

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (5): 1250-1258.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.05.023
• Prataculture·Animal Husbandry Veterinarian • Previous Articles Next Articles
GENG Meiju1,2( ), WANG Xinhui1,2(
), WANG Xinhui1,2( ), LIU Xiaoying1,2, LYU Pei1,2
), LIU Xiaoying1,2, LYU Pei1,2
Received:2023-10-11
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-07-09
Correspondence author:
WANG Xinhui
Supported by:
耿美菊1,2( ), 王新绘1,2(
), 王新绘1,2( ), 刘晓颖1,2, 吕佩1,2
), 刘晓颖1,2, 吕佩1,2
通讯作者:
王新绘
作者简介:耿美菊(1998-),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为土壤微生物,(E-mail)1743270502@qq.com
基金资助: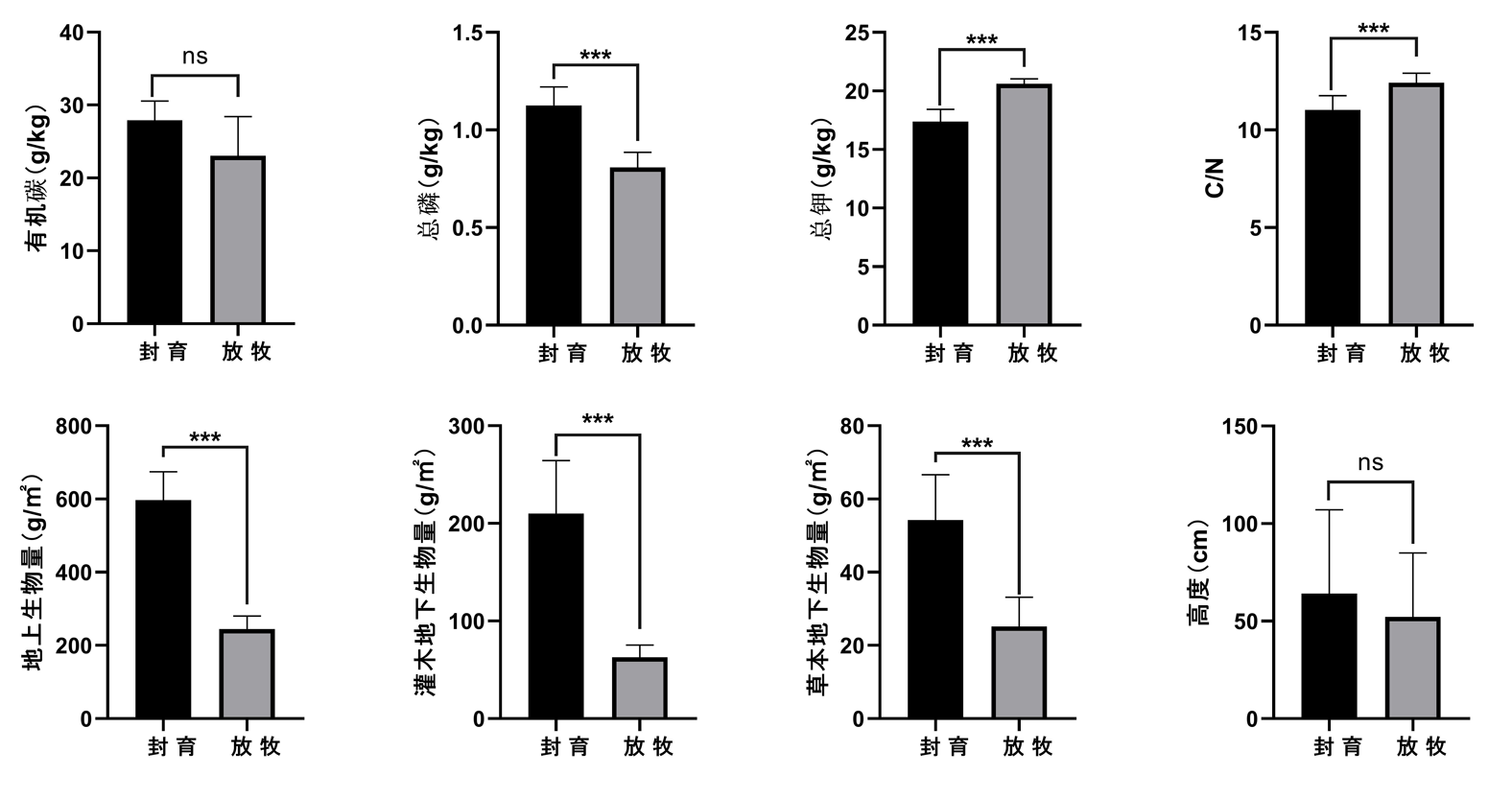
Fig.1 Changes in soil physicochemical properties and plant biomass during the sealing process Note:where P < 0.001 is marked as ***, P < 0.01 is marked as **, P < 0.05 is marked as *, and ns marked as insignificant
| 指标 Indexes | 封育均值 Mean enclosed population | 封育标准差 Sealing standard deviation | 放牧均值 Grazing average | 放牧标准差 Grazing standard deviation | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ace | 561.26 | 119.34 | 359.65 | 61.03 | 0.010 |
| Sobs | 538.80 | 107.93 | 353.80 | 61.64 | 0.010 |
| Chao | 567.20 | 117.75 | 361.40 | 60.46 | 0.008 |
| Simpson | 0.0760 | 0.0271 | 0.0604 | 0.059 | 0.606 |
| Shannon | 3.8882 | 0.3389 | 4.1200 | 0.570 | 0.457 |
| Coverage | 0.9994 | 0.0003 | 0.9998 | 0.000 | 0.011 |
Tab.1 Changes in the fungal alpha diversity index during the sealing process
| 指标 Indexes | 封育均值 Mean enclosed population | 封育标准差 Sealing standard deviation | 放牧均值 Grazing average | 放牧标准差 Grazing standard deviation | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ace | 561.26 | 119.34 | 359.65 | 61.03 | 0.010 |
| Sobs | 538.80 | 107.93 | 353.80 | 61.64 | 0.010 |
| Chao | 567.20 | 117.75 | 361.40 | 60.46 | 0.008 |
| Simpson | 0.0760 | 0.0271 | 0.0604 | 0.059 | 0.606 |
| Shannon | 3.8882 | 0.3389 | 4.1200 | 0.570 | 0.457 |
| Coverage | 0.9994 | 0.0003 | 0.9998 | 0.000 | 0.011 |
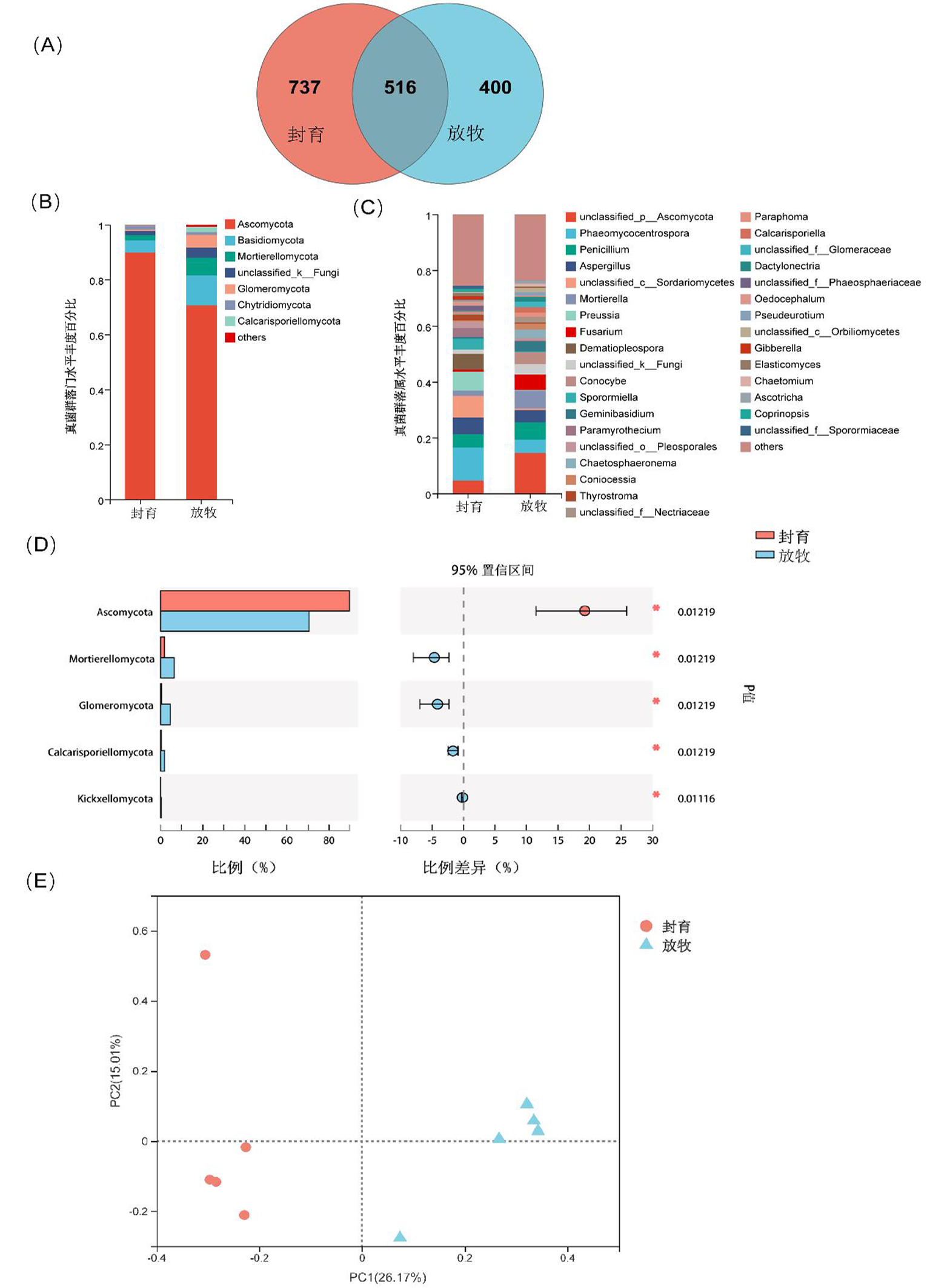
Fig.2 Distribution of OTUs of sequestered fungi Note:Study area(A), the composition of phyla (B) and genera (C), comparison of differential fungi (D), and fungal β diversity (E)

Fig.3 Redundancy analysis of the correlation between phylum level fungal communities and physicochemical factors Note: Total phosphorus (TP), total potassium (TK), organic carbon (SOC), aboveground biomass, shrub root biomass, herbal root biomass;(A), soil physicochemical properties (B), differential metabolites (C), and differential fungi during sealing(where P < 0.001 is marked as ***, P < 0.01 is marked as **, and P < 0.05 is marked as *)
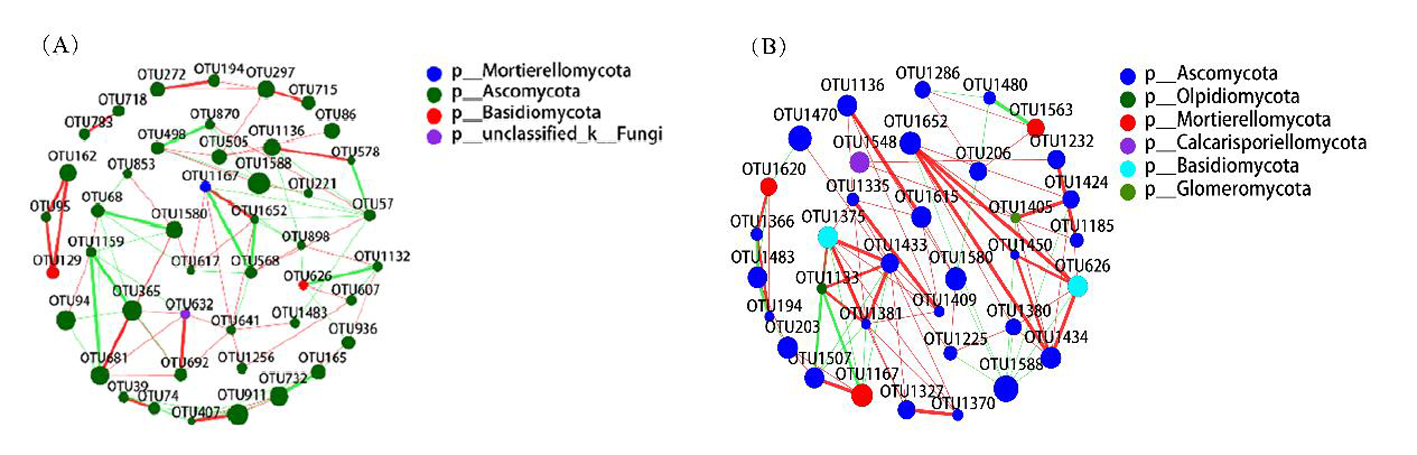
Fig.4 Network diagram of the internal linkage between the fungal communities of sequestration (A) and grazing (B) Note:red represents positive correlation, green represents negative correlation
| [1] | Dlamini P, Chivenge P, Chaplot V. Overgrazing decreases soil organic carbon stocks the most under dry climates and low soil pH: a meta-analysis shows[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2016, 221: 258-269. |
| [2] | Kang B, Bowatte S, Hou F. Soil microbial communities and their relationships to soil properties at different depths in an alpine meadow and desert grassland in the Qilian mountain range of China[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 2021, 184: 104316. |
| [3] | Liu S B, Zamanian K, Schleuss P M, et al. Degradation of Tibetan grasslands: consequences for carbon and nutrient cycles[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2018, 252: 93-104. |
| [4] | Gao X X, Dong S K, Xu Y D, et al. Resilience of revegetated grassland for restoring severely degraded alpine meadows is driven by plant and soil quality along recovery time: a case study from the Three-river Headwater Area of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2019, 279: 169-177. |
| [5] |
Huhe, Chen X J, Hou F J, et al. Bacterial and fungal community structures in Loess Plateau grasslands with different grazing intensities[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 606.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Cheng J M, Jing G H, Wei L, et al. Long-term grazing exclusion effects on vegetation characteristics, soil properties and bacterial communities in the semi-arid grasslands of China[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2016, 97: 170-178. |
| [7] | Zhang C, Liu G B, Song Z L, et al. Interactions of soil bacteria and fungi with plants during long-term grazing exclusion in semiarid grasslands[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2018, 124: 47-58. |
| [8] | Yin Y L, Wang Y Q, Li S X, et al. Soil microbial character response to plant community variation after grazing prohibition for 10years in a Qinghai-Tibetan alpine meadow[J]. Plant and Soil, 2021, 458(1): 175-189. |
| [9] |
单贵莲, 陈功, 宁发, 等. 典型草原恢复演替过程中土壤微生物及酶活性动态变化研究[J]. 草地学报, 2012, 20(2): 292-297.
DOI |
|
SHAN Guilian, CHEN Gong, NING Fa, et al. Dynamics of soil microorganism and enzyme activity in typical steppe of restoration succession process[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2012, 20(2): 292-297.
DOI |
|
| [10] | Sun S, Li S, Avera B N, et al. Soil bacterial and fungal communities show distinct recovery patterns during forest ecosystem restoration[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2017, 83(14): e00966-e00917. |
| [11] |
Li H L, Ostermann A, Karunarathna S C, et al. The importance of plot size and the number of sampling seasons on capturing macrofungal species richness[J]. Fungal Biology, 2018, 122(7): 692-700.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Ladwig L M, Bell-Dereske L P, Bell K C, et al. Soil fungal composition changes with shrub encroachment in the northern Chihuahuan Desert[J]. Fungal Ecology, 2021, 53: 101096. |
| [13] |
Wu D, Zhang M M, Peng M, et al. Variations in soil functional fungal community structure associated with pure and mixed plantations in typical temperate forests of China[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 1636.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Schulz S, Brankatschk R, Dümig A, et al. The role of microorganisms at different stages of ecosystem development for soil formation[J]. Biogeosciences, 2013, 10(6): 3983-3996. |
| [15] |
Buyer J S, Vinyard B, Maul J, et al. Combined extraction method for metabolomic and PLFA analysis of soil[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2019, 135: 129-136.
DOI |
| [16] | Bi B Y, Wang K Y, Zhang H, et al. Plants use rhizosphere metabolites to regulate soil microbial diversity[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 2021, 32(18): 5267-5280. |
| [17] |
Jones O A H, Sdepanian S, Lofts S, et al. Metabolomic analysis of soil communities can be used for pollution assessment[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2014, 33(1): 61-64.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Li Y X, Laborda P, Xie X L, et al. Spartina alterniflora invasion alters soil microbial metabolism in coastal wetland of China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2020, 245: 106982. |
| [19] | Xu M P, Li W J, Wang J Y, et al. Soil ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals microbial phosphorus limitation after vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau, China[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 815: 152918. |
| [20] | Wang X, Cui Y X, Zhang X C, et al. A novel extracellular enzyme stoichiometry method to evaluate soil heavy metal contamination: evidence derived from microbial metabolic limitation[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 738: 139709. |
| [21] | Coince A, Caël O, Bach C, et al. Below-ground fine-scale distribution and soil versus fine root detection of fungal and soil oomycete communities in a French beech forest[J]. Fungal Ecology, 2013, 6(3): 223-235. |
| [22] | Liu J J, Sui Y Y, Yu Z H, et al. Soil carbon content drives the biogeographical distribution of fungal communities in the black soil zone of Northeast China[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2015, 83: 29-39. |
| [23] |
Lladó S, López-Mondéjar R, Baldrian P. Drivers of microbial community structure in forest soils[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(10): 4331-4338.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Chen L, Xiang W H, Wu H L, et al. Contrasting patterns and drivers of soil fungal communities in subtropical deciduous and evergreen broadleaved forests[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(13): 5421-5433.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Schappe T, Albornoz F E, Turner B L, et al. The role of soil chemistry and plant neighbourhoods in structuring fungal communities in three Panamanian rainforests[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2017, 105(3): 569-579. |
| [26] | 向雪梅, 德科加, 张琳, 等. 氮素添加下短期内高寒草甸生物量与养分间的关系[J]. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(1): 53-61. |
| XIANG Xuemei, DE Kejia, ZHANG Lin, et al. Relationship between biomass and nutrients of alpine meadows in the short term under nitrogen addition[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(1): 53-61. | |
| [27] |
刘文兰, 师尚礼, 田福平, 等. 紫花苜蓿生物量空间层次分布与叶片C、N、P化学计量特征对P添加的响应[J]. 草地学报, 2017, 25(2): 322-329.
DOI |
|
LIU Wenlan, SHI Shangli, TIAN Fuping, et al. Spatial distribution of alfalfa biomass and response of leaf C, N, P ecological stoichiometry to P addition[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2017, 25(2): 322-329.
DOI |
|
| [28] | Toju H, Kishida O, Katayama N, et al. Networks depicting the fine-scale co-occurrences of fungi in soil horizons[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(11): e0165987. |
| [29] |
张彬, 李邵宇, 古琛, 等. 内蒙古荒漠草原4种优势植物生物量分配对不同放牧强度的响应[J]. 草地学报, 2022, 30(12): 3355-3363.
DOI |
|
ZHANG Bin, LI Shaoyu, GU Chen, et al. Biomass allocation of four dominant plant species in Inner Mongolia Desert grasslands in response to different grazing intensities[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(12): 3355-3363.
DOI |
|
| [30] | Qiu L P, Wei X R, Zhang X C, et al. Ecosystem carbon and nitrogen accumulation after grazing exclusion in semiarid grassland[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(1): e55433. |
| [31] | Wang Z, Ding Y, Jin K, et al. Soil bacterial and fungal communities are linked with plant functional types and soil properties under different grazing intensities[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2022, 73(1): e13195. |
| [32] |
Cassman N A, Leite M F A, Pan Y, et al. Plant and soil fungal but not soil bacterial communities are linked in long-term fertilized grassland[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 23680.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Xiao C C, Ran S J, Huang Z W, et al. Bacterial diversity and community structure of supragingival plaques in adults with dental health or caries revealed by 16S pyrosequencing[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2016, 7: 1145.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | Chao Y Q, Liu W S, Chen Y M, et al. Structure, variation, and co-occurrence of soil microbial communities in abandoned sites of a rare earth elements mine[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(21): 11481-11490. |
| [35] | Wang J X, Gao J, Zhang H Q, et al. Changes in rhizosphere soil fungal communities ofPinus tabuliformisplantations at different development stages on the Loess Plateau[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(12): 6753. |
| [36] |
Hartmann M, Brunner I, Hagedorn F, et al. A decade of irrigation transforms the soil microbiome of a semi-arid pine forest[J]. Molecular Ecology, 2017, 26(4): 1190-1206.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Wang Z, Zhang Q, Staley C, et al. Impact of long-term grazing exclusion on soil microbial community composition and nutrient availability[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2019, 55(2): 121-134.
DOI |
| [38] | 程红岩. 旱作农田土壤微生物群落及代谢产物对磷肥管理的响应[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2022. |
| CHENG Hongyan. Response of Soil Microbial Communities and Metabolites to Phosphorus Fertilizer Management in Dryland Farmland[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2022. | |
| [39] | Cui J L, Gong Y, Vijayakumar V, et al. Correlation in chemical metabolome and endophytic mycobiome in Cynomorium songaricum from different desert locations in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2019, 67(13): 3554-3564. |
| [40] | Yang X, Lai J L, Zhang Y, et al. Microbial community structure and metabolome profiling characteristics of soil contaminated by TNT, RDX, and HMX[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 285: 117478. |
| [41] | Csorba C, RodiĈ N, Zhao Y Y, et al. Metabolite production inAlkanna tinctoria links plant development with the recruitment of individual members of microbiome thriving at the root-soil interface[J]. mSystems, 2022, 7(5): e0045122. |
| [42] | Cheng H Y, Yuan M S, Tang L, et al. Integrated microbiology and metabolomics analysis reveal responses of soil microorganisms and metabolic functions to phosphorus fertilizer on semiarid farm[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 817: 152878. |
| [1] | GUO Xiaowen, DU Siyao, WANG Fangxia, YE Yang, YANG Maoqi, MIN Wei. Effects of Long-Term Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Bacteria and Fungi Community Structure in Cotton Field [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(12): 2909-2923. |
| [2] | GU Mei-ying, XU Wan-li, ZHANG Zhi-dong, TANG Guang-mu, LIU Hong-liang, LI Zhi-qiang, LIU Xiao-wei, PU Sheng-hai, FENG Lei, ZHANG Ji-feng. Relationships between Fungi Diversity, Physicochemical Properties and Verticillium Wilt in Continuous Cropping Cotton Rhizosphere Soil with Cotton Stover Biochar [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(9): 1698-1709. |
| [3] | JIN Gui-li;HE Long;LIANG Na;BAO Wen-jing. The Community Dynamic Change of Degraded Seriphidium transiliense in Desert Grassland duing the Growing Season [J]. , 2014, 51(9): 1754-1759. |
| [4] | XIE Yun;FAN Yan-min;WU Hong-qi;GUAN Guang-yu;CHAI Da-pan;HE Jing. Effects of Enclosure on Soil Quality in Mountain Desert Grassland [J]. , 2014, 51(9): 1699-1705. |
| [5] | CUI Nan;QIN Lu;LIU Dong;WEI Xue-feng;RAN Qi-yang;LV Guang-hui. Research on Soil CH4 Flux of Change Rule and the Relationship between Environmental Impact Factors of Desert Grassland and Euphrates poplar Forest in Ebinur Lake Area [J]. , 2014, 51(1): 81-88. |
| [6] | FAN Yan-min;ZHU Jin-zhong;WU Hong-qi;ZHU Xin-ping;SHI Chong;WANG Ji-yun. Study on Soil Microorganisms and Enzyme Activities of the Degraded Seriphidium transiliense Desert Grassland [J]. , 2009, 46(6): 1288-1293. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 23
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 115
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||