

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (11): 2750-2760.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.11.016
赵莎莎( ), 王世伟(
), 王世伟( ), 张翠芳, 郝洪龙, 郭桐, 杨先安, 杨雯洁
), 张翠芳, 郝洪龙, 郭桐, 杨先安, 杨雯洁
收稿日期:2024-04-02
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2025-01-08
通信作者:
王世伟(1984-),男,河南周口人,教授,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为森林培育,(E-mail)wsw850204@163.com作者简介:赵莎莎(1997-),女,云南大理人,硕士研究生,研究方向为森林培育技术与应用,(E-mail)1439172753@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHAO Shasha( ), WANG Shiwei(
), WANG Shiwei( ), ZHANG Cuifang, HAO Honglong, GUO Tong, YANG Xianan, YANG Wenjie
), ZHANG Cuifang, HAO Honglong, GUO Tong, YANG Xianan, YANG Wenjie
Received:2024-04-02
Published:2024-11-20
Online:2025-01-08
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】分析树体营养水平调控增强核桃抗焦叶病能力,为核桃焦叶病科学防控提供理论依据。【方法】通过系统比较健康、轻度、中度、重度核桃焦叶病生产园以及不同施肥处理后核桃样园和核桃叶片中矿质元素含量变化。【结果】核桃不同发病程度叶片矿质元素含量之间差异比较:大量元素为健康园叶片中N、P、K、Ca含量显著高于中度园和重度园(P<0.05),而健康园叶片中Mg含量显著低于发病园(P<0.05);微量元素:健康园叶片中Fe、Mn、Cu含量显著高于发病园(P<0.05),Cl、Na和Zn含量显著低于发病园(P<0.05)。核桃不同发病程度土壤矿质元素含量之间差异比较:大量元素为健康土壤中TN、TP、TK、AN、AP、AK含量显著高于中度园和重度园(P<0.05);微量元素为健康土壤中Fe、Cu、Zn含量显著高于中度园和重度园(P<0.05)。健康土壤中Na、Cl含量显著低于中度园和重度园(P<0.05)。N和K在PC1和PC2中均为正值,并且呈正相关,对焦叶病发挥主要作用。施肥处理后,合理的根施N、K和叶喷N、K相结合效果最佳,发病率降到8%,并且土壤和叶片中的氮钾含量都显著上升。【结论】核桃焦叶病的发生与N、K含量低和Cl含量高有密切关系,合理补充N、K可有效防控核桃焦叶病。
中图分类号:
赵莎莎, 王世伟, 张翠芳, 郝洪龙, 郭桐, 杨先安, 杨雯洁. 核桃焦叶病与矿质元素关系分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2750-2760.
ZHAO Shasha, WANG Shiwei, ZHANG Cuifang, HAO Honglong, GUO Tong, YANG Xianan, YANG Wenjie. Analysis of the relationship between walnut leaf scorch disease and mineral elements[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2750-2760.

图1 核桃焦叶病发病症状 注:A:正常叶片;B:轻度发病叶片;C:中度发病叶片;D:重度发病叶片
Fig.1 Symptoms of walnut leaf scorch disease Notes: A: Healthy leaves; B: Mildly onset leaves; C: Moderate onset leaves; D: Severe onset leaves
| 施肥 Fertilize | 对应处理 Correspondence processing comtente |
|---|---|
| 对照1(CK1) Comparison 1 | 根部浇水50 kg |
| 处理1(T1) Treatment 1 | 根施氮钾肥,(1 kg尿素+1 kg硫酸钾+ 50 kg水,充分溶解)/棵 |
| 对照2(CK2) Comparison 2 | 叶面喷水 |
| 处理2(T2) Treatment 2 | 叶片喷氮钾肥,(2 kg尿素+2 kg硫酸钾 溶入1 000 kg水)/30棵 |
| 对照3(CK3) Comparison 3 | 根部浇水50 kg+叶面喷水 |
| 处理3(T3) Treatment 3 | 处理1+处理2(根施氮钾肥+叶片喷氮钾肥) |
表1 防治试验设计
Tab.1 Prevention and control test program
| 施肥 Fertilize | 对应处理 Correspondence processing comtente |
|---|---|
| 对照1(CK1) Comparison 1 | 根部浇水50 kg |
| 处理1(T1) Treatment 1 | 根施氮钾肥,(1 kg尿素+1 kg硫酸钾+ 50 kg水,充分溶解)/棵 |
| 对照2(CK2) Comparison 2 | 叶面喷水 |
| 处理2(T2) Treatment 2 | 叶片喷氮钾肥,(2 kg尿素+2 kg硫酸钾 溶入1 000 kg水)/30棵 |
| 对照3(CK3) Comparison 3 | 根部浇水50 kg+叶面喷水 |
| 处理3(T3) Treatment 3 | 处理1+处理2(根施氮钾肥+叶片喷氮钾肥) |
| 分析指标 Analysis project | 分析方法 Analysis method |
|---|---|
| 有机质Organic matter(OM) | 油浴外加热, 重铬酸钾氧化容量法 |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen(TN) | H2SO4-HClO4 消煮,凯氏定氮法 |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus(TP) | H2SO4-HClO4 消煮,钼锑抗分光光度比色法 |
| 全钾 Total potassium(TK) | H2SO4-HClO4 消煮,火焰光度计法 |
| 速效氮 Available nitrogen(AN) | 碱解快散法 |
| 速效磷 Available phosphorus(AP) | NHCO3浸提, 钼锑抗分光光度比色法 |
| 速效钾 Available potassium(AK) | 醋酸铵浸提,火焰光度计法 |
| Cl | 离子色谱法 |
| Ca、Mg、Fe、Mn、 Cu、Zn、Na | DTPA浸提, 原子吸收分光光度法 |
表2 各指标分析方法
Tab 2 Methods for measuring each index
| 分析指标 Analysis project | 分析方法 Analysis method |
|---|---|
| 有机质Organic matter(OM) | 油浴外加热, 重铬酸钾氧化容量法 |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen(TN) | H2SO4-HClO4 消煮,凯氏定氮法 |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus(TP) | H2SO4-HClO4 消煮,钼锑抗分光光度比色法 |
| 全钾 Total potassium(TK) | H2SO4-HClO4 消煮,火焰光度计法 |
| 速效氮 Available nitrogen(AN) | 碱解快散法 |
| 速效磷 Available phosphorus(AP) | NHCO3浸提, 钼锑抗分光光度比色法 |
| 速效钾 Available potassium(AK) | 醋酸铵浸提,火焰光度计法 |
| Cl | 离子色谱法 |
| Ca、Mg、Fe、Mn、 Cu、Zn、Na | DTPA浸提, 原子吸收分光光度法 |
| 核桃样园号 Walnut garden number | 主栽品种 Main variety | 授粉品种 Pollinated variety | 样园位置 Sample garden location | 发病率 Incidence rate(%) | 发病程度 Degree of onset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县361县道(喀拉库杰克村旁) | 61 | 中度 |
| 2 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县玉斯屯克巴格托格拉克村四组 | 92 | 重度 |
| 3 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县托万克巴格托格拉克村 | 80 | 重度 |
| 4 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县喀拉塔勒村 | 16 | 轻度 |
| 5 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县361县道(阿布迪尔曼村和夏喀勒村之间) | 89 | 重度 |
| 6 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县代热亚博依村5组 | 20 | 轻度 |
| 7 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县代热亚博依村1组 | 19 | 轻度 |
| 8 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县代热亚博依村2组 | 72 | 中度 |
| 9 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县阿布迪尔曼村 | 18 | 轻度 |
| 10 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县夏克勒村 | 0 | 健康 |
| 11 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县代热亚博依村363县道附近 | 0 | 健康 |
表3 11个核桃样园焦叶病发病率的变化
Tab.3 Changes of results of the incidence of leaf scorch in 11 walnut producing orchards
| 核桃样园号 Walnut garden number | 主栽品种 Main variety | 授粉品种 Pollinated variety | 样园位置 Sample garden location | 发病率 Incidence rate(%) | 发病程度 Degree of onset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县361县道(喀拉库杰克村旁) | 61 | 中度 |
| 2 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县玉斯屯克巴格托格拉克村四组 | 92 | 重度 |
| 3 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县托万克巴格托格拉克村 | 80 | 重度 |
| 4 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县喀拉塔勒村 | 16 | 轻度 |
| 5 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县361县道(阿布迪尔曼村和夏喀勒村之间) | 89 | 重度 |
| 6 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县代热亚博依村5组 | 20 | 轻度 |
| 7 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县代热亚博依村1组 | 19 | 轻度 |
| 8 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县代热亚博依村2组 | 72 | 中度 |
| 9 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县阿布迪尔曼村 | 18 | 轻度 |
| 10 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县夏克勒村 | 0 | 健康 |
| 11 | 温185 | 新新2 | 阿瓦提县代热亚博依村363县道附近 | 0 | 健康 |
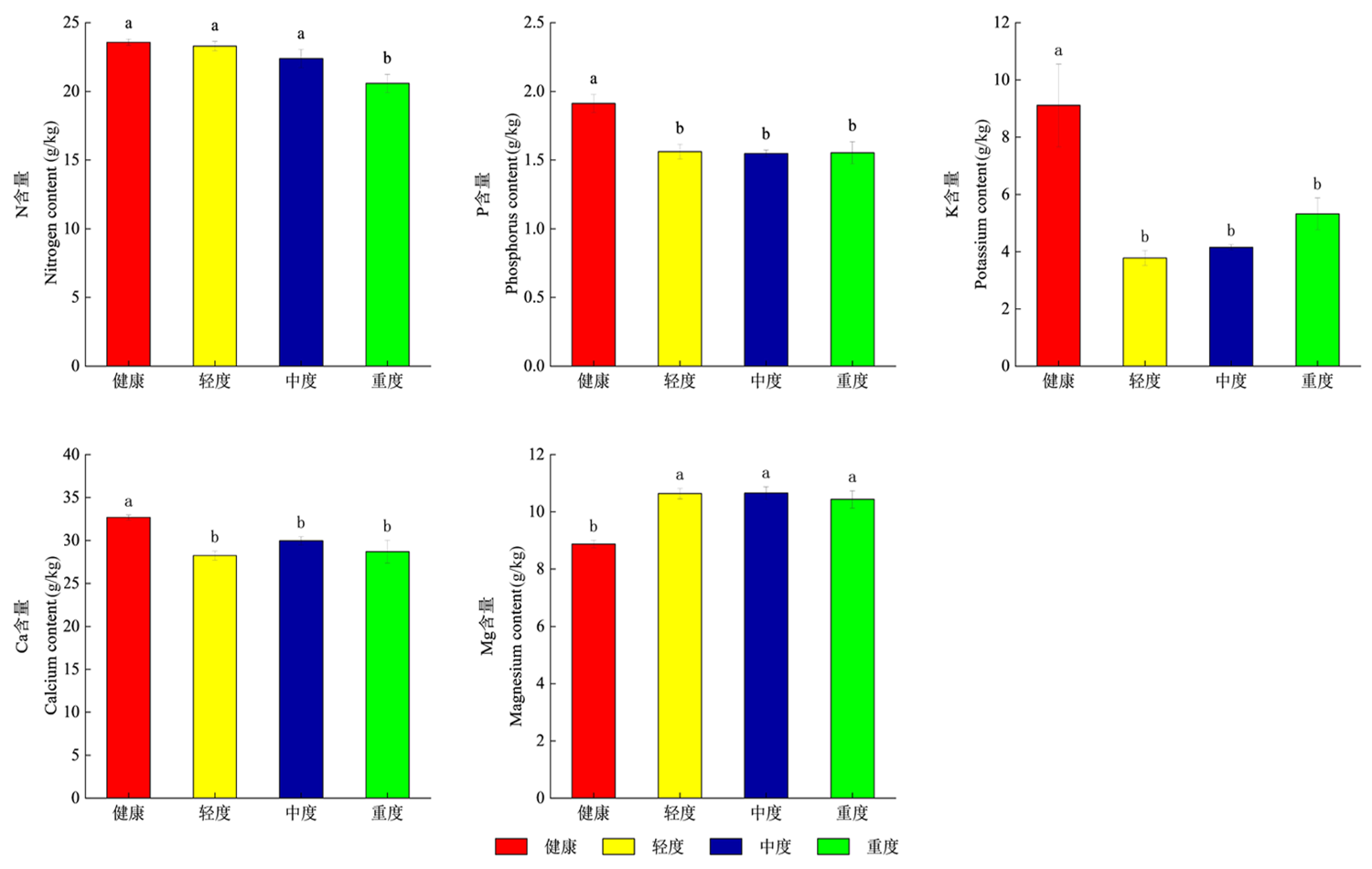
图2 不同发病程度叶片中大量元素含量 注:不同小写字母表示差异在P<0.05水平具有显著性,下同
Fig.2 A large amount of elements in leaves with different degrees of disease Notes: Different lowercase letters indicate that the difference is significant at the P<0.05 level,the same as below
| 组件 Component | 初始特征值 Initial eigenvalues | 提取载荷平方和 Extraction sums of squared loadings | 旋转载荷平方和 Rotation sums of squared loadings | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总计 Total | 方差百分比 Variance percentage (%) | 累积 Cumulative (%) | 总计 Total | 方差百分比 Variance percentage (%) | 累积 Cumulative (%) | 总计 Total | 方差百分比 Variance percentage (%) | 累积 Cumulative (%) | |
| 1 | 5.224 | 58.046 | 58.046 | 5.224 | 58.046 | 58.046 | 4.448 | 49.417 | 49.417 |
| 2 | 2.225 | 24.717 | 82.763 | 2.225 | 24.717 | 82.763 | 3.001 | 33.345 | 82.763 |
| 3 | 1.235 | 13.726 | 96.488 | ||||||
| 4 | 0.135 | 1.501 | 97.989 | ||||||
| 5 | 0.081 | 0.904 | 98.894 | ||||||
| 6 | 0.056 | 0.618 | 99.511 | ||||||
| 7 | 0.028 | 0.312 | 99.824 | ||||||
| 8 | 0.013 | 0.146 | 99.970 | ||||||
| 9 | 0.003 | 0.030 | 100.000 | ||||||
表4 解释的总方程
Tab.4 total variance explained
| 组件 Component | 初始特征值 Initial eigenvalues | 提取载荷平方和 Extraction sums of squared loadings | 旋转载荷平方和 Rotation sums of squared loadings | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总计 Total | 方差百分比 Variance percentage (%) | 累积 Cumulative (%) | 总计 Total | 方差百分比 Variance percentage (%) | 累积 Cumulative (%) | 总计 Total | 方差百分比 Variance percentage (%) | 累积 Cumulative (%) | |
| 1 | 5.224 | 58.046 | 58.046 | 5.224 | 58.046 | 58.046 | 4.448 | 49.417 | 49.417 |
| 2 | 2.225 | 24.717 | 82.763 | 2.225 | 24.717 | 82.763 | 3.001 | 33.345 | 82.763 |
| 3 | 1.235 | 13.726 | 96.488 | ||||||
| 4 | 0.135 | 1.501 | 97.989 | ||||||
| 5 | 0.081 | 0.904 | 98.894 | ||||||
| 6 | 0.056 | 0.618 | 99.511 | ||||||
| 7 | 0.028 | 0.312 | 99.824 | ||||||
| 8 | 0.013 | 0.146 | 99.970 | ||||||
| 9 | 0.003 | 0.030 | 100.000 | ||||||
| 矿质元素 Mineral element | 主成分Principal component | |
|---|---|---|
| 第1主成分 Principal component 1 | 第2主成分 Principal component 2 | |
| 氮Nitrogen(N) | 0.765 | 0.604 |
| 磷Phosphorus(P) | 0.856 | 0.014 |
| 钾Potassium(K) | 0.445 | 0.757 |
| 钠Natrium(Na) | -0.703 | 0.661 |
| 铜Copper(Cu) | -0.528 | -0.733 |
| 锌Zine(Zn) | 0.797 | -0.194 |
| 锰Manganese(Mn) | 0.811 | -0.416 |
| 钙Calcium(Ca) | -0.875 | -0.059 |
| 氯Chlorine(Cl) | -0.936 | 0.313 |
表5 主成分矩阵
Tab.5 Principal component matrix
| 矿质元素 Mineral element | 主成分Principal component | |
|---|---|---|
| 第1主成分 Principal component 1 | 第2主成分 Principal component 2 | |
| 氮Nitrogen(N) | 0.765 | 0.604 |
| 磷Phosphorus(P) | 0.856 | 0.014 |
| 钾Potassium(K) | 0.445 | 0.757 |
| 钠Natrium(Na) | -0.703 | 0.661 |
| 铜Copper(Cu) | -0.528 | -0.733 |
| 锌Zine(Zn) | 0.797 | -0.194 |
| 锰Manganese(Mn) | 0.811 | -0.416 |
| 钙Calcium(Ca) | -0.875 | -0.059 |
| 氯Chlorine(Cl) | -0.936 | 0.313 |
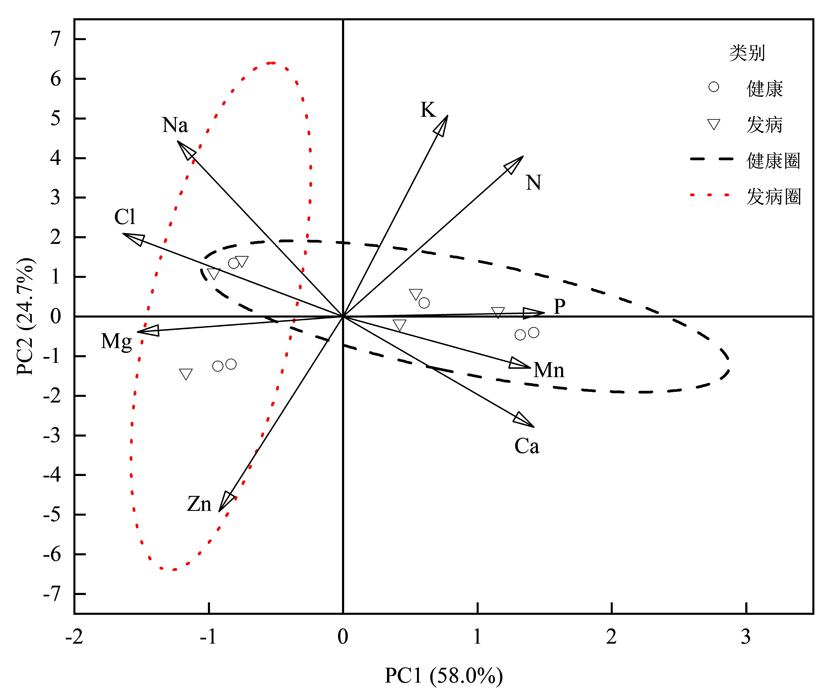
图6 不同发病程度叶片元素主成分 注:○:焦叶病未发病 ▽:焦叶病发病 黑色圈:健康叶片聚集区 红色圈:发病叶片聚集区
Fig.6 Analysis of leaf element principal components with different degrees of pathogenesis Note:○: Leaf scorch does not develop ▽: Leaf scorch disease. Black circle: healthy leaf aggregation area Red circle: diseased leaf aggregation area
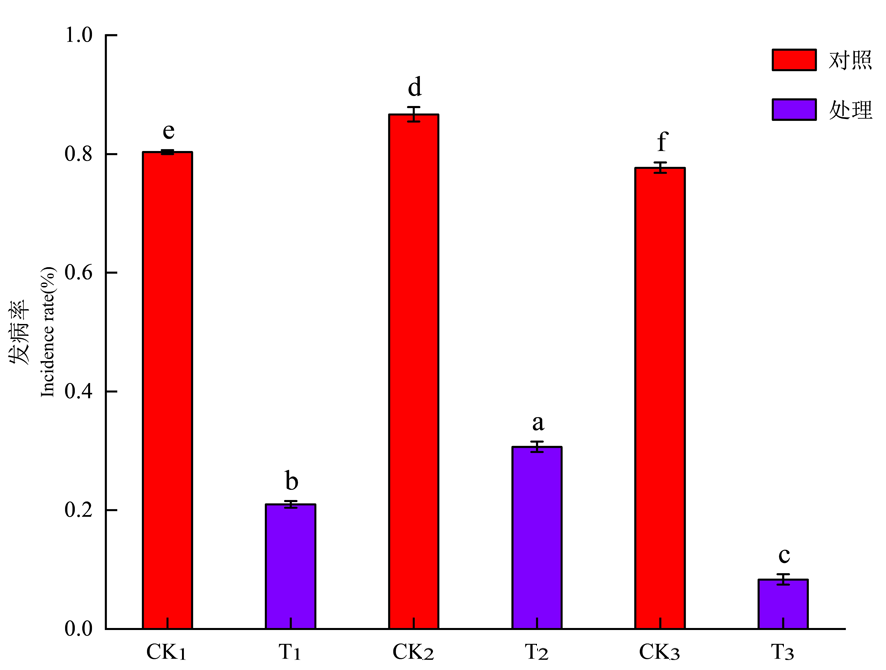
图 7 不同施肥措施焦叶病发病率的变化 注:不同小写字母表示差异在P<0.05水平具有显著性,下同
Fig.7 Changes incidence of coke leaf disease with different fertilization measures Notes: Different lowercase letters indicate that the difference is significant at the P<0.05 level,the same as below
| [1] | 武鹏雨, 马治浩, 张锐, 等. 和田地区核桃主要病虫害种类与综合防治[J]. 新疆农垦科技, 2021, 44(1): 27-29. |
| WU Pengyu, MA Zhihao, ZHANG Rui, et al. Main species inteqrated control of walnut disease and pests in Hotan area[J]. Xinjiang Farm Research of Science and Technology, 2021, 44(1): 27-29. | |
| [2] | Xing C J, Wang S W, Zhang C F, et al. Effects of leaf scorch on chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of walnut leaves[J]. Journal of Plant Diseases and Protection, 2023, 130(1): 115-124. |
| [3] | Wang S W, Xing C J, Zhang C F, et al. Photosynthetic performance of walnut leaves during the occurrence of leaf scorch[J]. Photosynthetica, 2023, 61(1): 13-24. |
| [4] | 高瑞霞. 新疆沙井子垦区环境因子对核桃焦叶病的影响[D]. 阿拉尔: 塔里木大学, 2017. |
| GAO Ruixia. Study on Effect of Environmental Factors on Disease of Walnut Leaf Scorch in Xinjiang Shajingzi[D]. Aral: Tarim University, 2017. | |
| [5] |
李源, 蒲胜海, 马晓鹏, 等. 核桃叶片焦枯症特征与成因分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(6): 1475-1481.
DOI |
|
LI Yuan, PU Shenghai, MA Xiaopeng, et al. Study on characteristics and causation of walnut withered leaf symptom[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(6): 1475-1481.
DOI |
|
| [6] | 梁智, 张计峰, 井然, 等. 核桃“叶缘焦枯” 生理病害调控技术[J]. 新疆农业科技, 2014,(1): 19-20. |
| Liang Zhi, Zhang Jifeng, Jing Ran, et al. Physiological disease control technology of walnut "leaf margin scorched"[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Science and Technology, 2014,(1): 19-20. | |
| [7] | 张计峰, 梁智, 邹耀湘, 等. 新疆南疆核桃叶缘焦枯病成因分析研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2012, 49(7): 1261-1265. |
| ZHANG Jifeng, LIANG Zhi, ZOU Yaoxiang, et al. Study on causation of walnut withered leaf symptom in southern Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 49(7): 1261-1265. | |
| [8] | 梁智, 张计峰, 井然, 等. 土壤及叶面调控对核桃“叶缘焦枯病” 的防控效果[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2014, 51(9): 1652-1657. |
| LIANG Zhi, ZHANG Jifeng, JING Ran, et al. The prevention effect of soil and foliar regulation on“leaf margin scorch disease” of walnut[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 51(9): 1652-1657. | |
| [9] | 陈小飞, 张锐, 罗立新, 等. 核桃焦叶病发病因素分析与防控技术要点[J]. 农业科技与信息, 2021,(14): 67-68. |
| CHEN Xiaofei, ZHANG Rui, LUO Lixin, et al. Analysis of pathogenesis factors and key points of prevention and control technology of walnut scorched leaf disease[J]. Agricultural Science-Technology and Information, 2021,(14): 67-68. | |
| [10] | 吐尔逊阿依·达吾提,艾米热古丽·艾比布拉. 和田地区核桃焦叶病发生的10个原因及防治措施[J]. 新疆林业, 2022,(4): 39-40. |
| Tuerxunayi Dawuzi, Aimireguti Aibibula. 10 Causes of Walnut Leaf Burnt Disease in Hotan Area and Its Control Measures[J]. Forestry of Xinjiang, 2022,(4): 39-40. | |
| [11] | 金为民. 土壤肥料[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2001. |
| JIN Weimin. Soil fertilizer[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2001. | |
| [12] | 张中社, 江世宏. 园林植物病虫害防治[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. |
| ZHANG Zhongshe, JIANG Shihong. Garden plant pest cintrol[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. | |
| [13] | 马斯纳. 高等植物的矿质营养[M]. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 1991. |
| Mahina. Mineral nutrition of higher plants[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 1991. | |
| [14] | 徐叶挺, 龚鹏, 杨磊, 等. 扁桃叶片矿质元素在不同生长时期的含量变化及相关性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2016, 53(11): 2015-2022. |
| XU Yeting, GONG Peng, YANG Lei, et al. Almond leaf mineral and trace element content changes and correlation analysis at different growth stages[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 53(11): 2015-2022. | |
| [15] | 王玉祥. 矿质营养与植物病害的关系研究[J]. 农业灾害研究, 2012, 2(6): 25-27. |
| WANG Yuxiang. Study on relationship between mineral nutrition and plant diseases[J]. Journal of Agricultural Catastrophology, 2012, 2(6): 25-27. | |
| [16] | 鲍士旦, 江荣风, 杨超光, 等. 土壤化学分析(第三版)[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2010: 25-250. |
| BAO Shidan, JIANG Rongfeng, YANG Chaoguang, et al. Soil chemical analysis (3rd edition)[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2010: 25-250. | |
| [17] | 陈欢, 曹承富, 张存岭, 等. 基于主成分-聚类分析评价长期施肥对砂姜黑土肥力的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2014, 51(3): 609-617. |
| CHEN Huan, CAO Chengfu, ZHANG Cunling, et al. Principal component-cluster analysis of effects of long-term fertilization on fertility of lime concretion black soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2014, 51(3): 609-617. | |
| [18] | 井大炜, 马海林, 杜振宇, 等. 核桃优质高产施肥技术研究进展[J]. 山东林业科技, 2020, 50(6): 105-108. |
| JING Dawei, MA Hailin, DU Zhenyu, et al. Research progress of fertilization in cultivation technology of good quality and high yield for walnut[J]. Journal of Shandong Forestry Science and Technology, 2020, 50(6): 105-108. | |
| [19] | 于年文, 李俊才, 王家珍, 等. 辽宁省‘南果梨’园土壤和叶片养分状况调查分析[J]. 果树学报, 2013, 30(2): 254-259. |
| YU Nianwen, LI Juncai, WANG Jiazhen, et al. Investigation and analysis on nutrient status of soil and leaves in ‘Nanguoli’ pear orchards in Liaoning Province[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2013, 30(2): 254-259. | |
| [20] | 刘金生, 陈旭亮, 韦才学, 等. 乌什县核桃叶片黄化与土壤矿质营养的关系[J]. 天津农业科学, 2019, 25(6): 68-71, 87. |
| LIU Jinsheng, CHEN Xuliang, WEI Caixue, et al. Relationships of walnut leaf yellowing and soil mineral nutrients in Wushi County[J]. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 25(6): 68-71, 87. | |
| [21] | Sharma S R, Kolte S J. Effect of soil-applied NPK fertilizers on severity of black spot disease (Alternaria brassicae) and yield of oilseed rape[J]. Plant and Soil, 1994, 167(2): 313-320. |
| [22] | Okori P, Rubaihayo P R, Adipala E, et al. Interactive effects of host, pathogen and mineral nutrition on grey leaf spot epidemics in Uganda[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2004, 110(2): 119-128. |
| [23] | 冯雷, 徐万里, 薛权宏, 等. 矿质元素对核桃腐烂病病害程度的影响[J]. 经济林研究, 2017, 35(4): 49-56. |
| FENG Lei, XU Wanli, XUE Quanhong, et al. Effects of mineral elements on harm degree of Juglans regia canker[J]. Nonwood Forest Research, 2017, 35(4): 49-56. | |
| [24] | Stroehlein J L, Janat M M, Pessarakli M. Response of grape cultivars to nitrogen and phosphorus grown with water harvesting[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 1990, 13(10): 1319-1334. |
| [25] | Patterson C C. Native copper, silver, and gold accessible to early metallurgists[J]. American Antiquity, 1971, 36(3): 286-321. |
| [26] | 张小雪, 巫伟峰, 傅振星, 等. '芙蓉李'焦叶症与矿质元素含量的关联性[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 49(6): 759-765. |
| ZHANG Xiaoxue, WU Weifeng, FU Zhenxing, et al. Correlation analysis between leaf scorch and mineral element contents in plum fruit cv.'Furongli '[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 49(6): 759-765. | |
| [27] | 徐华, 戴小华, 杨耘, 等. 不同脐橙生理病害对叶片矿质元素含量及营养物质代谢的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2010,(14): 166-168. |
| XU Hua, DAI Xiaohua, YANG Yun, et al. The effects of different physiological diseases of navel orange on mineral element contents and nutrient metabolism in leaves[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2010,(14): 166-168. | |
| [28] | 陈久耿, 晁代印. 矿质元素互作及重金属污染的研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2014, 50(5): 585-590. |
| CHEN Jiugeng, CHAO Daiyin. Advances in mineral element interactions and heavy metal pollution[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2014, 50(5): 585-590. | |
| [29] |
田永强, 黄丽萍, 张正. 矿质元素缺失或不平衡与植物病害发生关系研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32(21): 174-176.
DOI |
|
TIAN Yongqiang, HUANG Liping, ZHANG Zheng. Research progress of the relationship between mineral nutrients deficiency or imbalance and plant disease[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2016, 32(21): 174-176.
DOI |
|
| [30] | Yener H, Altuntaş Ö. Effects of potassium fertilization on leaf nutrient content and quality attributes of sweet cherry fruits (Prunus Avium L.)[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2021, 44(7): 946-957. |
| [1] | 帕孜丽耶·艾合麦提, 王新勇, 周燕, 宋彬, 玉苏甫·阿不力提甫. 微生物菌剂对核桃叶片生理及光合特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2299-2306. |
| [2] | 亚森·吐尔迪, 马天宇, 图尔迪麦麦提·努尔麦麦提, 阿地力·沙塔尔. 苹果蠹蛾和梨小食心虫迷向丝在核桃园中的使用模式[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1757-1765. |
| [3] | 周光辉, 陈凤, 孙守霞, 吕威, 朴涵琪, 郝金莲, 张述斌, 陈虹. 水肥耦合对核桃光合特性及产量和品质的效应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(5): 1151-1159. |
| [4] | 刘钧庆, 梁国成, 张欣, 王庆勇, 赵经华. 调亏灌溉对滴灌核桃树根系空间分布特征的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(5): 1160-1171. |
| [5] | 付彦博, 扁青永, 魏亚媛, 魏彦宏, 张万旭, 朱锦泉. 配方施肥对滴灌玉米生理生长及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 878-884. |
| [6] | 马合木提·阿不来提, 木合塔尔·扎热, 米热古力·外力, 哈地尔·依沙克. 核桃叶缘焦枯病与其养分含量的相关性回归分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 945-953. |
| [7] | 王文窈, 施万斌, 芦屹, 图尔荪托合提·阿卜杜拉, 叶尔胜·哈尔肯, 马荣. 两种助剂在核桃腐烂病化学防控中的减药增效分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(3): 672-680. |
| [8] | 杨茂琪, 侯振安, 闵伟. 压差式和泵吸式施肥装置对棉花产量和氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 271-278. |
| [9] | 欧源, 罗莎莎, 王如月, 孙雅丽, 虎海防. 盐胁迫对美国黑核桃幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 393-401. |
| [10] | 叶晓琴, 曹小艳, 阿地力·沙塔尔. 苹果蠹蛾生物学特性及其幼虫对核桃果实的为害习性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 434-440. |
| [11] | 文霞, 郭发城, 高桂珍. 集团外猎物种类及猎物密度对七星瓢虫集团内捕食作用的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 441-447. |
| [12] | 李慧, 毕莹, 王新宇, 雷雅馨, 张琪, 黄帅, 热扎·库忘德克, 王静. 核桃青皮多酚调控对哈密瓜采后活性氧代谢水平及腐烂率的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(12): 2966-2975. |
| [13] | 王贺亚, 罗静静, 艾海峰, 李怀胜, 孟玲, 王鹏. 种植密度与减量施肥对食葵产量及相关性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(1): 55-62. |
| [14] | 王苹, 孔娜, 潘俨, 孙席平, 徐斌, 张婷. ClO2熏蒸处理对湿鲜核桃贮藏效果的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1940-1949. |
| [15] | 徐静, 石书兵, 秦小钢, 朱军. 核桃林间作西红花对其土壤微生物数量的动态变化[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 2022-2027. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 20
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 90
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||