

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2022, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (6): 1466-1474.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2022.06.018
• Plant Protection·Microbes • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIN Qing1( ), SHI Yingwu1, WANG Na2, HUA Lanlan3, YANG Hongmei1, CHU Min1, ZENG Jun1, GAO Yan1, HUO Xiangdong1(
), SHI Yingwu1, WANG Na2, HUA Lanlan3, YANG Hongmei1, CHU Min1, ZENG Jun1, GAO Yan1, HUO Xiangdong1( )
)
Received:2021-10-15
Online:2022-06-20
Published:2022-07-07
Correspondence author:
HUO Xiangdong
Supported by:
林青1( ), 史应武1, 王娜2, 华兰兰3, 杨红梅1, 楚敏1, 曾军1, 高雁1, 霍向东1(
), 史应武1, 王娜2, 华兰兰3, 杨红梅1, 楚敏1, 曾军1, 高雁1, 霍向东1( )
)
通讯作者:
霍向东
作者简介:林青(1985-),女,山东人,硕士,助理研究员,研究方向为微生物生态,(E-mail) qinglinxj@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LIN Qing, SHI Yingwu, WANG Na, HUA Lanlan, YANG Hongmei, CHU Min, ZENG Jun, GAO Yan, HUO Xiangdong. Screening and Identification of Systemic Resistant Inducing Growth-Promoting Bacteria and Their Effects on Growth and Disease Prevention of Processing Tomatoes[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(6): 1466-1474.
林青, 史应武, 王娜, 华兰兰, 杨红梅, 楚敏, 曾军, 高雁, 霍向东. 加工番茄系统抗性诱导促生菌的筛选鉴定及其促生防病效果[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(6): 1466-1474.
| 样本数量 Number of samples | 根际土壤 细菌数量 The number of bacteria in rhizosp here soil | 根区土壤 细菌数量 The number of bacteria in root zone soil | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 番茄 Tomato | 15 | 48 | 32 |
| 辣椒 Chilli Pepper | 5 | 24 | 12 |
| 豆角 Beans | 4 | 19 | 12 |
Table 1 The number of bacteria isolated from rhizosphere and root zone soil of different crops
| 样本数量 Number of samples | 根际土壤 细菌数量 The number of bacteria in rhizosp here soil | 根区土壤 细菌数量 The number of bacteria in root zone soil | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 番茄 Tomato | 15 | 48 | 32 |
| 辣椒 Chilli Pepper | 5 | 24 | 12 |
| 豆角 Beans | 4 | 19 | 12 |
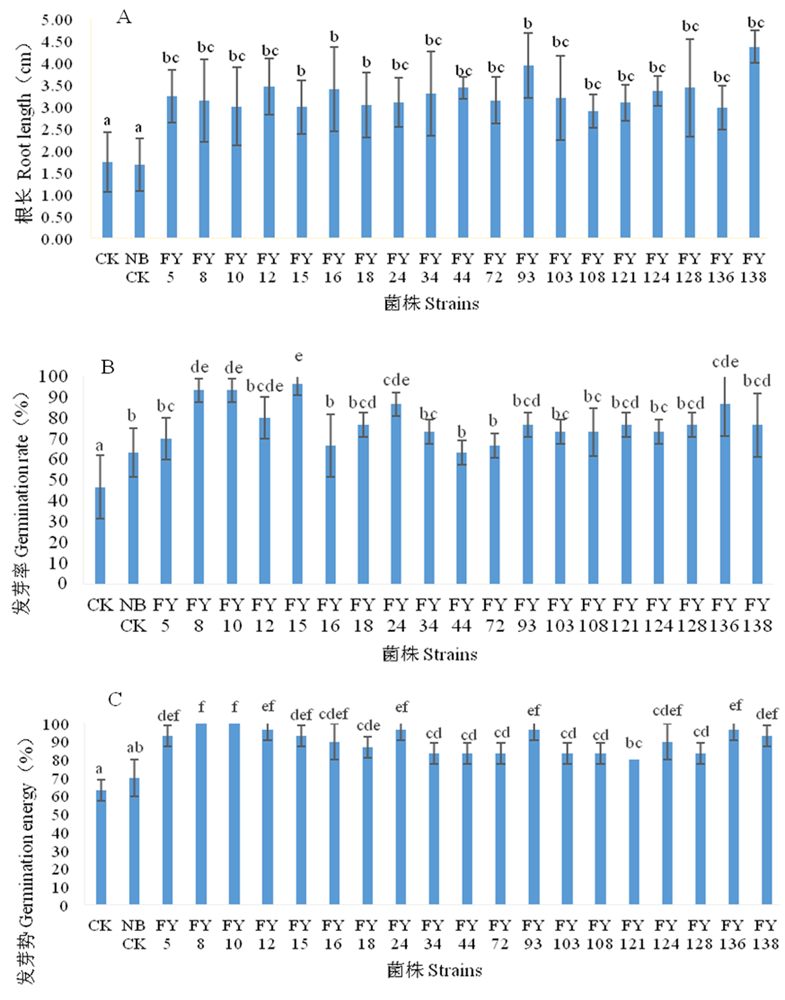
Fig.1 Growth-promoting effect of processing tomato growth-promoting bacteria Note:A: Root length of processing tomato seeds; B: Germination rate of processing tomato seeds; C: Germination potential of processing tomato seeds
| 菌株 Strain | 早疫病 Early blight | 灰霉病 Gray mold | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病情指数 Disease index (%) | 诱抗效果 Induced effect(%) | 病情指数 Disease index(%) | 诱抗效果 Induced effect (%) | |||||
| 5 d | 14 d | 5 d | 14 d | 5 d | 14 d | 5 d | 14 d | |
| CK | 16.00d | 50.67c | - | - | 16.67b | 56.00c | - | - |
| FY10 | 4.67b | 34.67b | 70.57b | 31.54b | 2.00a | 35.33a | 88.33a | 36.67a |
| FY12 | 1.33a | 30.67a | 92.13c | 39.44c | 4.67a | 39.33b | 88.33a | 29.63a |
| FY93 | 3.33ab | 36.67b | 78.90bc | 27.59b | 4.00a | 38.00ab | 75.48a | 31.85a |
| FY136 | 8.00c | 51.33c | 50.07a | -1.33a | 3.33a | 36.67ab | 78.81a | 34.32a |
Table 2 Inducing effect of induced strains on early blight and gray mold of processing tomato
| 菌株 Strain | 早疫病 Early blight | 灰霉病 Gray mold | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病情指数 Disease index (%) | 诱抗效果 Induced effect(%) | 病情指数 Disease index(%) | 诱抗效果 Induced effect (%) | |||||
| 5 d | 14 d | 5 d | 14 d | 5 d | 14 d | 5 d | 14 d | |
| CK | 16.00d | 50.67c | - | - | 16.67b | 56.00c | - | - |
| FY10 | 4.67b | 34.67b | 70.57b | 31.54b | 2.00a | 35.33a | 88.33a | 36.67a |
| FY12 | 1.33a | 30.67a | 92.13c | 39.44c | 4.67a | 39.33b | 88.33a | 29.63a |
| FY93 | 3.33ab | 36.67b | 78.90bc | 27.59b | 4.00a | 38.00ab | 75.48a | 31.85a |
| FY136 | 8.00c | 51.33c | 50.07a | -1.33a | 3.33a | 36.67ab | 78.81a | 34.32a |
| [1] | 刘峰娟, 朱靖蓉, 周俊, 等. 新疆主栽加工番茄品种营养品质比较研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2016, 53(2):225-231. |
| LIU Fengjuan, ZHU Jingrong, ZHOU Jun, et al. Isolation and Identification of Filamentous Fungi F161 and Its Biosorption and Enrichment Characteristics of Strontiu[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 53(2):225-231. | |
| [2] | 李凯, 谭丹. 新疆番茄产业国际竞争力分析[J]. 现代商业, 2018,(35):65-68. |
| LI Kai, TAN Dan. Analysis on the International Competitiveness of Xinjiang Tomato Industry[J]. Modern Business, 2018,(35):65-68. | |
| [3] | 崔元玙, 杨华, 孙晓军, 等. 新疆加工番茄主要病害发生[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2004, 41(3):160-163. |
| CUI Yuanyu, YANG Hua, SUN Xiaojun, et al. Occurrence and Damage of Important Diseases of Processing Tomato in Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2004, 41(3):160-163. | |
| [4] | 李平, 王晓东, 张莉. 新疆加工番茄品种抗早疫病测定及防治药剂筛选[J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 32(1):17-20. |
| LI Ping, WANG Xiaodong, ZHANG Li. Screen Varieties Resistance and Fungicide to Early Blight of Processing Tomato[J]. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science), 2014, 32(1):17-20. | |
| [5] |
Asmaa E, Abdelnaser A,. Elzaawely, Naglaa A, et al. The Antifungal Activity of Gallic Acid and Its Derivatives against Alternaria solani, the Causal Agent of Tomato Early Blight[J]. Agronomy. 2020, 10(9):1402.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Pooja K, Krishna K, Akhileshwar Ka, et al. PGPR bioelicitors: induced systemic resistance (ISR) and proteomic perspective on biocontrol. 2019. In: Singh, A.K., Kumar,A., Singh, P.K. (Eds.), PGPR Amelioration in Sustainable Agriculture: Food Security and Environmental management.[M]. Wood head Publishing, Cambridge, UK, 67-84. |
| [7] | 陶晶, 李春, 吴艳, 等. 加工番茄促生拮抗菌的筛选及其抑菌效果测定[J]. 石河子大学学报( 自然科学版). 2006, 24(1):34-37. |
| TAO Jing, LI Chun, WU Yan, et al. The Selection of Growth-Promoting Bacteria and the Measurement of Bacteria Control Effect[J]. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science), 2006, 24(1):34-37. | |
| [8] | 孙广正, 侯栋, 岳宏忠, 等. 番茄早疫病菌拮抗细菌的筛选及其抑制作用[J]. 草原与草坪, 2015, 35(1):32-36,43. |
| SUN Guangzheng, HOU Dong, YUE Hongzhong, et al. Screening of bacteria antagonizing Alternaria solani and its inhibitory effects[J]. Grassland and Turf. 2015, 35(1):32-36,43. | |
| [9] |
杨蓉, 杨文琦, 张峥, 等. 2株番茄早疫病拮抗菌的分离筛选与拮抗作用研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2017, 54(8):1496-1504.
DOI |
|
YANG Rong, YANG Wenqi, ZHANG Zheng, et al. Isolation and Screening for 2 Stains of Antagonistic Bacteria against Alternaria solani of Tomato and Study on Antagonistic Effect[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 54(8):1496-1504.
DOI |
|
| [10] | 贺字典, 高玉峰. 生防菌在植物病害防治中的研究进展(综述)[J]. 河北职业技术师范学院学报, 2003, 17(2):56-59. |
| HE Zidian, GAO Yufeng. Research Development of Biological Control Germ in Preventing and Controling Plants Disease and Insects (Summary)[J]. Journal of Hebei Vocation Technical Teachers College, 2003, 17(2):56-59. | |
| [11] |
刘晓光, 高克祥, 康振生, 等. 生防菌诱导植物系统抗性及其生化和细胞学机制[J]. 应用生态学报. 2007, 18(8):1861-1868.
PMID |
|
LIU Xiaoguang, GAO Kexiang, KANG Zhensheng, et al. Systemic resistance induced by biocontrol agents in plants and its biochemical and cytological mechanisms[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2007, 18(8):1861-1868.
PMID |
|
| [12] |
段佳丽, 舒志明, 魏良柱, 等. 丹参红叶病发生的微生态机制[J]. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(7):1991-1999.
PMID |
|
DUAN Jiali, SHU Zhiming, WEI Liangzhu, et al. Microecological mechanisms of red-leaf disease occurrence in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(7):1991-1999.
PMID |
|
| [13] | 赵伟进, 王孝先, 杨洋, 等. 黑青稞根际促生菌筛选及其对种子萌发的影响[J]. 种子, 2018, 37(12):1-5,10. |
| ZHAO Weijin, WANG Xiaoxian, YANG Yang, et al. Selection of Rhizotrophic Bacteria from Rhizosphere and Its Effect on Seed Germination of Black Barley[J]. Seed, 2018, 37(12):1-5,10. | |
| [14] | Gao H, Guo M, Song J, et al. Signals in systemic acquired resistance of plants against microbial pathogens[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2021, 48(4):1-13. |
| [15] | 戚益平, 何逸建, 许煜泉. 根际细菌诱导的植物系统抗性[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2003,(3):273-278. |
| QI Yiping, HE Yijian, XU Yuquan. Rhizobacteria-Mediated Induced Systemic Resistance in Plant[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2003,(3):273-278. | |
| [16] | 孔庆科, 丁爱云, 刘招舰, 等. 根际细菌诱导的系统抗性[J]. 山东科学, 2001,(4):18-25. |
| KONG Qingke, DING Aiyun, LIU Zhaojian, et al. Systemic resistance induced by rhizosphere bacteria[J]. Shandong Science, 2001,(4):18-25. | |
| [17] | 陈奕鹏, 杨扬, 桑建伟, 等. 拮抗内生芽孢杆菌BEB17分离鉴定及其挥发性物质抑菌活性分析[J]. 植物病理学报, 2018, 48(4):537-546. |
| CHEN Yipeng, YANG Yang, SANG Jianwei, et al. Isolation and identification of antagonistic endophytic bacillus BEB17 and analysis of antibacterial activity of volatile organic compounds[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2018, 48(4):537-546. | |
| [18] | 王华, 聂蓓蓓, 包立军, 等. 生防芽孢杆菌抑真菌机制及其在桑树真菌病害防治中的潜在应用价值[J]. 蚕业科学, 2021, 47(2):186-193. |
| WANG Hua, NIE Beibei, BAO Lijun, et al. Antifungal Mechanism of Biocontrol Bacillus and Its Potential Application in the Control of Mulberry Fungal Diseases[J]. Science of Sericulture, 2021, 47(2):186-193. | |
| [19] |
Gao Z, Zhang B, Liu H, et al. Identification of endophytic Bacillus velezensis ZSY-1 strain and antifungal activity of its volatile compounds against Alternaria solani and Botrytis cinerea[J]. Biological Control, 2017, 105:27-39.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 花东来, 欧秀玲, 祝建波, 等. PGPR菌液处理对新疆加工番茄种子萌发的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2013, 50(3):484-489. |
| HUA Donglai, OU Xiuling, ZHU Jianbo, et al. Effect of PGPR Bacterial Liquid on Germination of Xinjiang Processing Tomato Seed[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 50(3):484-489. | |
| [21] |
Zhang L, Khabbaz S E, Wang A, et al. Detection and characterization of broad-spectrum antipathogen activity of novel rhizobacterial isolates and suppression of Fusarium crown and root rot disease of tomato[J]. Journal of applied microbiology, 2015, 118(3):685-703.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | 孙韵雅, 陈佳, 王悦, 等. 根际促生菌促生机理及其增强植物抗逆性研究进展[J]. 草地学报, 2020, 28(5):1203-1215. |
| SUN Yunya, CHEN Jia, WANG Yue, et al. Advances in Growth Promotion Mechanisms of PGPRs and Their Effects on Improving Plant Stress Tolerance[J]. Acta Agrestia Sineca, 2020, 28(5):1203-1215. | |
| [23] | Akhtar N, Ilyas N, Mashwani Z, et al. Synergistic effects of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and silicon dioxide nano-particles for amelioration of drought stress in wheat[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021,(166):160-176. |
| [24] |
Samaras A, Roumeliotis E, Ntasiou P, et al. Bacillus subtilis MBI 600 Promotes Growth of Tomato Plants and Induces Systemic Resistance Contributing to the Control of Soilborne Pathogens[J]. Plants (Basel, Switzerland), 2021, 10(6):1113.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Ayaz M, Ali Q, Farzand A, et al. Nematicidal Volatiles from Bacillus atrophaeus GBSC56 Promote Growth and Stimulate Induced Systemic Resistance in Tomato against Meloidogyne incognita[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(9):5049.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Xing Z, Wu X, Zhao J, et al. Isolation and identification of induced systemic resistance determinants from Bacillus simplex Sneb545 against Heterodera glycines[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1):11586.
DOI URL |
| [1] | CHEN Fang, LI Zihui, SUNXiaogui , ZHANG Tingjun. Different dosage of microbial agents on the yield and quality of processed tomatoes [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2285-2289. |
| [2] | RUAN Xiangyang, PU Min, XIAO Lele, LUO Linyi, CHEN Ruijie, LI Ran, CHEN Guoyong, YE Jun. Effect of magnesium sulfate fertilizer application strategy on the yield and quality of processed tomato [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 916-925. |
| [3] | ZHAO Wenxuan, CHENG Yunxia, TAN Zhanming, LI Chunyu, SHU Sheng, Ayimaimu Shawuti, YANG Liyu, MIAO Xianjun. Comparison of chlorophyll fluorescence and photosynthetic characteristics of different processed tomato varieties based on principal component analysis [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2667-2675. |
| [4] | HE Wei, LUO Wenfang, YU Zhenhua, XU Jianjun, SUN Xiaojun. Growth Promoting Effect and Safety Evaluation of Bacillus velezensis JTB8-2 on Processed Tomato [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(5): 1260-1269. |
| [5] | WANG Fei, QIU Guang, LUO Wenfang, SUN Xiaojun, YANG Hongmei, LIU Chengjun, XU Jianjun, HE Wei. Study on Application Technology of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B1619 in Promoting Healthy Growth of Tomato Seedlings [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(5): 1252-1259. |
| [6] | GUO Huijing, LI Ziqin, LI Jixin, ZHAO Zhiyong, SONG Fangyuan. Design and Performance Evaluation of Automatic Pressure Tester for Processing Tomato [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(10): 2495-2501. |
| [7] | WANG Haiqi, PANG Shengqun, DU Hongyan, JI Xuehua, MA Haixiang, ZHANG Xiaoyan. Correlation Analysis between Source Hormone Content and Plant Growth during Processing Tomato Growth [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(1): 40-48. |
| [8] | SONG Fangyuan, ZHAO Zhiyong, LI Jixin. Selection of Main-Planted Tomato Varieties in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(7): 1267-1275. |
| [9] | HE Wei;XU Jian-jun;YANG Hua;CUI Yuan-yu;SUN Xiao-jun. Study on Pest Species and Population Dynamics Based on Application of Insect Sex Lures in Processing Tomato Fields [J]. , 2016, 53(9): 1618-1624. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 54
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 152
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||