

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (4): 857-864.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.04.009
• Crop Genetics and Breeding·Cultivation Physiology·Germplasm Resources • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chen Guo( ), Hao Xiaoyan, Gao Shengqi, Hu Wenran, Zhao Zhun, Huang Quansheng(
), Hao Xiaoyan, Gao Shengqi, Hu Wenran, Zhao Zhun, Huang Quansheng( )
)
Received:2022-09-20
Online:2023-04-20
Published:2023-05-06
Correspondence author:
HUANG Quansheng (1964-), Male, Urumqi, researcher, doctor, research direction: molecular biology of crop resistance, (E-mail) Supported by:
陈果( ), 郝晓燕, 高升旗, 胡文冉, 赵准, 黄全生(
), 郝晓燕, 高升旗, 胡文冉, 赵准, 黄全生( )
)
通讯作者:
黄全生(1964-),男,乌鲁木齐人,研究员,博士,研究方向为作物抗逆分子生物学,(E-mail) 作者简介:陈果(1984-),男,四川仪陇人,副研究员,博士,研究方向为玉米分子生物学,(E-mail)252931257@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Chen Guo, Hao Xiaoyan, Gao Shengqi, Hu Wenran, Zhao Zhun, Huang Quansheng. Genome-wide identification of the maize calcium-dependent protein kinase and drought expression analysis of the CDPK gene family in maize[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(4): 857-864.
陈果, 郝晓燕, 高升旗, 胡文冉, 赵准, 黄全生. 玉米钙依赖蛋白激酶全基因组鉴定及抗旱表达分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(4): 857-864.
| 名称 Name | 序列号 ID | CDs | 氨基酸 Amino acid | 分子量 MW (kDa) | EF手型数量 No. of EF Hands | N端序列 N-terminal | N端豆蔻酰化基元 N-Myristoylation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZmCDPK1 | GRMZM2G028926_T01 | 1 827 | 608 | 66.4 | 4 | MGNTCVGP | No |
| ZmCDPK2 | GRMZM2G320506_T01 | 1 863 | 620 | 67.7 | 4 | MGNTCVGP | No |
| ZmCDPK3 | GRMZM2G025387_T01 | 1 593 | 530 | 59.9 | 4 | MGNRASRH | Yes |
| ZmCDPK4 | GRMZM2G035843_T01 | 1 527 | 508 | 56.5 | 4 | MQPDPSGN | No |
| ZmCDPK5 | GRMZM2G314396_T01 | 1 644 | 547 | 60.4 | 4 | MGNACSGA | Yes |
| ZmCDPK6 | GRMZM2G321239_T01 | 1 671 | 556 | 61.2 | 4 | MGNACGGA | Yes |
| ZmCDPK7 | GRMZM2G104125_T01 | 1 608 | 535 | 60.3 | 4 | MGNCCATP | Yes |
| ZmCDPK8 | AC210013.4_FGP014 | 1 617 | 538 | 60.4 | 4 | MGNCCAAP | Yes |
| ZmCDPK9 | GRMZM2G154489_T01 | 1 596 | 531 | 59.4 | 4 | MGQCCSRA | Yes |
| ZmCDPK10 | GRMZM2G030673_T01 | 1 626 | 541 | 60.5 | 4 | MGNCCRSP | No |
| ZmCDPK11 | GRMZM2G463464_T01 | 1 548 | 515 | 56.8 | 4 | MQPDPQGP | No |
| ZmCDPK12 | GRMZM2G047486_T01 | 1 533 | 510 | 60.2 | 4 | MQPDPSGN | No |
| ZmCDPK13 | GRMZM2G311220_T01 | 1 611 | 536 | 60.2 | 4 | MGNCCRSP | No |
| ZmCDPK14 | GRMZM2G028086_T01 | 1 620 | 539 | 60.8 | 4 | MGNCCVTP | Yes |
| ZmCDPK15 | GRMZM2G058305_T01 | 1 620 | 539 | 60.7 | 4 | MGGRASRH | Yes |
| ZmCDPK16 | GRMZM2G015703_T01 | 1 779 | 592 | 65.4 | 1 | MGLCHGKP | Yes |
| ZmCDPK17 | GRMZM2G167276_T01 | 1 533 | 510 | 56.2 | 4 | MGNCCPGS | Yes |
| ZmCDPK18 | GRMZM2G157068_T02 | 1 569 | 522 | 58.5 | 4 | MGACFSSA | Yes |
| ZmCDPK19 | GRMZM2G347047_T01 | 1 467 | 488 | 53.9 | 4 | MGGHQLHL | No |
| ZmCDPK20 | GRMZM2G121228_T01 | 1 743 | 580 | 63.7 | 4 | MGNTCVGP | No |
| ZmCDPK21 | GRMZM2G027351_T01 | 1 755 | 584 | 64.1 | 4 | MGNTCVGP | No |
| ZmCDPK22 | GRMZM2G347226_T01 | 1 548 | 515 | 56.8 | 4 | MQPDPQGS | No |
| ZmCDPK23 | GRMZM2G040743_T01 | 1 623 | 540 | 60.9 | 4 | MGNQCQNG | No |
| ZmCDPK24 | GRMZM2G080871_T02 | 1 536 | 511 | 57.0 | 3 | MGGCHSAI | No |
| ZmCDPK25 | GRMZM2G353957_T01 | 1 941 | 646 | 71.7 | 4 | MGNVCVGP | No |
| ZmCDPK26 | GRMZM2G081310_T01 | 1 689 | 562 | 61.9 | 4 | MGNTCGVT | No |
| ZmCDPK27 | GRMZM2G032852_T02 | 1 635 | 544 | 61.7 | 4 | MGNQCPNG | No |
| ZmCDPK28 | GRMZM2G365035_T01 | 1 539 | 512 | 57.5 | 4 | MGLCSSST | Yes |
| ZmCDPK29 | GRMZM2G112057_T01 | 1 620 | 539 | 61.0 | 4 | MGNCFTRK | Yes |
| ZmCDPK30 | GRMZM2G088361_T01 | 1 623 | 540 | 60.2 | 4 | MGNCCRSP | No |
| ZmCDPK31 | GRMZM5G856738_T03 | 1 575 | 524 | 59.5 | 4 | MGNRASRH | Yes |
| ZmCDPK32 | GRMZM2G099425_T01 | 1 620 | 539 | 60.8 | 4 | MGNCCVTP | Yes |
| ZmCDPK33 | GRMZM2G168706_T01 | 1 596 | 531 | 59.4 | 4 | MGQCCSRA | Yes |
| ZmCDPK34 | GRMZM2G340224_T01 | 1 842 | 613 | 67.5 | 4 | MRPSVSMI | Yes |
| ZmCDPK35 | GRMZM2G365815_T01 | 1 659 | 552 | 60.0 | 4 | MGQCCSKG | Yes |
| ZmCDPK36 | GRMZM2G472311_T01 | 1 746 | 581 | 63.4 | 4 | MGQCCSKG | Yes |
| ZmCDPK37 | AC203294.3_FGP001 | 1 395 | 464 | 50.9 | 4 | MGNCCPGS | No |
| ZmCDPK38 | GRMZM2G332660_T01 | 1 707 | 568 | 62.8 | 4 | MGGCYSAF | Yes |
| ZmCDPK39 | GRMZM2G097533_T01 | 1 317 | 438 | 48.5 | 1 | MGNCCVSR | Yes |
Tab.1 Characteristics of CDPKs from maize
| 名称 Name | 序列号 ID | CDs | 氨基酸 Amino acid | 分子量 MW (kDa) | EF手型数量 No. of EF Hands | N端序列 N-terminal | N端豆蔻酰化基元 N-Myristoylation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZmCDPK1 | GRMZM2G028926_T01 | 1 827 | 608 | 66.4 | 4 | MGNTCVGP | No |
| ZmCDPK2 | GRMZM2G320506_T01 | 1 863 | 620 | 67.7 | 4 | MGNTCVGP | No |
| ZmCDPK3 | GRMZM2G025387_T01 | 1 593 | 530 | 59.9 | 4 | MGNRASRH | Yes |
| ZmCDPK4 | GRMZM2G035843_T01 | 1 527 | 508 | 56.5 | 4 | MQPDPSGN | No |
| ZmCDPK5 | GRMZM2G314396_T01 | 1 644 | 547 | 60.4 | 4 | MGNACSGA | Yes |
| ZmCDPK6 | GRMZM2G321239_T01 | 1 671 | 556 | 61.2 | 4 | MGNACGGA | Yes |
| ZmCDPK7 | GRMZM2G104125_T01 | 1 608 | 535 | 60.3 | 4 | MGNCCATP | Yes |
| ZmCDPK8 | AC210013.4_FGP014 | 1 617 | 538 | 60.4 | 4 | MGNCCAAP | Yes |
| ZmCDPK9 | GRMZM2G154489_T01 | 1 596 | 531 | 59.4 | 4 | MGQCCSRA | Yes |
| ZmCDPK10 | GRMZM2G030673_T01 | 1 626 | 541 | 60.5 | 4 | MGNCCRSP | No |
| ZmCDPK11 | GRMZM2G463464_T01 | 1 548 | 515 | 56.8 | 4 | MQPDPQGP | No |
| ZmCDPK12 | GRMZM2G047486_T01 | 1 533 | 510 | 60.2 | 4 | MQPDPSGN | No |
| ZmCDPK13 | GRMZM2G311220_T01 | 1 611 | 536 | 60.2 | 4 | MGNCCRSP | No |
| ZmCDPK14 | GRMZM2G028086_T01 | 1 620 | 539 | 60.8 | 4 | MGNCCVTP | Yes |
| ZmCDPK15 | GRMZM2G058305_T01 | 1 620 | 539 | 60.7 | 4 | MGGRASRH | Yes |
| ZmCDPK16 | GRMZM2G015703_T01 | 1 779 | 592 | 65.4 | 1 | MGLCHGKP | Yes |
| ZmCDPK17 | GRMZM2G167276_T01 | 1 533 | 510 | 56.2 | 4 | MGNCCPGS | Yes |
| ZmCDPK18 | GRMZM2G157068_T02 | 1 569 | 522 | 58.5 | 4 | MGACFSSA | Yes |
| ZmCDPK19 | GRMZM2G347047_T01 | 1 467 | 488 | 53.9 | 4 | MGGHQLHL | No |
| ZmCDPK20 | GRMZM2G121228_T01 | 1 743 | 580 | 63.7 | 4 | MGNTCVGP | No |
| ZmCDPK21 | GRMZM2G027351_T01 | 1 755 | 584 | 64.1 | 4 | MGNTCVGP | No |
| ZmCDPK22 | GRMZM2G347226_T01 | 1 548 | 515 | 56.8 | 4 | MQPDPQGS | No |
| ZmCDPK23 | GRMZM2G040743_T01 | 1 623 | 540 | 60.9 | 4 | MGNQCQNG | No |
| ZmCDPK24 | GRMZM2G080871_T02 | 1 536 | 511 | 57.0 | 3 | MGGCHSAI | No |
| ZmCDPK25 | GRMZM2G353957_T01 | 1 941 | 646 | 71.7 | 4 | MGNVCVGP | No |
| ZmCDPK26 | GRMZM2G081310_T01 | 1 689 | 562 | 61.9 | 4 | MGNTCGVT | No |
| ZmCDPK27 | GRMZM2G032852_T02 | 1 635 | 544 | 61.7 | 4 | MGNQCPNG | No |
| ZmCDPK28 | GRMZM2G365035_T01 | 1 539 | 512 | 57.5 | 4 | MGLCSSST | Yes |
| ZmCDPK29 | GRMZM2G112057_T01 | 1 620 | 539 | 61.0 | 4 | MGNCFTRK | Yes |
| ZmCDPK30 | GRMZM2G088361_T01 | 1 623 | 540 | 60.2 | 4 | MGNCCRSP | No |
| ZmCDPK31 | GRMZM5G856738_T03 | 1 575 | 524 | 59.5 | 4 | MGNRASRH | Yes |
| ZmCDPK32 | GRMZM2G099425_T01 | 1 620 | 539 | 60.8 | 4 | MGNCCVTP | Yes |
| ZmCDPK33 | GRMZM2G168706_T01 | 1 596 | 531 | 59.4 | 4 | MGQCCSRA | Yes |
| ZmCDPK34 | GRMZM2G340224_T01 | 1 842 | 613 | 67.5 | 4 | MRPSVSMI | Yes |
| ZmCDPK35 | GRMZM2G365815_T01 | 1 659 | 552 | 60.0 | 4 | MGQCCSKG | Yes |
| ZmCDPK36 | GRMZM2G472311_T01 | 1 746 | 581 | 63.4 | 4 | MGQCCSKG | Yes |
| ZmCDPK37 | AC203294.3_FGP001 | 1 395 | 464 | 50.9 | 4 | MGNCCPGS | No |
| ZmCDPK38 | GRMZM2G332660_T01 | 1 707 | 568 | 62.8 | 4 | MGGCYSAF | Yes |
| ZmCDPK39 | GRMZM2G097533_T01 | 1 317 | 438 | 48.5 | 1 | MGNCCVSR | Yes |

Fig.1 Phylogenetic tree of CDPKs from maize, rice and Arabidopsis Note:Neighbor-joining tree was created using MEGA5.0 program with 1,000 bootstrap using full length sequences of 39 maize, 29 rice, and 34 Arabidopsis CDPK proteins. Brown, maize orthologs; blue, rice orthologs, black, Arabidopsis orthologs
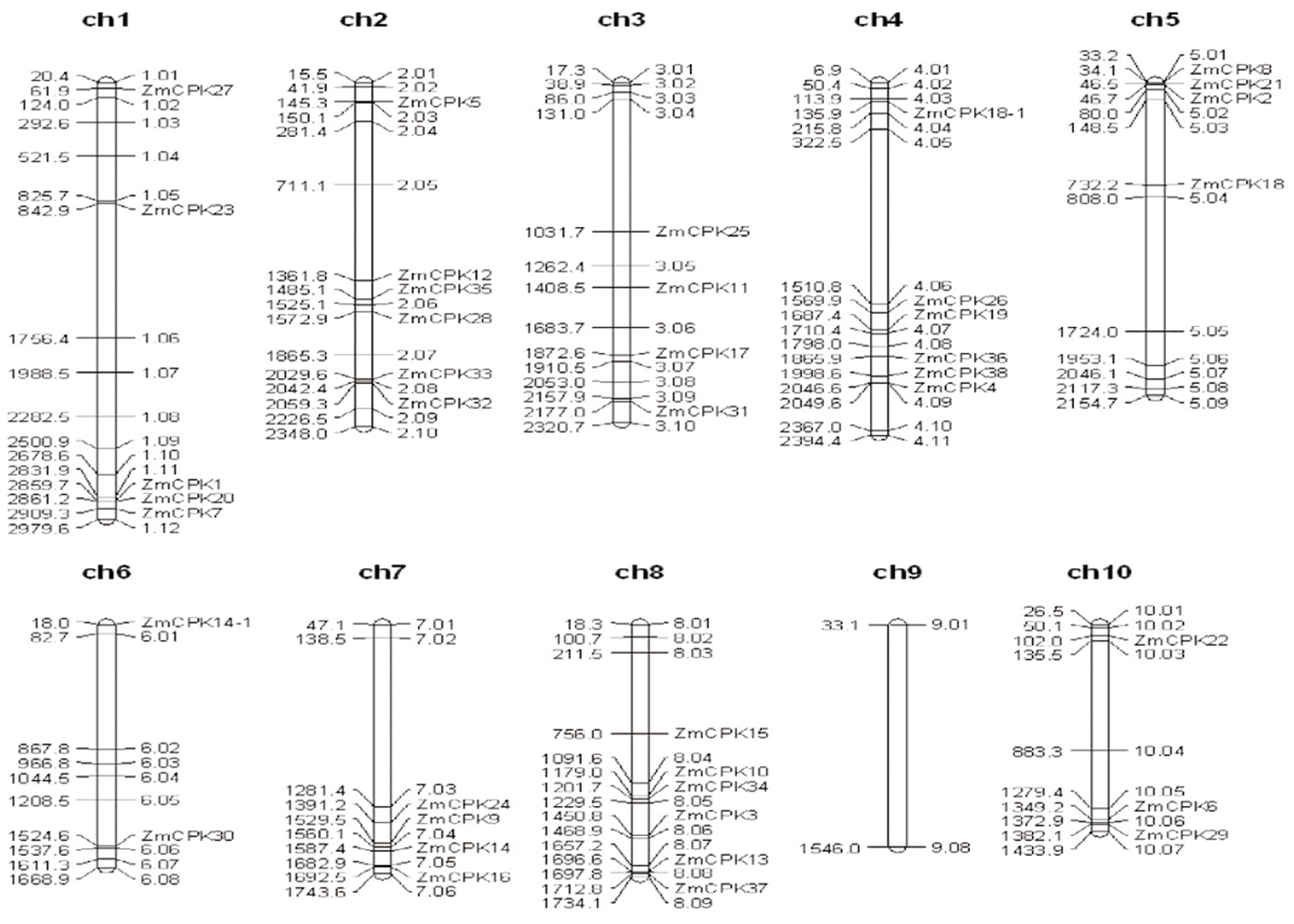
Fig.2 Chromosomal distributions of CDPK genes in the maize genome Note:The chromosome number is indicated at the top of each chromosome representation
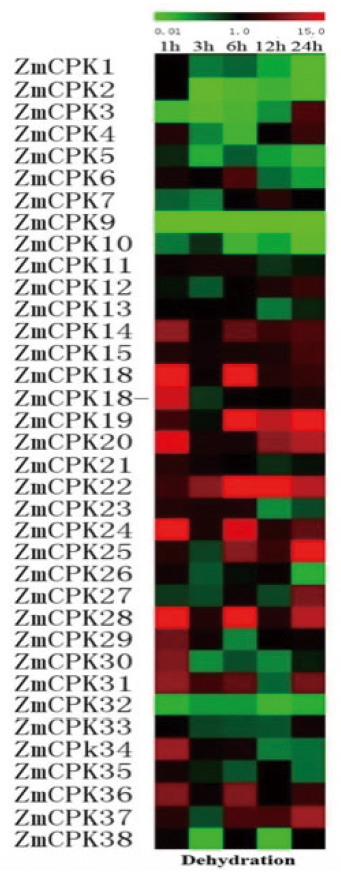
Fig.3 Expression analysis of 39 CDPK genes under drought stress for various times as indicated by quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis Note:The scale representing the relative signal intensity values is shown above. Hierarchical clustering was played in data analysis
| [1] | 梁晓玲, 刘文欣, 阿布来提·阿布拉, 等. 干旱胁迫对玉米杂交种产量及穗部性状的影响[J]. 玉米科学, 2021, 29(2):75-80. |
| Liang Xiaoling, Liu Wenxin, Abulaiti Abra, et al. Influence of drought stress on yield and ear traits of maize hybrids[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2021, 29(2):75-80. | |
| [2] | Hu H, Xiong L. Genetic engineering and breeding of drought-resistant crops[J]. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 2014,(65):715-741. |
| [3] |
Tuteja N, Mahajan S. Calcium signaling network in plants: an overview[J]. Plant Signal Behav, 2007, (2):79-85.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Harper JF, Harmon A. Plants symbiosis and parasites: a calcium signaling connection[J]. Nature Rev, 2005, (6):555-566. |
| [5] | Lourido S, Shuman J, Zhang C, et al. Calcium dependent protein kinase 1 is an essential regulator of exocytosis in Toxoplasma[J]. Nature, 2010, (465):359-362. |
| [6] |
Klimecka M, Muszynska G. Structure and functions of plant calcium dependent protein kinases[J]. Acta Biochim Pol, 2007, 54:219-233.
PMID |
| [7] |
Romeis T, Ludwig AA, Martin R, et al. Calcium-dependent protein kinases play an essential role in a plant defence response[J]. EMBO J, 2001, (20):5556-5567.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Asano T, Hayashi N, Kikuchi S, et al. CDPK-mediated abiotic stress signaling[J]. Plant Signal Behav, 2012, (7):1-5. |
| [9] | Lee J, Rudd JJ. Calcium-dependent protein kinases: versatile plant signaling components necessary for pathogen defence[J]. Trends Plant Sci, 2002, (7):97-98. |
| [10] | Ludwig AA, Romeis T, Jones JD. CDPK-mediated signalling pathways: specificity and cross-talk[J]. J Exp Bot, 2004, (55):181-188. |
| [11] | Zhu SY, Yu XC, Wang XJ, et al. Two calcium-dependent protein kinases CPK4 and CPK11 regulate abscisic acid signal transduction in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Cell, 2007, (19):3019-3036. |
| [12] | Mori IC, Murata Y, Yang Y, et al. CDPKs CPK6 and CPK3 function in ABA regulation of guard cell S-type anion- and Ca2+-permeable channels and stomatal closure[J]. PLoS Biol, 2006, (4): e327. |
| [13] | Munemasa S, Hossain MA, Nakamura Y, et al. The Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK6 functions as a positive regulator of methyl jasmonate signaling in guard cells[J]. Plant Physiol, 2011, (155):553-561. |
| [14] | Ma SY, Wu WH. AtCPK23 functions in Arabidopsis responses to drought and salt stresses[J]. Plant Mol Biol, 2007, (65):511-518. |
| [15] | Franz S, Ehlert B, Liese A, et al. Calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK21 functions in abiotic stress response in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Mol Plant, 2011, (4):83-96. |
| [16] |
Choi HI, Park HJ, Park JH, et al. Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase AtCPK32 interacts with ABF4 a transcriptional regulator of abscisic acid-responsive gene expression and modulates its activity[J]. Plant Physiol, 2005, 139:1750-1761.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Boudsocq M, Willmann MR, McCormack M, et al. Differential innate immune signaling via Ca2+sensor protein kinases[J]. Nature, 2010, (464):418-422. |
| [18] | Saijo Y, Hata S, Kyozuka J, et al. Over-expression of a single Ca2+dependent protein kinase confers both cold and salt/drought tolerance on rice plants[J]. Plant J, 2000, (23):319-327. |
| [19] | Asano T, Hakata M, Nakamura H, et al. Functional characterisation of OsCPK21 a calcium-dependent protein kinase that confers salt tolerance in rice[J]. Plant Mol Biol, 2011, (75):179-191. |
| [20] | Asano T, Hayashi N, Kobayashi M, et al. A rice calcium-dependent protein kinase OsCPK12 oppositely modulates salt-stress tolerance and blast disease resistance[J]. Plant J, 2012, (69):26-36. |
| [21] | Cheng SH, Willmann MR, Chen HC, et al. Calcium signaling through protein kinases: The Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase gene family[J]. Plant Physiol, 2002, (129):469-485. |
| [22] | Asano T, Tanaka N, Yang G, et al. Genome-wide identification of the rice calcium-dependent protein kinase and its closely related kinase gene families: comprehensive analysis of the CDPKs gene family in rice[J]. Plant Cell Physiol, 2005, (46):356-366 |
| [23] | Li AL, Zhu YF, Tan XM, et al. Evolutionary and functional study of the CDPK gene family in wheat (Triticum aestivum L)[J]. Plant Mol Biol, 2008, (66):429-443. |
| [24] | Yang DH, Hettenhausen C, Baldwin IT, et al. Nicotiana attenuata calcium-dependent protein kinases CDPK4 and CDPK5 strongly downregulate wound- and herbivory-induced jasmonic acid accumulations[J]. Plant Physiol, 2012, (159):1561-1607. |
| [25] | Giammaria V, Grandellis C, Bachmann S, et al. StCDPK2 expression and activity reveal a highly responsive potato calcium-dependent protein kinase involved in light signaling[J]. Planta, 2011, (233):593-609. |
| [26] | Chang WJ, Su HS, Li WJ, et al. Expression profiling of a novel calcium-dependent protein kinase gene LeCPK2 from tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) under heat and pathogen-related hormones[J]. Biosci Biotech Bioch, 2009, (73):2427-2431. |
| [27] | Berberich T, Kusano T. Cycloheximide induces a subset of low temperature-inducible genes in maize[J]. Mol Gen Genet, 1997, (254):275-283. |
| [28] | Saijo Y, Hata S, Sheen J, et al. cDNA cloning and prokaryotic expression of maize calcium-dependent protein kinases[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1997, (1350):109-114. |
| [29] | Murillo I, Jaeck E, Cordero MJ, et al. Transcriptional activation of a maize calcium-dependent protein kinase gene in response to fungal elicitors and infection[J]. Plant Mol Biol, 2001, (45):145-158. |
| [30] | Klimecka M, Szczegielniak J, Godecka L, et al. Regulation of wound-responsive calcium dependent protein kinase from maize (ZmCPK11) by phosphatidic acid[J]. Acta Biochim Pol, 2011, (58):589-595. |
| [31] | Schnable PS, Ware D, Fulton RS, et al. The B73 maize genome: complexity diversity and dynamics[J]. Science, 2009, (326):1112-1115. |
| [32] | Matschi S, Werner S, Schulze WX, et al. Function of calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK28 of Arabidopsis thaliana in plant stem elongation and vascular development[J]. Plant J, 2013, (73):883-896. |
| [1] | ZENG Wanying, GENG Hongwei, CHENG Yukun, LI Sizhong, QIAN Songting, GAO Weishi, ZHANG Liming. Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance during the rapid growth stage of sugar beet cultivars [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2140-2151. |
| [2] | Areziguli Tuxun, GAO Jie. Effects of drought stress and planting density on physiological characteristics and yield of onion bulblets [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2211-2222. |
| [3] | YANG Minghua, LIU Qiang, FENG Guorui, LIAO Biyong, Dawulai Jiekeshan, PENG Yuncheng, Buayixiamu Namanti, CHEN Yanping. Study on suitable harvesting time and grain water content of fresh waxy maize [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1626-1630. |
| [4] | JU Le, QI Juncang, NIU Yinting, SHI Peichun, SONG Ruijiao, SONG Lingyu, YIN Zhigang, CHEN Peiyu, QIANG Xuelan. RNA-seq-based mining and analysis of drought-related genes in barley seedlings [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(5): 1077-1084. |
| [5] | ZHANG Lei, YAO Mengyao, LIU Zhigang, LI Juan, YANG Yang, CAI Darun, CHEN Guo, LI Bo, LI Xiaorong, CHEN Xunji, ZHAI Yunlong. Research of maize yield estimation based on unmanned aerial vehicle multispectral NDVI [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 845-851. |
| [6] | GAO Mutian, XIAO Yanmei, LIAO Zhijie, HUANG Cheng. Comprehensive evaluation of kernel and quality traits in maize-teosinte introgression line population [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 885-891. |
| [7] | ZHANG Wei, YANG Guohui, YU Hui. Effects of 2,4-epibrassinolide on growth and related genes expression of watermelon seedlings under drought Stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(3): 615-622. |
| [8] | MENG Hanying, GUO Dandan, HE Wanjie, ZHANG Weiwei, ZHANG Jianping, CHEN Jing. Effects of different feeding time of Monolepta Signata on the composition and content of volatile in maize leaves [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(2): 421-433. |
| [9] | CHENG Yunxia, TAN Zhanming, GUO Ling, LI Wenwen, DU Jiageng. Effects of different drought stresses on anatomical structure of roots, stems and leaves of two apricot varieties [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2684-2692. |
| [10] | LIAO Caiyun, MA Gui, ZHOU Yanyan, DING Jiafu, ZHOU Yue, BI Kexin, SUN Rong, LI Youhua. Effects of combined exposure of zinc and different microplastics on seed germination and growth of maize [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2713-2721. |
| [11] | LI Chi, CHEN Gang, YANG Jige, YANG Tingrui, ZHAO Jinghua, MA Mingjie. Stu dy on leaf information collection of spring maize under different water nitrogen treatment conditions based on ground-based multispectrum [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(10): 2374-2387. |
| [12] | SHAO Jiang, ZHAO Yun, HU Xiangwei, LIU Jie, Nasirula Keremu, SHI Shubing, FENG Guojun. Effects of drought stress on foxtail millet yield and dry matter accumulation in different periods [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(10): 2388-2395. |
| [13] | WANG Xiaoyu, WANG Xiaoping, SHI Wenyu, LIU Meiyan, MA Jian, GUO Yunpeng, SONG Ruixin, WANG Qingtao. Responses of photosynthetic characteristics, dry matter accumulation and yield to drought stress in winter wheat at jointing stage [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2163-2172. |
| [14] | XIANG Li, WANG Xian, DONG Yusheng, GUO Xiaoling, FANG Furong, CHEN Zhijun, MA Yanming, MIAO Yu. Effects of exogenous butyric acid on yield and quality of barley under drought stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2173-2181. |
| [15] | Mierzhati Mutalifu, SHI Xiunan, BO Junbing, Zubaidai Abudukerimu, Wulejialehasi Azhati, SHI Shubing. Effects of different delinting modes on seed vigor and seedling characteristics of cotton under PEG stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(7): 1561-1568. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 64
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 253
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||