

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (12): 3097-3104.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.12.025
袁如薏( ), 韩志立, 潘斯瑶, 马红钰, 黄铖, 赵丹, 程军回(
), 韩志立, 潘斯瑶, 马红钰, 黄铖, 赵丹, 程军回( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-22
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2025-01-16
通信作者:
程军回(1983-),男,甘肃庄浪人,副教授,硕士生导师,研究方向为生态学,(E-mail)cjhgraymice@126.com作者简介:袁如薏(1999-),女,新疆北屯人,硕士研究生,研究方向为植物营养学,(E-mail)1607270371@qq.com
基金资助:
YUAN Ruyi( ), HAN Zhili, PAN Siyao, MA Hongyu, HUANG Cheng, ZHAO Dan, CHENG Junhui(
), HAN Zhili, PAN Siyao, MA Hongyu, HUANG Cheng, ZHAO Dan, CHENG Junhui( )
)
Received:2024-04-22
Published:2024-12-20
Online:2025-01-16
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】 验证灌木个体大小、空间位置和采样方向对其冠下土壤化学计量比的影响。【方法】 在准噶尔荒漠西北缘选取4种个体大小不同的里海盐爪爪个体,在其冠下4个不同采样方向(东、南、西、北)和4个空间位置上(主根周围、冠幅中央、冠幅边缘和株间空地),分别采集0~10 cm和10~20 cm土壤样品,在测定有机碳(SOC)、全氮(TN)、全磷(TP)含量的基础上,分析个体大小、空间位置和采样方向对土壤C/N、C/P和N/P变化的影响。【结果】 里海盐爪爪冠下土壤C/N、C/P和N/P表现出由主根周围向株间空地逐渐递减的趋势。其中,C/N在较小个体里海盐爪爪冠下10~20 cm土层表现出主根周围高出冠幅中央13.6%;C/P在0~10 cm和10~20 cm土层各空间位置间均存在显著性差异,且10~20 cm土层主根周围C/P高出株间空地15.6%-16.3%;N/P在10~20 cm土层中表现为大个体里海盐爪爪主根周围是冠幅边缘的1.3倍,较小个体里海盐爪爪冠幅中央显著高出主根周围40%。土壤SOC、TN、TP与土壤化学计量比表现出显著的相关性(P<0.01)。【结论】 该区域C/N较为稳定,C/P与N/P成为该区域养分限制性指标。
中图分类号:
袁如薏, 韩志立, 潘斯瑶, 马红钰, 黄铖, 赵丹, 程军回. 里海盐爪爪冠下土壤化学计量比变化特征[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(12): 3097-3104.
YUAN Ruyi, HAN Zhili, PAN Siyao, MA Hongyu, HUANG Cheng, ZHAO Dan, CHENG Junhui. Variation characteristics of soil stoichiometric ratio under the canopy of Kalidium caspicum[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(12): 3097-3104.
| 里海盐爪爪个体大小 plant individual sizes of Kalidium caspicum | 冠幅面积 Capsicum crown area (m2) |
|---|---|
| 大个体 Large individuals | 1.06~12.69 |
| 中等个体 Medium individuals | 0.63~1.05 |
| 小个体 Small individuals | 0.33~0.62 |
| 较小个体 Relatively small individuals | 0.05~0.32 |
表1 里海盐爪爪个体大小分类
Tab.1 Classification of individual size of Kalidium caspicum
| 里海盐爪爪个体大小 plant individual sizes of Kalidium caspicum | 冠幅面积 Capsicum crown area (m2) |
|---|---|
| 大个体 Large individuals | 1.06~12.69 |
| 中等个体 Medium individuals | 0.63~1.05 |
| 小个体 Small individuals | 0.33~0.62 |
| 较小个体 Relatively small individuals | 0.05~0.32 |
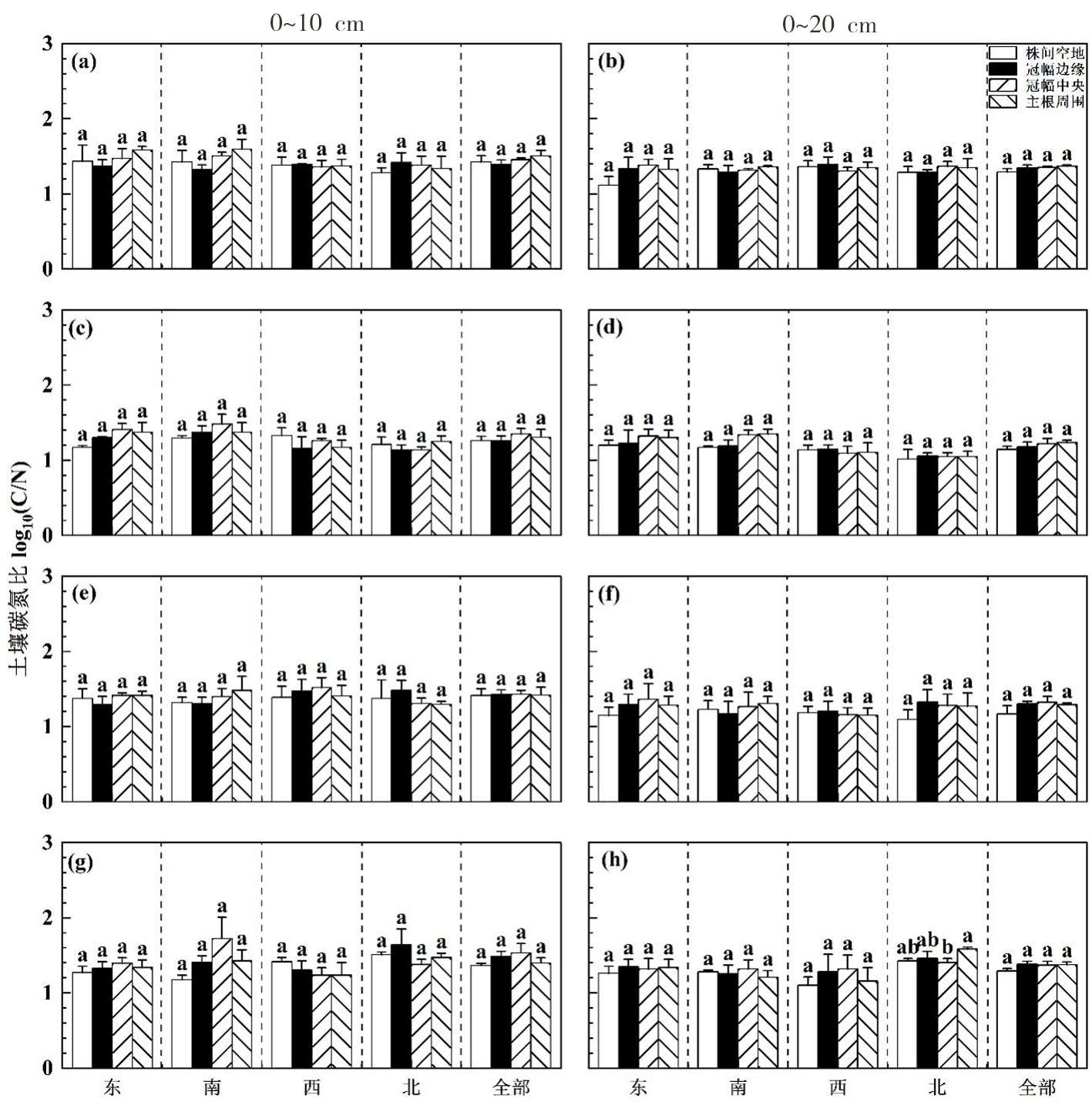
图1 里海盐爪爪冠幅土壤碳氮比在0~10 cm和10~12 cm的变化特征(平均值±标准误)。 注:图中(a,b),(c,d),(e,f)和(g,h)分别代表里海盐爪爪的大个体、中等个体、小个体和较小个体
Fig.1 Variations of C/N under canopies of Kalidium caspicum at 0-10 cm and 10-20 cm (average value+standard error) Notes:(a,b),(c,d),(e,f) and (g,h) represented the large, medium, small and relatively small individuals of Kalidium caspicum respectively
| 土层 Soil layers | 指标 Indexes | log10 SOC | log10 TN | log10 TP | log10 (C/N) | log10 (C/P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 cm | log10 TN | 0.318** | ||||
| log10 TP | -0.193** | -0.065 | ||||
| log10 (C/N) | 0.322** | -0.795** | -0.061 | |||
| log10 (C/P) | 0.955** | 0.303** | -0.473** | 0.309** | ||
| log10 (N/P) | 0.346** | 0.979** | -0.266** | -0.756** | 0.389** | |
| 10~20 cm | log10 TN | 0.465** | ||||
| log10 TP | -0.305** | -0.219** | ||||
| log10 (C/N) | 0.404** | -0.621** | -0.045 | |||
| log10 (C/P) | 0.973** | 0.474** | -0.514** | 0.373** | ||
| log10 (N/P) | 0.496** | 0.978** | -0.415** | -0.571** | 0.549** |
表2 土壤化学计量比之间相关系数
Tab.2 Correlation coefficients among soil stoichiometric ratios
| 土层 Soil layers | 指标 Indexes | log10 SOC | log10 TN | log10 TP | log10 (C/N) | log10 (C/P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 cm | log10 TN | 0.318** | ||||
| log10 TP | -0.193** | -0.065 | ||||
| log10 (C/N) | 0.322** | -0.795** | -0.061 | |||
| log10 (C/P) | 0.955** | 0.303** | -0.473** | 0.309** | ||
| log10 (N/P) | 0.346** | 0.979** | -0.266** | -0.756** | 0.389** | |
| 10~20 cm | log10 TN | 0.465** | ||||
| log10 TP | -0.305** | -0.219** | ||||
| log10 (C/N) | 0.404** | -0.621** | -0.045 | |||
| log10 (C/P) | 0.973** | 0.474** | -0.514** | 0.373** | ||
| log10 (N/P) | 0.496** | 0.978** | -0.415** | -0.571** | 0.549** |
| [1] |
Zhou Y, Boutton T W, Wu X B. Soil phosphorus does not keep pace with soil carbon and nitrogen accumulation following woody encroachment[J]. Global Change Biology, 2018, 24(5): 1992-2007.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | 苟博文, 魏博, 马松梅, 等. 古尔班通古特沙漠南缘梭梭根区土壤养分的分布特征研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 2020, 33(6): 1229-1234. |
| GOU Bowen, WEI Bo, MA Songmei, et al. Distribution characteristics of soil nutrients in roots of Haloxylon ammodendron in southern margin of Gurbantunggut Desert[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 33(6): 1229-1234. | |
| [3] | 程滨, 赵永军, 张文广, 等. 生态化学计量学研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(6): 1628-1637. |
| CHENG Bin, ZHAO Yongjun, ZHANG Wenguang, et al. The research advances and prospect of ecological stoichiometry[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(6): 1628-1637. | |
| [4] | 王绍强, 于贵瑞. 生态系统碳氮磷元素的生态化学计量学特征[J]. 生态学报, 2008, 28(8): 3937-3947. |
| WANG Shaoqiang, YU Guirui. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of ecosystem carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus elements[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(8): 3937-3947. | |
| [5] | Bui E N, Henderson B L. C: N: P stoichiometry in Australian soils with respect to vegetation and environmental factors[J]. Plant and Soil, 2013, 373(1): 553-568. |
| [6] |
陶冶, 吴甘霖, 刘耀斌, 等. 古尔班通古特沙漠典型灌木群落土壤化学计量特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(2): 305-314.
DOI |
|
TAO Ye, WU Ganlin, LIU Yaobin, et al. Soil stoichiometry and their influencing factors in typical shrub communities in the Gurbantunggut Desert, China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2017, 37(2): 305-314.
DOI |
|
| [7] | 黄郡, 苑泽宁. 土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征及影响因素概述[J]. 现代农业研究, 2020, 26(1): 73-76. |
| HUANG Jun, YUAN Zening. An overview of the ecological stoichiometry characteristics and influencing factors of soil carbon, nitrgen and phosphorus[J]. Modern Agriculture Research, 2020, 26(1): 73-76. | |
| [8] | Yang Y, Liu H, Yang X, et al. Plant and soil elemental C: N: P ratios are linked to soil microbial diversity during grassland restoration on the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 806: 150557. |
| [9] | 姜沛沛, 曹扬, 陈云明, 等. 不同林龄油松(Pinus tabulaeformis)人工林植物、凋落物与土壤C、N、P化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(19): 6188-6197. |
| JIANG Peipei, CAO Yang, CHEN Yunming, et al. Variation of C, N, and P stoichiometry in plant tissue, litter, and soil during stand development in Pinus tabulaeformis plantation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(19): 6188-6197. | |
| [10] | Tian H Q, Chen G S, Zhang C, et al. Pattern and variation of C: N: P ratios in China’s soils: a synthesis of observational data[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2010, 98(1): 139-151. |
| [11] |
Augusto L, Achat D L, Jonard M, et al. Soil parent material-a major driver of plant nutrient limitations in terrestrial ecosystems[J]. Global Change Biology, 2017, 23(9): 3808-3824.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Jiao F, Shi X R, Han F P, et al. Increasing aridity, temperature and soil pH induce soil C-N-P imbalance in grasslands[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 19601.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
那尔格孜·阿力甫, 肖钰鑫, 宋泊沂, 等. 荒漠植物“肥岛” 效应对土壤养分空间分布的影响[J]. 植物研究, 2023, 43(6): 868-880.
DOI |
|
Naergezi Alifu, XIAO Yuxin, SONG Boyi, et al. Effects of “fertilizer island” effect of desert plants on spatial distribution of soil nutrients[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(6): 868-880.
DOI |
|
| [14] | Wezel A, Rajot J L, Herbrig C. Influence of shrubs on soil characteristics and their function in Sahelian agro-ecosystems in semi-arid Niger[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 2000, 44(4): 383-398. |
| [15] |
舒向阳, 胡玉福, 何佳, 等. 川西北高寒沙地不同大小高山柳对土壤氮素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(7): 55-61.
DOI |
|
SHU Xiangyang, HU Yufu, HE Jia, et al. Effect of Salix cupularis shrubs on soil nitrogen in the alpine sandy land of Northwest Sichuan[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(7): 55-61.
DOI |
|
| [16] | 李从娟, 马健, 李彦, 等. 梭梭和白梭梭主根周围土壤养分的梯度分布[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(5): 1174-1180. |
| LI Congjuan, MA Jian, LI Yan, et al. Nutrient gradient distribution in soil around taproots of Haloxylon ammodendron and Haloxylon persicum[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2011, 31(5): 1174-1180. | |
| [17] | Chang Y B, Liu W G, Mao Y Q, et al. Biochar addition alters C: N: P stoichiometry in moss crust-soil continuum in gurbantünggüt desert[J]. Plants, 2022, 11(6): 814. |
| [18] | 陈荣毅, 张元明, 潘伯荣, 等. 古尔班通古特沙漠土壤养分空间分异与干扰的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2007, 27(2): 257-265. |
| CHEN Rongyi, ZHANG Yuanming, PAN Borong, et al. Relation between disturbance and spatial heterogeneity of soil nitration in Gurbantunggut Desert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2007, 27(2): 257-265. | |
| [19] | 孙特生, 李文彦, 刘继亮. 黑河中游荒漠绿洲人工梭梭土壤养分特征[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2017, 31(5): 179-185. |
| SUN Tesheng, LI Wenyan, LIU Jiliang. Soil nutrient characteristics of Haloxylon ammodendron plantation in a desert-oasis region in the middle reaches of Heihe River Basin[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2017, 31(5): 179-185. | |
| [20] | 陈婧, 崔向新, 丁延龙, 等. 基于“肥岛” 效应探讨人工梭梭土壤养分时空演变趋势[J]. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(6): 71-79. |
| CHEN Jing, CUI Xiangxin, DING Yanlong, et al. Exploring the temporal and spatial evolution trend of soil nutrients of different plantation ages based on the fertile island[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 26(6): 71-79. | |
| [21] | 曹艳峰, 丁俊祥, 于亚军, 等. 不同质地土壤中荒漠灌木梭梭“肥岛” 的初步探讨[J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(1): 261-270. |
| CAO Yanfeng, DING Junxiang, YU Yajun, et al. Preliminary studies on Haloxylon ammodendron ‘fertile islands' in desert soils different in texture[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016, 53(1): 261-270. | |
| [22] | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(3版)[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. |
| BAO Shidan. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis(3rd ed.)[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. | |
| [23] | 董雪, 郝玉光, 辛智鸣, 等. 科尔沁沙地4种典型灌木灌丛下土壤碳、氮、磷化学计量特征[J]. 西北植物学报, 2019, 39(1): 164-172. |
| DONG Xue, HAO Yuguang, XIN Zhiming, et al. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus of four typical shrubs in horqin sandy land[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2019, 39(1): 164-172. | |
| [24] | R-Core-Team (2014) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. |
| [25] | Fei C, Dong Y Q, An S Z. Factors driving the biomass and species richness of desert plants in northern Xinjiang China[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(7): e0271575. |
| [26] | 任雪, 褚贵新, 宋日权, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘绿洲——荒漠过渡带梭梭“肥岛” 效应特征[J]. 土壤通报, 2010, 41(1): 100-104. |
| REN Xue, CHU Guixin, SONG Riquan, et al. The characteristics of “fertile island” on Haloxylon ammodendron at an Oasis—desert ecotone in the south edge of Junggar basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2010, 41(1): 100-104. | |
| [27] |
罗维成, 赵文智, 任珩, 等. 不同气候区灌丛沙堆形态及土壤养分积累特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 191-199.
DOI |
|
LUO Weicheng, ZHAO Wenzhi, REN Heng, et al. Nebkha morphological characteristics and soil nutrition content in three regions with different climates in North China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 191-199.
DOI |
|
| [28] |
瞿王龙, 杨小鹏, 张存涛, 等. 干旱、半干旱地区天然草原灌木及其肥岛效应研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(4): 201-207.
DOI |
|
QU Wanglong, YANG Xiaopeng, ZHANG Cuntao, et al. Shrub-mediated“fertile island” effects in arid and semi-arid grassland[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(4): 201-207.
DOI |
|
| [29] | Qu L Y, Wang Z B, Huang Y Y, et al. Effects of plant coverage on shrub fertile islands in the Upper Minjiang River Valley[J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2018, 61(3): 340-347. |
| [30] | 成彩霞, 马剑, 赵维俊, 等. 甘肃祁连山西水林区典型灌丛土壤C、N、P生态化学计量特征研究[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2022, 57(3): 121-128. |
| CHENG Caixia, MA Jian, ZHAO Weijun, et al. Ecological stoichiometry of soils C, N and P of typical shrubs in Xishui forest area of Qilian Mountains in China[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2022, 57(3): 121-128. | |
| [31] | 朱秋莲, 邢肖毅, 张宏, 等. 黄土丘陵沟壑区不同植被区土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(15): 4674-4682. |
| ZHU Qiulian, XING Xiaoyi, ZHANG Hong, et al. Soil ecological stoichiometry under different vegetation area on loess hillygully region[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(15): 4674-4682. |
| [1] | 李志鹏, 杨鹏年, 张胜江, 盛统民, 冶秉瑞, 袁凯, 王永鹏. 灌排协同下冬灌期土壤水盐调控效应分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2722-2732. |
| [2] | 李嘉琦, 冯宇华, 陈署晃, 王子傲, 刘鹏, 梁智永, 孙法福, 陈荣, 耿庆龙. 基于高光谱的土壤有机质及全氮估测[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(10): 2491-2499. |
| [3] | 钟辉丽, 武均, 陆祥生. 甜玉米不同生育期施用改良剂组合对其产量及河西走廊次生盐碱化土壤性质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1615-1625. |
| [4] | 侯献飞, 李强, 苗昊翠, 贾东海, 顾元国, 买买提依明·斯马依, 崔福洋. 棉花-花生轮作模式对土壤养分及其产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1657-1665. |
| [5] | 杨吉祥, 李新国. 湖滨绿洲土壤有机碳含量的支持向量机估算模型[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1477-1486. |
| [6] | 刘富余, 张江辉, 白云岗, 赵经华, 曹彪. 基于Meta法定量分析亏缺灌溉作物产量及水分利用效率[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1487-1496. |
| [7] | 热依汗·阿布力孜, 何学敏, 杨欢, 黄鹏程, 冯海鹏, 王勇志. 不同水盐生境下小叶碱蓬叶绿素荧光参数特征及其对土壤因子的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 485-494. |
| [8] | 佘玲艺, 哈丽哈什·依巴提, 张炎, 陈创洲, 樊林鑫, 张优. 基于养分专家系统的棉花推荐施肥效应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(12): 2911-2920. |
| [9] | 朱珠, 王则玉, 许咏梅, 刘迪, 李杨. 磁化不同水质滴灌对土壤盐分的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(12): 3086-3093. |
| [10] | 吴刚, 赵强, 谢佳, 张启越, 占东霞, 田阳青, 李欣欣. 植物生长调节剂复配不同叶面肥对棉花干物质积累及产量品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(11): 2646-2652. |
| [11] | 潘洋, 付秋萍, 海英, 祁通, 洪明, 马英杰, 潘俊杰. 新疆滴灌机采棉生长及产量的最佳水氮组合[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(11): 2674-2686. |
| [12] | 吕亮雨, 樊光辉, 付全, 苏彩风, 李发毅. 生物有机肥对枸杞生长及土壤性状的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(11): 2779-2789. |
| [13] | 朱玉洁, 林玲, 唐光木, 张云舒, 徐万里. 改性棉秆炭对新疆灰漠土氮肥氨挥发特征的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2128-2137. |
| [14] | 席丽, 李思瑶, 夏晓莹, 陈玉雯, 李林, 王杰, 马小龙, 米尔扎提·柯尼加里木, 阿丽耶·麦麦提, 王卫霞. 不同郁闭度天山云杉林土壤养分特征[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2216-2222. |
| [15] | 王燕, 武兴宝, 秦新惠, 张永久, 杨丽, 赵哈林. 荒漠绿洲农田盐渍化过程中的土壤碳、氮、磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1996-2005. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 18
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 105
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||