

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (5): 1292-1300.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.05.029
• Microbes·Animal Husbandry Veterinarian • Previous Articles
CHEN Kaixu( ), GUO Cuijie, YANG Fan, REN Feier, LI Xiaobin, LIU Wujun(
), GUO Cuijie, YANG Fan, REN Feier, LI Xiaobin, LIU Wujun( )
)
Received:2022-09-01
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-05-22
Correspondence author:
LIU Wujun (1966-), female, Luyi, Henan. Ph. D, professor, research field: animal genetics and breeding, (E-mail) Supported by:
陈开旭( ), 郭翠洁, 杨帆, 任斐儿, 李晓斌, 刘武军(
), 郭翠洁, 杨帆, 任斐儿, 李晓斌, 刘武军( )
)
通讯作者:
刘武军(1966-),女,河南鹿邑人,教授,博士,硕士生/博士生导师研究方向为动物遗传育种,(E-mail) 作者简介:陈开旭(1983-),男,四川三台人,讲师,博士,研究方向为动物遗传育种,(E-mail) chenkaixu@126.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
CHEN Kaixu, GUO Cuijie, YANG Fan, REN Feier, LI Xiaobin, LIU Wujun. Genetic diversity analysis of xinjiang sheep with fine wool based on whole-genome Re-sequencing[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(5): 1292-1300.
陈开旭, 郭翠洁, 杨帆, 任斐儿, 李晓斌, 刘武军. 基于全基因组重测序分析新疆细毛羊遗传多样性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(5): 1292-1300.
| 样品编号 Sample number | 纯度 OD260/OD280 | 浓度 concentration (ng/μL) |
|---|---|---|
| XFW01 | 1.83 | 81.426 |
| XFW02 | 1.91 | 67.261 |
| XFW03 | 1.88 | 79.537 |
| XFW04 | 1.97 | 94.253 |
| XFW05 | 1.89 | 88.051 |
| XFW06 | 1.89 | 62.306 |
| XFW07 | 2.07 | 105.364 |
| XFW08 | 1.89 | 78.859 |
| XFW09 | 1.88 | 96.857 |
| XFW10 | 1.95 | 79.925 |
Tab.1 Detection of DNA concentration and purity of Xinjiang fine wool sheep
| 样品编号 Sample number | 纯度 OD260/OD280 | 浓度 concentration (ng/μL) |
|---|---|---|
| XFW01 | 1.83 | 81.426 |
| XFW02 | 1.91 | 67.261 |
| XFW03 | 1.88 | 79.537 |
| XFW04 | 1.97 | 94.253 |
| XFW05 | 1.89 | 88.051 |
| XFW06 | 1.89 | 62.306 |
| XFW07 | 2.07 | 105.364 |
| XFW08 | 1.89 | 78.859 |
| XFW09 | 1.88 | 96.857 |
| XFW10 | 1.95 | 79.925 |
| 样品编号 Sample number | 比对率 Mapping rate (%) | 全基因组 覆盖度 Coverage (%) | 测序深度 Sequencing depth | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XFW01 | 99.01 | 97.81 | 8.943 3X | 97.14 | 92.32 |
| XFW02 | 99.46 | 97.89 | 8.167 2X | 97.22 | 92.48 |
| XFW03 | 99.44 | 97.93 | 7.566 7X | 97.12 | 92.22 |
| XFW04 | 99.28 | 97.80 | 7.223 8X | 96.88 | 91.66 |
| XFW05 | 99.32 | 97.90 | 7.484 3X | 97.22 | 92.41 |
| XFW06 | 74.88 | 97.91 | 6.075 4X | 96.81 | 91.62 |
| XFW07 | 99.22 | 97.87 | 7.613 8X | 96.93 | 91.82 |
| XFW08 | 94.48 | 97.93 | 8.478 5X | 96.91 | 91.81 |
| XFW09 | 99.31 | 97.89 | 7.104 6X | 96.73 | 91.47 |
| XFW10 | 99.38 | 97.91 | 8.189 1X | 96.77 | 91.5 |
Tab.2 Whole genome sequencing data quality statistics
| 样品编号 Sample number | 比对率 Mapping rate (%) | 全基因组 覆盖度 Coverage (%) | 测序深度 Sequencing depth | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XFW01 | 99.01 | 97.81 | 8.943 3X | 97.14 | 92.32 |
| XFW02 | 99.46 | 97.89 | 8.167 2X | 97.22 | 92.48 |
| XFW03 | 99.44 | 97.93 | 7.566 7X | 97.12 | 92.22 |
| XFW04 | 99.28 | 97.80 | 7.223 8X | 96.88 | 91.66 |
| XFW05 | 99.32 | 97.90 | 7.484 3X | 97.22 | 92.41 |
| XFW06 | 74.88 | 97.91 | 6.075 4X | 96.81 | 91.62 |
| XFW07 | 99.22 | 97.87 | 7.613 8X | 96.93 | 91.82 |
| XFW08 | 94.48 | 97.93 | 8.478 5X | 96.91 | 91.81 |
| XFW09 | 99.31 | 97.89 | 7.104 6X | 96.73 | 91.47 |
| XFW10 | 99.38 | 97.91 | 8.189 1X | 96.77 | 91.5 |
| 单核苷酸多态性SNP | Indel | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type (alphabetical order) | Count | Percent(%) | Type (alphabetical order) | Count | Percent(%) |
| DOWNSTREAM | 2 232 463 | 2.29 | DOWNSTREAM | 469 219 | 2.95 |
| EXON | 775 956 | 0.79 | EXON | 234 723 | 1.48 |
| INTERGENIC | 56 743 016 | 58.11 | INTERGENIC | 8 705 661 | 54.80 |
| INTRON | 34 744 752 | 35.58 | INTRON | 5 588 596 | 35.18 |
| SPLICE_SITE_ACCEPTOR | 995 | 0.00 | SPLICE_SITE_ACCEPTOR | 11 111 | 0.07 |
| SPLICE_SITE_DONOR | 2108 | 0.00 | SPLICE_SITE_DONOR | 12865 | 0.08 |
| SPLICE_SITE_REGION | 54 513 | 0.06 | SPLICE_SITE_REGION | 15 675 | 0.10 |
| UPSTREAM | 2 350 282 | 2.41 | UPSTREAM | 684 523 | 4.31 |
| UTR_3_PRIME | 511 316 | 0.52 | UTR_3_PRIME | 88 686 | 0.56 |
| UTR_5_PRIME | 232 034 | 0.24 | UTR_5_PRIME | 75 211 | 0.47 |
Tab.3 The genetic variation information of SNPs and indels in sheep breeds
| 单核苷酸多态性SNP | Indel | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type (alphabetical order) | Count | Percent(%) | Type (alphabetical order) | Count | Percent(%) |
| DOWNSTREAM | 2 232 463 | 2.29 | DOWNSTREAM | 469 219 | 2.95 |
| EXON | 775 956 | 0.79 | EXON | 234 723 | 1.48 |
| INTERGENIC | 56 743 016 | 58.11 | INTERGENIC | 8 705 661 | 54.80 |
| INTRON | 34 744 752 | 35.58 | INTRON | 5 588 596 | 35.18 |
| SPLICE_SITE_ACCEPTOR | 995 | 0.00 | SPLICE_SITE_ACCEPTOR | 11 111 | 0.07 |
| SPLICE_SITE_DONOR | 2108 | 0.00 | SPLICE_SITE_DONOR | 12865 | 0.08 |
| SPLICE_SITE_REGION | 54 513 | 0.06 | SPLICE_SITE_REGION | 15 675 | 0.10 |
| UPSTREAM | 2 350 282 | 2.41 | UPSTREAM | 684 523 | 4.31 |
| UTR_3_PRIME | 511 316 | 0.52 | UTR_3_PRIME | 88 686 | 0.56 |
| UTR_5_PRIME | 232 034 | 0.24 | UTR_5_PRIME | 75 211 | 0.47 |
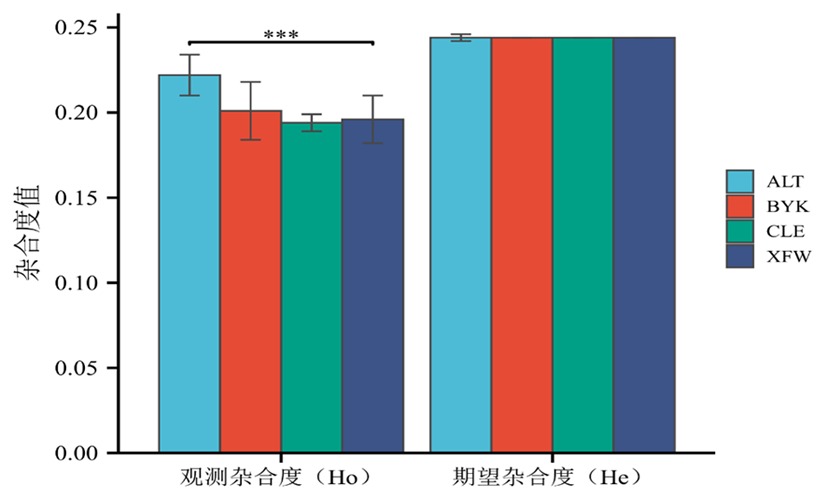
Fig.2 Heterozygosity analysis of 4 sheep populations Note:* indicated the heterozygosity of different sheep groups was significantly different (P<0.05),** indicated the heterozygosity of different sheep groups was extremely significantly different
| 品种 Breed | ROH长度 Length of ROH (Mb) | 基因组近交系数 Inbreeding coefficient (FROH) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值±标准误 Mean±SE | ROH长度区间 Range | 平均值±标准误 Mean±SE | FROH区间 Range | |
| XFW | 110.665±8.744 | 89.609-178.833 | 0.042 3±0.003 2 | 0.034 26-0.068 37 |
| CLE | 93.532±6.956 | 74.687-151.767 | 0.035 8±0.002 5 | 0.028 56-0.058 03 |
| BYK | 88.417±10.694 | 47.985-148.081 | 0.033 8±0.003 9 | 0.018 34-0.056 62 |
| ALT | 74.445±21.225 | 57.063-131.694 | 0.028 5±0.0024 | 0.021 82-0.050 35 |
Tab.4 Average length and genomic inbreeding coefficient of four sheep groups
| 品种 Breed | ROH长度 Length of ROH (Mb) | 基因组近交系数 Inbreeding coefficient (FROH) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值±标准误 Mean±SE | ROH长度区间 Range | 平均值±标准误 Mean±SE | FROH区间 Range | |
| XFW | 110.665±8.744 | 89.609-178.833 | 0.042 3±0.003 2 | 0.034 26-0.068 37 |
| CLE | 93.532±6.956 | 74.687-151.767 | 0.035 8±0.002 5 | 0.028 56-0.058 03 |
| BYK | 88.417±10.694 | 47.985-148.081 | 0.033 8±0.003 9 | 0.018 34-0.056 62 |
| ALT | 74.445±21.225 | 57.063-131.694 | 0.028 5±0.0024 | 0.021 82-0.050 35 |
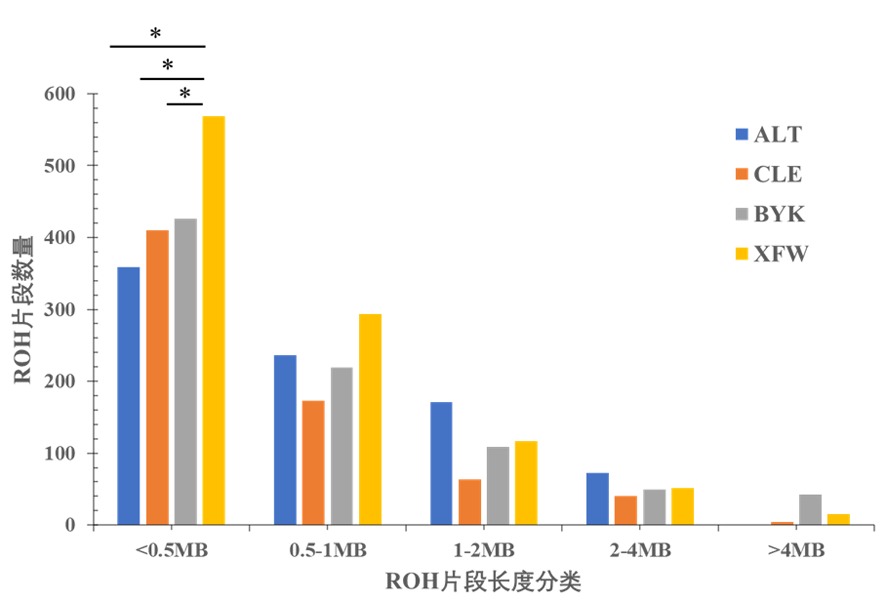
Fig.3 The total length of ROH in different length categories Note:* indicated the length of ROH fragment was significantly different among different sheep groups(P<0.05)
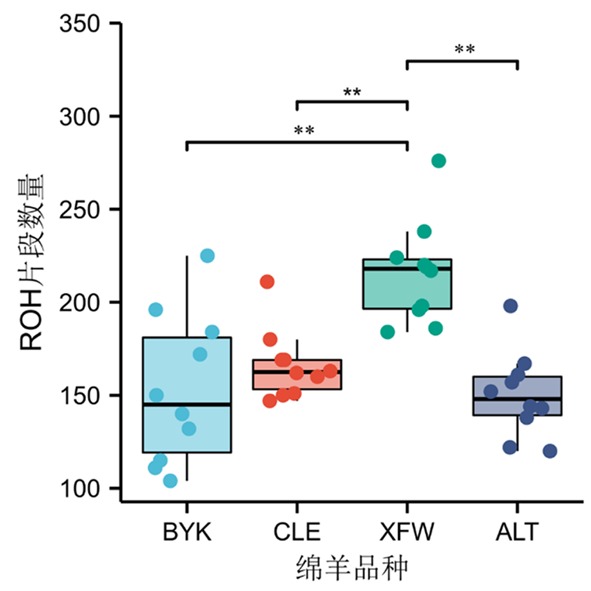
Fig.4 The average number of ROH and the number of ROH per individual in 4 sheep groups Note:** indicated the average number of ROH fragments among different sheep groups was extremely significantly different(P<0.01)
| [1] | 刘慧. 中国羊毛贸易发展情况分析[J]. 农业展望, 2010, 6(6): 46-49. |
| LIU Hui. Analysis of the Chinese wool trade development trend[J]. Agricultural Outlook, 2010, 6(6): 46-49. | |
| [2] | 田春英, 王峰, 荣威恒. 内蒙古细毛羊产业可持续发展对策探讨[J]. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2005, 26(4): 48-50. |
| TIAN Chunying, WANG Feng, RONG Weiheng. Countermeasures for sustainable development of Inner Mongolia fine-wool sheep industry[J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2005, 26(4): 48-50. | |
| [3] | 赵有璋. 羊生产学[M]. 中国农业出版社, 2011. |
| ZHAO Youzhang. Sheep And Goat Production[M]. China Agriculture Press, 2011. | |
| [4] | 曾献存. 新疆绵羊遗传多样性及主要经济性状候选基因研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2010. |
| ZENG Xiancun. Studies on the genetic diversity of Xinjiang sheep breeds and candidate genes of major economic traits[D]. Shehezi: Shihezi University, 2010. | |
| [5] | 沈文, 孙延鸣, 崔茹鹏, 等. 新疆细毛羊KAP6.1基因的克隆及序列分析[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2013, 3: 31-34. |
| SHEN Wen, SUN Yanming, CUI Rupeng, et al. Cloning and sequence analysis of KAP 6.1 gene in Xinjiang fine-wool sheep[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2013(3): 31-34. | |
| [6] | 肖非. 新疆绵羊种质资源调查、保护及遗传多样性[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2009. |
| XIAO Fei. Investigation, conservation and genetic diversity of germplasm resources in Xinjiang sheep[D]. Shiehzi: Shihezi University, 2009. | |
| [7] | 赵永欣, 李孟华. 中国绵羊起源, 进化和遗传多样性研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(11):958-973. |
| ZHAO Yongxin, LI Menghua. Research advances on the origin, evolution and genetic diversity of Chinese native sheep breeds[J]. Hereditas, 2017, 39(11): 958-973. | |
| [8] | 王秀蓉. 基于SSR标记评估青海省家牦牛和藏绵羊遗传多样性及近交程度[D]. 西宁: 青海师范大学, 2019. |
| WANG Xiurong. Study on genetic diversity and inbreeding degree of domestic Yak and Tibetan sheep in Qinghai Province based on SSR markers [D]. Xining: Qinghai Normal University, 2019. | |
| [9] | Li H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM[J]. arXiv e-prints, 2013: arXiv: 1303.3997. |
| [10] |
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, et al. The sequence alignment/map format and SAM tools[J]. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(16): 2078-2079.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data[J]. Genome Research, 2010, 20(9): 1297-1303.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Wang K, Li M, Hakonarson H. ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, 38(16): e164. |
| [13] |
Yang H, Wang K. Genomic variant annotation and prioritization with ANNOVAR and ANNOVAR[J]. Nature Protocols, 2015, 10(10): 1556-1566.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Haubold B, Pfaffelhuber P, Lynch M. mlRho-a program for estimating the population mutation and recombination rates from shotgun-sequenced diploid genomes[J]. Molecular Ecology, 2010, 19: 277-284.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses[J]. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 2007, 81(3): 559-575.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Bosse M, Megens H J, Madsen O, et al. Regions of homozygosity in the porcine genome: consequence of demography and the recombination landscape[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2012, 8(11): e1003100. |
| [17] |
Ceballos F C, Joshi P K, Clark D W, et al. Runs of homozygosity: windows into population history and trait architecture[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2018, 19(4): 220.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Garvin M R, Saitoh K, Gharrett A J. Application of single nucleotide polymorphisms to non‐model species: a technical review[J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 2010, 10(6): 915-934.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | Fan B, Du Z Q, Gorbach D M, et al. Development and application of high-density SNP arrays in genomic studies of domestic animals[J]. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 2010, 23(7): 833-847. |
| [20] | 张彦斌, 罗海涛, 范鑫, 等. 锡林郭勒绵羊品种遗传多样性研究进展[J]. 中国畜禽种业, 2020, 16(3): 3-6. |
| ZHANG Yanbin, LUO Haitao, FAN Xin, et al. Research progresses of the varietal genetic polymorphism of Xilinguole sheep[J]. The Chinese Livestock and Poultry Breeding, 2020, 16(3): 3-6. | |
| [21] |
Ceballos F C, Joshi P K, Clark D W, et al. Runs of homozygosity: windows into population history and trait architecture[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2018, 19(4): 220.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Broman K W, Weber J L. Long homozygous chromosomal segments in reference families from the centre d'Etude du polymorphisme humain[J]. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 1999, 65(6): 1493-1500.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Caballero A, Villanueva B, Druet T. On the estimation of inbreeding depression using different measures of inbreeding from molecular markers[J]. Evolutionary Applications, 2021, 14(2): 416-428.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
D’ambrosio J, Phocas F, Haffray P, et al. Genome-wide estimates of genetic diversity, inbreeding and effective size of experimental and commercial rainbow trout lines undergoing selective breeding[J]. Genetics Selection Evolution, 2019, 51(1): 1-15.
DOI |
| [25] |
Letko A, Minor K M, Jagannathan V, et al. Genomic diversity and population structure of the Leonberger dog breed[J]. Genetics Selection Evolution, 2020, 52(1): 1-12.
DOI |
| [26] | Fang Y, Hao X, Xu Z, et al. Genome-wide detection of runs of homozygosity in Laiwu pigs revealed by sequencing data[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2021: 463. |
| [27] |
Liu D, Chen Z, Zhao W, et al. Genome-wide selection signatures detection in Shanghai Holstein cattle population identified genes related to adaption, health and reproduction traits[J]. BMC Genomics, 2021, 22(1): 1-19.
DOI |
| [28] |
Gorssen W, Meyermans R, Janssens S, et al. A publicly available repository of ROH islands reveals signatures of selection in different livestock and pet species[J]. Genetics Selection Evolution, 2021, 53(1): 1-10.
DOI |
| [29] |
Stoffel M A, Johnston S E, Pilkington J G, et al. Mutation load decreases with haplotype age in wild Soay sheep[J]. Evolution Letters, 2021, 5(3): 187-195.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Zhang X, Kim B, Lohmueller K E, et al. The impact of recessive deleterious variation on signals of adaptive introgression in human populations[J]. Genetics, 2020, 215(3): 799-812.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Khan A, Patel K, Shukla H, et al. Genomic evidence for inbreeding depression and purging of deleterious genetic variation in Indian tigers[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2021, 118(49): e2023018118. |
| [32] | Addo S, Klingel S, Thaller G, et al. Genetic diversity and the application of runs of homozygosity-based methods for inbreeding estimation in German White-headed Mutton sheep[J]. PloS One, 2021, 16(5): e0250608. |
| [33] | Suezawa R, Nikadori H, Sasaki S. Genetic diversity and genomic inbreeding in Japanese Black cows in the islands of Okinawa Prefecture evaluated using single‐nucleotide polymorphism array[J]. Animal Science Journal, 2021, 92(1): e13525. |
| [34] | Roh H J, Kim S C, Cho C Y, et al. Estimating genetic diversity and population structure of 22 chicken breeds in Asia using microsatellite markers[J]. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 2020, 33(12): 1896. |
| [35] | Humble E, Paijmans A J, Forcada J, et al. An 85K SNP array uncovers inbreeding and cryptic relatedness in an Antarctic fur seal breeding colony[J]. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics, 2020, 10(8): 2787-2799. |
| [36] | 杨湛澄, 黄河天, 闫青霞, 等. 利用高密度 SNP 标记分析中国荷斯坦牛基因组近交[J]. 遗传, 2017, 39(1): 16-23. |
| YANG Zhancheng, HUANG Hetian, YAN Qingxia, et al. Estimation of genomic inbreeding coefficients based on high-density SNP markers in Chinese Holstein cattle[J]. Hereditas, 2017, 39(1): 16-23. | |
| [37] |
Stoffel M A, Johnston S E, Pilkington J G, et al. Genetic architecture and lifetime dynamics of inbreeding depression in a wild mammal[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1-10.
DOI |
| [38] |
Ghoreishifar S M, Moradi-Shahrbabak H, Fallahi M H, et al. Genomic measures of inbreeding coefficients and genome-wide scan for runs of homozygosity islands in Iranian river buffalo, Bubalus bubalis[J]. BMC Genetics, 2020, 21(1): 1-12.
DOI |
| [39] | Suezawa R, Nikadori H, Sasaki S. Genetic diversity and genomic inbreeding in Japanese Black cows in the islands of Okinawa Prefecture evaluated using single‐nucleotide polymorphism array[J]. Animal Science Journal, 2021, 92(1): e13525. |
| [40] | Lewontin R C, Kojima K. The evolutionary dynamics of complex polymorphisms[J]. Evolution, 1960: 458-472. |
| [41] |
Slatkin M. Linkage disequilibrium—understanding the evolutionary past and mapping the medical future[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2008, 9(6): 477-485.
DOI |
| [1] | ZENG Wanying, GENG Hongwei, CHENG Yukun, LI Sizhong, QIAN Songting, GAO Weishi, ZHANG Liming. Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance during the rapid growth stage of sugar beet cultivars [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2140-2151. |
| [2] | XU Maomao, GAO Jie, LI Junming, LI Xin, LIU Lei, PAN Feng. Population diversity analysis of 20 commercial tomato cultivars [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2191-2196. |
| [3] | MIAO Yu, CHEN Cuixia, MA Yanming, XING Guofang, DONG Yusheng, CHEN Zhijun, WANG Xian, XIANG Li. Genetic diversity analysis of phenotypic traits of 276 Central Asian barley germplasm resources [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1888-1895. |
| [4] | YANG Lu, WANG Na, FAN Shaoli, CHENG Ping, LI Hong, WANG Yangdong. Analysis of phenotypic trait variation characteristics of Morus nigra L.germplasm resources [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(5): 1172-1181. |
| [5] | WANG Fan, LI Yushan, WANG Wei, DENG Chaohong, ZHAO Lianjia, MA Yue, XIAO Jing, ZHUANG Hongmei, Xu Hongjun. Genetic diversity analysis of major nutritional growth traits in 74 turnip germplasm resources [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2601-2613. |
| [6] | LI Chao, YANG Ying, ZHENG Heyun, YANG Jianli, CHEN Wei, YANG Mi, SUN Yuping. Genetic diversity and population structure analysis of melon germplasm resources in Xinjiang based on SSR fluorescence markers [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2614-2625. |
| [7] | Wang Tianling, Hou Xianfei, Shi Junjie, Sun Quanxi, Jia Donghai, Gu Yuanguo, Shan Shihua, Miao Haocui, Li Qiang. Genetic diversity analysis of 67 creeping peanut germplasm resources [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(1): 42-54. |
| [8] | LUO Ying, Nurziya Yalimaimaiti, JIA Wenjie, LIU Jieying, JIA Peisong. Identification and genetic diversity of wild Macrolepiota in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(10): 2501-2508. |
| [9] | YAO Yingying, LI Jiahui, LI Haiying, WU Yingping, ZHAO Xiaoyu, ZHOU Jun, ZHAO Quanzhuang, LI Zongfu. Analysis of genetic diversity of Yemili chicken by microsatellite [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(10): 2574-2582. |
| [10] | ZHAO Shuangyin, WANG Weiran, YAN Xuexue, Bimairemu Abuduaihaiti, DONG Jie, Tuerxon Tuerhong, Alip Aierxi. Analysis of Quality Traits and Genetic Diversity of 120 Cotton Germplasm Resources [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(1): 17-24. |
| [11] | LI Yueyan, LI Yushan, WANG Fan, GUO Yawen, WANG Feiyan, GAO Jie, SONG Yu. Genetic Diversity and Cluster Analysis of Tomato Fruit Characters in Different Varieties [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(9): 2147-2157. |
| [12] | YUAN Lei, JI Xuehua, ZHANG Guoru, SHI Linyuan, GUO Heyao, TANG Yaping, YANG Tao, YANG Shengbao. Genetic Diversity and Cluster Analysis on the Main Fruit Characters of 52 Accessions of Capsicum [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(8): 1935-1944. |
| [13] | WU Qiaoyu, HE Tianjiu. Morphological and ISSR Analysis of Purple Sweet Potato Resources [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(7): 1625-1631. |
| [14] | YANG Yanlong, MA Jun, SHI Weijun. Analysis of Genetic Diversity of Phenotypic Characters of Upland Cotton Germplasm Resources Imported [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(2): 310-319. |
| [15] | Rebiya Yusun, Wumaier Kurban, ZHANG Zhe, Maimaiti Moming, AI Xiantao. Analysis of Genetic Diversity of Main Characters in 288 Upland Cotton Germplasm Resources [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(12): 2879-2887. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 75
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 329
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||