

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (4): 954-963.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.04.020
• 植物保护·微生物·农业装备工程与机械化 • 上一篇 下一篇
收稿日期:2023-07-11
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-05-31
通信作者:
孙倩(1986-),女,新疆沙湾人,副教授,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为林业遥感技术,(E-mail)sq061@163.com作者简介:郭正宇(1998-),男,山西太原人,硕士研究生,研究方向为林业遥感与荒漠化防治,(E-mail)1061050069@qq.com
基金资助:
GUO Zhengyu( ), SUN Qian(
), SUN Qian( ), HU Xinyue, HUANG Jinyi
), HU Xinyue, HUANG Jinyi
Received:2023-07-11
Published:2024-04-20
Online:2024-05-31
Correspondence author:
SUN Qian (1986-), female, from Shawan, Xinjiang, Aassociate professor, Ph.D., research direction: forestry remote sensing, (E-mail)sq061@163.comSupported by:摘要:
【目的】研究地表温度、土壤含水量对春尺蠖羽化的影响,为提高虫害防治效率、降低防治成本提供理论依据。【方法】以新疆克拉玛依市开发区为例,选择有代表性的12块林地(P0~P11),利用实测春尺蠖羽化量数据、地表温度及土壤含水量卫星数据,采用趋势、相关性及回归方法,分析春尺蠖羽化量的时空分布特征及其变化趋势,研究地表温度、土壤含水量在时空维度对其羽化的影响。【结果】(1)点P3、P4、P10、P11所处林分春尺蠖虫害最严重,P6所处林分虫害水平始终较低。(2)春尺蠖逐日羽化量与地表温度呈正相关,与土壤含水量呈负相关,且这种相关性主要集中在羽化高峰日前。(3)点P5、P7、P8所处林分内土壤含水量与春尺蠖逐日羽化量的负相关性较大。(4)2021年羽化高峰日前,地表温度主要通过蒸发效应影响土壤含水量进而间接影响羽化进程,而2022年地表温度对羽化则主要表现为直接影响。【结论】地表温度、土壤含水量对春尺蠖羽化的影响是一种综合效应。在适宜春尺蠖羽化的土壤温湿度范围内,地表温度的上升或土壤含水量的下降会促进羽化,反之则抑制羽化,且这种影响主要集中在羽化高峰日前。点P5、P7、P8所处林分内土壤含水量与春尺蠖逐日羽化量的负相关性较大,可在这些区域内开展人工灌溉从而抑制春尺蠖的发生。
中图分类号:
郭正宇, 孙倩, 胡馨月, 黄瑾依. 基于遥感主要环境影响因子与春尺蠖羽化的相关性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 954-963.
GUO Zhengyu, SUN Qian, HU Xinyue, HUANG Jinyi. Correlation analysis of main environmental impact factors based on remote sensing and Apocheima cinerarius Erschoff emergence[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 954-963.
| 编号 Number | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude | 海拔高度 Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P0 | 45°29'23.677″N | 84°57'31.775″E | 265.7 |
| P1 | 45°29'04.871″N | 84°57'04.359″E | 270.6 |
| P2 | 45°28'31.136″N | 84°56'03.698″E | 270.9 |
| P3 | 45°27'52.396″N | 84°54'59.708″E | 282.1 |
| P4 | 45°26'50.943″N | 84°53'20.656″E | 270.5 |
| P5 | 45°26'20.926″N | 84°52'31.890″E | 272.3 |
| P6 | 45°25'11.995″N | 84°50'42.600″E | 269.8 |
| P7 | 45°23'51.086″N | 84°52'27.672″E | 267.9 |
| P8 | 45°24'46.507″N | 84°53'56.956″E | 268.7 |
| P9 | 45°25'59.900″N | 84°55'48.645″E | 268.7 |
| P10 | 45°27'31.857″N | 84°58'20.894″E | 268.5 |
| P11 | 45°25'09.826″N | 84°58'27.850″E | 267.7 |
表1 春尺蠖羽化量采样点空间信息
Tab.1 Spatial information statistics of Apocheima cinerarius Erschoff emergence sampling points
| 编号 Number | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude | 海拔高度 Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P0 | 45°29'23.677″N | 84°57'31.775″E | 265.7 |
| P1 | 45°29'04.871″N | 84°57'04.359″E | 270.6 |
| P2 | 45°28'31.136″N | 84°56'03.698″E | 270.9 |
| P3 | 45°27'52.396″N | 84°54'59.708″E | 282.1 |
| P4 | 45°26'50.943″N | 84°53'20.656″E | 270.5 |
| P5 | 45°26'20.926″N | 84°52'31.890″E | 272.3 |
| P6 | 45°25'11.995″N | 84°50'42.600″E | 269.8 |
| P7 | 45°23'51.086″N | 84°52'27.672″E | 267.9 |
| P8 | 45°24'46.507″N | 84°53'56.956″E | 268.7 |
| P9 | 45°25'59.900″N | 84°55'48.645″E | 268.7 |
| P10 | 45°27'31.857″N | 84°58'20.894″E | 268.5 |
| P11 | 45°25'09.826″N | 84°58'27.850″E | 267.7 |
| 日期(月/日) Data (M/D) | 每日研究区羽化量均值(只)及标准差 Daily mean value and standard deviation of emergence in the study area | 每日采样点羽化量均值(只)及标准差 Mean and standard deviation of emergence at daily sampling points | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021年 | 2022年 | 2021年 | 2022年 | |
| 3/20 | 7.77±2.21 | 7.77±1.73 | 7.67±2.33 | 7.42±2.14 |
| 3/21 | 9.79±3.46 | 11.70±1.85 | 8.92±3.85 | 11.25±3.61 |
| 3/22 | 16.15±5.08 | 8.50±0.25 | 15.08±5.49 | 8.50±2.13 |
| 3/23 | 12.61±3.91 | 8.77±0.18 | 11.75±4.80 | 8.67±2.30 |
| 3/24 | 19.45±4.41 | 12.21±0.41 | 18.75±5.42 | 12.00±1.78 |
| 3/25 | 23.52±4.78 | 17.48±4.64 | 22.75±5.25 | 17.33±5.41 |
| 3/26 | 21.00±4.16 | 21.59±6.21 | 20.00±5.26 | 21.50±7.18 |
| 3/27 | 21.84±3.79 | 25.82±4.30 | 21.00±4.09 | 25.67±5.42 |
| 3/28 | 16.94±2.96 | 30.11±0.12 | 16.42±4.37 | 29.92±3.93 |
| 3/29 | 20.08±3.46 | 38.68±15.97 | 19.58±5.06 | 35.83±18.25 |
| 3/30 | 14.97±3.03 | 32.06±14.96 | 14.75±3.67 | 26.42±15.06 |
| 3/31 | 10.72±2.36 | 19.33±4.19 | 10.50±2.42 | 18.33±5.05 |
| 4/1 | 8.92±1.77 | 13.43±2.79 | 8.92±2.60 | 12.92±3.19 |
| 4/2 | 7.93±1.37 | 9.36±1.84 | 7.75±1.70 | 9.00±2.91 |
| 4/3 | 6.07±1.22 | 6.88±2.28 | 6.08±1.43 | 6.58±3.15 |
| 4/4 | 4.65±1.05 | 4.83±0.20 | 4.67±1.10 | 4.83±0.37 |
| 4/5 | 3.36±1.16 | 3.68±0.40 | 3.42±1.15 | 3.75±0.76 |
| 4/6 | 2.11±0.87 | 2.33±0.66 | 2.17±1.59 | 2.50±1.51 |
表2 春尺蠖羽化量日均值及标准差
Tab.2 Statistics of daily mean and standard deviation of Apocheima cinerarius Erschoff emergence
| 日期(月/日) Data (M/D) | 每日研究区羽化量均值(只)及标准差 Daily mean value and standard deviation of emergence in the study area | 每日采样点羽化量均值(只)及标准差 Mean and standard deviation of emergence at daily sampling points | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021年 | 2022年 | 2021年 | 2022年 | |
| 3/20 | 7.77±2.21 | 7.77±1.73 | 7.67±2.33 | 7.42±2.14 |
| 3/21 | 9.79±3.46 | 11.70±1.85 | 8.92±3.85 | 11.25±3.61 |
| 3/22 | 16.15±5.08 | 8.50±0.25 | 15.08±5.49 | 8.50±2.13 |
| 3/23 | 12.61±3.91 | 8.77±0.18 | 11.75±4.80 | 8.67±2.30 |
| 3/24 | 19.45±4.41 | 12.21±0.41 | 18.75±5.42 | 12.00±1.78 |
| 3/25 | 23.52±4.78 | 17.48±4.64 | 22.75±5.25 | 17.33±5.41 |
| 3/26 | 21.00±4.16 | 21.59±6.21 | 20.00±5.26 | 21.50±7.18 |
| 3/27 | 21.84±3.79 | 25.82±4.30 | 21.00±4.09 | 25.67±5.42 |
| 3/28 | 16.94±2.96 | 30.11±0.12 | 16.42±4.37 | 29.92±3.93 |
| 3/29 | 20.08±3.46 | 38.68±15.97 | 19.58±5.06 | 35.83±18.25 |
| 3/30 | 14.97±3.03 | 32.06±14.96 | 14.75±3.67 | 26.42±15.06 |
| 3/31 | 10.72±2.36 | 19.33±4.19 | 10.50±2.42 | 18.33±5.05 |
| 4/1 | 8.92±1.77 | 13.43±2.79 | 8.92±2.60 | 12.92±3.19 |
| 4/2 | 7.93±1.37 | 9.36±1.84 | 7.75±1.70 | 9.00±2.91 |
| 4/3 | 6.07±1.22 | 6.88±2.28 | 6.08±1.43 | 6.58±3.15 |
| 4/4 | 4.65±1.05 | 4.83±0.20 | 4.67±1.10 | 4.83±0.37 |
| 4/5 | 3.36±1.16 | 3.68±0.40 | 3.42±1.15 | 3.75±0.76 |
| 4/6 | 2.11±0.87 | 2.33±0.66 | 2.17±1.59 | 2.50±1.51 |

图3 羽化高峰日前后的春尺蠖逐日羽化量变化趋势空间分布
Fig.3 Spatial distribution of the daily emergence trend of Apocheima cinerarius Erschoff around the peak days of emergence
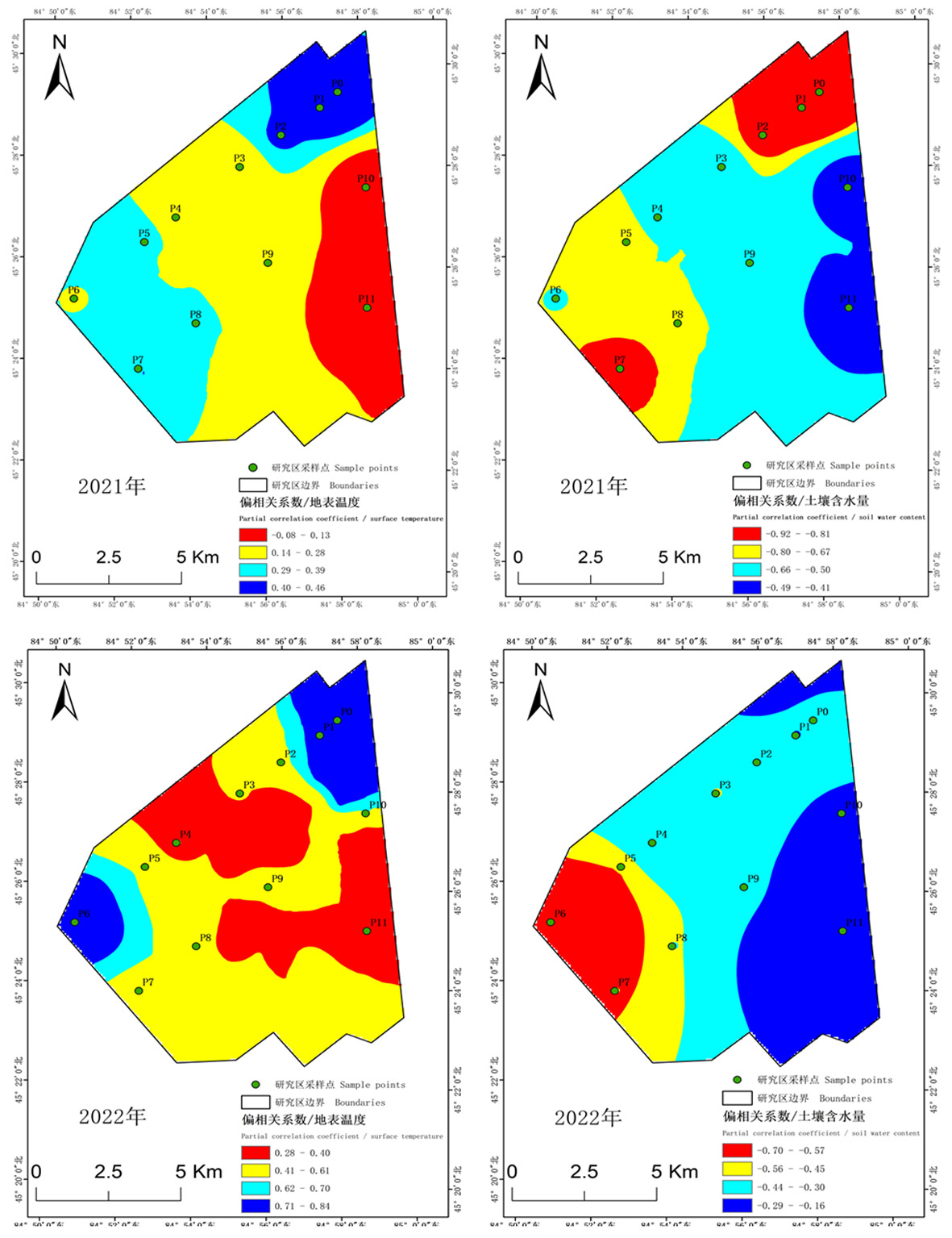
图4 羽化高峰日前地表温度、土壤含水量与逐日羽化量的偏相关系数空间分布
Fig.4 Spatial distribution of partial correlation coefficients between surface temperature, soil water content and daily emergence before emergence peak day
| 自变量 Indepe- ndent variable | 与Y的简单 相关系数 Simple correlation coefficient with Y | 通径系数 (直接作用) Path coefficient (direct effect) | 间接通径系数 (间接作用) Indirect path coefficient (indirect effect) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | |||
| X1 | 0.493 | 0.194 | 0.299 | |
| X2 | -0.571 | -0.438 | -0.133 | |
表3 2021年X1及X2分别与Y的简单相关系数的分解
Tab.3 Decomposition of the simple correlation coefficients of X1 and X2 with Y in 2021
| 自变量 Indepe- ndent variable | 与Y的简单 相关系数 Simple correlation coefficient with Y | 通径系数 (直接作用) Path coefficient (direct effect) | 间接通径系数 (间接作用) Indirect path coefficient (indirect effect) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | |||
| X1 | 0.493 | 0.194 | 0.299 | |
| X2 | -0.571 | -0.438 | -0.133 | |
| 自变量 Indepe- ndent variable | 与Y的简单 相关系数 Simple correlation coefficient with Y | 通径系数 (直接作用) Path coefficient (direct effect) | 间接通径系数 (间接作用) Indirect path coefficient (indirect effect) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | |||
| X1 | 0.480 | 0.404 | 0.076 | |
| X2 | -0.352 | -0.188 | -0.164 | |
表4 2022年X1及X2分别与Y的简单相关系数的分解
Tab.4 Decomposition of the simple correlation coefficients of X1 and X2 with Y in 2022
| 自变量 Indepe- ndent variable | 与Y的简单 相关系数 Simple correlation coefficient with Y | 通径系数 (直接作用) Path coefficient (direct effect) | 间接通径系数 (间接作用) Indirect path coefficient (indirect effect) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | |||
| X1 | 0.480 | 0.404 | 0.076 | |
| X2 | -0.352 | -0.188 | -0.164 | |
| [1] | 黄晓曦, 刘占国. 春尺蠖生物学特性及综合防治的研究[J]. 中国农业信息, 2013,(17): 98. |
| HUANG Xiaoxi, LIU Zhanguo. Study on biological characteristics and integrated control of inchworm[J]. China Agriculture Information, 2013,(17): 98. | |
| [2] | 娄国强, 吕文彦, 余昊, 等. 基于GS和GIS的春尺蠖种群分布动态研究[J]. 昆虫学报, 2006, 49(4): 613-618. |
| LOU Guoqiang, LYU Wenyan, YU Hao, et al. Distribution pattern and dynamics of Apocheima cinerarius Erschoff populations studied with GS and GIS[J]. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 2006, 49(4): 613-618. | |
| [3] | 陈龙, 单艳敏, 廖桂堂, 等. 春尺蠖转录组及嗅觉相关基因分析[J]. 西南农业学报, 2022, 35(1): 120-129. |
| CHEN Long, SHAN Yanmin, LIAO Guitang, et al. Analysis of transcriptome and olfaction-related genes of Apocheima cinerarius Erschoff[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 35(1): 120-129. | |
| [4] | 孙倩, 阿地力·沙塔尔, 孙晶. 基于3S技术的生态景观变化对春尺蠖时空分布的影响——以克拉玛依市开发区为例[J]. 西南农业学报, 2020, 33(12): 2955-2961. |
| SUN Qian, Adili Shataer, SUN Jing. Effect of ecological landscape changes on spatial-temporal distribution of Apocheima cinerarius based on 3S technology: a case study of Karamay development zone[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 33(12): 2955-2961. | |
| [5] |
张炳坤, 李瑜, 周黎, 等. 温湿度对蔡氏胡杨个木虱越冬成虫存活的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(10): 1893-1899.
DOI |
|
ZHANG Bingkun, LI Yu, ZHOU Li, et al. Effects of temperature and humidity on survival of the overwintering adults of eeirotrioza ceardi[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(10): 1893-1899.
DOI |
|
| [6] |
丁新华, 王小武, 付开赟, 等. 温度、相对湿度对亚洲玉米螟Ostrinia furnacalis(Guenée)越冬幼虫化蛹及羽化的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(11): 2668-2674.
DOI |
|
DIN Xinhua, WANG Xiaowu, FU Kaiyun, et al. Effects of temperature and relative humidity on pupation and emergence of overwintering larvae of Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée)[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(11): 2668-2674.
DOI |
|
| [7] | 王志平, 鄂晓明, 杨建军, 等. 春尺蠖生物学特性与防控技术探讨[J]. 内蒙古林业, 2020,(2): 22-23. |
| WANG Zhiping, E Xiaoming, YANG Jianjun, et al. Discussion on biological characteristics and control techniques of inchworm[J]. Inner Mongolia Forestry, 2020,(2): 22-23. | |
| [8] | 卿薇, 阿地力·沙塔尔, 闫文兵. 主要气象因子对克拉玛依市春尺蠖成虫羽化率的影响[J]. 新疆农业大学学报, 2015, 38(6): 465-469. |
| QING Wei, Adili Shataer, YAN Wenbing. Impacts of main meteorological factors on eclosion rate of Apocheima cinerarius erschoff adult in Karamay city[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2015, 38(6): 465-469. | |
| [9] | Ding W C, Li H Y, Wen J B. Climate change impacts on the potential distribution of Apocheima cinerarius (Erschoff) (Lepidoptera: Geometridae)[J]. Insects, 2022, 13(1): 59. |
| [10] | 陈孟禹, 贾翔, 陈蜀江, 等. 叶尔羌河流域胡杨春尺蠖发生期遥感预测[J]. 生态科学, 2020, 39(2): 145-156. |
| CHEN Mengyu, JIA Xiang, CHEN Shujiang, et al. The prediction of the occurrence period of Populus euphratica Apocheima cinerius Erschoff in the Yarkant River Basin based on remote sensing[J]. Ecological Science, 2020, 39(2): 145-156. | |
| [11] | 刘逸豪, 贾翔, 侯博展, 等. 叶尔羌河流域胡杨春尺蠖虫态发育节律对地表温度的响应[J]. 生态科学, 2019, 38(2): 119-129. |
| LIU Yihao, JIA Xiang, HOU Bozhan, et al. The response of developmental rhythm of Populus euphratica Apocheima Cinerius Erschoff in Yarkant River Basin to surface temperature[J]. Ecological Science, 2019, 38(2): 119-129. | |
| [12] | 吴雪海. 北疆春尺蠖发生动态及防治技术研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2017. |
| WU Xuehai. The Occurrence Dynamics and Control Techniques of Apocheima Cinerarius (Lepidoptera: Geometridae) in Northern Xinjiang[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2017. | |
| [13] | 汪航, 师茁, 王岩, 等. 基于MODIS时间序列数据的春尺蠖虫害遥感监测方法研究——以新疆巴楚胡杨为例[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2018, 33(4): 686-695. |
| WANG Hang, SHI Zhuo, WANG Yan, et al. A method for detecting the damage of Apocheima cinerarius erschoffbased on MODIS time series: case studies in Bachu Populus euphratica forest of Xinjiang Province[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2018, 33(4): 686-695. | |
| [14] | 卿薇, 阿地力·沙塔尔, 闫文兵. 土壤因子对春尺蠖蛹羽化率的影响研究[J]. 新疆农业大学学报, 2016, 39(5): 406-413. |
| QING Wei, Adili Shataer, YAN Wenbing. Effects of soil factor on the eclosion of Apocheima cinerarius erschoff Pupa[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2016, 39(5): 406-413. | |
| [15] | 杨玉峰, 李中邵, 陈胜权. 新疆克拉玛依市农业开发区地下水动态规律研究[J]. 江西水利科技, 2016, 42(6): 398-403. |
| YANG Yufeng, LI Zhongshao, CHEN Shengquan. Study on the dynamic law of groundwater in the agricultural development zone of Karamay city[J]. Jiangxi Hydraulic Science & Technology, 2016, 42(6): 398-403. | |
| [16] | 李琴, 陈曦, 包安明, 等. 干旱/半干旱区MODIS地表温度反演与验证研究[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2008, 23(6): 643-647, 图版4-5. |
| LI Qin, CHEN Xi, BAO Anming, et al. Validation of land surface temperatures retrieving in arid/semi-arid regions[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2008, 23(6): 643-647, 图版4-5. | |
| [17] | 李韶颖, 车风, 邵军, 等. 基于MODIS数据的湖北省地级以上城市城区地表温度变化分析[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2020, 43(2): 76-78. |
| LI Shaoying, CHE Feng, SHAO Jun, et al. Analysis on land surface temperature changes of prefecture-level city urban areas in Hubei Province based on MODIS data[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2020, 43(2): 76-78. | |
| [18] | 周兆丁, 吕锟, 沈瑾, 等. 统计软件SPSS相关分析及应用[J]. 电脑知识与技术, 2019, 15(20): 301-302. |
| ZHOU Zhaoding, LYU Kun, SHEN Jin, et al. Correlation analysis and application of statistical software SPSS[J]. Computer Knowledge and Technology, 2019, 15(20): 301-302. | |
| [19] | 张琪, 丛鹏, 彭励. 通径分析在Excel和SPSS中的实现[J]. 农业网络信息, 2007, (3): 109-110. |
| ZHANG Qi, CONG Peng, PENG Li. The realization of path analysis in Excel and SPSS[J]. Agricultural Network Information, 2007, (3) : 109-110. | |
| [20] | Jiang Z L, Wu J W, Huang F, et al. A novel adaptive Kriging method: time-dependent reliability-based robust design optimization and case study[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2021, 162: 107692. |
| [21] | Zhao H D, Zhang N, Lin C S, et al. Construction method of geomagnetic reference map for satellite communication navigation through Kriging method[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021, 2033(1): 012034. |
| [22] |
黄葵, 卢毅敏, 魏征, 等. 土地利用和气候变化对海河流域蒸散发时空变化的影响[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2019, 21(12): 1888-1902.
DOI |
| HUANG Kui, LU Yimin, WEI Zheng, et al. Effects of land use and climate change on spatiotemporal changes of evapotranspiration in Haihe River Basin[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2019, 21(12): 1888-1902. | |
| [23] | 贾翔, 陈蜀江, 尹小英, 等. 基于CLUE-S模型模拟胡杨春尺蠖的发生蔓延过程[J]. 植物保护学报, 2019, 46(5): 1018-1028. |
| JIA Xiang, CHEN Shujiang, YIN Xiaoying, et al. Simulation of the propagation process of mulberry looper Apocheima cinerarius based on the CLUE-S model[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2019, 46(5): 1018-1028. | |
| [24] | 王瑾杰, 丁建丽, 张喆, 等. 基于多源遥感数据的艾比湖流域盐土SWAT模型参数修正[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(23): 139-144. |
| WANG Jinjie, DING Jianli, ZHANG Zhe, et al. SWAT model parameters correction based on multi-source remote sensing data in saline soil in Ebinur Lake Watershed[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(23): 139-144. | |
| [25] | 赵安周, 张安兵, 冯莉莉, 等. 海河流域生态水分利用效率时空变化及其与气候因子的相关性分析[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(4): 1452-1462. |
| ZHAO Anzhou, ZHANG Anbing, FENG Lili, et al. Spatio-temporal characteristics of water-use efficiency and its relationship with climatic factors in the Haihe River Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(4): 1452-1462. | |
| [26] | 冯宏祖, 王兰, 胡卫江, 等. 沙雅县天然胡杨林春尺蠖发生规律的初步研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2005, 42(1): 57-58. |
| FENG Hongzu, WANG Lan, HU Weijiang, et al. The preliminary study on occurrence of Apocheima cinerarius erschoff in natural poplar of Shaya County[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2005, 42(1): 57-58. | |
| [27] | 张德利, 鲁增辉, 贺宗毅, 等. 环境因子对云南蝠蛾羽化的影响[J]. 植物保护, 2019, 45(2): 148-152. |
| ZHANG Deli, LU Zenghui, HE Zongyi, et al. Effects of environmental factors on adult emergence of Hepialus yunnanensis[J]. Plant Protection, 2019, 45(2): 148-152. |
| [1] | 肖淑婷, 颜安, 王卫霞, 张青青, 侯正清, 马梦倩, 孙哲. 天山中部典型林区地上生物量时空变化及影响因素分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2237-2244. |
| [2] | 党旭伟, 林馨园, 贺正, 陈燕, 慈宝霞, 马学花, 郭晨荔, 贺亚星, 刘扬, 马富裕. 基于无人机热红外遥感图像提取滴灌棉花冠层温度及精度评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(3): 565-575. |
| [3] | 陈荣, 赖宁, 耿庆龙, 李永福, 信会男, 吕彩霞, 李娜, 陈署晃. 基于遥感数据构建冬小麦孕穗期变量施氮模型[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2705-2712. |
| [4] | 赵昊楠, 马海燕, 阿斯娅·曼力克, 田聪, 徐俊, 潘竟, 孙宗玖, 郑逢令. 基于深度学习和GEE的作物遥感分类[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2807-2814. |
| [5] | 秦叶康阳, 李嘉欣, 靳瑰丽, 刘文昊, 马建, 李文雄, 陈梦甜. 基于UAV和CNN ResNet 18参数调节的伊犁绢蒿荒漠草地植物识别性能分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(10): 2547-2556. |
| [6] | 才仁加甫, 曹彪, 白云岗, 刘旭辉, 余其鹰, 刘敏杰. 和田河沙漠段生态输水植被恢复遥感评价和植被变化驱动因素分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(8): 2041-2050. |
| [7] | 丁新华, 王小武, 付开赟, 贾尊尊, 吐尔逊・阿合买提, 郭文超. 温度、相对湿度对亚洲玉米螟Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée)越冬幼虫化蛹及羽化的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(11): 2668-2674. |
| [8] | 杨勇强, 王振锡, 师玉霞, 连玲, 高亚利. 基于无人机影像的天山云杉林单木树冠信息提取[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(8): 1484-1492. |
| [9] | 魏青, 张宝忠, 魏征. 基于无人机多光谱影像的地物识别[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(5): 932-939. |
| [10] | 王蕾, 罗磊, 刘平, 侯晓臣, 邱琴, 高亚琪, 李曦光. 基于MaxEnt模型分析新疆特色林果区春尺蠖发生风险[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(9): 1691-1700. |
| [11] | 葛元梅, 陈翔宇, 洪帅, 马露露, 吕新, 张泽. 基于红边参数不同品种的估算模型[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(6): 1032-1040. |
| [12] | 崔美娜,戴建国,王守会,张国顺,薛金利. 基于无人机多光谱影像的棉叶螨识别方法[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(8): 1457-1466. |
| [13] | 罗磊,王蕾,刘平,李曦光,高亚琪. 新疆天山中部沙湾林场生态系统健康评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(8): 1505-1515. |
| [14] | 祁亚琴,张显峰,张立福,吕新,张泽,陈剑, 李新伟,王飞,彭奎. 基于高光谱数据的农田土壤养分含量估测模型研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(3): 490-495. |
| [15] | 邱琳,王蕾,罗磊,郑江华. 基于时间序列塔里木河中游胡杨林春尺蠖危害的遥感监测[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(3): 518-527. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 28
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 133
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||