

新疆农业科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (9): 2163-2172.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.09.010
• 作物遗传育种·种质资源·分子遗传学·土壤肥料 • 上一篇 下一篇
王晓雨1, 王小平2, 史文宇1, 刘美艳1, 马健1, 郭云鹏1, 宋瑞欣3, 王清涛1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-11
出版日期:2023-09-20
发布日期:2023-09-19
通信作者:
王清涛(1979-),男,山东聊城人,讲师,博士,研究方向为植物生态学,(E-mail)作者简介:王晓雨(1995- ),女,安徽马鞍山人,硕士研究生,研究方向为农田节水灌溉,(E-mail)wangxiaoyu0316@126.com
基金资助:
WANG Xiaoyu1, WANG Xiaoping2, SHI Wenyu1, LIU Meiyan1, MA Jian1, GUO Yunpeng1, SONG Ruixin3, WANG Qingtao1,2( )
)
Received:2022-12-11
Online:2023-09-20
Published:2023-09-19
Correspondence author:
WANG Qingtao(1979-),male,Liaocheng Shandong, lecturer,Doctor,mainly engaged in plant ecology research,(E-mail)Supported by:摘要:
【目的】研究冬小麦光合特性、干物质积累和产量对干旱胁迫的响应,为冬小麦春季灌溉制度提供基础理论依据。【方法】采用盆栽试验,以冬小麦品种邯麦17号为材料,在拔节期设置充分灌水(CK)、轻度干旱(T1)、中度干旱(T2)和重度干旱(T3)4个处理。【结果】拔节期冬小麦叶片水分利用效率在T2处理下最高;净光合速率、蒸腾速率、气孔导度、胞间二氧化碳浓度和叶绿素含量随着干旱胁迫的加剧均有所降低。光系统Ⅱ(PSⅡ)最大光化学效率(Fv/Fm) 、PSⅡ 的潜在活性(Fv/Fo)和经过PSⅡ的电子传递速率(Fm/Fo)均表现为T1 > CK > T2 >T3。与CK相比,T1和T2处理地下部分干物质积累量分别提高11.8%和3.0%,T3处理降低4.0%;T1、T2和T3处理地下部分干物质占比分别提高4.0%、6.0%和11.0%。灌溉水利用效率在T1处理下最高,且籽粒产量略有增加,T2和T3处理籽粒产量则分别降低14.8%和42.4%(P<0.05)。叶片水分利用效率与地上部干物质积累量呈极显著正相关关系(P<0.01),与总干物质积累量、籽粒产量和灌溉水利用效率呈显著正相关关系(P<0.05),与胞间二氧化碳浓度呈极显著负相关关系(P<0.01)。【结论】轻度干旱处理下,拔节期冬小麦通过调节光合作用和增加地下部分干物质积累量及其占比以适应干旱环境,并提高籽粒产量和灌溉水利用效率;但随着干旱加剧,冬小麦光合速率明显降低,影响干物质积累,导致冬小麦产量降低。
中图分类号:
王晓雨, 王小平, 史文宇, 刘美艳, 马健, 郭云鹏, 宋瑞欣, 王清涛. 拔节期冬小麦光合特性、干物质积累和产量对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2163-2172.
WANG Xiaoyu, WANG Xiaoping, SHI Wenyu, LIU Meiyan, MA Jian, GUO Yunpeng, SONG Ruixin, WANG Qingtao. Responses of photosynthetic characteristics, dry matter accumulation and yield to drought stress in winter wheat at jointing stage[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2163-2172.
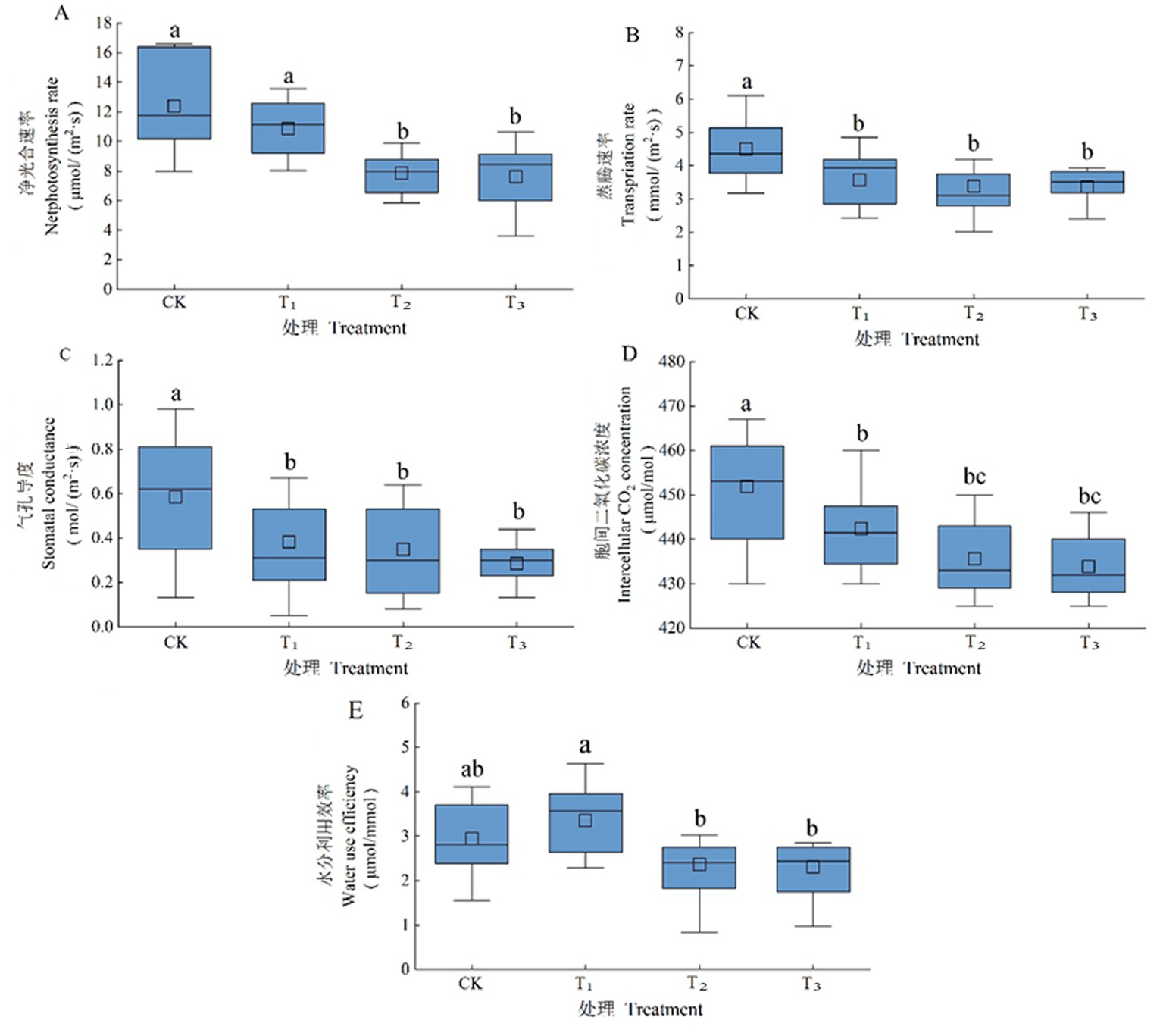
图1 冬小麦光合参数对干旱胁迫的响应 注:不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。CK:充分灌水;T1:轻度干旱;T2:中度干旱;T3:重度干旱,下同
Fig.1 Responses of photosynthetic parameters of winter wheat to drought stress Note: Different lowercase letters above the box mean significant difference among treatments(P<0.05).CK: full irrigation; T1: mild drought; T2: moderate drought; T3: Severe drought,the same as below
| 处理 Treat- ments | Fv/Fm | Fv/Fo | Fm/Fo |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.795±0.008ab | 3.876±0.181ab | 4.876±0.182ab |
| T1 | 0.802±0.005a | 4.054±0.134a | 5.055±0.134a |
| T2 | 0.791±0.011ab | 3.793±0.252b | 4.793±0.252b |
| T3 | 0.786±0.018b | 3.711±0.359b | 4.712±0.360b |
表1 冬小麦PSⅡ 最大化学效率、潜在活性及电子传递速率对干旱胁迫的响应
Tab.1 Responses of winter wheat maximum efficiency, potential activity and electron transfer of PSⅡ to drought stress
| 处理 Treat- ments | Fv/Fm | Fv/Fo | Fm/Fo |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.795±0.008ab | 3.876±0.181ab | 4.876±0.182ab |
| T1 | 0.802±0.005a | 4.054±0.134a | 5.055±0.134a |
| T2 | 0.791±0.011ab | 3.793±0.252b | 4.793±0.252b |
| T3 | 0.786±0.018b | 3.711±0.359b | 4.712±0.360b |

图6 Pearson相关系数 注;*表示显著相关(P<0.05), **表示极显著相关(P<0.01)
Fig.6 Pearson correlation coefficient analysis Note: * means significant correlation at the 0.05 level,** means significant correlation at the 0.01 level
| [1] | 赵广才. 中国小麦种植区划研究(一)[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2010, 30(5):886-895. |
| ZHAO Guangcai. Study on Chinese Wheat Planting Regionalization (Ⅰ)[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2010, 30(5):886-895. | |
| [2] | 刘涛, 周广胜, 谭凯炎, 等. 华北地区冬小麦灌溉制度及其环境效应研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(19):5979-5986. |
| LIU Tao, ZHOU Guangsheng, TAN Kaiyan, et al. Review on research of irrigation regime and its environmental effect in winter wheat field of North China Plain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(19):5979-5986. | |
| [3] |
赵舒怡, 宫兆宁, 刘旭颖. 2001-2013年华北地区植被覆盖度与干旱条件的相关分析[J]. 地理学报, 2015, 70(5):717-729.
DOI |
|
ZHAO Shuyi, GONG Zhaoning, LIU Xuying, et al. Correlation analysis between vegetation coverage and climate drought conditions in North China during 2001 - 2013[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2015, 70(5):717-729.
DOI |
|
| [4] | 孙爽, 杨晓光, 张镇涛, 等. 华北平原不同等级干旱对冬小麦产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2021, 37(14):69-78. |
| SUN Shuang, YANG Xiaoguang, ZHANG Zhentao, et al. Impacts of different grades of drought on winter wheat yield in North China Plain[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 37(14):69-78. | |
| [5] | Yu Y C. Effect of Drought Stress and Rewatering on the Photosynthetic Physiological Characteristics of Leaves and Bark of '84K' Poplar[J]. Journal of Landscape Research, 2020, 12(4):93-96,102. |
| [6] | 张玉顺, 路振广, 张明智, 等. 冬小麦叶片气体交换参数对水分胁迫的响应[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2020, 39 (12) :32-40. |
| ZHANG Yushun, LU Zhenguang, ZHANG Mingzhi, et al. The Response of Gas Exchange Parameters of Winter Wheat Leaves to Water Stress[J]. Wheat Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2020, 39 (12) :32-40. | |
| [7] | 李彦彬, 冯娅, 边泽鹏, 等. 花前干旱胁迫对冬小麦生长指标的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2021, 40(3):23-30. |
| LI Yanbin, FENG Ya, BIAN Zepeng, et al. Effect of Drought Stress before Anthesis on Growth Indexes of Winter[J]. WheatJournal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2021, 40(3):23-30. | |
| [8] | 刘培, 蔡焕杰, 王健. 土壤水分胁迫下冬小麦籽粒灌浆特性的研究[J]. 节水灌溉, 2010,(1):1-4. |
| LIU Pei, CAI Huanjie, WANG Jian. Study on Grain Filling Characteristic of Winter Wheat Seed under Soil Water Stress[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2010,(1):1-4. | |
| [9] | 汤秋香, 林涛, 董文杰, 等. 干旱胁迫对滴灌冬小麦产量形成及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2015, 52(3):429-435. |
| TANG Qiuxiang, LIN Tao, DONG Wenjie, et al. Analysis of Winter Wheat Yield Formation and Water Use Efficiency of Drip Irrigation under Drought Condition[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 52(3):429-435. | |
| [10] | 刘明, 武建军, 吕爱锋, 等. 黄淮海平原典型区冬小麦水分胁迫规律与灌溉策略[J]. 农业工程学报, 2010, 26 (5) :40-44. |
| LIU Ming, WU Jianjun, LYU Aifeng, et al. Water stress of winter wheat and irrigation strategy in typical region of Huang-Huai-Hai Plain[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2010, 26 (5) :40-44. | |
| [11] | 薛佳欣, 张江伟, 陈宗培, 等. 灌浆期冬小麦生理特性和产量对不同灌水量的响应[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2020, 40(9):1111-1119. |
| XUE Jiaxin, ZHANG Jiangwei, CHEN Zongpei, et al. Response of Physiological Characteristic at Grain Filling Stage and Yield of Winter Wheat to Different Irrigation Treatments[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2020, 40(9):1111-1119. | |
| [12] | 黄峰, 杜太生, 王素芬, 等. 华北地区农业水资源现状和未来保障研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 2019, 21(5):28-37. |
|
HUANG Feng, DU Taisheng, WANG Sufen, et al. Current Situation and Future Security of Agricultural Water Resources in North China[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2019, 21(5):28-37.
DOI URL |
|
| [13] |
郭丽丽, 张茜茜, 郝立华, 等. 大气CO2倍增条件下冬小麦气体交换对高温干旱及复水过程的响应[J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45 (6) :949-956.
DOI |
|
GUO Lili, ZHANG Xixi, HAO Lihua, et al. Responses of leaf gas exchange to high temperature and drought combination as well as re-watering of winter wheat under doubling atmospheric CO2 concentration[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 45 (6) :949-956.
DOI |
|
| [14] | 王清涛, 潘存德, 王世伟, 等. 与冬小麦间作条件下轮台白杏间作巷道光环境特征[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2013, 50(5):817-822. |
| WANG Qingtao, PAN Cunde, WANG Shiwei, et al. Light Environmental Characteristics in Intercropping Alley of Armeniaca vulgaris 'Luntaibaixing' with Winter Wheat[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 50(5):817-822. | |
| [15] |
杨磊, 靳娟, 冯贝贝, 等. 高温环境下枣光合特性及相关生理指标日变化[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(9):1639-1646.
DOI |
|
YANG Lei, JIN Juan, FENG Beibei, et al. Study on Diurnal Variation of Photosynthetic Characteristics and Related Physiological Indexes of Jujube under High Temperature Environment[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(9):1639-1646.
DOI |
|
| [16] | 努尔凯麦尔·木拉提, 杨亚杰, 帕尔哈提·阿布都克日木, 等. 小麦叶绿素含量测定方法比较[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2021, 49 (9) :156-159. |
| Nuerkaimaer Mulati, YANG Yajie, Paerhati Abudukerimu, et al. Comparative study on determination methods of chlorophyll content in wheat[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49 (9) :156-159. | |
| [17] |
周宁, 景立权, 王云霞, 等. 开放式空气中CO2浓度和温度增高对水稻叶片叶绿素含量和SPAD值的动态影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31 (5) :524-532.
DOI |
|
ZHOU Ning, JING Liquan, WANG Yunxia, et al. Effects of Elevated Atmospheric CO2 and Temperature on Dynamics of Leaf Chlorophyll Contents and SPAD Value of Rice in Open-Air Field Conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31 (5) : 524-532.
DOI |
|
| [18] | 王世伟, 潘存德, 张大海, 等. 新疆11个杏品种叶绿素荧光特征比较[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2010, 47 (4):637 -643. |
| WANG Shiwei, PAN Cunde, ZHANG Dahai, et al. Comparison of Chlorophyll Fluorescence Characters in Eleven Apricot Varieties in Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 47 (4):637 -643. | |
| [19] |
陈慧, 黄振江, 王冀川, 等. 水氮耦合对滴灌冬小麦氮素吸收、转运及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(1):44-56.
DOI |
|
CHEN Hui, HUANG Zhenjiang, WANG Jichuan, et al. Effect of Water and Nitrogen Coupling on N Absorption, Translocation and Yield of Winter Wheat under Drip Irrigation[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(1):44-56.
DOI |
|
| [20] | 黄晓玉, 王兰会. SPSS 24.0统计分析[M]. 北京: 中国人民大学出版社, 2021. |
| HUANG Xiaoyu, WANG Lanhui. SPSS 24.0 statistical analysis[M]. Beijing: Renmin University of China Press, 2021. | |
| [21] |
SOFO A, DICHIO B, MONTANARO G, et al. Photosynthetic performance and light response of two olive cultivars under different water and light regimes[J]. Photosynthetica, 2009, 47 (4) :602-608.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
HUANG Bingru, Yu Jingjin, CHEN Yajun. Effects of elevated CO2 concentration on water relations and photosynthetic responses to drought stress and recovery during rewatering in Tall Fescue[J]. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 2015, 140 (1) :19-26.
DOI URL |
| [23] | 赵福年, 王润元, 张凯, 等. 叶片光合生理参数变化特征与小麦受旱状态的关系[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2020, 38(1):107-116. |
| ZHAO Funian, WANG Runyuan, ZHANG Kai, et al. Relationship between drought severity and leaf photosynthetic physiological parameter variation of spring wheat[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2020, 38(1):107-116. | |
| [24] | 张继波, 薛晓萍, 李楠, 等. 水分胁迫对扬花期冬小麦光合特性和干物质生产及产量的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37 (3): 447-453. |
| ZHANG Jibo, XUE Xiaoping, LI Nan, et al. Effects of Water Stress on Photosynthetic Characteristics,Dry Matter Production and Yield of Winter Wheat at Flowering Stage[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37 (3) :447-453. | |
| [25] | 陈斐, 闫霜, 王鹤龄, 等. 不同水分胁迫下的春小麦叶片气体交换参数和水分利用效率研究[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38 (3) :821-832. |
| CHEN Fei, YAN Shuang, WANG Heling, et al. Study on gas exchange parameters and water use efficiency of spring wheat leaves under different levels of water stress[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38 (3) :821-832. | |
| [26] | ZHAO Biyan, HU Yufeng, LI Juanjuan, et al. BnaABF2,a bZIP transcription factor from rapeseed (Brassica napus L.),enhances drought and salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis[J]. Journal of Engineering, 2016, 57 (1) :12. |
| [27] | Yavas I, Unay A. Effects of zinc and salicylic acid on wheat under drought stress[J]. The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 2016, 26 (4) :1012-1018. |
| [28] | 刘月岩, 刘会灵, 乔匀周, 等. CO2浓度升高对不同水分条件下冬小麦生长和水分利用的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21 (11) :1365-1370. |
| LIU Yueyan, LIU Huiling, QIAO Yunzhou, et al. Effects of elevated CO2 concentration and different water conditions on winter wheat growth and water use[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2013, 21 (11) :1365-1370. | |
| [29] | 丛建鸥, 李宁, 许映军, 等. 干旱胁迫下冬小麦产量结构与生长、生理、光谱指标的关系[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2010, 18 (1) :67-71. |
| CONG Jianou, LI Ning, XU Yingjun, et al. Relationship between indices of growth,physiology and reflectivity and yield of winter wheat under water stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2010, 18 (1) :67-71. | |
| [30] |
Woo N S, Badger M R, Pogson B J. A rapid,non-invasive procedure for quantitative assessment of survival using chlorophyll fluorescence[J]. Plant Methods, 2008, 4:27.
DOI |
| [31] | 吴金芝, 王志敏, 李友军, 等. 不同冬小麦品种旗叶叶绿素荧光特性及其对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2015, 35 (5) :699-706. |
| WU Jinzhi, WANG Zhimin, LI Youjun, et al. Flag Leaf Chlorophyll Fluorescence Characteristics and Its Response to Drought Stress in Different Cultivars of Winter Wheat[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2015, 35 (5) :699-706. | |
| [32] | 赵宝平, 任鹏, 徐忠山, 等. 水分胁迫对不同抗旱性燕麦品种光合及产量形成的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2020, 40 (11) : 1399-1407. |
| ZHAO Baoping, REN Peng, XU Zhongshan, et al. Effects of Water Stress on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Yield Formation in Oats(Avena sativa L.) with Different Drought Resistance[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2020, 40 (11) :1399-1407. | |
| [33] |
郭增江, 于振文, 石玉, 等. 拔节期与开花期测墒补灌对小麦旗叶荧光特性和水分利用效率的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38 (7) :757-766.
DOI |
|
GUO Zengjiang, YU Zhenwen, SHI Yu, et al. Effects of supplemental irrigation by measuring the moisture content at jointing and anthesis on fluorescence characteristics and water use efficiency in flag leaves of wheat[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38 (7) :757-766.
DOI |
|
| [34] |
吴姗姗, 徐学欣, 张霞, 等. 不同品种冬小麦苗期叶绿素荧光参数与抗旱性关系研究[J]. 华北农学报, 2020, 35(6):90-99.
DOI |
| WU Shanshan, XU Xuexin, ZHANG Xia, et al. Relationship Analysis of Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters and Drought Resistance in Different Winter Wheat Varieties at Seedling Stage[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2020, 35(6):90-99. | |
| [35] |
Cattivelli L, Rizza F, Badeck F W, et al. Drought tolerance improvement in crop plants:an integrated view from breeding to genomics[J]. Field Crops Research, 2008, 105(1/2):1-14.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 高小锋, 王进鑫, 张波, 等. 不同生长期干旱胁迫对刺槐幼树干物质分配的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2010, 29 (6) :1103-1108. |
| GAO Xiaofeng, WANG Jinxin, ZHANG Bo, et al. Effects of drought stress on dry matter partitioning of young Robinia pseudoacacia at its different growth stages[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2010, 29 (6) :1103-1108. | |
| [37] | 闫永銮, 郝卫平, 梅旭荣, 等. 拔节期水分胁迫-复水对冬小麦干物质积累和水分利用效率的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 2011, 32 (2) :190-195,202. |
| YAN Yongluan, HAO Weiping, MEI Xurong, et al. Effects of Water Stress-Rewatering at Jointing Stage on Dry Matter Accumulation and WUE of Winter Wheat[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2011, 32 (2) :190-195,202. | |
| [38] | 李文娆, 张岁岐, 丁圣彦, 等. 干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿根系形态变化及与水分利用的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30 (19) :5140. |
| LI Wenrao, ZHANG Suiqi, DING Shengyan, et al. Root morphological variation and water use in alfalfa under drought stress[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30 (19) :5140. | |
| [39] |
赵花荣, 任三学, 齐月. 高湿和干旱对夏玉米灌浆期叶片光合特性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2017, 33(31) :15-21.
DOI |
|
ZHAO Huarong, REN Sanxue, QI Yue. High Humidity and Drought: Effects on Photosynthetic Characteristics of Summer Maize at Grain Filling Stage[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2017, 33(31) :15-21.
DOI |
|
| [40] | 谷艳芳, 丁圣彦, 高志英, 等. 干旱胁迫下冬小麦光合产物分配格局及其与产量的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(5):1167-1173. |
| GU Yanfang, DING Shenyan, GAO Zhiying, et al. The pattern of photosynthate partitioning in drought-stressed winter wheat and its relationship with yield[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(5):1167-1173. | |
| [41] | 马青荣, 刘荣花, 胡程达, 等. 干旱及灌溉对冬小麦根系和产量的影响研究[J]. 气象, 2020, 46(7):971-981. |
| MA Qingrong, LIU Ronghua, HU Chengda, et al. Impacts of Drought and Irrigation on Root and Yield of Winter Wheat[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2020, 46(7):971-981. | |
| [42] | 王彦芹, 沈李丽, 罗来鑫, 等. 基于mRNA-Seq的沙漠植物花花柴干旱胁迫表达谱分析[J]. 植物生理学报, 2018, 54(5):879-885. |
| WANG Yanqin, SHEN Lili, LUO Laixin, et al. Analysis of expression profile in Karelinia caspia seedling under drought stress based on mRNA-Seq[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2018, 54(5):879-885. | |
| [43] | 黄彩霞, 柴守玺, 赵德明, 等. 灌溉对干旱区冬小麦干物质积累、分配和产量的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(12):1333-1344. |
|
HUANG Caixia, CHAI Shouxi, ZHAO Deming, et al. Effects of irrigation on accumulation and distribution of dry matter and grain yield in winter wheat in arid regions of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(12):1333-1344.
DOI |
|
| [44] |
Zhang Yanqun, Wang Jiandong, Gong Shihong. Effects of film mulching on evapotranspiration.yield and water use efficiency of a maize field with drip irrigation in northeastern China[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2018, 205:90-99.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Bu Lingduo, Lin Zhu, Liu Jianliang, et al. Source-sink capacity responsible for higher maize yield with removal of plastic film[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2013, 105(3):591-598.
DOI URL |
| [46] | 薛丽华, 段俊杰, 王志敏, 等. 不同水分条件对冬小麦根系时空分布、土壤水利用和产量的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(19):5296-5305. |
| XUE Lihua, DUAN Junjie, WANG Zhimin, et al. Effects of different irrigation regimes on spatial-temporal distribution of roots, soil water use and yield in winter wheat[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(19):5296-5305. | |
| [47] | 张绪成, 于显枫, 马一凡, 等. 半干旱区箭舌豌豆播期对间作马铃薯生物量和水分利用效率的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(6):1618-1626. |
| ZHANG Xucheng, YU Xianfeng, MA Yifan, et al. Effects of the sowing date on aboveground biomass and water utilization of potato and spring vetch intercropping systems with vertical rotary subsoiling tillage on a semi-arid area[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(6):1618-1626. | |
| [48] | 杨霖, 黄郑雯, 毛开泽, 等. 望天树幼苗光合特性与功能性状对光照和施肥的响应[J]. 西部林业科学, 2021, 50 (6) :46-52. |
| YANG Lin, HUANG Zhengwen, MAO Kaize, et al. Response of Photosynthetic Characteristics and Functional Traits of Parashorea chinensis' seedlings to Light and Fertilization[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2021, 50 (6) :46-52. |
| [1] | 罗林毅, 陈瑞杰, 阮向阳, 任晓辉, 曲奥, 苏海婷, 冶军. 微生物菌剂对滴灌棉田土壤养分和棉花产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(1): 26-33. |
| [2] | 王贺亚, 罗静静, 艾海峰, 李怀胜, 孟玲, 王鹏. 种植密度与减量施肥对食葵产量及相关性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(1): 55-62. |
| [3] | 刘海军, 张昊, 王一帆, 陈茂光, 吴凤全, 林涛, 汤秋香. 不同覆盖材料和灌溉量对机采棉产量形成及有效积温生产效率的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2091-2100. |
| [4] | 陈茂光, 林涛, 张昊, 刘海军, 王一帆, 汤秋香. 地膜类型对棉花生长的影响及自身降解和回收特性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2101-2108. |
| [5] | 杨国江, 陈云, 林祥群, 何江勇, 刘盛林, 曲永清. 氮肥减施下有机肥替代对滴灌棉花产量、氮素吸收利用及土壤硝态氮的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2138-2145. |
| [6] | 陈传信, 张永强, 聂石辉, 孔德鹏, 赛力汗·赛, 徐其江, 雷钧杰. 生物质炭施用量对滴灌冬小麦生长发育和产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2146-2151. |
| [7] | 王立红, 张宏芝, 张跃强, 李剑峰, 王重, 高新, 时佳, 王春生, 夏建强, 樊哲儒. 不同产量水平冬小麦产量差异形成的干物质生产、转运及氮肥利用分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2152-2162. |
| [8] | 向莉, 王仙, 董裕生, 郭小玲, 方伏荣, 陈智军, 马艳明, 苗雨. 外源丁酸对干旱胁迫下大麦产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2173-2181. |
| [9] | 杨红梅, 张跃强, 史应武, 吾买尔江·库尔班, 林青, 王宁, 楚敏, 曾军. 不同类型叶面肥喷施对冬小麦籽粒产量和品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2182-2188. |
| [10] | 马明杰, 赵经华, 李冬民, 杨胜春, 王克贤, 李池. 不同灌溉方式对苜蓿土壤水分与灌溉水利用效率的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2306-2313. |
| [11] | 王心, 林涛, 崔建平, 吴凤全, 唐志轩, 崔来园, 郭仁松, 王亮, 郑子漂. 种植模式与灌溉定额对机采长绒棉产量及纤维品质形成的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1821-1829. |
| [12] | 董艳雪, 贾永红, 张金汕, 李丹丹, 王凯, 罗四维, 王润琪, 石书兵. 不同生态区环境下春小麦干物质积累及产量形成分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1848-1857. |
| [13] | 李怀胜, 艾洪玉, 孟玲, 王贺亚, 张磊, 艾海峰. 减氮下运筹养分吸收高峰期追施比例对春小麦的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1866-1872. |
| [14] | 张永强, 陈传信, 聂石辉, 徐其江, 赛力汗·赛, 雷钧杰. 矮壮素滴施时期对冬小麦茎秆抗倒伏能力的调控分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1873-1878. |
| [15] | 韩守安, 王敏, 麦合木提·图如普, 谢辉, 艾尔买克·才卡斯木, 刘佳乐, 张雯, 潘明启. 不同光质处理对赤霞珠葡萄叶片光合特性及果实品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1894-1903. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||