

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (8): 1873-1878.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.08.007
• Crop Genetics and Breeding · Germplasm Resources · Molecular Genetics · Soil Fertilizer • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Yongqiang( ), CHEN Chuanxin, NIE Shihui, XU Qijiang, Sailihan Sai, LEI Junjie(
), CHEN Chuanxin, NIE Shihui, XU Qijiang, Sailihan Sai, LEI Junjie( )
)
Received:2022-11-11
Online:2023-08-20
Published:2023-08-14
Correspondence author:
LEI Junjie(1972-),male, Gansu Gulang County, Doctor,Researcher, Research direction for crop yield cultivation,(E-mail)leijunjie@sohu.comSupported by:
张永强( ), 陈传信, 聂石辉, 徐其江, 赛力汗·赛, 雷钧杰(
), 陈传信, 聂石辉, 徐其江, 赛力汗·赛, 雷钧杰( )
)
通讯作者:
雷钧杰(1972-),男,甘肃古浪人,研究员,博士,研究方向为小麦高产栽培生理,(E-mail)leijunjie@sohu.com作者简介:张永强(1988-),男,河南平舆人,副研究员,研究方向为作物高产优质栽培生理,(E-mail)zyq988@yeah.net
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHANG Yongqiang, CHEN Chuanxin, NIE Shihui, XU Qijiang, Sailihan Sai, LEI Junjie. Regulation of chlormequat on lodging resistance of winter wheat stem during the period of drip application of CCC[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1873-1878.
张永强, 陈传信, 聂石辉, 徐其江, 赛力汗·赛, 雷钧杰. 矮壮素滴施时期对冬小麦茎秆抗倒伏能力的调控分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1873-1878.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.xjnykx.com/EN/10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.08.007
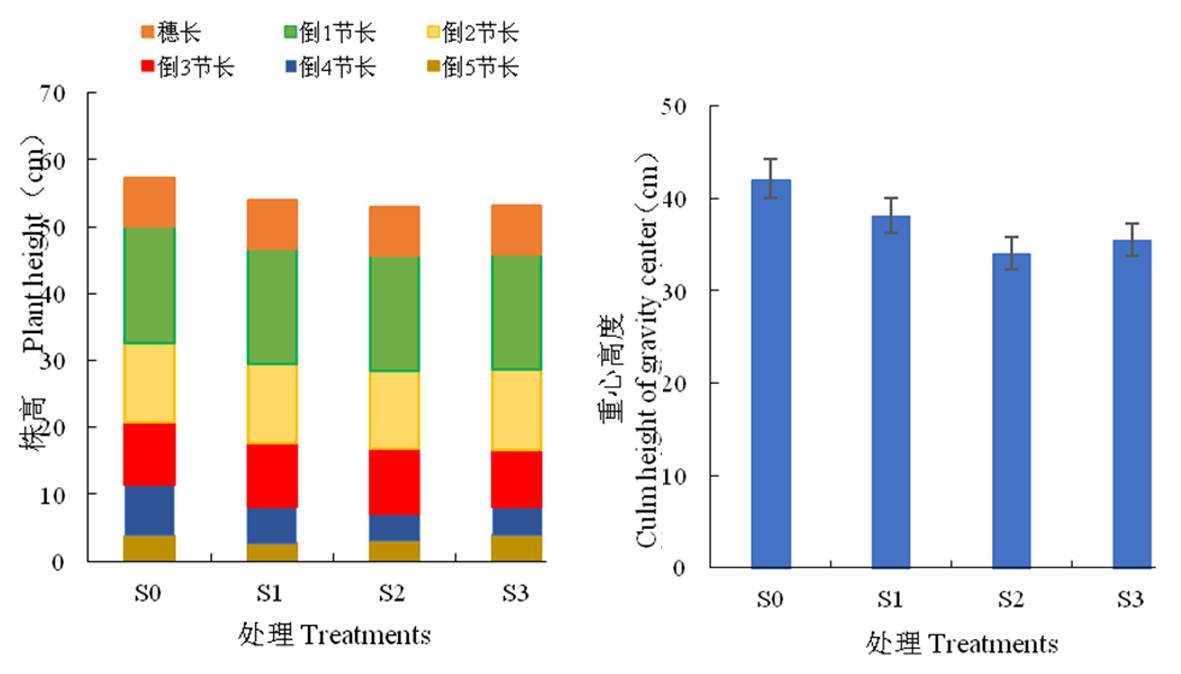
Fig.1 Effect of chlormequat drip application period on wheat plant height and center of gravity height Note:The different letters indicate significant difference at 0.05, the same as below
| 处理 Treat- ments | 长度 Length (cm) | 直径 Outer diameter (mm) | 壁厚 Wall thickness (mm) | 充实度 Filling Degree (mg/cm) | 抗折力 Culm mecha- nical Strength (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | 7.53a | 3.18b | 0.477c | 20.71d | 3.94c |
| S1 | 5.43b | 3.24a | 0.507b | 21.53c | 4.87b |
| S2 | 4.07c | 3.38a | 0.543a | 25.57a | 5.44a |
| S3 | 4.27c | 3.29a | 0.517b | 22.85b | 4.77b |
Tab.1 Effects ofchlormequat drip application period on the characteristics of the second internode at the base Stem of wheat
| 处理 Treat- ments | 长度 Length (cm) | 直径 Outer diameter (mm) | 壁厚 Wall thickness (mm) | 充实度 Filling Degree (mg/cm) | 抗折力 Culm mecha- nical Strength (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | 7.53a | 3.18b | 0.477c | 20.71d | 3.94c |
| S1 | 5.43b | 3.24a | 0.507b | 21.53c | 4.87b |
| S2 | 4.07c | 3.38a | 0.543a | 25.57a | 5.44a |
| S3 | 4.27c | 3.29a | 0.517b | 22.85b | 4.77b |
| 处理 Treat- ments | 单茎 生物量 Single stem biomass (g/茎) | 不孕小穗 Fertile spikelets (个) | 可孕小穗 Infertile spikelets (个) | 穗粒数 Ggrain number per spike (粒) | 穗粒重 Grain weight per spike (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | 3.05c | 3.14a | 15.50c | 37.20a | 1.56b |
| S1 | 3.18b | 3.00b | 17.90a | 38.50a | 1.6 |
| S2 | 3.42a | 1.86d | 17.4 | 38.30a | 1.68a |
| S3 | 3.32a | 2.00c | 16.80b | 38.30a | 1.66a |
Tab.2 Effect of chlormequat drip application period on grain yield of wheat
| 处理 Treat- ments | 单茎 生物量 Single stem biomass (g/茎) | 不孕小穗 Fertile spikelets (个) | 可孕小穗 Infertile spikelets (个) | 穗粒数 Ggrain number per spike (粒) | 穗粒重 Grain weight per spike (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | 3.05c | 3.14a | 15.50c | 37.20a | 1.56b |
| S1 | 3.18b | 3.00b | 17.90a | 38.50a | 1.6 |
| S2 | 3.42a | 1.86d | 17.4 | 38.30a | 1.68a |
| S3 | 3.32a | 2.00c | 16.80b | 38.30a | 1.66a |
| [1] | 李波, 魏亚凤, 汪波, 等. 水稻秸秆还田和耕作方式对小麦抗倒伏能力的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2013, 33(4):758-764. |
| LI Bo, WEI Yafeng, WANG Bo, et al. Effects of rice straw returning into field and different tillage methods on culm lodging resistance of wheat[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2013, 33(4):758-764. | |
| [2] |
Acreche M M, Slafer G A. Lodging yield penalties as affected by breeding in Mediterranean wheat[J]. Field Crop Research, 2011, 122(1):40.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
梁玉超, 张永强, 石书兵, 等. 种植密度对滴灌冬小麦茎秆特性及抗倒伏性能的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(6):1056-1064.
DOI |
| LIANG Yuchao, ZHANG Yongqiang, SHI Shubing, et al. Effects of different plant densities on stem morphology characteristics and lodging resistance in winter wheat under drip irrigation[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2018, 38(6):710-717. | |
| [4] |
Beerry p m spink J. Predicting yield losses caused by lodging in wheat[J]. Field Crop Research, 2012, 137(1):19.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Peake As, Huth N I, Craberr P S, et al. Quantifying potential yield and lodging-related yield gaps for irrigated spring wheat in sub-tropical Australia[J]. Field Crop Research, 2014, 158(1):1.
DOI URL |
| [6] | 新疆维吾尔自治区统计年鉴[J]. 北京:中国统计出版社, 2020. |
| Statistics Bureau of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Xinjiang Statistical Yearbook[J]. Beijing: China Statistic Press, 2020. | |
| [7] | 王成雨, 李静, 张一, 等化控剂对冬小麦茎秆抗倒性能、植株整齐度及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 2015, 36(2):170-177. |
| WANG Chengyu, LI Jing, ZHANG Yi, et al. Effects of chemical regulators on culm lodging resistance, plant uniformity and yield of winter wheat[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2015, 36(2):170-177. | |
| [8] | 熊乐, 马富裕, 樊华, 等. 冬灌与化学调控互作对滴灌春小麦抗倒伏能力和产量的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2012, 32(5):932-936. |
| XIONG Le, MA Fuyu, FAN Hua, et al. Interaction effects of winter irrigation and chemical regulation on lodging-resistance and yield of drip irrigated spring wheat[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2012, 32(5):932-936. | |
| [9] | 郭建文, 田新会, 张舒芸, 等. 不同浓度矮壮素对黑麦抗倒伏性和种子产量的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2018, 35(5):1128-1137. |
| GUO Jianwen, TIAN Xinhui, ZHANG Shuyun, et al. Effect of different chlorocholine chlorid (CCC) concentrations on lodging resistance and seed yield of rye[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(5):1128-1137. | |
| [10] | 孙岩, 张宏纪, 辛文利, 等. 苗期镇压与矮壮素结合处理对小麦生育及其基部节生长的影响[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2013,(2):14-16. |
| SUN Yan, ZHANG Hongji, XIN Wenli, et al. Influence of rolling and spraying TUR at seedling stage on growth period and growth of base stem for wheat[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2013,(2):14-16. | |
| [11] | 马瑞, 亓振, 常旭虹, 等. 化控剂对冬小麦植株性状及产量品质的调节效应[J]. 作物杂志, 2018,(1):133-140. |
| MA Rui, QI Zhen, CHANG Xuhong, et al. Regulation effects of growth regulators on plant characters,yield and quality of winter wheat[J]. Crops, 2018,(1):133-140. | |
| [12] | 华智锐, 李小玲. 矮壮素对小麦抗倒伏性能的诱导效应研究[J]. 河北农业科学, 2017, 21(2):47-51,71. |
| HUA Zhirui, LI Xiaoling. Researches of CCC in induction lodging resistance of wheat[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 21(2):47-51,71. | |
| [13] | 朱新开, 王祥菊, 郭凯泉, 等. 小麦倒伏的茎秆特征及对产量与品质的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2006, 26(1):87-92. |
| ZHU Xinkai, WANG Xiangju, GUO Kaiquan, et al. Stem Characteristics of wheat with stem lodging and effects of lodging on grain yield and quality[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2006, 26(1):87-92. | |
| [14] | 周洁, 王旭, 朱玉磊, 等. 氮肥运筹模式对小麦茎秆抗倒性能与产量的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2019, 39(8):979-987. |
| ZHOU Jie, WANG Xu, ZHU Yulei, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer management on stem lodging reeesistance and yield of wheat[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2019, 39(8):979-987. | |
| [15] | Chen X G, Wang J, Wang Z L, et al. Optimized nitrogen fertilizer application mode increased culms lignin accumulation and lodging resistance in culms of winter wheat[J]. Field Crops Research, 2018,228. |
| [16] | Khan A, Liu H H, Ahmad A, et al. Impact of Nitrogen Regimes and Planting Densities on Stem Physiology, Lignin Biosynthesis and Grain Yield in Relation to Lodging Resistance in Winter Wheat[J]. Cereal Research Communications, 2019, 47(3). |
| [17] |
Berry P M, Griffin J M, Sylvester-Bradley R, et al. Controlling plant forms through husbandry to minimize lodging in whea[J]. Field Crops Research, 2000, 67: 59-81.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 魏凤珍, 李金才, 王成雨, 等. 氮肥运筹模式对小麦茎秆抗倒性能的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2008,(6):1080-1085. |
| WEI Fengzhen, LI Jincai, WANG Chengyu, et al. Effects of nitrogenous fertilizer application model on culm lodging resistance in winter wheat[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2008,(6):1080-1085. |
| [1] | CHEN Chuanxin, ZHNAG Yongqiang, NIE Shihui, KONG Depeng, Sailihan Sai, XU Qijiang, LEI Junjie. Effects of biomass charcoal application rate on the growth, development, and yield of winter wheat under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2146-2151. |
| [2] | WANG Xiaoyu, WANG Xiaoping, SHI Wenyu, LIU Meiyan, MA Jian, GUO Yunpeng, SONG Ruixin, WANG Qingtao. Responses of photosynthetic characteristics, dry matter accumulation and yield to drought stress in winter wheat at jointing stage [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2163-2172. |
| [3] | YANG Hongmei, ZHANG Yueqiang, SHI Yingwu, Omarjan Kurban, LIN Qing, WANG Ning, CHU Min, ZENG Jun. Effects of different types of foliar fertilizers on grain yield and 1uality of winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2182-2188. |
| [4] | TIAN Wenqiang, DONG Yanxue, SHI Yongqing, LEI Junjie, SUN Ganggang, WANG Hongyi, NIE Lingfan, GOU Fei, AI Hongyu, SHI Shubing, ZHANG Jinshan. Effects of sowing date on stem traits and population dynamics of ultra late winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1301-1307. |
| [5] | ZHANG Yongqiang, CHEN Chuanxin, XU Qijiang, NIE Shihui, LEI Junjie, LIU Changwen. Effects of combined application of nitrogen enhancer and nitrogen reduction on leaf physiology and yield of winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1319-1325. |
| [6] | LUO Siwei, JIA Yonghong, ZHANG Jinshan, WANG Kai, LI Dandan, WANG Runqi, DONG Yanxue, SHI Shubing. Effects of drip irrigation capillary spacing and emitter spacing on the spatial distribution of soil water, root morphology and yield of uniformly sown winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1344-1352. |
| [7] | JIANG Zhu, ZHANG Jianghui, BAI Yungang, YANG Pengnian, LIU Hongbo, XIAO Jun, LIU Xuhui. Effects of fertilizer and salt regulation on cotton growth and yield under plastic film drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1389-1397. |
| [8] | TIAN Wenqiang, GOU Fei, NIE Lingfan, SUN Ganggang, WANG Hongyi, SHI Yongqing, SHANG Yanming, WU Li, SHI Shubing, ZHANG Jinshan. Effects of super late sowing on photosynthetic characteristics, dry matter accumulation and yield of winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(5): 1059-1066. |
| [9] | ZHANG Jingcan, ZHANG Yongqiang, LEI Junjie, CHEN Chuanxin, XU Qijiang, NIE Shihui, XU Wenxiu. Effects of different growth regulators on stem characteristics and lodging resistance of winter wheat under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(5): 1067-1074. |
| [10] | ZHANG Yongqiang, XU Qijiang, CHEN Chuanxin, MA Xin, ZHANG Humei, NIE Shihui, LEI Junjie. Effects of basal fertilizer types and fertilization methods on the growth and yield of winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(5): 1075-1081. |
| [11] | ZHU Baoguo, KUANG Enjun, TENG Zhanglin, MENG Qingying, WANG Nannan, FENG Haoyuan, QIU Lei, GAO Xuedong, ZHANG Chunfeng. Effects of different bio-organic fertilizers application combined with conventional fertilization on growth, disease resistance and yield of soybean [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(5): 1127-1133. |
| [12] | YANG Minghua, LIU Qiang, LIAO Biyong, PEN Yuncheng, Buayxam Namat, Dawulai Jiekeshan. Comprehensive evaluation of lodging resistance of NCII maize combinations [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(4): 832-840. |
| [13] | ZHANG Yongqiang, FANG Hui, CHEN Chuanxin, NIE Shihui, Sailihan Sai, XU Qijiang, CHEN Xingwu, LEI Junjie. Effect of Exogenous Silicon Drip Application on Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Winter Wheat under Low Light Stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(2): 336-343. |
| [14] | ZHU Zhu, ZHANG Xuxian, WANG Shichang, WEN Hao, CAI Guixiang. Effects of Insertion Subsurface Drip Irrigation on Soil Infiltration and Distribution of Water and Salt [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(2): 440-447. |
| [15] | Abdukeyoumu Abudurezike, Tuerson Tuerhong, Gulimira Aikebaier, Ayixiamu Shawuer. Effects of Different Drip Irrigation Rates on Quality Components of Cultivated Glycyrrhiza uralensis root in Desert Area [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(9): 2224-2231. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||