

新疆农业科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (6): 1485-1491.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.06.022
王冠玉1,2( ), 贾平平2,3, 靳娟2, 阿布都卡尤木·阿依麦提2, 樊丁宇2, 赵晓梅2, 郝庆2, 杨磊2(
), 贾平平2,3, 靳娟2, 阿布都卡尤木·阿依麦提2, 樊丁宇2, 赵晓梅2, 郝庆2, 杨磊2( ), 耿文娟1(
), 耿文娟1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-10-15
出版日期:2023-06-20
发布日期:2023-06-20
通信作者:
杨磊(1981-),男,新疆吉木萨尔人,副研究员,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为果树种质资源与育种,(E-mail) yanglei9961@163.com; 耿文娟(1983-),女,新疆阿勒泰人,教授,博士,博士生导师,研究方向为果树种质资源及栽培生理,(E-mail) gwj0526@163.com
作者简介:王冠玉(1999-),女,河北衡水人,硕士研究生, 研究方向为果树种质资源与栽培生理,(E-mail)wang19990123@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Guanyu1,2( ), JIA Pingping2,3, JIN Juan2, Abudoukayoumu Ayimaiti2, FAN Dingyu2, ZHAO Xiaomei2, HAO Qing2, YANG Lei2(
), JIA Pingping2,3, JIN Juan2, Abudoukayoumu Ayimaiti2, FAN Dingyu2, ZHAO Xiaomei2, HAO Qing2, YANG Lei2( ), GENG Wenjuan1(
), GENG Wenjuan1( )
)
Received:2022-10-15
Online:2023-06-20
Published:2023-06-20
Correspondence author:
YANG Lei(1981-), male, Jimusaer, Xinjiang, associate researcher, doctor,master's sapervisor research direction is fruit tree germplasm resources andbreeding, (E-mail) yanglei9961@163.com; GENG Wenjuan(1983-),female, Aletai, Xinjiang, professor,doctor,doctoral supervisor,associate professor, doctor, doctoral tutor, research direction is Germplasm resources and cultivation physiology of fruit trees, (E-mail) gwj0526@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】分析高温胁迫下伏脆蜜和骏枣花器官的生理特征差异,为红枣花器官的耐热性研究提供理论依据。【方法】以3年生伏脆蜜和骏枣盆栽苗为材料,测定45℃高温胁迫不同时间(0、2、6、24 h)对2个品种花器官相对电导率、丙二醛、脯氨酸、可溶性糖、超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化物酶、过氧化氢酶、多酚氧化酶等相关生理指标的影响。【结果】随着高温胁迫时间的延长,2个品种的相对电导率显著上升,细胞膜遭受高温胁迫后受损伤程度增大,且在不同时长高温胁迫处理下骏枣花器官的相对电导率和MDA含量始终大于伏脆蜜,高温胁迫下骏枣花器官细胞膜受损害程度较大。随着高温胁迫时间的延长,2个品种花器官脯氨酸和可溶性糖含量均呈现先上升后下降趋势,但骏枣花器官脯氨酸含量比伏脆蜜提前下降。2个品种的抗氧化酶活性随着温度的升高基本呈现上升趋势,且伏脆蜜花器官的POD、CAT酶活性始终大于骏枣,伏脆蜜提高更多的自身抗氧化酶活性以此抵御高温胁迫。【结论】高温胁迫下,伏脆蜜花器官细胞膜稳定性优于骏枣,在生理特征上表现出比骏枣花器官有更强的耐热性。
中图分类号:
王冠玉, 贾平平, 靳娟, 阿布都卡尤木·阿依麦提, 樊丁宇, 赵晓梅, 郝庆, 杨磊, 耿文娟. 高温胁迫对枣花器官生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1485-1491.
WANG Guanyu, JIA Pingping, JIN Juan, Abudoukayoumu Ayimaiti, FAN Dingyu, ZHAO Xiaomei, HAO Qing, YANG Lei, GENG Wenjuan. Effects of high temperature stress on physiological characteristics on jujube flower organs[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1485-1491.
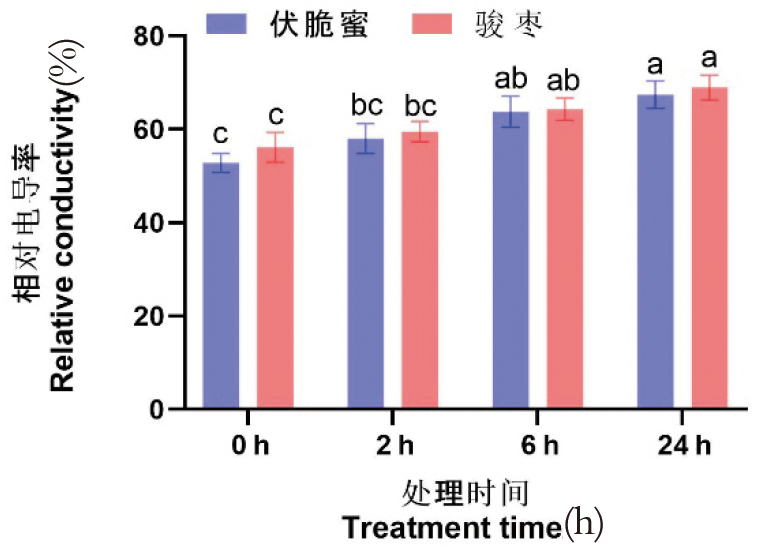
图1 高温胁迫下枣花器官相对电导率变化 注:柱形图中不同小写字母表示同一品种不同处理间的差异显著(P<0.05),下同
Fig.1 Effect of high temperature stress on relative conductivity of jujube flower organs Note:Different letters in the column indicate significant difference among different treatment of the same variety(P<0.05),the same as below
| [1] | 曲泽洲, 王永蕙, 彭士琪, 等. 中国果树志·枣卷[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1993:5-7. |
| QU Zezhou, WANG Yonghui, PENG Shiqi, et al. China's fruit trees·Jujube volume[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Press, 1993: 5-7. | |
| [2] | 孙劭. 我国极端天气气候事件发生规律、特点及影响[J]. 中国减灾, 2021,(15):10-17. |
| SUN Shao. The occurrence of extreme weather and climate events in China occurs, characteristics and impacts[J]. Disaster Reduction in China, 2021,(15):10-17. | |
| [3] | 李茂春, 胡云喜, 李新建, 等. 塔里木灌区红枣生产的农业气象灾害调查分析[J]. 北京农业, 2015,(15):256-257. |
| LI Maochun, HU Yunxi, LI Xinjian, et al. Investigation and analysis of agricultural meteorological disasters in jujube production in Tarim Shrubland[J]. Beijing Agriculture, 2015,(15):256-257. | |
| [4] |
邓娇燕, 黄斌, 吕立军, 等. 叶面喷施1-MCP缓解辣椒幼苗高温伤害的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2019, 46(5):891-900.
DOI |
|
DENG Jiaoyan, HUANG Bin, LV Lijun, et al. Mechanisms of Foliar-spraying 1-MCP to alleviate injury of pepper seedlings caused by high temperature[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2019, 46(5):891-900.
DOI |
|
| [5] | 田佳, 王辉, 孙宇, 等. 高温胁迫对苹果叶片生理生化指标的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2021,(10):28-34. |
| TIAN Jia, WANG Hui, SUN Yu, et al. Effects of high temperature stress on physiological and biochemical indexes of apple leaves[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2021,(10):28-34. | |
| [6] |
刘敏, 房玉林. 高温胁迫对葡萄幼树生理指标和超显微结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2020, 53(7):1444-1458.
DOI |
|
LIU Min, FANG Yulin. Effects of heat stress on physiological indexes and ultrastructure of grapevines[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2020, 53(7):1444-1458.
DOI |
|
| [7] | 项延军, 李新芝. 扶芳藤等3种藤本植物耐热性生理生化指标初探[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2011, 39(3):241-243. |
| XIANG Yanjun, LI Xinzhi. A preliminary study on the physiological and biochemical indexes of heat tolerance of three kinds of vines, including Fufang vine[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 39(3):241-243. | |
| [8] | 夏惠, 高帆, 胡荣平, 等. 褪黑素预处理对高温下猕猴桃幼苗抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2019, 39(8):1425-1433. |
| XIA Hui, GAO Fan, HU Rongping, et al. Effects of melatonin application on antioxidant capacity in kiwifruit seedlings under high temperature stress[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2019, 39(8):1425-1433. | |
| [9] | 李元生, 徐珊珊, 李强, 等. 外源褪黑素对高温胁迫下葡萄幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 林业科技通讯, 2021,(4):66-69. |
| LI Yuansheng, XU Shanshan, LI Qiang, et al. Effects of Exogenous Melatonin on Physiological Characteristics of Grape Seedlings under High Temperature Stress[J]. Forest Science and Technology, 2021,(4):66-69. | |
| [10] |
徐超, 王明田, 杨再强, 等. 高温对温室草莓光合生理特性的影响及胁迫等级构建[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(1):231-240.
DOI |
|
XU Chao, WANG Mingtian, YANG Zaiqiang, et al. Effects of high temperature on photosynthetic physiological characteristics of strawberry seedlings in greenhouse and construction of stress level[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(1):231-240.
DOI |
|
| [11] | 田佳, 李佳, 孟清波, 等. 不同苹果品种叶片耐热阈值及高温下生理生化响应[J]. 河南农业科学, 2021, 50(1):121-128. |
| TIAN Jia, LI Jia, MENG Qingbo, et al. Heat tolerance threshold and physiological and biochemical responses of leaves of different apple varieties[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 50(1):121-128. | |
| [12] | 耶兴元, 马锋旺, 王顺才, 等. 高温胁迫对猕猴桃幼苗叶片某些生理效应的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2004,(12):33-37. |
| YE Xingyuan, MA Fengwang, WANG Shuncai, et al. Physiological effects of kiwifruit lamina under high temperature stress[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Ed.), 2004,(12):33-37. | |
| [13] | 孙军利, 赵宝龙, 郁松林. 外源水杨酸对高温胁迫下葡萄几种抗氧化酶活性和抗氧化物含量的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 2014, 50(7):1014-1018. |
| SUN Junli, ZHAO Baolong, YU Songlin. Effect of exogenous salicylic acid on antioxidant enzymes activities and antioxidants contents in grape seedlings under high temperature stress[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2014, 50(7):1014-1018. | |
| [14] |
庞强强, 周曼, 孙晓东, 等. 菜心耐热性评价及酶促抗氧化系统对高温胁迫的响应[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2020, 32(1):72-79.
DOI |
|
PANG Qiangqiang, ZHOU Man, SUN Xiaodong, et al. Evaluation of heat tolerance and response of enzymatic antioxidant system to heat stress in Brassica parachinensis L[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2020, 32(1):72-79.
DOI |
|
| [15] |
杨磊, 靳娟, 冯贝贝, 等. 高温环境下枣光合特性及相关生理指标日变化[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(9):1639-1646.
DOI |
|
YANG Lei, JIN Juan, FENG Beibei, et al. Study on diurnal variation of photosynthetic characteristics and related physiological indexes of jujube under high temperature environment[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(9):1639-1646.
DOI |
|
| [16] | 李合生, 孙群, 赵世杰, 等. 植物生理生化学实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000: 164-165. |
| LI Hesheng, SUN Qun, ZHAO Shijie, et al. Experimental principles and techniques of plant physiology and biochemistry[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000: 164-165. | |
| [17] | Qian Z, Xiaojun X, Yani H, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of heat resistance in 68 Vitis germplasm resources[J]. VITIS, 2018, 57(2). |
| [18] | Sergi M-B, Leonor A. Drought-induced changes in the redox state of alpha-tocopherol, ascorbate, and the diterpene carnosic acid in chloroplasts of Labiatae species differing in carnosic acid contents[J]. Plant Physiology, 2003, 131(4). |
| [19] |
李燕, 李玲, 李少旋, 等. 高温对设施甜樱桃花器官发育的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(10):2101-2108.
DOI |
|
LI Yan, LI Ling, LI Shaoxuan, et al. Effect of high temperature on the flower development of sweet cherry in solar greenhouse[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(10):2101-2108.
DOI |
|
| [20] | 夏莹莹, 叶航, 马锦林, 等. 4个油茶品种的半致死温度与耐热性研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2012, 28(4):58-61. |
|
XIA Yingying, YE Hang, MA Jinlin, et al. The study on semi-lethal high temperature and heat tolerance of four camellia oleifera abel clones[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2012, 28(4):58-61.
DOI |
|
| [21] | 王涛, 田雪瑶, 谢寅峰, 等. 植物耐热性研究进展[J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 28(5):719-726. |
| WANG Tao, TIAN Xueyao, XIE Yinfeng, et al. Research advance on heat-stress tolerance in plants[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science Ed.), 2013, 28(5):719-726. | |
| [22] | 张方静, 罗峰, 谭殷殷, 等. 高温胁迫对月季生理特性和叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 2019, 48(4):108-115. |
| ZHANG Fangjing, LUO Feng, TAN Yinyin, et al. Effects of high temperature stress on the physiological characteristics and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Chinese rose[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 48(4):108-115. | |
| [23] | 于金平, 俞珊, 梁有旺, 等. NaCl胁迫对美国白蜡幼苗部分生理指标的影响[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2014, 23(1):110-112. |
| YU Jinping, YU Shan, LIANG Youwang, et al. Effect of NaCl stress on some physiological indexes of Fraxinus americana seedling[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2014, 23(1):110-112. | |
| [24] | 张琨, 王琦, 张玫云. 高温胁迫时长对菜心幼苗生理指标的影响研究[J]. 上海蔬菜, 2021,(4):77-79, 85. |
| ZHANG Kun, WANG Qi, ZHANG Meiyun. Effect of high temperature stress duration on physiological indexes of cabbage seedlings[J]. Shanghai Vegetables, 2021,(4):77-79, 85. | |
| [25] | TOAN C V, 罗聪, 何新华, 等. 高温胁迫对杧果幼苗生理生化指标的影响[J]. 热带作物学报, 2016, 37(1):53-58. |
| TOAN C V, LUO Cong, HE Xinhua, et al. Effect of High Temperature Stress on Physiology Indices of Mango Seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2016, 37(1):53-58. | |
| [26] |
吴燕, 乔晓燕, 葛伟强, 等. 高温强光下外源褪黑素对栝楼雌花生理生化特性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2020, 32(3):421-429.
DOI |
|
WU Yan, QIAO Xiaoyan, GE Weiqiang, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on physiological and biochemical characteristics in female flowers of Trichosanthes kirilowii under high temperature and strong light[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2020, 32(3):421-429.
DOI |
|
| [27] |
靳娟, 杨磊, 樊丁宇, 等. 高温胁迫对枣苗生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(3):439-447.
DOI |
|
JIN Juan, YANG Lei, FAN Dingyu, et al. Effects of High Temperature Stress on Physiological Characteristics on Jujube Seedlings[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(3):439-447.
DOI |
|
| [28] | Almeselmani M, Deshmukh P S, Sairam R K, et al. Protective role of antioxidant enzymes under high temperature stress[J]. Plant Science, 2006, 171(3). |
| [29] | Xie D F, Zhang G C, Xia X X, et al. The effects of phenolic acids on the photosynthetic characteristics and growth of Populus × euramericana cv. 'Neva' seedlings[J]. Photosynthetica, 2018, 56(4):1-8. |
| [30] | Tsikas D. Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: Analytical and biological challenges[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 2016, 524. |
| [31] | Wang L J, LI S H. Thermotolerance and related antioxidant enzyme activities induced by heat acclimation and salicylic acid in grape (Vitis vinifera L.) leaves[J]. Plant Growth Regulation: An International Journal on Natural and Synthetic Regulators, 2006, 48(2). |
| [32] | 张哲, 闵红梅, 夏关均, 等. 高温胁迫对植物生理影响研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(16):8338-8339, 8342. |
| ZHANG Zhe, MIN Hongmei, XIA Guanjun, et al. Research advances on influence of high temperature stress on some physiological characteristics of plants[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(16):8338-8339, 8342. |
| [1] | 王辉, 郭金成, 宋佳, 张庭军, 何良荣. 高温胁迫下陆地棉GhCIPK6转基因后代生理生化分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2109-2119. |
| [2] | 李自芹, 陈雅, 李文绮, 贾文婷, 郭慧静, 宋方圆, 赵志永, 刘成江. 不同预冷方式结合H2O2处理对绿糖心冬枣贮藏期间品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2208-2215. |
| [3] | 靳娟, 苏比娜·肖克来提, 阿布都卡尤木·阿依麦提, 杨磊, 郝庆, 樊丁宇. 灰枣扩展蛋白基因ZjEXPA8的克隆及序列分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2223-2230. |
| [4] | 鞠乐, 齐军仓, 陈培育, 牛银亭, 阴志刚. 干旱胁迫对大麦种子萌发、幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1879-1886. |
| [5] | 魏迎凤, 张全成, 查慧, 王小丽, 王俊刚. 二甲戊灵对龙葵苗期主要生长发育和生理指标的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 2013-2021. |
| [6] | 李凯亮, 张振宇, 胡红英. 新疆哈密地区枣园昆虫群落结构及多样性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 2028-2037. |
| [7] | 张雁飞, 苏比娜·肖克来提, 杨磊, 郝庆, 靳娟, 樊丁宇. 26个鲜食枣品种SSR指纹图谱构建与遗传多样性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(7): 1671-1678. |
| [8] | 杨晓娟, 靳娟, 樊丁宇, 郝庆, 杨磊, 耿文娟. 极端高温环境对骏枣和伏脆蜜枣光合特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(7): 1679-1688. |
| [9] | 陈艳, 黄璐瑶, 邓昌蓉, 张彦君, 侯全刚, 邵登魁. 冷害对多茸毛型线辣椒幼苗生理水平的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1492-1498. |
| [10] | 刘衍晨, 刘志刚, 白新慧, 乔鹏, 徐诚, 白慧敏, 张娟. 蛭石复混基质对辣椒育苗的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(5): 1190-1199. |
| [11] | 王文军, 陈奇凌, 郑强卿, 王晶晶, 张桂兵, 李海霞. 模式改造对灰枣树个体和群体冠层特性及机械适应性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(4): 925-934. |
| [12] | 李爽, 谢丹露, 吴继周, 马瑞, 谢艾迪, 邵蕾, 高娟娟, 韩海霞. 不同炮制方法下若羌灰枣主要功能成分及抗氧化活性的对比[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(4): 935-942. |
| [13] | 程利华, 杨红兰, 马清倩, 史莹, 张大伟, Alisher A. Abdullaev, 张道远. 陆地棉种质黄萎病抗性生理鉴定分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(4): 992-1002. |
| [14] | 杨植, 董梦怡, 王振磊, 闫芬芬, 吴翠云, 王玖瑞, 刘孟军, 林敏娟. 基于TPA法枣酸枣杂交F1果实质地与裂果对比分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(3): 608-615. |
| [15] | 王德娟, 汪健平, 冯建中, 井双泉, 许士东, 隋立春, 黄光辉. 基于DNDC模型的红枣生长模拟参数敏感性和产量不确定性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(3): 651-663. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||