

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (7): 1793-1804.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.07.028
• Prataculture·Agricultural Equipment Engineering and Mechanization·Animal Husbandry Veteri-narian • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Yong1( ), LIU Hui1,2(
), LIU Hui1,2( ), GAO Hhongmei1, KANG Xue1, MA Chunhui1
), GAO Hhongmei1, KANG Xue1, MA Chunhui1
Received:2023-12-05
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-09-04
Correspondence author:
LIU Hui
Supported by:
马勇1( ), 刘慧1,2(
), 刘慧1,2( ), 高红梅1, 康雪1, 马春晖1
), 高红梅1, 康雪1, 马春晖1
通讯作者:
刘慧
作者简介:马勇(1998-),男,新疆伊宁人,硕士研究生,研究方向为饲草加工与生产,(E-mail)1435995281@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
MA Yong, LIU Hui, GAO Hhongmei, KANG Xue, MA Chunhui. Effects of mixed seeding of alfalfa and perennial ryegrass on yield and nutritional quality under different nitrogen levels[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1793-1804.
马勇, 刘慧, 高红梅, 康雪, 马春晖. 不同氮素水平下紫花苜蓿与多年生黑麦草混播对其产量和营养品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1793-1804.
| 处理 Treatments | 播种方式 Sowing method | 氮素水平 Nitrogen level | 基肥 Basal fertilizer (kg/hm2) | 追肥 Nitrogen topdressing (kg /hm2) | 总施氮量 Total nitrogen application (kg /hm2) | 比例 Rate | 播种量 Seeding rate (kg/hm2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分枝期 Branching | 现蕾期 Squaring | 豆科 Legumes | 禾本科 Grasses | ||||||
| M | 紫花苜蓿 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 22.5 | - |
| N1 | 20 | 20 | 0 | 40 | |||||
| N2 | 20 | 30 | 0 | 50 | |||||
| L | 多年生黑麦草 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | 60 |
| N1 | 20 | 20 | 60 | 100 | |||||
| N2 | 20 | 30 | 50 | 100 | |||||
| M7+L3 | 紫花苜蓿+多年黑麦草 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7∶3 | 15.75 | 18 |
| N1 | 20 | 20 | 60 | 100 | |||||
| N2 | 20 | 30 | 50 | 100 | |||||
| M6+L4 | 紫花苜蓿+多年黑麦草 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6∶4 | 13.5 | 24 |
| N1 | 20 | 20 | 60 | 100 | |||||
| N2 | 20 | 30 | 50 | 100 | |||||
| M5+L5 | 紫花苜蓿+多年黑麦草 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5∶5 | 11.25 | 50 |
| N1 | 20 | 20 | 60 | 100 | |||||
| N2 | 20 | 30 | 50 | 100 | |||||
| M4+L6 | 紫花苜蓿+多年黑麦草 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4∶6 | 9 | 36 |
| N1 | 20 | 20 | 60 | 100 | |||||
| N2 | 20 | 30 | 50 | 100 | |||||
| M3+L7 | 紫花苜蓿+多年黑麦草 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3∶7 | 6.75 | 42 |
| N1 | 20 | 20 | 60 | 100 | |||||
| N2 | 20 | 30 | 50 | 100 | |||||
Tab.1 The amount of sowing and nitrogen application in the experimental plot
| 处理 Treatments | 播种方式 Sowing method | 氮素水平 Nitrogen level | 基肥 Basal fertilizer (kg/hm2) | 追肥 Nitrogen topdressing (kg /hm2) | 总施氮量 Total nitrogen application (kg /hm2) | 比例 Rate | 播种量 Seeding rate (kg/hm2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分枝期 Branching | 现蕾期 Squaring | 豆科 Legumes | 禾本科 Grasses | ||||||
| M | 紫花苜蓿 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 22.5 | - |
| N1 | 20 | 20 | 0 | 40 | |||||
| N2 | 20 | 30 | 0 | 50 | |||||
| L | 多年生黑麦草 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | 60 |
| N1 | 20 | 20 | 60 | 100 | |||||
| N2 | 20 | 30 | 50 | 100 | |||||
| M7+L3 | 紫花苜蓿+多年黑麦草 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7∶3 | 15.75 | 18 |
| N1 | 20 | 20 | 60 | 100 | |||||
| N2 | 20 | 30 | 50 | 100 | |||||
| M6+L4 | 紫花苜蓿+多年黑麦草 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6∶4 | 13.5 | 24 |
| N1 | 20 | 20 | 60 | 100 | |||||
| N2 | 20 | 30 | 50 | 100 | |||||
| M5+L5 | 紫花苜蓿+多年黑麦草 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5∶5 | 11.25 | 50 |
| N1 | 20 | 20 | 60 | 100 | |||||
| N2 | 20 | 30 | 50 | 100 | |||||
| M4+L6 | 紫花苜蓿+多年黑麦草 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4∶6 | 9 | 36 |
| N1 | 20 | 20 | 60 | 100 | |||||
| N2 | 20 | 30 | 50 | 100 | |||||
| M3+L7 | 紫花苜蓿+多年黑麦草 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3∶7 | 6.75 | 42 |
| N1 | 20 | 20 | 60 | 100 | |||||
| N2 | 20 | 30 | 50 | 100 | |||||
| 处理 Treatments | 粗蛋白 CP(%) | 干物质 DM(%) | 中性 洗涤纤维 NDF(%) | 酸性 洗涤纤维 ADF(%) | 饲料 相对价值 RFV | 总可 消化养分 TND | 单位面积 CP产量 (unit area)CP (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0 | M | 20.27±0.01Cc | 23.35±0.01Bc | 35.31±0.01Ab | 22.79±0.01Aab | 144.54±7.0Ab | 71.12±0.37Bc | 68.97±4.72Bb |
| L | 17.65±0.02Bd | 28.90±0.02Ba | 47.31±0.01Aa | 25.48±0.01Aa | 132.59±4.41Ac | 71.19±0.94Bc | 25.80±4.61Cc | |
| M7+L3 | 24.21±0.12Ba | 27.59±0.01Bb | 31.92±0.02Ac | 20.27±0.12Ac | 151.13±5.31Aa | 74.49±1.50Bb | 115.71±9.25Ba | |
| M6+L4 | 22.32±0.01Bb | 24.98±0.01Bbc | 33.78±0.01Ab | 23.71±0.02Aab | 150.57±5.98Aa | 71.16±1.14Bc | 82.01±2.23Cb | |
| M5+L5 | 23.32±0.01Bab | 25.17±0.01Bbc | 28.09±0.01Bd | 17.95±0.01Bd | 154.40±6.00Aa | 75.95±0.75Bb | 81.53±8.09Bb | |
| M4+L6 | 23.65±0.01Aab | 26.43±0.03Babc | 24.51±0.07Ce | 15.38±0.03Ce | 153.08±4.2Aa | 78.05±0.54Aa | 74.81±14.25Bb | |
| M3+L7 | 22.33±0.02Ab | 23.79±0.01Bce | 27.45±0.01Cd | 15.47±0.01Ce | 153.65±3.91Aa | 78.22±0.95Aa | 87.52±7.31Bb | |
| N1 | M | 25.05±0.01Ab | 27.63±0.01Ac | 30.47±0.03Bb | 19.43±0.02Ba | 145.24±9.73Ab | 75.43±0.76Ab | 119.52±1.49Ab |
| L | 17.43±0.03Ad | 33.76±0.01Aa | 48.98±0.02Ba | 19.62±0.05Ba | 130.76±0.30Ab | 72.54±1.40Ac | 48.73±4.78Ac | |
| M7+L3 | 26.39±0.05Aa | 27.39±0.03Bc | 30.61±0.02Bb | 18.96±0.02Bab | 151.02±3.11Aa | 75.94±0.91Ab | 164.49±7.12Aa | |
| M6+L4 | 24.86±0.02Ac | 30.02±0.02Aa | 30.43±0.01Bb | 20.02±0.03Ba | 150.82±1.31Aa | 74.91±0.48Ab | 175.01±5.47Aa | |
| M5+L5 | 26.05±0.01Aa | 25.31±0.02Bc | 26.03±0.03Cc | 15.34±0.04Cb | 154.00±1.78Aa | 78.07±0.70Aa | 168.03±12.21Aa | |
| M4+L6 | 22.44±0.03Ac | 19.29±0.03Cd | 29.33±0.02Bb | 18.08±0.02Bb | 152.90±7.36Aa | 74.99±0.66Bb | 112.92±9.31Ab | |
| M3+L7 | 22.74±0.01Bc | 27.05±0.02Ac | 31.07±0.02Bb | 20.28±0.02Ba | 150.61±4.00Aa | 74.10±0.30Bbc | 116.01±8.62Ab | |
| N2 | M | 23.06±0.01Bc | 27.86±0.01Abc | 27.65±0.02Bd | 18.64±0.01Bbc | 142.56±3.24Ab | 75.33±0.25Aab | 82.07±9.12Be |
| L | 19.00±0.02Bf | 34.23±0.04Aa | 40.64±0.03Ba | 18.04±0.02Bbc | 136.49±3.29Ac | 74.32±0.19Ab | 48.19±8.06Bf | |
| M7+L3 | 25.43±0.01Ba | 29.59±0.01Abc | 30.14±0.01Bc | 16.50±0.05Bc | 148.72±4.25Aab | 74.55±047Bb | 183.65±7.01Aa | |
| M6+L4 | 22.00±0.03Bd | 28.95±0.02Abc | 29.33±0.01Bc | 19.19±0.01Babc | 150.18±3.91Aa | 74.52±1.04Ab | 121.01±4.43Bc | |
| M5+L5 | 23.87±0.01Ab | 28.75±0.01Abc | 30.24±0.01Ac | 20.02±0.01Aabc | 148.12±3.14Aab | 77.83±4.38ABa | 141.85±9.98ABb | |
| M4+L6 | 20.24±0.05Be | 31.69±0.01Aab | 35.10±0.01Ab | 23.55±0.03Aa | 152.02±4.77Aa | 70.53±0.90Cc | 106.19±9.99Ad | |
| M3+L7 | 24.20±0.01Ab | 26.23±0.01Ac | 35.76±0.02Ab | 21.53±0.01Aab | 152.08±1.31Aa | 73.51±0.37Bbc | 101.03±1.25ABd | |
Tab.2 Changes of mixed sowing of alfalfa + perennial ryegrass on nutritional quality under different nitrogen levels
| 处理 Treatments | 粗蛋白 CP(%) | 干物质 DM(%) | 中性 洗涤纤维 NDF(%) | 酸性 洗涤纤维 ADF(%) | 饲料 相对价值 RFV | 总可 消化养分 TND | 单位面积 CP产量 (unit area)CP (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0 | M | 20.27±0.01Cc | 23.35±0.01Bc | 35.31±0.01Ab | 22.79±0.01Aab | 144.54±7.0Ab | 71.12±0.37Bc | 68.97±4.72Bb |
| L | 17.65±0.02Bd | 28.90±0.02Ba | 47.31±0.01Aa | 25.48±0.01Aa | 132.59±4.41Ac | 71.19±0.94Bc | 25.80±4.61Cc | |
| M7+L3 | 24.21±0.12Ba | 27.59±0.01Bb | 31.92±0.02Ac | 20.27±0.12Ac | 151.13±5.31Aa | 74.49±1.50Bb | 115.71±9.25Ba | |
| M6+L4 | 22.32±0.01Bb | 24.98±0.01Bbc | 33.78±0.01Ab | 23.71±0.02Aab | 150.57±5.98Aa | 71.16±1.14Bc | 82.01±2.23Cb | |
| M5+L5 | 23.32±0.01Bab | 25.17±0.01Bbc | 28.09±0.01Bd | 17.95±0.01Bd | 154.40±6.00Aa | 75.95±0.75Bb | 81.53±8.09Bb | |
| M4+L6 | 23.65±0.01Aab | 26.43±0.03Babc | 24.51±0.07Ce | 15.38±0.03Ce | 153.08±4.2Aa | 78.05±0.54Aa | 74.81±14.25Bb | |
| M3+L7 | 22.33±0.02Ab | 23.79±0.01Bce | 27.45±0.01Cd | 15.47±0.01Ce | 153.65±3.91Aa | 78.22±0.95Aa | 87.52±7.31Bb | |
| N1 | M | 25.05±0.01Ab | 27.63±0.01Ac | 30.47±0.03Bb | 19.43±0.02Ba | 145.24±9.73Ab | 75.43±0.76Ab | 119.52±1.49Ab |
| L | 17.43±0.03Ad | 33.76±0.01Aa | 48.98±0.02Ba | 19.62±0.05Ba | 130.76±0.30Ab | 72.54±1.40Ac | 48.73±4.78Ac | |
| M7+L3 | 26.39±0.05Aa | 27.39±0.03Bc | 30.61±0.02Bb | 18.96±0.02Bab | 151.02±3.11Aa | 75.94±0.91Ab | 164.49±7.12Aa | |
| M6+L4 | 24.86±0.02Ac | 30.02±0.02Aa | 30.43±0.01Bb | 20.02±0.03Ba | 150.82±1.31Aa | 74.91±0.48Ab | 175.01±5.47Aa | |
| M5+L5 | 26.05±0.01Aa | 25.31±0.02Bc | 26.03±0.03Cc | 15.34±0.04Cb | 154.00±1.78Aa | 78.07±0.70Aa | 168.03±12.21Aa | |
| M4+L6 | 22.44±0.03Ac | 19.29±0.03Cd | 29.33±0.02Bb | 18.08±0.02Bb | 152.90±7.36Aa | 74.99±0.66Bb | 112.92±9.31Ab | |
| M3+L7 | 22.74±0.01Bc | 27.05±0.02Ac | 31.07±0.02Bb | 20.28±0.02Ba | 150.61±4.00Aa | 74.10±0.30Bbc | 116.01±8.62Ab | |
| N2 | M | 23.06±0.01Bc | 27.86±0.01Abc | 27.65±0.02Bd | 18.64±0.01Bbc | 142.56±3.24Ab | 75.33±0.25Aab | 82.07±9.12Be |
| L | 19.00±0.02Bf | 34.23±0.04Aa | 40.64±0.03Ba | 18.04±0.02Bbc | 136.49±3.29Ac | 74.32±0.19Ab | 48.19±8.06Bf | |
| M7+L3 | 25.43±0.01Ba | 29.59±0.01Abc | 30.14±0.01Bc | 16.50±0.05Bc | 148.72±4.25Aab | 74.55±047Bb | 183.65±7.01Aa | |
| M6+L4 | 22.00±0.03Bd | 28.95±0.02Abc | 29.33±0.01Bc | 19.19±0.01Babc | 150.18±3.91Aa | 74.52±1.04Ab | 121.01±4.43Bc | |
| M5+L5 | 23.87±0.01Ab | 28.75±0.01Abc | 30.24±0.01Ac | 20.02±0.01Aabc | 148.12±3.14Aab | 77.83±4.38ABa | 141.85±9.98ABb | |
| M4+L6 | 20.24±0.05Be | 31.69±0.01Aab | 35.10±0.01Ab | 23.55±0.03Aa | 152.02±4.77Aa | 70.53±0.90Cc | 106.19±9.99Ad | |
| M3+L7 | 24.20±0.01Ab | 26.23±0.01Ac | 35.76±0.02Ab | 21.53±0.01Aab | 152.08±1.31Aa | 73.51±0.37Bbc | 101.03±1.25ABd | |
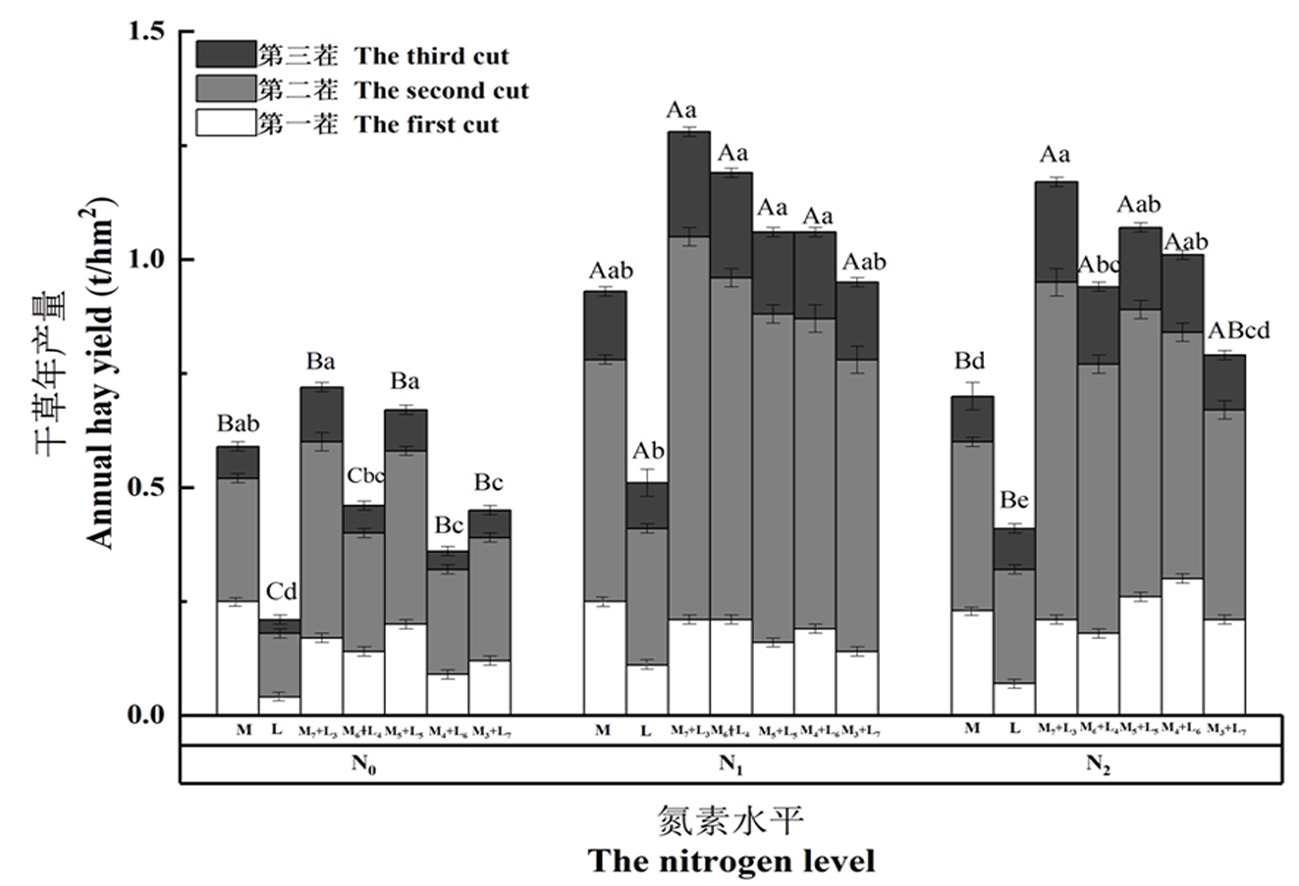
Fig.1 Compares hay yield of mixed sowing alfalfa + perennial ryegrass in different stubbles under different nitrogen levels Note : The annual hay yield is the sum of three crops
| 处理 Treatments | 土地当量比(LER) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| N0 | N1 | N2 | |
| M7+L3 | 1.60±0.23Ba | 1.67±0.36Ba | 1.92±0.33Aa |
| M6+L4 | 1.08±0.06Cb | 1.36±0.11Bb | 1.61±0.11Aab |
| M5+L5 | 1.55±0.24Aa | 1.61±0.41Aa | 1.72±0.28Aab |
| M4+L6 | 1.24±0.17Aab | 1.44±0.48Aab | 1.36±0.10Ab |
| M3+L7 | 1.23±0.19Aab | 1.38±0.42Aab | 1.40±0.10Ab |
Tab.3 Changes of mixed sowing of alfalfa + perennial ryegrass on land equivalent ratio under different nitrogen levels
| 处理 Treatments | 土地当量比(LER) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| N0 | N1 | N2 | |
| M7+L3 | 1.60±0.23Ba | 1.67±0.36Ba | 1.92±0.33Aa |
| M6+L4 | 1.08±0.06Cb | 1.36±0.11Bb | 1.61±0.11Aab |
| M5+L5 | 1.55±0.24Aa | 1.61±0.41Aa | 1.72±0.28Aab |
| M4+L6 | 1.24±0.17Aab | 1.44±0.48Aab | 1.36±0.10Ab |
| M3+L7 | 1.23±0.19Aab | 1.38±0.42Aab | 1.40±0.10Ab |
| 处理 Treatments | CP(叶) CP (leaves) | CP(茎) CP (stems) | 茎(DM) Stem (DM) | 叶(DM) Leaf (DM) | 吸氮量 Nitrogen uptake | 氮素利用率 Nitrogen utilization rate | 株高(豆) Plant height (Legumes) | 株高(禾) Plant height (Grasses) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0 | L | 13.41±0.21Bb | 7.47±0.21Be | 33.31±0.31Bb | 28.89±0.31Ca | 26.10±1.91Ba | 49.5±0.30Bc | 31.6±1.96Ab | |
| M7+L3 | 14.96±0.10Ab | 9.37±0.31Bd | 27.96±0.31Ad | 22.58±0.32Ac | 9.38±2.08Cc | 56.7±2.08Aa | 42.3±2.41Aa | ||
| M6+L4 | 14.54±0.12Bb | 10.58±0.21Bc | 35.41±0.25Aa | 27.22±0.36Aab | 12.01±1.26Bbc | 55.5±1.50Aa | 26.6±1.91Ac | ||
| M5+L5 | 14.10±0.13Ab | 10.24±0.51Bc | 32.60±0.23Bb | 27.97±0.88Aab | 9.81±1.06Cc | 54.4±1.21Aab | 26.8±0.20Bc | ||
| M4+L6 | 17.60±0.50Aa | 12.30±0.52Ab | 23.89±0.24Ce | 22.44±0.84Cc | 14.01±1.46Bb | 56.4±3.24Aa | 34.0±2.64Ab | ||
| M3+L7 | 16.71±0.51Aa | 13.62±0.41Aa | 33.52±0.65Ab | 26.21±0.56Ab | 14.89±2.35Cb | 51.7±1.61Bbc | 30.7±1.52Ab | ||
| N1 | L | 13.59±0.21Bc | 9.44±0.21Bc | 36.39±0.01Aa | 33.82±0.21Aa | 57.96±6.87Aa | 54.2±0.85Ac | 34.7±1.47Ac | |
| M7+L3 | 15.03±0.05Abc | 7.76±0.24Cd | 23.08±0.56Bd | 20.26±0.11Bf | 23.23±2.14Ae | 13.89±0.21Ac | 57.7±3.86Aabc | 42.8±1.96Aa | |
| M6+L4 | 18.39±0.13Aa | 12.36±0.10Aa | 23.65±0.85Bd | 21.76±0.23Be | 31.22±3.57Ace | 19.21±0.35Abc | 57.3±5.74Aabc | 28.8±1.36Ad | |
| M5+L5 | 16.21±0.25Ab | 11.99±0.05Aa | 31.17±0.95Bc | 25.04±0.35Bd | 34.60±3.36Ac | 24.80±0.33Ab | 56.5±3.74Abc | 32.3±2.41Ac | |
| M4+L6 | 15.35±0.63Bbc | 10.35±0.09Bb | 32.10±0.23Abc | 26.14±0.25Bc | 38.19±7.22Abc | 24.19±0.72Ab | 61.3±2.08Aab | 38.0±1.73Ab | |
| M3+L7 | 15.16±0.23Bbc | 9.85±0.56Bbc | 32.55±0.87Bb | 27.31±0.25Ab | 44.62±1.24Ab | 29.62±0.12Aa | 63.2±0.72Aa | 33.2±1.05Ac | |
N2 | L | 14.91±0.25Ace | 9.95±0.58Ab | 33.10±0.25Ba | 29.61±0.35Ba | 53.42±7.38Aa | 50.1±0.90Bc | 33.7±1.13Abc | |
| M7+L3 | 15.72±0.23Ac | 10.14±0.36Ae | 27.06±0.35Aa | 22.91±0.58Ad | 16.07±3.37Be | 6.73±0.35Be | 59.7±0.57Aab | 39.1±4.41Aa | |
| M6+L4 | 18.65±0.35Aa | 12.03±0.58Af | 24.81±0.54Ba | 19.74±0.65Be | 29.30±3.87Ac | 17.29±0.38Bbc | 58.1±1.87Ab | 28.8±0.58Ac | |
| M5+L5 | 15.27±0.23Ac | 9.06±0.56Ba | 35.92±0.56Aa | 26.99±0.98Cb | 21.79±2.01Be | 11.99±0.30Bce | 56.3±3.75Ab | 29.3±1.08ABc | |
| M4+L6 | 16.98±0.35Ab | 12.14±0.65Ac | 31.39±0.58Ba | 29.18±0.58Aa | 32.20±2.56bAc | 18.20±0.25Bb | 59.5±1.80Aab | 34.7±3.40Aab | |
| M3+L7 | 14.12±0.68Ce | 9.35±0.65Bd | 30.03±0.57Ca | 23.81±0.54Bc | 38.77±2.54b | 23.77±0.25Ba | 61.9±0.98Aa | 35.6±3.54Aab | |
Tab.4 Changes of mixed sowing of alfalfa + perennial ryegrass on nitrogen utilization under different nitrogen utilization rate
| 处理 Treatments | CP(叶) CP (leaves) | CP(茎) CP (stems) | 茎(DM) Stem (DM) | 叶(DM) Leaf (DM) | 吸氮量 Nitrogen uptake | 氮素利用率 Nitrogen utilization rate | 株高(豆) Plant height (Legumes) | 株高(禾) Plant height (Grasses) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0 | L | 13.41±0.21Bb | 7.47±0.21Be | 33.31±0.31Bb | 28.89±0.31Ca | 26.10±1.91Ba | 49.5±0.30Bc | 31.6±1.96Ab | |
| M7+L3 | 14.96±0.10Ab | 9.37±0.31Bd | 27.96±0.31Ad | 22.58±0.32Ac | 9.38±2.08Cc | 56.7±2.08Aa | 42.3±2.41Aa | ||
| M6+L4 | 14.54±0.12Bb | 10.58±0.21Bc | 35.41±0.25Aa | 27.22±0.36Aab | 12.01±1.26Bbc | 55.5±1.50Aa | 26.6±1.91Ac | ||
| M5+L5 | 14.10±0.13Ab | 10.24±0.51Bc | 32.60±0.23Bb | 27.97±0.88Aab | 9.81±1.06Cc | 54.4±1.21Aab | 26.8±0.20Bc | ||
| M4+L6 | 17.60±0.50Aa | 12.30±0.52Ab | 23.89±0.24Ce | 22.44±0.84Cc | 14.01±1.46Bb | 56.4±3.24Aa | 34.0±2.64Ab | ||
| M3+L7 | 16.71±0.51Aa | 13.62±0.41Aa | 33.52±0.65Ab | 26.21±0.56Ab | 14.89±2.35Cb | 51.7±1.61Bbc | 30.7±1.52Ab | ||
| N1 | L | 13.59±0.21Bc | 9.44±0.21Bc | 36.39±0.01Aa | 33.82±0.21Aa | 57.96±6.87Aa | 54.2±0.85Ac | 34.7±1.47Ac | |
| M7+L3 | 15.03±0.05Abc | 7.76±0.24Cd | 23.08±0.56Bd | 20.26±0.11Bf | 23.23±2.14Ae | 13.89±0.21Ac | 57.7±3.86Aabc | 42.8±1.96Aa | |
| M6+L4 | 18.39±0.13Aa | 12.36±0.10Aa | 23.65±0.85Bd | 21.76±0.23Be | 31.22±3.57Ace | 19.21±0.35Abc | 57.3±5.74Aabc | 28.8±1.36Ad | |
| M5+L5 | 16.21±0.25Ab | 11.99±0.05Aa | 31.17±0.95Bc | 25.04±0.35Bd | 34.60±3.36Ac | 24.80±0.33Ab | 56.5±3.74Abc | 32.3±2.41Ac | |
| M4+L6 | 15.35±0.63Bbc | 10.35±0.09Bb | 32.10±0.23Abc | 26.14±0.25Bc | 38.19±7.22Abc | 24.19±0.72Ab | 61.3±2.08Aab | 38.0±1.73Ab | |
| M3+L7 | 15.16±0.23Bbc | 9.85±0.56Bbc | 32.55±0.87Bb | 27.31±0.25Ab | 44.62±1.24Ab | 29.62±0.12Aa | 63.2±0.72Aa | 33.2±1.05Ac | |
N2 | L | 14.91±0.25Ace | 9.95±0.58Ab | 33.10±0.25Ba | 29.61±0.35Ba | 53.42±7.38Aa | 50.1±0.90Bc | 33.7±1.13Abc | |
| M7+L3 | 15.72±0.23Ac | 10.14±0.36Ae | 27.06±0.35Aa | 22.91±0.58Ad | 16.07±3.37Be | 6.73±0.35Be | 59.7±0.57Aab | 39.1±4.41Aa | |
| M6+L4 | 18.65±0.35Aa | 12.03±0.58Af | 24.81±0.54Ba | 19.74±0.65Be | 29.30±3.87Ac | 17.29±0.38Bbc | 58.1±1.87Ab | 28.8±0.58Ac | |
| M5+L5 | 15.27±0.23Ac | 9.06±0.56Ba | 35.92±0.56Aa | 26.99±0.98Cb | 21.79±2.01Be | 11.99±0.30Bce | 56.3±3.75Ab | 29.3±1.08ABc | |
| M4+L6 | 16.98±0.35Ab | 12.14±0.65Ac | 31.39±0.58Ba | 29.18±0.58Aa | 32.20±2.56bAc | 18.20±0.25Bb | 59.5±1.80Aab | 34.7±3.40Aab | |
| M3+L7 | 14.12±0.68Ce | 9.35±0.65Bd | 30.03±0.57Ca | 23.81±0.54Bc | 38.77±2.54b | 23.77±0.25Ba | 61.9±0.98Aa | 35.6±3.54Aab | |
| 指标 Indexes | 处理Treatments | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 混播比例 Mixture ratio | 氮素水平 Nitrogen level | 氮素水平* 混播比例 Nitrogen level *Mixture ratio | |
| 粗蛋白 CP(%) | 111.99** | 7.17** | 22.41** |
| 干物质 DM(%) | 10.83** | 31.28** | 12.44** |
| 中性洗涤纤维 NDF(%) | 163.66** | 0.21* | 23.51** |
| 酸性洗涤纤维 ADF(%) | 4.36** | 1.62* | 9.94** |
| 饲料相对价值 RFV(%) | 17.37** | 3.30 | 4.62** |
| 总可消化养分 TND(%) | 10.25** | 2.74 | 13.08** |
| 单位面积CP产量 (unit area)CP (%) | 18.12** | 23.81** | 1.78* |
| 叶 leaves CP(%) | 21.12** | 4.31 | 3.20 |
| 茎stems CP(%) | 15.41** | 6.42 | 19.52** |
| 叶 leaves DM(%) | 12.10** | 25.62** | 18.20** |
| 茎stems DM(%) | 11.52** | 8.78 | 24.10** |
| 吸氮量 nitrogen uptake | 16.52** | 25.62** | 7.42 |
| 氮素利用率 Nitrogen utilization rate(%) | 18.20** | 28.20** | 5.82 |
| 豆科株高 Legumes height plant height/cm | 25.42** | 11.46 | 3.18 |
| 禾本科株高 Plant height of Grasses/cm | 10.20* | 4.52 | 6.23 |
Tab.5 Changes of nitrogen level, mixed sowing ratio and nitrogen level * mixed sowing ratio interaction on alfalfa + perennial ryegrass
| 指标 Indexes | 处理Treatments | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 混播比例 Mixture ratio | 氮素水平 Nitrogen level | 氮素水平* 混播比例 Nitrogen level *Mixture ratio | |
| 粗蛋白 CP(%) | 111.99** | 7.17** | 22.41** |
| 干物质 DM(%) | 10.83** | 31.28** | 12.44** |
| 中性洗涤纤维 NDF(%) | 163.66** | 0.21* | 23.51** |
| 酸性洗涤纤维 ADF(%) | 4.36** | 1.62* | 9.94** |
| 饲料相对价值 RFV(%) | 17.37** | 3.30 | 4.62** |
| 总可消化养分 TND(%) | 10.25** | 2.74 | 13.08** |
| 单位面积CP产量 (unit area)CP (%) | 18.12** | 23.81** | 1.78* |
| 叶 leaves CP(%) | 21.12** | 4.31 | 3.20 |
| 茎stems CP(%) | 15.41** | 6.42 | 19.52** |
| 叶 leaves DM(%) | 12.10** | 25.62** | 18.20** |
| 茎stems DM(%) | 11.52** | 8.78 | 24.10** |
| 吸氮量 nitrogen uptake | 16.52** | 25.62** | 7.42 |
| 氮素利用率 Nitrogen utilization rate(%) | 18.20** | 28.20** | 5.82 |
| 豆科株高 Legumes height plant height/cm | 25.42** | 11.46 | 3.18 |
| 禾本科株高 Plant height of Grasses/cm | 10.20* | 4.52 | 6.23 |
| [1] | 胡自治. 人工草地在我国21世纪草业发展和环境治理中的重要意义[J]. 草原与草坪, 2000, 20(1): 12-15. |
| HU Zizhi. The importance of artificial grassland in the development of prataculture and the control of environment in China of 21 century[J]. Grassland and Turf, 2000, 20(1): 12-15. | |
| [2] | 韩永芬, 覃涛英, 付薇, 等. 紫花苜蓿与扁穗雀麦、鸭茅混播效果研究[J]. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2018, 39(6):62-66. |
| HAN Yongfen, QIN Taoying, FU Wei, et al. Effect of Mixed Seeding of Medicago sativa with Bromus catharticus and Dactylis glomerata[J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2018, 39(6): 62-66. | |
| [3] | 同延安, 梁东丽, 张树兰, 等. 氮肥与环境[C]// 氮素循环与农业和环境学术研讨会论文. 2001. |
| TONG Yanan, LIANG Dongli, ZHANG Shulan, et al. Symposium on Nitrogen Fertilizer and Environment[C]// Nitrogen Cycle and Agriculture and Environment Paper, 2001. | |
| [4] | Liu X S, Zhao J W, Liu J Y, et al. Water-phosphorus coupling enhances fine root turnover and dry matter yield of alfalfa under drip irrigation[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2021, 113(5): 4161-4175. |
| [5] |
McDonald I, Baral R, Min D. Effects of alfalfa and alfalfa-grass mixtures with nitrogen fertilization on dry matter yield and forage nutritive value[J]. Journal of Animal Science and Technology, 2021, 63(2): 305-318.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Zhang Q B, Liu J Y, Liu X S, et al. Optimizing water and phosphorus management to improve hay yield and water- and phosphorus-use efficiency in alfalfa under drip irrigation[J]. Food Science & Nutrition, 2020, 8(5): 2406-2418. |
| [7] |
刘春英, 孙学映, 朱体超, 等. 不同黑麦草品种生产性能比较与优势品种筛选[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(4): 39-48.
DOI |
|
LIU Chunying, SUN Xueying, ZHU Tichao, et al. Comparison of the production performance of ryegrass cultivars and screening of dominant varieties[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(4): 39-48.
DOI |
|
| [8] | 郭宏宇. 基于海流图轻度盐碱地的禾草与苜蓿混播建植研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2019. |
| GUO Hongyu. Analysis of Mixed Seeding Pasture of Grass and Alfalfa on Saline-alkali Soil in Hailiutu[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| [9] |
周鹏, 耿燕, 马文红, 等. 温带草地主要优势植物不同器官间功能性状的关联[J]. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(1): 7-16.
DOI |
|
ZHOU Peng, GENG Yan, MA Wenhong, et al. Linkages of functional traits among plant organs in the dominant species of the Inner Mongolia grassland, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2010, 34(1): 7-16.
DOI |
|
| [10] | 陆姣云, 杨惠敏, 田宏, 等. 水分对不同生育时期紫花苜蓿茎叶碳、氮、磷含量及化学计量特征的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(6): 25-34. |
| LU Jiaoyun, YANG Huimin, TIAN Hong, et al. Effect of water addition on carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations, and stoichiometric characteristics of alfalfa stems and leaves at different growth stage[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(6): 25-34. | |
| [11] | 霍延卫. 种植牧草的意义与牧草施肥技术[J]. 畜牧兽医科技信息, 2021, (10): 46-47. |
| HUO Yanwei. Significance of planting forage and forage fertilization technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2021, (10): 46-47. | |
| [12] | 陈娟. 优质牧草的种植技术分析[J]. 种子科技, 2021, 39(20): 31-32. |
| CHEN Juan. Analysis of planting techniques of high quality forage grass[J]. Seed Science & Technology, 2021, 39(20): 31-32. | |
| [13] | 邢宇俊, 程智慧, 周艳丽, 等. 保护地蔬菜连作障碍原因及其调控[J]. 西北农业学报, 2004, 13(1): 120-123. |
| XING Yujun, CHENG Zhihui, ZHOU Yanli, et al. Causes and modulations of protected vegetable continuous cropping obstacles[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2004, 13(1): 120-123. | |
| [14] |
熊乙, 许庆方, 玉柱, 等. 不同苜蓿干草营养成分及饲用价值评价[J]. 草地学报, 2018, 26(5): 1262-1266.
DOI |
|
XIONG Yi, XU Qingfang, YU Zhu, et al. Evaluation of nutritional components and feeding value of DifferentAlfalfa hay[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(5): 1262-1266.
DOI |
|
| [15] | 蔡宏宇, 董宇, 马艳, 等. 五种非常规饲料营养成分分析与体外降解效果评价[J/OL]. 饲料工业:1-11[2023-06-07]. |
| CAI Hongyu, DONG Yu, MA Yan, et al. Evaluation of Nutrient Content and In Vitro Degradation Rate of Five Unconventional Feeds[J / OL]. Feed Industry: 1-11 [ 2023-06-07 ]. | |
| [16] | 马金慧, 范富, 包呼格吉乐图, 等. 不同收获时期的玉米饲用生物学产量和营养价值的比较研究[J]. 饲料研究, 2022, 45(19):104-108. |
| MA Jinhui, FAN Fu, BAO Hugejiletu, et al. Comparative study on feeding biological yield and nutritional value of maize in different harvest periods[J]. Feed Research, 2022, 45(19):104-108. | |
| [17] |
刘启宇, 云岚, 陈逸凡, 等. 苜蓿——禾草混播草地牧草产量及种间竞争关系的动态研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 181-191.
DOI |
|
LIU Qiyu, YUN Lan, CHEN Yifan, et al. The dynamic analysis of forage yield and interspecific competition in alfalfa-grass mixed pasture[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 181-191.
DOI |
|
| [18] | 方伟. 高寒地区不同禾豆混播组合与比例对牧草产量及品质的影响[J]. 青海草业, 2022, 31(4): 1-8. |
| FANG Wei. Effects of different mixtures and proportions of legume-grass mixtures on productivity and quality in alpine cold region[J]. Qinghai Prataculture, 2022, 31(4): 1-8. | |
| [19] | 田昌玉, 林治安, 徐久凯, 等. 有机肥氮素利用率的几种典型计算方法比较[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(10): 1909-1916. |
| TIAN Changyu, LIN Zhian, XU Jiukai, et al. Comparison of organic fertilizer nitrogen use efficiency calculated by several typical methods[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(10): 1909-1916. | |
| [20] | 聂兆君, 秦世玉, 刘红恩, 等. 氮锌配施对冬小麦产量及土壤氮素转化相关酶活性的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(3): 431-441. |
| NIE Zhaojun, QIN Shiyu, LIU Hongen, et al. Effects of combined application of nitrogen and zinc on winter wheat yield and soil enzyme activities related to nitrogen transformation[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(3): 431-441. | |
| [21] | 平措, 吴玉江, 索朗达, 等. 西藏拉萨地区施肥及混播比例对燕麦+箭筈豌豆生产性能的影响[J]. 中国草食动物科学, 2022, 42(02):39-42. |
| PING Cuo, WU Yujiang, SUO Langda, et al. Effects of Fertilization and Mixed Planting on the Forage Yield and Nutritional Quality of Oat and Vetch in Lhasa, Tibet[J]. China Herbivore Science, 2022, 42 (02): 39-42. | |
| [22] | 王乐, 张玉霞, 于华荣, 等. 氮肥对沙地燕麦生长特性及产量的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2017, 34(7): 1516-1521. |
| WANG Le, ZHANG Yuxia, YU Huarong, et al. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer application on growth characteristics and yield of oats in sandy soil[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(7): 1516-1521. | |
| [23] | 魏孔涛, 鱼小军, 白梅梅, 等. 混播比例对半干旱区放牧型混播草地草产量及品质的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(9): 56-65. |
| WEI Kongtao, YU Xiaojun, BAI Meimei, et al. Effect of mixed sowing ratio on the forage yield and quality of grazing mixed sowing grassland in semi-arid area[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(9): 56-65. | |
| [24] | 冯廷旭, 德科加, 向雪梅, 等. 三江源区小黑麦与豆科饲草混播最佳组合及比例研究[J]. 西北农业学报, 2023, 32(2): 232-241. |
| FENG Tingxu, DE Kejia, XIANG Xuemei, et al. Optimal combination and proportion of Triticale and leguminous forage grass in established artificial grassland at three-river source region[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2023, 32(2): 232-241. | |
| [25] |
赵京东, 宋彦涛, 徐鑫磊, 等. 施氮和刈割对辽西北退化草地牧草产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 36-48.
DOI |
|
ZHAO Jingdong, SONG Yantao, XU Xinlei, et al. Effects of nitrogen application and mowing on yield and quality of forage in degraded grassland in northwest Liaoning Province[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(8): 36-48.
DOI |
|
| [26] | 何亚灵, 韦潇, 曾泰儒, 等. 氮肥水平对豆禾混播草地产量和营养品质的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2022, 40(5): 721-727, 745. |
| HE Yaling, WEI Xiao, ZENG Tairu, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer levels on yield and quality of legume-grass mixtures[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2022, 40(5): 721-727, 745.[万方] | |
| [27] | 陈香来, 潘佳, 陈利军, 等. 施肥对黄土高原紫花苜蓿产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2019, 36(12): 3145-3154. |
| CHEN Xianglai, PAN Jia, CHEN Lijun, et al. Effects of fertilization on hay yield and quality of alfalfa on the Loess Plateau[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(12): 3145-3154. | |
| [28] | 王晓力, 王静. 紫花苜蓿种子生产田间管理关键技术[J]. 内蒙古草业, 2004, 16(1): 59. |
| WANG Xiaoli, WANG Jing. Key techniques for field management of alfalfa seed production[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Prataculture, 2004, 16(1): 59. | |
| [29] | 刘文兰. 紫花苜蓿叶片植物学特征及化学计量特征对植株密度和磷素供给的响应[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2018. |
| LIU Wenlan. Responses of Botanical Features and Stoichiometric Traits of Alfalfa Leaf to Plant Density and Phosphorus Supply[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| [30] | 刘敏, 龚吉蕊, 王忆慧, 等. 豆禾混播建植人工草地对牧草产量和草质的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2016, 33(1): 179-185. |
| LIU Min, GONG Jirui, WANG Yihui, et al. Effects of legume-grass mixed sowing on forage grass yield and quality in artificial grassland[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2016, 33(1): 179-185. | |
| [31] | 王丹, 王俊杰, 李凌浩, 等. 旱作条件下苜蓿与冰草不同混播方式的产草量及种间竞争关系[J]. 中国草地学报, 2014, 36(5): 27-31. |
| WANG Dan, WANG Junjie, LI Linghao, et al. Forage yield and interspecific competition of mixed sowing of alfalfa and wheatgrass under dry farming[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2014, 36(5): 27-31. | |
| [32] | 何玮, 张新全, 杨春华. 刈割次数、施肥量及混播比例对牛鞭草和白三叶混播草地牧草品质的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2006, 23(4): 39-42. |
| HE Wei, ZHANG Xinquan, YANG Chunhua. The effects of cutting frequency, seeding rates and nitrogen fertilizer on the yield and quality of mixture pasture ofHemarthria compressaandTrifolium repens[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2006, 23(4): 39-42. | |
| [33] | Xu R R, Shi W, Kamran M, et al. Grass-legume mixture and nitrogen application improve yield, quality, and water and nitrogen utilization efficiency of grazed pastures in the Loess Plateau[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14: 1088849. |
| [34] |
冯琴, 王斌, 王腾飞, 等. 不同播种量毛苕子与燕麦混播对草地生产性能及营养品质的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2022, 30(12): 3439-3446.
DOI |
|
FENG Qin, WANG Bin, WANG Tengfei, et al. Effects of mixed sowing of vetch and oat on production performance and nutrient quality of grassland[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(12): 3439-3446.
DOI |
|
| [35] | Cong W F, Hoffland E, Li L, et al. Intercropping enhances soil carbon and nitrogen[J]. Global Change Biology, 2015, 21(4): 1715-1726. |
| [36] | 郝凤. 紫花苜蓿氮效率差异机制与氮营养阶段生育期划分的研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2017. |
| HAO Feng. Study on Nitrogen Efficiency Mechanism and Division Growth Period by Nitrogen Nutrition Stage of Alfalfa[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| [37] | 陈波浪, 吴海华, 曹公利, 等. 不同肥力水平下立架栽培甜瓜干物质累积和氮、磷、钾养分吸收特性[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(1): 142-149. |
| CHEN Bolang, WU Haihua, CAO Gongli, et al. Characteristics of dry matter accumulation and N, P and K assimilations of trellis-cultivated melon under different fertility rates[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2013, 19(1): 142-149. | |
| [38] |
冯琴, 王斌, 海艺蕊, 等. 毛苕子不同播种量与燕麦混播对群落竞争及燕麦生物量分配的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2022, 30(9): 2423-2429.
DOI |
|
FENG Qin, WANG Bin, HAI Yirui, et al. Effects of mixed sowing of vetch and oat on community competition and biomass allocation of oats[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(9): 2423-2429.
DOI |
|
| [39] | Fan K K, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Guo X S, et al. Suppressed N fixation and diazotrophs after four decades of fertilization[J]. Microbiome, 2019, 7(1): 143. |
| [40] | 巨晓棠, 张福锁. 关于氮肥利用率的思考[J]. 生态环境, 2003, 12(2): 192-197. |
| JU Xiaotang, ZHANG Fusuo. Thinking about nitrogen recovery rate[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2003, 12(2): 192-197. | |
| [41] | 马雪琴. 高寒牧区播期和氮肥对燕麦产量及其构成和氮素吸收利用与分配的影响[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2007. |
| MA Xueqin. Effects of sowing date and N application on yield and its components, N uptake and allocation in oats in alpine region[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2007. | |
| [42] | 田永雷, 张玉霞, 朱爱民, 等. 施氮对科尔沁沙地饲用燕麦产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 草原与草坪, 2018, 38(5): 54-58. |
| TIAN Yonglei, ZHANG Yuxia, ZHU Aimin, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of oat in Horqin sandy land[J]. Grassland and Turf, 2018, 38(5): 54-58. | |
| [43] | 苟志文, 胡发龙, 赵财, 等. 氮肥后移满足绿洲灌区全膜覆盖玉米的氮素需求[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2018, 24(4): 888-895. |
| GOU Zhiwen, HU Falong, ZHAO Cai, et al. Postponed topdressing of nitrogen fertilizers to meet nitrogen requirement of maize under full plastic film mulching in Oasis Irrigation Region[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2018, 24(4): 888-895. | |
| [44] |
杨蕊, 耿石英, 王小燕. 江汉平原不同氮肥运筹模式下豆麦和稻/麦轮作系统小麦产量和经济效益差异[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(2): 441-448.
DOI |
|
YANG Rui, GENG Shiying, WANG Xiaoyan. Differences of wheat yield and economic benefits between soybean-wheat and rice-wheat cropping under different nitrogen fertilization patterns in Jianghan Plain, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(2): 441-448.
DOI |
|
| [45] | Simili da Silva M, Tremblay G F, Bélanger G, et al. Forage energy to protein ratio of several legume-grass complex mixtures[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2014, 188: 17-27. |
| [46] | Bo P T, Dong Y L, Zhang R F, et al. Optimization of alfalfa-based mixed cropping with winter wheat and ryegrass in terms of forage yield and quality traits[J]. Plants, 2022, 11(13): 1752. |
| [1] | FANG Hui, DING Yindeng, FAN Guiqiang, GAO Yonghong, HUANG Tianrong. Research report on the development status of wheat industry in southern Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 75-80. |
| [2] | YANG Minghua, LIAO Biyong, LIU Qiang, PENG Yuncheng, Dawulai Jiekeshan, FENG Guorui, TANG Shimin. Study on variation of grain nutritional quality of glutinous maize [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2087-2093. |
| [3] | ZHANG Zehua, YE Hanchun, WANG Zhenhua, LI Wenhao, LI Haiqiang, LIU Jian. Effects of equal nitrogen applied with urease inhibitor on cotton growth, yield, and quality under mulched drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2103-2111. |
| [4] | CHEN Ruijie, LUO Linyi, RUAN Xiangyang, YE Jun. Effects of humic acid on soil nutrients, cotton yield and quality in cotton fields under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2112-2121. |
| [5] | HUANG Boxuan, LI Pengcheng, ZHENG Cangsong, SUN Miao, SHAO Jingjing, FENG Weina, PANG Chaoyou, XU Wenxiu, DONG Helin. Effects of different nitrogen inhibitors on growth, nitrogen utilization and yield of cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2122-2131. |
| [6] | LIU Jing, DU Mingchuan, ZHANG Wenting, BAO Haijuan, JING Meiling, DU Wenhua. Screening of triticale germplasm in different areas of Qinghai [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2183-2190. |
| [7] | CHEN Fang, LI Zihui, SUNXiaogui , ZHANG Tingjun. Different dosage of microbial agents on the yield and quality of processed tomatoes [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2285-2289. |
| [8] | ZHANG Chengjie, HU Haoran, DUAN Songjiang, WU Yifan, ZHANG Jusong. Effects of nitrogen-dense interaction on growth, development, yield and quality of Gossypium barbadense L. [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1821-1830. |
| [9] | HOU Lili, WANG Wei, CUI Xinju, ZHOU Dawei. Effects of organic and inorganic combined application on yield, soil nutrients and enzyme activities of winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1845-1852. |
| [10] | CHEN Fang, LI Zihui, WANG Bingyue, SUN Xiaogui, ZHANG Tingjun. Effects of microbial inoculants on growth and yield of winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1853-1860. |
| [11] | YUAN Yingying, ZHAO Jinghua, Dilimulati Simayi, YANG Tingrui. Study on physiological indexes and yield analysis of spring wheat in pots based on apriori algorithm [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1861-1871. |
| [12] | NIU Tingting, MA Mingsheng, ZHANG Jungao. Effects of straw returning and plastic film mulching on soil physical and chemical properties and spring maize yield in rain-fed upland farmland [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1896-1906. |
| [13] | ZHAO Minhua, SONG Bingxi, ZHANG Yupeng, GAO Zhihong, ZHU Yongyong, CHEN Xiaoyuan. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer reduction on rice yield and nitrogen partial factor productivity under dry farming conditions [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1907-1915. |
| [14] | ZHANG Caihong, WANG Guoqiang, JIANG Luyan, LIU Tao, DE Xianming. Variation of environmental factors and analysis of tomato traits in low-energy assembly-type deep-winter production solar greenhouse [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 2043-2053. |
| [15] | YANG Mei, ZHAO Hongmei, Dilireba Xiamixiding, YANG Weijun, ZHANG Jinshan, HUI Chao. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer reduction and biochar application on population structure, photosynthetic characteristics and yield of spring wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1582-1589. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 31
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 109
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||