

新疆农业科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (5): 1253-1262.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.05.025
田敬宇1( ), 高雁2, 高兴旺3(
), 高雁2, 高兴旺3( ), 曾军2(
), 曾军2( ), 赵鹏安3, 苏比努尔·居来提3
), 赵鹏安3, 苏比努尔·居来提3
收稿日期:2022-09-10
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2023-05-22
通信作者:
高兴旺(1983-),男,新疆乌鲁木齐人,讲师,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为植物-微生物互作,(E-mail)gxw@xju.edu.cn;作者简介:田敬宇(1998-),女,河北人,硕士,研究方向为修复生态学,(E-mail)1178798094@stu.xju.edu.cn
基金资助:
TIAN Jingyu1( ), GAO Yan2, GAO Xingwang3(
), GAO Yan2, GAO Xingwang3( ), ZENG Jun2(
), ZENG Jun2( ), ZHAO Pengan3, Subinuer Julaiti3
), ZHAO Pengan3, Subinuer Julaiti3
Received:2022-09-10
Published:2023-05-20
Online:2023-05-22
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】研究哈密瓜种植后根际土壤细菌群落结构的变化规律,为筛选功能菌株及开展哈密瓜连作障碍的防控研究奠定基础。【方法】以新疆五家渠市甜瓜之乡3个大田的哈密瓜根际土和非根际土为材料,检测其土壤理化性质和细菌群落结构,并分析环境因子与细菌群落之间的相关性,研究种植哈密瓜后根际土壤细菌群落的变化规律。【结果】哈密瓜种植后呈现出根际土壤pH显著增加,而土壤有机质、总磷、总钾等指标总体呈下降变化(P<0.05);哈密瓜种植后细菌α和β多样性指数均呈现略微降低趋势,但差异不显著;三个样地共检测到细菌43门、103纲、271目、440科、820属,其中变形菌门、放线菌门、酸杆菌门、芽单胞菌门、拟杆菌门、绿弯菌门、粘球菌门、厚壁菌门为主要类群,甜瓜种植后显著改变了细菌群落组成,其中厚壁菌门相对丰度随哈密瓜的种植而增加,酸杆菌门和绿弯菌门相对丰度下降;全磷和pH是影响哈密瓜根际土壤细菌优势类群的主要因素。【结论】哈密瓜种植显著影响了土壤理化性质从而导致其根际土壤细菌群落结构发生显著变化。
中图分类号:
田敬宇, 高雁, 高兴旺, 曾军, 赵鹏安, 苏比努尔·居来提. 哈密瓜种植对根际土壤细菌群落组成和多样性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(5): 1253-1262.
TIAN Jingyu, GAO Yan, GAO Xingwang, ZENG Jun, ZHAO Pengan, Subinuer Julaiti. Analysis of rhizospheric bacterial community structure and diversity of Hami melon under field cultivation[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(5): 1253-1262.
| 理化性质 physicochemical properties | W1 | W2 | W3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W10 | W11 | W20 | W21 | W30 | W31 | |
| pH | 7.00±0.12a | 7.26±0.15b | 6.79±0.25a | 7.11±0.09b | 7.60±0.10a | 7.78±0.13b |
| EC(mg/L) | 472.4±0.41a | 615.2±1.30b | 1038.4±1.14b | 293.6±6.58a | 716.4±3.84b | 619.6±3.84a |
| 有机质 Soil organic matter(g/kg) | 21.83±0.43b | 21.23±0.24a | 13.81±0.38b | 13.11±0.37a | 9.11±0.03a | 9.11±0.03a |
| 全氮 Total N(g/kg) | 1.02±0.01a | 1.11±0.03a | 0.68±0.03a | 0.68±0.01a | 0.43±0.01a | 0.43±0.01a |
| 全磷 Total P(g/kg) | 1.03±0.02a | 1.06±0.01a | 0.92±0.01b | 0.90±0.01a | 0.89±0.01b | 0.84±0.03a |
| 全钾 Total K(g/kg) | 21.93±0.24b | 21.52±0.11a | 19.92±0.16a | 19.91±0.23a | 20.94±0.14b | 20.61±0.02a |
| 碱解氮 Available N(mg/kg) | 49.80±0.43a | 49.95±0.44a | 44.05±1.32b | 42.54±0.61a | 28.81±2.07b | 10.70±0.88a |
| 有效磷 Available P(mg/kg) | 49.85±0.25a | 50.50±0.46b | 33.59±1.34a | 34.55±0.94a | 27.08±2.30b | 20.67±0.86a |
| 速效钾 Available P(mg/kg) | 330.3±6.46b | 310.6±5.32a | 190.8±5.84a | 201.7±6.91b | 129±6.15a | 151.3±6.74b |
表1 3个哈密瓜样地根际土/非根际土的土壤理化性质
Tab.1 The physicochemical properties of rhizosphere soil/non-rhizosphere soil from the three Hami melon samplings
| 理化性质 physicochemical properties | W1 | W2 | W3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W10 | W11 | W20 | W21 | W30 | W31 | |
| pH | 7.00±0.12a | 7.26±0.15b | 6.79±0.25a | 7.11±0.09b | 7.60±0.10a | 7.78±0.13b |
| EC(mg/L) | 472.4±0.41a | 615.2±1.30b | 1038.4±1.14b | 293.6±6.58a | 716.4±3.84b | 619.6±3.84a |
| 有机质 Soil organic matter(g/kg) | 21.83±0.43b | 21.23±0.24a | 13.81±0.38b | 13.11±0.37a | 9.11±0.03a | 9.11±0.03a |
| 全氮 Total N(g/kg) | 1.02±0.01a | 1.11±0.03a | 0.68±0.03a | 0.68±0.01a | 0.43±0.01a | 0.43±0.01a |
| 全磷 Total P(g/kg) | 1.03±0.02a | 1.06±0.01a | 0.92±0.01b | 0.90±0.01a | 0.89±0.01b | 0.84±0.03a |
| 全钾 Total K(g/kg) | 21.93±0.24b | 21.52±0.11a | 19.92±0.16a | 19.91±0.23a | 20.94±0.14b | 20.61±0.02a |
| 碱解氮 Available N(mg/kg) | 49.80±0.43a | 49.95±0.44a | 44.05±1.32b | 42.54±0.61a | 28.81±2.07b | 10.70±0.88a |
| 有效磷 Available P(mg/kg) | 49.85±0.25a | 50.50±0.46b | 33.59±1.34a | 34.55±0.94a | 27.08±2.30b | 20.67±0.86a |
| 速效钾 Available P(mg/kg) | 330.3±6.46b | 310.6±5.32a | 190.8±5.84a | 201.7±6.91b | 129±6.15a | 151.3±6.74b |
| α-多样性指数 Alpha-diversity indices | W1 | W2 | W3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W10 | W11 | W20 | W21 | W30 | W31 | |
| 丰富度指数 Richness index | 1 702.2±158.0a | 1 618.7±107.9a | 1 522.2±189.3a | 1 678.0±140.6a | 1 726.0±200.9a | 1 882.6±232.2a |
| Chao 1指数 Chao1 index | 1 712.2±167.0a | 1 624.5±108.0a | 1 528.18±194.83a | 1 693.2±151.0a | 1 372.7±206.1a | 1 903.2±238.6a |
| Shannon指数 Shannon index | 9.87±0.08a | 9.74±0.23a | 9.64±0.17a | 9.69±0.10a | 9.90±0.19a | 9.80±0.62a |
表2 3个哈密瓜样地根际土/非根际土细菌群落α多样性指数
Tab.2 Alpha-diversity indices of rhizosphere soil/non-rhizosphere soil bacterial community from the three Hami melon samplings(n=5)
| α-多样性指数 Alpha-diversity indices | W1 | W2 | W3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W10 | W11 | W20 | W21 | W30 | W31 | |
| 丰富度指数 Richness index | 1 702.2±158.0a | 1 618.7±107.9a | 1 522.2±189.3a | 1 678.0±140.6a | 1 726.0±200.9a | 1 882.6±232.2a |
| Chao 1指数 Chao1 index | 1 712.2±167.0a | 1 624.5±108.0a | 1 528.18±194.83a | 1 693.2±151.0a | 1 372.7±206.1a | 1 903.2±238.6a |
| Shannon指数 Shannon index | 9.87±0.08a | 9.74±0.23a | 9.64±0.17a | 9.69±0.10a | 9.90±0.19a | 9.80±0.62a |
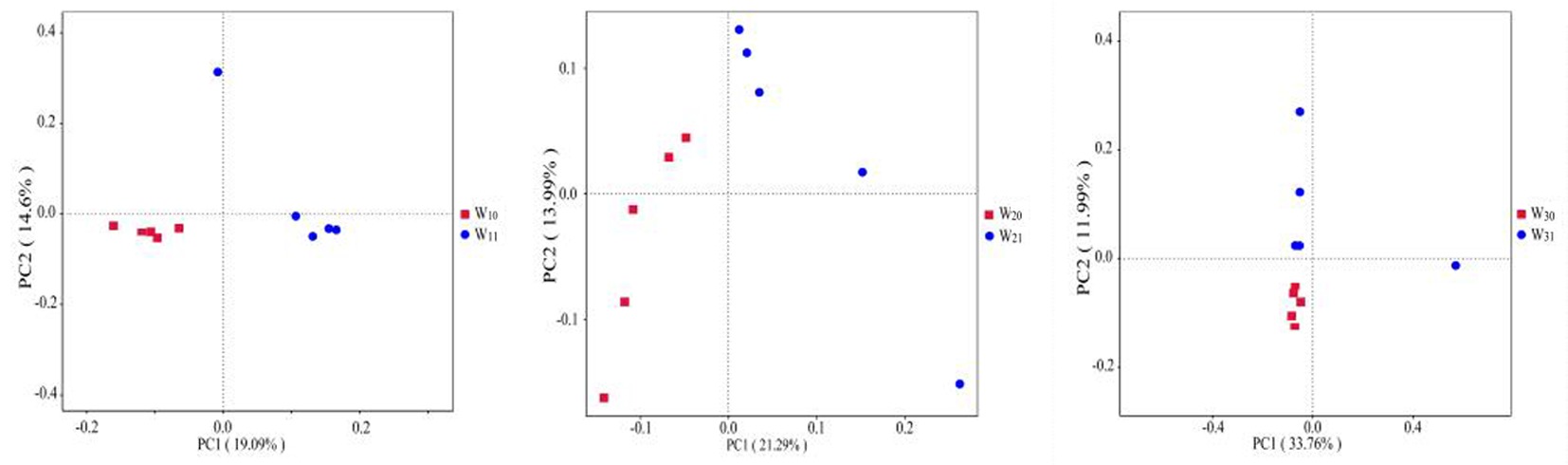
图1 3个哈密瓜样地根际土/非根际土细菌群落主坐标(PCoA)
Fig.1 Principal Co-ordinates Analysis (PCoA) of rhizosphere soil/non-rhizosphere soil bacterial community from the three Hami melon samplings
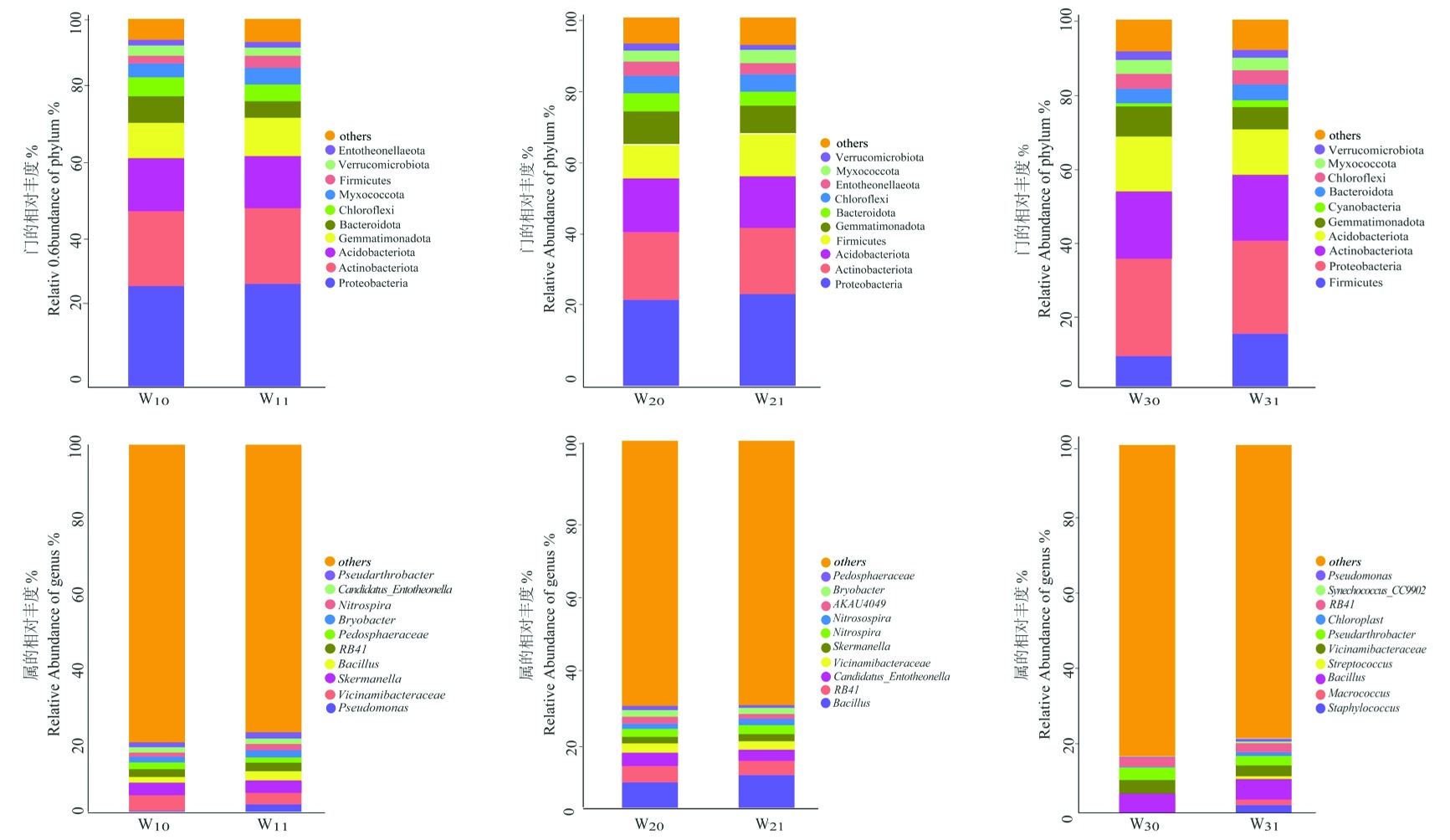
图2 3个哈密瓜样地根际土/非根际土细菌群落相对丰度
Fig.2 The relative abundance of rhizosphere soil/non-rhizosphere soil bacterial community from the three Hami melon samplings
| 分类 Classification | W1 | W2 | W3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W10 | W11 | W20 | W21 | W30 | W31 | |
| 变形菌门Proteobacteria | 27.41±2.45a | 27.95±2.94a | 23.59±1.76a | 25.29±1.57a | 26.42±2.17a | 25.33±0.93a |
| Skermanella属 | 3.50±0.90a | 3.26±0.54a | 1.92±0.26a | 1.86±0.68a | 1.50±0.25a | 1.33±0.38a |
| Pseudomonas属 | 0.38±0.10a | 2.07±4.14a | 0.24±0.06a | 0.25±0.15a | 0.09±0.03a | 0.68±1.24a |
| Acidibacter属 | 0.69±0.11a | 0.58±0.03a | 0.29±0.05a | 0.27±0.07a | 0.55±0.16a | 0.44±0.13a |
| 放线菌门Actinobacteriota | 20.36±1.08a | 20.78±1.69a | 18.44±1.12a | 18.08±1.06a | 18.45±1.27a | 17.89±4.56a |
| Pseudarthrobacter属 | 1.27±0.23a | 1.71±0.25b | 1.12±0.12a | 1.33±0.22a | 3.33±0.44a | 2.62±0.63a |
| 酸杆菌门Acidobacteriota | 14.37±0.85a | 14.11±0.40a | 14.65±0.94a | 13.93±1.22a | 14.94±0.42a | 12.41±3.75a |
| Vicinamibacteraceae属 | 4.25±0.32b | 3.29±0.11a | 2.49±0.21a | 2.48±0.34a | 3.77±0.43b | 2.89±0.65a |
| RB41属 | 2.18±0.27a | 2.50±0.17a | 4.59±0.52a | 4.00±0.61a | 2.61±0.29a | 2.51±0.72a |
| 芽单胞菌门Gemmatimonadota | 9.74±1.68a | 10.46±0.62b | 8.99±0.75b | 7.35±0.64a | 8.33±1.07b | 6.05±1.71a |
| 拟杆菌门Bacteroidota | 7.20±0.61a | 4.45±0.51a | 4.80±0.85b | 3.85±0.19a | 4.00±0.62a | 4.37±1.06a |
| Pontibacter属 | 0.18±0.04a | 0.32±0.14a | 1.18±0.40b | 0.19±0.07a | 0.12±0.04a | 0.15±0.04a |
| 绿弯菌门Chloroflexi | 5.10±0.33a | 4.64±0.34a | 4.86±0.47a | 4.76±0.36a | 4.12±0.08a | 3.96±1.38a |
| JG30-KF-CM45属 | 0.93±0.12a | 0.90±0.16a | 0.88±0.18a | 0.68±0.15a | 0.63±0.03a | 0.56±0.23a |
| 粘球菌门Myxococcota | 3.81±0.20a | 4.43±0.49b | 3.09±0.16a | 3.35±0.29a | 3.70±0.27a | 3.23±1.10a |
| 厚壁菌门Firmicutes | 2.07±0.61a | 3.36±1.00b | 8.96±1.95a | 11.42±0.86b | 8.56±1.59a | 14.60±10.64a |
| Bacillus属 | 1.49±0.36a | 2.52±0.90a | 7.06±1.57a | 9.02±0.82b | 5.39±0.98a | 5.38±1.02a |
| Staphylococcus属 | 0.00±0.00a | 0.01±0.02a | 0.00±0.00a | 0.01±0.01a | 0.00±0.00a | 2.11±4.71a |
| 微菌门Verrucomicrobiota | 1.54±0.19a | 1.60±0.32a | 1.91±0.59a | 1.43±0.49a | 27.08±2.30b | 1.48±0.51a |
| Entotheonellaeota门 | 2.82±1.06a | 2.17±0.59a | 3.78±0.42a | 3.20±0.42a | 8.56±1.59a | 14.60±10.64a |
| Candidatus_ Entotheonella属 | 1.47±0.19a | 1.52±0.30a | 3.47±0.40a | 2.89±0.40a | 1.34±0.14a | 1.29±0.43a |
表3 3个样地哈密瓜根际土/非根际土细菌在门、属水平上的相对丰度
Tab.3 The relative abundance of soil bacterial community at the phylum and genus levels from the three Hami melon samplings
| 分类 Classification | W1 | W2 | W3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W10 | W11 | W20 | W21 | W30 | W31 | |
| 变形菌门Proteobacteria | 27.41±2.45a | 27.95±2.94a | 23.59±1.76a | 25.29±1.57a | 26.42±2.17a | 25.33±0.93a |
| Skermanella属 | 3.50±0.90a | 3.26±0.54a | 1.92±0.26a | 1.86±0.68a | 1.50±0.25a | 1.33±0.38a |
| Pseudomonas属 | 0.38±0.10a | 2.07±4.14a | 0.24±0.06a | 0.25±0.15a | 0.09±0.03a | 0.68±1.24a |
| Acidibacter属 | 0.69±0.11a | 0.58±0.03a | 0.29±0.05a | 0.27±0.07a | 0.55±0.16a | 0.44±0.13a |
| 放线菌门Actinobacteriota | 20.36±1.08a | 20.78±1.69a | 18.44±1.12a | 18.08±1.06a | 18.45±1.27a | 17.89±4.56a |
| Pseudarthrobacter属 | 1.27±0.23a | 1.71±0.25b | 1.12±0.12a | 1.33±0.22a | 3.33±0.44a | 2.62±0.63a |
| 酸杆菌门Acidobacteriota | 14.37±0.85a | 14.11±0.40a | 14.65±0.94a | 13.93±1.22a | 14.94±0.42a | 12.41±3.75a |
| Vicinamibacteraceae属 | 4.25±0.32b | 3.29±0.11a | 2.49±0.21a | 2.48±0.34a | 3.77±0.43b | 2.89±0.65a |
| RB41属 | 2.18±0.27a | 2.50±0.17a | 4.59±0.52a | 4.00±0.61a | 2.61±0.29a | 2.51±0.72a |
| 芽单胞菌门Gemmatimonadota | 9.74±1.68a | 10.46±0.62b | 8.99±0.75b | 7.35±0.64a | 8.33±1.07b | 6.05±1.71a |
| 拟杆菌门Bacteroidota | 7.20±0.61a | 4.45±0.51a | 4.80±0.85b | 3.85±0.19a | 4.00±0.62a | 4.37±1.06a |
| Pontibacter属 | 0.18±0.04a | 0.32±0.14a | 1.18±0.40b | 0.19±0.07a | 0.12±0.04a | 0.15±0.04a |
| 绿弯菌门Chloroflexi | 5.10±0.33a | 4.64±0.34a | 4.86±0.47a | 4.76±0.36a | 4.12±0.08a | 3.96±1.38a |
| JG30-KF-CM45属 | 0.93±0.12a | 0.90±0.16a | 0.88±0.18a | 0.68±0.15a | 0.63±0.03a | 0.56±0.23a |
| 粘球菌门Myxococcota | 3.81±0.20a | 4.43±0.49b | 3.09±0.16a | 3.35±0.29a | 3.70±0.27a | 3.23±1.10a |
| 厚壁菌门Firmicutes | 2.07±0.61a | 3.36±1.00b | 8.96±1.95a | 11.42±0.86b | 8.56±1.59a | 14.60±10.64a |
| Bacillus属 | 1.49±0.36a | 2.52±0.90a | 7.06±1.57a | 9.02±0.82b | 5.39±0.98a | 5.38±1.02a |
| Staphylococcus属 | 0.00±0.00a | 0.01±0.02a | 0.00±0.00a | 0.01±0.01a | 0.00±0.00a | 2.11±4.71a |
| 微菌门Verrucomicrobiota | 1.54±0.19a | 1.60±0.32a | 1.91±0.59a | 1.43±0.49a | 27.08±2.30b | 1.48±0.51a |
| Entotheonellaeota门 | 2.82±1.06a | 2.17±0.59a | 3.78±0.42a | 3.20±0.42a | 8.56±1.59a | 14.60±10.64a |
| Candidatus_ Entotheonella属 | 1.47±0.19a | 1.52±0.30a | 3.47±0.40a | 2.89±0.40a | 1.34±0.14a | 1.29±0.43a |
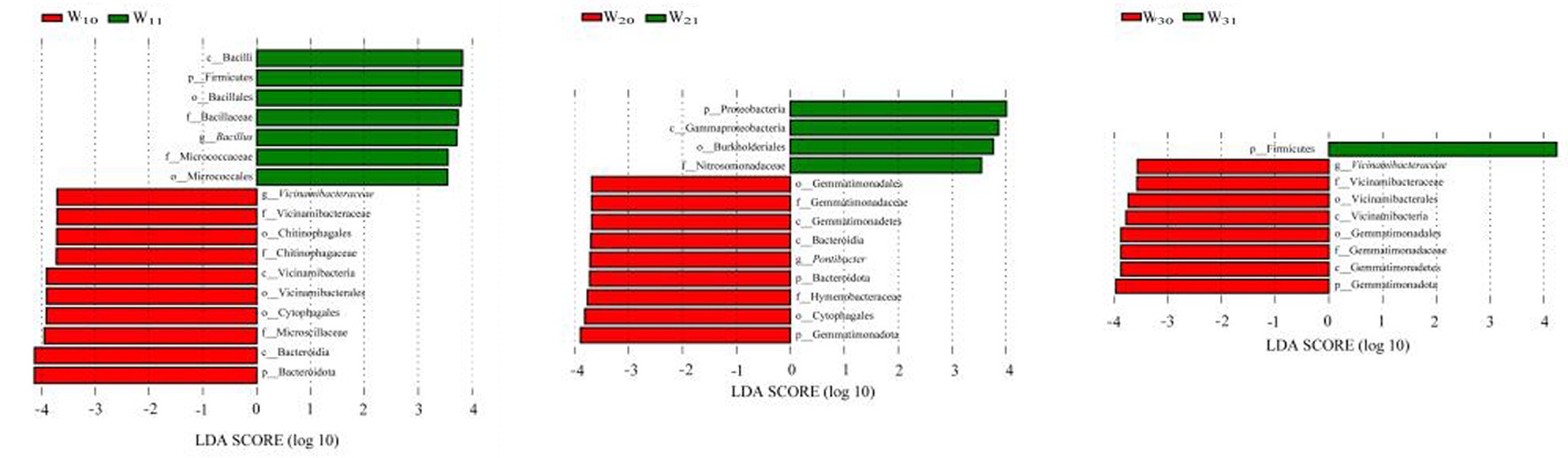
图3 3个哈密瓜样地根际土/非根际土细菌群落LEfSe分析(LDA Effect Size) 注:设定LDA阈值为3.5。红色和绿色分类分别代表每个样地根际土和非根际土中起重要作用的生物标志物
Fig.3 The LEfSe (LDA Effect Size) and random forest analyses of rhizosphere soil/ non-rhizosphere soil bacterial community from the three Hami melon samplings Note:The threshold value of LDA is 3.5.The red and green taxonomies represent the biomarkers playing an important role in the two tests of three groups, respectively
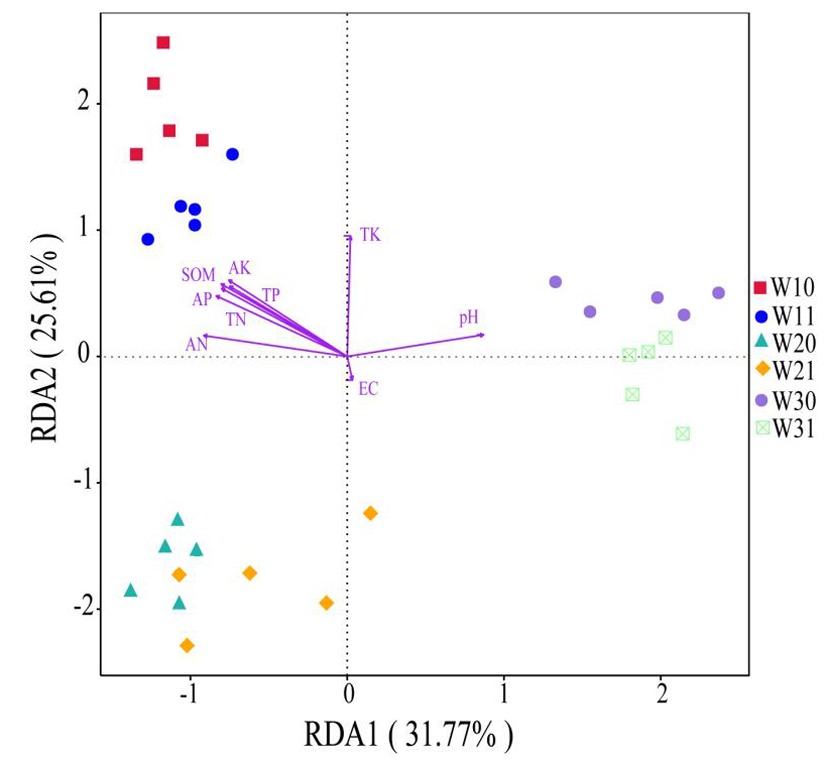
图4 3个哈密瓜样地根际土/非根际土细菌门水平种类与理化因子基于距离的冗余分析(db-RDA)
Fig.4 The distance based redundancy analysis (db-RDA) of environmental factors with rhizosphere soil/ non-rhizosphere soil bacterial at the phylum level from the three Hami melon samplings
| 因子组合 Different combination of environmental factors | Mantel检验 | |
|---|---|---|
| rM | P | |
| TK | 0.442 4 | 0.001 |
| pH | 0.456 9 | 0.001 |
| TK+pH | 0.529 3 | 0.001 |
| TK+pH+TP | 0.628 6 | 0.001 |
| TK+pH+TP+AK | 0.700 5 | 0.001 |
| TK+pH+TP+AK+TN | 0.729 1 | 0.001 |
| TK+AK+pH+TP+TN+AP | 0.722 6 | 0.001 |
| TK+pH+TP+AK+TN+AP+AN | 0.742 7 | 0.001 |
| TK+pH+TP+AK+TN+AP+AN+EC | 0.702 4 | 0.001 |
| TK+pH+AK+TN+AP+AN+TP+SOM+EC | 0.709 7 | 0.001 |
表4 3个样地哈密瓜根际土/非根际土中不同环境因子组合与细菌群落的相关关系
Tab.4 The relationship between different combination of environmental variables and soil bacterial community of rhizosphere soil/non-rhizosphere soil bacterial community from the three Hami melon samplings
| 因子组合 Different combination of environmental factors | Mantel检验 | |
|---|---|---|
| rM | P | |
| TK | 0.442 4 | 0.001 |
| pH | 0.456 9 | 0.001 |
| TK+pH | 0.529 3 | 0.001 |
| TK+pH+TP | 0.628 6 | 0.001 |
| TK+pH+TP+AK | 0.700 5 | 0.001 |
| TK+pH+TP+AK+TN | 0.729 1 | 0.001 |
| TK+AK+pH+TP+TN+AP | 0.722 6 | 0.001 |
| TK+pH+TP+AK+TN+AP+AN | 0.742 7 | 0.001 |
| TK+pH+TP+AK+TN+AP+AN+EC | 0.702 4 | 0.001 |
| TK+pH+AK+TN+AP+AN+TP+SOM+EC | 0.709 7 | 0.001 |
| [1] |
Bai Y, Wang G, Cheng Y, et al. Soil acidification in continuously cropped tobacco alters bacterial community structure and diversity via the accumulation of phenolic acids[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 1-18.
DOI |
| [2] | 林德佩. 甜瓜(Cucumis melo L.)种下分类专论[J]. 中国瓜菜, 2012, 25(5): 42-46. |
| LIN Depei. Comments on Intraspecific Classification of Melon[J]. China Cucurbits and Vegetables, 2012, 25(5): 42-46. | |
| [3] | 徐小军, 张桂兰, 周亚峰, 等. 甜瓜设施栽培连作土壤的理化性质及生物活性[J]. 果树学报, 2016, 33(9): 1131-1138. |
| XU Xiaojun, ZHANG Guilan, ZHOU Yafeng, et al. Studies on the physical-chemical and biological properties of soils cropped continuously with melon under protected cultivation condition[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2016, 33(9): 1131-1138. | |
| [4] | 周艳丽, 乔宏宇, 高红春, 等. 甜瓜连作对其根际土壤微生物和酶活性的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2015,(19): 158-161. |
| ZHOU Yanli, QIAO Hongyu, GAO Hongchun, et al. Effect of Melon Continuous Cropping on Rhizosphere Soil Microorganisms and Enzyme Activities[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2015,(19): 158-161. | |
| [5] | 唐小付, 刘岳飞, 张传进, 等. 设施甜瓜种植年限对土壤生物学特性和细菌多样性的影响[J]. 热带作物学报, 2018, 39(8): 1493-1500. |
| TANG Xiaofu, LIU Yuefei, ZHANG Chuanjin, et al. Effect of Different Planting Years on Soil Biological Properties and Bacterial Diversity in Protected Cultivation of Cucumis melo L.[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2018, 39(8): 1493-1500. | |
| [6] | 郑立伟, 赵阳阳, 王一冰, 等. 不同连作年限甜瓜种植土壤性质和微生物多样性[J]. 微生物学通报, 2022, 49(1): 101-114. |
| ZHENG Liwei, ZHAO Yangyang, WANG Yibing, et al. Soil properties and microbial diversity in the muskmelon fields after continuous cropping for different years[J]. Microbiology China, 2022, 49(1): 101-114. | |
| [7] | 刘旻霞, 李博文, 孙瑞弟, 等. 高寒草甸黄帚橐吾种群根际/非根际土壤可培养微生物群落特征[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(12):4853-4863. |
| LIU Minxia, LI Bowen, SUN Ruidi, et al. Characteristics of culturable microbial communities in rhizosphere/non-rhizosphere soil of Ligularia virgaurea in alpine meadow elevation gradient[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(12): 4853-4863. | |
| [8] | 陈悦, 吕光辉, 李岩. 独山子区优势草本植物根际与非根际土壤微生物功能多样性[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(9): 3110-3117. |
| CHEN Yue, LU Guanghui, LI Yan, et al. Soil microbial functional diversity of rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere of three dominant herbaceous plants in the Dushanzi District[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(9): 3110-3117. | |
| [9] | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2005. |
| BAO Shidan. Soil and Agricultural Chemical Analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2005. | |
| [10] |
Berg J, Brandt K K, Al-Soud W A, et al. Selection for Cu-tolerant bacterial communities with altered composition, but unaltered richness, via long-term Cu exposure[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2012, 78(20): 7438-7446.
PMID |
| [11] |
Michelsen C F, Pedas P, Glaring M A, et al. Bacterial diversity in Greenlandic soils as affected by potato cropping and inorganic versus organic fertilization[J]. Polar Biology, 2014, 37(1): 61-71.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Magoĉ T, Salzberg S L. FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies[J]. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27(21): 2957-2963.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Haas B J, Gevers D, Earl A M, et al. Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons[J]. Genome Research, 2011, 21(3): 494-504.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | 张丽娜, 于勇, 韩冰, 等. 甜瓜连作对土壤肥力及酶活性的影响[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2016,(6): 79-81. |
| ZHANG Lina, YU Yong, HAN Bing, et al. Effect of Melon Continuous Cropping on Soil Fertility and Soil Enzyme Activity[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2016,(6): 79-81. | |
| [15] | 刘垠霖, 蔡立群, 赵瑞, 等. 吐鲁番哈密瓜土壤养分及酶活性对连作年限的响应[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021,(1): 273-281. |
| LIU Yinlin, CAI Liqun, ZHAO Rui, et al. Response of soil nutrient and enzyme activity to continuous cropping years of Turpan Hami melon[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021,(1): 273-281. | |
| [16] |
Huang Y, Xiao X, Huang H, et al. Contrasting beneficial and pathogenic microbial communities across consecutive cropping fields of greenhouse strawberry[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(13): 5717-5729.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
YAN N, Marschner P. Response of microbial activity and biomass to increasing salinity depends on the final salinity, not the original salinity[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2012, 53: 50-55.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 武均. 不同管理措施下陇中黄土高原旱作农田土壤生态化学计量学特征研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2018. |
| WU Jun. Study on Soil Ecological Stoichiometry under Different Soil Management Practices in Dry Farmland of the Loess Plateau of Central Gansu Province[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| [19] |
LIU Q, Wang S, Li K, et al. Responses of soil bacterial and fungal communities to the long-term monoculture of grapevine[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2021, 105(18): 7035-7050.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Obalum S E, Chibuike G U, Peth S, et al. Soil organic matter as sole indicator of soil degradation[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2017, 189(4): 1-19.
DOI URL |
| [21] | ZHU S, WANG Y, XU X, et al. Potential use of high-throughput sequencing of soil microbial communities for estimating the adverse effects of continuous cropping on ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.Gaud)[J]. PloS One, 2018, 13(5): e0197095. |
| [22] |
Berendsen R L, Vismans G, Yu K, et al. Disease-induced assemblage of a plant-beneficial bacterial consortium[J]. The ISME Journal, 2018, 12(6): 1496-1507.
DOI |
| [23] |
Kalam S, Basu A, Ahmad I, et al. Recent understanding of soil acidobacteria and their ecological significance: a critical review[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 580024.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Pang Z, Dong F, Liu Q, et al. Soil metagenomics reveals effects of continuous sugarcane cropping on the structure and functional pathway of rhizospheric microbial community[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12: 627569.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Li Q, Song A, Yang H, et al. Impact of rocky desertification control on soil bacterial community in Karst Graben Basin, Southwestern China[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12: 636405.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Sarkar S, Ward K, Jansson J K, et al. Detection of stress functional responses in bacterial populations under dry soil conditions show potential microbial mechanisms to resist drought conditions[J]. BioRxiv, 2020. |
| [27] |
Mannaa M, Han G, Jeon H W, et al. Influence of resistance-inducing chemical elicitors against pine wilt disease on the rhizosphere microbiome[J]. Microorganisms, 2020, 8(6): 884.
DOI URL |
| [28] | SHEN M, ZHANG Y, BO G, et al. Microbial responses to the reduction of chemical fertilizers in the rhizosphere soil of flue-cured tobacco[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2021: 1464. |
| [29] |
Badri D V, Chaparro J M, Zhang R, et al. Application of natural blends of phytochemicals derived from the root exudates of Arabidopsis to the soil reveal that phenolic-related compounds predominantly modulate the soil microbiome[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2013, 288(7): 4502-4512.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Chevrot R, Rosen R, Haudecoeur E, et al. GABA controls the level of quorum-sensing signal in Agrobacterium tumefaciens[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2006, 103(19): 7460-7464.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Berlanga-Clavero M V, Molina-Santiago C, Caraballo-Rodríguez A M, et al. Bacillus subtilis biofilm matrix components target seed oil bodies to promote growth and anti-fungal resistance in melon[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2022: 1-15. |
| [32] |
Santoyo G, Orozco-Mosqueda M C, Govindappa M. Mechanisms of biocontrol and plant growth-promoting activity in soil bacterial species of Bacillus and Pseudomonas: a review[J]. Biocontrol Science and Technology, 2012, 22(8): 855-872.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Alibrandi P, Cardinale M, Rahman M D, et al. The seed endosphere of Anadenanthera colubrina is inhabited by a complex microbiota, including Methylobacterium spp.and Staphylococcus spp.with potential plant-growth promoting activities[J]. Plant and Soil, 2018, 422(1): 81-99.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 张浩, 梁其干, 张学军, 符小发, 陈积豪, 周勃, 黄远. 刺角瓜砧木抗性分析及其嫁接对甜瓜品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1963-1968. |
| [2] | 陈积豪, 张浩, 梁其干, 符小发, 张学军, 毛建才. 减施化肥增施蚯蚓粪有机肥对连作甜瓜的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1969-1975. |
| [3] | 卡地尔阿依·买买提, 周婷婷, 韩盛, 梅丽克汗·热西提, 玉山江·麦麦提. 不同甜瓜品种遗传转化再生体系的建立与基因编辑植株的快速获取[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1666-1672. |
| [4] | 杨君妍, 闫淼, 吴海波, 杨文莉, 王豪杰, 毛建才, 翟文强, 李俊华. 高温对不同厚皮甜瓜品种种子萌发的影响及其耐热性综合评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1386-1396. |
| [5] | 刘阳, 张郑啸, 白羽嘉, 冯作山. 链格孢菌侵染对甜瓜不同组织活性氧代谢的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1397-1406. |
| [6] | 马凌, 沈琦, 康琪, 张忠祥, 贾宏涛, 王成. 甜瓜不同生长阶段5种重金属在植株中富集分配的变化及关联分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 892-899. |
| [7] | 杨文莉, 许丽蓉, 刘斌, 凌悦铭, 李寐华, 杨永, 范蓉, 黎玉顺, 张永兵, 张学军. 盐胁迫对薄皮甜瓜‘灰鼠’离子平衡、膜脂过氧化及渗透调节物质积累的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 900-907. |
| [8] | 梁其干, 张浩, 胡国智, 陈积豪, 冯烔鑫, 曹庆, 王敏, 符小发, 闫淼, 高强, 张学军, 周勃, 王豪杰. 施肥调控对设施甜瓜生长与产量、品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(3): 599-606. |
| [9] | 李慧, 毕莹, 王新宇, 雷雅馨, 张琪, 黄帅, 热扎·库忘德克, 王静. 核桃青皮多酚调控对哈密瓜采后活性氧代谢水平及腐烂率的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(12): 2966-2975. |
| [10] | 李超, 杨英, 郑贺云, 杨建丽, 陈伟, 杨咪, 孙玉萍. 基于SSR荧光标记分析新疆甜瓜种质资源遗传多样性与群体结构[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2614-2625. |
| [11] | 沈悦, 凌悦铭, 段晓宇, 杨文莉, 李寐华, 王懿柔, 王惠林, 张学军. 甜瓜抗霜霉病KASP分子标记的开发与验证[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2626-2634. |
| [12] | 姚军, 秦勇, 郑贺云, 张翠环, 再吐娜·买买提, 汪志伟, 耿新丽. 无花果叶提取液复合保鲜膜的研制及其在甜瓜保鲜上的应用[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(1): 118-126. |
| [13] | 郑贺云, 姚军, 李超, 张翠环, 耿新丽. 不同贮藏温度对甜瓜品质的影响及预测模型建立[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1950-1957. |
| [14] | 姚军, 郑贺云, 张翠环, 再吐娜·买买提, 耿新丽. LED持续光照处理对甜瓜贮藏特性及糖代谢的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(7): 1689-1697. |
| [15] | 李自芹, 李文绮, 贾文婷, 李宇辉, 刘成江. 氯化钙与1-MCP对西州蜜甜瓜采后贮藏品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(7): 1698-1704. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||