

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (9): 2120-2127.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.09.005
• Crop Genetics and Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Genetics·Soil Fertilizer • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Chuan1( ), ZHANG Kai1(
), ZHANG Kai1( ), CHEN Bing1, ZHANG Hui1, LIU Ping1, CHANG Song1, SHENG Jiandong2
), CHEN Bing1, ZHANG Hui1, LIU Ping1, CHANG Song1, SHENG Jiandong2
Received:2022-12-02
Online:2023-09-20
Published:2023-09-19
Correspondence author:
ZHANG Kai (1986-), male, native place: Huojia, Henan Province, associate professor, research field: cropland nutrient cycling,(E-mail) Supported by:
杨川1( ), 张凯1(
), 张凯1( ), 陈冰1, 张慧1, 柳萍1, 常松1, 盛建东2
), 陈冰1, 张慧1, 柳萍1, 常松1, 盛建东2
通讯作者:
张凯(1986-),男,河南获嘉人,副教授,博士,研究方向为养分循环,(E-mail)作者简介:杨川(1998-),男,云南昆明人,硕士研究生,研究方向为养分循环,(E-mail)729179663@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
YANG Chuan, ZHANG Kai, CHEN Bing, ZHANG Hui, LIU Ping, CHANG Song, SHENG Jiandong. Responses of morphological characteristics of cotton to different water conditions[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2120-2127.
杨川, 张凯, 陈冰, 张慧, 柳萍, 常松, 盛建东. 棉花植株形态特征对不同水分状况的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2120-2127.
| 处理 Treatments | 滴灌时间及滴灌量 Date and quantity of drip irrigation(m3/hm2) | 滴灌总量 Total irrigation (m3/hm2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5/10 | 6/13 | 6/26 | 7/13 | 7/22 | 7/30 | 8/10 | ||
| W100 | 650 | 807 | 323 | 344 | 286 | 229 | 432 | 3 071 |
| W85 | 650 | 682 | 271 | 292 | 245 | 193 | 354 | 2 687 |
| W75 | 650 | 641 | 250 | 219 | 193 | 177 | 292 | 2 422 |
| W60 | 650 | 490 | 167 | 151 | 139 | 125 | 234 | 1 956 |
Tab.1 Drip irrigation date and quantity of different experimental treatments
| 处理 Treatments | 滴灌时间及滴灌量 Date and quantity of drip irrigation(m3/hm2) | 滴灌总量 Total irrigation (m3/hm2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5/10 | 6/13 | 6/26 | 7/13 | 7/22 | 7/30 | 8/10 | ||
| W100 | 650 | 807 | 323 | 344 | 286 | 229 | 432 | 3 071 |
| W85 | 650 | 682 | 271 | 292 | 245 | 193 | 354 | 2 687 |
| W75 | 650 | 641 | 250 | 219 | 193 | 177 | 292 | 2 422 |
| W60 | 650 | 490 | 167 | 151 | 139 | 125 | 234 | 1 956 |

Fig.1 Morphological characteristics and moisture content change trend of cotton in drought cycle at bud stage (mean±se) Note:The arrow is marked as irrigation date, the same as below
| 时间 Time | 顶两叶距离 Distance of top petioles (cm) | 叶柄夹角 Angle stem- petiole (°) | 叶夹角 Angle leaf (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10:00~11:00 | -0.441** | 0.436** | 0.034 |
| 13:00~14:00 | -0.370** | 0.322** | 0.231 |
| 16:00~17:00 | -0.569** | 0.351** | 0.307* |
| 19:00~20:00 | -0.434** | 0.304** | 0.104 |
Tab.2 Relationship between cotton morphology and water content in different time periods
| 时间 Time | 顶两叶距离 Distance of top petioles (cm) | 叶柄夹角 Angle stem- petiole (°) | 叶夹角 Angle leaf (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10:00~11:00 | -0.441** | 0.436** | 0.034 |
| 13:00~14:00 | -0.370** | 0.322** | 0.231 |
| 16:00~17:00 | -0.569** | 0.351** | 0.307* |
| 19:00~20:00 | -0.434** | 0.304** | 0.104 |
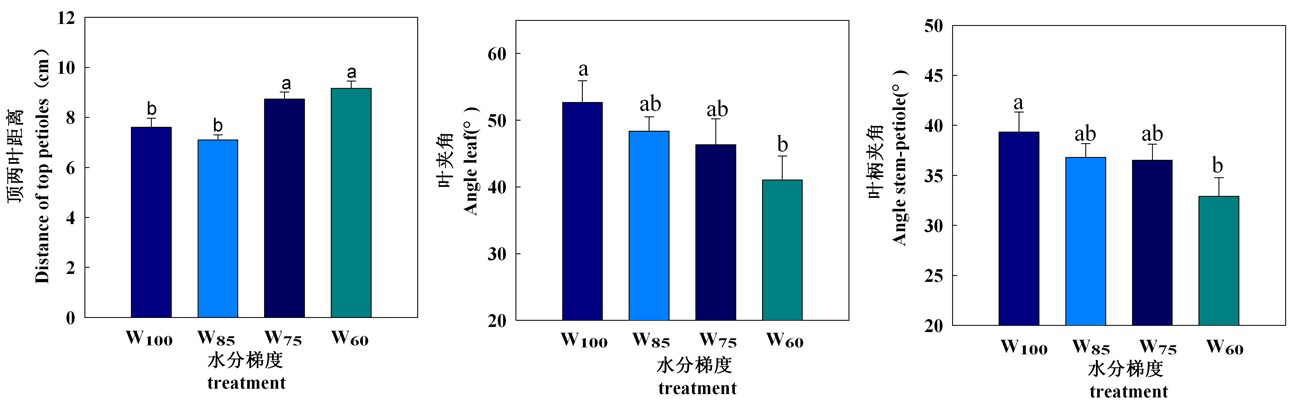
Fig.2 Effects of different irrigation gradients on morphological characteristics of cotton at bud stage (mean±se) Note: Different letters indicate that the difference between treatments reached a significant level (P<0.05), the same as below
| 生育期 Reproductive period | 顶两叶 距离 Distance of top petioles (cm) | 叶柄夹角 Angle stem- petiole (°) | 叶夹角 Angle leaf (°) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花蕾期 Bud stage | 植株含水率 | -0.569** | 0.351** | 0.307* |
| 叶含水率 | -0.481** | 0.311** | 0.365** | |
| 茎含水率 | -0.557** | 0.340** | 0.370** | |
| 根含水率 | -0.570** | 0.319** | 0.396** | |
| 花铃期 Flowering and boll stage | 植株含水率 | -0.382** | 0.381** | -0.387** |
| 叶含水率 | -0.217* | 0.226* | -0.247* | |
| 茎含水率 | -0.405** | 0.396** | -0.402** | |
| 根含水率 | -0.403** | 0.400** | -0.393** | |
Tab.3 Relationship between cotton morphology and moisture content at flowering and boll stage(during 16:00-17:00)
| 生育期 Reproductive period | 顶两叶 距离 Distance of top petioles (cm) | 叶柄夹角 Angle stem- petiole (°) | 叶夹角 Angle leaf (°) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花蕾期 Bud stage | 植株含水率 | -0.569** | 0.351** | 0.307* |
| 叶含水率 | -0.481** | 0.311** | 0.365** | |
| 茎含水率 | -0.557** | 0.340** | 0.370** | |
| 根含水率 | -0.570** | 0.319** | 0.396** | |
| 花铃期 Flowering and boll stage | 植株含水率 | -0.382** | 0.381** | -0.387** |
| 叶含水率 | -0.217* | 0.226* | -0.247* | |
| 茎含水率 | -0.405** | 0.396** | -0.402** | |
| 根含水率 | -0.403** | 0.400** | -0.393** | |
| [1] | 闫建峰. 新疆维吾尔自治区棉花生产现状及发展对策[J]. 乡村科技, 2020, 11(22): 47-48. |
| YAN Jianfeng. Present situation and development countermeasures of cotton production in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region[J]. Xiang Cun Ke Ji, 2020, 11(22): 47-48. | |
| [2] | 李雪源, 王俊铎, 郑巨云, 等. 新疆棉花产业发展与供给侧改革[J]. 中国棉花, 2017, 44(8): 1-7. |
| LI Xueyuan, WANG Junduo, ZHENG Juyun, et al. Cotton industry development and the supply-side reformin Xinjiang, China[J]. China Cotton, 2017, 44(8): 1-7. | |
| [3] | 郑媛芳. 新疆水资源分布及脆弱性评价[J]. 2018: 39-41. |
| ZHENG Yuanfang. Distribution and vulnerability assessment of water resources in Xinjiang[J]. Shaanxi Water Resources, 2018: 39-41. | |
| [4] | 郑力嘉, 孙宇瑞, 蔡祥. 基于激光扫描3D图像的植物亏水体态辨识与萎蔫指数比较[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(2): 79-86. |
| ZHENG Lijia, SUN Yurui, CAI Xiang. Comparison of plant water deficit posture identification and wilting index based on laser scanning 3D images[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(2): 79-86. | |
| [5] | 张智韬, 边江, 韩文霆, 等. 无人机热红外图像计算冠层温度特征数诊断棉花水分胁迫[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(15): 77-84. |
| ZHANG Zhitao, BIAN Jiang, HAN Wenting, et al. Diagnosis of cotton water stress by calculating canopy temperature characteristic number from UAV thermal infrared image[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(15): 77-84. | |
| [6] | 尚晓英, 张智韬, 边江, 等. 基于无人机热红外的水分胁迫指数与土壤含水率关系研究[J]. 节水灌溉, 2019, 284(4): 16-21. |
| SHANG Xiaoying, ZHANG Zhitao, BIAN Jiang, et al. Study on the relationship between water stress index and soil moisture content based on UAV thermal infrared[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2019, 284(4): 16-21. | |
| [7] | Jones H G. Use of Infrared Thermometry for Estimation of Stomatal Conductance as a Possible Aid to Irrigation Scheduling[J]. Agricultural & Forest Meteorology, 1999, 95(3): 139-149. |
| [8] | 王娟. 基于计算机视觉的棉花干旱诊断研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2014. |
| WANG Juan. Research on Cotton Drought Diagnosis Based on Computer Vision[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2014. | |
| [9] | 吴晓磊, 张寄阳, 刘浩, 等. 基于红外热像仪的棉花水分状况诊断方法[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(1): 165-172. |
|
WU Xiaolei, ZHANG Jiyang, LIU Hao, et al. Diagnosis method of cotton water status based on infrared thermal imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(1): 165-172.
PMID |
|
| [10] | 王方永, 王克如, 王崇桃, 等. 基于图像识别的棉花水分状况诊断研究[J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, (4): 404-407. |
| WANG Fangyong, WANG Keru, WANG Chongtao, et al. Research on cotton moisture condition diagnosis based on image recognition[J]. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science Ed.), 2007,(4): 404-407. | |
| [11] | 张寄阳, 段爱旺, 孟兆江, 等. 不同水分状况下棉花茎直径变化规律研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2005, (5): 7-11. |
| ZHANG Jiyang, DUAN Aiwang, MENG Zhangjiang, et al. Stem diameter Variations of cotton under different Water conditions[J]. Transactions of Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2005, (5): 7-11. | |
| [12] | 李志博, 徐建伟, 李衡, 等. 后期持续干旱对北疆棉花生长发育的影响及其抗旱适应性评价[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2014, 32(3): 45-49, 82. |
| LI Zhibo, XU Jianwei, LI Heng, et al. Effect of persistent drought on cotton growth and development in northern Xinjiang and its drought-resistant adaptability evaluation[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2014, 32(3): 45-49, 82. | |
| [13] | 肖俊夫, 刘祖贵, 孙景生, 等. 不同生育期干旱对棉花生长发育及产量的影响[J]. 灌溉排水, 1999,(1): 24-28. |
| XIAO Junfu, LIU Zugui, SUN Jingsheng, et al. Effects of drought at different growth stages on cotton growth and yield[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 1999,(1): 24-28. | |
| [14] | 龙海燕, 邓伦秀. 植物形态对干旱胁迫的反应与适应性研究[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2019, 58(8): 5-7. |
| LONG Haiyan, DENG Lunxiu. Response and adaptability of plant morphology to drought stress[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 58(8): 5-7. | |
| [15] | 高阳. 土壤水分梯度变化对内蒙古典型草原草本植物形态及成分的影响[D]. 北京: 中央民族大学, 2021. |
| GAO Yang. Effects of soil moisture gradient on the morphology and composition of herbaceous plants in typical grasslands of Inner Mongolia[D]. Beijing: Minzu University of China, 2021. | |
| [16] | 冯先伟, 陈曦, 包安明, 等. 水分胁迫条件下棉花生理变化及其高光谱响应分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2004,(2): 250-255. |
| FENG Xianwei, CHEN Xi, BAO Anming, et al. Physiological changes and hyperspectral response analysis of cotton under water stress[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2004,(2): 250-255. | |
| [17] | 李彦, 雷晓云, 白云岗. 不同灌水下限对棉花产量及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2013, 32(4): 132-134. |
| LI Yan, LEI Xiaoyun, BAI Yungang. Effects of different irrigation limits on cotton yield and water use efficiency[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2013, 32(4): 132-134. | |
| [18] | 郭金强, 危常州, 侯振安, 等. 北疆棉花膜下滴灌耗水规律的研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2005, 42(4): 205-209. |
| GUO Jinqiang, WEI Changzhou, HOU Zhen 'an, et al. Study on water consumption law of drip irrigation under plastic film for cotton in northern Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2005, 42(4): 205-209. | |
| [19] | 江柱, 张江辉, 白云岗, 等. 不同灌水频率水分胁迫对北疆棉花生长及产量的影响[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2021,(5): 49-54. |
| JIANG Zhu, ZHANG Jianghui, BAI Yungang, et al. Effects of water stress with different irrigation frequencies on cotton growth and yield in northern Xinjiang[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2021,(5): 49-54. | |
| [20] | 赵燕东, 刘贺, 刘卫平. 基于叶片分形维数的植物亏水胁迫萎蔫体态测量方法[J]. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(9): 191-195. |
| ZHAO Yandong, LIU He, LIU Weiping. Measurement method of plant wilting posture under water deficit stress based on fractal dimension of leaves[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2011, 27(9): 191-195. | |
| [21] | 吕新, 张伟, 王登伟, 等. 棉花冠层对不同灌水量的反应[J]. 棉花学报, 2004,(1): 21-25. |
| LYU Xin, ZHANG Wei, WANG Dengwei, et al. Response of cotton canopy to different irrigation amounts[J]. Cotton Science, 2004,(1): 21-25. | |
| [22] | 张伟, 吕新. 棉花冠层对不同灌水量的反应及其产量形成研究[J]. 干旱区研究, 2004,(4): 425-429. |
| ZHANG Wei, LYU Xin. Response of cotton canopy to different irrigation amount and its yield formation[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2004,(4): 425-429. | |
| [23] | 张世民. 调亏灌溉对棉花生长生理和产量的影响[D], 阿拉尔: 塔里木大学, 2017. |
| Zhang Shimin. Effects of regulated deficit irrigation on cotton growth physiology and yield[D]. Aral: Tarim University, 2017. |
| [1] | ZHOU Xin, LIU Xuanfeng, JIANG Yuhan, ZHANG Haichun, YANG Yuxin, Yeerbdati Tiemuer, JIANG Yongxin, ZHANG Li. Current situation and development proposal of mechanized recovery and resource utilization of used mulch film in cotton fields in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 131-141. |
| [2] | MIAO Hongping, WANG Xiaowei, TIAN Conghua, LI Zhi, ZHANG Yuxin, DAI Junsheng. Evolution characteristics and driving factors of cotton production and distribution in Tarim River basin [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 217-226. |
| [3] | WANG Junduo, CUI Yujiang, LIANG Yajun, GONG Zhaolong, ZHENG Junyun, LI Xueyuan. Xinjiang cotton production advantageous regional layout scheme [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 60-69. |
| [4] | ZHENG Juyun, GONG Zhaolong, LIANG Yajun, GENG Shiwei, SUN Fenglei, YANG ni, LI Xueyuan, WANG Junduo. Key technology model of machine-picked cotton production in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 70-74. |
| [5] | LI Jie, LIU Jia, WANG Liang, ZHANG Na, YANG Yanlong, ZHENG Zipiao, WEI Xin, WANG Meng, ZHOU Zixin, YANG Ni, GONG Zhaolong, HOU Xianfei, HUANG Qixiu, Abudukadier kuerban, ZHANG Jipeng, CHANG Pengzhong. Current situation of transformation and application of scientific and technological achievements of "cotton, oil and sugar" [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 89-94. |
| [6] | BIAN Qingyong, FU Yanbo, QI Tong, HUANG Jian, PU Shenghai, MENG Ajing, Halihashi Yibati. Study on influencing factors of cotton emergence and protection measures in saline-alkali land in southern Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 95-100. |
| [7] | LI Yongtai, GAO Axiang, LI Yanjun, ZHANG Xinyu. Effects of defoliants on the physiological characteristics of cotton varieties with different sensitivities [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2094-2102. |
| [8] | ZHANG Zehua, YE Hanchun, WANG Zhenhua, LI Wenhao, LI Haiqiang, LIU Jian. Effects of equal nitrogen applied with urease inhibitor on cotton growth, yield, and quality under mulched drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2103-2111. |
| [9] | CHEN Ruijie, LUO Linyi, RUAN Xiangyang, YE Jun. Effects of humic acid on soil nutrients, cotton yield and quality in cotton fields under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2112-2121. |
| [10] | HUANG Boxuan, LI Pengcheng, ZHENG Cangsong, SUN Miao, SHAO Jingjing, FENG Weina, PANG Chaoyou, XU Wenxiu, DONG Helin. Effects of different nitrogen inhibitors on growth, nitrogen utilization and yield of cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2122-2131. |
| [11] | WANG Chao, XU Wenxiu, LI Pengcheng, ZHENG Cangsong, SUN Miao, FENG Weina, SHAO Jingjing, DONG Helin. Response of cotton seedling growth and development to soil available potassium levels [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2132-2139. |
| [12] | ZHANG Tingjun, LI Zihui, CUI Yujiang, SUN Xiaogui, CHEN Fang. Effects of microbial agents on cotton growth and soil physico-chemical properties [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2269-2276. |
| [13] | DONG Zhiduo, XU Fei, FU Qiuping, HUANG Jian, QI Tong, MENG Ajing, FU Yanbo, Kaisaier Kuerban. Effects of different types of salt and alkali stress on cotton seed germination [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1831-1844. |
| [14] | LI Ying, GUO Wenwen, LI Jiangbo, QU Yanying, CHEN Quanjia, ZHENG Kai. Evaluation of adaptability of 90 BT transgenic insectresistant cotton varieties (lines) in early cotton areas of Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1561-1573. |
| [15] | LIU Huijie, WANG Junhao, GONG Zhaolong, LIANG Yajun, WANG Junduo, LI Xueyuan, ZHENG Juyun, WANG Jichuan. Identification of salt tolerance of 197 upland cotton varieties at germination stage [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1574-1581. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 58
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 1236
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||