

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (9): 2239-2247.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.09.019
• Plant Protection·Microbes • Previous Articles Next Articles
SONG Bingmei1,2( ), JIANG Yan2, CHEN Xin2,3, ZHANG Yu4, CHENG Wannan4, PAN Hongsheng2(
), JIANG Yan2, CHEN Xin2,3, ZHANG Yu4, CHENG Wannan4, PAN Hongsheng2( )
)
Received:2022-12-10
Online:2023-09-20
Published:2023-09-19
Correspondence author:
PAN Hongsheng (1982-), male, native place: Zhaodong, Heilongjiang Province, researcher, master tutor, research direction for safety evaluation of transgenic crops, (E- mail) Supported by:
宋冰梅1,2( ), 姜岩2, 陈鑫2,3, 张宇4, 程宛楠4, 潘洪生2(
), 姜岩2, 陈鑫2,3, 张宇4, 程宛楠4, 潘洪生2( )
)
通讯作者:
潘洪生(1982-),男,黑龙江肇东人,研究员,博士,研究方向为转基因作物安全性评价,(E-mail)作者简介:宋冰梅(1999-),女,四川自贡人,硕士研究生,研究方向为转基因作物安全性评价,(E-mail)2446620106@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
SONG Bingmei, JIANG Yan, CHEN Xin, ZHANG Yu, CHENG Wannan, PAN Hongsheng. Evaluation of saline/alkali tolerance of new transgenic High-Yield cotton at germination and seedling stages[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2239-2247.
宋冰梅, 姜岩, 陈鑫, 张宇, 程宛楠, 潘洪生. 新型转基因高产棉花萌发期和苗期耐盐性与耐碱性评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2239-2247.
| 直接指标 Direct index | 盐胁迫 Saline stress | 碱胁迫 Alkali stress | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 mmol/L NaCl (CK) | 150 mmol/L NaCl | 0 mmol/L NaHCO3 (CK) | 70 mmol/L NaHCO3 | |
| 鲜重量Fresh weight(g) | 0.36±0.01a | 0.26±0.01b | 0.36±0.01a | 0.26±0.01b |
| 下胚轴长Hypocotyl length(cm) | 1.72±0.05a | 1.41±0.14b | 1.70±0.03a | 1.37±0.02b |
| 根长Root length(cm) | 4.43±0.05a | 2.22±0.08b | 4.31±0.04a | 0.00±0.00c |
| 发芽势Germination potential(%) | 66.25±0.48a | 27.50±0.29c | 67.50±0.29a | 43.00±0.91b |
| 发芽率Germination rate(%) | 98.25±0.48a | 72.00±0.82c | 98.25±0.48a | 78.00±0.00b |
| 发芽指数Germination index | 95.42±0.19a | 56.40±0.48c | 95.85±0.13a | 71.04±0.33b |
| 活力指数Vigor index | 34.26±0.59a | 14.92±0.68c | 33.80±0.62a | 18.03±0.40b |
Tab.1 Effects of saline/alkali stress on the direct index of new transgenic high-yield cotton HN9311 at germination stage
| 直接指标 Direct index | 盐胁迫 Saline stress | 碱胁迫 Alkali stress | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 mmol/L NaCl (CK) | 150 mmol/L NaCl | 0 mmol/L NaHCO3 (CK) | 70 mmol/L NaHCO3 | |
| 鲜重量Fresh weight(g) | 0.36±0.01a | 0.26±0.01b | 0.36±0.01a | 0.26±0.01b |
| 下胚轴长Hypocotyl length(cm) | 1.72±0.05a | 1.41±0.14b | 1.70±0.03a | 1.37±0.02b |
| 根长Root length(cm) | 4.43±0.05a | 2.22±0.08b | 4.31±0.04a | 0.00±0.00c |
| 发芽势Germination potential(%) | 66.25±0.48a | 27.50±0.29c | 67.50±0.29a | 43.00±0.91b |
| 发芽率Germination rate(%) | 98.25±0.48a | 72.00±0.82c | 98.25±0.48a | 78.00±0.00b |
| 发芽指数Germination index | 95.42±0.19a | 56.40±0.48c | 95.85±0.13a | 71.04±0.33b |
| 活力指数Vigor index | 34.26±0.59a | 14.92±0.68c | 33.80±0.62a | 18.03±0.40b |
| 直接指标 Direct index | 盐胁迫 Saline stress | 碱胁迫 Alkali stress | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 mmol/L NaCl (CK) | 150 mmol/L NaCl | 0 mmol/L NaHCO3 (CK) | 70 mmol/L NaHCO3 | |
| 真叶数Number of true leaves | 3.75±0.25ab | 3.25±0.25b | 4.00±0.00a | 2.25±0.08c |
| 株高Plant height(cm) | 15.00±0.41a | 14.00±0.00b | 15.80±0.15a | 9.93±0.38c |
| 根长Root length(cm) | 21.63±0.38a | 14.00±0.41b | 21.70±0.10a | 9.83±0.94c |
| 根鲜重Root fresh weight(g) | 2.57±0.02a | 1.93±0.05b | 2.55±0.05a | 1.56±0.05c |
| 地上部鲜重Shoot fresh weight(g) | 5.28±0.06a | 3.33±0.06b | 5.23±0.03a | 2.10±0.10c |
| 鲜重量Fresh weight(g) | 7.85±0.04a | 5.25±0.10b | 7.78±0.09a | 3.66±0.15c |
| 根冠比Root/shoot | 0.49±0.01c | 0.58±0.01b | 0.49±0.01c | 0.74±0.01a |
Tab.2 Effects of saline/alkali stress on the direct index of new transgenic high-yield cotton HN9311 at seedling stage
| 直接指标 Direct index | 盐胁迫 Saline stress | 碱胁迫 Alkali stress | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 mmol/L NaCl (CK) | 150 mmol/L NaCl | 0 mmol/L NaHCO3 (CK) | 70 mmol/L NaHCO3 | |
| 真叶数Number of true leaves | 3.75±0.25ab | 3.25±0.25b | 4.00±0.00a | 2.25±0.08c |
| 株高Plant height(cm) | 15.00±0.41a | 14.00±0.00b | 15.80±0.15a | 9.93±0.38c |
| 根长Root length(cm) | 21.63±0.38a | 14.00±0.41b | 21.70±0.10a | 9.83±0.94c |
| 根鲜重Root fresh weight(g) | 2.57±0.02a | 1.93±0.05b | 2.55±0.05a | 1.56±0.05c |
| 地上部鲜重Shoot fresh weight(g) | 5.28±0.06a | 3.33±0.06b | 5.23±0.03a | 2.10±0.10c |
| 鲜重量Fresh weight(g) | 7.85±0.04a | 5.25±0.10b | 7.78±0.09a | 3.66±0.15c |
| 根冠比Root/shoot | 0.49±0.01c | 0.58±0.01b | 0.49±0.01c | 0.74±0.01a |
| 相对指标 Relative index | 盐胁迫 Saline stress | 碱胁迫 Alkali stress | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中棉所12号 CCRI-12 | HN9311 | 中棉所12号 CCRI-12 | HN9311 | |
| 相对鲜重量Relative fresh weight | 0.86±0.02* | 0.74±0.03 | 0.95±0.0 | 0.72±0.02 |
| 相对下胚轴长Relative hypocotyl length | 0.98±0.02 | 0.82±0.08 | 0.73±0.01 | 0.81±0.0 |
| 相对根长Relative root length | 0.56±0.03 | 0.50±0.02 | 0.28±0.00 | 0.28±0.01 |
| 相对发芽势Relative germination potential | 0.56±0.0 | 0.42±0.00 | 0.65±0.01 | 0.64±0.01 |
| 相对发芽率Relative germination rate | 0.77±0.0 | 0.73±0.01 | 0.78±0.00 | 0.79±0.00 |
| 相对发芽指数Relative germination index | 0.70±0.0 | 0.59±0.00 | 0.72±0.00 | 0.74±0.00* |
| 相对活力指数 Relative vigor index | 0.60±0.0 | 0.43±0.02 | 0.68±0.01 | 0.53±0.01 |
Tab.3 Effects of saline/alkali stress on the relative index of new transgenic high-yield cotton HN9311 at germination stage
| 相对指标 Relative index | 盐胁迫 Saline stress | 碱胁迫 Alkali stress | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中棉所12号 CCRI-12 | HN9311 | 中棉所12号 CCRI-12 | HN9311 | |
| 相对鲜重量Relative fresh weight | 0.86±0.02* | 0.74±0.03 | 0.95±0.0 | 0.72±0.02 |
| 相对下胚轴长Relative hypocotyl length | 0.98±0.02 | 0.82±0.08 | 0.73±0.01 | 0.81±0.0 |
| 相对根长Relative root length | 0.56±0.03 | 0.50±0.02 | 0.28±0.00 | 0.28±0.01 |
| 相对发芽势Relative germination potential | 0.56±0.0 | 0.42±0.00 | 0.65±0.01 | 0.64±0.01 |
| 相对发芽率Relative germination rate | 0.77±0.0 | 0.73±0.01 | 0.78±0.00 | 0.79±0.00 |
| 相对发芽指数Relative germination index | 0.70±0.0 | 0.59±0.00 | 0.72±0.00 | 0.74±0.00* |
| 相对活力指数 Relative vigor index | 0.60±0.0 | 0.43±0.02 | 0.68±0.01 | 0.53±0.01 |
| 相对指标 Relative index | 盐胁迫 Saline stress | 碱胁迫 Alkali stress | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中棉所12号 CCRI-12 | HN9311 | 中棉所12号 CCRI-12 | HN9311 | |
| 相对真叶数Relative true leaf number | 0.89±0.00 | 0.87±0.07 | 0.56±0.02 | 0.60±0.02 |
| 相对株高Relative plant height | 0.95±0.03 | 0.93±0.00 | 0.77±0.01* | 0.66±0.03 |
| 相对根长Relative root length | 0.60±0.01 | 0.65±0.02 | 0.59±0.03 | 0.46±0.04 |
| 相对根鲜重Relative root fresh weight | 0.90±0.0 | 0.75±0.02 | 0.86±0.0 | 0.61±0.02 |
| 相对地上部鲜重Relative shoot fresh weight | 0.87±0.07* | 0.63±0.01 | 0.75±0.0 | 0.40±0.02 |
| 相对鲜重量Relative fresh weight | 0.88±0.0 | 0.67±0.01 | 0.79±0.0 | 0.47±0.02 |
| 相对根冠比Relative root/shoot | 1.06±0.09 | 1.19±0.03 | 1.14±0.01 | 1.53±0.0 |
Tab.4 Effects of saline/alkali stress on the relative index of new transgenic high-yield cotton HN9311 at seedling stage
| 相对指标 Relative index | 盐胁迫 Saline stress | 碱胁迫 Alkali stress | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中棉所12号 CCRI-12 | HN9311 | 中棉所12号 CCRI-12 | HN9311 | |
| 相对真叶数Relative true leaf number | 0.89±0.00 | 0.87±0.07 | 0.56±0.02 | 0.60±0.02 |
| 相对株高Relative plant height | 0.95±0.03 | 0.93±0.00 | 0.77±0.01* | 0.66±0.03 |
| 相对根长Relative root length | 0.60±0.01 | 0.65±0.02 | 0.59±0.03 | 0.46±0.04 |
| 相对根鲜重Relative root fresh weight | 0.90±0.0 | 0.75±0.02 | 0.86±0.0 | 0.61±0.02 |
| 相对地上部鲜重Relative shoot fresh weight | 0.87±0.07* | 0.63±0.01 | 0.75±0.0 | 0.40±0.02 |
| 相对鲜重量Relative fresh weight | 0.88±0.0 | 0.67±0.01 | 0.79±0.0 | 0.47±0.02 |
| 相对根冠比Relative root/shoot | 1.06±0.09 | 1.19±0.03 | 1.14±0.01 | 1.53±0.0 |
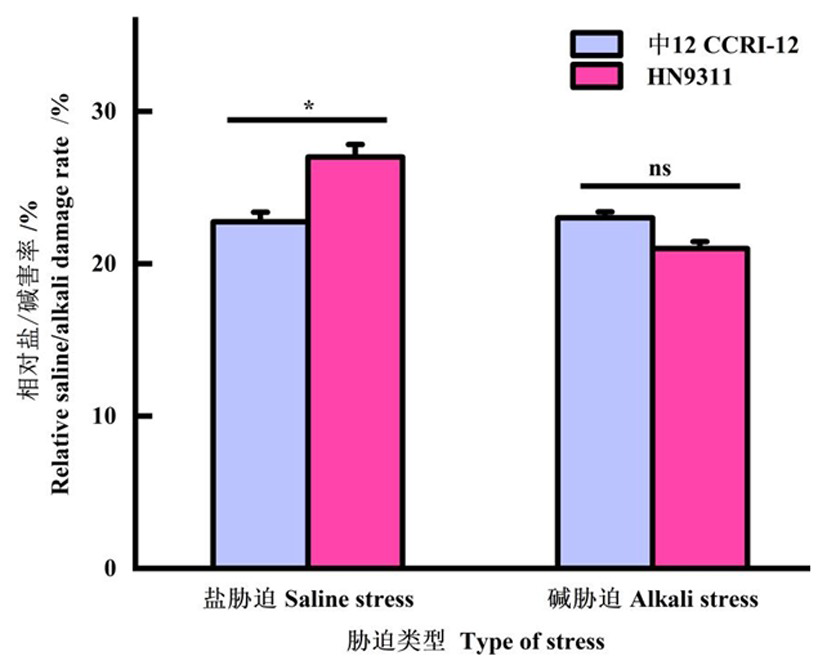
Fig.1 Effects of saline/alkali stress on relative saline/alkali damage rate of new transgenic high-yield cotton HN9311 at germination stage Note:* and ns respectively represent significant difference (P<0.05) or not represent significant difference (P>0.05) for the relative saline damage rate between HN9311 and CCRI-12 (independent sample T test)
| [1] |
Guo J X, Lu X Y, Tao Y F, et al. Comparative ionomics and metabolic responses and adaptive strategies of cotton to salt and alkali stress[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 871387.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 陆宴辉, 梁革梅, 张永军, 等. 二十一世纪以来棉花害虫治理成就与展望[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2020, 57(3): 477-490. |
| LU Yanhui, LIANG Gemei, ZHANG Yongjun, et al. Advances in the management of insect pests of cotton in China since the 21st century[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2020, 57(3): 477-490. | |
| [3] | Abdelraheem A, Kuraparthy V, Hinze L, et al. Genome-wide association study for tolerance to drought and salt tolerance and resistance to thrips at the seedling growth stage in US upland cotton[J]. Industrial Crops & Products, 2021, 169: 113645. |
| [4] |
Zhang M, Zheng X L, Song S Q, et al. Spatiotemporal manipulation of auxin biosynthesis in cotton ovule epidermal cells enhances fiber yield and quality[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2011, 29(5): 453-461.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Sun F, Liu C L, Zhang C J, et al. A conserved RNA recognition motif (RRM) domain of brassica napus FCA improves cotton fiber quality and yield by regulating cell size[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2012, 30(1): 93-101.
DOI URL |
| [6] | 雒珺瑜, 刘传亮, 张帅, 等. 转RRM2基因棉生长势和产量及对棉田节肢动物群落的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2020, 38(7): 785-794. |
| LUO Junyu, LIU Chuanliang, ZHANG Shuai, et al. Growth vigor and yield of transgenic RRM2 (RNA recognition motif 2) cotton and their effects on arthropod community in cotton field[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2020, 38(7): 785-794. | |
| [7] | 刘小玲, 徐道青, 王维, 等. 转RRM2和ACO2-E6基因棉花冠层特征和光合特性与产量形成的关系[J]. 棉花学报, 2016, 28(6): 628-634. |
| LIU Xiaoling, XU Daoqing, WANG Wei, et al. Relationship of canopy properties and photosynthetic characteristics with construction of lint yield in transgenic RRM2 and ACO2-E6 cotton[J]. Cotton Science, 2016, 28(6): 628-634. | |
| [8] |
Zhu G Z, Gao W W, Song X H, et al. Genome-wide association reveals genetic variation of lint yield components under salty field conditions in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2020, 20(1): 23.
DOI |
| [9] |
Qadir M, Quillérou E, Nangia V, et al. Economics of salt-induced land degradation and restoration[J]. In Natural Resources Forum, 2014, 38(4): 282-295.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 王俊铎, 黎玉华, 龚照龙, 等. 棉花耐盐性研究进展[J]. 棉花科学, 2021, 43(5): 3-10. |
| WANG Junduo, LI Yuhua, GONG Zhaolong, et al. Research progresses on salt tolerance of cotton[J]. Cotton Sciences, 2021, 43(5): 3-10. | |
| [11] | Zẽrb C, Geilfus C M, Dietz K J. Salinity and crop yield[J]. Plant Biology (Stuttgart, Germany), 2019,(S1): 31-38. |
| [12] |
Liang W, Cui W, Ma X, et al. Function of wheat Ta-UnP gene in enhancing salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis and rice[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2014, 450(1): 794-801.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Ashraf J, Zuo D, Wang Q, et al. Recent insights into cotton functional genomics: progress and future perspectives[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 16(3): 699-713.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Ullah A, Sun H, et al. Drought coping strategies in cotton: increased crop per drop[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15(3): 271-284.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Li W H, Wang Z H, Zhang J Z, et al. Soil salinity variations and cotton growth under long-term mulched drip irrigation in saline-alkali land of arid oasis[J]. Irrigation Science, 2022, 40: 103-113.
DOI |
| [16] | Mottaleb S A, Darwish E, Mostafa M, et al. Phenotyping root system architecture of cotton (Gossypium barbadense L.) grown under salinity[J]. Agriculture/Pol'nohospodárstvo, 2017, 63(4): 142-150. |
| [17] | 许艳超. 复合盐碱胁迫下半野生棉抗性评价与调控机理初步分析[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2017. |
| XU Yanchao. Primary studies on integrated evaluation and regulated mechanism of semi-wild cotton under complex salt-alkali stress[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2017. | |
| [18] | 马盼盼, 赵曾强, 祝建波, 等. 棉花耐旱耐盐碱生理和分子机制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 23(2): 27-36. |
| MA Panpan, ZHAO Zengqiang, ZHU Jiangbo, et al. Physiological and molecular mechanisms of drought and salt tolerance in cotton[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 23(2): 27-36. | |
| [19] | 苏莹, 郭安慧, 华金平. 棉花耐盐性鉴定方法探讨[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2021, 26(12): 11-19. |
| SU Ying, GUO Anhui, HUA Jinping. Strategies for evaluation the salt tolerance in cotton[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2021, 26(12): 11-19. | |
| [20] | 庞学兵, 王朝阳, 王爱英, 等. 根际促生菌对棉苗盐碱胁迫的缓解效应[J]. 西北农业学报, 2017, 26(1): 101-109. |
| PANG Xuebing, WANG Chaoyang, WANG Aiying, et al. Mitigative effect PGPR cotton seedings subjected to salt-alkaline stress[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2017, 26(1): 101-109. | |
| [21] | 赵云丽, 李刚, 修伟明, 等. 非抗虫转基因棉花对土壤细菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(4): 716-721. |
| ZHAO Yunli, LI Gang, XIU Weiming, et al. Effects of insect non-resistant transgenic cottons on bacterial community diversity in soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(4): 716-721. | |
| [22] |
李淑英, 朱加保, 路献勇, 等. 转RRM2基因棉田昆虫群落多样性及其时序动态[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(11): 1190-1203.
DOI |
|
LI Shuying, ZHU Jiabao, LU Xianyong, et al. The diversity of insect communities and its dynamic changes in transgenic RRM2(RNA recognition motif 2) cotton fields[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2018, 26(11): 1190-1203.
DOI |
|
| [23] | 付媛媛, 江晓慧, 申孝军, 等. 盐胁迫下棉花幼苗叶片K+、Na+含量与光合参数的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(6): 1716-1722. |
| FU Yuanyuan, JIANG Xiaohui, SHEN Xiaojun, et al. The relationship between foliar K+ and Na+ concentrations and photosynthetic parameters of cotton seedlings under salt stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(6): 1716-1722. | |
| [24] | 张国伟, 路海玲, 张雷, 等. 棉花萌发期和苗期耐盐性评价及耐盐指标筛选[J]. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(8): 2045-2053. |
|
ZHANG Guowei, LU Hailing, ZHANG Lei, et al. Salt tolerance evaluation of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum)at its germinating and seedling stages and selection of related indices[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011, 22(8): 2045-2053.
PMID |
|
| [25] | Guo R, Shi L X, Yang C W, et al. Comparison of ionomic and metabolites response under alkali stress in old and young leaves of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) seedlings[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 25(7): 1785. |
| [26] |
Xu Y, Magwanga Ro, Yang X, et al. Genetic regulatory networks for salt-alkali stress in Gossypium hirsutum with differing morphological characteristics[J]. BMC Genomics, 2020, 21(1): 15.
DOI |
| [27] | Zhang G W, Liu R X, Yang C Q, et al. Application of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method based on entropy weight theory in evaluation of salt tolerance of cotton[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology, 2014, 15(9): 1441-1445. |
| [28] | Manikandan A, Sahu D K, Blaise D, et al. Cotton response to differential salt stress[J]. International Journal of Agriculture Science, 2019, 11(6): 8059-8065. |
| [29] |
刘瑞显, 张国伟, 杨长琴. 基于熵权理论的灰色关联度法在棉花耐盐性评价中的应用[J]. 核农学报, 2017, 31(2): 402-409.
DOI |
|
LIU Ruixian, ZHANG Guowei, YANG Changqin. Using gray related degree method based on entropy weight theory to evaluate salt tolerance of cotton[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 31(2): 402-409.
DOI |
|
| [30] | 赵康, 杨涛, 王红刚, 等. 42个新疆海岛棉品种萌发期耐盐性评价[J]. 作物杂志, 2022, 38(5): 27-33. |
| ZHAO Kang, YANG Tao, WANG Honggang, et al. Evaluation on salt tolerance of 42 sea-lsland cotton (Gossypium barbadense) varieties in Xinjiang during germination period[J]. Crops, 2022, 38(5): 27-33. | |
| [31] | ZHeng J Y, Zhang Z L, Gong Z L, et al. Genome-wide association analysis of salt-tolerant traits in terrestrial cotton at seedling stage. Plants (Basel, Switzerland), 2021, 11(1): 97-120. |
| [32] | 谢志霞, 李茂营, 杜明伟, 等. 冠菌素对棉花幼苗盐害的缓解效应[J]. 棉花学报, 2020, 24(6): 511-517. |
| XIE Zhixia, LI Maoying, DU Mingwei, et al. Ameliorating effect of the phytotoxin coronatine on seedlings of transgenic insect-resistant cotton variety under salt stress[J]. Cotton Science, 2020, 24(6): 511-517. | |
| [33] |
马宏秀, 王开勇, 张开祥, 等. 棉粕对盐碱胁迫下棉花生理及生长补偿效应[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(2): 208-216.
DOI |
| MA Hongxiu, WANG Kaiyong, ZHANG Kaixiang, et al. Effect of cottonseed meal on cotton physiology and growth compensation under salinity-alkalinity stress[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(2): 208-216. | |
| [34] |
Mai W X, Tian C Y, Li C J. Soil salinity dynamics under drip irrigation and mulch film and their effects on cotton root length[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2013, 44(9): 1489-1502.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Chen W L, Jin M G, FERRÉ T, et al. Soil conditions affect cotton root distribution and cotton yield under mulched drip irrigation[J]. Field Crops Research, 2020, 249: 107743.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Min W, Guo H J, Zhou G W, et al. Root distribution and growth of cotton as affected by drip irrigation with saline water[J]. Field Crops Research, 2014, 169: 1-10.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 叶武威, 庞念厂, 王俊娟, 等. 盐胁迫下棉花体内Na+的积累、分配及耐盐机制研究[J]. 棉花学报, 2006, 33(5): 279-283. |
| YE Wuwei, PANG Nianchang, WANG Junjuan, et al. Characteristics of absorbing, accumulating and distribution of Na+ under the salinity stress on cotton[J]. Cotton Science, 2006, 33(5): 279-283. | |
| [38] | Gupta B, Huang B R. Mechanism of salinity tolerance in plants: physiological, biochemical, and molecular characterization[J]. Corporation International Journal of Genomics, 2014, 2014: 701596. |
| [39] |
Yin Z P, Zhang H, Zhao Q, et al. Physiological and comparative proteomic analyses of saline-alkali NaHCO3-responses in leaves of halophyte Puccinellia Tenuiflora[J]. Plant Soil, 2019, 437(1-2): 137-158.
DOI |
| [40] | 苏孟杞. 陆地棉对NaCl、Na2CO3及NaHCO3的耐性鉴定[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2015. |
| SU Mengqi. Salt tolerance identification of upland cotton Nacl, Na2CO3 and NaHCO3[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2015. | |
| [41] | 辛承松, 罗振, 孔祥强, 等. 不同基因型陆地棉亲本及其杂交后代的耐盐性差异[J]. 棉花学报, 2011, 23(3): 235-240. |
| XIN Chengsong, LUO Zhen, KONG Xiangqiang, et al. Salt tolerant variation among parents of different genotype upland cotton and their hybrids[J]. Cotton Science, 2011, 23(3): 235-240. | |
| [42] |
徐婷, 柳延涛, 王海江, 等. 盐碱胁迫对花生种子发芽特性影响及盐害综合鉴定评价[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2022, 44(5): 1037-1047.
DOI |
|
XU Ting, LIU Yantao, WANG Haijiang, et al. Effects of saline-alkali stress on germination characteristics of peanut seeds and comprehensive identification and evaluation of salt damage[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2022, 44(5): 1037-1047.
DOI |
|
| [43] | 王立红, 孙影影, 李星星, 等. 水杨酸浸种对NaCl胁迫下棉花种子萌发和幼苗根系生长的影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2016, 21(4): 10-17. |
| WANG Lihong, SUN Yingying, LI Xingxing, et al. Effects of salicylic acid soaking on seed germination and root growth of cotton under salt stress[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2016, 21(4): 10-17. | |
| [44] | 白灯莎·买买提艾力, 张少民, 孙良斌, 等. 新疆不同年代27个棉花品种(系)种子萌发阶段耐盐能力比较[J]. 西北农业学报, 2012, 21(1): 72-79. |
| Baidengsha Maimaitiaili, ZHANG Shaomin, SUN Liangbin, et al. Comparisons of salt resistances during germination stage among 27 cotton varieties (Line) grown in Xinjiang[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2012, 21(1): 72-79. | |
| [45] |
Dai J L, Duan L S, Dong H Z. Improved nutrient uptake enhance cotton growth and salinity tolerance in saline media[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2014, 37(8): 1269-1286.
DOI URL |
| [46] | 孙娜, 王劲, 左开井. 陆地棉GhbHLH4基因的克隆与功能分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2014, 16(3): 29-35. |
|
SUN Na, WANG Jin, ZUO Kaijing. Cloning and functional analysis of GhbHLH4 gene from upland cotton[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2014, 16(3): 29-35.
DOI |
|
| [47] |
Niñerola V B, Navarro-Pedreño J, Lucas I G, et al. Geostatistical assessment of soil salinity and cropping systems used as soil phytoremediation strategy[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 174(S1): 53-58.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
郑琦, 王海江, 吕新, 等. 新疆棉田土壤质量综合评价方法[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(4): 1291-1301.
DOI |
|
ZHENG Qi, WANG Haijiang, LYU Xin, et al. Comprehensive method for evaluating soil quality in cotton fields in Xinjiang,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(4): 1291-1301.
DOI |
|
| [49] |
Ma H X, Meng C M, Zhang K X, et al. Study on physiological mechanism of using cottonseed meal to improve saline-alkali tolerance of cotton[J]. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2021, 40(1): 126-136.
DOI |
| [50] | 汪保华, 王亚峰, 王长彪, 等. 中棉所35及中棉所12盐胁迫下的丙二醛含量变化及其SSR指纹图谱构建[J]. 中国棉花, 2011, 38(11): 20-23. |
| WANG Baohua, WANG Yafeng, WANG Changbiao, et al. Effect of salt stress on malondialdehyde content variation and SSR fingerprint construction for CCRI 35 and CCRI 12[J]. China Cotton, 2011, 38(11): 20-23. | |
| [51] | 刘雅辉, 王秀萍, 鲁雪林, 等. 棉花耐盐相关序列扩增多态性(SRAP)分子标记筛选[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2015, 31(3): 484-488. |
| LIU Yahui, WANG Xiuping, LU Xuelin, et al. Selection of sequence-related amplified polymorphism molecular marker associated withs salt tolerance of cotton[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 31(3): 484-488. |
| [1] | WANG Chao, XU Wenxiu, LI Pengcheng, ZHENG Cangsong, SUN Miao, FENG Weina, SHAO Jingjing, DONG Helin. Response of cotton seedling growth and development to soil available potassium levels [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2132-2139. |
| [2] | ZHANG Chengjie, HU Haoran, DUAN Songjiang, WU Yifan, ZHANG Jusong. Effects of nitrogen-dense interaction on growth, development, yield and quality of Gossypium barbadense L. [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1821-1830. |
| [3] | LIU Huijie, WANG Junhao, GONG Zhaolong, LIANG Yajun, WANG Junduo, LI Xueyuan, ZHENG Juyun, WANG Jichuan. Identification of salt tolerance of 197 upland cotton varieties at germination stage [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1574-1581. |
| [4] | YAO Qing, WANG Jiehua, Xiernayi Abudula, Dilimulati Tulahong, CUI Hongliang. Physiological responses of different quinoa varieties during seedling stage under low temperature stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1597-1604. |
| [5] | MA Baihuan, ZHAO Qiang, XIE Jia, XU Kaiyue, REN Ruofei, SONG Xinghu. Effects of biopharmaceutical mixture on the control and growth of cotton Verticillium wilt [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1748-1756. |
| [6] | ZHAO Yun, FENG Guojun, Gulizhati Bazierbieke, HU Xiangwei, Subinuer Kadeer, LI Pengbing, SHAO Jiang, LIU Jie. Effects of potassium fertilizer dosage on growth and yield of drip irrigated millet in northern Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1378-1385. |
| [7] | HUANG Jinyue, XU Min, WANG Longfei, LIU Xinyi, GUO Yuqing, WU Xiaolan, WANG Yatong, ZHANG Shikui, FAN Guoquan. Changes of pectin components and enzyme activities during the development of apricot fruits [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1407-1415. |
| [8] | WANG Runqi, JIA Yonghong, WANG Yujiao, LIU Yue, LI Dandan, DONG Yanxue, Gulinigaer Tuerhong, ZHANG Lulu, ZHANG Jinshan, SHI Shubing. Effect of different drip irrigation on the growth, development, and yield of uniform sowing winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(5): 1048-1056. |
| [9] | LI Xuerui, ZHAI Menghua, XU Xinlong, SUN Minghui, ZHANG Jusong. Effects of spraying different concentrations of SAH by UAV on cotton growth and development [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(5): 1085-1093. |
| [10] | Gulipari Aikebai, SHEN Xuemei, YU Shigang, WANG Gang, YANG Yaling, LIU Wujun. Identification of chicken circMICAL2, tissue expression profile analysis and its functional prediction [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(5): 1284-1291. |
| [11] | HOU Xianfei, SONG Xianming, LI Qiang, GU Yuanguo, MIAO Haocui, ZENG Youling, GUO Meili, JIA Donghai. Effects of water and nitrogen coupling on growth and yield of Carthamus tinctorius L. under mulch drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 791-803. |
| [12] | SUN Minghui, Yeerlan Muhetar, ZHAI Menghua, LI Xuerui, XU Xinlong, ZHANG Jusong. Effects of different planting patterns and varieties on the production of photosynthetic substances in cotton and the impact of output [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(3): 537-546. |
| [13] | CHEN Chuanxin, ZHNAG Yongqiang, NIE Shihui, KONG Depeng, Sailihan Sai, XU Qijiang, LEI Junjie. Effects of biomass charcoal application rate on the growth, development, and yield of winter wheat under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2146-2151. |
| [14] | WEI Yingfeng, ZHANG Quancheng, ZHA Hui, WANG Xiaoli, WANG Jungang. Effect of pendimethalin on the main growth and development and physiological indicators of Solanum nigrum L. [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 2013-2021. |
| [15] | CHEN Yan, HUANG Luyao, DENG Changrong, ZHANG Yanjun, HOU Quangang, SHAO Dengkui. Analysis on related physiological indexes of pepper with hair characteristic under chilling stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1492-1498. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 69
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 1416
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||