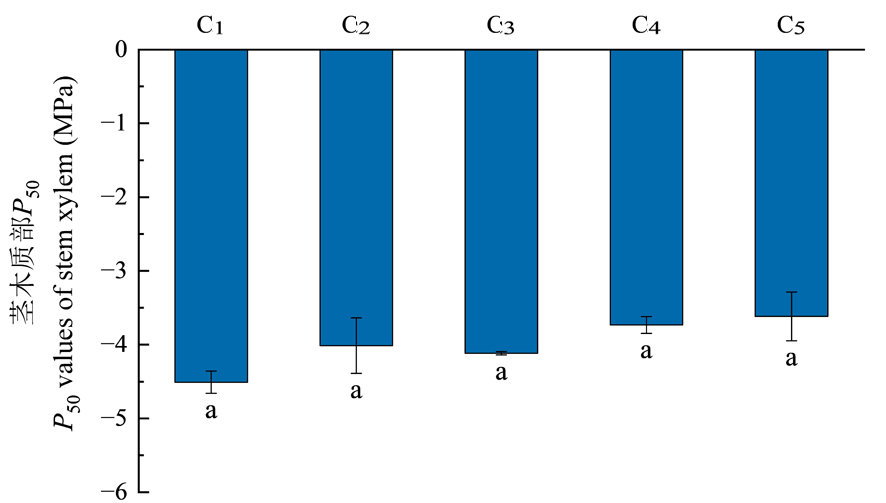
Fig.2 Vulnerability of stem xylem embolism in different rootstock resources of almond (Mean ± SE) Notes: C1: Dabadan; C2: Kubadan; C3: Tianrentaobadan; C4: Kurentaobadan; C5: Peach; Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in the same index between different rootstock resources in the same group (P<0.05)
| 修复时间 Repair time(min) | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 9.75±0.36Ba | 12.05±0.76Ba | 14.62±0.26Ca | 12.30±1.24Ca | 10.88±2.17Ca |
| 80 | 12.61±1.53Bb | 25.25±5.72ABab | 21.26±5.44BCab | 24.92±1.24Bab | 29.50±5.90Ba |
| 130 | 24.81±3.76Ab | 32.35±6.72Ab | 29.53±4.82Bb | 46.07±2.41Aa | 54.46±1.57Ab |
| 180 | 30.73±5.68Ac | 40.28±5.65Abc | 52.01±0.65Aa | 49.79±1.16Aab | 59.52±0.53Aa |
Tab.2 Repair percentage of stem xylem embolism in different rootstock resources of almond (Mean ± SE) (%)
| 修复时间 Repair time(min) | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 9.75±0.36Ba | 12.05±0.76Ba | 14.62±0.26Ca | 12.30±1.24Ca | 10.88±2.17Ca |
| 80 | 12.61±1.53Bb | 25.25±5.72ABab | 21.26±5.44BCab | 24.92±1.24Bab | 29.50±5.90Ba |
| 130 | 24.81±3.76Ab | 32.35±6.72Ab | 29.53±4.82Bb | 46.07±2.41Aa | 54.46±1.57Ab |
| 180 | 30.73±5.68Ac | 40.28±5.65Abc | 52.01±0.65Aa | 49.79±1.16Aab | 59.52±0.53Aa |
| 项目 Items | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 导管直径 Vessel diameter(μm) | 16.65±0.26c | 18.27±0.63b | 16.58±0.44c | 19.66±0.51b | 22.45±0.52a |
| 连接导管壁厚度 Intervessel wall thickness(μm) | 5.84±0.26a | 6.37±0.32a | 4.87±0.20b | 6.11±0.41a | 4.66±0.26b |
| 单导管指数 Solitary vessel index | 0.73±0.01bc | 0.74±0.01b | 0.72±0.01bc | 0.83±0.01a | 0.70±0.01c |
| 导管密度 Vessel density(mm-2) | 354.50±23.22ab | 384.27±27.37a | 413.59±31.08a | 282.12±31.78b | 332.25±17.69ab |
| 导管组指数 Vessel grouping index | 1.40±0.02ab | 1.37±0.03b | 1.45±0.02a | 1.25±0.01c | 1.46±0.02a |
| 导管壁理论机械强度 Theoretical vessel implosion resistance | 0.13±0.01a | 0.13±0.02a | 0.09±0.01a | 0.10±0.02a | 0.04±0.01b |
| 导管水力直径 Hydraulic diameter of vessel(μm) | 18.48±0.42c | 20.80±0.80b | 18.26±0.38c | 21.87±0.52b | 24.68±0.71a |
| 木材密度 Wood density(g/cm3) | 0.73±0.01a | 0.69±0.01a | 0.64±0.02b | 0.60±0.02b | 0.51±0.02c |
| 纹孔膜面积 Pit membrane(μm2) | 11.82±3.18a | 17.69±1.44a | 19.49±3.18a | 14.55±3.96a | 14.94±3.15a |
| 纹孔膜直径 Pit membrane diameter(μm) | 3.81±0.50a | 4.73±0.19a | 4.96±0.39a | 4.22±0.59a | 4.32±0.50a |
| 微孔面积 Microporous area(nm2) | 494.85±66.75b | 499.76±24.51b | 647.11±75.07b | 632.35±38.55b | 962.32±86.81a |
| 微孔直径 Microporous diameter(nm) | 24.69±1.86b | 24.98±0.31b | 28.63±1.48b | 28.24±0.72b | 34.84±1.61a |
Tab.3 Differences in the anatomical structure of the stem xylem of different rootstock resources of almond (Mean ± SE)
| 项目 Items | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 导管直径 Vessel diameter(μm) | 16.65±0.26c | 18.27±0.63b | 16.58±0.44c | 19.66±0.51b | 22.45±0.52a |
| 连接导管壁厚度 Intervessel wall thickness(μm) | 5.84±0.26a | 6.37±0.32a | 4.87±0.20b | 6.11±0.41a | 4.66±0.26b |
| 单导管指数 Solitary vessel index | 0.73±0.01bc | 0.74±0.01b | 0.72±0.01bc | 0.83±0.01a | 0.70±0.01c |
| 导管密度 Vessel density(mm-2) | 354.50±23.22ab | 384.27±27.37a | 413.59±31.08a | 282.12±31.78b | 332.25±17.69ab |
| 导管组指数 Vessel grouping index | 1.40±0.02ab | 1.37±0.03b | 1.45±0.02a | 1.25±0.01c | 1.46±0.02a |
| 导管壁理论机械强度 Theoretical vessel implosion resistance | 0.13±0.01a | 0.13±0.02a | 0.09±0.01a | 0.10±0.02a | 0.04±0.01b |
| 导管水力直径 Hydraulic diameter of vessel(μm) | 18.48±0.42c | 20.80±0.80b | 18.26±0.38c | 21.87±0.52b | 24.68±0.71a |
| 木材密度 Wood density(g/cm3) | 0.73±0.01a | 0.69±0.01a | 0.64±0.02b | 0.60±0.02b | 0.51±0.02c |
| 纹孔膜面积 Pit membrane(μm2) | 11.82±3.18a | 17.69±1.44a | 19.49±3.18a | 14.55±3.96a | 14.94±3.15a |
| 纹孔膜直径 Pit membrane diameter(μm) | 3.81±0.50a | 4.73±0.19a | 4.96±0.39a | 4.22±0.59a | 4.32±0.50a |
| 微孔面积 Microporous area(nm2) | 494.85±66.75b | 499.76±24.51b | 647.11±75.07b | 632.35±38.55b | 962.32±86.81a |
| 微孔直径 Microporous diameter(nm) | 24.69±1.86b | 24.98±0.31b | 28.63±1.48b | 28.24±0.72b | 34.84±1.61a |

Fig.4 Cross-sectional anatomical structure of stem xylem of different rootstock resources of almond Notes: C1: Dabadan; C2: Kubadan; C3: Tianrentaobadan; C4: Kurentaobadan; C5:Peach
| [1] | 木巴热克·阿尤普,伊丽米努尔, 荆卫民. 不同水分处理下几种柽柳属植物幼株木质部栓塞及其解剖结构特征[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(10): 42-52. |
| Mubareke Ayoupu, Yiliminuer, JING Weimin. Xylem anatomical features and native xylem embolism of several Tamarix spp.species seedlings under different water treatments[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2017, 39(10): 42-52. | |
| [2] | McDowell N G, Beerling D J, Breshears D D, et al. The interdependence of mechanisms underlying climate-driven vegetation mortality[J]. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 2011, 26(10): 523-532. |
| [3] |
Nardini A, Battistuzzo M, Savi T. Shoot desiccation and hydraulic failure in temperate woody angiosperms during an extreme summer drought[J]. New Phytologist, 2013, 200(2): 322-329.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Domec J C, Gartner B L. Cavitation and water storage capacity in Bole xylem segments of mature and young Douglas-fir trees[J]. Trees, 2001, 15(4): 204-214. |
| [5] | Choat B, Jansen S, Brodribb T J, et al. Global convergence in the vulnerability of forests to drought[J]. Nature, 2012, 491(7426): 752-755. |
| [6] | 党维. 耐旱树种木质部栓塞恢复状况的研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2016. |
| DANG Wei. The Refilling of Embolized Xylem of Drought-tolerant Tree Species[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2016. | |
| [7] | Awad H, Barigah T, Badel E, et al. Poplar vulnerability to xylem cavitation acclimates to drier soil conditions[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2010, 139(3): 280-288. |
| [8] |
Ogasa M, Miki N H, Murakami Y, et al. Recovery performance in xylem hydraulic conductivity is correlated with cavitation resistance for temperate deciduous tree species[J]. Tree Physiology, 2013, 33(4): 335-344.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Rolland V, Bergstrom D M, Lenné T, et al. Easy come, easy go: capillary forces enable rapid refilling of embolized primary xylem vessels[J]. Plant Physiology, 2015, 168(4): 1636-1647.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Love D M, Sperry J S. In situ embolism induction reveals vessel refilling in a natural aspen stand[J]. Tree Physiology, 2018, 38(7): 1006-1015. |
| [11] | 孟凤. 七种槭树科植物木质部栓塞及其恢复与植物抗旱性的关系[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2019. |
| MENG Feng. The Relationship between Xylem Embolism and Embolism Recovery and Plant Drought Resistance in Seven Genus Acer[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2019. | |
| [12] |
McCulloh K A, Meinzer F C. Further evidence that some plants can lose and regain hydraulic function daily[J]. Tree Physiology, 2015, 35(7): 691-693.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | Hacke U G, Jansen S. Embolism resistance of three boreal conifer species varies with pit structure[J]. The New Phytologist, 2009, 182(3): 675-686. |
| [14] | Plavcová L, Hacke U G, Sperry J S. Linking irradiance-induced changes in pit membrane ultrastructure with xylem vulnerability to cavitation[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2011, 34(3): 501-513. |
| [15] |
Levionnois S, Kaack L, Heuret P, et al. Pit characters determine drought-induced embolism resistance of leaf xylem across 18 Neotropical tree species[J]. Plant Physiology, 2022, 190(1): 371-386.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Avila R T, Kane C N, Batz T A, et al. The relative area of vessels in xylem correlates with stem embolism resistance within and between Genera[J]. Tree Physiology, 2023, 43(1): 75-87. |
| [17] | Christensen-Dalsgaard K K, Tyree M T. Frost fatigue and spring recovery of xylem vessels in three diffuse-porous trees in situ[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2014, 37(5): 1074-1085. |
| [18] | 党维, 姜在民, 李荣, 等. 6个树种1年生枝木质部的水力特征及与栓塞修复能力的关系[J]. 林业科学, 2017, 53(3): 49-59. |
| DANG Wei, JIANG Zaimin, LI Rong, et al. Relationship between hydraulic traits and refilling of embolism in the xylem of one-year-old twigs of six tree species[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2017, 53(3): 49-59. | |
| [19] | 李美琦, 姜在民, 赵涵, 等. 加杨水力学与生理特性对不同土壤水分条件响应研究[J]. 植物生理学报, 2017, 53(4): 632-640. |
| LI Meiqi, JIANG Zaimin, ZHAO Han, et al. Study on the adaptability of hydraulic and physiological characteristics to different soil moisture conditions in Populus x canadensis Moench[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2017, 53(4): 632-640. | |
| [20] | 梁艳霞, 张亚楠, 王占和. 扁桃薄壳品种‘蒙特瑞’在山西中部地区的引种表现及栽培技术[J]. 果树资源学报, 2022, 3(6): 88-90. |
| LIANG Yanxia, ZHANG Yanan, WANG Zhanhe. Introduction performance and cultivation technology of the thin-shelled variety 'Monterey' of lentil in central Shanxi[J]. Journal of Fruit Tree Resource, 2022, 3(6): 88-90. | |
| [21] | 侯江涛, 张毅芳, 沈聪聪, 等. 扁桃引种栽培技术研究综述[J]. 林业科技通讯, 2020,(2): 11-14. |
| HOU Jiangtao, ZHANG Yifang, SHEN Congcong, et al. Review on introduction and cultivation techniques of Amygdalus communis[J]. Forest Science and Technology, 2020,(2): 11-14. | |
| [22] | 梁艳霞, 王占和, 张亚楠, 等. 扁桃特性及其丰产栽培技术[J]. 黑龙江粮食, 2021,(10): 108-109. |
| LIANG Yanxia, WANG Zhanhe, ZHANG Yanan, et al. Characteristics of almond and its high-yield cultivation techniques[J]. Heilongjiang Grain, 2021,(10): 108-109. | |
| [23] | 任哲, 贡翔, 张锐, 等. 扁桃优株叶片解剖结构与其抗旱性关系研究[J]. 农业与技术, 2022, 42(3): 10-14. |
| REN Zhe, GONG Xiang, ZHANG Rui, et al. 扁桃优株叶片解剖结构与其抗旱性关系研究[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2022, 42(3): 10-14. | |
| [24] | Ayup M, Yang B, Gong P, et al. Evaluation of drought resistance of native almond-rootstock varieties in Xinjiang, China[J]. New Zealand Journal of Crop and Horticultural Science, 2022, 50(1): 48-68. |
| [25] | 李荣. 耐旱树种木质部结构与耐旱性关系研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2016. |
| LI Rong. Relationships between Xylem Strucrure And Drought Tolerance of Drought Tolerant Tree Species[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2016. | |
| [26] | 木巴热克·阿尤普, 杨波, 艾沙江·买买提, 等. 基于当年生枝木质部解剖结构的扁桃品种栓塞抗性分析[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2021, 36(5): 99-105. |
| Rebareke Ayoupu, YANG Bo, Ashajiang Maimaiti, et al. Xylem embolism resistance of different AlmondCultivars based on the xylem anatomical characteristics of current-year shoot[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2021, 36(5): 99-105. | |
| [27] |
Jansen S, Choat B, Pletsers A. Morphological variation of intervessel pit membranes and implications to xylem function in angiosperms[J]. American Journal of Botany, 2009, 96(2): 409-419.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Torres-Ruiz J M, Jansen S, Choat B, et al. Direct X-ray microtomography observation confirms the induction of embolism upon xylem cutting under tension[J]. Plant Physiology, 2015, 167(1): 40-43.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Sperry J S, Christman M A, Torres-Ruiz J M, et al. Vulnerability curves by centrifugation: is there an open vessel artefact, and are ‘r’ shaped curves necessarily invalid?[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2012, 35(3): 601-610. |
| [30] |
Cochard H, Barigah S T, Kleinhentz M, et al. Is xylem cavitation resistance a relevant criterion for screening drought resistance among Prunus species[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2008, 165(9): 976-982.
PMID |
| [31] | Tyree M T, Engelbrecht B M J, Vargas G, et al. Desiccation tolerance of five tropical seedlings in Panama.relationship to a field assessment of drought performance[J]. Plant Physiology, 2003, 132(3): 1439-1447. |
| [32] | Cai J, Zhang S X, Tyree M T. A computational algorithm addressing how vessel length might depend on vessel diameter[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2010: 33(7): 1234-1238. |
| [33] | Markesteijn L, Poorter L, Paz H, et al. Ecological differentiation in xylem cavitation resistance is associated with stem and leaf structural traits[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2011, 34(1): 137-148. |
| [34] | Wheeler J K, Sperry J S, Hacke U G, et al. Inter-vessel pitting and cavitation in woody Rosaceae and other vesselled plants: a basis for a safety versus efficiency trade-off in xylem transport[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2005, 28(6): 800-812. |
| [35] | Cochard H, Bréda N, Granier A, et al. Vulnerability to air embolism of three European oak species (Quercus petraea (Matt) Liebl, Q pubescens Willd, Q robur L)[J]. Annales Des Sciences Forestières, 1992, 49(3): 225-233. |
| [36] |
Johnson D M, McCulloh K A, Woodruff D R, et al. Hydraulic safety margins and embolism reversal in stems and leaves: Why are conifers and angiosperms so different[J]. Plant Science, 2012, 195: 48-53.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Hacke U G, Sperry J S, Pockman W T, et al. Trends in wood density and structure are linked to prevention of xylem implosion by negative pressure[J]. Oecologia, 2001, 126(4): 457-461.
DOI PMID |
| [38] | 刘丽, 张立, 蔡靖, 等. 干旱胁迫及复水后84K杨栓塞修复及其他水力学特性的研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2021, 43(7): 22-30. |
| LIU Li, ZHANG Li, CAI Jing, et al. Hydraulic characteristics and embolism repair of Populus alba × P.glandulosa after drought stress and rehydration[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2021, 43(7): 22-30. | |
| [39] | 安锋, 蔡靖, 姜在民, 等. 八种木本植物木质部栓塞恢复特性及其与PV曲线水分参数的关系[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 34(1): 38-44. |
| AN Feng, CAI Jing, JIANG Zaimin, et al. Refilling of embolism in the xylem of eight tree species and its relationship with Pressure-Volume parameters[J]. Journal of Northwest Sci-Tech University of Agriculture and Forestry (Natural Science Edition), 2006, 34(1): 38-44. |
| [1] | SONG Danbo, ZHANG Guoxin, WANG Quan, LIU Baojun, HUANG Tao, HAN Hongwei, BAI Jianyu, GUO Qingyuan. Study on the biological characteristics of the pathogen of bacterial perforation of alternaria alternata in Xinjiang and the screening of laboratory agents [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1515-1522. |
| [2] | TANG Xixi, Mubarek Ayup, XU Panyun, YU Qiuhong, GUO Chunmiao, ZHANG Ping, GONG Peng. Response of root anatomical structure of different rootstock resources of almond to drought stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(4): 897-907. |
| [3] | XIE Hui, HAN Shouan, WANG Min, ZHANG Wen. Effect of Trees from on Grain Yield and Photosynthetic Characteristics at Different Growth Stage of Wheat under Almond Wheat Intercropping [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(9): 1610-1623. |
| [4] | ZHANG Li, BIAN Bo, Tuluhong Tuerdi, WANG Xuenong. Experiment and Optimization Analysis of Air Suction Type for Almonds Shell Kernel Sorting Device [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(8): 1540-1546. |
| [5] | YANG Bo, GUO Chunmiao, Mubareke Ayoupu, GONG Peng. Study on Genetic Diversity and Probability Grading of Quantitative Traits in Stones of Native Almond Germplasm Resources in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(7): 1297-1305. |
| [6] | BIAN Bo, Tuluhong Tuerdi, ZHANG Li, WANG Xuenong. Research and Experiment on Material and Aerodynamic Characteristics of Almonds Shell and Kernel [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(5): 893-902. |
| [7] | YANG Bo, GUO Chunmiao, Mubareke Ayoupu, XIAO Li, XU Juan, GONG Peng, XU Yeting. Researches between Lignification of Almond Fruit Endocarp and the Activities of Related Enzyme [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(1): 23-29. |
| [8] | ZHANG Wen, ZHOU Hao, LIU Cuirong, ZHOU Yumei, XIE Hui. Effects of Different Tree Shapes on Regional Light Environment in Almond-Winter Wheat Intercropping Areas [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(9): 1639-1649. |
| [9] | ZHANG Xiangfei, YUE Wanwan, LIU Quanxin, ZENG Bin, HAO Qing, Abudoukayoumu Ayimaiti. Comparative Study on Pollen Viability and Stigma Availability (Prunus dulcis) [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(8): 1450-1456. |
| [10] | WANG Min, LI Jiang, LI Peng, TIAN Jia, LUO Shuping. Cloning and Prokaryotic Expression of Almond AcDHN1 Gene [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(12): 2221-2229. |
| [11] | SUN Zezhao, ZHANG Renfu, WANG Wei, LIU Haiyang, YAO Ju. Effects of Main Pests and Predatory Natural Enemies on Cotton under Almond-cotton Interplanting [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(11): 2044-2049. |
| [12] | LI Shao-ze, ZHANG Zhi-gang, CHENG Ping, YANG Lu, LI Hong, REN Ya-qin, WANG Dong-liang, WANG Zi-long. The Change of Endogenous Hormone of Apricot Tree in Flowering and Setting Period [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(2): 258-266. |
| [13] | ZHANG Qi, LI Peng, TIAN Jia, LI Jiang. Study on Photosynthetic and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Characteristics of Transgenic Tobacco with AcCBF1 Gene [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(2): 267-277. |
| [14] | LIU Yan-bin, Tuluhong Tuerdi, YANG Hui-min, SAN Yun-long, WANG Xue-nong. Effects of Thickness and Moisture Content on Mechanical Properties of Almond Shell Breaking [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(7): 1293-1304. |
| [15] | GUO Chun-miao, ZHU Zheng-yang, Mubareke Ayoupu, XU Juan, XIAO Li, GONG Peng, YANG Bo. Response of the Sucrose Synthase (SuSy) to Physiological Fruit Shedding of Almond Young Fruit [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(11): 2012-2020. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||