

新疆农业科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (10): 2532-2540.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.10.023
左筱筱1( ), 颜安1(
), 颜安1( ), 宁松瑞2, 杨利1, 孙萌1, 卢前成1
), 宁松瑞2, 杨利1, 孙萌1, 卢前成1
收稿日期:2023-01-03
出版日期:2023-10-20
发布日期:2023-11-01
通信作者:
颜安(1983-),男,四川资阳人,教授,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为农业资源与环境,(E-mail)作者简介:左筱筱(1998-),女,四川内江人,硕士研究生,研究方向为土壤改良与培肥,(E-mail)zuoxiaoxiao710@163.com
基金资助:
ZUO Xiaoxiao1( ), YAN An1(
), YAN An1( ), NING Songrui2, YANG Li1, SUN Meng1, LU Qiancheng1
), NING Songrui2, YANG Li1, SUN Meng1, LU Qiancheng1
Received:2023-01-03
Online:2023-10-20
Published:2023-11-01
Correspondence author:
YAN An (1983 -), Male, from Ziyang, Sichuan;Ph.D.supervisor, Mainly engaged in agricultural resources and environmental research,(E-mail)Supported by:摘要:
【目的】 研究不同生物有机肥对盐碱胁迫春小麦生长和土壤改良培肥的效果,为盐碱地的生物有机肥施用提供理论基础。【方法】 采用盆栽试验,设置9个处理:不施肥处理(CK),4种不同菌种及配比的生物有机肥(A、B、C、D),每种生物有机肥设2个施量水平(1 125,2 250 kg/hm2)。【结果】 与CK相比,施用生物有机肥后春小麦LAI、SPAD、理论产量、土壤有机质和速效养分含量等均显著增加(P<0.05),其中春小麦理论产量比CK处理增加了41.85%~74.93%,0~10 cm土层土壤有机质、碱解氮、速效磷和速效钾含量分别比CK提高了19.57%~66.24%、20.73%~40.12%、37.70%~75.72%和11.98%~31.12%,10~20 cm土层土壤有机质、碱解氮、速效磷和速效钾含量分别比CK提高了19.13%~74.63%、17.38%~29.93%、21.76%~59.52%和11.98%~31.12%,且随着生物有机肥施量的增加呈上升趋势;各施肥处理与不施肥CK相比显著降低了土壤pH和电导率(P<0.05),0~10 cm土层土壤pH、电导率分别比CK降低了2.55%~5.02%、10.33%~40.51%,10~20 cm土层土壤pH、电导率分别比CK降低了1.69%~4.20%、21.3%~43.60%。各施肥处理春小麦根际土壤细菌和放线菌数量显著高于CK(P<0.05),真菌数量显著低于CK(P<0.05),根际土壤细菌和放线菌数量随生物有机肥施量的增加呈上升趋势,真菌数量呈现下降趋势。【结论】 D生物有机肥(沼泽红假单胞菌∶肉桂褐链霉菌∶胶冻样芽孢杆菌∶枯草芽孢杆菌=1∶2∶2∶2)施用量为2 250 kg/hm2时,对盐碱土壤改良培肥和调节微生物数量结构作用效果较好,且促进了小麦生产量的提高。
中图分类号:
左筱筱, 颜安, 宁松瑞, 杨利, 孙萌, 卢前成. 盐碱麦田生物有机肥促生增产培肥效果[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(10): 2532-2540.
ZUO Xiaoxiao, YAN An, NING Songrui, YANG Li, SUN Meng, LU Qiancheng. Study on the effect of Bio-Organic fertilizer on promoting growth and increasing yield in saline alkali wheat field[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(10): 2532-2540.
| 处理 Treatments | 施量1 Application rate 1 (1 125 kg/hm2) | 施量2 Application rate 2 (2 250 kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|
| CK | / | / |
| A | A1 | A2 |
| B | B1 | B2 |
| C | C1 | C2 |
| D | D1 | D2 |
表1 施肥处理设计
Tab.1 Fertilization treatment design
| 处理 Treatments | 施量1 Application rate 1 (1 125 kg/hm2) | 施量2 Application rate 2 (2 250 kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|
| CK | / | / |
| A | A1 | A2 |
| B | B1 | B2 |
| C | C1 | C2 |
| D | D1 | D2 |
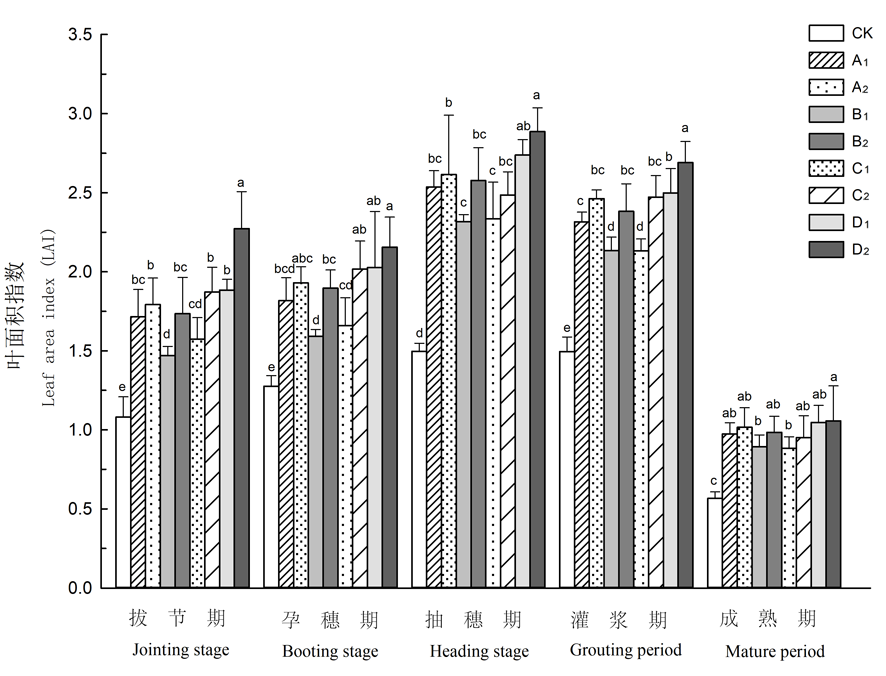
图1 施加不同生物有机肥下春小麦LAI变化 注:不同小写字母表示各处理间有显著差异(P<0.05),下同
Fig.1 Effects of different bio organic fertilizers on LAI value of Spring Wheat Note: different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments (P < 0.05),the same as below
| 处理 Treatments | 穗长 Spike length (cm) | 穗数 Panicle number (104 /hm2) | 穗粒数 Grains per panicle (粒) | 千粒重 1000 grain weight (g) | 理论产量 Grain yield (kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 8.03±0.10c | 487.28±18.99a | 18.30±0.58b | 31.33±1.00c | 2 969.33±111.25c |
| A1 | 9.22±0.59b | 509.85±13.71a | 26.70±4.16a | 37.95±1.94ab | 4 541.14±299.60ab |
| A2 | 9.75±0.24ab | 528.25±67.84a | 28.70±3.06a | 38.31±2.79ab | 4 870.87±172.79ab |
| B1 | 9.11±0.15b | 510.93±48.23a | 24.00±1.00a | 35.93±2.00b | 4 212.25±214.39b |
| B2 | 9.19±0.31b | 518.33±19.13a | 28.00±2.83a | 37.86±1.50ab | 4 565.46±234.36ab |
| C1 | 9.22±0.21b | 559.15±72.48a | 24.30±1.53a | 36.10±1.43b | 4 517.22±380.55ab |
| C2 | 9.55±0.02ab | 546.76±45.78a | 27.50±2.12a | 38.13±4.42ab | 4 798.89±514.37ab |
| D1 | 9.51±0.14ab | 580.61±6.69a | 27.00±7.07a | 38.59±2.30ab | 4 774.79±232.06ab |
| D2 | 9.84±0.10a | 541.05±26.29a | 28.00±2.83a | 40.14±2.88a | 5 194.13±224.64a |
表2 春小麦产量及其构成因素
Tab.2 Spring wheat yield and its components
| 处理 Treatments | 穗长 Spike length (cm) | 穗数 Panicle number (104 /hm2) | 穗粒数 Grains per panicle (粒) | 千粒重 1000 grain weight (g) | 理论产量 Grain yield (kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 8.03±0.10c | 487.28±18.99a | 18.30±0.58b | 31.33±1.00c | 2 969.33±111.25c |
| A1 | 9.22±0.59b | 509.85±13.71a | 26.70±4.16a | 37.95±1.94ab | 4 541.14±299.60ab |
| A2 | 9.75±0.24ab | 528.25±67.84a | 28.70±3.06a | 38.31±2.79ab | 4 870.87±172.79ab |
| B1 | 9.11±0.15b | 510.93±48.23a | 24.00±1.00a | 35.93±2.00b | 4 212.25±214.39b |
| B2 | 9.19±0.31b | 518.33±19.13a | 28.00±2.83a | 37.86±1.50ab | 4 565.46±234.36ab |
| C1 | 9.22±0.21b | 559.15±72.48a | 24.30±1.53a | 36.10±1.43b | 4 517.22±380.55ab |
| C2 | 9.55±0.02ab | 546.76±45.78a | 27.50±2.12a | 38.13±4.42ab | 4 798.89±514.37ab |
| D1 | 9.51±0.14ab | 580.61±6.69a | 27.00±7.07a | 38.59±2.30ab | 4 774.79±232.06ab |
| D2 | 9.84±0.10a | 541.05±26.29a | 28.00±2.83a | 40.14±2.88a | 5 194.13±224.64a |

图4 施加不同生物有机肥下土壤有机质、碱解氮、速效磷、速效钾含量变化
Fig.4 Effects of applying different bio organic fertilizers on the contents of soil organic matter, alkali hydrolyzable nitrogen, available phosphorus and available potassium
| 处理 Treat- ments | 细菌 Bacteria ( 106 cfu/g) | 真菌 Fungus ( 104 cfu/g) | 放线菌 Actinomycetes ( 105 cfu/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1.15±0.07d | 4.95±0.49a | 2.40±0.14e |
| A1 | 2.85±0.07bc | 3.35±1.48b | 5.25±0.49bc |
| A2 | 3.55±0.01b | 1.45±0.49cde | 5.55±0.91b |
| B1 | 2.30±0.04c | 0.76±0.21e | 3.75±0.49d |
| B2 | 2.70±0.06bc | 0.61±0.21e | 4.80±0.28bcd |
| C1 | 2.35±0.01c | 0.93±0.01de | 4.20±1.13cd |
| C2 | 3.25±0.08bc | 0.89±0.01e | 4.80±0.28bcd |
| D1 | 3.40±0.04b | 2.65±0.77bc | 5.35±0.21bc |
| D2 | 5.150±0.06a | 2.30±0.14bcd | 7.00±0.42a |
表3 不同生物有机肥下土壤微生物数量变化
Tab.3 Effects of different bio organic fertilizers on the number of soil microorganisms
| 处理 Treat- ments | 细菌 Bacteria ( 106 cfu/g) | 真菌 Fungus ( 104 cfu/g) | 放线菌 Actinomycetes ( 105 cfu/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1.15±0.07d | 4.95±0.49a | 2.40±0.14e |
| A1 | 2.85±0.07bc | 3.35±1.48b | 5.25±0.49bc |
| A2 | 3.55±0.01b | 1.45±0.49cde | 5.55±0.91b |
| B1 | 2.30±0.04c | 0.76±0.21e | 3.75±0.49d |
| B2 | 2.70±0.06bc | 0.61±0.21e | 4.80±0.28bcd |
| C1 | 2.35±0.01c | 0.93±0.01de | 4.20±1.13cd |
| C2 | 3.25±0.08bc | 0.89±0.01e | 4.80±0.28bcd |
| D1 | 3.40±0.04b | 2.65±0.77bc | 5.35±0.21bc |
| D2 | 5.150±0.06a | 2.30±0.14bcd | 7.00±0.42a |
| 项目 Projects | 特征值 Characteristic value | 方差贡献率 Variance contribution rate (%) | 累积方差 贡献率 Cumulative variance contribution rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 主成分1 Principal component 1 | 15.957 | 88.649 | 88.649 |
| 主成分2 Principal component 2 | 1.004 | 5.575 | 94.224 |
表4 主成分的特征值与方差贡献率
Tab.4 eigenvalues and variance contribution rate of principal component analysis
| 项目 Projects | 特征值 Characteristic value | 方差贡献率 Variance contribution rate (%) | 累积方差 贡献率 Cumulative variance contribution rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 主成分1 Principal component 1 | 15.957 | 88.649 | 88.649 |
| 主成分2 Principal component 2 | 1.004 | 5.575 | 94.224 |
| 项目 Projects | 主成分1 Principal component 1 | 主成分2 Principal component 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 载荷值 Load value | 特征向量 Feature vector | 载荷值 Load value | 特征向量 Feature vector | |
| LAI(X1) | 0.946 | 0.237 | -0.133 | -0.133 |
| SPAD(X2) | 0.946 | 0.237 | -0.104 | -0.104 |
| 产量(X3) | 0.978 | 0.245 | -0.127 | -0.126 |
| 0~10 cm pH(X4) | -0.987 | -0.247 | -0.067 | -0.067 |
| 10~20 cm pH(X5) | -0.962 | -0.241 | -0.160 | -0.160 |
| 0~10 cm电导率(X6) | -0.966 | -0.242 | 0.109 | 0.108 |
| 10~20 cm电导率(X7) | -0.973 | -0.244 | -0.070 | -0.069 |
| 0~10 cm有机质(X8) | 0.938 | 0.235 | 0.127 | 0.126 |
| 10~20 cm有机质(X9) | 0.894 | 0.224 | 0.077 | 0.077 |
| 0~10 cm碱解氮(X10) | 0.985 | 0.246 | -0.083 | -0.083 |
| 10~20 cm碱解氮(X11) | 0.967 | 0.242 | -0.144 | -0.144 |
| 0~10 cm速效钾(X12) | 0.981 | 0.246 | -0.054 | -0.054 |
| 10~20 cm速效钾(X13) | 0.956 | 0.239 | 0.122 | 0.122 |
| 0~10 cm速效磷(X15) | 0.985 | 0.246 | 0.022 | 0.022 |
| 10~20 cm速效磷(X16) | 0.970 | 0.243 | 0.023 | 0.023 |
| 细菌(X17) | 0.943 | 0.236 | 0.294 | 0.293 |
| 真菌(X18) | -0.514 | -0.129 | 0.832 | 0.831 |
| 放线菌(X19) | 0.954 | 0.239 | 0.254 | 0.253 |
表5 主成分分析的载荷值与特征向量
Tab.5 load value and eigenvector of principal component analysis
| 项目 Projects | 主成分1 Principal component 1 | 主成分2 Principal component 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 载荷值 Load value | 特征向量 Feature vector | 载荷值 Load value | 特征向量 Feature vector | |
| LAI(X1) | 0.946 | 0.237 | -0.133 | -0.133 |
| SPAD(X2) | 0.946 | 0.237 | -0.104 | -0.104 |
| 产量(X3) | 0.978 | 0.245 | -0.127 | -0.126 |
| 0~10 cm pH(X4) | -0.987 | -0.247 | -0.067 | -0.067 |
| 10~20 cm pH(X5) | -0.962 | -0.241 | -0.160 | -0.160 |
| 0~10 cm电导率(X6) | -0.966 | -0.242 | 0.109 | 0.108 |
| 10~20 cm电导率(X7) | -0.973 | -0.244 | -0.070 | -0.069 |
| 0~10 cm有机质(X8) | 0.938 | 0.235 | 0.127 | 0.126 |
| 10~20 cm有机质(X9) | 0.894 | 0.224 | 0.077 | 0.077 |
| 0~10 cm碱解氮(X10) | 0.985 | 0.246 | -0.083 | -0.083 |
| 10~20 cm碱解氮(X11) | 0.967 | 0.242 | -0.144 | -0.144 |
| 0~10 cm速效钾(X12) | 0.981 | 0.246 | -0.054 | -0.054 |
| 10~20 cm速效钾(X13) | 0.956 | 0.239 | 0.122 | 0.122 |
| 0~10 cm速效磷(X15) | 0.985 | 0.246 | 0.022 | 0.022 |
| 10~20 cm速效磷(X16) | 0.970 | 0.243 | 0.023 | 0.023 |
| 细菌(X17) | 0.943 | 0.236 | 0.294 | 0.293 |
| 真菌(X18) | -0.514 | -0.129 | 0.832 | 0.831 |
| 放线菌(X19) | 0.954 | 0.239 | 0.254 | 0.253 |
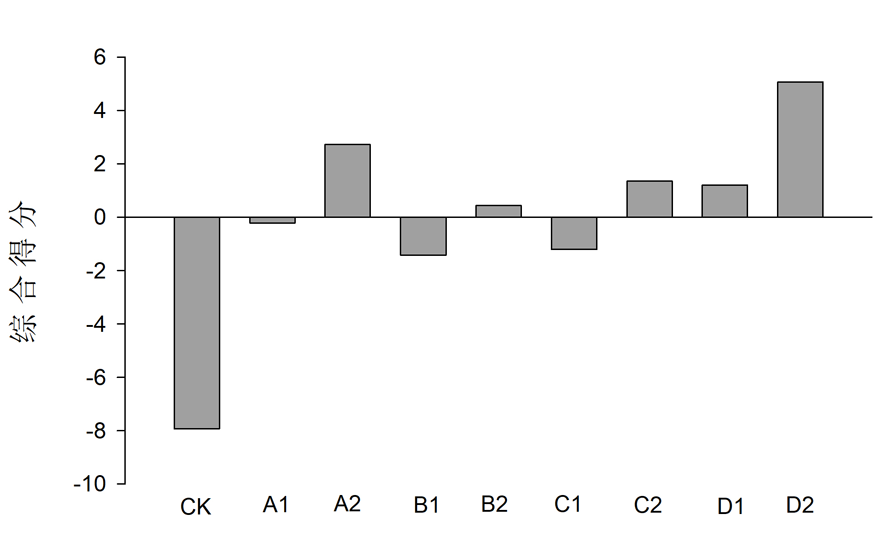
图5 不同生物有机肥促生增产培肥效果综合得分
Fig.5 comprehensive score of theeffect of different bio organic fertilizers on promoting growth, increasing yield and fertilizing
| [1] | 张龙. 近二十年新疆灌区盐碱地变化情况分析和对策研究[J]. 水资源开发与管理, 2020,(6): 72-76. |
| ZHANG Long. Analysis and countermeasure research on saline-alkali land change in Xinjiang irrigation area in recent 20 years[J]. Water Resources Development and Management, 2020,(6): 72-76. | |
| [2] | 宁松瑞, 赵雪, 姬美玥, 等. 脱硫石膏和磁化水对盐碱胁迫荞麦光合特性的影响[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(10): 310-317. |
| NING Songrui, ZHAO Xue, JI Meiyue, et al. Effect of Desulfurized Gypsum and Magnetized Water on Photosynthetic Characteristics of Buckwheat under Salt-alkali Stress[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(10): 310-317. | |
| [3] | 颜安, 宁松瑞, 万江春, 等. 养分配比对盐胁迫膜下滴灌棉花生长与产量和水肥效率的影响[J]. 新疆农业大学学报, 2021, 44(1): 1-7. |
| YANG An, NING Songrui, WAN Jianchun, et al. Effects of Different Nutrient Ratios on Growth and Yield of Cotton and Its Efficiency of Water and Fertilizer under Salt Stress[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2021, 44(1): 1-7. | |
| [4] | 刘艳, 李波, 孙文涛, 等. 生物有机肥对盐碱地春玉米生理特性及产量的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2017,(2): 98-103. |
| LIU Yan, LI Bo, SUN Wentao, et al. Effects of Bio-organic Fertilizer on Physiological Characters and Yield of Maize in Saline-Alkali Soil[J]. Crops, 2017,(2): 98-103. | |
| [5] | 韩正砥. 生物有机肥对节水灌溉水稻生理生长指标的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2020. |
| HAN Zhengdi. Effects of bioorganic fertilizers on physilological growth indexes of rice under water-saving irrigation[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2020. | |
| [6] |
王俊红, 王星琳, 王康, 等. 生物有机肥替代化肥对小麦根际土壤环境的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2021, 36(4): 155-162.
DOI |
| WANG Junhong, WANG Xinglin, WANG Kang, et al. Effects of Replacing Chemical Fertilizers with Bio-organic Fertilizers on Microenvironment of Wheat Rhizosphere Soil[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2021, 36(4): 155-162. | |
| [7] | 朱利霞, 曹萌萌, 桑成琛, 等. 生物有机肥替代化肥对玉米土壤肥力及酶活性的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2022, 40(1): 67-72. |
| ZHU Lixia, CAO Mengmeng, SANG Chengchen, et al. Effects of Bio-Fertilizer Partially Substituting Chemical Fertilizer on Soil Fertility and Enzyme Activity in Maize Field[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2022, 40(1): 67-72. | |
| [8] | Mosa W F A E G, Paszt L S, Frac M, et al. Microbial products and biofertilizers in improving growth and productivity of apple-a review[J]. Polish Journal of Microbiology, 2016, 65(3): 3. |
| [9] | 吴晓卫, 付瑞敏, 郭彦钊, 等. 耐盐碱微生物复合菌剂的选育、复配及其对盐碱地的改良效果[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2015, 43(6): 346-349. |
| WU Xiaowei, FU Ruimin, GUO Yanzhao, et al. Breeding and compound of saline-resistant microorganisms and its improvement effect on saline-alkali land[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(6): 346-349. | |
| [10] | Hafez M, Popov A I, Rashad M. Integrated use of bio-organic fertilizers for enhancing soil fertility-plant nutrition, germination status and initial growth of corn (Zea mays L.)[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2021, 21: 101329. |
| [11] |
Li W, Zhang F, Cui G, et al. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on soil fertility, microbial community composition, and potato growth[J]. Science Asia, 2021, 47: 347.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 张彭良, 李静, 王丹丹. 生物有机肥对春小麦生理特性及土壤养分和微生物的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2018, 46(9): 66-72. |
| ZHANG Pengliang, LI Jing, WANG Dandan. Effect of biological organic fertilizer on physiological characteristics and soil nutrients and microorganisms in spring wheat[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(9): 66-72. | |
| [13] |
王家宝, 孙义祥, 李虹颖, 等. 生物有机肥用量及部分替代化肥对小麦产量效应的研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(36): 6-11.
DOI |
|
WANG Jiabao, SUN Yixiang, LI Hongying, et al. Effects of Bio-organic Fertilizer and Partial Substitution of Chemical Fertilizer on Wheat Yield[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(36): 6-11.
DOI |
|
| [14] | 杨利, 颜安, 宁松瑞, 等. 生物有机肥对盐胁迫小麦幼苗生长和土壤培肥的影响[J]. 新疆农业大学学报, 2021, 44(4): 291-299. |
| YANG Li, YAN An, NING Songrui, et al. Effects of Bio-organic Fertilizer on Wheat Seedling Growth and Soil Fertility Improvement under Salt Stress[J]. Journal of Xinjiang University, 2021, 44(4): 291-299. | |
| [15] | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(3 版)[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. |
| BAO Shidan. Soil Agrochemical Analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. | |
| [16] | 林先贵. 土壤微生物研究原理与方法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2010. |
| LIN Xiangui. Principles and Methods of Soil Microbiology Research[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2010. | |
| [17] | 张迎春, 颉建明, 李静, 等. 生物有机肥部分替代化肥对莴笋及土壤理化性质和微生物的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(4):196-205. |
| ZHANG Yingchun, XIE Jianming, LI Jing, et al. Effects of Partial Substitution of Chemical Fertilizer by Bio-organic Fertilizer on Asparagus Lettuce and Soil Physical-chemical Properties and Microorganisms[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(4):196-205. | |
| [18] | 邹尊涛. 生物有机肥对盐碱地改良的研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2017. |
| ZOU Zuntao. Study on the improvement of saline-alkali soill byi bio-organic fertilizer[D]. Tai’an: Shangdong Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| [19] |
Yuan S, Wang L, Wu K, et al. Evaluation of Bacillus-fortified organic fertilizer for controlling tobacco bacterial wilt in greenhouse and field experiments[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2014, 75: 86-94.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 刘柳, 朱丽, 张晓霞, 等. 一种复合菌肥的研制及其在草莓种植中的应用[J]. 沈阳大学学报, 2017, 29(5): 384-388. |
| LIU Liu, ZHU Li, ZHANG Xiaoxia, et al. Development of a Compound Bacterial Manure and Application in Strawberry Planting[J]. Journal of Shenyang University, 2017, 29(5): 384-388. | |
| [21] | 陈智坤, 冯璞阳, 井光花, 等. 不同改良措施对关中典型设施盐碱土质量的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2020, (20): 83-91. |
| CHEN Zhikun, FENG Puyang, JIN Guanghua, et al. Effects of Different Improvement Measures on Quality of Typical Saline-alkali Soil With Plastic Shed in the Middle of Shaanxi[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2020,(20): 83-91. | |
| [22] | 宋以玲, 于建, 陈士更, 等. 化肥减量配施生物有机肥对油菜生长及土壤微生物和酶活性影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(1): 352-360. |
| SONG Yiling, YU Jian, CHEN Shigeng, et al. Effects of Reduced Chemical Fertilizer with Application of Bio-organic Fertilizer on Rape Growth, Microorganism and Enzymes Activities in Soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 32(1): 352-360. | |
| [23] |
Zhao J, Liu J, Liang H, et al. Manipulation of the rhizosphere microbial community through application of a new bio-organic fertilizer improves watermelon quality and health[J]. Plos One, 2018, 13(2): e0192967.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 冯梅, 肖莉娟, 张世卿, 王晶晶. 骏枣果园土壤养分含量对果实氨基酸的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(1): 136-147. |
| [2] | 邓永辉, 郑强卿, 兖攀, 王文军, 陈奇凌, 王晶晶, 张锦强, 王振东. 干旱区骏枣根系分布和土壤养分关系分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(1): 156-164. |
| [3] | 席丽, 李思瑶, 夏晓莹, 陈玉雯, 李林, 王杰, 马小龙, 米尔扎提·柯尼加里木, 阿丽耶·麦麦提, 王卫霞. 不同郁闭度天山云杉林土壤养分特征[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2216-2222. |
| [4] | 董艳雪, 贾永红, 张金汕, 李丹丹, 王凯, 罗四维, 王润琪, 石书兵. 不同生态区环境下春小麦干物质积累及产量形成分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1848-1857. |
| [5] | 李怀胜, 艾洪玉, 孟玲, 王贺亚, 张磊, 艾海峰. 减氮下运筹养分吸收高峰期追施比例对春小麦的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1866-1872. |
| [6] | 王兴州, 时晓磊, 张恒, 曲可佳, 耿洪伟, 丁孙磊, 张金波, 严勇亮. 引进春小麦品种萌发期耐盐性鉴定及评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1353-1362. |
| [7] | 曲可佳, 时晓磊, 张恒, 王兴州, 耿洪伟, 丁孙磊, 张金波, 严勇亮. PEG处理下引进春小麦品种苗期抗旱性评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1363-1371. |
| [8] | 刘兴宇, 袁建钰, 李广, 张娟, 徐万恒, 张霞霞. 陇中黄土高原春小麦品种和优化施肥[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1398-1405. |
| [9] | 朱宝国, 匡恩俊, 滕占林, 孟庆英, 王囡囡, 冯浩原, 邱磊, 高雪冬, 张春峰. 不同生物有机肥配施化肥对大豆植株生长、抗病及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(5): 1127-1133. |
| [10] | 封帆, 谢开云, 艾比布拉·伊马木, 万江春. 果园生草对苹果园杂草控制、土壤养分及果树营养状况的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(4): 982-991. |
| [11] | 贾永红, 魏海鹏, 侯殿亮, 曾潮武, 纳斯如拉·克热木, 梁晓东. 新疆自育春小麦品种抗旱性及农艺性状相关性评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(12): 2940-2948. |
| [12] | 罗晓颖, 房彦飞, 孙婷婷, 唐江华, 王鲁振, 唐甜, 王晨, 徐文修. 播种量对旱地春小麦干物质积累、灌浆特性及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(11): 2704-2711. |
| [13] | 吕亮雨, 樊光辉, 付全, 苏彩风, 李发毅. 生物有机肥对枸杞生长及土壤性状的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(11): 2779-2789. |
| [14] | 石学萍, 张谦, 王燕, 董明, 祁虹, 冯国艺, 孙红春, 王树林. 有机肥替代部分化肥对棉田土壤养分含量与棉花产量收益的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(1): 192-196. |
| [15] | 赵经华, 杨庭瑞, 张恒, 虎胆·吐马尔白, 马亮, 陈凯丽. 基于响应面法的多砾石砂土滴灌春小麦水肥条件优选[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(1): 43-51. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||