

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (6): 1487-1496.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.06.023
刘富余1( ), 张江辉2(
), 张江辉2( ), 白云岗2, 赵经华1, 曹彪2
), 白云岗2, 赵经华1, 曹彪2
收稿日期:2023-11-04
出版日期:2024-06-20
发布日期:2024-08-08
通信作者:
张江辉(1963-),男,陕西兴平人,研究员,博士生导师,研究方向为农业水土工程,(E-mail)skyzjh@163.net作者简介:刘富余(1999-),男,山东临沂人,硕士研究生,研究方向为节水灌溉,(E-mail)1759606539@qq.com
基金资助:
LIU Fuyu1( ), ZHANG Jianghui2(
), ZHANG Jianghui2( ), BAI Yungang2, ZHAO Jinghua1, CAO Biao2
), BAI Yungang2, ZHAO Jinghua1, CAO Biao2
Received:2023-11-04
Published:2024-06-20
Online:2024-08-08
Correspondence author:
ZHANG Jianghui (1963-), male, researcher, research direction: agricultural soil and water engineering research,(E-mail)skyzjh@163.netSupported by:摘要:
【目的】综合分析亏缺灌溉对我国北方地区主要作物产量和水分利用效率的影响。【方法】应用Meta分析法,定量分析亏缺灌溉后作物产量和水分利用效率的变化,通过亚组分析不同区域、作物、降水量及灌溉方式下的变化。【结果】亏缺灌溉显著降低了我国北方地区作物产量,平均减产率6.66%,东北地区平均减产率最为显著,达9.43%;显著提高了作物水分利用效率,平均提升率10.59%,西北地区水分利用效率提升最为显著,达到12.70%,而东北地区水分利用效率无显著提升;小麦、玉米和棉花均显著减产,棉花减产率最高为10.67%;水分利用效率均显著提升,棉花水分利用效率提升率最高,达到了15.63%;在不同降水量区间存在显著减产效应,200~400 mm区间内减产10.74%,而在此区间内水分利用效率并无显著提升;传统地面灌、滴灌和膜下滴灌下产量均显著降低,滴灌减产率最高为8.93%,水分利用效率均显著提升,滴灌下WUE提升率最高为15.95%。【结论】亏缺灌溉可显著提升作物水分利用效率,显著降低作物产量,但在不同种植区域、作物种类、气候条件和灌溉方式下作用效果各不相同。
中图分类号:
刘富余, 张江辉, 白云岗, 赵经华, 曹彪. 基于Meta法定量分析亏缺灌溉作物产量及水分利用效率[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1487-1496.
LIU Fuyu, ZHANG Jianghui, BAI Yungang, ZHAO Jinghua, CAO Biao. Analysis of yield and water use efficiency of under-irrigated crops based on meta-analysis[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1487-1496.
| 试验区域 Pilot area | 省(区) Province | 年平均降水量 Average annual precipitation (mm) | 灌溉方式 Irrigation methods | 种植条件 Planting conditions | 作物类型 Crop type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 华北地区 North China | 北京、河北、山西、 内蒙古中部地区、河南 | <200(北部) 200~400(南部) | 传统地面灌、 滴灌、喷灌 | 大田 | 小麦、玉米、棉花 |
| 西北地区 Northwest China | 新疆、陕西、宁夏、 甘肃、内蒙古西部地区 | <200(北部) 200~400(南部) | 滴灌、传统地面灌 | ||
| 东北地区 Northeast China | 黑龙江、吉林、辽宁、 内蒙古东部地区 | >400(北部) 200~400(南部) | 传统地面灌、滴灌 |
表1 样本基本信息
Tab.1 Basic sample information
| 试验区域 Pilot area | 省(区) Province | 年平均降水量 Average annual precipitation (mm) | 灌溉方式 Irrigation methods | 种植条件 Planting conditions | 作物类型 Crop type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 华北地区 North China | 北京、河北、山西、 内蒙古中部地区、河南 | <200(北部) 200~400(南部) | 传统地面灌、 滴灌、喷灌 | 大田 | 小麦、玉米、棉花 |
| 西北地区 Northwest China | 新疆、陕西、宁夏、 甘肃、内蒙古西部地区 | <200(北部) 200~400(南部) | 滴灌、传统地面灌 | ||
| 东北地区 Northeast China | 黑龙江、吉林、辽宁、 内蒙古东部地区 | >400(北部) 200~400(南部) | 传统地面灌、滴灌 |
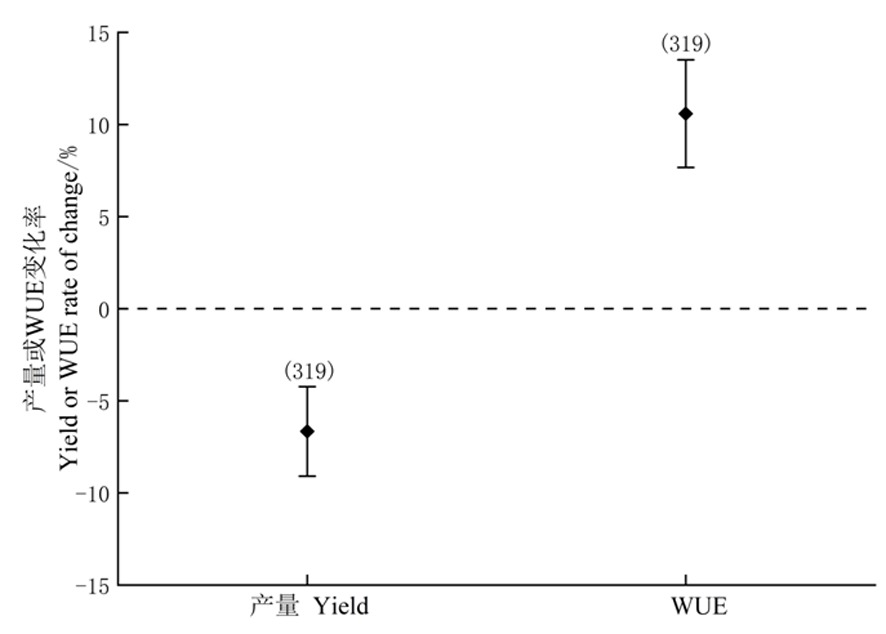
图1 作物产量及水分利用效率综合变化率 注:1.误差限表示Z值的95%置信区间,括号中的数字表示所研究的相应分组数据的样本量;2.置信区间不包含0表示有显著影响,包含0表示无显著影响,下同
Fig.1 Yield and WUE comprehensive rate of change Note:1.Error limit shows Z-value is 95% confidence interral of the difference,the numbers in parentheses ropresent the asmple sixa of the corresponding group of data being studied;Confidence inferval excluding in dicates significant impact,including 0 indicates significant impact,including 0 indicates no significant impact,the same as below
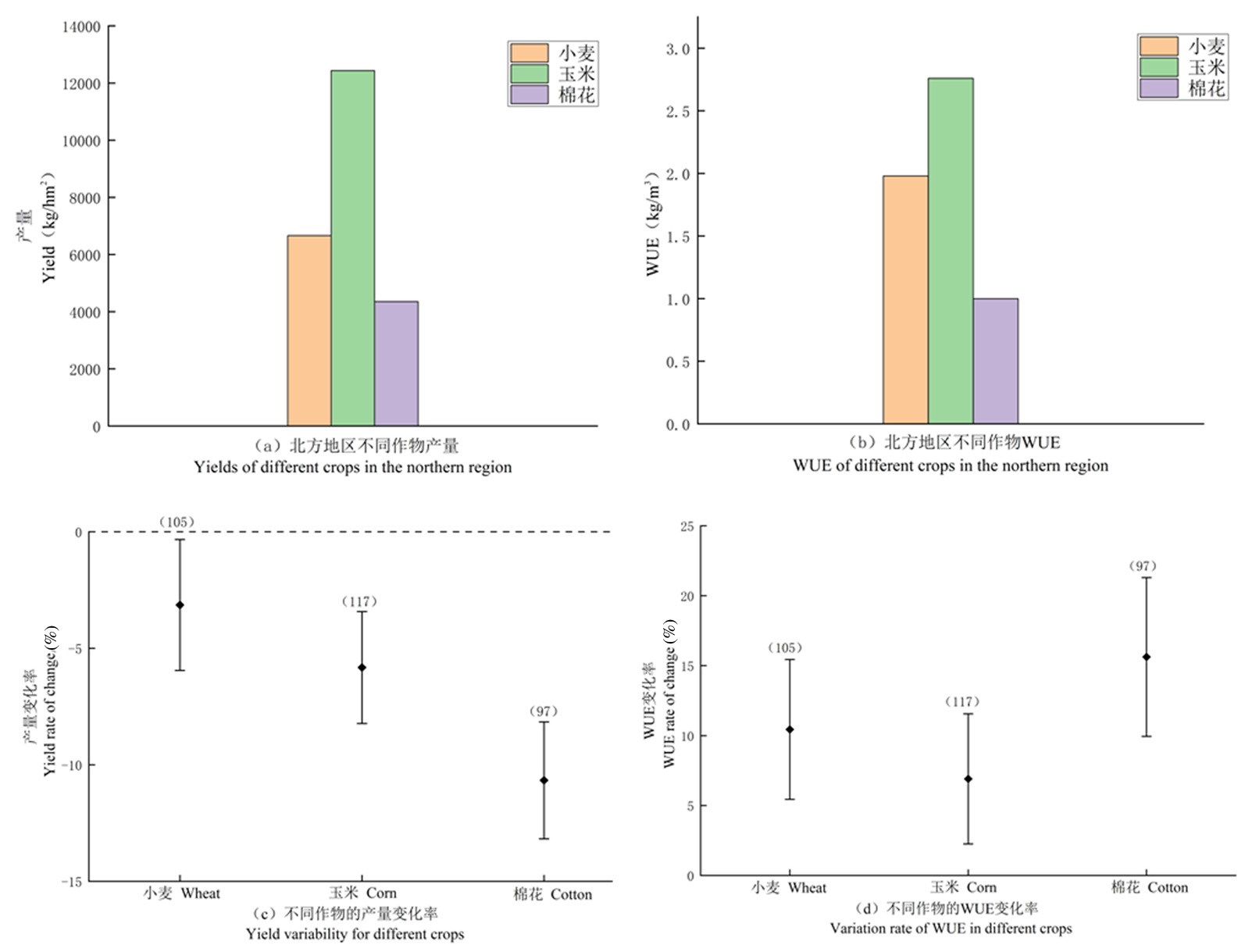
图2 不同作物的产量、水分利用效率以及亏缺灌溉下不同作物产量、水分利用效率变化
Fig.2 Changes of the yield of different crops, WUE and the impact of insufficient irrigation on different crop yields and WUE
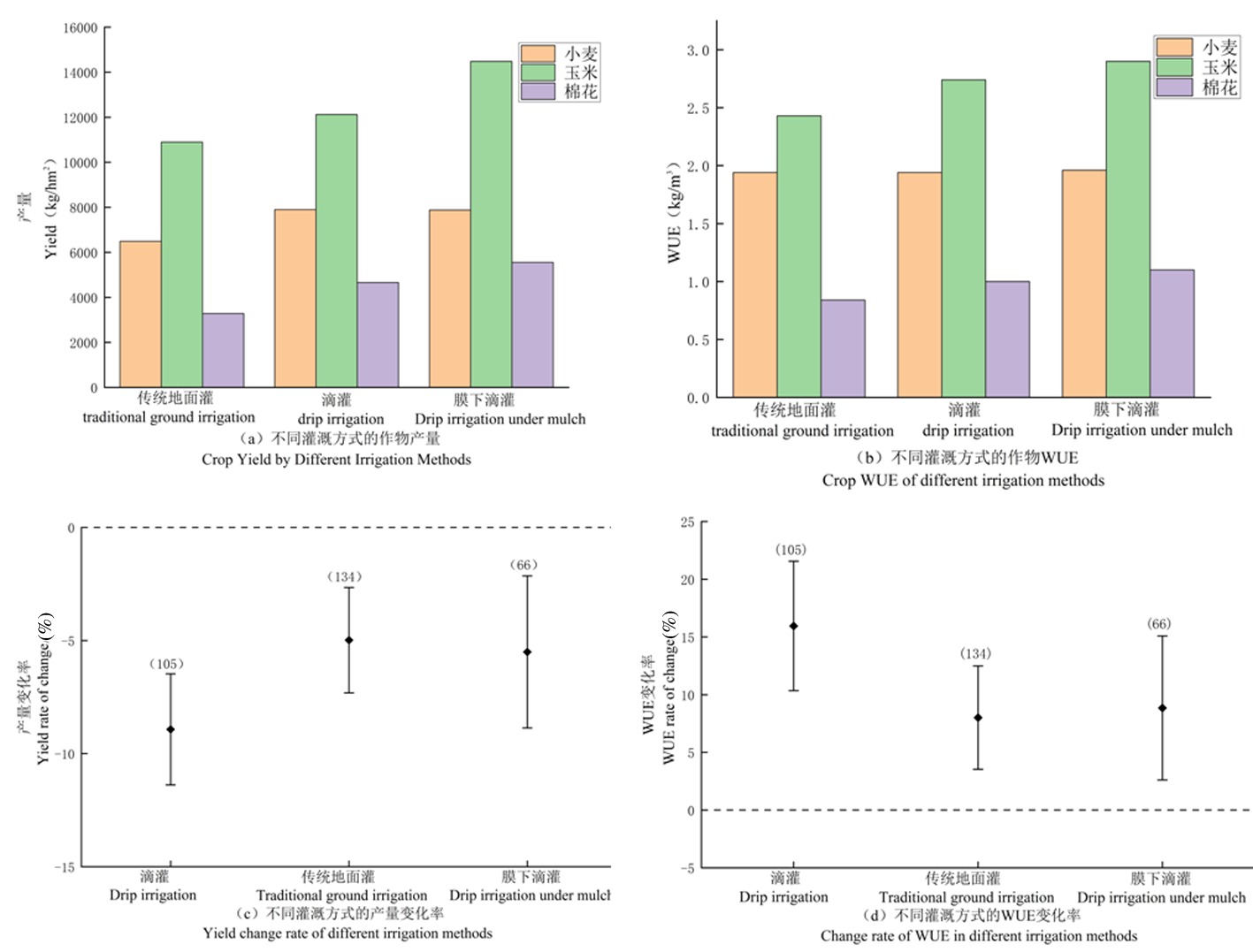
图5 不同灌溉方式的作物产量、水分利用效率及亏缺灌溉下作物产量、水分利用效率的变化
Fig.5 Changes of crop yield, WUE and the effects of deficit irrigation on crop yield and WUE under different irrigation methods
| 类别 Category | 分组 Grouping | 类别 Category | 是否显著 Whether it is significant | 失安全数 Number of unsafe | 5n+10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 产量 Yield | 整体 | \ | 是 | 2 911.7 | 1 650 |
| 地区 | 华北 | 是 | 935.6 | 485 | |
| 西北 | 是 | 974 | 910 | ||
| 东北 | 是 | 434.6 | 215 | ||
| 作物 | 小麦 | 是 | 1 022.9 | 535 | |
| 玉米 | 是 | 837.2 | 595 | ||
| 棉花 | 是 | 2 277.3 | 495 | ||
| 降水量 | <200 | 是 | 1 024.8 | 610 | |
| 200-400 | 是 | 837.4 | 405 | ||
| >400 | 是 | 798 | 610 | ||
| 灌溉 方式 | 滴灌 | 是 | 1 726.4 | 535 | |
| 传统地面灌 | 是 | 824.8 | 680 | ||
| 膜下滴灌 | 是 | 422.2 | 340 | ||
| 水分利 用效率 WUE | 整体 | 是 | 6 160.6 | 1 650 | |
| 地区 | 华北 | 是 | 655.8 | 485 | |
| 西北 | 是 | 5 090 | 910 | ||
| 东北 | 否 | \ | \ | ||
| 作物 | 小麦 | 是 | 1 619.4 | 535 | |
| 玉米 | 是 | 804.4 | 595 | ||
| 棉花 | 是 | 729.8 | 495 | ||
| 降水量 | <200 | 是 | 5 386.2 | 610 | |
| 200-400 | 否 | \ | \ | ||
| >400 | 是 | 728.1 | 610 | ||
| 灌溉 方式 | 滴灌 | 是 | 1 777.9 | 535 | |
| 传统地面灌 | 是 | 818.1 | 680 | ||
| 膜下滴灌 | 是 | 522.8 | 340 |
表2 整体及分组状态下的失安全数检验
Tab.2 Verification of the number of safety failures in the overall and grouped state
| 类别 Category | 分组 Grouping | 类别 Category | 是否显著 Whether it is significant | 失安全数 Number of unsafe | 5n+10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 产量 Yield | 整体 | \ | 是 | 2 911.7 | 1 650 |
| 地区 | 华北 | 是 | 935.6 | 485 | |
| 西北 | 是 | 974 | 910 | ||
| 东北 | 是 | 434.6 | 215 | ||
| 作物 | 小麦 | 是 | 1 022.9 | 535 | |
| 玉米 | 是 | 837.2 | 595 | ||
| 棉花 | 是 | 2 277.3 | 495 | ||
| 降水量 | <200 | 是 | 1 024.8 | 610 | |
| 200-400 | 是 | 837.4 | 405 | ||
| >400 | 是 | 798 | 610 | ||
| 灌溉 方式 | 滴灌 | 是 | 1 726.4 | 535 | |
| 传统地面灌 | 是 | 824.8 | 680 | ||
| 膜下滴灌 | 是 | 422.2 | 340 | ||
| 水分利 用效率 WUE | 整体 | 是 | 6 160.6 | 1 650 | |
| 地区 | 华北 | 是 | 655.8 | 485 | |
| 西北 | 是 | 5 090 | 910 | ||
| 东北 | 否 | \ | \ | ||
| 作物 | 小麦 | 是 | 1 619.4 | 535 | |
| 玉米 | 是 | 804.4 | 595 | ||
| 棉花 | 是 | 729.8 | 495 | ||
| 降水量 | <200 | 是 | 5 386.2 | 610 | |
| 200-400 | 否 | \ | \ | ||
| >400 | 是 | 728.1 | 610 | ||
| 灌溉 方式 | 滴灌 | 是 | 1 777.9 | 535 | |
| 传统地面灌 | 是 | 818.1 | 680 | ||
| 膜下滴灌 | 是 | 522.8 | 340 |
| [1] | 付凌晖, 刘爱华. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2021:261-262. |
| FU Linghui, LIU Aihua. China Statistical Yearbook[M]Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2021: 261-262. | |
| [2] | 中华人民共和国水利部. 2021年中国水资源公报[R]. 2021. |
| Ministry of Water Resources of the People's Republic of China. 2021 China Water Resources Bulletin[R].2021. | |
| [3] | 王庆伟, 于大炮, 代力民, 等. 全球气候变化下植物水分利用效率研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(12): 3255-3265. |
|
WANG Qingwei, YU Dapao, DAI Limin, et al. Research progress in water use efficiency of plants under global climate change[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2010, 21(12): 3255-3265.
PMID |
|
| [4] | 杨鑫, 穆月英. 中国粮食生产与水资源的时空匹配格局[J]. 华南农业大学学报(社会科学版), 2019, 18(4): 91-100. |
| YANG Xin, MU Yueying. Spatial-temporal matching patterns of grain production and water resources[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University (Social Science Edition), 2019, 18(4): 91-100. | |
| [5] | 胡化广, 张振铭, 吴生才, 等. 植物水分利用效率及其机理研究进展[J]. 节水灌溉, 2013,(3): 11-15. |
| HU Huaguang, ZHANG Zhenming, WU Shengcai, et al. Advance of research on water use efficiency of plant and its mechanism[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2013,(3): 11-15. | |
| [6] |
杨北方, 杨国正, 冯璐, 等. 亏缺灌溉对棉花生长和水分利用效率的影响研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(3): 1112-1118.
DOI |
|
YANG Beifang, YANG Guozheng, FENG Lu, et al. Effects of deficit irrigation on cotton growth and water use efficiency: a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(3): 1112-1118.
DOI |
|
| [7] | Jiang J, Huo Z L, Feng S Y, et al. Effect of irrigation amount and water salinity on water consumption and water productivity of spring wheat in Northwest China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2012, 137: 78-88. |
| [8] | 张洁梅, 武继承, 杨永辉, 等. 不同节水灌溉方式对小麦产量及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 节水灌溉, 2016,(8): 30-32, 37. |
| ZHANG Jiemei, WU Jicheng, YANG Yonghui, et al. Effect of different irrigation technology on yield and water use efficiency of wheat[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2016,(8): 30-32, 37. | |
| [9] | 罗迪汉, 王勇, 宇宙. 不同灌水定额对覆膜滴灌玉米生长、产量及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 节水灌溉, 2015,(7): 5-8. |
| LUO Dihan, WANG Yong, YU Zhou. Influence of drip irrigation quota on film maize growth, yield and water use efficiency[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2015,(7): 5-8. | |
| [10] | Zhang D M, Luo Z, Liu S H, et al. Effects of deficit irrigation and plant density on the growth, yield and fiber quality of irrigated cotton[J]. Field Crops Research, 2016, 197: 1-9. |
| [11] | 申孝军, 陈红梅, 孙景生, 等. 调亏灌溉对膜下滴灌棉花生长、产量及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2010, 29(1): 40-43. |
| SHEN Xiaojun, CHEN Hongmei, SUN Jingsheng, et al. Response of different water deficit on cotton growth and water use efficiency and yield under mulched drip irrigation[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2010, 29(1): 40-43. | |
| [12] | Çoĝaltay N, KaradaĝE. Introduction to meta-analysis[J]. Leadership and organizational outcomes: Meta-analysis of empirical studies, 2015: 19-28. |
| [13] | Gurevitch J, Curtis P S, Jones M H. Meta-analysis in ecology[M]// Advances in Ecological Research. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2001: 199-247. |
| [14] | Hedges L V, Gurevitch J, Curtis P S. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology[J]. Ecology, 1999, 80(4): 1150. |
| [15] | Gurevitch J, Morrow L L, Wallace A, et al. A meta-analysis of competition in field experiments[J]. The American Naturalist, 1992, 140(4): 539-572. |
| [16] |
Crouzeilles R, Curran M, Ferreira M S, et al. A global meta-analysis on the ecological drivers of forest restoration success[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 11666.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Romero-Olivares A L, Allison S D, Treseder K K. Soil microbes and their response to experimental warming over time: a meta-analysis of field studies[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2017, 107: 32-40. |
| [18] | 陆欣, 谢英荷. 土壤肥料学[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2011. |
| LU Xin, Soil fertilizer science[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 2011. | |
| [19] | 郑凤英, 彭少麟. 生态学整合分析中两种常用效应值的实例应用比较[J]. 生态科学, 2005, 24(3): 250-253. |
| ZHENG Fengying, PENG Shaolin. Comparison of two effect sizes of meta-analysis commonly used in ecology[J]. Ecologic Science, 2005, 24(3): 250-253. | |
| [20] | Morgan P B, Ainsworth E A, Long S P. How does elevated ozone impact soybean A meta‐analysis of photosynthesis, growth and yield[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2003, 26(8): 1317-1328. |
| [21] |
Luo Y Q, Hui D F, Zhang D Q. Elevated CO2 stimulates net accumulations of carbon and nitrogen in land ecosystems: a meta-analysis[J]. Ecology, 2006, 87(1): 53-63.
PMID |
| [22] |
Niu Z D, Nie Y X, Zhou Q, et al. A brain-region-based meta-analysis method utilizing the Apriori algorithm[J]. BMC Neuroscience, 2016, 17(1): 23.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | 陈利军, 宝哲, 林涛, 等. 基于Meta-analysis的新疆主要作物地膜覆盖产量及水分利用效率分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 2022, 41(4): 661-667. |
|
CHEN Lijun, BAO Zhe, LIN Tao, et al. A meta-analysis on the yield and water use efficiency of main crops covered with plastic film in Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2022, 41(4): 661-667.
DOI |
|
| [24] |
Chen H H, Li X C, Hu F, et al. Soil nitrous oxide emissions following crop residue addition: a meta-analysis[J]. Global Change Biology, 2013, 19(10): 2956-2964.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Nakagawa S, Noble D W A, Senior A M, et al. Meta-evaluation of meta-analysis: ten appraisal questions for biologists[J]. BMC Biology, 2017, 15(1): 18.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
贾涛涛, 廖李容, 王杰, 等. 基于Meta分析的放牧对黄土高原草地生态系统的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2022, 30(10): 2772-2781.
DOI |
|
JIA Taotao, LIAO Lirong, WANG Jie, et al. Effects of grazing on grassland ecosystem on the Loess Plateau based on A meta-analysis[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(10): 2772-2781.
DOI |
|
| [27] |
Hoeve M, Stams G J J M, van der Put C E, et al. A meta-analysis of attachment to parents and delinquency[J]. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 2012, 40(5): 771-785.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | 朱飙, 张强, 李春华, 等. 我国干旱半干旱区气候变化特征及其对干湿波动的影响[J]. 大气科学学报, 2023, 46(1): 42-54. |
| ZHU Biao, ZHANG Qiang, LI Chunhua, et al. Characteristics of climate change in arid and semi-arid areas of China and its influence on climatic dry-wet fluctuation[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2023, 46(1): 42-54. | |
| [29] | Wittig V E, Ainsworth E A, Naidu S L, et al. Quantifying the impact of current and future tropospheric ozone on tree biomass, growth, physiology and biochemistry: a quantitative meta-analysis[J]. Global Change Biology, 2009, 15(2): 396-424. |
| [30] | 赵翔, 李娜, 王棚涛, 等. 脱落酸调节植物抵御水分胁迫的机制研究[J]. 生命科学, 2011, 23(1): 115-120. |
| ZHAO Xiang, LI Na, WANG Pengtao, et al. Regulation of abscisic acid on plant resistance to water stress[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2011, 23(1): 115-120. | |
| [31] | 吴荣军. 地表臭氧和土壤水分亏缺对植物的交互效应研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(3): 846-853. |
| WU Rongjun. Research advance in interactive effects of ozone concentration and soil water deficit on plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(3): 846-853. | |
| [32] | 颉君丽, 张恒嘉, 李有先, 等. 膜下滴灌调亏对加工番茄产量和水分利用效率的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2012, 31(1): 78-81. |
| XIE Junli, ZHANG Hengjia, LI Youxian, et al. Effect of regulated deficit drip irrigation on economic yield and water use efficiency of processing tomato mulched with plastic film[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2012, 31(1): 78-81. | |
| [33] | 康绍忠, 杜太生, 孙景生, 等. 基于生命需水信息的作物高效节水调控理论与技术[J]. 水利学报, 2007, 38(6): 661-667. |
| KANG Shaozhong, DU Taisheng, SUN Jingsheng, et al. Theory and technology of improving irrigation water use efficiency based on crop growing water demand information[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2007, 38(6): 661-667. | |
| [34] | Yang X S, Short T H, Fox R D, et al. Transpiration, leaf temperature and stomatal resistance of a greenhouse cucumber crop[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 1990, 51(3/4): 197-209. |
| [35] | 丁蓓蓓, 张雪靓, 赵振庭, 等. 华北平原限水灌溉条件下冬小麦产量及水分利用效率变化的Meta分析[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2021, 40(12): 7-17. |
| DING Beibei, ZHANG Xueliang, ZHAO Zhenting, et al. Change in winter wheat yield and its water use efficiency as affected by limited irrigation in North China Plain: a meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2021, 40(12): 7-17. | |
| [36] | 黄悦, 李思恩, 胡丹, 等. 基于Meta-Analysis方法分析滴灌对玉米水分利用效率及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2022, 27(5): 96-105. |
| HUANG Yue, LI Sien, HU Dan, et al. Effects of drip irrigation on water use efficiency and yield of maize based on Meta-Analysis[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2022, 27(5): 96-105. | |
| [37] | Takamura Y, Takeuchi S, Hasegawa H. Studies on the Effects of Soil Temperature upon the Growth of Crop Plants: III Soil temperature and leaf emergence of rice plant.: VIII Relation of temperature of several parts of rice plant to the rate of leaf emergence[J]. Japanese Journal of Crop Science, 1961, 29(2): 195-198. |
| [38] | 郑健, 潘占鹏, 颜斐, 等. 基于Meta评价控制性分根交替灌溉的作物水分利用效率[J]. 江苏大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 40(3): 332-337. |
| ZHENG Jian, PAN Zhanpeng, YAN Fei, et al. Evaluation of crop water use efficiency for controlled root-dividing alternate irrigation based on Meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 40(3): 332-337. | |
| [39] | 刘一龙, 张忠学, 郭亚芬, 等. 膜下滴灌条件下不同灌溉制度的玉米产量与水分利用效应[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2010, 41(10): 53-57. |
| LIU Yilong, ZHANG Zhongxue, GUO Yafen, et al. Corn yield and water using efficiency of different irrigation schedule with the drip irrigation under mulch[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2010, 41(10): 53-57. |
| [1] | 张泽华, 叶含春, 王振华, 李文昊, 李海强, 刘健. 等氮配施脲酶抑制剂对滴灌棉花生长发育和产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2103-2111. |
| [2] | 陈瑞杰, 罗林毅, 阮向阳, 冶军. 腐植酸对滴灌棉田土壤养分和棉花产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2112-2121. |
| [3] | 黄铂轩, 李鹏程, 郑苍松, 孙淼, 邵晶晶, 冯卫娜, 庞朝友, 徐文修, 董合林. 不同氮素抑制剂对棉花生长发育、氮素利用与产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2122-2131. |
| [4] | 张鸟, 王卉, 冯国郡, 再吐尼古丽·库尔班. 不同粒用高粱品种产量和农艺性状及品质的差异性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2160-2167. |
| [5] | 陈芳, 李字辉, 孙孝贵, 张庭军. 不同剂量的微生物菌剂对加工番茄产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2285-2289. |
| [6] | 张承洁, 胡浩然, 段松江, 吴一帆, 张巨松. 氮肥与密度互作对海岛棉生长发育及产量和品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1821-1830. |
| [7] | 候丽丽, 王伟, 崔新菊, 周大伟. 有机无机肥配施对冬小麦产量和土壤养分及酶活性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1845-1852. |
| [8] | 陈芳, 李字辉, 王兵跃, 孙孝贵, 张庭军. 微生物菌剂对冬小麦生长发育及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1853-1860. |
| [9] | 袁莹莹, 赵经华, 迪力穆拉提·司马义, 杨庭瑞. 基于apriori算法对盆栽春小麦生理指标及产量的分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1861-1871. |
| [10] | 牛婷婷, 马明生, 张军高. 秸秆还田和覆膜对旱作雨养农田土壤理化性质及春玉米产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1896-1906. |
| [11] | 赵敏华, 宋秉曦, 张宇鹏, 高志红, 朱勇勇, 陈晓远. 旱作条件下氮肥减施对水稻产量及氮肥偏生产力的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1907-1915. |
| [12] | 李锁丞, 柳延涛, 董红业, 孙振博, 李紫薇, 张春媛, 王开勇, 李强, 杨明凤. 不同施钾量对滴灌花生光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1926-1936. |
| [13] | 张彩虹, 王国强, 姜鲁艳, 刘涛, 德贤明. 低能耗组装式深冬生产型日光温室环境因子变化及番茄性状分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 2043-2053. |
| [14] | 杨梅, 赵红梅, 迪丽热巴·夏米西丁, 杨卫君, 张金汕, 惠超. 氮肥减量配施生物质炭对春小麦群体结构、光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1582-1589. |
| [15] | 鲁伟丹, 周远航, 马小龙, 高江龙, 樊晓琴, 郭建富, 李健强, 林明. 不同比例有机肥替代化肥对甜菜植株养分及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1631-1639. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||