

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (1): 61-68.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.01.008
• Horticultural Special Local Products • Previous Articles Next Articles
CAI Yi1( ), DAI Dongyang1,2, TAN Hai1, WANG Di3, YANG Fen1, WANG Ling1, SHENG Yunyan1(
), DAI Dongyang1,2, TAN Hai1, WANG Di3, YANG Fen1, WANG Ling1, SHENG Yunyan1( )
)
Received:2022-05-09
Online:2023-01-20
Published:2023-03-07
Correspondence author:
SHENG Yunyan(1979-), female, Harbin City, Heilongjiang Province, Professor,Master Supervisor, research field: Molecular genetics and breeding of melons,(E-mail)shengyunyan@byau.edu.cn
Supported by:
才羿1( ), 戴冬洋1,2, 谭海1, 王迪3, 杨芬1, 王岭1, 盛云燕1(
), 戴冬洋1,2, 谭海1, 王迪3, 杨芬1, 王岭1, 盛云燕1( )
)
通讯作者:
盛云燕(1979-),女,黑龙江哈尔滨人,教授,硕士生导师,研究方向为瓜类分子遗传育种,(E-mail)shengyunyan@byau.edu.cn
作者简介:才羿(1997-),女,黑龙江齐齐哈尔人,硕士研究生,研究方向为瓜类分子遗传育种,(E-mail)1299234359@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
CAI Yi, DAI Dongyang, TAN Hai, WANG Di, YANG Fen, WANG Ling, SHENG Yunyan. Analysis of Genetic Structure and Construction of Gene Editing Vector of Melon AMS Gene[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(1): 61-68.
才羿, 戴冬洋, 谭海, 王迪, 杨芬, 王岭, 盛云燕. 甜瓜AMS基因结构分析及基因编辑载体构建[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(1): 61-68.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 (5'-3') Primer sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|
| sgAMS-1.F | ATTG CATCATGCAAATAAACCTTG |
| sgAMS-1.R | AAAC CAAGGTTTATTTGCATGATG |
| sgAMS-2.F | ATTG CCAACTTTTAGTACCCACAA |
| sgAMS-2.R | AAAC TTGTGGGTACTAAAAGTTGG |
| sgAMS-3.F | ATTG GGAGAGACTAAGACCCCTTG |
| sgAMS-3.R | AAAC CAAGGGGTCTTAGTCTCTCC |
| 测序引物 Sequencing primer | GGATAAACCTTTTCACGCCC |
| 鉴定引物F Identification Primer F | GGATAAACCTTTTCACGCCC |
| 鉴定引物R Identification Primer R | ATTGAACGCCGAAGAACA |
Table 1 Primer sequence
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 (5'-3') Primer sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|
| sgAMS-1.F | ATTG CATCATGCAAATAAACCTTG |
| sgAMS-1.R | AAAC CAAGGTTTATTTGCATGATG |
| sgAMS-2.F | ATTG CCAACTTTTAGTACCCACAA |
| sgAMS-2.R | AAAC TTGTGGGTACTAAAAGTTGG |
| sgAMS-3.F | ATTG GGAGAGACTAAGACCCCTTG |
| sgAMS-3.R | AAAC CAAGGGGTCTTAGTCTCTCC |
| 测序引物 Sequencing primer | GGATAAACCTTTTCACGCCC |
| 鉴定引物F Identification Primer F | GGATAAACCTTTTCACGCCC |
| 鉴定引物R Identification Primer R | ATTGAACGCCGAAGAACA |
| 基因ID Gene ID | 氨基酸数目 Amino acid number/aa | 分子量 Molecular weight /Da | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | 染色体 Chromosome | 染色体定位 Chromosomal location (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MELO3C021653.2.1 | 605 | 68637.8 | 5.04 | 细胞核 | Chr 09 | 5019154-5023770 |
| MELO3C013851.2.1 | 537 | 58 489.77 | 6.45 | 细胞核 | Chr 06 | 33991207-33993509 |
| MELO3C024041.2.1 | 501 | 55 262.12 | 6.16 | 细胞核/胞间层 | Chr 04 | 23240046-23242216 |
| MELO3C003412.2.1 | 511 | 55 934.34 | 5.87 | 细胞核/细胞质 | Chr 04 | 995627-998314 |
| MELO3C006016.2.1 | 526 | 58 428.33 | 5.72 | 细胞核 | Chr 06 | 590163-592617 |
Table 2 Physicochemical properties and chromosome location of AMS gene in Melon
| 基因ID Gene ID | 氨基酸数目 Amino acid number/aa | 分子量 Molecular weight /Da | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | 染色体 Chromosome | 染色体定位 Chromosomal location (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MELO3C021653.2.1 | 605 | 68637.8 | 5.04 | 细胞核 | Chr 09 | 5019154-5023770 |
| MELO3C013851.2.1 | 537 | 58 489.77 | 6.45 | 细胞核 | Chr 06 | 33991207-33993509 |
| MELO3C024041.2.1 | 501 | 55 262.12 | 6.16 | 细胞核/胞间层 | Chr 04 | 23240046-23242216 |
| MELO3C003412.2.1 | 511 | 55 934.34 | 5.87 | 细胞核/细胞质 | Chr 04 | 995627-998314 |
| MELO3C006016.2.1 | 526 | 58 428.33 | 5.72 | 细胞核 | Chr 06 | 590163-592617 |
| 基因ID Gene ID | α-螺旋 α-helix | 延长链 Extended strand | β-折叠 β-sheet | 无规则卷曲 Random coil | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量(个) Number | 所占比例 Percentage(%) | 数量(个) Number | 所占比例 Percentage(%) | 数量(个) Number | 所占比例 Percentage(%) | 数量(个) Number | 所占比例 Percentage(%) | |
| MELO3C021653.2.1 | 200 | 33.06 | 68 | 11.24 | 22 | 3.64 | 315 | 52.07 |
| MELO3C013851.2.1 | 180 | 33.52 | 67 | 12.48 | 13 | 2.42 | 277 | 51.58 |
| MELO3C024041.2.1 | 182 | 36.33 | 68 | 13.57 | 14 | 2.79 | 237 | 47.31 |
| MELO3C003412.2.1 | 153 | 29.94 | 65 | 12.72 | 10 | 1.96 | 283 | 55.38 |
| MELO3C006016.2.1 | 160 | 30.42 | 60 | 11.41 | 13 | 2.47 | 293 | 55.70 |
Table 3 Proportions of secondary structure of AMS genes
| 基因ID Gene ID | α-螺旋 α-helix | 延长链 Extended strand | β-折叠 β-sheet | 无规则卷曲 Random coil | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量(个) Number | 所占比例 Percentage(%) | 数量(个) Number | 所占比例 Percentage(%) | 数量(个) Number | 所占比例 Percentage(%) | 数量(个) Number | 所占比例 Percentage(%) | |
| MELO3C021653.2.1 | 200 | 33.06 | 68 | 11.24 | 22 | 3.64 | 315 | 52.07 |
| MELO3C013851.2.1 | 180 | 33.52 | 67 | 12.48 | 13 | 2.42 | 277 | 51.58 |
| MELO3C024041.2.1 | 182 | 36.33 | 68 | 13.57 | 14 | 2.79 | 237 | 47.31 |
| MELO3C003412.2.1 | 153 | 29.94 | 65 | 12.72 | 10 | 1.96 | 283 | 55.38 |
| MELO3C006016.2.1 | 160 | 30.42 | 60 | 11.41 | 13 | 2.47 | 293 | 55.70 |
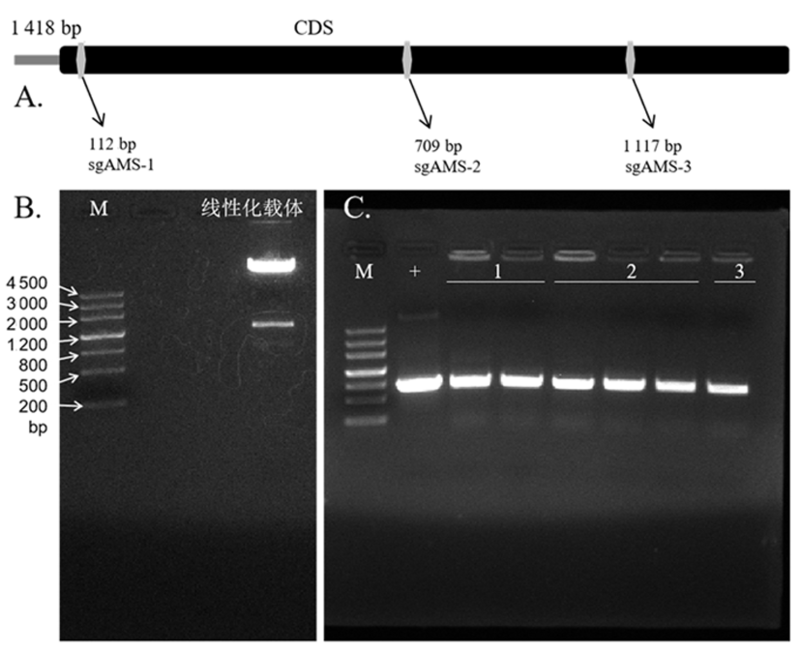
Fig.4 The target site location of AMS gene in melon and construction of knockout vector Note: M: DL4500 DNA Maker; +: positive control; 1, 2, and 3 are plasmids AMS-pHSN401-1, AMS-pHSN401-2 and AMS-pHSN401-3 respectively
| [1] | Perez-Prat E, van Lookeren Campagne M M. Hybrid seed production andthe challenge of propagating male-sterile plants[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2002,(7): 199-203. |
| [2] |
Xu J, Ding Z, Vizcay-Barrena G, et al. ABORTED MICROSPORES Acts as a Master Regulator of Pollen Wall Formation in Arabidopsis[J]. The Plant Cell, 2014, 26(4):1544-1556.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | Goldberg R B, Beals T P, Sanders P M. Anther development: basic principles and practical applications[J]. Plant Cell, 1993,(5): 1217-1229. |
| [4] | Zheng X L, He L L, Liu Y, et al. A study of male fertility control in Medicago truncatula uncovers an evolutionarily conserved recruitment of two tapetal bHLH subfamilies in plant sexual reproduction[J]. New Phytologist, 2020, 1-19. |
| [5] |
Rowley J R, Skvarla J J, et al. Exine, onciform zone and intine structure in Ravenala and Phenakospermum and early wall development in Strelitzia and Phenakospermum (Strelitziaceae) based on aborted microspores[J]. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 1997, 98(3-4):293-301.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Sui J, Cao X, Yi M, et al. Isolation and characterization of LoAMS gene in anther development of lily (Lilium oriental hybrids)[J]. New Zealand Journal of Crop and Horticultural Science, 2020.1-13. |
| [7] |
Li N, Zhang D, Liu H, et al. The rice tapetum degeneration retardation gene is required for tapetum degradation and anther development[J]. Plant Cell, 2006, 18:2999-3014.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Ferguson A C, Pearce S, Band L R, et al. Biphasic regulation of the transcription factor ABORTED MICROSPORES (AMS) is essential for tapetum and pollen development in Arabidopsis[J]. New Phytol, 2017, 213:778-790.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Sorensen A M, Krber S, Unte U S, et al. The Arabidopsis aborted microspores (ams) gene encodes a MYC class transcription factor[J]. The Plant Journal, 2003, 33(2):413-423.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Sheng Y, Wang Y, Jiao S, et al. Mapping and preliminary analysis of ABORTED MICROSPORES (AMS) as the candidate gene underlying the male sterility (MS-5) mutant in melon (Cucumis melo L.)[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8:902.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Dai D, Xiong A, Yuan L, et al. Transcriptome analysis of differentially expressed genes during anther development stages on male sterility and fertility in Cucumis melo L.line[J]. Gene, 2019, 707:65-77.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 戴冬洋, 曾双, 张南, 等. 调控甜瓜败育基因AMS转录因子的筛选[J/OL]. 分子植物育种:1-17[2020-12-03]. |
| DAI Dongyang, ZENG Shuang, ZHANG Nan, et al. Screening of transcription factors regulating abortion genes AMS melon[J/OL]. Molecular Plant Breeding:1-17[2020-12-03]. | |
| [13] | Lecouviour M, Pitrat M, Risser G. A fifth gene for male sterility in Cucumis melo[J]. Report-Cucurbit Genetics Cooperative, 1990, 13:34-35.. |
| [14] | 于彩虹, 吕庆雪, 李建勇, 等. 利用RNAi方法构建MS26基因雄性不育植物表达载体及农杆菌介导玉米遗传转化研究[J]. 玉米科学, 2020, 28(4):48-55. |
| YU Caihong, LU Qingxue, LI Jianyong, et al. Construction of MS26 male sterile plant expression vector and agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Maize by RNAi method[J]. Corn Science, 2020, 28(4):48-55. | |
| [15] | 刘淑娟, 朱祺, 幸学俊, 等. 植物雄性不育影响因素研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2014, 30(34):46-50. |
| LIU Shujuan, ZHU Qi, XING Xuejun, et al. Research progress on influencing factors of male sterility in plants[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2014, 30(34):46-50. | |
| [16] | 王保明, 陈永忠, 李红波, 等. 植物雄性不育的机制及应用研究进展[J]. 河南农业科学, 2019, 48(5):1-9. |
| WANG Baoming, CHENG Yongzhong, LI Hongbo, et al. Research progress in the mechanism and application of male sterility in plants[J]. Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 48(5):1-9 | |
| [17] | 刘永明, 张玲, 周建瑜, 等. 植物细胞核雄性不育相关bHLH转录因子研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2015, 37(12):1194-1203. |
| LIU Yongming, ZHANG Ling, ZHOU Jianyu, et al. Research progress of bHLH transcription factors related to nuclear male sterility in plants[J]. Heredity, 2015, 37(12):1194-1203. | |
| [18] | 戴艳丽, 刘倩纯, 张雨菲, 等. 大葱ALS基因的克隆及其CRISPR/Cas9载体的构建[J]. 分子植物育种, 2019, 17(16):5314-5319. |
| DAI Yanli, LIU Qianchun, ZHANG Yufei, et al. Cloning of ALS gene and construction of CRISPR/Cas9 vector in Leeks[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2019, 17(16):5314-5319. | |
| [19] |
岳宁波, 李云洲, 王勇, 等. CRISPR/Cas9介导的番茄SlMAPK6突变对植株形态的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2020, 34(9):1881-1888.
DOI |
| YUE Ningbo, LI Yunzhou, WANG Yong, et al. Effects of CRISPR/Cas9 mediated tomato SlMAPK6 mutation on plant morphology[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agriculture, 2020, 34(9):1881-1888. | |
| [20] | 霍晋彦, 李姣, 荆雅峰, 等. CRISPR/Cas9系统在植物基因功能研究中的应用进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2019, 55(3):241-246. |
| HUO Jinyan, LI Jiao, JING Yafeng, et al. Advances in the application of CRISPR/Cas9 system in the study of plant gene function[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2019, 55(3):241-246. | |
| [21] | 谢园园. CRISPR/Cas9技术在观赏植物改良育种上的应用研究进展[J]. 现代农业科技, 2020,(8):134-136,143. |
| XIE Yuanyuan. Research progress of CRISPR/Cas9 technology in ornamental plant improvement breeding[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020,(8):134-136,143. | |
| [22] | 王雪, 李冠. CRISPR-Cas9系统敲除甜瓜ACC合成酶基因表达载体的构建[J]. 北方园艺, 2017,(12):114-118. |
| WANG Xue, LI Guan. Construction of ACC synthase gene Expression Vector for Muskmelon knocked out by CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2017,(12):114-118. | |
| [23] |
杨晶, 王旭辉, 王东, 等. CRISPR-Cas9技术敲除甜瓜eIF4E基因表达载体的构建[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(5):821-828.
DOI |
|
YANG Jing, WANG Xuhui, WANG Dong, et al. Construction of CRISPR-Cas9 knockout eIF4E gene Expression Vector in Melon[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(5):821-828.
DOI |
| [1] | LI Junhua, MAO Jiancai, YANG Junyan, WANG Haojie. Analysis of the Current Situation of the Jiashi Melon Industry and discussion of Development Countermeasures [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 101-105. |
| [2] | ZHANG Hao, LIANG Qigan, ZHANG Xuejun, FU Xiaofa, CHEN Jihao, ZHOU Bo, HUANG Yuan. The resistance analysis of Cucumis metuliferus and its effect of grafting on melon quality [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1963-1968. |
| [3] | CHEN Jihao, ZHANG Hao, LIANG Qigan, FU Xiaofa, ZHANG Xuejun, MAO Jiancai. Effects of optimal fertilization and organic fertilizer application on the yield and quality of oriental melon [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1969-1975. |
| [4] | Kadierayi Maimaiti, ZHOU Tingting, HAN Sheng, Meilikehan Rexiti, Yushanjiang Maimaiti. Establishment of genetic transformation and regeneration systems for different melon varieties and rapid acquisition of gene edited plants [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1666-1672. |
| [5] | WU Fengyang, HUANG Wenqian, TIAN Xi, YANG Yulin. Research on recognition and localization of unordered stacked watermelons based on machine vision [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1805-1813. |
| [6] | MA Shangjie, LI Shengmei, YANG Tao, WANG Honggang, ZHAO Kang, PANG Bo, GAO Wenwei. Cloning and subcellular localization of the GHWAT1-35 gene in Gossypium hirsutum [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1310-1317. |
| [7] | YANG Junyan, YAN Miao, WU Haibo, YANG Wenli, WANG Haojie, MAO Jiancai, ZHAI Wenqiang, LI Junhua. The impact of high temperature on different thick -skinned melon varieties and comprehensive evaluation of its heat resistance [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1386-1396. |
| [8] | LIU Yang, ZHANG Zhengxiao, BAI Yujia, FENG Zuoshan. Effects of Alternaria alternata infection on active oxygen metabolism in different tissues of melon [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1397-1406. |
| [9] | MA Ling, SHEN Qi, KANG Qi, ZHANG Zhongxiang, JIA Hongtao, WANG Cheng. Change and association analysis of five heavy metals in melon plants at different growth stages [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 892-899. |
| [10] | YANG Wenli, XU Lirong, LIU Bin, LING Yueming, LI Meihua, YANG Yong, FAN Rong, LI Yushun, ZHANG Yongbin, ZHANG Xuejun. Effects of salt stress on ion balance, membrane lipid peroxidation, and osmotic regulation substance accumulation in thin skin muskmelon ‘Huishu’ [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 900-907. |
| [11] | LIANG Qigan, ZHANG Hao, HU Guozhi, CHEN Jihao, FENG Tongxin, CAO Qing, WANG Min, FU Xiaofa, YAN Miao, GAO Qiang, ZHANG Xuejun, ZHOU Bo, WANG Haojie. Growth,yield and quality of muskmelon in fertilization control facilities [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(3): 599-606. |
| [12] | ZHANG Wei, YANG Guohui, YU Hui. Effects of 2,4-epibrassinolide on growth and related genes expression of watermelon seedlings under drought Stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(3): 615-622. |
| [13] | LI Hui, BI Ying, WANG Xinyu, LEI Yaxin, ZHANG Qi, HUANG Shuai, Rezha kuwangdeke, WANG Jing. Effects of regulation of walnut green peel polyphenols on postharvest active oxygen metabolism and reduction of rotten in Hami melon [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(12): 2966-2975. |
| [14] | LI Chao, YANG Ying, ZHENG Heyun, YANG Jianli, CHEN Wei, YANG Mi, SUN Yuping. Genetic diversity and population structure analysis of melon germplasm resources in Xinjiang based on SSR fluorescence markers [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2614-2625. |
| [15] | SHEN Yue, LING Yueming, DUAN Xiaoyu, YANG Wenli, LI Meihua, WANG Yirou, WANG Huilin, ZHANG Xuejun. Development and verification of KASP marker for resistance to downy mildew in muskmelon [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2626-2634. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||