

新疆农业科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (4): 975-981.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.04.022
王欢1( ), 张轶腾1, 王斌1, 周童1, 梁清2, 张宏2(
), 张轶腾1, 王斌1, 周童1, 梁清2, 张宏2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-15
出版日期:2025-04-20
发布日期:2025-06-20
通信作者:
张宏(1975-),男,内蒙古武川人,教授,硕士,研究方向为特色农产品无损检测,(E-mail)zhghog@163.com作者简介:王欢(1989-),女,重庆潼南人,硕士研究生,副高级工程师;研究方向为乳制品,(E-mail)3115261705@qq.com
基金资助:
WANG Huan1( ), ZHANG Yiteng1, WANG Bin1, ZHOU Tong1, LIANG Qing2, ZHANG Hong2(
), ZHANG Yiteng1, WANG Bin1, ZHOU Tong1, LIANG Qing2, ZHANG Hong2( )
)
Received:2024-09-15
Published:2025-04-20
Online:2025-06-20
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】探索牛奶介电特性和含水率之间的关系,为有效预测生鲜牛奶含水率、实现含水率快速检测提供参考。【方法】采用矢量网络分析仪和同轴探头测量2~20 GHz频率范围内牛奶样品的介电常数(ε')和介质损耗因数(ε″)。采用偏最小二乘回归(PLSR)、支持向量回归(SVR)和基于粒子群优化的最小二乘支持向量回归(PSO-LSSVR)3种建模方法,依次以ε'和ε″为变量建立6种数学模型对牛奶含水率进行预测并选优,精准预测牛奶含水率。【结果】随着频率的增加,ε'呈逐渐减小的趋势,ε″呈逐渐增大的趋势。6种模型中基于PSO-LSSVR方法下以ε″为变量建立的模型具有最好的含水率预测性能,其R2和RMSE分别为0.996 3和0.001 3。【结论】在2~20 GHz,随着频率的增加,ε'呈逐渐减小的趋势,而ε″则逐渐增加,介电特性可有效地预测牛奶的含水率。
中图分类号:
王欢, 张轶腾, 王斌, 周童, 梁清, 张宏. 基于介电特性的生鲜牛奶含水率检测方法[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(4): 975-981.
WANG Huan, ZHANG Yiteng, WANG Bin, ZHOU Tong, LIANG Qing, ZHANG Hong. Study on the moisture content detection method of fresh milk based on dielectric property[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(4): 975-981.
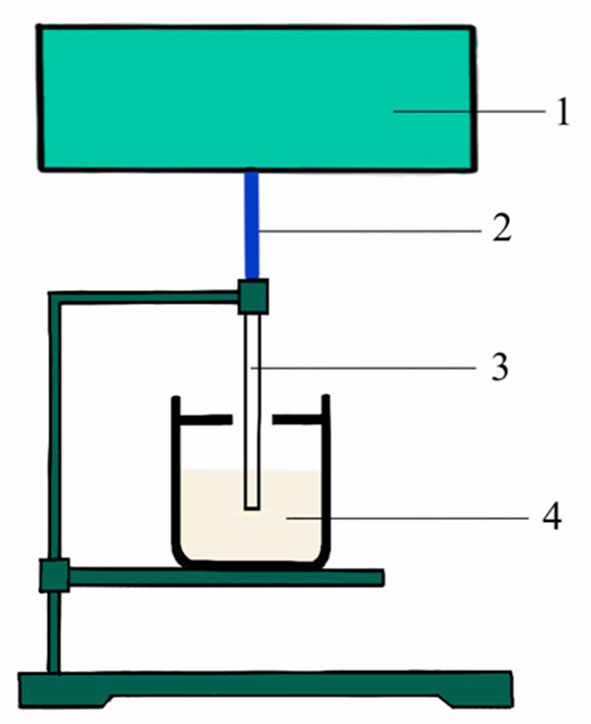
图1 生鲜牛奶电参数测量试验台 注:1:矢量网络分析仪;2:连接电缆;3:末端开口的同轴探头;4:待测液体
Fig.1 Test bench for Electrical parameters of fresh milk Notes:1,Vector network analyzer;2,Connecting cable;3,End opening coaxial probe;4,Liquid to be tested
| 参数 Parameter | 最小值 Minimum(%) | 最大值 Maximum(%) | 平均值±标准偏差 Average value± standard deviation(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 含水率Water content | 86.900 | 92.900 | 89.900± 2.16 |
| 非脂乳固体质量分数Non-fat milk solid mass fraction | 4.390 | 8.100 | 6.245±1.336 |
| 碳水化合物质量分数Carbohydrate mass fraction | 2.710 | 5.000 | 3.855±0.824 |
| 脂肪质量分数Fat mass fraction | 1.897 | 3.500 | 2.698±0.577 |
| 蛋白质质量分数Protein mass fraction | 1.789 | 3.300 | 2.544±0.544 |
表1 生鲜牛乳的主要成分
Tab.1 Main components of the fresh cow milk
| 参数 Parameter | 最小值 Minimum(%) | 最大值 Maximum(%) | 平均值±标准偏差 Average value± standard deviation(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 含水率Water content | 86.900 | 92.900 | 89.900± 2.16 |
| 非脂乳固体质量分数Non-fat milk solid mass fraction | 4.390 | 8.100 | 6.245±1.336 |
| 碳水化合物质量分数Carbohydrate mass fraction | 2.710 | 5.000 | 3.855±0.824 |
| 脂肪质量分数Fat mass fraction | 1.897 | 3.500 | 2.698±0.577 |
| 蛋白质质量分数Protein mass fraction | 1.789 | 3.300 | 2.544±0.544 |
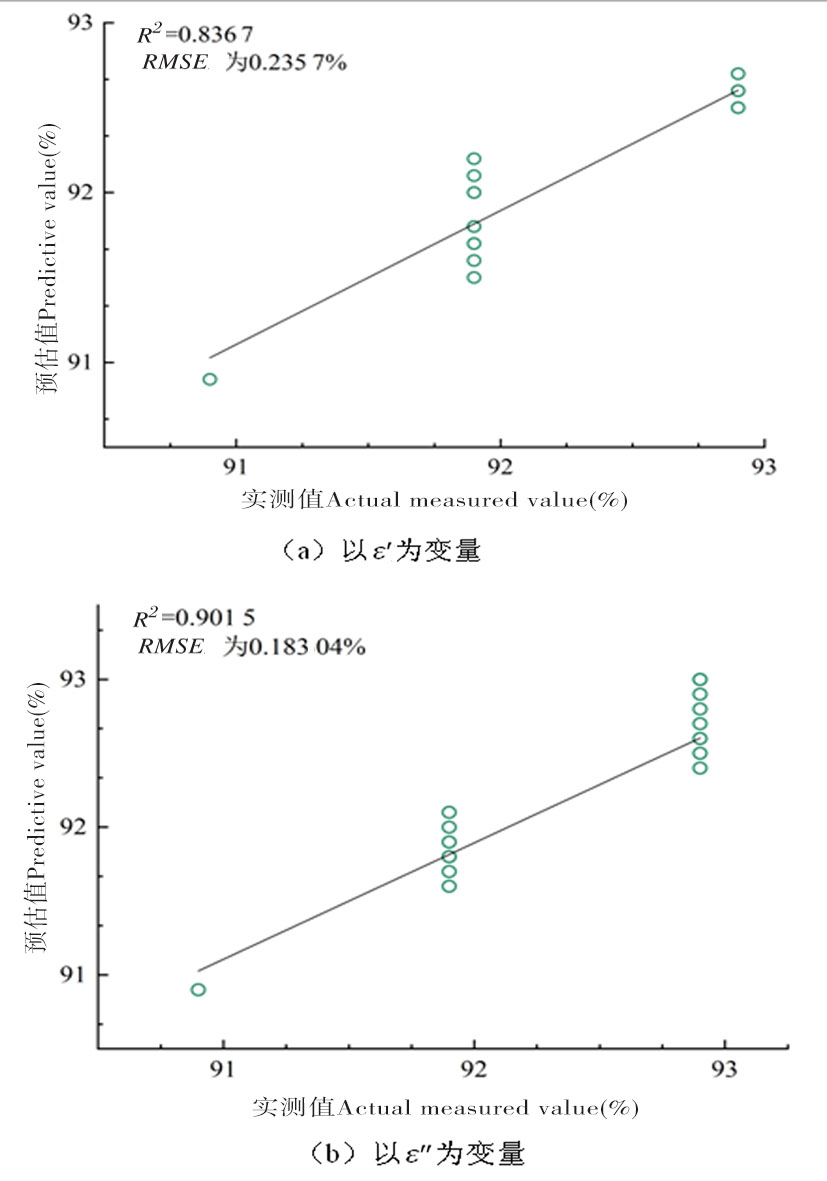
图3 不同变量预测集中含水率的实测值与PLSR模型预测值的比较
Fig.3 Measured values and PLSR of water content of different variables Comparison of the predicted values of the model
| 建模 方法 Modeling method | 建模 变量 Mode- ling variable | 训练阶段 Training phase | 预测阶段 Prediction phase | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | ||||||||
| PLSR | ε' | 0.994 4 | 0.001 0 | 0.867 | 0.002 4 | ||||||
| ε″ | 0.999 3 | 0.000 4 | 0.901 5 | 0.001 8 | |||||||
| SVR | ε' | 0.993 6 | 0.001 8 | 0.978 1 | 0.004 0 | ||||||
| ε″ | 0.997 9 | 0.001 5 | 0.792 2 | 0.010 2 | |||||||
| PSO- LSSVR | ε' | 0.991 7 | 0.001 7 | 0.992 0 | 0.002 6 | ||||||
| ε″ | 0.995 3 | 0.001 4 | 0.996 3 | 0.001 3 | |||||||
表2 不同建模方法对牛奶含水率的预测结果比较
Tab.2 Comparisons of prediction results for different modeling methods
| 建模 方法 Modeling method | 建模 变量 Mode- ling variable | 训练阶段 Training phase | 预测阶段 Prediction phase | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | ||||||||
| PLSR | ε' | 0.994 4 | 0.001 0 | 0.867 | 0.002 4 | ||||||
| ε″ | 0.999 3 | 0.000 4 | 0.901 5 | 0.001 8 | |||||||
| SVR | ε' | 0.993 6 | 0.001 8 | 0.978 1 | 0.004 0 | ||||||
| ε″ | 0.997 9 | 0.001 5 | 0.792 2 | 0.010 2 | |||||||
| PSO- LSSVR | ε' | 0.991 7 | 0.001 7 | 0.992 0 | 0.002 6 | ||||||
| ε″ | 0.995 3 | 0.001 4 | 0.996 3 | 0.001 3 | |||||||
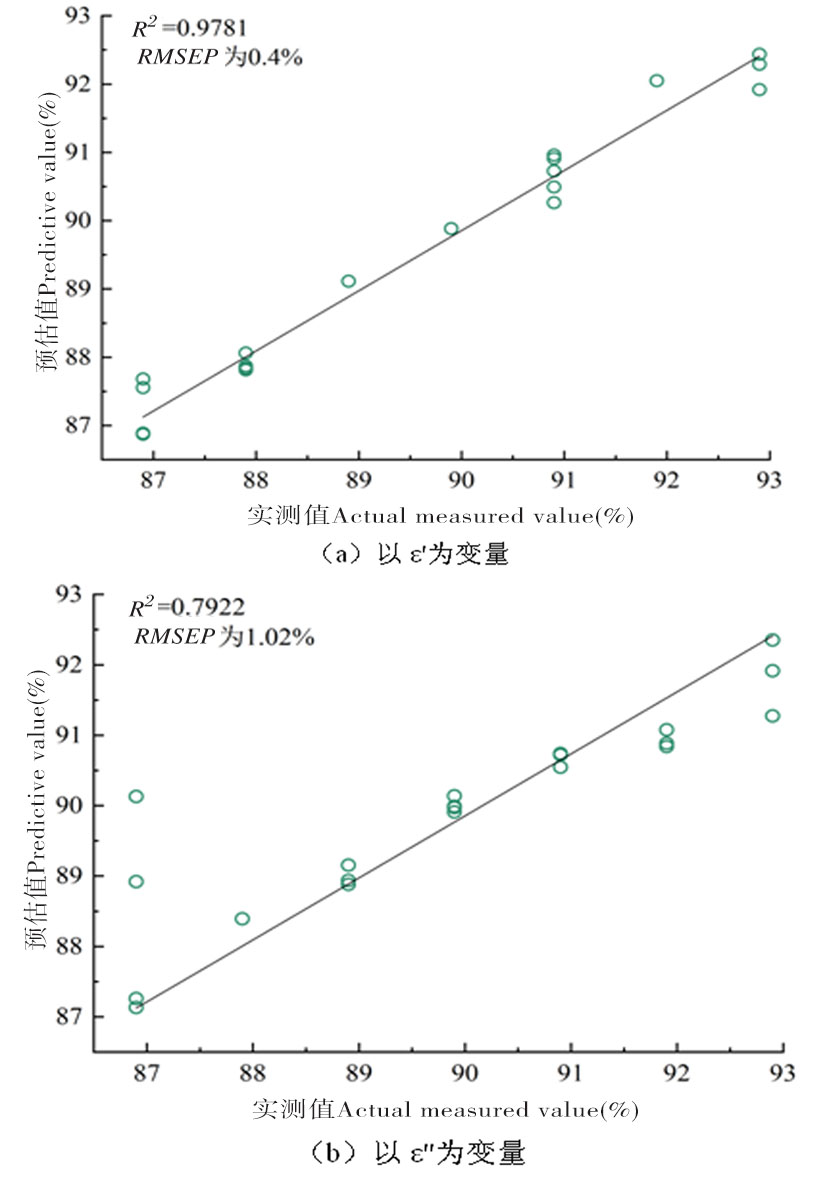
图4 不同变量预测集中含水率的实测值与SVR模型预测值的比较
Fig.4 Comparisons measured values and SVR of water content in different variables Comparison of the predicted values of the model
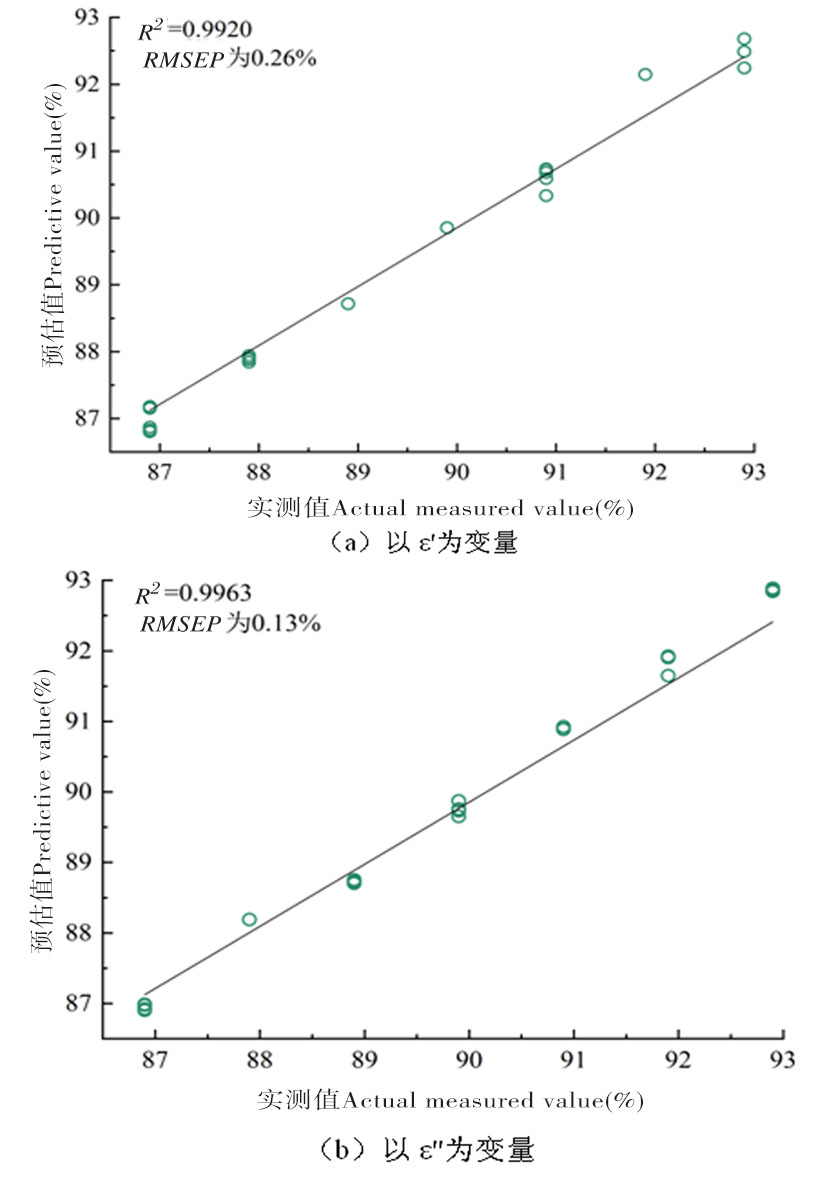
图5 不同变量预测集中含水率的实测值与PSO-LSSVR模型预测值的比较
Fig.5 Comparisons measured values of predicted content of different variables and PSO-LSSVR Comparison of the predicted values of the model
| [1] | GB 5009.3—2016.食品安全国家标准食品中水分的测定[S]. |
| GB 5009.3—2016. National Food Safety Standard Determination of Moisture in Food:[S]. | |
| [2] |
Kasemsumran S, Thanapase W, Kiatsoonthon A. Feasibility of near-infrared spectroscopy to detect and to quantify adulterants in cow milk[J]. Analytical Sciences, 2007, 23(7): 907-910.
PMID |
| [3] | Eltemur D, Robatscher P, Oberhuber M, et al. Applications of solution NMR spectroscopy in quality assessment and authentication of bovine milk[J]. Foods, 2023, 12(17): 3240. |
| [4] | Mabrook M F, Petty M C. A novel technique for the detection of added water to full fat milk using single frequency admittance measurements[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2003, 96(1/2): 215-218. |
| [5] |
佀博学, 张养东, 郑楠, 等. 生乳新鲜度评价指标研究进展[J]. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35(6): 3499-3507.
DOI |
|
SI Boxue, ZHANG Yangdong, ZHENG Nan, et al. Research progress on freshness evaluation indices of raw milk[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2023, 35(6): 3499-3507.
DOI |
|
| [6] | 曹玉栋, 祁伟彦, 李娴, 等. 苹果无损检测和品质分级技术研究进展及展望[J]. 智慧农业, 2019, 1(3): 29-45. |
|
CAO Yudong, QI Weiyan, LI Xian, et al. Research progress and prospect on non-destructive detection and quality grading technology of apple[J]. Smart Agriculture, 2019, 1(3): 29-45.
DOI |
|
| [7] | 胡志晨. 基于介电特性的苹果无损分级测量模块的设计与实现[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2016. |
| HU Zhichen. Design and implementation of measurement module for nondestructive classification of apples based on dielectric property[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2016. | |
| [8] | Clerjon S, Daudin J D, Damez J L. Water activity and dielectric properties of gels in the frequency range 200 MHz-6 GHz[J]. Food Chemistry, 2003, 82(1): 87-97. |
| [9] | 郭文川, 孔繁荣. 不同类型蛋白质及其添加量对牛乳介电特性的影响[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(8): 248-254. |
| GUO Wenchuan, KONG Fanrong. Influence of different proteins and their additive amounts on permittivities of milk[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(8): 248-254. | |
| [10] | 梁志斌. 生鲜牛乳介电特性与脂肪含量关系的试验研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2014. |
| LIANG Zhibin. study of experiment on the relationshiop between dielectric properties and at content of raw milk.[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2014. | |
| [11] | Nelson S O, Trabelsi S. Factors influencing the dielectric properties of agricultural and food products[J]. The Journal of Microwave Power and Electromagnetic Energy: a Publication of the International Microwave Power Institute, 2012, 46(2): 93-107. |
| [12] | Sacilik K, Colak A. Determination of dielectric properties of corn seeds from 1 to 100 MHz[J]. Powder Technology, 2010, 203(2): 365-370. |
| [13] | 张本华, 钱长钱, 焦晋康, 等. 基于介电特性与SPA-SVR算法的水稻含水率检测方法[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(18): 237-244. |
| ZHANG Benhua, QIAN Changqian, JIAO Jinkang, et al. Rice moisture content detection method based on dielectric properties and SPA-SVR algorithm[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(18): 237-244. | |
| [14] | 武新慧, 郭玉明, 孙静鑫, 等. 苹果介电特性与微波干燥含水率相关性研究[J]. 农机化研究, 2018, 40(10): 194-198. |
| WU Xinhui, GUO Yuming, SUN Jingxin, et al. Study on coaxial electric properties of apple as a function of microwave drying moisture content[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2018, 40(10): 194-198. | |
| [15] | 李大伟, 陈超, 兰海鹏, 等. 基于电特性的新疆骏枣含水率的试验研究[J]. 农机化研究, 2016, 38(7): 212-215. |
| LI Dawei, CHEN Chao, LAN Haipeng, et al. Experimental research on the electrical characteristics of Xinjiang Junzao moisture[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2016, 38(7): 212-215. | |
| [16] | 周世平, 张海红, 李海峰, 等. 基于果品介电特性的无损检测技术研究综述[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2015, 36(1): 131-134, 144. |
| ZHOU Shiping, ZHANG Haihong, LI Haifeng, et al. Review of fruit nondestructive testing technology research based on the dielectric characteristics[J]. Food Research and Development, 2015, 36(1): 131-134, 144. | |
| [17] | McKeown M S, Trabelsi S, Tollner E W, et al. Dielectric spectroscopy measurements for moisture prediction in Vidalia Onions[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2012, 111(3): 505-510. |
| [18] | 郭文川, 林碧莹. 牛奶含水率介电谱结合化学计量学检测方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(9): 249-255. |
| GUO Wenchuan, LIN Biying. Detecting moisture content of cow’s milk using dielectric spectra and chemometrics[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(9): 249-255. | |
| [19] | GB/T 35680—2017.中国国家标准化管理委员会.液体材料微波频段使用开口同轴探头的电磁参数测量方法[S]. |
| GB/T 35680—2017. Measuring method for electromagnetic parameters of liquid materials at microwave frequencies using an open-ended coaxial probe[S]. | |
| [20] | Wold S, Sjöström M, Eriksson L. PLS-regression: a basic tool of chemometrics[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2001, 58(2): 109-130. |
| [21] | 王建国, 张文兴. 支持向量机建模及其智能优化[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2015: 12-16. |
| WANG Jianguo, ZHANG Wenxing. The SVM modeling and its intelligent optimization[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2015: 12-16. | |
| [22] | Chang C C, Lin C J. LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2011, 2(3): 1-27. |
| [23] |
刘昱, 赵国新. 基于粒子群优化算法的无摩擦气缸结构优化[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2018, 30(9): 3564-3570.
DOI |
|
LIU Yu, Zhao Guoxin. Optimization of frictionless cylinder-structure based on PSO[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2018, 30(9): 3564-3570.
DOI |
|
| [24] | 刘贺, 张弘强, 刘斌. 基于粒子群优化神经网络算法的深基坑变形预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(5): 1609-1614. |
| LIU He, ZHANG Hongqiang, LIU Bin. A prediction method for the deformation of deep foundation pit based on the particle swarm optimization neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2014, 44(5): 1609-1614. | |
| [25] |
朱新华, 郭文川. 影响食品射频-微波介电特性的因素及影响机理分析[J]. 食品科学, 2010, 31(17): 410-414.
DOI |
|
ZHU Xinhua, GUO Wenchuan. A review of affecting factors and their mechanisms of the radio frequency-microwave dielectric properties of foods[J]. Food Science, 2010, 31(17): 410-414.
DOI |
|
| [26] | Zhu X H, Guo W C, Liang Z B. Determination of the fat content in cow’s milk based on dielectric properties[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2015, 8(7): 1485-1494. |
| [27] | Zhu X H, Guo W C, Jia Y P, et al. Dielectric properties of raw milk as functions of protein content and temperature[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2015, 8(3): 670-680. |
| [1] | 张凌健, 张凯, 张慧, 郭小梦, 陈国悦, 王奕丁, 贾庆宇. 棉花全生育期植株含水率与顶部茎叶形态特征的关系[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(3): 531-538. |
| [2] | 张磊, 姚梦瑶, 刘志刚, 李娟, 杨洋, 蔡大润, 陈果, 李波, 李晓荣, 陈勋基, 翟云龙. 基于无人机多光谱NDVI值估测玉米产量[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 845-851. |
| [3] | 卢红琴, 白云岗, 柴仲平, 卢震林, 刘洪波, 郑明, 肖军. 拱棚环境下“干播湿出”棉田保苗技术效果评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(12): 2872-2882. |
| [4] | 刘晨阳, 张立萍, 郑威强, 罗豪威. 不同含水率对罗布麻力学特性及剥麻效果的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2797-2806. |
| [5] | 李嘉琦, 冯宇华, 陈署晃, 王子傲, 刘鹏, 梁智永, 孙法福, 陈荣, 耿庆龙. 基于高光谱的土壤有机质及全氮估测[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(10): 2491-2499. |
| [6] | 杨川, 张凯, 陈冰, 张慧, 柳萍, 常松, 盛建东. 棉花植株形态特征对不同水分状况的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2120-2127. |
| [7] | 李雪玲, 郭俊先, 陈莉, 宋鹤岭, 张众. 不同覆膜宽度对棉花农田环境的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1840-1847. |
| [8] | 杨寒珺, 黄星宇, 王旭哲, 张凤华, 鲁为华, 张凡凡. 田间晾晒时间对饲用油菜发酵品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1433-1441. |
| [9] | 忠智博, 何帅, 张万恒, 周建伟, 郑国玉, 马军勇, 程鸿, 石聪, 张欣. 盐渍化条件下棉花成苗及水盐分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(10): 2390-2395. |
| [10] | 徐彦军, 廉苇佳, 刘翔宇, 斯拉依丁·司马义, 唐秋菊, 艾尼瓦尔·阿不都拉. 水氮耦合对棉田土壤水分时空分布及产量效应的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(5): 1051-1059. |
| [11] | 贺宏伟, 张巨松, 陈振, 卡地力亚·阿不都克力木, 彭增莹, 刘群, 崔建平, 林涛, 郭仁松. 水氮调配对等行距机采棉土壤、叶片水分及棉铃分布的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(1): 1-10. |
| [12] | 杨庭瑞, 赵经华, 杨磊, 彭艳平, 周和平. 基于正交试验的玉米最优产量渗灌技术组合分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(9): 1585-1593. |
| [13] | 王玉刚, 王磊, 李建新, 蔡云霄, 刘斌, 邓星. 脱叶时间和含水率对机采棉采摘力学特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(5): 911-919. |
| [14] | 李志, 苏武峥, 李新国, 王银方, 毛东雷, 麦麦提吐尔逊·艾则孜. 基于高光谱特征参数优选的土壤盐分含量建模及其验证[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(12): 2342-2352. |
| [15] | 吴乐天, 宋兵伟, 慈军, 王亮, 马皓诚, 史慧锋. 不同击实功对新疆非耕地固化戈壁土力学性能的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(9): 1756-1764. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||