

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (2): 485-494.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.02.026
• Microbes·Physiology and Biochemistry·Animal Husbandry Veterinarian • Previous Articles Next Articles
Reyihan Abulizi1,2( ), HE Xuemin1,2(
), HE Xuemin1,2( ), YANG Huan1,2, HUANG Pengcheng1,2, FENG Haipeng1,2, WANG Yongzhi1,2
), YANG Huan1,2, HUANG Pengcheng1,2, FENG Haipeng1,2, WANG Yongzhi1,2
Received:2023-06-05
Online:2024-02-20
Published:2024-03-19
Correspondence author:
HE Xuemin(1986-), male, from Xincai Henan, associate professor, research field:desert plant physiology and ecology,(E-mail)Supported by:
热依汗·阿布力孜1,2( ), 何学敏1,2(
), 何学敏1,2( ), 杨欢1,2, 黄鹏程1,2, 冯海鹏1,2, 王勇志1,2
), 杨欢1,2, 黄鹏程1,2, 冯海鹏1,2, 王勇志1,2
通讯作者:
何学敏(1986-),男,河南新蔡人,副教授,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为荒漠植物生理生态,(E-mail)作者简介:热依汗·阿布力孜(1996-),女,新疆吐鲁番人,硕士,研究方向为荒漠植物生理生态,(E-mail)2454459083@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Reyihan Abulizi, HE Xuemin, YANG Huan, HUANG Pengcheng, FENG Haipeng, WANG Yongzhi. Characteristics of chlorophyll-fluorescence parameters of Suaeda microphylla Pall.and their responses to soil factors in different water-salt habitats[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(2): 485-494.
热依汗·阿布力孜, 何学敏, 杨欢, 黄鹏程, 冯海鹏, 王勇志. 不同水盐生境下小叶碱蓬叶绿素荧光参数特征及其对土壤因子的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 485-494.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.xjnykx.com/EN/10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.02.026
| 生境 Habitat | pH | 电导率 Electrical conductivity (mS/cm) | 土壤含盐量 Soil salinity (g/kg) | 土壤含水率 Soil water content (%) | 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter (g/kg) | 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen (g/kg) | 土壤速效磷 Soil available phosphorus (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 8.1±0.07a | 8.9±0.68bc | 8.62±0.65bc | 13.59±0.51b | 9.46±0.9b | 1.49±0.7a | 13.59±0.51b |
| Ⅱ | 8.12±0.03a | 5.17±0.47a | 5.05±0.45a | 7.98±0.68a | 6.61±0.31ab | 0.94±0.42a | 7.98±0.68a |
| Ⅲ | 7.95±0.06a | 6.8±0.61ab | 6.61±0.58ab | 12.82±0.45b | 8.57±1.37ab | 0.97±0.56a | 12.82±0.45b |
Tab.1 Differences of soil factors in Suaeda microphylla Pall.in different habitats
| 生境 Habitat | pH | 电导率 Electrical conductivity (mS/cm) | 土壤含盐量 Soil salinity (g/kg) | 土壤含水率 Soil water content (%) | 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter (g/kg) | 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen (g/kg) | 土壤速效磷 Soil available phosphorus (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 8.1±0.07a | 8.9±0.68bc | 8.62±0.65bc | 13.59±0.51b | 9.46±0.9b | 1.49±0.7a | 13.59±0.51b |
| Ⅱ | 8.12±0.03a | 5.17±0.47a | 5.05±0.45a | 7.98±0.68a | 6.61±0.31ab | 0.94±0.42a | 7.98±0.68a |
| Ⅲ | 7.95±0.06a | 6.8±0.61ab | 6.61±0.58ab | 12.82±0.45b | 8.57±1.37ab | 0.97±0.56a | 12.82±0.45b |
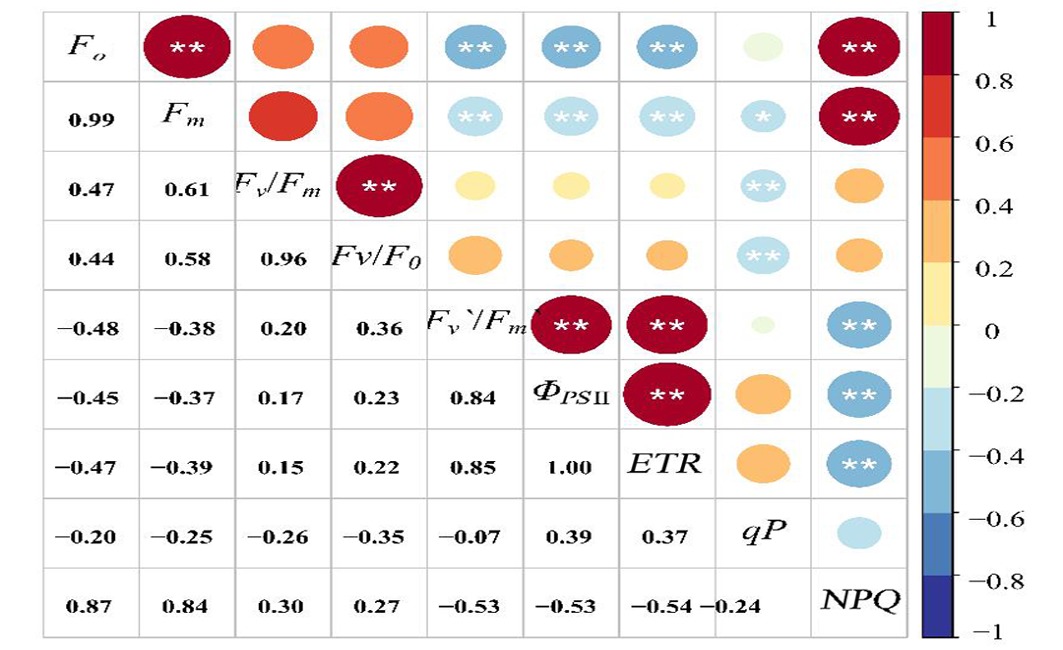
Fig.2 Correlation between chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Suaeda microphylla Pall.in different habitats Note:P<0.01**,P<0.05*.Fo:Initial fluorescence; Fm:Maximum fluorescence; Fv/Fm:PSⅡ maximum photochemical efficiency; Fv/Fo:Photosynthetic efficiency potential; Fv'/Fm':PSⅡ reflects the excitation energy capture efficiency of the center; ΦPSⅡ:Actual photochemical quantum efficiency of PSⅡ; ETR:Electron transport efficiency; qP:Photo chemical quenching coefficient; NPQ:Non-photochemical quenching.
| 叶绿素荧光参数 Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameter | 主成分1 Principal Component 1 | 主成分2 Principal Component 2 | 主成分3 Principal Component 3 | 综合得分 Comprehensive score | 综合位次 Comprehensive ranking | 公因子方差 Communality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 初始荧光Fo | 0.900 | 0.252 | 0.270 | 0.552 | 2 | 0.947 |
| 最大荧光Fm | 0.876 | 0.393 | 0.216 | 0.579 | 1 | 0.969 |
| PSⅡ最大光化学效Fv/Fm | 0.362 | 0.862 | -0.034 | 0.448 | 4 | 0.875 |
| 光合效率潜能Fv/Fo | 0.305 | 0.920 | -0.134 | 0.426 | 5 | 0.958 |
| PSⅡ反应中心的激发能捕获效率Fv'/Fm' | -0.686 | 0.622 | -0.231 | -0.164 | 8 | 0.911 |
| PSⅡ实际的光化学量子效率ΦPS Ⅱ | -0.757 | 0.578 | 0.255 | -0.152 | 7 | 0.972 |
| 电子传递效率ETR | -0.772 | 0.564 | 0.224 | -0.168 | 9 | 0.965 |
| 光化学淬灭系数qP | -0.397 | -0.167 | 0.874 | -0.139 | 6 | 0.949 |
| 非光化学淬灭系数NPQ | 0.882 | 0.079 | 0.198 | 0.479 | 3 | 0.824 |
| 特征值Eigenvalues | 4.379 | 2.881 | 1.110 | |||
| 贡献率Contribution(%) | 48.655 | 32.007 | 12.338 | |||
| 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution(%) | 48.655 | 80.662 | 93.000 |
Tab.2 Initial factor loading matrix and principal component contribution rate
| 叶绿素荧光参数 Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameter | 主成分1 Principal Component 1 | 主成分2 Principal Component 2 | 主成分3 Principal Component 3 | 综合得分 Comprehensive score | 综合位次 Comprehensive ranking | 公因子方差 Communality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 初始荧光Fo | 0.900 | 0.252 | 0.270 | 0.552 | 2 | 0.947 |
| 最大荧光Fm | 0.876 | 0.393 | 0.216 | 0.579 | 1 | 0.969 |
| PSⅡ最大光化学效Fv/Fm | 0.362 | 0.862 | -0.034 | 0.448 | 4 | 0.875 |
| 光合效率潜能Fv/Fo | 0.305 | 0.920 | -0.134 | 0.426 | 5 | 0.958 |
| PSⅡ反应中心的激发能捕获效率Fv'/Fm' | -0.686 | 0.622 | -0.231 | -0.164 | 8 | 0.911 |
| PSⅡ实际的光化学量子效率ΦPS Ⅱ | -0.757 | 0.578 | 0.255 | -0.152 | 7 | 0.972 |
| 电子传递效率ETR | -0.772 | 0.564 | 0.224 | -0.168 | 9 | 0.965 |
| 光化学淬灭系数qP | -0.397 | -0.167 | 0.874 | -0.139 | 6 | 0.949 |
| 非光化学淬灭系数NPQ | 0.882 | 0.079 | 0.198 | 0.479 | 3 | 0.824 |
| 特征值Eigenvalues | 4.379 | 2.881 | 1.110 | |||
| 贡献率Contribution(%) | 48.655 | 32.007 | 12.338 | |||
| 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution(%) | 48.655 | 80.662 | 93.000 |
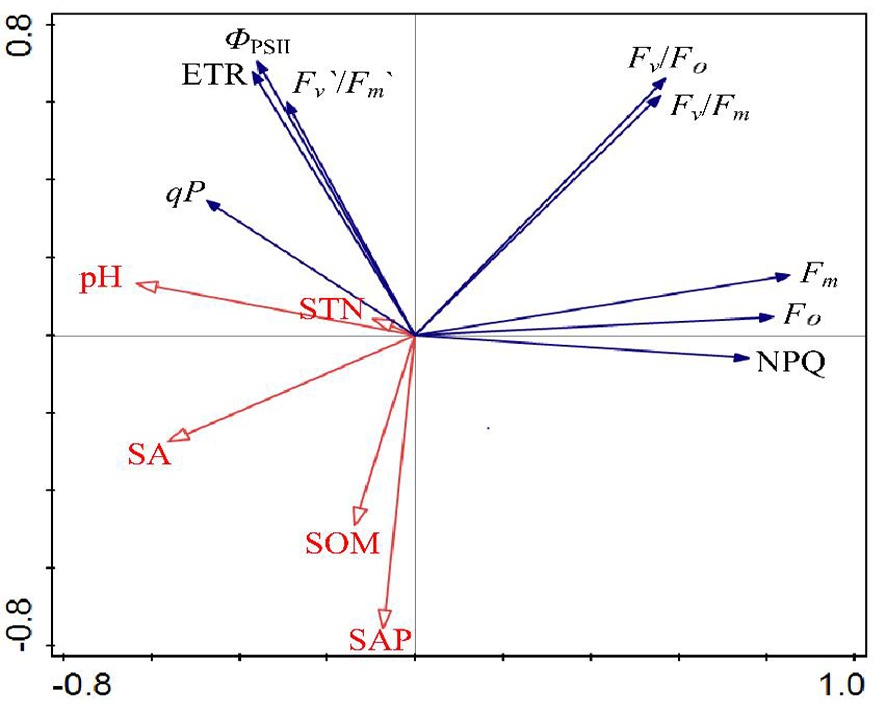
Fig.3 RDA ranking of chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and soil factors of Suaeda microphylla Pall. Note:STN:Soil total nitrogen; SA:Soil salinity; SOM:Soil organic matter; SAP:Soil available phosphorus, Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters are as shown in Fig.2
| 土壤因子 Soil factors | 解释量 Explains (%) | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤速效磷 Soil available phosphorus | 17.2 | 24.3 | 1.5 | 0.254 |
| 土壤含盐量 Soil salinity | 24.2 | 34.2 | 2.5 | 0.076 |
| pH | 13.5 | 19.1 | 1.5 | 0.216 |
| 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen | 6.7 | 9.4 | 0.7 | 0.63 |
| 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter | 9.2 | 13.0 | 0.9 | 0.474 |
Tab.3 Monde Carlo test for soil factors
| 土壤因子 Soil factors | 解释量 Explains (%) | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤速效磷 Soil available phosphorus | 17.2 | 24.3 | 1.5 | 0.254 |
| 土壤含盐量 Soil salinity | 24.2 | 34.2 | 2.5 | 0.076 |
| pH | 13.5 | 19.1 | 1.5 | 0.216 |
| 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen | 6.7 | 9.4 | 0.7 | 0.63 |
| 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter | 9.2 | 13.0 | 0.9 | 0.474 |
| [1] | 朱海强, 李艳红, 李发东. 近10年艾比湖湿地不同植物群落土壤水分-盐分-养分变化特征[J]. 西北植物学报, 2018, 38(3):535-543. |
| ZHU Haiqiang, LI Yanhong, LI Fadong. Characteristics of soil moisture, salinity and nutrients in different plant communities of ebinur lake wetland during the past decade[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2018, 38(3):535-543. | |
| [2] | 张立华, 陈小兵. 盐碱地怪柳“盐岛”和“肥岛”效应及其碳氮磷生态化学计量学特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(3):653-658. |
|
ZHANG Lihua, CHEN Xiaobing. Characteristics of ‘salt island’ and ‘fertile island’ for Tamarix chinensis and soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus ecological stoichiometry in saline-alkali land[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(3):653-658.
PMID |
|
| [3] | 张立华, 陈沛海, 李健, 等. 黄河三角洲怪柳植株周围土壤盐分离子的分布[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(18):5741-5749. |
| ZHANG Lihua, CHEN Peihai, LI Jian, et al. Distribution of soil salt ions around Tamarix chinensis individuals in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(18):5741-5749. | |
| [4] |
Mishara A, Tanna B. Halophytes:potential resources for salt stress tolerance genes and promoters[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8:829.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 陈海银, 沈晖, 田军仓, 等. 植物叶绿素荧光参数对水盐胁迫的响应机制综述[J]. 现代农业科技, 2021, (19):168-169,176. |
| CHEN Haiyin, SHEN Hui, TIAN Juncang, et al. Review on response mechanism of chlorophyll fluorescence parameters to water and salt stress in plants[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, (19):168-169,176. | |
| [6] | 李永梅, 张学俭. 基于光谱指数的构祀叶片水分含量遥感监测研究[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2019, 35(5):16-21. |
| LI Yongmei, ZHANG Xuejian. Remote sensing monitoring of leaf water content in Lycium barbarum based on spectral index[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2019, 35(5):16-21. | |
| [7] |
Borawska-Jarmułowicz B, Mastalerczuk G, Pietkiewicz S, et al. Low temperature and hardening effects on photosynthetic apparatus efficiency and survival of forage grass varieties[J]. Plant Soil and Environment, 2014, 60(4):177-183.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Zushi K, Matsuzoe N. Using of chlorophyll a fluorescence OJIP transients for sensing salt stress in the leaves and fruits of tomato[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2017, 219:216-221.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 殷元峰, 胡宇凯, 胡守林. 不同栽培模式下棉花花铃期叶绿素荧光参数分析[J]. 农业与技术, 2022, 42(16):6-10. |
| YIN Yuanfeng, HU Yukai, HU Shoulin. Analysis of chlorophyll fluorescence parameters at flowering boll stage of cotton under different cultivation modes[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2022, 42(16):6-10. | |
| [10] |
杨淑萍, 危常州, 梁永超. 盐胁迫对不同基因型海岛棉光合作用及荧光特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(8):1585-1593.
DOI |
| YANG Shuping, WEI Changzhou, LIANG Yongchao. Effects of NaCl stress on the characteristics of photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence at seedlings stage in different sea island cotton genotypes[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(8):1585-1593. | |
| [11] |
Mehta P, Jajoo A, Mathur S, et al. Chlorophyll a fluorescence study revealing effects of high salt stress on Photosystem II in wheat leaves[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2010, 48(1):16-20.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Kumari A, Kumar A, Wany A, et al. Identification and annotation of abiotic stress responsive candidate genes in peanut ESTs[J]. Bioinformation, 2012, 8(24):1211-1219.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | 孙文君, 江晓慧, 付媛媛, 等. 盐分胁迫对棉花幼苗叶片叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2021, 40(7):23-28,121. |
| SUN Wenjun, JIANG Xiaohui, FU Yuanyuan, et al. The effects of salt stress on chlorophyll fluorescence of cotton seeding leaves[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2021, 40(7):23-28,121. | |
| [14] |
张玲, 王华, 周静, 等. NaCl胁迫对两个辣椒品种幼苗叶绿素荧光参数等生理特性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2017, 29(4):597-604.
DOI |
|
ZHANG Ling, WANG Hua, ZHOU Jing, et al. Effects of NaCl stress on chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics and other physiological characteristics in seedlings of two pepper cultivars[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2017, 29(4):597-604.
DOI |
|
| [15] | 杜美娥, 王红霞, 张伟, 等. 盐胁迫对金叶榆幼苗叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2019, (5):90-94. |
| DU Meie, WANG Hongxia, ZHANG Wei, et al. Effects of different concentration of salt stress on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Ulmus pumila seedlings[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2019, (5):90-94. | |
| [16] | 刘莉娜, 张卫强, 黄芳芳, 等. 盐胁迫对银叶树幼苗光合特性与叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 森林与环境学报, 2019, 39(6):601-607. |
| LIU Lina, ZHANG Weiqiang, HUANG Fangfang, et al. Effects of NaCl stress on photosynthetic characteristics and chlorophyll fluorescence of Heritiera littoralis seedlings[J]. Journal of Forest and Environment, 2019, 39(6):601-607. | |
| [17] |
孙璐, 周宇飞, 李丰先, 等. 盐胁迫对高粱幼苗光合作用和荧光特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2012, 45(16):3265-3272.
DOI |
|
SUN Lu, ZHOU Yufei, LI Fengxian, et al. Impact of salt stress on characteristics of photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence of Sorghum seedlings[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012, 45(16):3265-3272.
DOI |
|
| [18] | 陈蜀江, 侯平, 李文华. 新疆艾比湖湿地自然保护区综合科学考察[M]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆科学技术出版社, 2006. |
| CHEN Shujiang, HOU Ping, LI Wenhua. Comprehensive scientific investigation of ebinur lake wetland nature reserve in Xinjiang[M]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Science and Technology Press, 2006. | |
| [19] | 王水献, 董新光, 杜卫东. 新疆阿瓦提灌区土壤盐渍化现状及特征分析[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2006,(5):170-175 |
| Wang Shuixian, Dong Xinguang, Du Weidong. Present situation and characteristic analysis of soil salinization in Awati irrigation area of Xinjiang[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2006,(5):170-175. | |
| [20] | 秦娟, 孔海燕, 刘华. 马尾松不同林型土壤C、N、P、K的化学计量特征[J] .西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 44(2):68-76,82. |
| QIN Juan, KONG Haiyan, LIU Hua. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil C, N, P and K in different Pinus types massonianaforests[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University(Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(2):68-76,82. | |
| [21] |
周帅, 林富平, 王玉魁, 等. 樟树幼苗机械损伤叶片对挥发性有机化合物及叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2012, 36(7):671-680.
DOI |
|
ZHOU Shuai, LIN Fuping, WANG Yukui, et al. Effects of mechanical damage of leaves on volatileorganic compounds and chlorophyll flourescence parameters in seedlings of Cinnamomun camohora[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2012, 36(7):671-680.
DOI |
|
| [22] | 李佳, 江洪, 余树全, 等. 模拟酸雨胁迫对青冈幼苗光合特性和叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2009, 20(9):2092-2096. |
|
LI Jia, JIANG Hong, YU Shuquan, et al. Effects of simulated acid rain stress on Quercus glauca seeding photosynthetic and chlorophyll fluorescence[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2009, 20(9):2092-2096.
PMID |
|
| [23] |
Murata N, Takahashi S, Nishiyama Y, et al. Photoinhibition of photosystem II under environmental stress[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta(BBA)-Bioenergetics, 2007,(6):414-421.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | 方怡然, 薛立. 盐胁迫对植物叶绿素荧光影响的研究进展[J]. 生态科学, 2019, 38(3):225-234. |
| FANG Yiran, XUE Li. Research advances in the effects of salt stress on plant chlorophyll fluorescence[J]. Ecological Science, 2019, 38(3):225-234. | |
| [25] |
蔡建国, 韦孟琪, 章毅, 等. 遮阴对绣球光合特性和叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(5):570-576.
DOI |
|
CAI Jianguo, WEI Mengqi, ZHANG Yi, et al. Effects of shading on photosynthetic characteristics and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2017, 41(5):570-576.
DOI |
|
| [26] |
Oukarroum A, Bussotti F, Goltsev V, et al. Correlation between reactive oxygen species production and photochemistry of photosystems I and Ⅱ in Lemna gibbal[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2015, 109:80-88.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Zhang J F, Wan L, Igathinathane C, et al. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of chlorophyll content and fluorescence response within rice(Oryza sativa L.) canopies under different nitrogen treatments[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12:645977.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
dos Santos V, VAHR Nelson B W, Rodrigues J V F C, et al. Fluorescence parameters among leaf photosynthesis-related traits are the best proxies for CO2 assimilation in Central Amazon trees[J]. Brazilian Journal of Botany, 2019, 42(2):239-247.
DOI |
| [29] | 姚春娟, 郭圣茂, 马英超, 等. 干旱胁迫对4种决明属植物光合作用和叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2017, 34(9):1880-1888. |
| YAO Chunjuan, GUO Shengmao, MA Yingchao, et al. Effects of drought stress on characteristics of photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence four species of Cassia[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(9):1880-1888. | |
| [30] | 孙敏, 李树斌, 唐飘, 等. 干旱胁迫对杉木无性系叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J]. 森林与环境学报, 2018, 38(2):202-208. |
| SUN Min, LI Shubin, TANG Piao, et al. Effects of drought stress on chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of Chinese fir clones[J]. Journal of Forest and Environment, 2018, 38(2):202-208. | |
| [31] |
李磊, 李向义, 林丽莎, 等. 两种生境条件下6种牧草叶绿素含量及荧光参数的比较[J]. 植物生态学报, 2011, 35(6):672-680.
DOI |
|
LI Lei, LI Xiangyi, LIN Lisha, et al. Comparison of chlorophyll content and fluorescence parameters of six pasture spescies in two habitats in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2011, 35(6):672-680.
DOI |
|
| [32] | 李灿, 曾凤, 赵阳阳, 等. 水涝胁迫对4种姜科植物叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 热带农业科学, 2019, 39(2):45-50. |
| LI Can, ZENG Feng, ZHAO Yangyang, et al. Effects of waterlogging stress on chlorophyll fluorescence of four Zingiberaceae species[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2019, 39(2):45-50. | |
| [33] | 刘丙花, 赵登超, 梁静, 等. 4个品种核桃砧木幼苗干旱生理响应及抗旱性评价[J]. 经济林研究, 2020, 38(1):11-19. |
| LIU Binghua, ZHAO Dengchao, LIANG Jing, et al. Physiological response to drought stress and resistances evaluation of four cultivars of walnut rootstock seedlings[J]. Non-wood Forest Research, 2020, 38(1):11-19. | |
| [34] |
Yang Z F, Tian J C, Feng K P, et al. Application of a hyperspectral imaging system to quantify leaf-scale chlorophyll, nitrogen and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in grapevine[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021, 166:723-737.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
金祎婷, 刘文辉, 刘凯强, 等. 全生育期干旱胁迫对‘青燕1号’燕麦叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6):112-126.
DOI |
|
JIN Yiting, LIU Wenhui, LIU Kaiqiang, et al. Effects of water deficit stress on the chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Avena sativa 'Qingyan No.1' over the whole crop growth period[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(6):112-126.
DOI |
|
| [36] |
杨程, 杜思梦, 张德奇, 等. 基于叶绿素荧光参数的小麦叶片叶绿素相对含量估算方法[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(1):175-181.
DOI |
|
YANG Cheng, DU Simeng, ZHANG Deqi, et al. Method for estimating relative chlorophyll content in wheat leaves based on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(1):175-181.
DOI |
|
| [37] |
Yamane K, Kawasaki M, Taniguchi M, et al. Correlation between chloroplast ultrastructure and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics in the leaves of rice(Oryza sativa L.) grown under salinity[J]. Plant Production Science, 2008, 11(1):139-145.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Shin Y K, Bhandari S B, Cho M C, et al. Evaluation of chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and proline content in tomato seedlings grown under different salt stress conditions[J]. Horticulture, Environment, and Biotechnology, 2020, 61(3):433-443. |
| [39] | 刘雷震, 武建军, 周洪奎, 等. 叶绿素荧光及其在水分胁迫监测中的研究进展[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(9):2780. |
| LIU Leizhen, WU Jianjun, ZHOU Hongkui, et al. Chlorophyll fluorescence and its progress in detecting water stress[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(9):2780. | |
| [40] | Gan T T, Zhao N J, Yin G F, et al. Optimal chlorophyll fluorescence parameter selection for rapid and sensitive detection of lead toxicity to marine microalgae Nitzschia closterium based on chlorophyll fluorescence technology[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology, B:Biology, 2019, 197:111551. |
| [41] | 孙云飞, 张文明, 巢建国, 等. 盐胁迫对茅苍术叶绿素含量及叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(4):146-149. |
| SUN Yunfei, ZHANG Wenming, CHAO Jianguo, et al. Impact of salt stress on chlorophyll contents and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Atractylodes lancea[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(4):146-149. | |
| [42] | 贾婷婷, 常伟, 范晓旭, 等. 盐胁迫下AM真菌对沙枣苗木光合与叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(4):1337-1347. |
| JIA Tingting, CHANG Wei, FAN Xiaoxu, et al. Effects of Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on photosynthetic and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of Elaeagnes angustifolia seedlings under salt stress[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(4):1337-1347. |
| [1] | YAO Yuxiang, WANG Guoqiang, WANG Ke, YI Sha, YANG Xinya, LUO Xioaxia. Analysis of the bacterial communities structure and diversty of the Tarim River in different habitats [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(3): 708-718. |
| [2] | MA Xinchao, XUAN Zhengying, MIN Haozhe, QI Zhiwen, CHENG Hongyu, TAN Zhanming, WANG Xufeng. Effects of water and nitrogen coupling on diurnal changes of photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of cucumber in sandy culture [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1966-1974. |
| [3] | DING Yu, ZHANG Jianghui, BAI Yungang, LIU Hongbo, ZHENG Ming, ZHAO Jinghua, XIAO Jun, HAN Zhengyu. Effects of different dry sowing and wet-out water treatments on cotton physiology, growth characteristics and yield under double film conditions [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(4): 810-822. |
| [4] | LYU Qi, JIANG Yu, ZHAO Fengyun, LEI Ye, YU Kun, YAO Dongdong, LI Xujiao, SHA Riye, WANG Fangxia. Effects of Biochar on Biomass, Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters and Ion Distribution of FIG under Salt Stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(3): 574-581. |
| [5] | QIN Guoli, WANG Weiran, WANG Meng, YANG Jing, HUANG Xinglei, LIU Zhiqing, ZHU Jiahui, Alifu Aierxi, KONG Jie, CHEN Guodong. Effects of agronomic characters and photosynthetic parameters of glyphosate on sea island cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(12): 2861-2868. |
| [6] | SONG Yu, QU Jisong, ZHANG Lijuan, ZHU Qiannan. Effects of Nitrogen Consumption on Gas Exchange and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters of Chives in Facilities [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(5): 852-858. |
| [7] | ZHANG Qi, LI Peng, TIAN Jia, LI Jiang. Study on Photosynthetic and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Characteristics of Transgenic Tobacco with AcCBF1 Gene [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(2): 267-277. |
| [8] | FU Yuan-yuan1, JIANG Ping1, LIU Ai-hua2 , ZHANG Jing-wen2, YUE Zhao-yuan2, TIAN Cheng-ming. Analysis of the Influence of Different Landscape Scales on the Spatial Distribution of Diaspidiotusslavonicus's Population [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(11): 2043-2053. |
| [9] | LIU Jin-yu,Dilnur,JIA Hai-ying,JIANG Ping. Study on Overwintering Survival of Mycelia and Conidia of Walnut Leaf Spot Pathogens [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(10): 1870-1878. |
| [10] | LI Xiao-dong;ZHANG Feng-hua;ZHU Yu. Agricultural Irrigation Water Quality and Soil Salinization in Typical Areas of Southern Xinjiang [J]. , 2016, 53(7): 1260-1267. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||