

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (2): 351-358.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.02.012
• Horticultural Special Local Products·Plant Protection·Microbes·Soil Fertilizer· Water Saving Irrigation • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHU Pusheng( ), LIU Huiying(
), LIU Huiying( ), CAO Ze, LIU Kaige, LI Xuezhen
), CAO Ze, LIU Kaige, LI Xuezhen
Received:2021-12-11
Online:2023-02-20
Published:2023-03-31
Correspondence author:
LIU Huiying(1970-), female, born in Shihezi, Xinjiang, Professor, majoring in vegetable cultivation physiology of protected horticulture, (E-mail)hyliuok@aliyun.com
Supported by:通讯作者:
刘慧英(1970-),女,新疆石河子人,教授,研究方向为设施蔬菜栽培生理,(E-mail)hyliuok@aliyun.com
作者简介:朱普生(1994-),男,江苏连云港人,硕士研究生,研究方向设施蔬菜栽培生理,(E-mail)875920571@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHU Pusheng, LIU Huiying, CAO Ze, LIU Kaige, LI Xuezhen. Effects of Exogenous GSNO on Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Tomato Seedlings under NaCl Stress[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(2): 351-358.
朱普生, 刘慧英, 曹泽, 刘凯歌, 李雪珍. 外源GSNO对NaCl胁迫下番茄幼苗生长及光合特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(2): 351-358.
| 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 茎粗 Stem diameter (mm) | 地上鲜重 Fresh weight over water (g) | 地下鲜重 Fresh weight under water (g) | 地上干重 Dry weight over water (g) | 地下干重 Dry weight under water (g) | 根冠比 Root/shoot ratio | 壮苗指数 Strong seedling index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 29.44±0.69a | 7.77±0.18a | 30.66±2.17a | 4.56±0.22ab | 2.16±0.24a | 0.18±0.01a | 0.08±0.01b | 0.81±0.06a |
| NaCl | 20.29±0.2cd | 6.32±0.31c | 12.88±0.67c | 3.94±0.26bc | 0.97±0.04c | 0.12±0.00b | 0.13±0.00a | 0.48±0.02c |
| NG | 22.62±0.3b | 6.74±0.08bc | 19.52±0.86b | 5.32±0.4a | 1.5±0.06b | 0.2±0.02a | 0.14±0.01a | 0.74±0.04ab |
| NP | 19.53±0.98d | 6.76±0.19bc | 15.64±1.1bc | 3.3±0.18c | 1.22±0.09bc | 0.14±0.01b | 0.11±0.00a | 0.62±0.03b |
| NGP | 22.19±0.75bc | 7.28±0.04ab | 18.77±0.9b | 4.61±0.41ab | 1.45±0.08b | 0.18±0.02a | 0.13±0.01a | 0.74±0.04ab |
Table 1 Effects of exogenous GSNO on tomato seedling biomass under NaCl stress
| 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 茎粗 Stem diameter (mm) | 地上鲜重 Fresh weight over water (g) | 地下鲜重 Fresh weight under water (g) | 地上干重 Dry weight over water (g) | 地下干重 Dry weight under water (g) | 根冠比 Root/shoot ratio | 壮苗指数 Strong seedling index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 29.44±0.69a | 7.77±0.18a | 30.66±2.17a | 4.56±0.22ab | 2.16±0.24a | 0.18±0.01a | 0.08±0.01b | 0.81±0.06a |
| NaCl | 20.29±0.2cd | 6.32±0.31c | 12.88±0.67c | 3.94±0.26bc | 0.97±0.04c | 0.12±0.00b | 0.13±0.00a | 0.48±0.02c |
| NG | 22.62±0.3b | 6.74±0.08bc | 19.52±0.86b | 5.32±0.4a | 1.5±0.06b | 0.2±0.02a | 0.14±0.01a | 0.74±0.04ab |
| NP | 19.53±0.98d | 6.76±0.19bc | 15.64±1.1bc | 3.3±0.18c | 1.22±0.09bc | 0.14±0.01b | 0.11±0.00a | 0.62±0.03b |
| NGP | 22.19±0.75bc | 7.28±0.04ab | 18.77±0.9b | 4.61±0.41ab | 1.45±0.08b | 0.18±0.02a | 0.13±0.01a | 0.74±0.04ab |
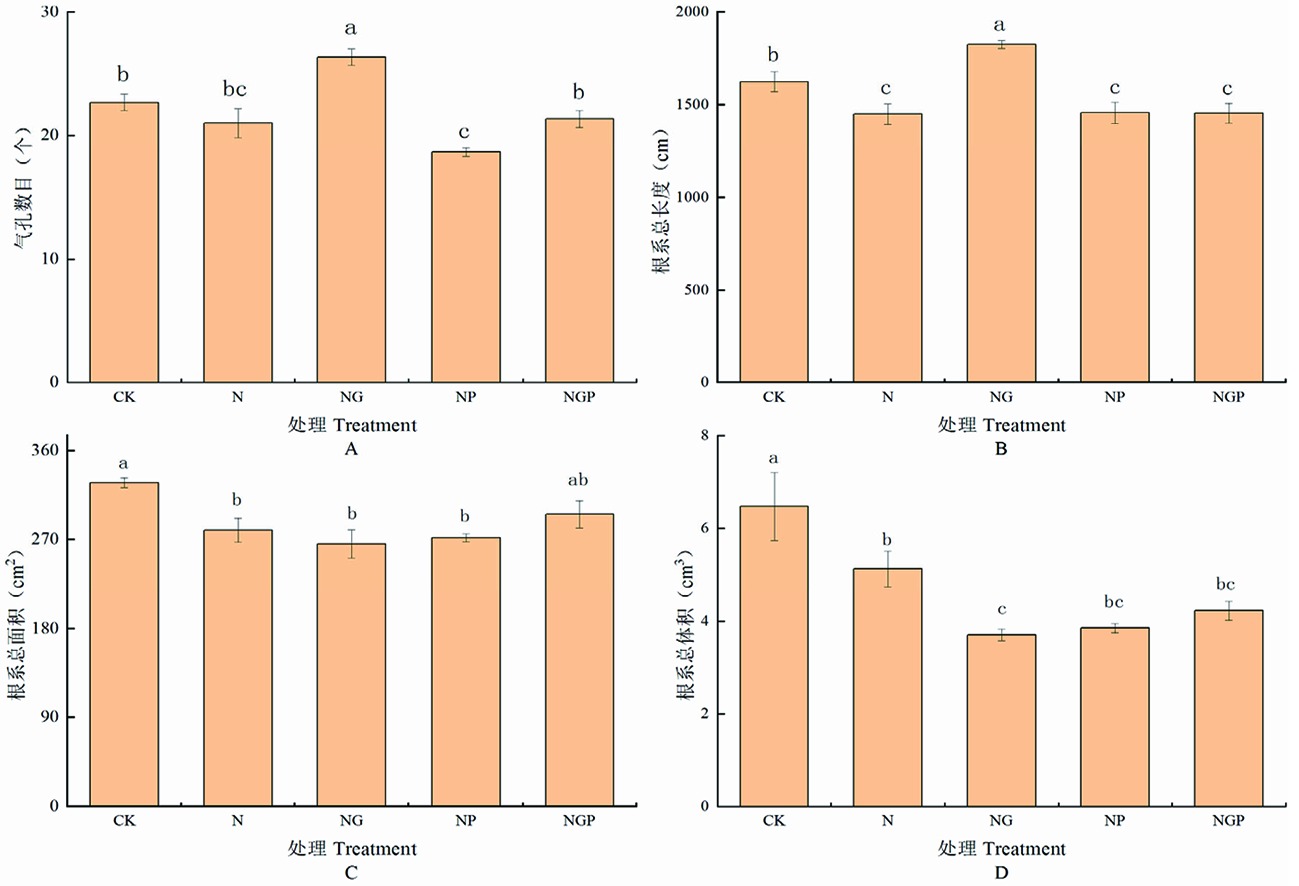
Fig.1 Effects of exogenous GSNO on stomatal number and root morphology of Tomato Seedlings under NaCl stress Note: A:the effect on stomatal number; B:the effect on total root length; C:the effect on total root area; D:the effect on total root volume; different small letters above figures indicates significant difference at 5% leve, the same as below
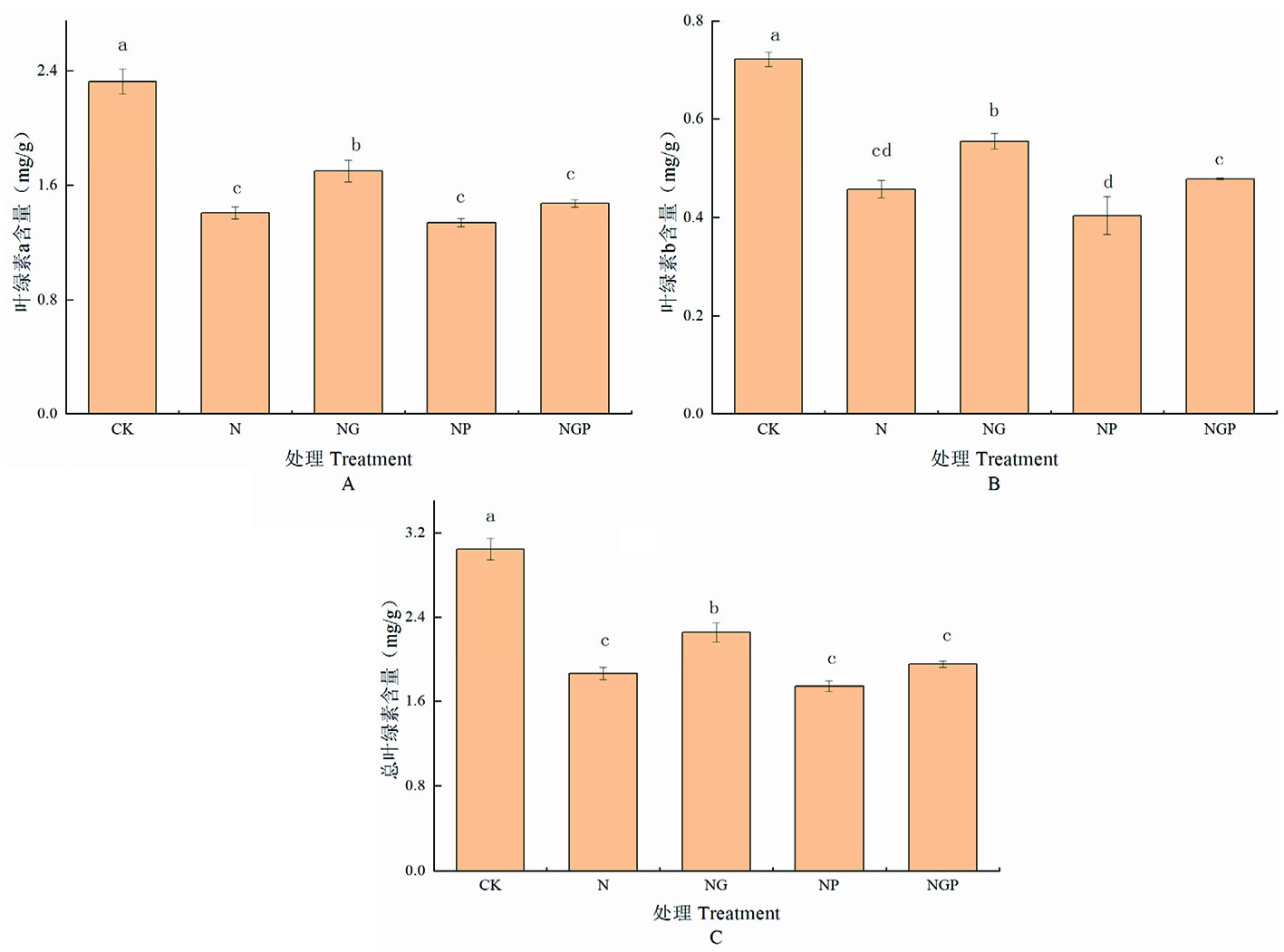
Fig.2 Effect of exogenous GSNO on chlorophyll content of Tomato Seedlings under NaCl stress Note:A:the effect on chlorophyll a content, B:the effect on chlorophyll b content, C:the effect on the content of total chlorophyll
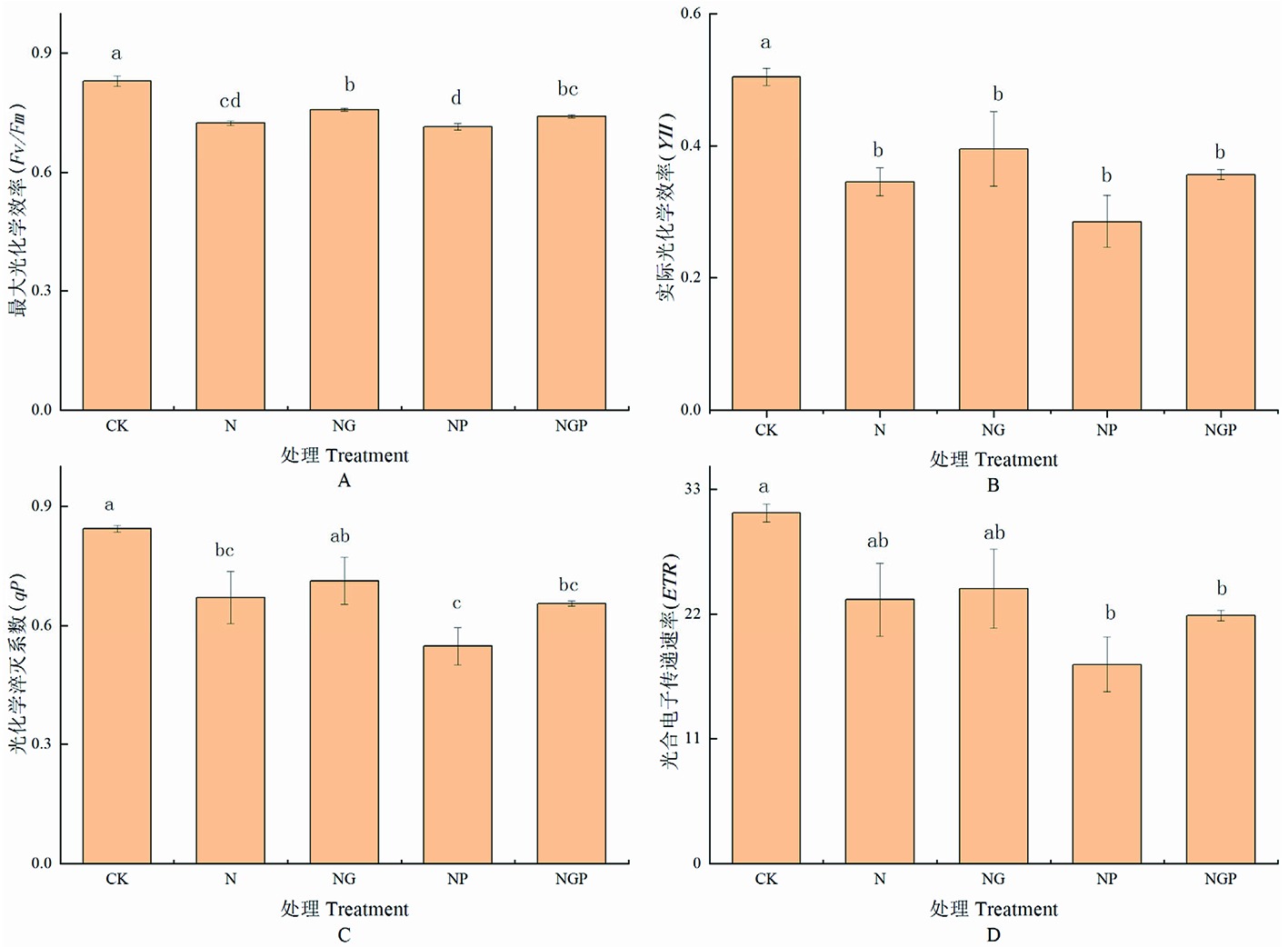
Fig.3 Effects of exogenous GSNO on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Tomato Seedlings under NaCl stress Note: A:the effect on maximum photochemical efficiency (Fv / Fm); B:the effect on actual photochemical efficiency (YII); C:the effect on chemical quenching coefficient (qP); D:the effect on photosynthetic electron transfer rate (ETR)
| 指标 Index | 处理 Treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | N | NG | NP | NGP | |
| 初始活性Rubisco(U/g) | 9.85±0.27a | 6.61±0.34c | 8.67±0.27b | 5.40±0.50d | 8.20±0.42b |
| 总活性Rubisco(U/g) | 30.82±0.72a | 12.59±0.28d | 24.34±1.27b | 15.40±0.66c | 17.10±0.82c |
| 活化酶Rubisco(RCA)活性(mU/g) | 1 827.33±87.05a | 1 221.15±83.85d | 1 672.63±22.10b | 1 114.68±36.29e | 1 356.19±7.71c |
| 磷酸甘油酸激酶(PGK)活性(U/g) | 1.79±0.02a | 1.40±0.04c | 1.55±0.06b | 1.15±0.05d | 1.44±0.02c |
| 磷酸甘油醛脱氢酶(GAPDH)活性(U/g) | 0.47±0.01a | 0.24±0.01d | 0.42±0.01b | 0.21±0.01e | 0.40±0.01c |
| 景天庚酮糖-1,7-二磷酸酶(SBPase) 活性(U/g) | 1.31±0.10a | 0.43±0.01d | 0.67±0.05c | 0.48±0.02d | 0.78±0.01b |
| 果糖-1,6-二磷酸酶(FBPase) 活性(mU/g) | 937.38±10.82a | 837.33±3.11b | 936.85±7.80a | 794.68±10.80c | 857.13±29.93b |
| 果糖-1,6-二磷酸醛缩酶(FBA) 活性(mU/g) | 1.38±0.03a | 1.27±0.04b | 1.22±0.05b | 1.01±0.02c | 1.28±0.03b |
Table 2 Effects of exogenous GSNO on activities of Calvin cycle related enzymes in tomato seedlings under NaCl stress
| 指标 Index | 处理 Treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | N | NG | NP | NGP | |
| 初始活性Rubisco(U/g) | 9.85±0.27a | 6.61±0.34c | 8.67±0.27b | 5.40±0.50d | 8.20±0.42b |
| 总活性Rubisco(U/g) | 30.82±0.72a | 12.59±0.28d | 24.34±1.27b | 15.40±0.66c | 17.10±0.82c |
| 活化酶Rubisco(RCA)活性(mU/g) | 1 827.33±87.05a | 1 221.15±83.85d | 1 672.63±22.10b | 1 114.68±36.29e | 1 356.19±7.71c |
| 磷酸甘油酸激酶(PGK)活性(U/g) | 1.79±0.02a | 1.40±0.04c | 1.55±0.06b | 1.15±0.05d | 1.44±0.02c |
| 磷酸甘油醛脱氢酶(GAPDH)活性(U/g) | 0.47±0.01a | 0.24±0.01d | 0.42±0.01b | 0.21±0.01e | 0.40±0.01c |
| 景天庚酮糖-1,7-二磷酸酶(SBPase) 活性(U/g) | 1.31±0.10a | 0.43±0.01d | 0.67±0.05c | 0.48±0.02d | 0.78±0.01b |
| 果糖-1,6-二磷酸酶(FBPase) 活性(mU/g) | 937.38±10.82a | 837.33±3.11b | 936.85±7.80a | 794.68±10.80c | 857.13±29.93b |
| 果糖-1,6-二磷酸醛缩酶(FBA) 活性(mU/g) | 1.38±0.03a | 1.27±0.04b | 1.22±0.05b | 1.01±0.02c | 1.28±0.03b |
| [1] |
Li R, Fei Z, Ling K S. Molecular and biological properties of tomato necrotic stunt virus and development of a sensitive real-time RT-PCR assay[J]. Archives of Virology, 2014, 159(2):353-358.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Simaei M, Khavari-nejad R A, Saadatmand S., et al. Effects of salicylic acid and nitric oxide on antioxidant capacity and proline accumulation in Glycinemax L. treated with NaCl salinity[J]. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 2011, 6(16): 3775-3782. |
| [3] |
蒋卫杰, 邓杰, 余宏军. 设施园艺发展概况、存在问题与产业发展建议[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(17): 3515-3523.
DOI |
|
JIANG Weijie, DENG Jie, YU Hongjun. Development Situation, Problems and Suggestions on Industrial Development of Protected Horticulture[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(17): 3515-3523.
DOI |
|
| [4] | 王学征, 李秋红, 吴凤芝. NaCl 胁迫下栽培型番茄 Na+、K+吸收、分配和转运特性[J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(7): 1423-1432. |
| WANG xuezheng, LI qiuhong, WU fengzhi. Study on the Characteristics of Absorption, Distribution and Selective Transport of Na+ and K+ in Tomato Plants under Salt Stress[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(7): 1423-1432. | |
| [5] | 李换丽. 硅对番茄幼苗抗盐性的影响及机理初探[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2015. |
| LI huanli. The effect and mechanism of exogenous silicon onsalt resistance of tomato seedlings[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2015. | |
| [6] | 李响, 高月, 王少贺. 设施蔬菜连作障碍治理对比试验探析[J]新农业. 2021,(3): 43-44. |
| LI Xiang, GAO Yue, WANG Shaohe. Contrast test analysis of facility vegetables continuous farming disorders[J]. Modern Agriculture, 2021,(3): 43-44. | |
| [7] |
Yu M, Lamattina L, Spoel S H, et al. Nitric oxide function in plant biology: a redox cue in deconvolution[J]. New Phytologist, 2014, 202(4):1142-1156.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Li Y Y, He J M. Effect of Nitric Oxide on Tomato Seeds Resisting against Chilling Imbibition[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2008, 28(4):709-717. |
| [9] |
Crawford G N M. Arabidopsis Nitric Oxide Synthase1 Is Targeted to Mitochondria and Protects against Oxidative Damage and Dark-Induced Senescence[J]. Plant Cell, 2005, 17(12):3436-3450.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Klessig, D F, Durner, et al. Nitric oxide and salicylic acid signaling in plant defense[J]. PROC NAT ACAD SCI USA, 2000, 97(16):8849-8855.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Asgher M, Per T S, Masood A, et al. Nitric oxide signaling and its crosstalk with other plant growth regulators in plant responses to abiotic stress[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(3):2273-2285.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Leitner M, Vandelle E, Gaupels F, et al. NO signals in the haze: nitric oxide signaling in plant defence[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2009, 12(4):451-458.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Feechan A, Kwon E, Yun B W, et al. A central role for S-nitrosothiols in plant disease resistance[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2005, 102(22):8054-8059.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 刘会芳, 王强, 韩豪. NaCl胁迫对不同辣椒品种幼苗光合作用及生长的影响[J]长江蔬菜. 2020,(24): 16-18. |
| LIU Huifang, WANG Qiang, HAN Hao. Effects of Na Cl Stress on Photosynthesis and Growth of Different Cultivars of Pepper Seedlings[J]. Journal of Changjiang Vegetables, 2020,(24): 16-18. | |
| [15] | 张志良, 瞿伟菁, 李小方. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2009. |
| ZHANG Zhiliang, ZHAI Weiqin, LI Xiaofang. Experimental Handbook for Plant Biology[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2009. | |
| [16] | 岳小红, 曹靖, 耿杰 等. 盐分胁迫对啤酒大麦幼苗生长、离子平衡和根际 pH 变化的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(20):7373-7380. |
| YUE Xiaohong, CAO Jing, GENG Jie, et al. Effects of different types of salt stress on growth, ion balance and rhizosphere pH changes in beer barley seedlings[J] Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(20):7373-7380. | |
| [17] |
孙德智, 杨恒山, 张庆国, 等. 外源一氧化氮供体硝普钠对番茄幼苗盐胁迫伤害的缓解作用[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2019, 31(8): 1286-1294.
DOI |
|
SUN Dezhi, YANG Hengshan, ZHANG Qingguo. Alleviating effect of exogenous nitric oxide donor sodium nitroprusside on tomato seedlings under salt stress[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2019, 31(8): 1286-1294.
DOI |
|
| [18] | 郑州元. 硫化氢调控盐胁迫下加工番茄种子萌发及幼苗生长的生理机制研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2017. |
| ZHENG Zhouyuan. Physiological mechanisms of hydrogen sulfide in regulating seed germination and seedlings growth of processing tomato under NaCl stress[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2017. | |
| [19] | 孙德智, 何淑平, 彭靖, 等. 水杨酸和硝普钠对NaCl胁迫下番茄幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2013, 33(3): 541-546. |
| SUN Dezhi, HE Shuping, PENG jing. Effects of Salicylic Acid and Sodium Nitropprusside on Tomato Seedling Growth and Physiological Characteristics under NaCl Stress[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2013, 33(3): 541-546. | |
| [20] | 周艳, 刘慧英, 王松, 等. 外源GSH对盐胁迫下番茄幼苗生长及抗逆生理指标的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2016, 36(3):515-520. |
| ZHOU Yan, LIU Huiying, WANG Song, et al. Effect of Exogenous GSH on Tomato Seedlings Growth and Physiological Indexes of Resistance Stress under Salt Stress[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2016, 36(3):515-520. | |
| [21] | 杜卓涛, 杨衍, 朱国鹏, 等. 外源一氧化氮对低温胁迫下苦瓜幼苗生长及部分抗逆指标的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2016, 28(5): 776-781. |
| DU Zhuotao, YANG Yan, ZHU Guopeng, et al. Effects of exogenous NO on plant growth and resistant characteristics of bitter melon seedlings under low-temperature stress[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2016, 28(5): 776-781. | |
| [22] | 温泽林. 外源GSH介导NO调控番茄幼苗盐适应性研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2018. |
| WEN Zelin. Study on Exogenous Glutathione Mediated Nitric Oxide to Regulate Salt Adaptability of Tomato Seedlings[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2018. | |
| [23] | 张静. 盐胁迫下NO和蛋白质S-亚硝基化对番茄幼苗生长发育的影响[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2020. |
| ZHANG Jing. Effects of NO and protein S-nitrosylation on tomato seedlings growth and development under salt stress[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| [24] |
杨小环, 杨文秀, 孙亮亮, 等. 外源NO缓解紫茎泽兰提取物对黄瓜根边缘细胞的化感胁迫[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(1):223-230.
DOI |
|
YANG Xiaohuan, YANG Wenxiu, SUN Liangliang, et al. Exogenous NO application effectively alleviates the allelochemical stress on cucumber root border cells caused by Eupatorium adenophorum extracts[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(1): 223-230.
DOI |
|
| [25] | 牛丽娟. 镉胁迫下蛋白质S-亚硝基化参与钙诱导黄瓜不定根发生[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2020. |
| NIU Lijuan. Protein S-Nitrosylation Was Involved in Ca2+-Induced Adventitious Rooting of Cucumber under Cd Stress[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| [26] | 孙德智, 韩晓日, 彭靖, 等. 外源NO和水杨酸对盐胁迫下番茄幼苗光合机构的保护作用[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2018, 24(3):457-464. |
| SUN Dezhi, HAN Xiaori, PENG Jing, et al. Protective effect of exogenous nitric oxide and salicylic acid on the photosynthetic apparatus of tomato seedling leaves under NaCl stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2018, 24(3): 457-464. |
| [1] | XU Maomao, GAO Jie, LI Junming, LI Xin, LIU Lei, PAN Feng. Population diversity analysis of 20 commercial tomato cultivars [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2191-2196. |
| [2] | TIAN Haiyan, ZHANG Zhanqin, XIE Jianhui, WANG Jianjiang, YANG Xiangkun. Study on the relationship between Lycopene and main quality characters of processing tomato [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2197-2202. |
| [3] | TIAN Chao, LI Yushan, MA Yue, SONG Yu. Effects of different concentrations of sophora alopecuroides extract on the growth and soil fertility of continuous cropping tomatoes [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2203-2210. |
| [4] | CHEN Fang, LI Zihui, SUNXiaogui , ZHANG Tingjun. Different dosage of microbial agents on the yield and quality of processed tomatoes [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2285-2289. |
| [5] | XI Rui, CHEN Yijia, LI Ning, YU Qinghui, WANG Qiang, QIN Yong. Effects of exogenous 2, 4-epibrassinolide on seed germination of different salt-sensitive tomatoes under salt stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1983-1992. |
| [6] | ZHANG Caihong, WANG Guoqiang, JIANG Luyan, LIU Tao, DE Xianming. Variation of environmental factors and analysis of tomato traits in low-energy assembly-type deep-winter production solar greenhouse [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 2043-2053. |
| [7] | ZHANG Fulin, LI Ning, LIU Yuxiang, CHEN Yijia, YU Qinghui, YAN Huizhuan. Effects of exogenous 2,4-Epibrassinolide and melatonin on fruit quality and peel morphology of cherry tomato [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1738-1747. |
| [8] | SHI Junjie, HOU Xianfei, YU Yuehua, LI Qiang, MIAO Haocui, JIA Donghai, GU Yuanguo, WANG Tianling. Effects of different mulching patterns and supplementary irrigation on peanut photosynthesis and dry matter accumulation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(5): 1122-1130. |
| [9] | RUAN Xiangyang, PU Min, XIAO Lele, LUO Linyi, CHEN Ruijie, LI Ran, CHEN Guoyong, YE Jun. Effect of magnesium sulfate fertilizer application strategy on the yield and quality of processed tomato [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 916-925. |
| [10] | LIU Yi, LI Jiangtao, JIANG Yinghong, YANG Ruwei, SUN Hui, WU Yan. Effect of exogenous spermidine on physiological characteristics of potato seedlings under NaCl stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(2): 336-344. |
| [11] | LI Chunyu, TAN Zhanming, CHENG Yunxia, GAO Yuan, MA Quanhui, LI Zhiguo, MA Xing. Effects of water and fertilizer coupling on diurnal changes of chlorophyll content and photosynthetic characteristics of sand-cultivated tomato [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(12): 3006-3013. |
| [12] | LI Yali, Halihashi , TANG Yali, DUAN jingjing, LI Qingjun. Effect of NP reduction and K synergism on yield and nutrient absorption of processing tomato [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(12): 3014-3019. |
| [13] | LIU Huifang, WANG Qiang, HAN Hongwei, ZHUANG Hongmei, WANG Hao, CHANG Yanan. Effects of salt, alkali and complex salt alkali stress on the photosynthetic characteristics and antioxidant enzyme activity of tomato seedlings [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2658-2666. |
| [14] | ZHAO Wenxuan, CHENG Yunxia, TAN Zhanming, LI Chunyu, SHU Sheng, Ayimaimu Shawuti, YANG Liyu, MIAO Xianjun. Comparison of chlorophyll fluorescence and photosynthetic characteristics of different processed tomato varieties based on principal component analysis [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2667-2675. |
| [15] | LI Chunyu, TAN Zhanming, CHENG Yunxia, SHU Sheng, MA Quanhui, HE Miao, DUAN Yifan, WU Hui. Comparative analysis of agronomic traits of different processing tomato varieties [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2676-2683. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 44
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 889
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||