

新疆农业科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (3): 555-566.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.03.005
郝曦煜1,2( ), 杨涛3, 张俊杰4, 李雪1, 张仲鹃1, 武晨清1, 宗绪晓3, 冷友斌1, 陈博1(
), 杨涛3, 张俊杰4, 李雪1, 张仲鹃1, 武晨清1, 宗绪晓3, 冷友斌1, 陈博1( ), 郭来春2(
), 郭来春2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-07-11
出版日期:2023-03-20
发布日期:2023-04-18
通信作者:
陈博(1982-),男,辽宁大连人,高级工程师,博士,研究方向为生物化工技术及应用,(E-mail)chenbo2@feihe.com;作者简介:郝曦煜(1990-),男,辽宁铁岭人,助理研究员,硕士,研究方向为作物育种与栽培,(E-mail)haoxiyu1990@foxmail.com
基金资助:
HAO Xiyu1,2( ), YANG Tao3, ZHANG Junjie4, LI Xue1, ZHANG Zhongjuan1, WU Chenqing1, ZONG Xuxiao3, LENG Youbin1, CHEN Bo1(
), YANG Tao3, ZHANG Junjie4, LI Xue1, ZHANG Zhongjuan1, WU Chenqing1, ZONG Xuxiao3, LENG Youbin1, CHEN Bo1( ), GUO Laichun2(
), GUO Laichun2( )
)
Received:2022-07-11
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2023-04-18
Correspondence author:
CHEN Bo(1982-), male, native place: Dalian, Liaoning. Senior engineer, research field: major in biochemical technology and other fields, (E-mail) Supported by:摘要:
【目的】研究不同氮、磷、钾处理对鹰嘴豆产量、农艺性状及经济效益的影响,建立肥效模型,提供能够有效增产的氮、磷、钾最佳施肥量,为集成鹰嘴豆高产栽培提供参考。【方法】2019~2020年以白鹰1号为材料,采用“3414”不完全正交回归设计进行田间试验。试验地常用施肥量为N: 58 kg/hm2、P2O5: 69 kg/hm2、K2O: 60 kg/hm2。设氮、磷、钾4个施肥水平为0(不施肥)、1(常用施肥量×0.5)、2(常用施肥量)、3(常用施肥量×1.5)。调查鹰嘴豆生育日数、株高、主茎分枝数、单株荚数、单荚粒数、百粒重、干重、根长和产量等指标,研究不同氮、磷、钾处理鹰嘴豆产量和农艺性状的变化,拟合并优化氮、磷、钾施肥效应进行方程,分析氮、磷、钾肥对鹰嘴豆产量和农艺性状单因素和互作效应,分别得到最高产量和最佳经济效益下的氮、磷、钾最佳施肥量。【结果】鹰嘴豆生育日数、主茎分枝数和单荚粒数受肥料施用量变化影响较小,单株荚数和百粒重共同决定了产量。N2P2K3处理下的株高、单株荚数、百粒重均为最高,根长较长。缺氮处理和缺钾处理的产量显著低于缺磷处理,对产量的影响为N>K2O>P2O5。氮、磷、钾3种肥料对鹰嘴豆产量和农艺性状均产生明显的单因素和互作效应,鹰嘴豆的经济效益与产量变化一致。各指标达到最大值时氮、磷、钾的施用量:产量Y1: 3 801 kg/hm2,N: 75.8 kg/hm2、P2O5: 82.5 kg/hm2、K2O: 90 kg/hm2;株高Y2: 84 cm,N: 74.1 kg/hm2、P2O5: 80.1 kg/hm2、K2O: 90 kg/hm2;单株荚数Y3: 164.9荚,N: 72.7 kg/hm2、P2O5: 83.7 kg/hm2、K2O: 90 kg/hm2;百粒重Y4: 38.7 g、地上干重Y5: 147.6 g、地下干重Y6: 6.3 g、根长Y7: 19.1 cm,N: 87 kg/hm2、P2O5: 103.5 kg/hm2、K2O: 90 kg/hm2。【结论】鹰嘴豆的生育日数、主茎分枝数和单荚粒数受肥料施用量影响较小。随氮、磷、钾施肥量的增加鹰嘴豆产量、单株荚数、百粒重、地上干重、地下干重和根长均表现出先增长后下降。鹰嘴豆地上干重、地下干重和根长持续受到氮、磷、钾3种肥料互作促进效应。当N: 75.8 kg/hm2、P2O5: 82.5 kg/hm2、K2O:90 kg/hm2时,产量达到最大(3 801 kg/hm2);当N: 74.6 kg/hm2、P2O5: 81.2 kg/hm2、K2O:90 kg/hm2时,经济效益最佳(36 853.6 元/hm2)。
中图分类号:
郝曦煜, 杨涛, 张俊杰, 李雪, 张仲鹃, 武晨清, 宗绪晓, 冷友斌, 陈博, 郭来春. 不同氮磷钾处理对鹰嘴豆产量、农艺性状及经济效益的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(3): 555-566.
HAO Xiyu, YANG Tao, ZHANG Junjie, LI Xue, ZHANG Zhongjuan, WU Chenqing, ZONG Xuxiao, LENG Youbin, CHEN Bo, GUO Laichun. Effects of Different Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium Treatments on Yield, Agronomic Traits and Economic Benefit of Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.)[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(3): 555-566.

图1 2019~2020年鹰嘴豆生育期内各月份平均温度、降雨量与日照时数
Fig.1 Effective accumulated temperature, precipitation and sunshine duration during chickpea growth period in 2019-2020
| 编号 No. | 处理 Treatment | 码值Code | 施肥量 Fertilizer rates (kg/hm2) | 生育日数 Growth period (d) | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 主茎分枝数 Branches (branch) | 单株荚数 Pods per plant (pod) | 单荚粒数 Seeds per pod (seed) | 百粒重 100-seed weight (g) | 地上干重 Shoot dry matter (g) | 地下干重 Root dry matter (g) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 产量 Yield (kg/hm2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | K2O | N | P2O5 | K2O | ||||||||||||
| 1 | N0P0K0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 86.0a | 68.3e | 2.9a | 82.7d | 1.0a | 33.2e | 69.9j | 3.3j | 14.7f | 1 908.3j |
| 2 | N0P2K2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0.0 | 69.0 | 60.0 | 87.0a | 68.5e | 2.7a | 90.6cd | 1.0a | 33.5de | 76.6ij | 3.6hij | 15.1ef | 2 090.0ij |
| 3 | N1P2K2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 29.0 | 69.0 | 60.0 | 88.0a | 75.7abcde | 2.7a | 133.8abcd | 1.0a | 35.9abcde | 109.9ef | 4.8cd | 16.9abcd | 3 086.7def |
| 4 | N2P0K2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 58.0 | 0.0 | 60.0 | 88.5a | 73.4cde | 3.0a | 100.6bcd | 1.1a | 34.5abcde | 85.1i | 3.8ghi | 15.5def | 2 723.3gh |
| 5 | N2P1K2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 58.0 | 34.5 | 60.0 | 89.0a | 80.4abc | 2.7a | 147.2ab | 1.0a | 36.9abc | 113.1def | 5.0bcd | 17.2abc | 3 395.0abc |
| 6 | N2P2K2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 58.0 | 69.0 | 60.0 | 87.3a | 81.2ab | 3.0a | 151.3ab | 1.1a | 37.2ab | 120.2bcd | 5.1bc | 17.3ab | 3 490.0ab |
| 7 | N2P3K2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 58.0 | 103.5 | 60.0 | 88.5a | 76.2abcd | 3.0a | 138.1abc | 1.1a | 36.4abcd | 127.9ab | 5.5a | 17.8a | 3 185cde |
| 8 | N2P2K0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 58.0 | 69.0 | 0.0 | 86.5a | 69.2de | 2.9a | 118.0abcd | 1.0a | 33.8cde | 97.2h | 3.5ij | 14.8f | 2 321.7i |
| 9 | N2P2K1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 58.0 | 69.0 | 30.0 | 87.5a | 74.3bcde | 3.5a | 126.7abcd | 1.1a | 35.2abcde | 116.7cde | 4.7de | 16.7abcd | 2 923.3efgh |
| 10 | N2P2K3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 58.0 | 69.0 | 90.0 | 89.0a | 82.4a | 3.0a | 158.7a | 1.4a | 37.6a | 124.4bc | 5.3ab | 17.7a | 3 660.0a |
| 11 | N3P2K2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 87.0 | 69.0 | 60.0 | 87.5a | 76.5abcd | 2.9a | 142.2abc | 1.2a | 36.7abc | 134.1a | 5.2abc | 17.5a | 3 280.0bcd |
| 12 | N1P1K2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 29.0 | 34.5 | 60.0 | 89.0a | 74.4bcde | 2.7a | 130.0abcd | 1.1a | 35.5abcde | 99.8gh | 4.2fg | 15.9bcdef | 2 998.3efg |
| 13 | N1P2K1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 29.0 | 69.0 | 30.0 | 86.3a | 71.2de | 3.0a | 115.0abcd | 1.3a | 34.2bcde | 105.5fgh | 4.4ef | 16.4abcde | 2 653.3h |
| 14 | N2P1K1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 58.0 | 34.5 | 30.0 | 89.0a | 73.5cde | 2.5a | 124.8abcd | 1.1a | 34.8abcde | 107.1efg | 4.0gh | 15.7cdef | 2 880.0fgh |
表1 不同氮、磷、钾处理下鹰嘴豆产量和农艺性状变化
Tab.1 The effects of different nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium on yield and agronomic traits of chickpea
| 编号 No. | 处理 Treatment | 码值Code | 施肥量 Fertilizer rates (kg/hm2) | 生育日数 Growth period (d) | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 主茎分枝数 Branches (branch) | 单株荚数 Pods per plant (pod) | 单荚粒数 Seeds per pod (seed) | 百粒重 100-seed weight (g) | 地上干重 Shoot dry matter (g) | 地下干重 Root dry matter (g) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 产量 Yield (kg/hm2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | K2O | N | P2O5 | K2O | ||||||||||||
| 1 | N0P0K0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 86.0a | 68.3e | 2.9a | 82.7d | 1.0a | 33.2e | 69.9j | 3.3j | 14.7f | 1 908.3j |
| 2 | N0P2K2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0.0 | 69.0 | 60.0 | 87.0a | 68.5e | 2.7a | 90.6cd | 1.0a | 33.5de | 76.6ij | 3.6hij | 15.1ef | 2 090.0ij |
| 3 | N1P2K2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 29.0 | 69.0 | 60.0 | 88.0a | 75.7abcde | 2.7a | 133.8abcd | 1.0a | 35.9abcde | 109.9ef | 4.8cd | 16.9abcd | 3 086.7def |
| 4 | N2P0K2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 58.0 | 0.0 | 60.0 | 88.5a | 73.4cde | 3.0a | 100.6bcd | 1.1a | 34.5abcde | 85.1i | 3.8ghi | 15.5def | 2 723.3gh |
| 5 | N2P1K2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 58.0 | 34.5 | 60.0 | 89.0a | 80.4abc | 2.7a | 147.2ab | 1.0a | 36.9abc | 113.1def | 5.0bcd | 17.2abc | 3 395.0abc |
| 6 | N2P2K2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 58.0 | 69.0 | 60.0 | 87.3a | 81.2ab | 3.0a | 151.3ab | 1.1a | 37.2ab | 120.2bcd | 5.1bc | 17.3ab | 3 490.0ab |
| 7 | N2P3K2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 58.0 | 103.5 | 60.0 | 88.5a | 76.2abcd | 3.0a | 138.1abc | 1.1a | 36.4abcd | 127.9ab | 5.5a | 17.8a | 3 185cde |
| 8 | N2P2K0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 58.0 | 69.0 | 0.0 | 86.5a | 69.2de | 2.9a | 118.0abcd | 1.0a | 33.8cde | 97.2h | 3.5ij | 14.8f | 2 321.7i |
| 9 | N2P2K1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 58.0 | 69.0 | 30.0 | 87.5a | 74.3bcde | 3.5a | 126.7abcd | 1.1a | 35.2abcde | 116.7cde | 4.7de | 16.7abcd | 2 923.3efgh |
| 10 | N2P2K3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 58.0 | 69.0 | 90.0 | 89.0a | 82.4a | 3.0a | 158.7a | 1.4a | 37.6a | 124.4bc | 5.3ab | 17.7a | 3 660.0a |
| 11 | N3P2K2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 87.0 | 69.0 | 60.0 | 87.5a | 76.5abcd | 2.9a | 142.2abc | 1.2a | 36.7abc | 134.1a | 5.2abc | 17.5a | 3 280.0bcd |
| 12 | N1P1K2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 29.0 | 34.5 | 60.0 | 89.0a | 74.4bcde | 2.7a | 130.0abcd | 1.1a | 35.5abcde | 99.8gh | 4.2fg | 15.9bcdef | 2 998.3efg |
| 13 | N1P2K1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 29.0 | 69.0 | 30.0 | 86.3a | 71.2de | 3.0a | 115.0abcd | 1.3a | 34.2bcde | 105.5fgh | 4.4ef | 16.4abcde | 2 653.3h |
| 14 | N2P1K1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 58.0 | 34.5 | 30.0 | 89.0a | 73.5cde | 2.5a | 124.8abcd | 1.1a | 34.8abcde | 107.1efg | 4.0gh | 15.7cdef | 2 880.0fgh |
| 项目 Item | 回归方程 Regression equation | 决定系数R2 Determination coefficient | 编号 No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 产量 Yield | Y1=1 896.096 5+21.254 1X1+5.940 2X2+9.047 5X3-0.323 7 | 0.991 6** | (1) |
| 株高 Plant height | Y2=67.971 3+0.191 9X1+0.043 3X2-0.017 1X3-0.002 8 | 0.932 9* | (2) |
| 单株荚数 Pods per plant | Y3=82.190 1+0.921 3X1+0.395 1X2+0.233 9X3-0.014 0 | 0.972 0** | (3) |
| 百粒重 100-seed weight | Y4=33.122 5+0.029 8X1+0.002 3X2+0.028 5X3-0.000 7 | 0.9581* | (4) |
| 地上干重 Shoot dry matter | Y5=70.080 8+0.401 0X1+0.429 4X2+0.181 2X3-0.006 7 | 0.990 6** | (5) |
| 地下干重 Root dry matter | Y6=3.271 0+0.002 1X1+0.015 2X2+0.008 5X3-0.000 3 | 0.972 3** | (6) |
| 根长 Root length | Y7=14.607 3+0.002 4X1+0.028 5X2+0.010 1X3-0.000 5 | 0.975 3** | (7) |
表2 回归方程
Tab.2 regression equation
| 项目 Item | 回归方程 Regression equation | 决定系数R2 Determination coefficient | 编号 No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 产量 Yield | Y1=1 896.096 5+21.254 1X1+5.940 2X2+9.047 5X3-0.323 7 | 0.991 6** | (1) |
| 株高 Plant height | Y2=67.971 3+0.191 9X1+0.043 3X2-0.017 1X3-0.002 8 | 0.932 9* | (2) |
| 单株荚数 Pods per plant | Y3=82.190 1+0.921 3X1+0.395 1X2+0.233 9X3-0.014 0 | 0.972 0** | (3) |
| 百粒重 100-seed weight | Y4=33.122 5+0.029 8X1+0.002 3X2+0.028 5X3-0.000 7 | 0.9581* | (4) |
| 地上干重 Shoot dry matter | Y5=70.080 8+0.401 0X1+0.429 4X2+0.181 2X3-0.006 7 | 0.990 6** | (5) |
| 地下干重 Root dry matter | Y6=3.271 0+0.002 1X1+0.015 2X2+0.008 5X3-0.000 3 | 0.972 3** | (6) |
| 根长 Root length | Y7=14.607 3+0.002 4X1+0.028 5X2+0.010 1X3-0.000 5 | 0.975 3** | (7) |
| 项目 Item | 产量Y1 Yield (kg/hm2) | 株高Y2 Plant height (cm) | 单株荚数Y3 Pods per plant | 百粒重Y4 100-seed weight (g) | 地上干重Y5 Shoot dry matter (g) | 地下干重Y6 Root dry matter (g) | 根长Y7 Root length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 Maximum | 3 801.0 | 84.0 | 164.9 | 38.7 | 147.6 | 6.3 | 19.1 |
| N(X1) | 75.8 | 74.1 | 72.7 | 87.0 | 87.0 | 87.0 | 87.0 |
| P2O5(X2) | 82.5 | 80.1 | 83.7 | 103.5 | 103.5 | 103.5 | 103.5 |
| K2O(X3) | 90.0 | 90.0 | 90.0 | 90 | 90.0 | 90.0 | 90.0 |
表3 产量和农艺性状最大值及氮、磷、钾施肥量变化
Tab.3 The maximum of yield and agronomic traits with the fertilizer rates of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium
| 项目 Item | 产量Y1 Yield (kg/hm2) | 株高Y2 Plant height (cm) | 单株荚数Y3 Pods per plant | 百粒重Y4 100-seed weight (g) | 地上干重Y5 Shoot dry matter (g) | 地下干重Y6 Root dry matter (g) | 根长Y7 Root length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 Maximum | 3 801.0 | 84.0 | 164.9 | 38.7 | 147.6 | 6.3 | 19.1 |
| N(X1) | 75.8 | 74.1 | 72.7 | 87.0 | 87.0 | 87.0 | 87.0 |
| P2O5(X2) | 82.5 | 80.1 | 83.7 | 103.5 | 103.5 | 103.5 | 103.5 |
| K2O(X3) | 90.0 | 90.0 | 90.0 | 90 | 90.0 | 90.0 | 90.0 |
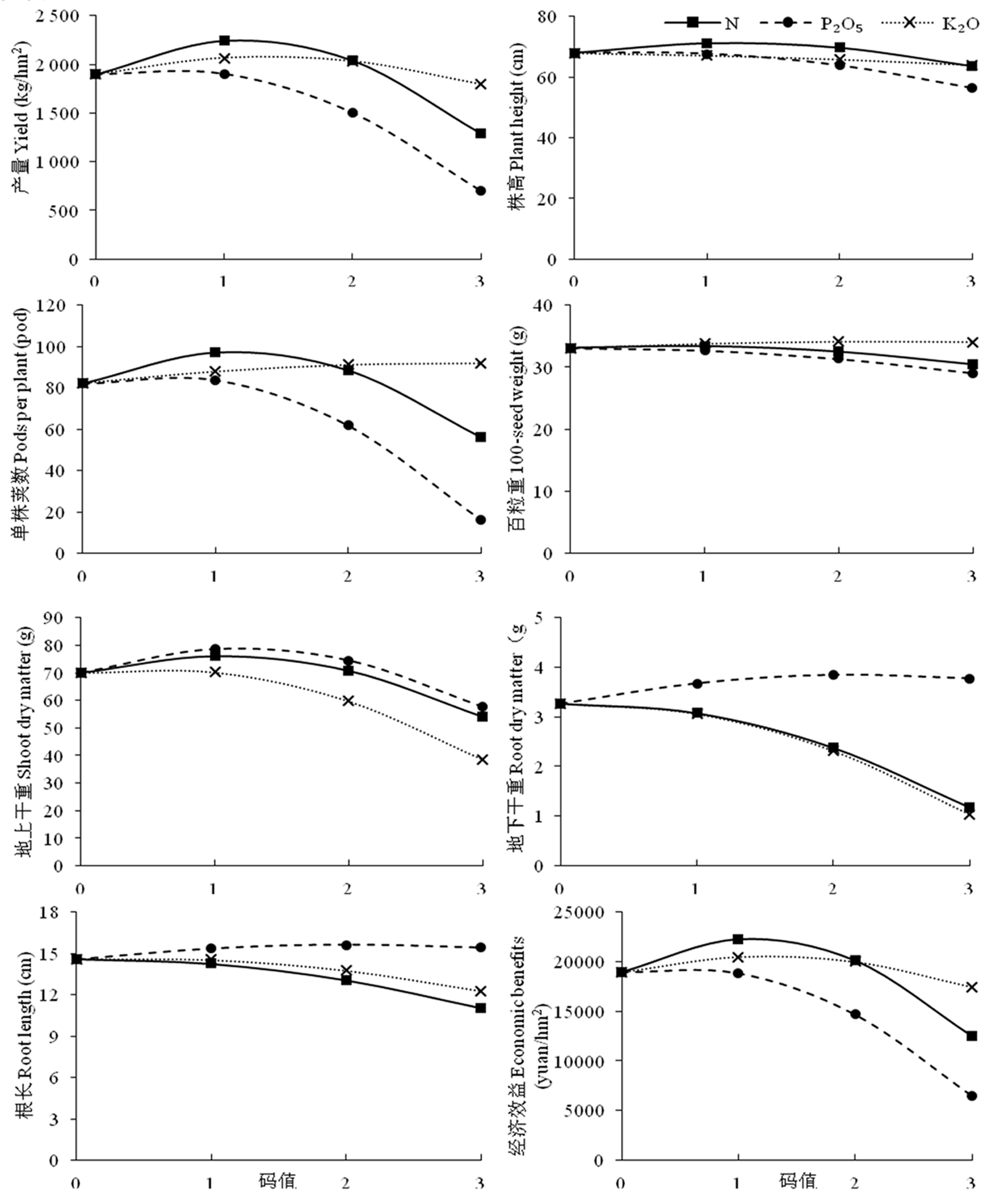
图2 不同氮、磷、钾下鹰嘴豆产量、农艺性状及经济效益的单因素变化
Fig.2 Single factor effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium on the yield, agronomic traits and economic benefits of chickpea

图3 氮、磷、钾对鹰嘴豆产量、农艺性状及经济效益的互作 注:图中响应面表现的是当某一种肥料为常规施肥量(码值为2)时,另2种肥料对产量的互作效应
Fig.3 Interaction analysis of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium on the yield, agronomic traits and economic benefits of chickpea Note: The response surface showed the interaction effect of two fertilizers with the other one was at conventional rate (code 2)
| [1] | 龙静宜, 林黎奋, 侯修身. 等. 食用豆类作物[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989. 305. |
| LONG Jinyi, LIN Lifeng, HOU Xiushen, et al. Edible Bean Crops[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989. 305. | |
| [2] | 郑卓杰. 中国食用豆类学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1997. 285. |
| ZHENG Zhuojie. Chinese Food Legumes[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1997. 285. | |
| [3] | 张旭娜, 么杨, 崔波. 等. 鹰嘴豆功能活性及应用研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2018, 9(9): 1983-1988. |
| ZHANG Xuna, YAO Yang, CUI Bo, et al. Research advance on the biological activity and application of chickpea[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2018, 9(9): 1983-1988. | |
| [4] | 陈文晋, 孔庆全, 赵存虎. 等. 鹰嘴豆营养功能研究进展[J]. 北方农业学报, 2019, 47(2): 119-123. |
| CHEN Wenji, KONG Qinquan, ZHAO Cunhu, et al. Review of progress in chickpea (Cicer arietinum) research[J]. Journal of Northern Agriculture, 2019, 47(2): 119-123. | |
| [5] |
Knudsen J C, Otte J, Olsen K, et al. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure on the conformation of β-lactoglobulin A as assessed by proteolytic peptide profiling[J]. International Dairy Journal, 2002, 12(10): 791-803.
DOI URL |
| [6] | 张俊杰, 郭晨, 杨旭. 等. 鹰嘴豆根瘤菌多样性研究进展[J]. 轻工学报, 2016, 31(6): 1-7. |
| ZHANG Junjie, GUO Chen, YANG Xu, et al. Research progress of the chickpea rhizoibal diversity[J]. Journal of Light Industry, 2016, 31(6): 1-7. | |
| [7] |
Varshney R K, Thudi M, Nayak S N, et al. Genetic dissection of drought tolerance in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.)[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2014, 127(2): 445-462.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Bhattarai T, Fettig S. Isolation and characterization of a dehydrin gene from Cicer pinnatifidum, a drought-resistant wild relative of chickpea[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2005, 123(4): 452-458.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Shukla R K, Raha S, Tripathi V, et al. Expression of CAP2, an APETALA2-family transcription factor from chickpea, enhances growth and tolerance to dehydration and salt stress in transgenic tobacco[J]. Plant Physiology, 2006, 142(1): 113-123.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | 聂石辉, 彭琳, 王仙. 等. 鹰嘴豆种质资源农艺性状遗传多样性分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2015, 16(1): 64-70. |
| NIE Shihui, PENG Ling, WANG Xian, et al. Genetic diversity of agronomic traits in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) germplasm resources[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2015, 16(1): 64-70. | |
| [11] | 郝曦煜, 梁杰, 郭文云. 等. 白城市特色食用豆产业发展优势分析[J]. 东北农业科学, 2019, 44(1): 87-90. |
| HAO Xiyu, LIANG Jie, GUO Wenyun, et al. Analysis of advantages of development of characteristic food legumes industry in Baicheng[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 44(1): 87-90. | |
| [12] | 陈文晋, 孔庆全, 赵存虎. 等. 鹰嘴豆种质资源主要农艺性状遗传多样性分析[J]. 北方农业学报, 2018, 46(5): 9-18. |
| CHEN Wenjin, KONG Qinquan, ZHAO Cunhu, et al. Analysis of genetic diversity of the main agronomic traits of chickpea germplasm resources[J]. Journal of Northern Agriculture, 2018, 46(5): 9-18. | |
| [13] | 郝曦煜, 梁杰, 肖焕玉, 等. 播期与密度对鹰嘴豆物质积累运转及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2020, 28(10):1568-1580. |
| HAO Xiyu, LIANG Jie, XIAO Huanyu, et al. Effect of sowing date and density on matter accumulation and translocation and on yield of chickpeas[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(10): 1568-1580. | |
| [14] | 赵永峰, 王斐, 关耀兵, 等. 干旱区鹰嘴豆的氮磷钾肥最优施用量[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(9):143-146. |
| ZHAO Yongfeng, WANG Fei, GUAN Yaobing, et al. Optimum application of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer to chickpea in arid area[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(9): 143-146. | |
| [15] | Bhowmick M K. Foliar nutrition and basal fertilization in chickpea under rainfed condition[J]. Environment & Ecology, 2006(4):1028-1030. |
| [16] | Barrios M A, Estrada J A S E, Gonzalez M T R, et al. Distancia entre hileras, nitrógeno y producción de garbanzo en humedad residual[J]. Revista Mexicana De Ciencias Pecuarias, 2016, 7(2):12. |
| [17] |
Meleta T, Abera G. Effects of rhizobium inoculation and phosphorus fertilizer rates on growth, yield and yield components of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) at Goro, Bale Zone, Oromia Regional State[J]. International Journal of Applied Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 5(3): 62.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Verma N K, Pandey B K. Studies on the effect of fertilizer doses and row spacing on growth and yield of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.)[J]. Agricultural Science Digest, 2008, 28(2):139-140. |
| [19] |
Dhima K, Vasilakoglou I, Stefanou S, et al. Effect of cultivar, irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on chickpea (Cicer arietinu L.) productivity[J]. Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 6(6):1187-1194.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Akuja T E, Kamithi D K, Kibe A M. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and plant population on growth, yield and harvest index (HI) of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) under dryland conditions in Kenya[J]. Journal of Applied Biosciences, 2009:1359-1367. |
| [21] | Laurie S, Stewart G R. Effects of nitrogen supply and high temperature on the growth and physiology of the chickpea[J]. Plant Cell & Environment, 2010, 16(6):609-621. |
| [22] |
Soltani A, Robertson M J, Manschadi A M. Modeling chickpea growth and development: Nitrogen accumulation and use[J]. Field Crops Research, 2006, 99(1):24-34.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Jain L K, Singh P, Balyah J K, et al. Productivity and profitability of chickpea (Cicer arietinumt L) cultivation as influenced by biofertilizers and phosphorus fertilization[J]. Indian Journal of Dryland Agricultural Research and Development, 2006, 21(1):82-84. |
| [24] | Das S, Pareek B L, Kumawat A, et al. Effect of phosphorus and biofertilizers on productivity of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) in north western Rajasthan, India[J]. Legume Research, 2013, 36(6): 511-514. |
| [25] | Goud V V, Konde N M, Mohod P V, et al. Response of chickpea to potassium fertilization on yield, quality, soil fertility and economic in vertisols[J]. Legume Research, 2014, 37(3):311. |
| [26] | Jaybhay B J, Jaybhay S A, Bhalerao G A, et al. Effect of potassium on yield and economics of Kabuli chickpea[J]. International Journal of Advanced Research, 2015, 3(6):436-438. |
| [27] | 张德军. 利用“3414”试验设计进行水稻测土配方施肥研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2009,(6):52-56. |
| ZHANG Dejun. Study on testing soil and rational blend fertilization of rice by utilizing “3414” experiment design[J]. Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China, 2009(6): 52-56. | |
| [28] | 孙义祥, 郭跃升, 于舜章, 等. 应用“3414”试验建立冬小麦测土配方施肥指标体系[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2009, 15(1):197-203. |
| SUN Yixiang, GUO Yaosheng, YU Shunzhang, et al. Establishing phosphorus and potassium fertilization recommendation index based on the“3414” field experiments[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2009, 15(1): 197-203. | |
| [29] | 丛野, 李艳君, 周灿金, 等. 氮磷钾对湿害胁迫下甘蓝型油菜产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2009, 15(5):1122-1129. |
| CONG Ye, LI Yangjun, ZHOU Canjin, et al. Effect of application of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers on yield in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) under the waterlogging stress[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2009, 15(5): 1122-1129. | |
| [30] | 祁大成, 冯旭东, 董红梅, 等. 花生“3414”肥料效应试验及推荐施肥分析[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2011, 50(14):2831-2834. |
| QI Dacheng, FENG Xudong, DONG Hongmei, et al. “3414”fertilizer trial of peanut and analysis on the optimal fertilization amounts[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 50(14): 2831-2834. | |
| [31] | 王志刚, 高强, 冯国忠. 吉林省大豆施肥指标体系初步建立[J]. 大豆科学, 2010, 29(4):669-672. |
| WANG Zhigang, GAO Qiang, FENG Guozhong. Preliminary raising fertilization index system for soybean in Jilin province[J]. Soybean Science, 2010, 29(4): 669-672. | |
| [32] | 宋朝玉, 高峻岭, 张继余, 等. 夏玉米氮肥减量化配套栽培技术研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2010,(5):50-53. |
| SONG Chaoyu, GAO Junling, ZHANG Jiyu, et al. Study on the supporting cultivation techniques for nitrogen reduction in corn[J]. Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China, 2010,(5): 50-53. | |
| [33] | 戴树荣. 应用“3414”试验设计建立二次肥料效应函数寻求马铃薯氮磷钾适宜施肥量的研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(12):154-159. |
| DAI Shurong. NPK reasonable application rate on potato by establishing fertilizer effect model of second degree polynomial using “3414” experimental design[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(12): 154-159. | |
| [34] | 林洪鑫, 袁展汽, 刘仁根, 等. 不同氮磷钾处理对木薯产量、养分积累、利用及经济效益的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(6):1457-1465. |
| LIN Hongxin, YUAN Zhaiqi, LIU Rengeng, et al. Effects of different N, P and K treatments on yield, nutrient accumulation and utilization and economic benefit of cassava[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2012, 18(6): 1457-1465. | |
| [35] | 郝曦煜, 肖焕玉, 梁杰, 等. 绿豆氮磷钾施肥效应与最优施肥量研究[J]. 作物杂志, 2020, (5):127-132. |
| HAO Xiyu, XIAO Huanyu, LIANG Jie, et al. Effects and optimum rates of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer for mung bean[J]. Crops, 2020, (5): 127-1132. | |
| [36] | 李鹏程, 董合林, 刘爱忠. 等. 施氮量对棉花功能叶片生理特性、氮素利用效率及产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(1):81-91. |
| LI Pengchen, DONG Helin, LIU Aizhong, et al. Effects of nitrogen application rates on physiological characteristics of functional leaves, nitrogen use efficiency and yield of cotton[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2015, 21(1):81-91. | |
| [37] | 田艳洪. 不同时期施用氮肥对大豆根瘤固氮酶活性及产量的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2007: 17-18. |
| TIAN Yanhong. Effects of N fertilization at different stages on nitrogenous activity and yield of soybean[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2007: 17-18. | |
| [38] | 邹娟. 冬油菜施肥效果及土壤养分丰缺指标研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2010: 63-74. |
| ZOU Juan. Study on response of winter rapeseed to NPKB fertilization and abundance and deficiency indices of soil nutrients[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2010: 63-74. | |
| [39] |
Cui Z L, Zhang F S, Chen X P, et al. In-season nitrogen management strategy for winter wheat: Maximizing yields, minimizing environmental impact in an over-fertilization context[J]. Field Crop Research, 2010, 116(1): 140-146.
DOI URL |
| [40] | 何萍, 金继运, 林葆. 等. 不同氮磷钾用量下春玉米生物产量及其组分动态与养分吸收模式研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 1998, (2): 123-130. |
| HE Ping, JIN Jiyun, LIN Bao, et al. Dynamics of biomass and its components and models of nutrients absorption by spring maize under different nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium application rates[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 1998(2): 123-130. | |
| [41] | Kuldeep B, Jajoria M, Verma R, et al. Nutrient content, uptake, quality of chickpea and fertility status of soil as influenced by fertilization of phosphorus and zinc[J]. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 2017, 6(1):392-398. |
| [1] | 陈茂光, 林涛, 张昊, 刘海军, 王一帆, 汤秋香. 地膜类型对棉花生长的影响及自身降解和回收特性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2101-2108. |
| [2] | 杨国江, 陈云, 林祥群, 何江勇, 刘盛林, 曲永清. 氮肥减施下有机肥替代对滴灌棉花产量、氮素吸收利用及土壤硝态氮的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2138-2145. |
| [3] | 陈传信, 张永强, 聂石辉, 孔德鹏, 赛力汗·赛, 徐其江, 雷钧杰. 生物质炭施用量对滴灌冬小麦生长发育和产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2146-2151. |
| [4] | 王立红, 张宏芝, 张跃强, 李剑峰, 王重, 高新, 时佳, 王春生, 夏建强, 樊哲儒. 不同产量水平冬小麦产量差异形成的干物质生产、转运及氮肥利用分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2152-2162. |
| [5] | 王晓雨, 王小平, 史文宇, 刘美艳, 马健, 郭云鹏, 宋瑞欣, 王清涛. 拔节期冬小麦光合特性、干物质积累和产量对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2163-2172. |
| [6] | 向莉, 王仙, 董裕生, 郭小玲, 方伏荣, 陈智军, 马艳明, 苗雨. 外源丁酸对干旱胁迫下大麦产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2173-2181. |
| [7] | 杨红梅, 张跃强, 史应武, 吾买尔江·库尔班, 林青, 王宁, 楚敏, 曾军. 不同类型叶面肥喷施对冬小麦籽粒产量和品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2182-2188. |
| [8] | 马明杰, 赵经华, 李冬民, 杨胜春, 王克贤, 李池. 不同灌溉方式对苜蓿土壤水分与灌溉水利用效率的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2306-2313. |
| [9] | 王心, 林涛, 崔建平, 吴凤全, 唐志轩, 崔来园, 郭仁松, 王亮, 郑子漂. 种植模式与灌溉定额对机采长绒棉产量及纤维品质形成的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1821-1829. |
| [10] | 马青山, 杜霄, 陶志鑫, 韩万里, 龙遗磊, 艾先涛, 胡守林. 陆地棉种质材料机采农艺性状鉴定分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1830-1839. |
| [11] | 董艳雪, 贾永红, 张金汕, 李丹丹, 王凯, 罗四维, 王润琪, 石书兵. 不同生态区环境下春小麦干物质积累及产量形成分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1848-1857. |
| [12] | 李怀胜, 艾洪玉, 孟玲, 王贺亚, 张磊, 艾海峰. 减氮下运筹养分吸收高峰期追施比例对春小麦的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1866-1872. |
| [13] | 张超, 白云岗, 郑明, 肖军, 丁平. 极端干旱区葡萄水肥协同效应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1931-1939. |
| [14] | 王挺, 张力, 张凡凡, 黄嵘峥, 李肖, 张玉琳, 陈永成, 赵建涛, 马春晖. 适合青贮的玉米品种生产性能筛选及营养价值评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(7): 1596-1605. |
| [15] | 时晓磊, 丁孙磊, 丛花, 张金波, 曲可佳, 王兴州, 韩岱, 严勇亮. 夏播大豆产量相关性状灰色关联度分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(7): 1641-1652. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||