

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (4): 982-992.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.04.023
• Plant Protection · Prataculture • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Jilong1( ), Aliya Baidurela1(
), Aliya Baidurela1( ), WANG Xinying2, LIU Maoxiu2, Aijier Abula2
), WANG Xinying2, LIU Maoxiu2, Aijier Abula2
Received:2024-09-13
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-06-20
Supported by:
马继龙1( ), 阿丽亚·拜都热拉1(
), 阿丽亚·拜都热拉1( ), 王新英2, 刘茂秀2, 艾吉尔·阿不拉2
), 王新英2, 刘茂秀2, 艾吉尔·阿不拉2
通讯作者:
阿丽亚·拜都热拉(1986-),女,新疆人,副教授,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为荒漠化防治,(E-mail)aliya@xjau.edu.cn
作者简介:马继龙(2000-),男,新疆伊犁人,硕士研究生,研究方向为荒漠化防治,(E-mail)mjl4ever888@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
MA Jilong, Aliya Baidurela, WANG Xinying, LIU Maoxiu, Aijier Abula. Characteristics and influencing factors of soil microbial community diversity in middle reaches of Tarim River[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(4): 982-992.
马继龙, 阿丽亚·拜都热拉, 王新英, 刘茂秀, 艾吉尔·阿不拉. 塔里木河中游土壤微生物群落多样性特征及影响因子分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(4): 982-992.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.xjnykx.com/EN/10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.04.023
| 生境 Habitats | 距河道 垂直距离 Vertical distance from river (km) | 平均 地下水位 Mean water table (m) | 主要植被情况 Main vegetation condition | 郁闭度/盖度 Canopy density/ coverage | 胡杨密度 Populus euphratica density (株/667m2) | 生长状况 Growth condition | 有无周期性 水淹 Whether is periodic flooding |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 荒漠生境 Desert habitats | 16.85 | 5.25 | 柽柳 | 0.20 | 正常 | 无 | |
| 胡杨林中生生境 Mesophytic habitat of Populus euphratica forest | 7.75 | 2.95 | 胡杨、柽柳 | 0.46/0.29 | 32 | 树冠完整, 极少枯枝 | 无 |
| 胡杨林周期性 水淹生境 Periodic flooding habitat of Populus euphratica forest | 0.75 | 0.06 | 胡杨、柽柳、 铃铛刺、琵琶柴、 芨芨草、蒿草、芦苇等 | 0.71/0.65 | 41 | 树冠完整, 无枯枝 | 有,最深 可达1.2 m |
Tab.1 Basic information on sample sites in different habitats
| 生境 Habitats | 距河道 垂直距离 Vertical distance from river (km) | 平均 地下水位 Mean water table (m) | 主要植被情况 Main vegetation condition | 郁闭度/盖度 Canopy density/ coverage | 胡杨密度 Populus euphratica density (株/667m2) | 生长状况 Growth condition | 有无周期性 水淹 Whether is periodic flooding |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 荒漠生境 Desert habitats | 16.85 | 5.25 | 柽柳 | 0.20 | 正常 | 无 | |
| 胡杨林中生生境 Mesophytic habitat of Populus euphratica forest | 7.75 | 2.95 | 胡杨、柽柳 | 0.46/0.29 | 32 | 树冠完整, 极少枯枝 | 无 |
| 胡杨林周期性 水淹生境 Periodic flooding habitat of Populus euphratica forest | 0.75 | 0.06 | 胡杨、柽柳、 铃铛刺、琵琶柴、 芨芨草、蒿草、芦苇等 | 0.71/0.65 | 41 | 树冠完整, 无枯枝 | 有,最深 可达1.2 m |
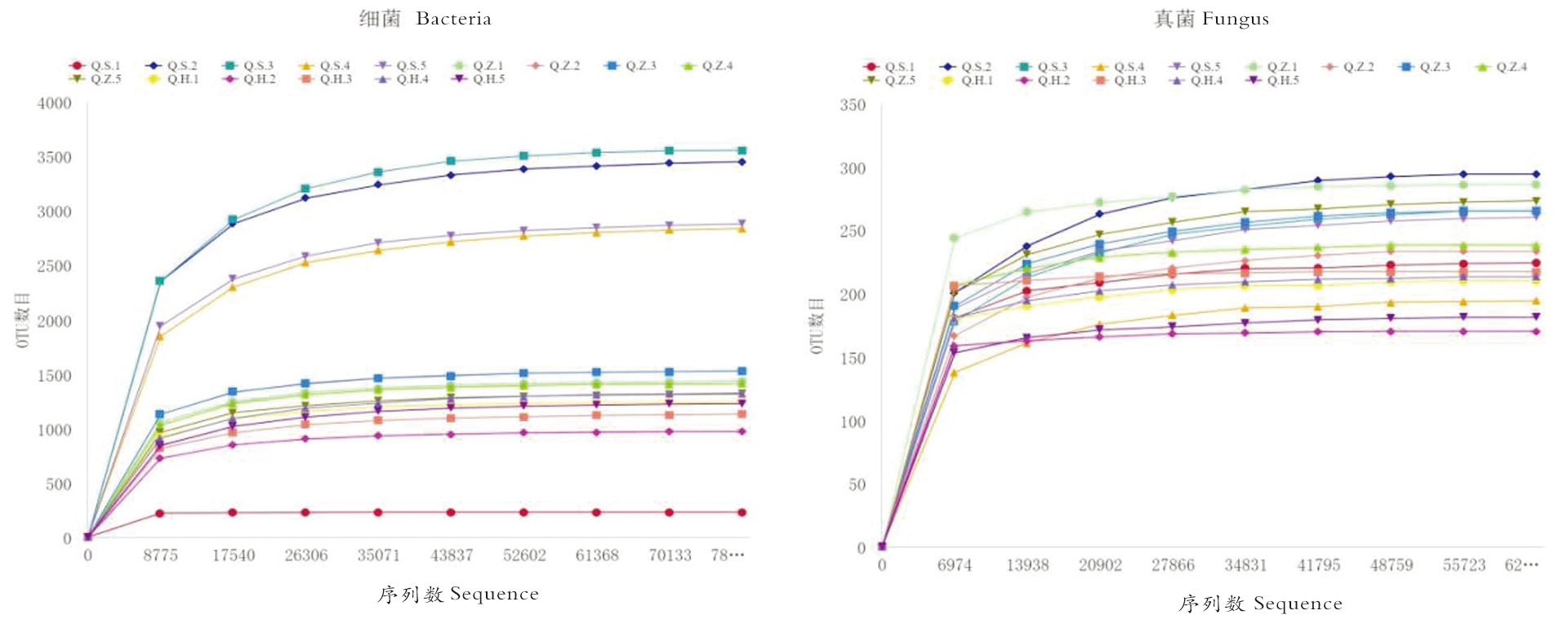
Fig.1 Dilution curve of microbial communities in soil samples Notes:Q.S.1-Q.S.5、Q.Z.1-Q.Z.5、Q.H.1-Q.H.5 representing the periodically flooded habitats of populus euphratica forest respe ctively、habitat in populus euphratica forest、sampling points of layers of soil in 3 different desert habitats,the same as below
| 土壤理化性质 Soil physicochemical properties | 胡杨林周期性水淹生境 Periodic flooding habitat of populus euphratica forest | 胡杨林中生生境 Mesophytic habitat of populus euphratica forest | 荒漠生境 Desert habitat |
|---|---|---|---|
| 含水量Soil water content(%) | 16.51±0.19a | 14.81±1.44a | 3.36±1.03b |
| 有机质Soil organic matter(g/kg) | 19.8±1.00b | 32.61±1.74a | 16.88±1.44c |
| 全氮Total nitrogen(g/kg) | 0.27±0.008b | 0.52±0.009a | 0.17±0.001c |
| 全磷Total phosphorus(g/kg) | 1.25±0.14b | 0.42±0.01c | 1.46±0.11a |
| 全钾Total Potassium(g/kg) | 12.06±0.22ab | 12.46±0.41a | 11.51±0.23b |
| 碱解氮Alkali hydrolyzed nitrogen(mg/kg) | 35.39±0.68b | 48.43±0.32a | 25.69±0.47c |
| 速效磷Rapidly available phosphorus(mg/kg) | 4.82±0.51b | 12.76±0.66a | 4.37±0.72b |
| 速效钾Rapidly available potassium(mg/kg) | 103.36±1.10c | 509.78±1.49a | 182.08±0.82b |
| 硝态氮Nitrate nitrogen(mg/kg) | 7.90±1.95b | 6.14±1.99b | 15.65±1.22a |
| 铵态氮Ammonium nitrogen(mg/kg) | 1.87±0.30a | 1.43±0.11b | 1.94±0.05a |
| 总盐Total salt(g/kg) | 0.58±0.05c | 7.12±0.10b | 9.93±0.29a |
Tab.2 Changes of soil physical and chemical properties in different habitats
| 土壤理化性质 Soil physicochemical properties | 胡杨林周期性水淹生境 Periodic flooding habitat of populus euphratica forest | 胡杨林中生生境 Mesophytic habitat of populus euphratica forest | 荒漠生境 Desert habitat |
|---|---|---|---|
| 含水量Soil water content(%) | 16.51±0.19a | 14.81±1.44a | 3.36±1.03b |
| 有机质Soil organic matter(g/kg) | 19.8±1.00b | 32.61±1.74a | 16.88±1.44c |
| 全氮Total nitrogen(g/kg) | 0.27±0.008b | 0.52±0.009a | 0.17±0.001c |
| 全磷Total phosphorus(g/kg) | 1.25±0.14b | 0.42±0.01c | 1.46±0.11a |
| 全钾Total Potassium(g/kg) | 12.06±0.22ab | 12.46±0.41a | 11.51±0.23b |
| 碱解氮Alkali hydrolyzed nitrogen(mg/kg) | 35.39±0.68b | 48.43±0.32a | 25.69±0.47c |
| 速效磷Rapidly available phosphorus(mg/kg) | 4.82±0.51b | 12.76±0.66a | 4.37±0.72b |
| 速效钾Rapidly available potassium(mg/kg) | 103.36±1.10c | 509.78±1.49a | 182.08±0.82b |
| 硝态氮Nitrate nitrogen(mg/kg) | 7.90±1.95b | 6.14±1.99b | 15.65±1.22a |
| 铵态氮Ammonium nitrogen(mg/kg) | 1.87±0.30a | 1.43±0.11b | 1.94±0.05a |
| 总盐Total salt(g/kg) | 0.58±0.05c | 7.12±0.10b | 9.93±0.29a |
| 微生物 Microorganism | 生境 Habitats | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | pielou_e指数 pielou_e index | 测序覆盖度 Goods coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌 Bacteria | 周期性水淹生境 | 10.36±0.34a | 0.998 3±0.000 8a | 3 104.29±319.91a | 0.890 6±0.018 2a | 0.999 9±0.000 5a |
| 中生生境 | 8.65±0.16b | 0.992 4±0.002 4b | 1 438.11±90.27b | 0.824 2±0.011 5b | 1±0.000 4a | |
| 荒漠生境 | 7.71±0.28c | 0.986 0±0.003 3c | 1 232.28±136.93c | 0.769 0±0.018 9c | 1±0.000 4a | |
| 统计结果 | F=114.477 | F=32.201 | F=153.29 | F=67.607 | F=1.313 | |
| P<0.001 | P<0.001 | P<0.001 | P<0.001 | P=0.305 | ||
| 真菌 Fungi | 周期性水淹生境 | 4.34±1.08b | 0.866 6±0.101 3b | 254.99±35.30a | 0.544 8±0.136 4b | 1a |
| 中生生境 | 4.92±01.03b | 0.893 8±0.058 1ab | 264.77±25.87a | 0.612 4±0.131 7b | 1a | |
| 荒漠生境 | 6.24±0.21a | 0.969 2±0.008 6a | 200.77±22.99b | 0.818 0±0.035 8a | 1a | |
| 统计结果 | F=6.254 | F=3.092 | F=7.294 | F=8.156 | ||
| P<0.05 | P=0.083 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 |
Tab.3 Changes of soil microbial diversity in different habitats
| 微生物 Microorganism | 生境 Habitats | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | pielou_e指数 pielou_e index | 测序覆盖度 Goods coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌 Bacteria | 周期性水淹生境 | 10.36±0.34a | 0.998 3±0.000 8a | 3 104.29±319.91a | 0.890 6±0.018 2a | 0.999 9±0.000 5a |
| 中生生境 | 8.65±0.16b | 0.992 4±0.002 4b | 1 438.11±90.27b | 0.824 2±0.011 5b | 1±0.000 4a | |
| 荒漠生境 | 7.71±0.28c | 0.986 0±0.003 3c | 1 232.28±136.93c | 0.769 0±0.018 9c | 1±0.000 4a | |
| 统计结果 | F=114.477 | F=32.201 | F=153.29 | F=67.607 | F=1.313 | |
| P<0.001 | P<0.001 | P<0.001 | P<0.001 | P=0.305 | ||
| 真菌 Fungi | 周期性水淹生境 | 4.34±1.08b | 0.866 6±0.101 3b | 254.99±35.30a | 0.544 8±0.136 4b | 1a |
| 中生生境 | 4.92±01.03b | 0.893 8±0.058 1ab | 264.77±25.87a | 0.612 4±0.131 7b | 1a | |
| 荒漠生境 | 6.24±0.21a | 0.969 2±0.008 6a | 200.77±22.99b | 0.818 0±0.035 8a | 1a | |
| 统计结果 | F=6.254 | F=3.092 | F=7.294 | F=8.156 | ||
| P<0.05 | P=0.083 | P<0.05 | P<0.05 |
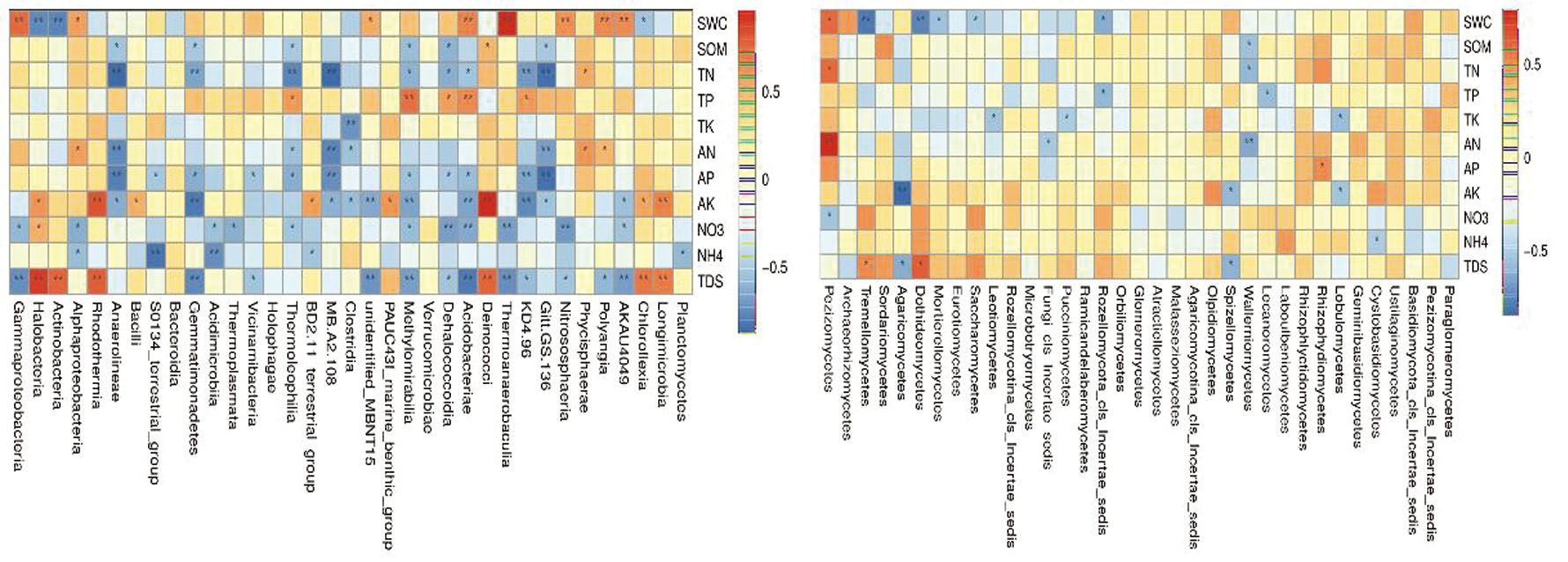
Fig.4 Spearman correlation between soil physicochemical properties and the composition of microbial community Notes:SWC:Soil moisture content;SOM:Soil organic matter;TN:Total nitrogen;TP:Total phosphorus;TK:Total potassium;AN:Alkali hydrolyzed nitroger;AP:Olsen-P;AK:Available K;N O 3 -:Nitrate nitrogen;N H 4 +:Ammonium nitrogen;TDS:Total salt,the same as below
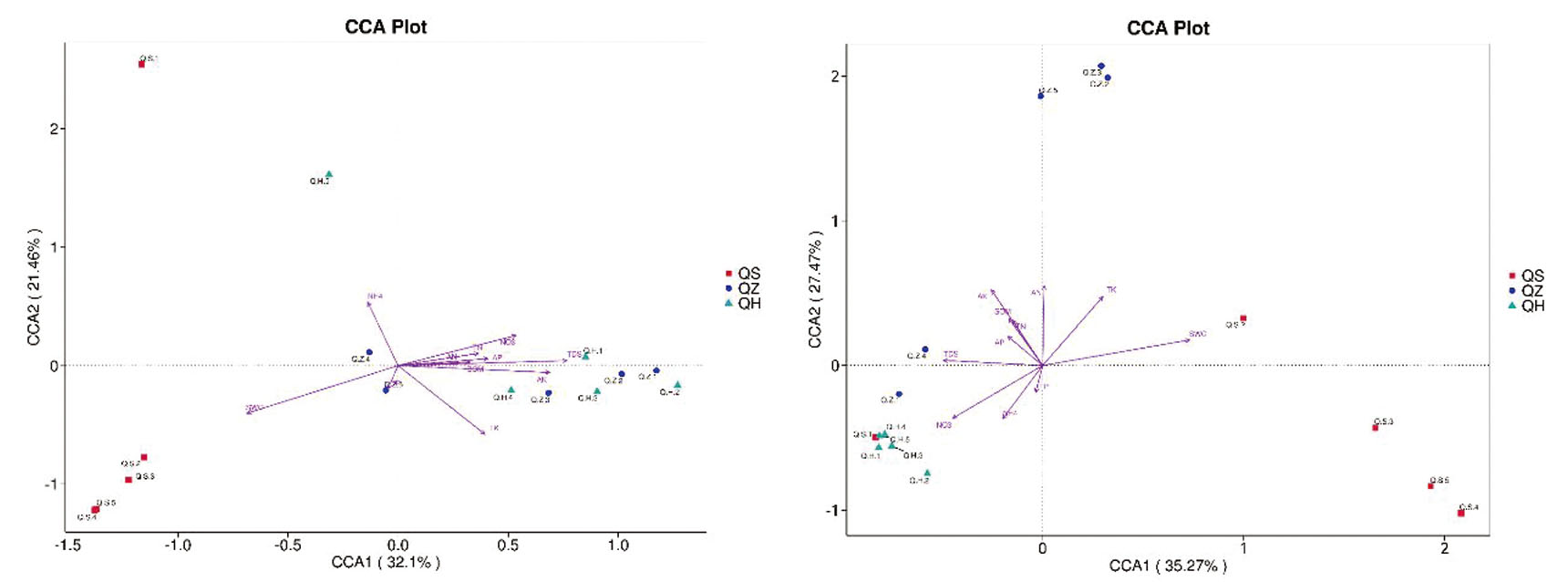
Fig.5 Changes of relationship between soil physicochemical properties and the composition of microbial community tested using classical canonicalcorrelation analysis
| [1] |
朱永官, 陈保冬, 付伟. 土壤生态学研究前沿[J]. 科技导报, 2022, 40(3): 25-31.
DOI |
| ZHU Yongguan, CHEN Baodong, FU Wei. Research frontiers in soil ecology[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2022, 40(3): 25-31. | |
| [2] | Chaparro J M, Sheflin A M, Manter D K, et al. Manipulating the soil microbiome to increase soil health and plant fertility[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2012, 48(5): 489-499. |
| [3] |
Falkowski P G, Fenchel T, Delong E F. The microbial engines that drive Earth’s biogeochemical cycles[J]. Science, 2008, 320(5879): 1034-1039.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Shi Y, Grogan P, Sun H B, et al. Multi-scale variability analysis reveals the importance of spatial distance in shaping Arctic soil microbial functional communities[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2015, 86: 126-134. |
| [5] | Van Horn D J, Van Horn M L, Barrett J E, et al. Factors controlling soil microbial biomass and bacterial diversity and community composition in a cold desert ecosystem: role of geographic scale[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(6): e66103. |
| [6] | He H R, Xu M Z, Li W T, et al. Linking soil depth to aridity effects on soil microbial community composition, diversity and resource limitation[J]. CATENA, 2023, 232: 107393. |
| [7] |
Jiao S, Chu H Y, Zhang B G, et al. Linking soil fungi to bacterial community assembly in arid ecosystems[J]. iMeta, 2022, 1(1): e2.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Bahram M, Hildebrand F, Forslund S K, et al. Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome[J]. Nature, 2018, 560(7717): 233-237. |
| [9] | Na X F, Yu H L, Wang P, et al. Vegetation biomass and soil moisture coregulate bacterial community succession under altered precipitation regimes in a desert steppe in northwestern China[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2019, 136: 107520. |
| [10] |
de Vries F T, Griffiths R I, Bailey M, et al. Soil bacterial networks are less stable under drought than fungal networks[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 3033.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Xu S, Geng W X, Sayer E J, et al. Soil microbial biomass and community responses to experimental precipitation change: a meta-analysis[J]. Soil Ecology Letters, 2020, 2(2): 93-103.
DOI |
| [12] | Jangid K, Williams M A, Franzluebbers A J, et al. Land-use history has a stronger impact on soil microbial community composition than aboveground vegetation and soil properties[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2011, 43(10): 2184-2193. |
| [13] | Zechmeister-Boltenstern S, Michel K, Pfeffer M. Soil microbial community structure in European forests in relation to forest type and atmospheric nitrogen deposition[J]. Plant and Soil, 2011, 343(1): 37-50. |
| [14] | Heitkötter J, Heinze S, Marschner B. Relevance of substrate quality and nutrients for microbial C-turnover in top- and subsoil of a Dystric Cambisol[J]. Geoderma, 2017, 302: 89-99. |
| [15] | Yost J L, Hartemink A E. How deep is the soil studied-an analysis of four soil science journals[J]. Plant and Soil, 2020, 452(1): 5-18. |
| [16] | Yu J L, Bing H J, Chang R Y, et al. Microbial metabolic limitation response to experimental warming along an altitudinal gradient in alpine grasslands, eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. CATENA, 2022, 214: 106243. |
| [17] | 王新英, 史军辉, 刘茂秀, 等. 洪水漫溢对塔里木河中游天然胡杨林叶渗透调节物质及抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(6): 1544-1551. |
| WANG Xinying, SHI Junhui, LIU Maoxiu, et al. Effects of flood overtopping on leaf osmotic adjustment substances and antioxidant enzyme activities of natural Populus euphratica forest in the middle reaches of the Tarim River[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(6): 1544-1551. | |
| [18] | 罗倩. 新疆干旱区三种不同植被类型土壤微生物多样性分析[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2012. |
| LUO Qian. Analysis of soil microbial diversity of three different vegetation types in arid areas of Xinjiang[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2012. | |
| [19] |
马继龙, 史军辉, 王新英, 等. 洪水漫溢对塔里木河中游河岸胡杨林土壤有机碳及活性组分的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(8): 1248-1257.
DOI |
|
Ma Jilong, Shi Junhui, Wang Xinying, et al. Effects of flood overflow on soil organic carbon and active components of Populus euphratica forest in the middle reaches of the Tarim River[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2023, 40(8): 1248-1257.
DOI |
|
| [20] | 马继龙, 王新英, 刘茂秀, 等. 塔里木河中游不同生境胡杨林土壤有机碳及活性组分特征[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2024, 39(2): 1-7. |
| MA Jilong, WANG Xinying, LIU Maoxiu, et al. Characteristics of soil organic carbon and active fractions in Populus euphratica of different habitats in the middle reaches of the Tarim River[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2024, 39(2): 1-7. | |
| [21] | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. |
| BAO Shidan. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. | |
| [22] | 赵裕栋, 周俊, 何璟. 土壤微生物总DNA提取方法的优化[J]. 微生物学报, 2012, 52(9): 1143-1150. |
|
ZHAO Yudong, ZHOU Jun, HE Jing. Optimization of soil microbial DNA isolation[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2012, 52(9): 1143-1150.
PMID |
|
| [23] |
金章利, 刘高鹏, 周明涛, 等. 喀斯特山地草地群落多样性海拔特征及土壤理化性质特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(4): 661-668.
DOI |
| JIN Zhangli, LIU Gaopeng, ZHOU Mingtao, et al. Elevation characteristics of grassland community diversity and effect of soil physical and chemical properties in Karst Mountain grassland[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(4): 661-668. | |
| [24] | 魏强, 凌雷, 柴春山, 等. 甘肃兴隆山森林演替过程中的土壤理化性质[J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(15): 4700-4713. |
| WEI Qiang, LING Lei, CHAI Chunshan, et al. Soil physical and chemical properties in forest succession process in Xinglong Mountain of Gansu[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(15): 4700-4713. | |
| [25] | 张海涛, 梁继业, 周正立, 等. 塔里木河中游荒漠河岸林土壤理化性质分布特征与植被关系[J]. 水土保持研究, 2016, 23(2): 6-12. |
| ZHANG Haitao, LIANG Jiye, ZHOU Zhengli, et al. Relationship between distribution characteristics of soil physicochemical properties and vegetation in desert riparian forest in the middle reaches of the Tarim River[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2016, 23(2): 6-12. | |
| [26] | 王亮, 王夏楠, 周正立, 等. 塔里木河中游典型样地土壤主要理化性质比较研究[J]. 北方园艺, 2014,(23): 148-151. |
| WANG Liang, WANG Xianan, ZHOU Zhengli, et al. Comparative study on soil physicochemical properties in the middle reaches of Tarim River[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2014,(23): 148-151. | |
| [27] |
李媛媛, 彭梦文, 党寒利, 等. 塔里木河下游胡杨根际土壤细菌群落多样性分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2021, 44(3): 750-758.
DOI |
|
LI Yuanyuan, PENG Mengwen, DANG Hanli, et al. Bacterial communities diversity of Populus euphratica rhizospheric soil in the lower reaches of Tarim River[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2021, 44(3): 750-758.
DOI |
|
| [28] |
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Reith F, Dennis P G, et al. Ecological drivers of soil microbial diversity and soil biological networks in the Southern Hemisphere[J]. Ecology, 2018, 99(3): 583-596.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
de Carvalho T S, Jesus E D, Barlow J, et al. Land use intensification in the humid tropics increased both alpha and beta diversity of soil bacteria[J]. Ecology, 2016, 97(10): 2760-2771.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Barberán A, Ramirez K S, Leff J W, et al. Why are some microbes more ubiquitous than others? Predicting the habitat breadth of soil bacteria[J]. Ecology Letters, 2014, 17(7): 794-802.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | 张静茹, 张雷一, 刘方, 等. 降雨对干旱半干旱地区土壤微生物影响研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2014, 27(4): 6-12. |
| ZHANG Jingru, ZHANG Leiyi, LIU Fang, et al. Research progress in effect of rainfall on soil microbe in arid and semi-arid area[J]. World Forestry Research, 2014, 27(4): 6-12. | |
| [32] | Kawaguchi M, Nonaka K, Masuma R, et al. New method for isolating antibiotic-producing fungi[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 2013, 66(1): 17-21. |
| [33] |
Xiao Y, Wei X M, Ebright R, et al. Antibiotic production by myxobacteria plays a role in predation[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2011, 193(18): 4626-4633.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
de Boer W, Folman L B, Summerbell R C, et al. Living in a fungal world: impact of fungi on soil bacterial niche development[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2005, 29(4): 795-811.
PMID |
| [35] | Yitbarek A, Weese J S, Alkie T N, et al. Influenza A virus subtype H9N2 infection disrupts the composition of intestinal microbiota of chickens[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2018, 94(1). DOI:10.1093/femsec/fix165. |
| [36] |
Rodriguez-Valera F. Biotechnological potential of halobacteria[J]. Biochemical Society Symposium, 1992, 58: 135-147.
PMID |
| [37] | 王雅芸, 隆彦昕, 李岩, 等. 胡杨土壤理化性质与微生物群落结构空间和分布的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(14): 5669-5684. |
| WANG Yayun, LONG Yanxin, LI Yan, et al. Relationships of soil physicochemical properties to the distribution and the composition of microbial community under Populus euphratica’s crown[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(14): 5669-5684. | |
| [38] | 乔沙沙, 周永娜, 刘晋仙, 等. 关帝山针叶林土壤细菌群落结构特征[J]. 林业科学, 2017, 53(2): 89-99. |
| QIAO Shasha, ZHOU Yongna, LIU Jinxian, et al. Characteristics of soil bacterial community structure in coniferous forests of guandi mountains, Shanxi Province[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2017, 53(2): 89-99. | |
| [39] | Mali T, Kuuskeri J, Shah F, et al. Interactions affect hyphal growth and enzyme profiles in combinations of coniferous wood-decaying fungi of Agaricomycetes[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(9): e0185171. |
| [40] | 李媛媛. 塔里木河下游胡杨根际微生物群落结构与土壤理化性质的相关性分析[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2022. |
| LI Yuanyuan. Correlation analysis between microbial community structure of Populus euphratica rhizosphere and soil physical and chemical properties in the lower reaches of Tarim River[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2022. | |
| [41] | Sardinha M, Müller T, Schmeisky H, et al. Microbial performance in soils along a salinity gradient under acidic conditions[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2003, 23(3): 237-244. |
| [42] | Rath K M, Fierer N, Murphy D V, et al. Linking bacterial community composition to soil salinity along environmental gradients[J]. The ISME Journal, 2019, 13(3): 836-846. |
| [43] | 张笑培, 杨改河, 任广鑫, 等. 黄土高原南部植被恢复对土壤理化性状与土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2010, 28(6): 64-68. |
| ZHANG Xiaopei, YANG Gaihe, REN Guangxin, et al. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil physical-chemical properties and activities of soil enzyme in the Gully Region of the Loess Plateau[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2010, 28(6): 64-68. | |
| [44] | Laurent P, Claire C, Andreas K, et al. The interplay between microbial communities and soil properties[J]. Nature reviews. Microbiology, 2023. |
| [45] | Schimel J P. Life in dry soils: effects of drought on soil microbial communities and processes[J]. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 2018, 49: 409-432. |
| [1] | YAO Yuxiang, WANG Guoqiang, WANG Ke, YI Sha, YANG Xinya, LUO Xioaxia. Analysis of the bacterial communities structure and diversty of the Tarim River in different habitats [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(3): 708-718. |
| [2] | ZHANG You, LIU Maoxiu, SHI Junhui, WANG Xinying, Aijier Abula, ZHANG Yan. Numerical analysis of soil and vegetation nutrient characteristics in the initial year of returning farmland in the core area of Tarim River Populus euphratica forest [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(3): 699-707. |
| [3] | Reyihan Abulizi, HE Xuemin, YANG Huan, HUANG Pengcheng, FENG Haipeng, WANG Yongzhi. Characteristics of chlorophyll-fluorescence parameters of Suaeda microphylla Pall.and their responses to soil factors in different water-salt habitats [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(2): 485-494. |
| [4] | TIAN Jingyu, GAO Yan, GAO Xingwang, ZENG Jun, ZHAO Pengan, Subinuer Julaiti. Analysis of rhizospheric bacterial community structure and diversity of Hami melon under field cultivation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(5): 1253-1262. |
| [5] | ZHENG Yannan, YAO Yongsheng, Guljiani Asghar, AN Shijie, LI Yanxia, ZHI Jinhu. Effects of Different Improvement Measures on Particle Composition and Fractal Characteristics of Sandy Soil [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(9): 1665-1671. |
| [6] | FU Yuan-yuan1, JIANG Ping1, LIU Ai-hua2 , ZHANG Jing-wen2, YUE Zhao-yuan2, TIAN Cheng-ming. Analysis of the Influence of Different Landscape Scales on the Spatial Distribution of Diaspidiotusslavonicus's Population [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(11): 2043-2053. |
| [7] | GU Mei-ying, XU Wan-li, ZHANG Zhi-dong, TANG Guang-mu, LIU Hong-liang, LI Zhi-qiang, LIU Xiao-wei, PU Sheng-hai, FENG Lei, ZHANG Ji-feng. Relationships between Fungi Diversity, Physicochemical Properties and Verticillium Wilt in Continuous Cropping Cotton Rhizosphere Soil with Cotton Stover Biochar [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(9): 1698-1709. |
| [8] | WANG Xin-ying, SHI Jun-hui, LIU Mao-xiu. Nutrient Accumulation Characteristics and Dynamic Change of Natural Populus euphratica Forest in the Tarim River Basin [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(6): 1036-1045. |
| [9] | LIU Jin-yu,Dilnur,JIA Hai-ying,JIANG Ping. Study on Overwintering Survival of Mycelia and Conidia of Walnut Leaf Spot Pathogens [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(10): 1870-1878. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||