

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (7): 1757-1765.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.07.023
亚森·吐尔迪1( ), 马天宇1, 图尔迪麦麦提·努尔麦麦提2, 阿地力·沙塔尔1(
), 马天宇1, 图尔迪麦麦提·努尔麦麦提2, 阿地力·沙塔尔1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-12-13
出版日期:2024-07-20
发布日期:2024-09-04
通信作者:
阿地力·沙塔尔(1968-),男,新疆莎车人,教授,博士,硕士生/博士生导师,研究方向为林业有害生物监测与防控,(E-mail)adl1968@126.com作者简介:亚森·吐尔迪(1996-),男,新疆拜城人,硕士研究生,研究方向为森林保护,(E-mail)2915251252@qq.com
基金资助:
Yasen Tuerdi1( ), MA Tianyu1, Tuerdimaimaiti Nuermaimaiti2, Adili Shataer1(
), MA Tianyu1, Tuerdimaimaiti Nuermaimaiti2, Adili Shataer1( )
)
Received:2023-12-13
Published:2024-07-20
Online:2024-09-04
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】筛选核桃园中苹果蠹蛾和梨小食心虫最佳防治与迷向丝放置密度与高度。【方法】于2021~2022连续两年在核桃园设置不同悬挂密度(300、450、600根/hm2)和高度(6~8 m、8 m、6 m)的迷向丝,通过田间迷向干扰试验,测定不同悬挂密度和高度的迷向丝对苹果蠹蛾和梨小食心虫的防治效果。【结果】与对照相比,设置密度为300、450、600根/hm2的苹果蠹蛾/梨小食心虫混合迷向丝和苹果蠹蛾、梨小食心虫迷向丝的迷向率和蛀果率之间存在显著差异(P<0.05),高密度处理的迷向丝迷向效果最好,且相同密度处理的各处理苹果蠹蛾/梨小食心虫混合迷向丝与苹果蠹蛾、梨小食心虫迷向丝迷向率和蛀果率之间无显著差异;与对照相比,迷向丝悬挂高度为6~8 m(双层)、8 m、6 m的迷向率和蛀果率之间存在显著差异(P<0.05),悬挂高度为8 m的迷向丝对苹果蠹蛾和梨小食心虫的迷向效果最佳,迷向率分别达到了96.41%、99.71%,防效达到了90.70%。【结论】核桃园苹果蠹蛾/梨小食心虫混合迷向丝最佳设置密度为450根/hm2,最佳悬挂高度为8 m为宜,大面积连片使用1年以上。
中图分类号:
亚森·吐尔迪, 马天宇, 图尔迪麦麦提·努尔麦麦提, 阿地力·沙塔尔. 苹果蠹蛾和梨小食心虫迷向丝在核桃园中的使用模式[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1757-1765.
Yasen Tuerdi, MA Tianyu, Tuerdimaimaiti Nuermaimaiti, Adili Shataer. Study on the using pattern of Cydia pomonella L. and Grapholitha molesta Busck Sex Pheromone in walnut orchard[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1757-1765.
| 迷向丝 悬挂时间 Suspension time of sex pheromone | 迷向丝类型 Type of sex pheromone | 悬挂密度 Suspension density (根/hm2) | 苹果蠹蛾 Cydia pomonella L. | 梨小食心虫 Grapholitha molesta Busck | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均诱捕量 (头/诱捕器) Average catch | 迷向率 Rates of mating disruption(%) | 平均诱捕量 (头/诱捕器) Average catch | 迷向率 Rates of mating disruption(%) | |||
| 4月11日~ 6月24日 April 11-June 24 | 苹果蠹蛾/ 梨小食心虫 混合迷向丝 | 300(处理1) | 18.50±0.56b | 87.67 | 0.17±0.17b | 98.43 |
| 450(处理2) | 9.17±0.31c | 93.88 | 0.00±0.00b | 100.00 | ||
| 600(处理3) | 4.83±0.31cd | 96.78 | 0.00±0.00b | 100.00 | ||
| 苹果蠹蛾、 梨小食心虫 迷向丝 | 300(处理1) | 18.0±0.48b | 88.00 | 0.17±0.17b | 98.43 | |
| 450(处理2) | 8.33±0.42c | 94.44 | 0.17±0.17b | 98.43 | ||
| 600(处理3) | 3.50±0.72d | 97.67 | 0.00±0.00b | 100.00 | ||
| CK | 150.00±3.97a | 10.83±1.22a | ||||
| 6月27日~ 8月29日 June 27-August 29 | 苹果蠹蛾/ 梨小食心虫 混合迷向丝 | 300(处理1) | 8.33±0.56b | 85.34 | 2.50±0.56b | 98.91 |
| 450(处理2) | 4.17±0.65c | 92.66 | 1.33±0.42b | 99.42 | ||
| 600(处理3) | 2.00±0.37c | 96.48 | 0.50±0.22b | 99.78 | ||
| 苹果蠹蛾、 梨小食心虫 迷向丝 | 300(处理1) | 8.17±0.48b | 85.62 | 3.17±0.79b | 98.61 | |
| 450(处理2) | 3.33±0.42c | 94.14 | 2.17±0.87b | 99.05 | ||
| 600(处理3) | 1.50±0.22c | 97.36 | 1.00±0.48b | 99.56 | ||
| CK | 56.83±3.45a | 229.00±10.37a | ||||
表1 不同密度迷向丝处理下苹果蠹蛾和梨小食心虫迷向率的变化
Tab.1 Changes of different density of misorientation filaments on the misorientation rate of Cydia pomonella L.and Grapholitha molesta Busck
| 迷向丝 悬挂时间 Suspension time of sex pheromone | 迷向丝类型 Type of sex pheromone | 悬挂密度 Suspension density (根/hm2) | 苹果蠹蛾 Cydia pomonella L. | 梨小食心虫 Grapholitha molesta Busck | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均诱捕量 (头/诱捕器) Average catch | 迷向率 Rates of mating disruption(%) | 平均诱捕量 (头/诱捕器) Average catch | 迷向率 Rates of mating disruption(%) | |||
| 4月11日~ 6月24日 April 11-June 24 | 苹果蠹蛾/ 梨小食心虫 混合迷向丝 | 300(处理1) | 18.50±0.56b | 87.67 | 0.17±0.17b | 98.43 |
| 450(处理2) | 9.17±0.31c | 93.88 | 0.00±0.00b | 100.00 | ||
| 600(处理3) | 4.83±0.31cd | 96.78 | 0.00±0.00b | 100.00 | ||
| 苹果蠹蛾、 梨小食心虫 迷向丝 | 300(处理1) | 18.0±0.48b | 88.00 | 0.17±0.17b | 98.43 | |
| 450(处理2) | 8.33±0.42c | 94.44 | 0.17±0.17b | 98.43 | ||
| 600(处理3) | 3.50±0.72d | 97.67 | 0.00±0.00b | 100.00 | ||
| CK | 150.00±3.97a | 10.83±1.22a | ||||
| 6月27日~ 8月29日 June 27-August 29 | 苹果蠹蛾/ 梨小食心虫 混合迷向丝 | 300(处理1) | 8.33±0.56b | 85.34 | 2.50±0.56b | 98.91 |
| 450(处理2) | 4.17±0.65c | 92.66 | 1.33±0.42b | 99.42 | ||
| 600(处理3) | 2.00±0.37c | 96.48 | 0.50±0.22b | 99.78 | ||
| 苹果蠹蛾、 梨小食心虫 迷向丝 | 300(处理1) | 8.17±0.48b | 85.62 | 3.17±0.79b | 98.61 | |
| 450(处理2) | 3.33±0.42c | 94.14 | 2.17±0.87b | 99.05 | ||
| 600(处理3) | 1.50±0.22c | 97.36 | 1.00±0.48b | 99.56 | ||
| CK | 56.83±3.45a | 229.00±10.37a | ||||
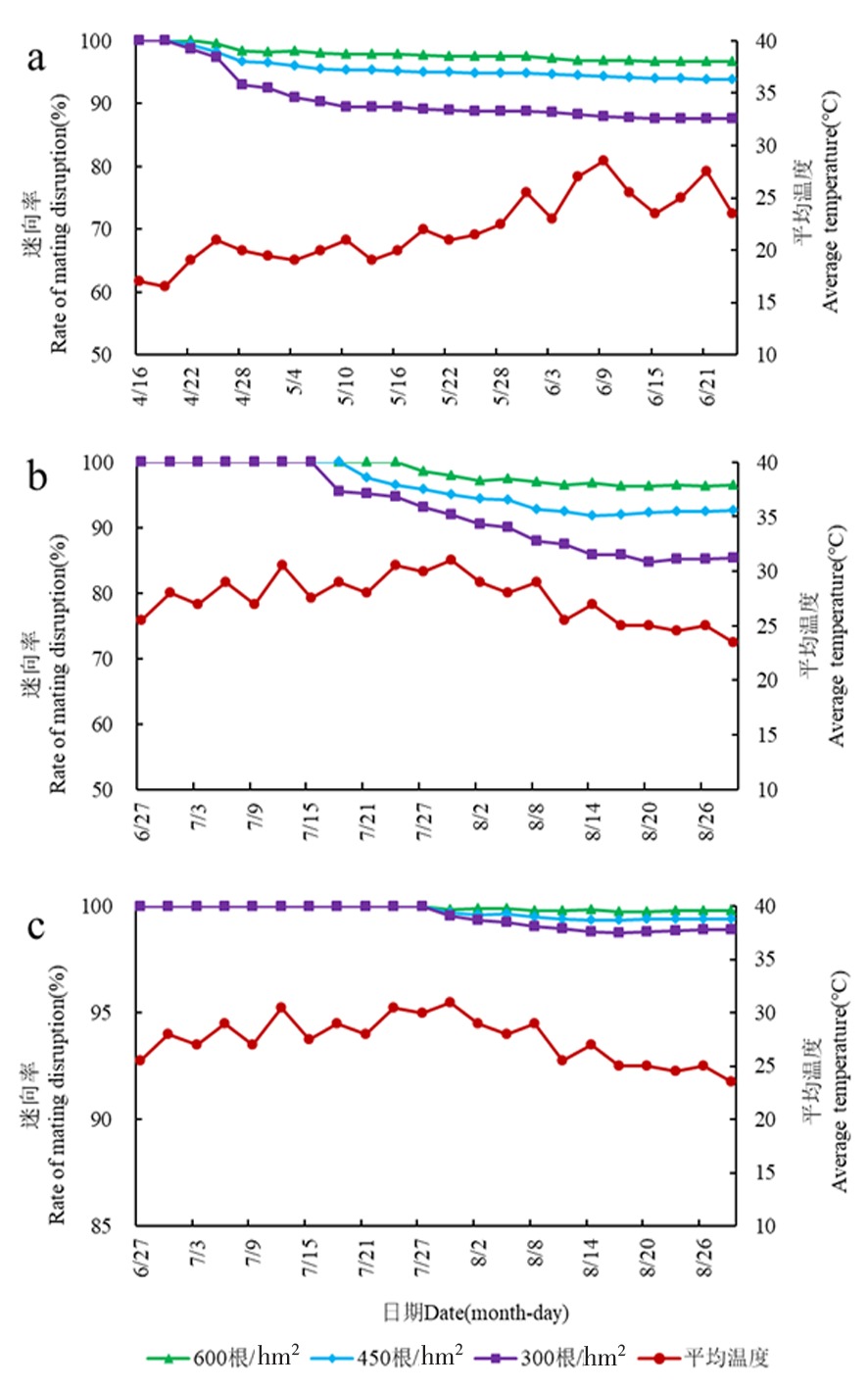
图1 苹果蠹蛾/梨小食心虫混合迷向园苹果蠹蛾、梨小食心虫迷向率 注:a.苹果蠹蛾迷向率(第1次悬挂迷向丝);b.苹果蠹蛾迷向率(第2次更换迷向丝);c.梨小食心虫迷向率
Fig.1 The rates of Mixed Sex Pheromone of Cydia pomonella L.and Grapholitha molesta Busck Note: a.Disorientation rate of Cydia pomonella L.(The first time hanging fascination to silk); b.Disorientation rate of Cydia pomonella L (The second time hanging fascination to silk); c.Disorientation rate of Grapholitha molesta Busck
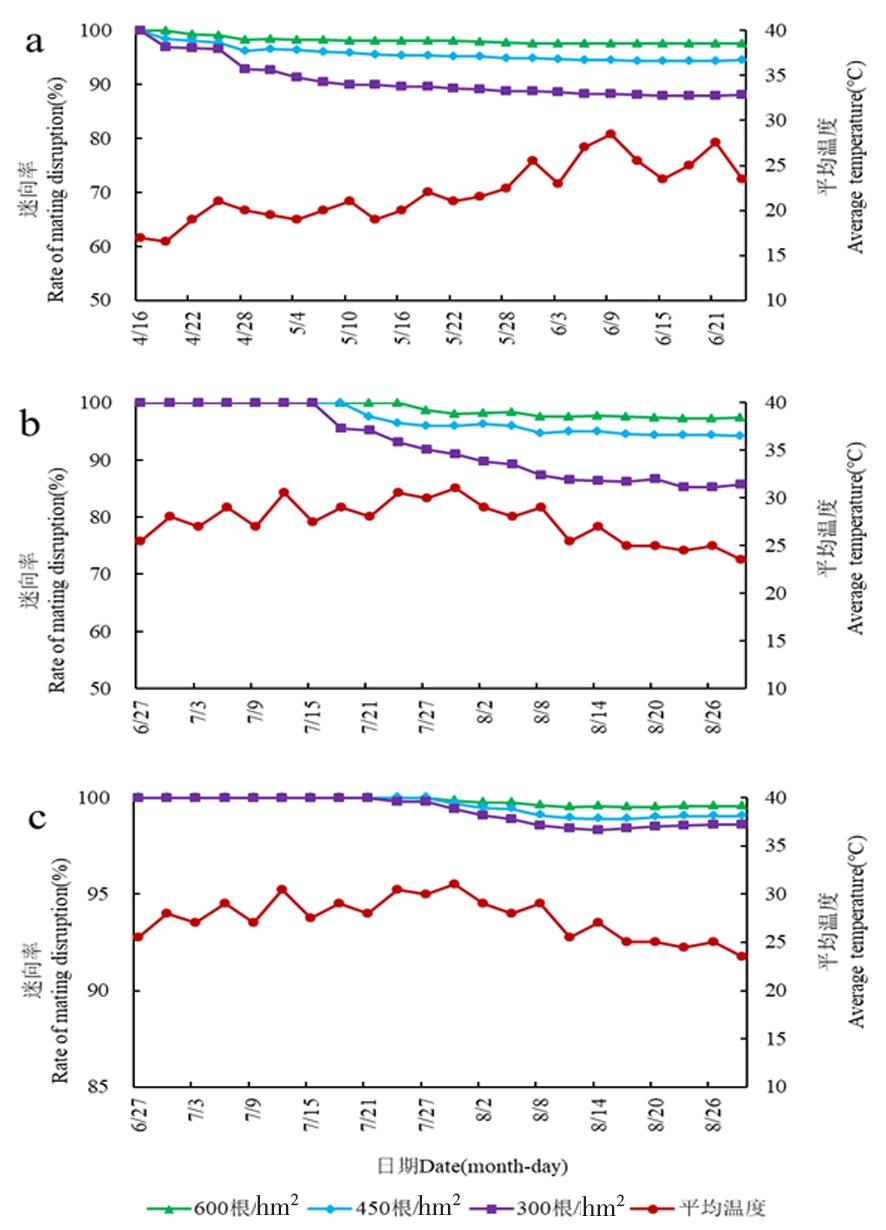
图2 苹果蠹蛾、梨小食心虫迷向园苹果蠹蛾、梨小食心虫的迷向率 注:a.苹果蠹蛾迷向率(第1次悬挂迷向丝);b.苹果蠹蛾迷向率( (第2次悬挂迷向丝);c.梨小食心虫迷向率
Fig.2 The rates of Sex Pheromone of Cydia pomonella L.and Grapholitha molesta Busck Note:a.Disorientation rate of Cydia pomonella L.(The first time hanging fascination to silk); b.Disorientation rate of Cydia pomonella L (The second time hanging fascination to silk); c.Disorientation rate of Grapholitha molesta Busck
| 迷向丝类型 Type of sex pheromone | 悬挂密度 Suspension density (根/hm2) | 调查果数 Research fruit numbers (颗) | 蛀果率 Rate of Infested fruits (%) | 防治效果 Control effect (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苹果蠹蛾/梨小食心虫混合迷向丝 Mixed Sex Pheromone of Cydia pomonella L.and Grapholitha molesta Busck | 300(处理1) | 500 | 3.20±0.37b | 73.33 |
| 450(处理2) | 500 | 1.80±0.20c | 85.00 | |
| 600(处理3) | 500 | 0.80±0.37c | 93.33 | |
| 苹果蠹蛾、梨小食心虫迷向丝 Sex Pheromone of Cydia pomonella L.and Grapholitha molesta Busck | 300(处理1) | 500 | 3.00±0.32b | 75.00 |
| 450(处理2) | 500 | 1.60±0.25c | 86.67 | |
| 600(处理3) | 500 | 0.60±0.25c | 95.00 | |
| CK | 500 | 12.00±1.58a |
表2 不同密度迷向丝处理下区域蛀果率的比较
Tab.2 Comparisons of fruit carious rate in different density filaments treated area
| 迷向丝类型 Type of sex pheromone | 悬挂密度 Suspension density (根/hm2) | 调查果数 Research fruit numbers (颗) | 蛀果率 Rate of Infested fruits (%) | 防治效果 Control effect (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苹果蠹蛾/梨小食心虫混合迷向丝 Mixed Sex Pheromone of Cydia pomonella L.and Grapholitha molesta Busck | 300(处理1) | 500 | 3.20±0.37b | 73.33 |
| 450(处理2) | 500 | 1.80±0.20c | 85.00 | |
| 600(处理3) | 500 | 0.80±0.37c | 93.33 | |
| 苹果蠹蛾、梨小食心虫迷向丝 Sex Pheromone of Cydia pomonella L.and Grapholitha molesta Busck | 300(处理1) | 500 | 3.00±0.32b | 75.00 |
| 450(处理2) | 500 | 1.60±0.25c | 86.67 | |
| 600(处理3) | 500 | 0.60±0.25c | 95.00 | |
| CK | 500 | 12.00±1.58a |
| 迷向丝悬挂时间 Suspension time of sex pheromone | 迷向丝悬挂高度 Hanging height of sex pheromone(m) | 苹果蠹蛾 Cydia pomonella L. | 梨小食心虫 Grapholitha molesta Busck | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均诱捕量 (头/诱捕器) Average catch (head) | 迷向率 Rates of mating disruption(%) | 平均诱捕量 (头/诱捕器) Average catch (head) | 迷向率 Rates of mating disruption(%) | ||
| 4月10日~6月21日 April 10-June 21 | 6(处理1) | 8.75±0.59b | 90.17 | 0.25±0.25b | 99.70 |
| 8(处理2) | 3.88±0.44c | 95.64 | 0.00±0.00b | 100.00 | |
| 6和8(双层)(处理3) | 2.63±0.50c | 97.04 | 0.00±0.00b | 100.00 | |
| CK | 89.00±3.16a | 85.13±12.45a | |||
| 6月21日~8月29日 June 21-August 29 | 6(处理1) | 6.50±0.42b | 90.20 | 1.63±0.32b | 99.47 |
| 8(处理2) | 2.38±0.26c | 96.41 | 0.88±0.40b | 99.71 | |
| 6和8(双层)(处理3) | 1.50±0.42c | 97.74 | 0.38±0.18b | 99.88 | |
| CK | 66.38±2.73a | 307.88±12.85a | |||
表3 不同迷向丝悬挂高度下苹果蠹蛾和梨小食心虫的迷向效果
Tab.3 The effects of different hanging heights of the filaments on the orientations of Cydia pomonella L.and Grapholitha molesta Busck
| 迷向丝悬挂时间 Suspension time of sex pheromone | 迷向丝悬挂高度 Hanging height of sex pheromone(m) | 苹果蠹蛾 Cydia pomonella L. | 梨小食心虫 Grapholitha molesta Busck | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均诱捕量 (头/诱捕器) Average catch (head) | 迷向率 Rates of mating disruption(%) | 平均诱捕量 (头/诱捕器) Average catch (head) | 迷向率 Rates of mating disruption(%) | ||
| 4月10日~6月21日 April 10-June 21 | 6(处理1) | 8.75±0.59b | 90.17 | 0.25±0.25b | 99.70 |
| 8(处理2) | 3.88±0.44c | 95.64 | 0.00±0.00b | 100.00 | |
| 6和8(双层)(处理3) | 2.63±0.50c | 97.04 | 0.00±0.00b | 100.00 | |
| CK | 89.00±3.16a | 85.13±12.45a | |||
| 6月21日~8月29日 June 21-August 29 | 6(处理1) | 6.50±0.42b | 90.20 | 1.63±0.32b | 99.47 |
| 8(处理2) | 2.38±0.26c | 96.41 | 0.88±0.40b | 99.71 | |
| 6和8(双层)(处理3) | 1.50±0.42c | 97.74 | 0.38±0.18b | 99.88 | |
| CK | 66.38±2.73a | 307.88±12.85a | |||
| 迷向丝类型 Type of sex pheromone | 迷向丝悬挂高度 Hanging height of sex pheromone(m) | 调查果数 Research fruit numbers (颗) | 蛀果率 Rate of infested fruits(%) | 防治效果 Control effect(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苹果蠹蛾/梨小食心虫混合迷向丝 Mixed Sex Pheromone of Cydia pomonella L. and Grapholitha molesta Busck | 6 | 500 | 2.00±0.32b | 77.27 |
| 8 | 500 | 0.80±0.37c | 90.70 | |
| 6~8(双层) | 500 | 0.60±0.25c | 93.02 | |
| CK | 500 | 8.60±0.51a |
表4 不同悬挂高度迷向丝处理下蛀果率的比较
Tab.4 Comparison of fruit decay rate with different hanging heights of filaments
| 迷向丝类型 Type of sex pheromone | 迷向丝悬挂高度 Hanging height of sex pheromone(m) | 调查果数 Research fruit numbers (颗) | 蛀果率 Rate of infested fruits(%) | 防治效果 Control effect(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苹果蠹蛾/梨小食心虫混合迷向丝 Mixed Sex Pheromone of Cydia pomonella L. and Grapholitha molesta Busck | 6 | 500 | 2.00±0.32b | 77.27 |
| 8 | 500 | 0.80±0.37c | 90.70 | |
| 6~8(双层) | 500 | 0.60±0.25c | 93.02 | |
| CK | 500 | 8.60±0.51a |
| [1] | Ju D, Mota-Sanchez D, Fuentes-Contreras E, et al. Insecticide resistance in theCydia pomonella(L): global status, mechanisms, and research directions[J]. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 2021, 178: 104925. |
| [2] | 沈志杰, 房明华, 洪文英, 等. 不同生境果园梨小食心虫各代成虫高峰期差异[J]. 植物保护, 2021, 47(3): 222-225, 236. |
| SHEN Zhijie, FANG Minghua, HONG Wenying, et al. Differences of adult peak periods of each generation of male oriental fruit moth, Grapholita molesta(Busck) in different habitat orchards[J]. Plant Protection, 2021, 47(3): 222-225, 236. | |
| [3] | 张学祖, 周绍来, 王庸俭. 苹果蠹蛾的初步研究[J]. 昆虫学报, 1958, (2): 136-151,194-195. |
| ZHANG Xuezu, ZHOU Shaolai, WANG Yongjian. A preliminary study on the codling moth in sinking[J]. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 1958, (2): 136-151,194-195. | |
| [4] | 张学祖. 苹果蠹蛾(Carpocapsa pomonella L.)在我国的新发现[J]. 昆虫学报, 1957, (4): 467-472. |
| Zhang Xuezu. Taxonomic notes on the codling moth, Carpocapsa pomonella L. in Sinkiang[J]. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 1957, (4): 467-472. | |
| [5] | 杨本立, 邓有金. 梨小食心虫的生活史及早期防治[J]. 中国南方果树, 1998, 27(1): 36. |
| YANG Benli, DENG Youjin. Life history and early control of pear fruit borer[J]. South China Fruits, 1998, 27(1):36. | |
| [6] | 于昕, 王玉晗, 李红卫, 等. 苹果蠹蛾的发生现状、监测技术及防治方法研究进展[J]. 植物检疫, 2020, 34(1): 1-6. |
| YU Xin, WANG Yuhan, LI Hongwei, et al. Research progress on occurrence status, monitoring technology and control methods of the codling moth[J]. Plant Quarantine, 2020, 34(1): 1-6. | |
| [7] | 罗进仓, 周昭旭, 刘月英, 等. 甘肃苹果蠹蛾的发生现状与研究进展[J]. 生物安全学报, 2015, 24(4): 281-286. |
| LUO Jincang, ZHOU Zhaoxu, LIU Yueying, et al. Occurrence status and research advance of the codling moth in Gansu[J]. Journal of Biosafety, 2015, 24(4): 281-286. | |
| [8] | 蒋秋双. 梨小食心虫高效控制技术研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2020. |
| Qiushuang Jiang. Research on high efficiency control technology of the Grapholitha molesta[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| [9] | 母小庆. 梨小食心虫与苹果蠹蛾种间竞争机制研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2020. |
| Mu Xiaoqing. Study on the interspecific competition mechanism between Grapholitha molestaandCydia pomonella[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2020. | |
| [10] | 冉红凡, 路子云, 刘文旭, 等. 梨小食心虫生物防治研究进展[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2016, 53(5): 931-941. |
| RAN Hongfan, LU Ziyun, LIU Wenxu, et al. Advances in research on the biological control of the oriental fruit moth[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2016, 53(5): 931-941. | |
| [11] | 孟宪佐. 我国昆虫信息素研究与应用的进展[J]. 昆虫知识, 2000, 37(2): 75-84. |
| MENG Xianzuo. Advances in the research and application of insect pheromones in China[J]. Entomological Knowledge, 2000, 37(2): 75-84. | |
| [12] | 张涛, 赵江华, 冯俊涛, 等. 苹果蠹蛾性信息素田间应用技术研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 39(5): 167-171, 178. |
| ZHANG Tao, ZHAO Jianghua, FENG Juntao, et al. Study on the applied technology of codling moth’s sex pheromone[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(5): 167-171, 178. | |
| [13] | 翟小伟, 刘万学, 张桂芬, 等. 苹果蠹蛾性信息素诱捕器田间诱捕效应影响因子[J]. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(3): 801-806. |
|
ZHAI Xiaowei, LIU Wanxue, ZHANG Guifen, et al. Affecting factors on capture efficacy of sex pheromone traps forCydia pomonella L[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2010, 21(3): 801-806.
PMID |
|
| [14] | Charmillot P J, Pasquier D, Hofer D. Control of codling mothCydia pomonellaby autosterilisation[J]. IOBC-WPRS Bulletin, 2002, 25(1): 1-4. |
| [15] | Ebbinghaus D, Lsel P M, Romeis J, et al. Appeal: efficacy and mode of action of attract and kill for codling moth control[J]. IOBC-WPRS Bulletin, 2001, 24(2): 95-99. |
| [16] | 周仙红, 李丽莉, 张思聪, 等. 梨小食心虫发生规律及无公害防治技术[J]. 山东农业科学, 2011, 43(10): 76-81. |
| ZHOU Xianhong, LI Lili, ZHANG Sicong, et al. Review on occurrence regularity and pollution-free control technology ofGrapholitha molestabusck[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 43(10): 76-81. | |
| [17] | 周洪旭, 李丽莉, 于毅. 信息素迷向法规模化防治梨小食心虫[J]. 植物保护学报, 2011, 38(5): 385-389. |
| ZHOU Hongxu, LI Lili, YU Yi. Scale control overGrapholitha molestawith mating disruption of sex pheromone[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2011, 38(5): 385-389. | |
| [18] | 木尼热·买买提. 杏园主要食心虫发生动态监测及迷向防控效果评价[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2021. |
| Munire Maimaiti. Dynamic Monitoring of the Occurrence of fruit borers in Apricot Orchards and Evaluation of Control Effect of Mating Disruption[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| [19] | 崔笑雄, 麻正辉, 马雪, 等. 苹果蠹蛾和梨小食心虫迷向丝复合干扰在南疆‘库尔勒香梨’园的应用效果[J]. 中国果树, 2021, 207(1): 33-37. |
| Effects of the compound interference ofCydia pomonellaandGrapholithamolestain Korla fragrant pear' orchard in South Xinjiang[J]. China Fruits, 2021, 207(1): 33-37. | |
| [20] | 崔笑雄, 熊仁次, 陈汉杰, 等. 复合式性信息素迷向丝对苹果蠹蛾和梨小食心虫的防控效果[J]. 北方园艺, 2020, (13): 42-46. |
| CUI Xiaoxiong, XIONG Renci, CHEN Hanjie, et al. Control Effect of Dual Sex Pheromone for Disrupting the Mating ofCydia pomonella andGrapholitha molesta in Apple Orchard[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2020, (13): 42-46. | |
| [21] | 王荣辕. 不同密度迷向丝防治梨小食心虫的效果[J]. 北方果树, 2020, (5): 6-8. |
| WANG Rongyuan. Study on the effect of different density sex pheromone silk on the prevention and control ofGrapholitha molesta[J]. Northern Fruits, 2020, (5): 6-8. | |
| [22] | 赵彤, 王得毓, 刘卫红, 等. 迷向防治技术对苹果蠹蛾的田间防治效果[J]. 植物保护, 2017, 43(6): 207-212. |
| ZHAO Tong, WANG Deyu, LIU Weihong, et al. Control ofCydia pomonella by mating disruption pheromones[J]. Plant Protection, 2017, 43(6): 207-212. | |
| [23] |
刘中芳, 庾琴, 高越, 等. 梨园梨小食心虫性信息素迷向防治技术[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2016, 32(2): 155-160.
DOI |
|
LIU Zhongfang, YU Qin, GAO Yue, et al. Mating disruption control ofGrapholitha molestaby using sex pheromone in pear orchard[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2016, 32(2): 155-160.
DOI |
|
| [24] |
金唯新, 姜义平, 沈斐, 等. 多年迷向防治对桃园梨小食心虫的控制作用评估[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2022, 38(2): 360-366.
DOI |
|
JIN Weixin, JIANG Yiping, SHEN Fei, et al. Control ofGrapholita molestaby using mating disruption in peach orchard for many years[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2022, 38(2): 360-366.
DOI |
|
| [25] | 朱虹昱, 徐婧, 张润志. 苹果蠹蛾性信息素对梨小食心虫的诱集和迷向作用[J]. 生物安全学报, 2015, 24(4): 320-326. |
| ZHU Hongyu, XU Jing, ZHANG Runzhi. Mating disrupting and trapping effects of the codling moth sex pheromone on oriental fruit moth, Grapholita molesta[J]. Journal of Biosafety, 2015, 24(4): 320-326. | |
| [26] | Carde R T, Minks A K. Control of moth pests by mating disruption: successes and constraints[J]. Annual Review of Entomology, 1995, 40(1): 559-585. |
| [27] |
Witzgall P, Stelinski L, Gut L, et al. Codling moth management and chemical ecology[J]. Annual Review of Entomology, 2008, 53: 503-522.
PMID |
| [28] | Vickers R A, Thwaite W G, Williams D G, et al. Control of codling moth in small plots by mating disruption: alone and with limited insecticide[J]. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 1998, 86(3): 229-239. |
| [29] | 朱虹昱, 刘伟, 崔艮中, 等. 苹果蠹蛾迷向防治技术效果初报[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2012, 49(1): 121-129. |
| ZHU Hongyu, LIU Wei, CUI Genzhong, et al. Field trials using domestic sex pheromone dispensers to disruptCydia pomonellamating behavior[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2012, 49(1): 121-129. |
| [1] | 帕孜丽耶·艾合麦提, 王新勇, 周燕, 宋彬, 玉苏甫·阿不力提甫. 微生物菌剂对核桃叶片生理及光合特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2299-2306. |
| [2] | 吐尔逊·阿合买提, 刘旭坤, 赵雯慧, 朱晓峰, 阿尔孜姑丽·肉孜, 帕丽达姆·塔依尔, 付开赟, 丁新华, 贾尊尊, 阿地力·沙塔尔, 郭文超. 10种杀虫剂对桃小食心虫防治效果评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1447-1453. |
| [3] | 周光辉, 陈凤, 孙守霞, 吕威, 朴涵琪, 郝金莲, 张述斌, 陈虹. 水肥耦合对核桃光合特性及产量和品质的效应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(5): 1151-1159. |
| [4] | 刘钧庆, 梁国成, 张欣, 王庆勇, 赵经华. 调亏灌溉对滴灌核桃树根系空间分布特征的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(5): 1160-1171. |
| [5] | 马合木提·阿不来提, 木合塔尔·扎热, 米热古力·外力, 哈地尔·依沙克. 核桃叶缘焦枯病与其养分含量的相关性回归分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 945-953. |
| [6] | 魏杨, 陈国祥, 阿地力·沙塔尔, 买买托合提·吐孙, 田光宇. 5种农药对梨小食心虫的室内毒力测定及田间药效评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(3): 665-671. |
| [7] | 王文窈, 施万斌, 芦屹, 图尔荪托合提·阿卜杜拉, 叶尔胜·哈尔肯, 马荣. 两种助剂在核桃腐烂病化学防控中的减药增效分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(3): 672-680. |
| [8] | 欧源, 罗莎莎, 王如月, 孙雅丽, 虎海防. 盐胁迫对美国黑核桃幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 393-401. |
| [9] | 叶晓琴, 曹小艳, 阿地力·沙塔尔. 苹果蠹蛾生物学特性及其幼虫对核桃果实的为害习性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 434-440. |
| [10] | 文霞, 郭发城, 高桂珍. 集团外猎物种类及猎物密度对七星瓢虫集团内捕食作用的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 441-447. |
| [11] | 李慧, 毕莹, 王新宇, 雷雅馨, 张琪, 黄帅, 热扎·库忘德克, 王静. 核桃青皮多酚调控对哈密瓜采后活性氧代谢水平及腐烂率的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(12): 2966-2975. |
| [12] | 赵莎莎, 王世伟, 张翠芳, 郝洪龙, 郭桐, 杨先安, 杨雯洁. 核桃焦叶病与矿质元素关系分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2750-2760. |
| [13] | 陈国祥, 魏杨, 郭文超, 李佩璇, 阿地力·沙塔尔. 核桃园苹果蠹蛾的空间分布型与抽样技术分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2769-2778. |
| [14] | 王苹, 孔娜, 潘俨, 孙席平, 徐斌, 张婷. ClO2熏蒸处理对湿鲜核桃贮藏效果的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1940-1949. |
| [15] | 徐静, 石书兵, 秦小钢, 朱军. 核桃林间作西红花对其土壤微生物数量的动态变化[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 2022-2027. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 32
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 106
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||