

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (4): 900-907.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.04.014
• 农产品分析检测·土壤肥料·农产品加工工程 • 上一篇 下一篇
杨文莉1( ), 许丽蓉2, 刘斌1, 凌悦铭1, 李寐华1, 杨永1, 范蓉1, 黎玉顺1, 张永兵1, 张学军1(
), 许丽蓉2, 刘斌1, 凌悦铭1, 李寐华1, 杨永1, 范蓉1, 黎玉顺1, 张永兵1, 张学军1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-08-01
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-05-31
通信作者:
张学军(1980-),男,吉林人,研究员,在读博士,研究方向为西甜瓜抗病育种与分子育种,(E-mail)zxj333@126.com作者简介:杨文莉(1994-),女,河南人,助理研究员,研究方向为西甜瓜抗逆育种,(E-mail)1481209164@qq.com
基金资助:
YANG Wenli1( ), XU Lirong2, LIU Bin1, LING Yueming1, LI Meihua1, YANG Yong1, FAN Rong1, LI Yushun1, ZHANG Yongbin1, ZHANG Xuejun1(
), XU Lirong2, LIU Bin1, LING Yueming1, LI Meihua1, YANG Yong1, FAN Rong1, LI Yushun1, ZHANG Yongbin1, ZHANG Xuejun1( )
)
Received:2023-08-01
Published:2024-04-20
Online:2024-05-31
Correspondence author:
ZHANG Xuejun(1980-), male, from Jilin,researcher, research direction: watermelon and melon disease resistance breeding and molecular breeding, (E-mail)zxj333@126.comSupported by:摘要:
【目的】研究薄皮甜瓜‘灰鼠’对盐(NaCl)胁迫的生理响应机制,为甜瓜栽培及示范推广提供理论依据。【方法】采用基质盆栽试验,分别观测其在100 mmol/L NaCl胁迫5 d及胁迫20 d后在幼苗生长、离子稳态、抗氧化酶系统及渗透调节物质的变化情况。【结果】盐胁迫抑制了幼苗生长,破坏了离子平衡及抗氧化系统。甜瓜株高、叶柄长、叶片数随盐胁迫时间的延长而显著降低,茎粗、叶柄粗、叶片厚度随盐胁迫时间的延长而显著增加。盐胁迫后Na+外排速度降低,Na+含量增加,K+外流流速增大,K+含量减少。丙二醛含量显著增加,SOD、POD、CAT酶活性先升高后降低;可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白、游离脯氨酸含量显著增加。【结论】盐胁迫下,薄皮甜瓜‘灰鼠’通过限制自身生长,增加叶片Na+含量、减少K+含量,并提高抗氧化酶活性,积累更多的渗透调节物质缓解盐胁迫。
中图分类号:
杨文莉, 许丽蓉, 刘斌, 凌悦铭, 李寐华, 杨永, 范蓉, 黎玉顺, 张永兵, 张学军. 盐胁迫对薄皮甜瓜‘灰鼠’离子平衡、膜脂过氧化及渗透调节物质积累的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 900-907.
YANG Wenli, XU Lirong, LIU Bin, LING Yueming, LI Meihua, YANG Yong, FAN Rong, LI Yushun, ZHANG Yongbin, ZHANG Xuejun. Effects of salt stress on ion balance, membrane lipid peroxidation, and osmotic regulation substance accumulation in thin skin muskmelon ‘Huishu’[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 900-907.
| 处理时间 Treatment Time (d) | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 茎粗 Diameter diameter (mm) | 叶片长 Leaf long (cm) | 叶片宽 Leaf side (cm) | 叶片厚度 Blade thickness (mm) | 叶柄长 Petiole length (mm) | 叶柄粗 Petiole thick (mm) | 叶片数 Leaf number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 64.83±3.25a | 3.98±0.41a | 9.83±0.76a | 12.43±0.43a | 0.35±0.03a | 10±1.68a | 3.36±0.1a | 8±1a |
| 5 | 54.3±5.5b | 4.15±0.5a | 7.5±0.58b | 9.83±0.76b | 0.44±0.02b | 8.7±1.89a | 3.36±0.06a | 6±0b |
| 20 | 40±8.54c | 4.46±0.32a | 6.5±0.71b | 9.25±1.06b | 0.55±0.06c | 7±2.65a | 3.43±0.02a | 5±1b |
表1 盐胁迫下薄皮甜瓜‘灰鼠’生长指标的变化
Tab.1 Changes of ‘Huishu’ growth indexes under salt stress
| 处理时间 Treatment Time (d) | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 茎粗 Diameter diameter (mm) | 叶片长 Leaf long (cm) | 叶片宽 Leaf side (cm) | 叶片厚度 Blade thickness (mm) | 叶柄长 Petiole length (mm) | 叶柄粗 Petiole thick (mm) | 叶片数 Leaf number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 64.83±3.25a | 3.98±0.41a | 9.83±0.76a | 12.43±0.43a | 0.35±0.03a | 10±1.68a | 3.36±0.1a | 8±1a |
| 5 | 54.3±5.5b | 4.15±0.5a | 7.5±0.58b | 9.83±0.76b | 0.44±0.02b | 8.7±1.89a | 3.36±0.06a | 6±0b |
| 20 | 40±8.54c | 4.46±0.32a | 6.5±0.71b | 9.25±1.06b | 0.55±0.06c | 7±2.65a | 3.43±0.02a | 5±1b |
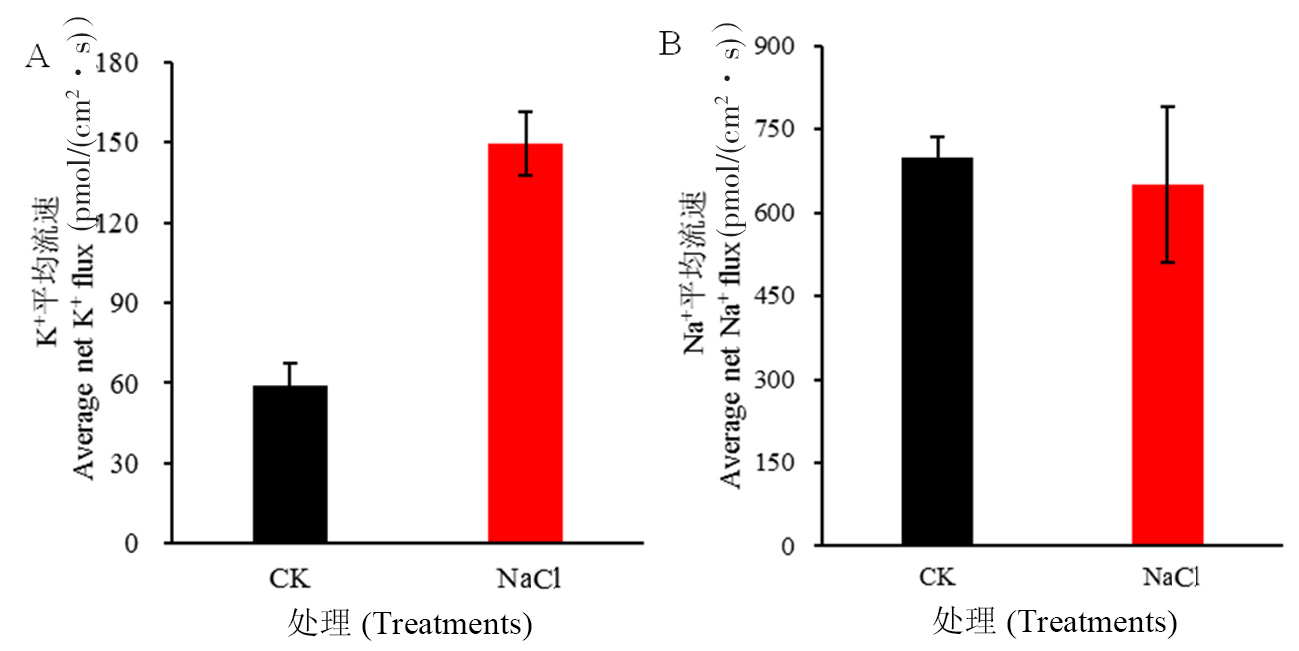
图1 100 mmol/L NaCl胁迫24 h下‘灰鼠’甜瓜幼苗叶片K+、Na+平均流速变化
Fig.1 Changes of average K+、Na+ fluxes in seedling leaves of ‘Huishu’ after 100 mmol/L NaCl stress for 24 hours
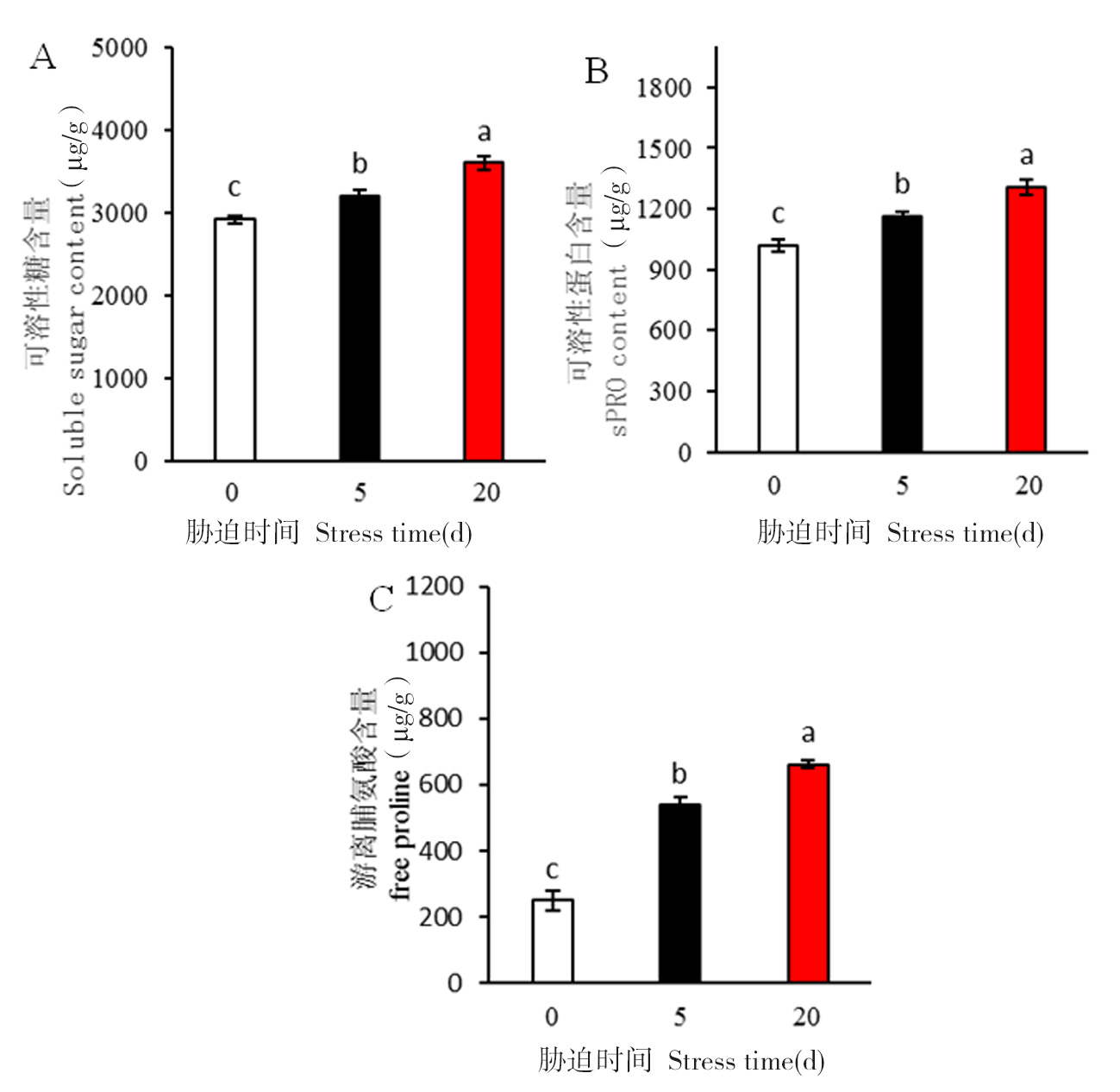
图5 盐胁迫下薄皮甜瓜‘灰鼠’幼苗叶片渗透调节物质变化 注:A、B、C分别为可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白和游离脯氨酸含量
Fig.5 Changes of salt stress on osmoregulation substances in leaves of ‘Huishu’ seedlings Note:A. B and C are the contents of soluble sugar, soluble protein and free proline, respectively
| [1] |
Tang X L, Mu X M, Shao H B, et al. Global plant-responding mechanisms to salt stress: physiological and molecular levels and implications in biotechnology[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2015, 35(4): 425-437.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Munns R, Tester M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2008, 59: 651-681.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | 朱生堡, 乌尔古丽·托尔逊, 唐光木, 等. 新疆盐碱地变化及其治理措施研究进展[J]. 山东农业科学, 2023, 55(3): 158-165. |
| ZHU Shengbao, Wuerguli Tuoerxun, TANG Guangmu, et al. Research progress on saline-alkali land changes and its treatment measures in Xinjiang[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 55(3): 158-165. | |
| [4] | Cui Y N, Li X T, Yuan J Z, et al. Chloride is beneficial for growth of the xerophyte Pugionium cornutum by enhancing osmotic adjustment capacity under salt and drought stresses[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2020, 71(14): 4215-4231. |
| [5] | Zhang Y B, Fan X B, Aierken Y, et al. Genetic diversity of melon landraces (Cucumis melo L.) in the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region on the basis of simple sequence repeat markers[J]. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 2017, 64(5): 1023-1035. |
| [6] |
李帜奇, 袁月, 苗荣庆, 等. 盐胁迫盐芥和拟南芥褪黑素含量及合成相关基因表达模式分析[J]. 生物技术通报, 2023, 39(5): 142-151.
DOI |
|
LI Zhiqi, YUAN Yue, MIAO Rongqing, et al. Melatonin contents in Eutrema salsugineum and Arabidopsis thaliana under salt stress, and expression pattern analysis of synthesis related genes[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2023, 39(5): 142-151.
DOI |
|
| [7] |
Apse M P, Blumwald E. Engineering salt tolerance in plants[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2002, 13(2): 146-150.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Yang Y Q, Guo Y. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses[J]. The New Phytologist, 2018, 217(2): 523-539. |
| [9] | Munns R, Passioura J B, Colmer T D, et al. Osmotic adjustment and energy limitations to plant growth in saline soil[J]. The New Phytologist, 2020, 225(3): 1091-1096. |
| [10] | Hauser F, Horie T. A conserved primary salt tolerance mechanism mediated by HKT transporters: a mechanism for sodium exclusion and maintenance of high K(+)/Na(+) ratio in leaves during salinity stress[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2010, 33(4): 552-565. |
| [11] | Li H, Wang H, Wen W J, et al. The antioxidant system in Suaeda salsa under salt stress[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2020, 15(7): 1771939. |
| [12] | Munns R. Comparative physiology of salt and water stress[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2002, 25(2): 239-250. |
| [13] | 李静, 韩庆庆, 段丽婕, 等. 非损伤微测技术在植物生理学研究中的应用及进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2014, 50(10): 1445-1452. |
| LI Jing, HAN Qingqing, DUAN Lijie, et al. Applications and advances of non-invasive micro-test technique in plant physiology researches[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2014, 50(10): 1445-1452. | |
| [14] | 董宏图, 解超杰, 侯佩臣, 等. 高盐胁迫下小麦幼苗离子吸收动态及耐盐性筛选[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2021, 29(4): 762-770. |
| DONG Hongtu, XIE Chaojie, HOU Peichen, et al. Dynamic of ionic absorption and salt tolerance screening in wheat seedling under salt stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2021, 29(4): 762-770. | |
| [15] | 赵卫星, 常高正, 康利允, 等. 甜瓜幼苗对KNO3+K2SO4混合盐胁迫的生理响应[J]. 西南农业学报, 2020, 33(7): 1423-1428. |
| ZHAO Weixing, CHANG Gaozheng, KANG Liyun, et al. Physiological response of muskmelon seedlings to KNO3-K2SO4 mixed salt stress[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 33(7): 1423-1428. | |
| [16] | Xiong M, Zhang X J, Shabala S, et al. Evaluation of salt tolerance and contributing ionic mechanism in nine Hami melon landraces in Xinjiang, China[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2018, 237: 277-286. |
| [17] | 刘美岑, 张子健, 张东. NaCl胁迫对甜瓜幼苗保护酶活性及光合性能的影响[J]. 分子植物育种, 2023,1-12 |
| LIU Meicen, ZHANG Zijian, ZHANG Dong, et al. Effects of NaCl stress on protective enzyme activities and photosynthetic performance of muskmelon seedlings[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2023,1-12. | |
| [18] | 颜志明. 外源脯氨酸提高甜瓜幼苗耐盐性的生理调节功能[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2011. |
| YAN Zhiming. Studies on Physiological Regulation Function of Exogenous Proline on Melon Seedlings Tolerance to Salt Stress[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2011. | |
| [19] | Kong L G, Wang F H, Si J S, et al. Increasing in ROS levels and callose deposition in peduncle vascular bundles of wheat (Triticum aestivumL.) grown under nitrogen deficiency[J]. Journal of Plant Interactions, 2013, 8(2): 109-116. |
| [20] | Gutiérrez D R, Chaves A R, Rodríguez S D C. UV-C and ozone treatment influences on the antioxidant capacity and antioxidant system of minimally processed rocket (Eruca sativa Mill.)[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 2018, 138: 107-113. |
| [21] | Assaha D V M, Ueda A, Saneoka H, et al. The role of Na+ and K+ transporters in salt stress adaptation in glycophytes[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2017, 8: 509. |
| [22] | Chevilly S, Dolz-Edo L, Martínez-Sánchez G, et al. Distinctive traits for drought and salt stress tolerance in melon (Cucumis melo L.)[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 777060. |
| [23] | Orozco C M, Ryan C A. Hydrogen peroxide is generated systemically in plant leaves by wounding and system in via the octadecanoid pathway[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 1999, 96(11):6553-6557. |
| [24] | 蒋文博, 陈钊, 曹新龙, 等. 外源NO对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿生长及膜脂过氧化的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2019, 36(10): 2580-2593. |
| JIANG Wenbo, CHEN Zhao, CAO Xinlong, et al. Effects of exogenous nitric oxide on the growth and membrane lipid peroxidation of Medicago sativa under salt stress[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(10): 2580-2593. | |
| [25] | 姜瑛, 周萌, 吴越, 等. 不同燕麦品种耐盐性差异及其生理机制[J]. 草业科学, 2018, 35(12): 2903-2914. |
| JIANG Ying, ZHOU Meng, WU Yue, et al. Evaluation of salt tolerance and its underlying physiological mechanisms in different oats[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(12): 2903-2914. | |
| [26] | Athar H U R, Khan A, Ashraf M. Exogenously applied ascorbic acid alleviates salt-induced oxidative stress in wheat[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2008, 63(1/2/3): 224-231. |
| [27] | 吕昕培. 梭梭木质素合成对盐和渗透胁迫的响应及HaLAC15和HaCOMT的功能鉴定[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2022. |
| LYU Xinpei. Responses of Lignin Synthesis in Haloxylon Ammodendron to Salt and Osmotic Stresses and Functional Identification of HaLAC15 and HaCOMT[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2022. | |
| [28] | 张永平. 氯化胆碱对盐胁迫黄瓜幼苗渗透调节物质及活性氧代谢系统的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2011, 31(1): 137-143. |
| ZHANG Yongping. Effects of choline chloride on osmotic adjustment substances and reactive oxygen species metabolism of cucumber seedlings under salt stress[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2011, 31(1): 137-143. | |
| [29] |
黄婷婷, 郑殿峰, 冯乃杰, 等. 亚精胺对盐胁迫下黄华占水稻幼苗根系抗氧化酶活性及Na+稳态的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(2): 43-47.
DOI |
|
HUANG Tingting, ZHENG Dianfeng, FENG Naijie, et al. Effects of spermidine on antioxidant enzyme activity and Na+Homeostasis of seedlings roots of Huanghuazhan rice under salt stress[J]. China Rice, 2023, 29(2): 43-47.
DOI |
|
| [30] | 冯肖莉, 樊寿德, 周莲洁, 等. 苗期盐穗木在不同盐浓度处理下的渗调和抗氧化系统[J]. 干旱区研究, 2018, 35(5): 1118-1128. |
| FENG Xiaoli, FAN Shoude, ZHOU Lianjie, et al. Osmotic and antioxidant system in Halostachys caspica seedlings under salt stress[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2018, 35(5): 1118-1128. | |
| [31] | 何子华. 盐胁迫下胀果甘草和乌拉尔甘草渗透调节特征的比较分析[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2022, 3-15. |
| HE Zihua. Comparative analysis of osmotic adjustment characteristics of Glycyrrhiza inflata and Glycyrrhiza uralensis under salt stress[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2022, 3-15. | |
| [32] | 王伟奇, 张蒙, 秦肇辰, 等. 南瓜耐盐性研究进展[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2020,(10): 18-26. |
| WANG Weiqi, ZHANG Meng, QIN Zhaochen, et al. Research progress on salt tolerance in Cucurbita[J]. China Vegetables, 2020,(10): 18-26. | |
| [33] | Pedrol N, Ramos P, Reigosa M J. Phenotypic plasticity and acclimationto water deficits in velvet-grass: a long-term green-house experiment. Changes in leaf morphology, photosynthesis and stress-induced metabolites[J]. Plant Physiology, 2000,(157):383-393. |
| [34] |
田甜, 王海江, 王金刚, 等. 盐胁迫下施加氮素对饲用油菜有机渗透调节物质积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 125-136.
DOI |
|
TIAN Tian, WANG Haijiang, WANG Jingang, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on accumulation of organic osmotic regulating substances in forage rapeseed(Brassica napus) under salt stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(10): 125-136.
DOI |
| [1] | 张浩, 梁其干, 张学军, 符小发, 陈积豪, 周勃, 黄远. 刺角瓜砧木抗性分析及其嫁接对甜瓜品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1963-1968. |
| [2] | 陈积豪, 张浩, 梁其干, 符小发, 张学军, 毛建才. 减施化肥增施蚯蚓粪有机肥对连作甜瓜的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1969-1975. |
| [3] | 卡地尔阿依·买买提, 周婷婷, 韩盛, 梅丽克汗·热西提, 玉山江·麦麦提. 不同甜瓜品种遗传转化再生体系的建立与基因编辑植株的快速获取[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1666-1672. |
| [4] | 杨君妍, 闫淼, 吴海波, 杨文莉, 王豪杰, 毛建才, 翟文强, 李俊华. 高温对不同厚皮甜瓜品种种子萌发的影响及其耐热性综合评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1386-1396. |
| [5] | 刘阳, 张郑啸, 白羽嘉, 冯作山. 链格孢菌侵染对甜瓜不同组织活性氧代谢的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1397-1406. |
| [6] | 马凌, 沈琦, 康琪, 张忠祥, 贾宏涛, 王成. 甜瓜不同生长阶段5种重金属在植株中富集分配的变化及关联分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 892-899. |
| [7] | 梁其干, 张浩, 胡国智, 陈积豪, 冯烔鑫, 曹庆, 王敏, 符小发, 闫淼, 高强, 张学军, 周勃, 王豪杰. 施肥调控对设施甜瓜生长与产量、品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(3): 599-606. |
| [8] | 李超, 杨英, 郑贺云, 杨建丽, 陈伟, 杨咪, 孙玉萍. 基于SSR荧光标记分析新疆甜瓜种质资源遗传多样性与群体结构[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2614-2625. |
| [9] | 沈悦, 凌悦铭, 段晓宇, 杨文莉, 李寐华, 王懿柔, 王惠林, 张学军. 甜瓜抗霜霉病KASP分子标记的开发与验证[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2626-2634. |
| [10] | 姚军, 秦勇, 郑贺云, 张翠环, 再吐娜·买买提, 汪志伟, 耿新丽. 无花果叶提取液复合保鲜膜的研制及其在甜瓜保鲜上的应用[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(1): 118-126. |
| [11] | 郑贺云, 姚军, 李超, 张翠环, 耿新丽. 不同贮藏温度对甜瓜品质的影响及预测模型建立[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1950-1957. |
| [12] | 姚军, 郑贺云, 张翠环, 再吐娜·买买提, 耿新丽. LED持续光照处理对甜瓜贮藏特性及糖代谢的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(7): 1689-1697. |
| [13] | 李自芹, 李文绮, 贾文婷, 李宇辉, 刘成江. 氯化钙与1-MCP对西州蜜甜瓜采后贮藏品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(7): 1698-1704. |
| [14] | 刘阳, 白羽嘉, 张郑啸, 楚晨俐, 王甜甜, 冯作山. 甜瓜抗链格孢侵染病程相关蛋白及苯丙烷代谢酶的变化[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(7): 1780-1789. |
| [15] | 贾斌鑫, 杨世英, 王艳, 杨朋朋, 何伟忠, 王成, 刘峰娟, 范盈盈. 不同品种厚皮甜瓜采后糖含量及糖代谢酶活性比较[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1476-1484. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 62
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 134
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||