

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (3): 739-747.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.03.024
• Plant Protection·Soil Fertilizer·Microbes • Previous Articles Next Articles
FU Pengyu1,2,3( ), LIANG Meng1, LI Chenhua1,2(
), LIANG Meng1, LI Chenhua1,2( )
)
Received:2024-09-10
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-05-14
Correspondence author:
LI Chenhua
Supported by:通讯作者:
李晨华
作者简介:傅鹏宇(1997-),男,重庆江津人,硕士研究生,研究方向为土壤微生物生态,(E-mail) fupengyu21@mails.ucas.ac.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
FU Pengyu, LIANG Meng, LI Chenhua. Effects of desert reclamation and fertilization on soil organic carbon storage and microbial community characteristics[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(3): 739-747.
傅鹏宇, 梁萌, 李晨华. 荒漠开垦与施肥对土壤有机碳储量与微生物群落特征的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(3): 739-747.
| 名称 Name | 引物全称 Primer name | 片段长度 Length of amplicons | 引物序列 Primer sequences |
|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌 Bacteria | 16S V3-V4 (338-806) | 469bp | 上游:ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG 下游:GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT |
| 古菌 Archaea | 古菌16S V3-V4 | 572bp | 上游:ACGGGGYGCAGCAGGCGCGA 下游:GGACTACVSGGGTATCTAAT |
| 真菌 Fungi | ITS1 | 98bp | 上游:CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA 下游:TGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC |
| 固氮菌 Azotobacter | nifH | 400bp | 上游:AAAGGYGGWATCGGYAARTCCACCAC 下游:TTGTTSGCSGCRTACATSGCCATCAT |
| 氨氧化细菌 AOB | AOB amoA | 490bp | 上游:GGGGTTTCTACTGGTGGT 下游:CCCCTCKGSAAAGCCTTCTTC |
| 氨氧化古菌 AOA | AOA amoA | 635bp | 上游:STAATGGTCTGGCTTAGACG 下游:GCGGCCATCCATCTGTATGT |
Tab.1 Fluorescent real-time quantitative PCR amplification primers
| 名称 Name | 引物全称 Primer name | 片段长度 Length of amplicons | 引物序列 Primer sequences |
|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌 Bacteria | 16S V3-V4 (338-806) | 469bp | 上游:ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG 下游:GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT |
| 古菌 Archaea | 古菌16S V3-V4 | 572bp | 上游:ACGGGGYGCAGCAGGCGCGA 下游:GGACTACVSGGGTATCTAAT |
| 真菌 Fungi | ITS1 | 98bp | 上游:CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA 下游:TGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC |
| 固氮菌 Azotobacter | nifH | 400bp | 上游:AAAGGYGGWATCGGYAARTCCACCAC 下游:TTGTTSGCSGCRTACATSGCCATCAT |
| 氨氧化细菌 AOB | AOB amoA | 490bp | 上游:GGGGTTTCTACTGGTGGT 下游:CCCCTCKGSAAAGCCTTCTTC |
| 氨氧化古菌 AOA | AOA amoA | 635bp | 上游:STAATGGTCTGGCTTAGACG 下游:GCGGCCATCCATCTGTATGT |
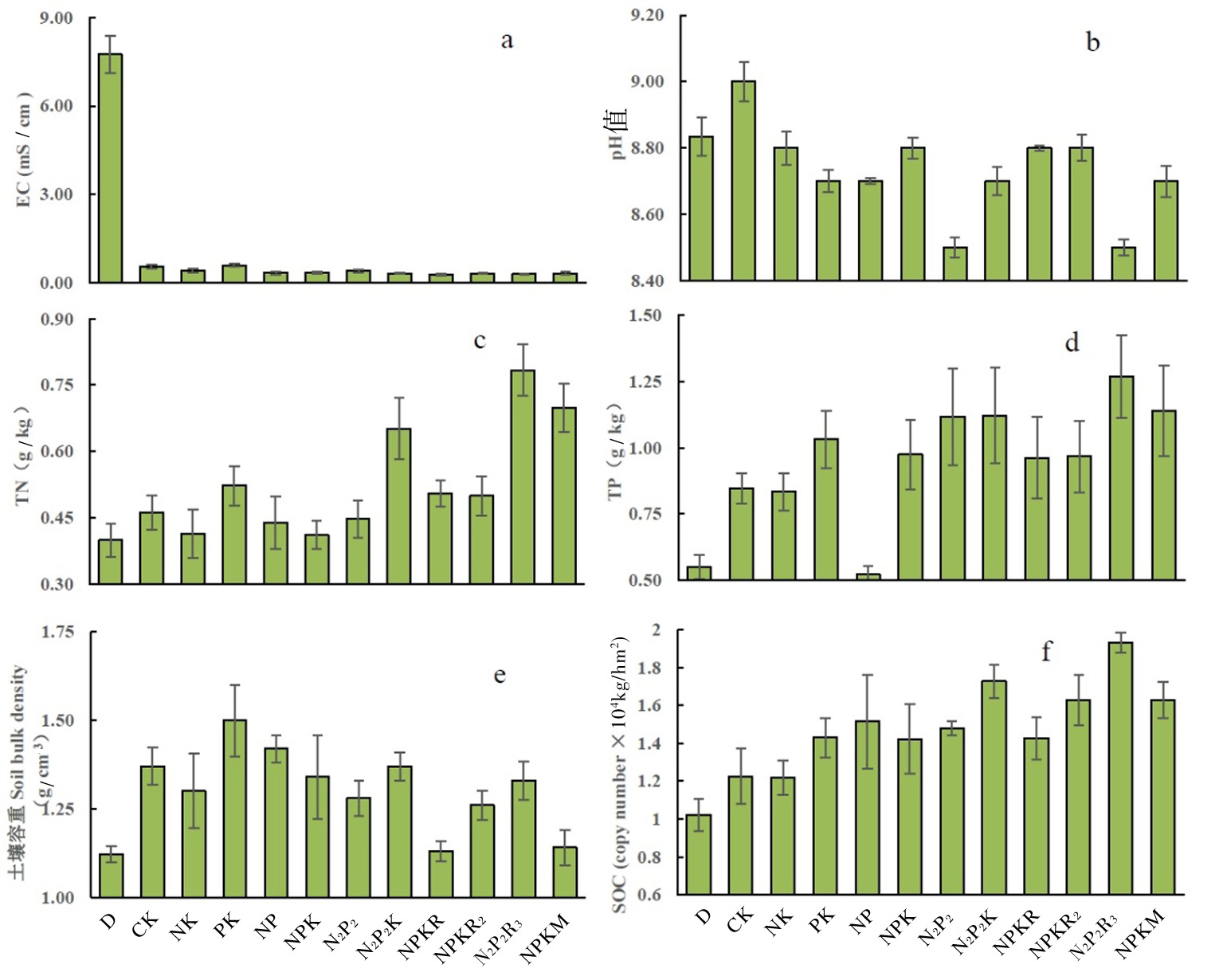
Fig.1 Changes of desert reclamation and fertilization on soil physical and chemical properties and organic carbon storage Notes: D, native desert soil; EC, electrical conductivity; TN, soil total nitrogen; TP, soil total phosphorus; SOC, soil organic carbon storage
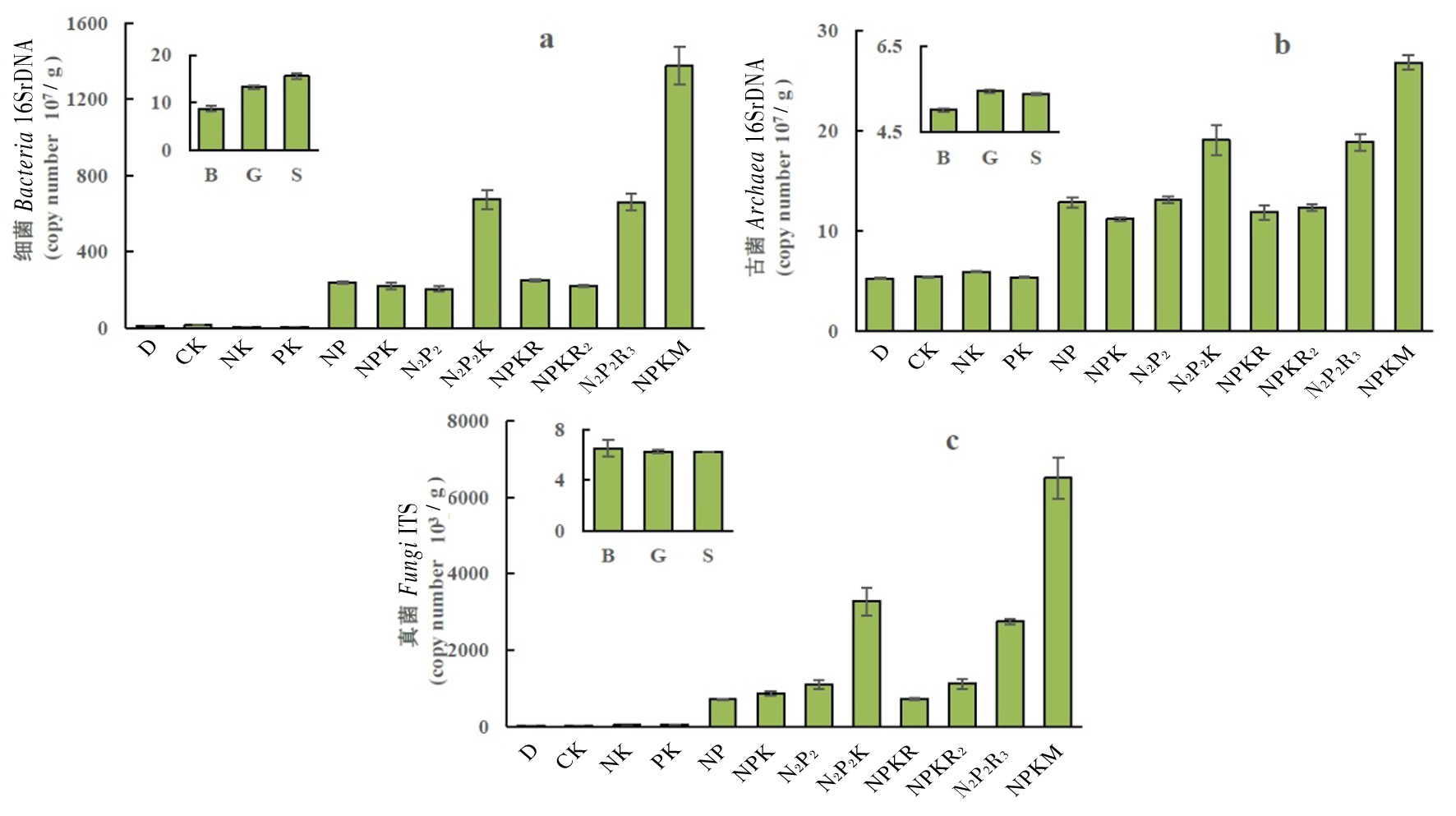
Fig.2 Changes of desert reclamation and fertilization on soil bacterial (a), archaea (b) and fungal (c) abundance Notes: D, native desert soil; B, desert bare land; G, soil under herbaceous cover; S, soil under shrub cover,the same as below
| 真菌/细菌 Fungi/Bacteria | 真菌/古菌 Fungi/Archaea | 细菌/古菌 Bacteria /Archaea | |
|---|---|---|---|
| B | 7.51×10-5±0.27×1 | 1.27×10-4±0.060×1 | 1.70±0.17a |
| G | 4.74×10-5±0.27×1 | 1.15×10-4±0.005×1 | 2.42±0.15b |
| S | 4.01×10-5±0.02×1 | 1.16×10-4±0.004×1 | 2.90±0.01c |
Tab.2 Soil microbial community structure of bare soil and the soil under different canopies
| 真菌/细菌 Fungi/Bacteria | 真菌/古菌 Fungi/Archaea | 细菌/古菌 Bacteria /Archaea | |
|---|---|---|---|
| B | 7.51×10-5±0.27×1 | 1.27×10-4±0.060×1 | 1.70±0.17a |
| G | 4.74×10-5±0.27×1 | 1.15×10-4±0.005×1 | 2.42±0.15b |
| S | 4.01×10-5±0.02×1 | 1.16×10-4±0.004×1 | 2.90±0.01c |
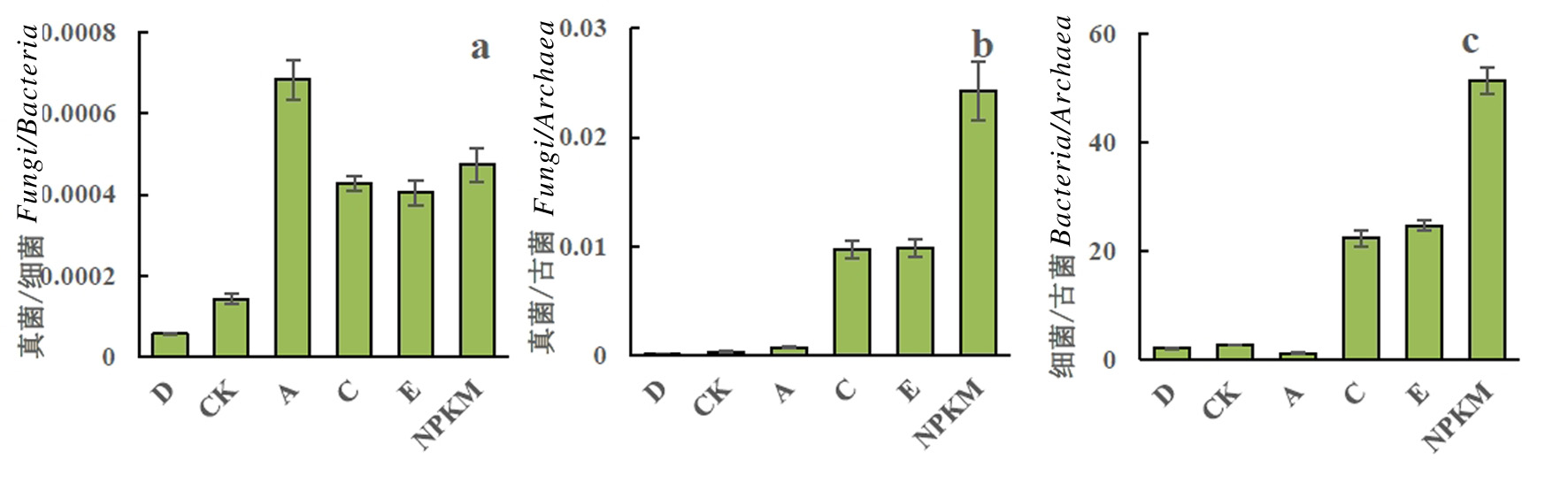
Fig.4 Changes of desert reclamation and fertilization on soil microbial community structure Notes: D, native desert soil; A, fertilization method lacking N or P (NK, PK); C: single application of chemical fertilizer (except NK and PK); E: chemical fertilizer combined with straw
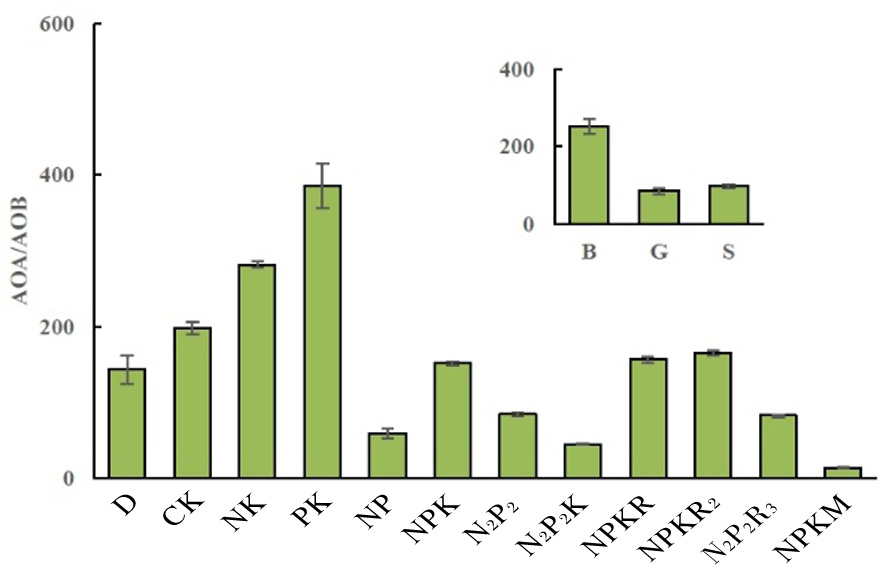
Fig.5 Changes of desert reclamation and fertilization on soil AOA/AOB ratio Notes: D, native desert soil; B, desert bare land; G, soil under herbaceous cover; S, soil under shrub cover
| nifH | AOA amoA | AOB amoA | 细菌16S | ITS1 | 古菌16S | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 相关系数 | 0.597 9 | -0.010 9 | 0.365 0 | 0.531 1 | 0.513 4 | 0.621 9 |
| P | 0.018 6* | 0.969 2 | 0.181 0 | 0.041 7* | 0.050 3 | 0.013 3* |
Tab.3 Correlations analysis between desert soil organic carbon storage and microbial abundance
| nifH | AOA amoA | AOB amoA | 细菌16S | ITS1 | 古菌16S | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 相关系数 | 0.597 9 | -0.010 9 | 0.365 0 | 0.531 1 | 0.513 4 | 0.621 9 |
| P | 0.018 6* | 0.969 2 | 0.181 0 | 0.041 7* | 0.050 3 | 0.013 3* |
| [1] | Hari M, Tyagi B. Terrestrial carbon cycle: tipping edge of climate change between the atmosphere and biosphere ecosystems[J]. Environmental Science: Atmospheres, 2022, 2(5): 867-890. |
| [2] | 杨元合, 石岳, 孙文娟, 等. 中国及全球陆地生态系统碳源汇特征及其对碳中和的贡献[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2022, 52(4): 534-574. |
| YANG Yuanhe, SHI Yue, SUN Wenjuan, et al. Terrestrial carbon sinks in China and around the world and their contribution to carbon neutrality[J]. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 2022, 52(4): 534-574. | |
| [3] |
Crowther T W, van den Hoogen J, Wan J, et al. The global soil community and its influence on biogeochemistry[J]. Science, 2019, 365(6455): 772-781.
DOI |
| [4] | Guillaume T, Makowski D, Libohova Z, et al. Soil organic carbon saturation in cropland-grassland systems: storage potential and soil quality[J]. Geoderma, 2022, 406: 115529. |
| [5] | 周正虎, 刘琳, 侯磊. 土壤有机碳的稳定和形成: 机制和模型[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2022, 44(10): 11-22. |
| ZHOU Zhenghu, LIU Lin, HOU Lei. Soil organic carbon stabilization and formation: mechanism and model[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2022, 44(10): 11-22. | |
| [6] | Malik A A, Martiny J B H, Brodie E L, et al. Defining trait-based microbial strategies with consequences for soil carbon cycling under climate change[J]. The ISME Journal, 2020, 14(1): 1-9. |
| [7] |
Lal R. Carbon cycling in global drylands[J]. Current Climate Change Reports, 2019, 5(3): 221-232.
DOI |
| [8] | Liu J, Wang C K, Guo Z Y, et al. The effects of climate on soil microbial diversity shift after intensive agriculture in arid and semiarid regions[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 821: 153075. |
| [9] |
Neilson J W, Quade J, Ortiz M, et al. Life at the hyperarid margin: novel bacterial diversity in arid soils of the Atacama desert, Chile[J]. Extremophiles, 2012, 16(3): 553-566.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Köberl M, Müller H, Ramadan E M, et al. Desert farming benefits from microbial potential in arid soils and promotes diversity and plant health[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(9): e24452. |
| [11] | Li X Y, Xiao D N, He X Y, et al. Factors associated with farmland area changes in arid regions: a case study of the Shiyang river basin, Northwestern China[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 2007, 5(3): 139-144. |
| [12] | Wang T, Xue X, Zhou L, et al. Combating aeolian desertification in Northern China[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 2015, 26(2): 118-132. |
| [13] | Brockett B F T, Prescott C E, Grayston S J. Soil moisture is the major factor influencing microbial community structure and enzyme activities across seven biogeoclimatic zones in western Canada[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2012, 44(1): 9-20. |
| [14] | 迟美静. 黑土开垦种稻土壤团聚体及其组分有机碳的变化特征[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2019. |
| CHI Meijing. Change characteristics of organic carbon in soil aggregates and aggregate fractions of reclamation for rice in Mollisol[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| [15] | Łabęda D, Kondras M. Influence of forest management on soil organic carbon stocks[J]. Soil Science Annual, 2020: 165-173. |
| [16] | 黄科朝, 沈育伊, 徐广平, 等. 垦殖对桂林会仙喀斯特湿地土壤养分与微生物活性的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(4): 1813-1823. |
| HUANG Kechao, SHEN Yuyi, XU Guangping, et al. Effects of reclamation on soil nutrients and microbial activities in the Huixian Karst wetland in Guilin[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(4): 1813-1823. | |
| [17] | He X Y, Su Y R, Liang Y M, et al. Land reclamation and short-term cultivation change soil microbial communities and bacterial metabolic profiles[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2012, 92(5): 1103-1111. |
| [18] | Li C H, Li Y, Ma J, et al. Microbial community variation and its relationship with soil carbon accumulation during long-term oasis formation[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2021, 168: 104126. |
| [19] | Wang Z Q. To afforest the desert with the technology of peat composed of rotten mosses and the sustainable development of the oases[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2002, 45(1): 87-90. |
| [20] | 李彦, 许皓. 梭梭对降水的响应与适应机制——生理、个体与群落水平碳水平衡的整合研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2008, 31(3): 313-323. |
| LI Yan, XU Hao. Water and carbon balances of Haloxylon ammodendron: intergated study at physiological, plant Abd community level[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2008, 31(3): 313-323. | |
| [21] | 李晨华, 李彦, 唐立松, 等. 盐化灰漠土开垦前后碳存贮与碳释放的分层特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2010, 27(3): 385-391. |
| LI Chenhua, LI Yan, TANG Lisong, et al. Layered characters of organic carbon storage and release in salinized gray desert soil before and after reclamation[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2010, 27(3): 385-391. | |
| [22] | Zhu H, Zhao C Y, Li J, et al. Analysis of impact factors on scrubland soil respiration in the southern Gurbantunggut Desert, central Asia[J]. Environmental Geology, 2008, 54(7): 1403-1409. |
| [23] | Li C H, Li Y, Tang L S. Soil organic carbon stock and carbon efflux in deep soils of desert and oasis[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2010, 60(3): 549-557. |
| [24] | 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2000. |
| LU Rukun. Methods for agrochemical analysis of soils[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000. | |
| [25] | 宋亚娜, 陈在杰, 林智敏. 水稻生育期内红壤稻田氨氧化微生物数量和硝化势的变化[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2010, 18(5): 954-958. |
| SONG Yana, CHEN Zaijie, LIN Zhimin. Abundance of ammonia-oxidizer and potential nitrification rate of quaternary red-clay paddy soil during rice growth[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2010, 18(5): 954-958. | |
| [26] |
Russell A E, Cambardella C A, Laird D A, et al. Nitrogen fertilizer effffects on soil carbon balances in midwestern U.S. agricultural systems[J]. Ecological Applications, 2009, 19(5): 1102-1113.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Lugato E, Berti A, Giardini L. Soil organic carbon (SOC) dynamics with and without residue incorporation in relation to different nitrogen fertilization rates[J]. Geoderma, 2006, 135: 135-321. |
| [28] | 张玉, 吴福忠, 艾灵, 等. 凋落物输入对土壤可溶性有机碳的影响[J/OL]. 生态学杂志, 2023 (2023-04-10). |
| ZHANG Yu, WU Fuzhong, AI Ling, et al. Litter input effect on dissolved organic carbon in soils[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2023 (2023-04-10). | |
| [29] |
Liang C, Schimel J P, Jastrow J D. The importance of anabolism in microbial control over soil carbon storage[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2017, 2: 17105.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Chapin F S III, Matson P A, Vitousek P M. Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology[M]. New York: NYSpringer New York, 2011 |
| [31] | Fierer N, Grandy A S, Six J, et al. Searching for unifying principles in soil ecology[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2009, 41(11): 2249-2256. |
| [32] | Strickland M S, Rousk J. Considering fungal: bacterial dominance in soils-Methods, controls, and ecosystem implications[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2010, 42(9): 1385-1395. |
| [33] | Bailey V L, Smith J L, Bolton H. Fungal-to-bacterial ratios in soils investigated for enhanced C sequestration[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2002, 34(7): 997-1007. |
| [34] | Six J, Frey S D, Thiet R K, et al. Bacterial and fungal contributions to carbon sequestration in agroecosystems[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2006, 70(2): 555-569. |
| [35] | Fan F L, Yin C, Tang Y J, et al. Probing potential microbial coupling of carbon and nitrogen cycling during decomposition of maize residue by 13C-DNA-SIP[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2014, 70: 12-21. |
| [1] | ZENG Wanqi, HAN Duohong, FENG Junren. Physiological study of frost damage on flower organs of nine apricot varieties in arid desert area [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2223-2229. |
| [2] | SUN Yao, ZHONG Wen, LI Yibo. Dominant insect pollinators and their biological characteristics of pollination of Tamarix ramosissima in the southeast margin of Tarim basin [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1497-1504. |
| [3] | GENG Meiju, WANG Xinhui, LIU Xiaoying, LYU Pei. Effects of sealing on fungal communities in desert grasslands [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(5): 1250-1258. |
| [4] | WANG Lijun, SUN Beibei, WANG Chunyan, XIA Zhanfeng, MA Guocai. Isolation and nitrogen-fixing activity detection of bacteria from four desert plants [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2742-2749. |
| [5] | SHEN Yuyang, WANG Xian, CHEN Li, GUO Xiaoling, MIAO Yu, DONG Yusheng, CHEN Zhijun, FANG Furong, XIANG Li, GAO Haifeng. Evaluation of chemical efficacy of broadleaf weed control in barley fields in the desert oasis area of Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(1): 184-189. |
| [6] | ZHU Yujie, LIN Ling, TANG Guangmu, ZHANG Yunshu, XU Wanli. Effect of modified cotton straw charcoal on ammonia volatilization characteristics of nitrogen fertilizer in grey desert soils of Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2128-2137. |
| [7] | ZHOU Shijie, DONG Yiqiang, Asitaiken Julihaiti, NIE Tingting, JIANG Anjing, AN Shazhou. Quantitative characteristics and diversity of sagebrush desert plant communities on the northern slope of Tianshan Mountains [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2298-2305. |
| [8] | WANG Yan, WU Xingbao, QIN Xinhui, ZHANG Yongjiu, YANG Li, ZHAO Halin. Ecological stoichiometry of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in farmland salinization in arid oasis [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1996-2005. |
| [9] | XU Jing, SHI Shubing, QIN Xiaogang, ZHU Jun. Walnut forests intercropping saffron on Its soil microorganism's dynamic change in quantity study [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 2022-2027. |
| [10] | LI Zhiqiang, CHEN Yudong, LYU Guanghui, WANG Jinlong, JIANG Lamei, WANG Hengfang, LI Hanpeng, ZHANG Lei. Soil water-salt response characteristics and ecological strategies for functional traits of desert herbaceous plants [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 2038-2045. |
| [11] | FEI Cheng, DONG Yiqiang, AN Shazhou. Study on desert community composition, interspecific association and correlation in northern Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 2055-2065. |
| [12] | WANG Xihe, LIU Hua, FENG Gu, YANG Jinyu, WANG Yanping, HUANG Jian. Balance and Activation of AP in Dry Area Grey Desert Soil under Long-term Fertilization [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(1): 197-205. |
| [13] | Abdukeyoumu Abudurezike, Tuerson Tuerhong, Gulimira Aikebaier, Ayixiamu Shawuer. Effects of Different Drip Irrigation Rates on Quality Components of Cultivated Glycyrrhiza uralensis root in Desert Area [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(9): 2224-2231. |
| [14] | Abdukeyoumu Abudurezike, Tuerson Tuerhong, Gulimira Aikebaier, ZHANG Yan, Ayixiamu Shawuer. Effects of Diffeent Drip Irrigation RateAmounts on Growth of Glycyrrhiza uralensis during Seedling Stage in Desert Areas [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(8): 1945-1955. |
| [15] | HAN Haixia, YOU Lin, ZHONG Zhiming, WANG Na, LI Shuang. Study on the Effects of Different Temperatures on Phenylethanol Glycosides duringthe Preparation of Cistanche deserticola Extractum and the Antioxidant Activities of the Extractum [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(8): 1975-1983. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 15
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 42
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||