

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (1): 63-78.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.01.008
收稿日期:2023-05-11
出版日期:2024-01-20
发布日期:2024-02-21
作者简介:户金鸽(1982-),女,新疆塔城人,副研究员,硕士,研究方向为葡萄栽培,(E-mail)hujinge2007@sina.com
基金资助:
HU Jinge( ), BAI Shijian, CHEN Guang, CAI Junshe
), BAI Shijian, CHEN Guang, CAI Junshe
Received:2023-05-11
Published:2024-01-20
Online:2024-02-21
Correspondence author:
HU Jinge(1982-),female,Xinjiang,research associate,research area:viticulture,(E-mail)hujinge2007@sina.comSupported by:摘要:
【目的】研究园艺地布覆盖和生草栽培两种不同地面覆盖方式下鲜食葡萄新郁果皮黄酮相关组分及其合成酶基因信息,为筛选新郁葡萄高效优质栽培新模式提供科学依据。【方法】以7年生新郁葡萄为试材,以清耕栽培为对照,分别进行行间铺设园艺地布和行间生草栽培两种地面覆盖方式处理,分析不同地面覆盖方式下葡萄果皮黄酮转录组和代谢物含量的差异。【结果】(1)园艺地布覆盖获得差异表达基因587个,其中上调基因317个、下调基因270个,生草栽培获得差异表达基因177个,其中上调基因56个、下调基因121个。(2)GO数据库将园艺地布覆盖注释的基因涉及45个功能组,将生草栽培覆盖注释的基因组涉及37个功能组,均主要集中在细胞组分、分子功能和生物学过程;KOG数据库分别将其注释到的175个和86个DEGs进行直系同源分类,各自获得22个和16个功能分类,园艺地布覆盖的193个差异基因被注释到KEGG通路中,与黄酮相关富集途径有次级代谢物生物合成、苯丙醇生物合成、类黄酮生物合成、苯丙氨酸生物合成、植物昼夜节律、二苯乙烯类二芳庚类和姜辣素类的生物合成;生草栽培的61个差异基因被注释到KEGG通路中,与黄酮相关富集途径有次级代谢物生物合成。(3)新郁葡萄果皮共检测到12类60个黄酮代谢物,其中地布覆盖差异代谢物7个(下调2个,上调5个),生草覆盖差异代谢物11个(全部下调)。黄烷醇含量占总黄酮含量的52.41%~63.70%,所占比例最高,生草栽培和园艺地布栽培的黄烷醇类含量均高于对照,分别比对照提高了19.42%和7.55%。(4)与黄酮合成相关富集途径主要集中在类黄酮生物合成、黄酮和黄酮醇生物合成,园艺地布覆盖筛选出7个候选基因:C4H、CHS、F3H、LAR、HCT、FLS和C12RT1,生草筛选出5个候选基因:CHS、F3H、F3'5'H、FLS和LAR。【结论】筛选出在地布和生草栽培模式下新郁葡萄黄酮生物合成候选基因。在新疆吐鲁番极端干旱地区鲜食葡萄新郁地面覆盖方式可选择生草栽培。
中图分类号:
户金鸽, 白世践, 陈光, 蔡军社. 不同地面覆盖方式下新郁葡萄果皮黄酮转录组和代谢组联合分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(1): 63-78.
HU Jinge, BAI Shijian, CHEN Guang, CAI Junshe. Transcriptome and metabolome integrated analysis of flavonoids in Xinyu grape peel under different ground mulch 5ypes[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(1): 63-78.
| 样本ID Sample ID | 原始读数 Raw reads | 干净数据 Clean reads (bp) | 碱基总数 Clean base (G) | 错误率 Error rate (%) | 测序准确度 在99% Q20(%) | 测序准确度 在99% Q30 (%) | G和C 2种碱 基占总碱基的 百分比GC(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 清耕Q-1 Clean tillage Q-1 | 57476100 | 55348990 | 8.30 | 0.03 | 97.00 | 91.94 | 46.03 |
| 清耕Q-2 Clean tillage Q-2 | 46791054 | 41704844 | 6.26 | 0.03 | 98.04 | 94.21 | 46.30 |
| 清耕Q-3 Clean tillage Q-3 | 47866130 | 41706034 | 6.26 | 0.03 | 98.01 | 94.16 | 46.10 |
| 园艺地布F-1 Horticultural ground cloth F-1 | 48420302 | 42003268 | 6.30 | 0.02 | 98.09 | 94.34 | 45.95 |
| 园艺地布F-2 Horticultural ground cloth F-2 | 48354116 | 44252400 | 6.64 | 0.03 | 97.89 | 93.91 | 46.46 |
| 园艺地布F-3 Horticultural ground cloth F-3 | 46448184 | 42513692 | 6.23 | 0.03 | 98.04 | 94.20 | 46.55 |
| 生草栽培S-1 Sod-culture-1 | 57847986 | 55154966 | 8.27 | 0.03 | 96.81 | 91.59 | 46.23 |
| 生草栽培S-2 Sod-culture-2 | 51485636 | 49924206 | 7.49 | 0.03 | 96.90 | 91.57 | 44.84 |
| 生草栽培S-3 Sod-culture-3 | 52146666 | 50057894 | 7.51 | 0.03 | 96.93 | 91.84 | 46.16 |
表1 不同地面覆盖方式转录组测序质量变化
Tab.1 Quality analysis of transcriptome sequencing of different mulching type
| 样本ID Sample ID | 原始读数 Raw reads | 干净数据 Clean reads (bp) | 碱基总数 Clean base (G) | 错误率 Error rate (%) | 测序准确度 在99% Q20(%) | 测序准确度 在99% Q30 (%) | G和C 2种碱 基占总碱基的 百分比GC(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 清耕Q-1 Clean tillage Q-1 | 57476100 | 55348990 | 8.30 | 0.03 | 97.00 | 91.94 | 46.03 |
| 清耕Q-2 Clean tillage Q-2 | 46791054 | 41704844 | 6.26 | 0.03 | 98.04 | 94.21 | 46.30 |
| 清耕Q-3 Clean tillage Q-3 | 47866130 | 41706034 | 6.26 | 0.03 | 98.01 | 94.16 | 46.10 |
| 园艺地布F-1 Horticultural ground cloth F-1 | 48420302 | 42003268 | 6.30 | 0.02 | 98.09 | 94.34 | 45.95 |
| 园艺地布F-2 Horticultural ground cloth F-2 | 48354116 | 44252400 | 6.64 | 0.03 | 97.89 | 93.91 | 46.46 |
| 园艺地布F-3 Horticultural ground cloth F-3 | 46448184 | 42513692 | 6.23 | 0.03 | 98.04 | 94.20 | 46.55 |
| 生草栽培S-1 Sod-culture-1 | 57847986 | 55154966 | 8.27 | 0.03 | 96.81 | 91.59 | 46.23 |
| 生草栽培S-2 Sod-culture-2 | 51485636 | 49924206 | 7.49 | 0.03 | 96.90 | 91.57 | 44.84 |
| 生草栽培S-3 Sod-culture-3 | 52146666 | 50057894 | 7.51 | 0.03 | 96.93 | 91.84 | 46.16 |
| 组 Group | 差异基 因总数 Total number of differentially expressed genes | 上调基 因数 Upregulated gene count | 下调基 因数 Number of down- regulated genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 清耕vs园艺地布Q_vs_F Clean tillage vs Horticultural ground cloth Q_vs_F | 587 | 270 | 317 |
| 清耕vs生草栽培Q_vs_S Clean tillage vs Sod-culture Q_vs_S | 177 | 121 | 56 |
表2 差异基因数量
Tab.2 Statistics of the number of differential genes
| 组 Group | 差异基 因总数 Total number of differentially expressed genes | 上调基 因数 Upregulated gene count | 下调基 因数 Number of down- regulated genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 清耕vs园艺地布Q_vs_F Clean tillage vs Horticultural ground cloth Q_vs_F | 587 | 270 | 317 |
| 清耕vs生草栽培Q_vs_S Clean tillage vs Sod-culture Q_vs_S | 177 | 121 | 56 |

图1 不同地面覆盖方式下葡萄果皮差异基因二级条目分类 注(Note):生物学过程(Biological process);细胞组分(Cellular component);分子功能(Molecular function);细胞膜(Membrane);胞外区(Extracellular region);细胞(Cell);细胞连接(Cell junction);膜内腔(Membrane-enclosed lumen);蛋白复合体(Protein-containing complex);细胞器(Organelle);细胞外基质部分(Extracellular region part);细胞器组件(Organelle part);细胞膜组件(Membrane part);细胞组件(Cell part);共质体(Symplast);超分子复合物(Supramolecular complex);翻译调节活性(Transcription regulator activity);催化活性(Catalytic activity);营养储层活动(Nutrient reservoir activity);结构分子活性(Structural molecule activity);转运器活动(Transporter activity);绑定(Binding);抗氧化活性(Antioxidant activity);分子功能调节(Moleular function regulator);分子传感器活性(Molecular transducer activity);生殖(Reproduction);代谢过程(Metabolic process);生长(Growth);细胞增殖(Cell proliferation);细胞进程(Cellular process);生殖过程(Reproductive process);生物黏附(Biological adhesion);信号(Signaling);多细胞有机体进程(Multicellular organismal process);发育进程(Developmental process);运动力(Locomotion);节律进程(Rhythmic process);生物过程的正调控(Positive regulation of biological process);生物过程的负调控(Negative regulation of biological process);应激反应(Response to stimulus);定位(Localization);多有机体进程(Multi-organism process);生物调节(Biological regulation);细胞成分组织或生物合成(Cellular component organization or biogenesis);解毒(Detoxification);横坐标表示二级GO条目,纵坐标表示GO条目的差异基因的数量(The abscissa represents the second-level GO entry,and the ordinate represents the number of differential genes in the GO entry)
Fig.1 Classification map of secondary entries of grape peel differential genes by different mulch type
| 差异表达基因集 Differentially expressed gene set | DEG数(个)Number of DEG | 有GO功能注释的DEG数 Number of DEGs with GO function annotations | DEG总数 Total of DEG | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物学过程 Biological process | 细胞组分 Cellular component | 分子功能 Molecular function | |||
| 清耕vs园艺地布Q_vs_F Clean tillage vs Horticultural ground cloth Q_vs_F | 425 | 23 | 308 | 155 | 364 |
| 清耕vs生草栽培Q_vs_S Clean tillage vs Sod-culture Q_vs_S | 119 | 15 | 132 | 57 | 108 |
表3 GO数据库三大功能主类DEG数
Tab.3 DEG number of three major GO database functions
| 差异表达基因集 Differentially expressed gene set | DEG数(个)Number of DEG | 有GO功能注释的DEG数 Number of DEGs with GO function annotations | DEG总数 Total of DEG | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物学过程 Biological process | 细胞组分 Cellular component | 分子功能 Molecular function | |||
| 清耕vs园艺地布Q_vs_F Clean tillage vs Horticultural ground cloth Q_vs_F | 425 | 23 | 308 | 155 | 364 |
| 清耕vs生草栽培Q_vs_S Clean tillage vs Sod-culture Q_vs_S | 119 | 15 | 132 | 57 | 108 |
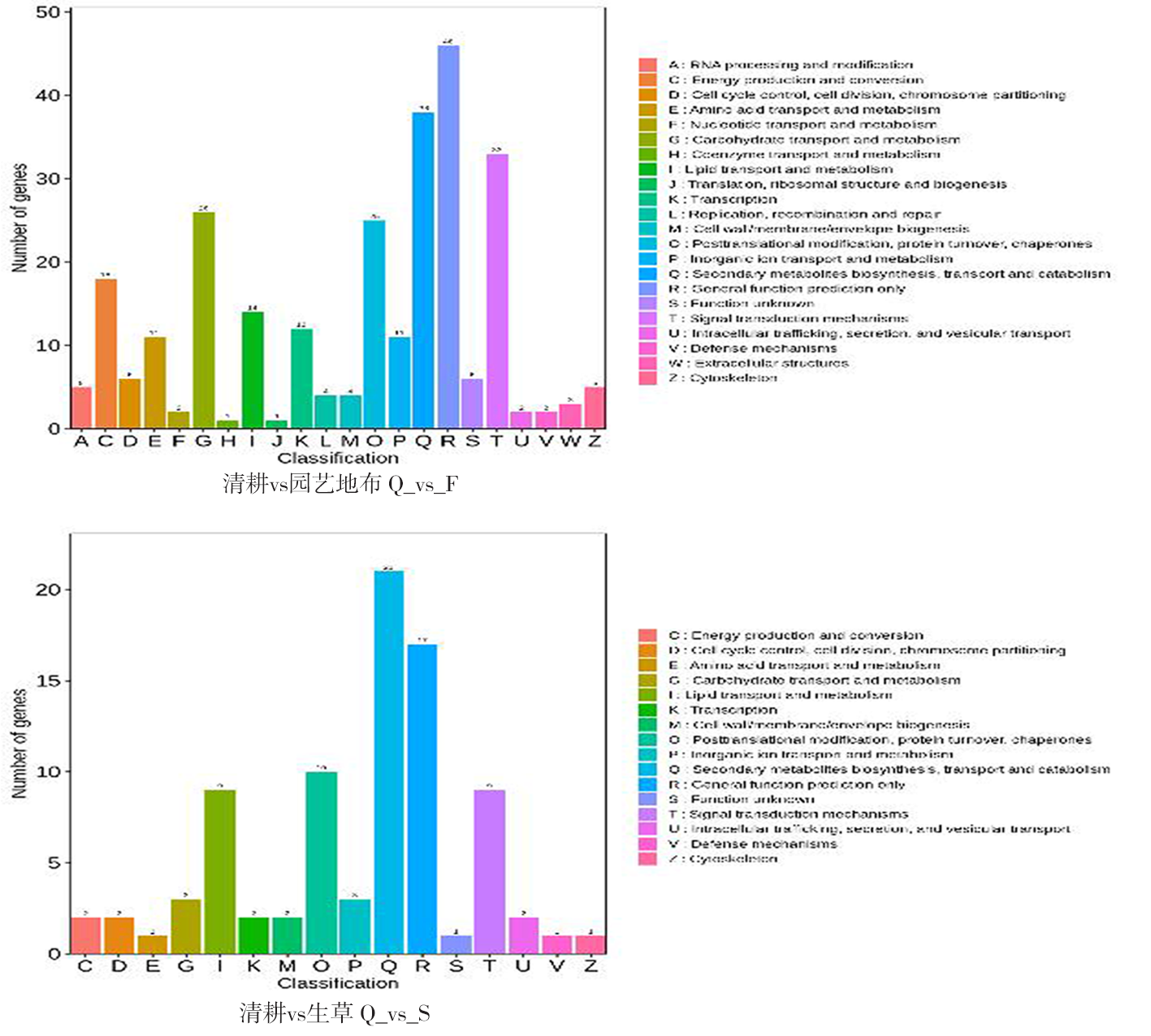
图2 不同地面覆盖方式下新郁葡萄果皮KOG注释的分类统计 注:(Note)A,RNA的加工与修饰(RNA processing and modification);C,能源的产生与转化(Energy production and conversion);D,细胞周期调控,细胞分裂,染色体分配(Cell cycle control,cell division,chromosome partitioning);E,(氨基酸转运与代谢)Amino acid transport and metabolism;F,(核苷酸转运与代谢)Nucleotide transport and metabolism;G,碳水化合物转运与代谢(Carbohydrate transport and metabolism);H,辅酶转运与代谢(Coenzyme transport and metabolism);I,脂质转运与代谢(Lipid transport and metabolism);J,翻译、核糖体结构和生物合成(Translation,ribosome structure and biosynthesis); K,转录(transcription);L,复制、重组和修复(Replication,recombination and repair);M,细胞壁/细胞膜的生物发生(Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis);O,次生代谢物合成、转运和代谢(Posttranslational modification,protein turnover,chaperones);P,无机离子转运与代谢(Inorganic ion transport and metabolism);Q,次级代谢物的生物合成、转运和代谢(Secondary metabolites biosynthesis,transport and cetabolism);R,一般功能预测(General function prediction only);S,未知功能(Function Unknown);T,信号转导机制(Signal transduction mechanisms);U,胞质运输、分泌和囊泡运动(intracellular trafficking,secretion and vesicle transport);V,防御机制(Defense mechanisms); W,细胞外结构(xtracellular structures);Z, 细胞骨架(cytoskeleton)
Fig.2 KOG annotated histogram of classification statistics of grape peel by different ground mulch methods
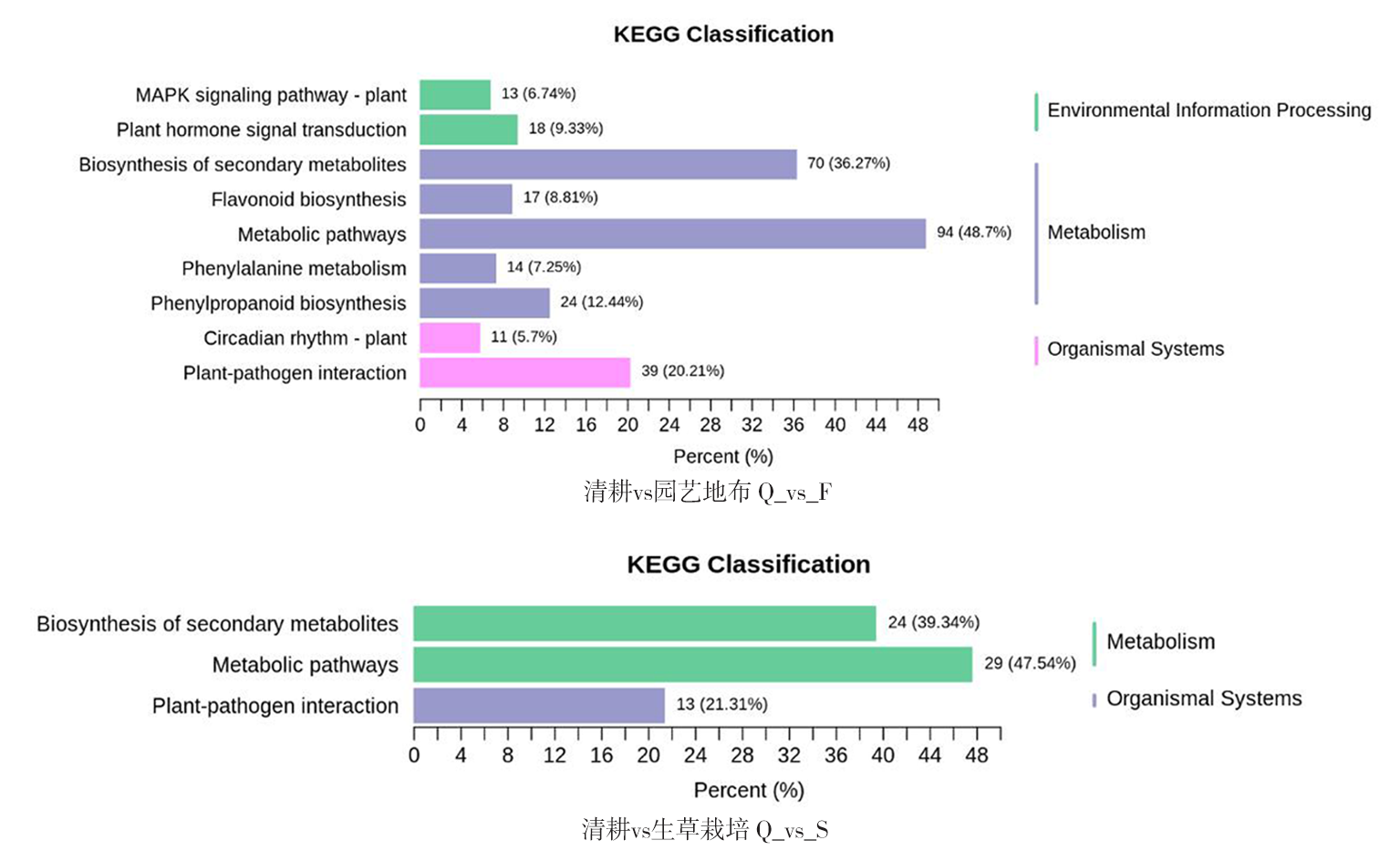
图3 不同地面覆盖方式下葡萄果皮差异表达基因KEGG pathway代谢通路 注(Note):横坐标表示注释到该通路的基因与有注释的基因总数的比例,纵坐标表示 KEGG 通路的名称。图形右侧的标签代表 KEGG 通路所属的分类(The abscissa represents the ratio of genes annotated to the pathway to the total number of annotated genes,and the ordinate represents the name of the KEGG pathway. The label on the right of the figure represents the classification to which the KEGG pathway belongs);环境信息处理(Environmental information processing);新陈代谢(Metabolism);有机系统(Organismal systems);MAPK信号通路-植物(MAPK signaling pathway-plant);植物激素信号转导(Plant hormone signal transduction);次级代谢物生物合成(Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites);类黄酮生物合成途径(Flavonoid biosynthesis);代谢途径(Metabolic pathways);苯丙烷类的代谢途径(Phenylalanine metabolism);苯丙烷类的生物合成(Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis);昼夜节律-植物(Circadian rhythm-plant);植物病原互作(Plant-pathogen interaction)。
Fig.3 Functional classification and pathway assignment of DEGs by KEGG by different mulch type
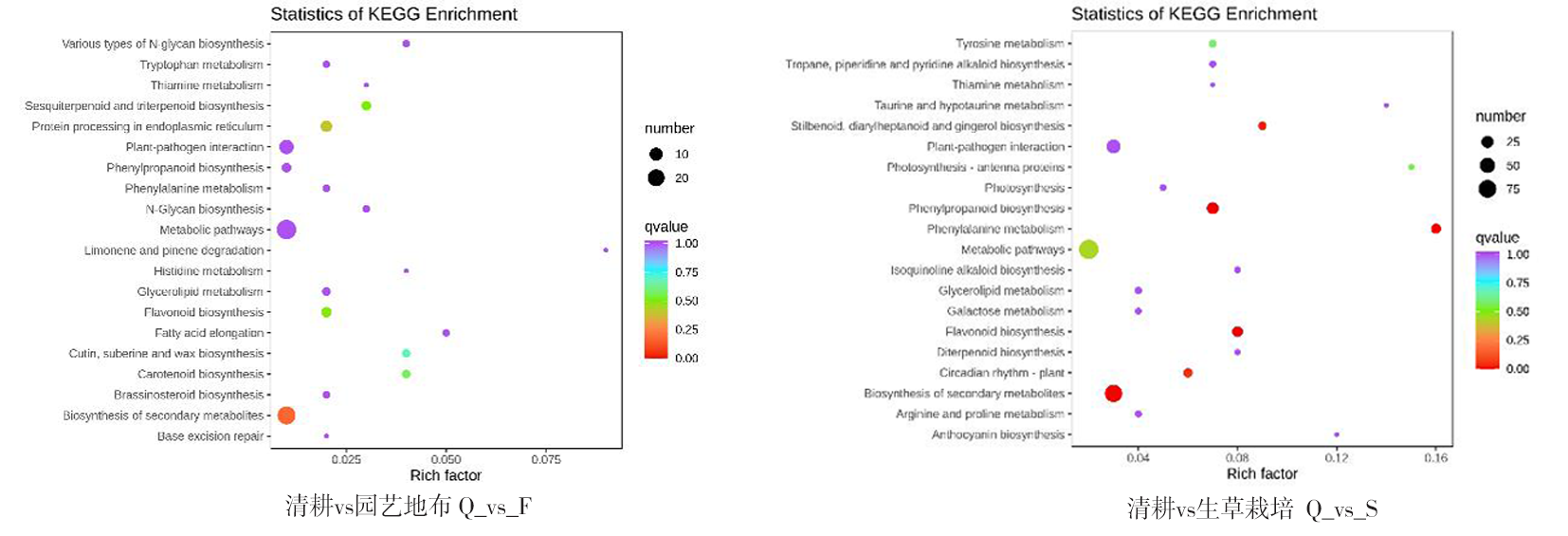
图4 不同地面覆盖方式下葡萄果皮差异表达基因富集散点图 注(Note):纵坐标表示KEGG通路。横坐标表示Rich factor。Rich factor越大,富集的程度越大。点越大,通路富集的差异基因的数量越多。点的颜色越红,代表富集越显著(The ordinate represents the KEGG pathway. Abscissa represents the Rich Factor. The larger the Rich factor,the greater the degree of enrichment. Larger point indicates more number of differential genes enriched by pathway. Color shows significance with most significant in red);酪氨酸代谢(Tyrosine metabolism);莨菪烷、哌啶和吡啶生物碱的生物合成(Tropane,piperidine and pyridine alkaloid biosynthesis);硫胺素新陈代谢(Thiamine metabolism);牛磺酸和次牛磺酸代谢(Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism);二芳基庚烷和姜醇的生物合成(Stilbenoid,diarylheptanoid and gingerol biosynthesis);植物-病原互作(Plant-pathogen interaction);光合作用-天线蛋白(Photosynthesis-antenna proteins);光合作用(Photosynthesis);苯丙烷生物合成途径(Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis);苯丙烷类的代谢途径(Phenylalanine metabolism);代谢途径(Metabolic pathways);异黄酮生物合成途径(Isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis);甘油酯代谢(Glycerolipid metabolism);半乳糖代谢(Galactose metabolism);类黄酮生物合成途径(Flavonoid biosynthesis);二萜生物合成(Diterpenoid biosynthesis);昼夜节律-植物(Circadian rhythm-plant);次级代谢物生物合成(Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites);精氨酸和脯氨酸代谢(Arginine and proline metabolism);花青素生物合成(anthocyanin biosynthesis);各种类型的N -聚糖生物合成(Various types of N-glycan biosynthesis);色氨酸代谢(Tryptophan metabolism);酪氨酸代谢(Thiamine metabolism);类倍半萜烯和三萜(Sesquiterpenoid and triterpenoid);内质网中的蛋白质加工(Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum);N-寡糖生物合成(N-Glycan biosynthesis);柠檬烯和蒎烯的降解(Limonene and pinene degradation);组氨酸代谢(Histidine metabolism);甘油酯代谢(Glycerolipid metabolism);脂肪酸延伸(Fatty acid elongation);角质、亚伯碱和蜡的生物合成(Cutin,suberine and wax biosynthesis);类胡萝卜素合成(Carotenoid biosynthesis);油菜素类固醇生物合成(Brassinosteroid biosynthesis);碱基切除修复(Base excision repair)。
Fig.4 Map of rich distribution points of differentially expressed genes of grape peel by different mulch types
| 代谢物ID Metabolite ID | 物质 Compound | 二级代谢产物 Class Ⅱ metabolite | 清耕Q (对照,CK) Clean tillage | 园艺地布 Horticultural ground cloth | 生草栽培 Sod-culture | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoid_145 | 原花青素B2 | 花青素 | 113.161±5.062a (3.489%) | 121.677±14.285a (3.387%) | 76.123±7.106b (2.302%) | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_65 | 查耳酮 | 17.546±1.872a | 18.213±2.625a | 15.875±0.745a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_191 | 柚皮素查尔酮 | 0.198±0.058b | 0.345±0.048a | 0.186±0.049b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_202 | 0.703±0.117a | 0.626±0.097a | 0.624±0.016a | |||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_22 | 新橙皮甙二氢查尔酮 | 0.023±0.017ab | 0.039±0.015a | 0.004±0.002b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_31 | 柚皮苷二氢查尔酮 | 0.010±0.004a | 0.011±0.002a | 0.006±0.002a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_177 | 总含量 | 0.008±0.001b 18.848±1.946a (0.57%) | 0.018±0.004a 19.253±2.706a (0.54%) | 0.005±0.001b 16.700±0.683a (0.51%) | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_195 | 没食子儿茶素(-) | 黄烷醇类 | 718.783±77.192b | 792.625±48.743ab | 903.325±68.297a | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_147 | (-)-表儿茶素 | 397.187±41.006a | 455.475±48.453a | 383.830±17.308a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_55 | (-)-儿茶素 | 385.300±6.333a | 328.490±16.378b | 404.035±10.757a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_84 | (-)-Epigallocatechin | 248.105±37.000c | 303.825±4.475b | 393.096±23.182a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_150 | 儿茶素没食子酸酯(-) | 9.069±1.240b | 10.132±0.997b | 12.403±0.370a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_80 | 没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(-) 总含量 | 6.282±1.771b 1 764.726±137.344b (54.41%) | 7.469±0.628b 1 898.014±115.200ab (52.83%) | 10.787±1.140a 2 107.475±103.044a (63.73%) | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_176 | 柚皮素7-O-葡萄糖苷 | 二氢黄酮 | 2.280±0.397a | 2.186±0.387a | 1.484±0.028b | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_126 | Eriodictyol | 0.184±0.026b | 0.263±0.046a | 0.140±0.020b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_78 | 圣草次甙 | 0.043±0.005ab | 0.047±0.014a | 0.026±0.006b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_108 | Pinocembrin | 0.026±0.022a 2.533±0.715a (0.08%) | 0.008±0.001a 2.503±0.631a (0.07%) | 0.016±0.009b 1.665±0.024b (0.05%) | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_01 | 落新妇苷 | 二氢黄酮醇 | 232.382±48.012ab | 262.966±16.701a | 176.495±16.215b | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_117 | 黄杞苷 | 24.027±6.243b | 33.018±2.330a | 16.988±1.595b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_56 | 花旗松素 | 2.236±0.037a | 2.327±0.048a | 1.735±0.226b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_40 | 二氢杨梅素 | 1.369±0.254a | 1.607±0.221a | 0.668±0.070b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_139 | 二氢山奈酚 | 0.240±0.034a | 0.251±0.055a | 0.208±0.019a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_04 | 异水飞蓟宾 总含量 | 0.008±0.001b 260.262±54.785ab (8.03%) | 0.011±0.002a 300.181±18.845a (8.36%) | 0.000±0.000c 196.094±17.889b (5.93%) | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_161 | 地奥司明 | 黄酮 | 82.793±9.443b | 135.293±20.719a | 43.813±5.059c | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_42 | Nicotiflorin | 13.405±2.472b | 20.647±2.846a | 6.015±0.631c | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_118 | 水仙苷 | 2.515±0.464bA | 4.043±0.852a | 1.741±0.480b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_90 | 木犀草苷 | 2.121±0.035a | 1.932±0.411a | 1.790±0.241a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_203 | 柠檬黄素 | 0.928±0.105b | 1.658±0.296a | 0.576±0.179b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_165 | 高车前苷 | 0.217±0.017a | 0.201±0.026a | 0.157±0.014b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_160 | 芹菜素7-葡萄糖苷 | 0.048±0.006a | 0.039±0.016ab | 0.014±0.014b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_187 | Tricetin | 0.025±0.007a | 0.032±0.006a | 0.037±0.012a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_50 | 木犀草素 | 0.007±0.002a | 0.008±0.001a | 0.009±0.004a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_61 | Chrysin | 0.007±0.013a | 0.000±0.000a | 0.001±0.001a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_06 | 香叶木素 总含量 | 0.002±0.001a 102.069±12.266b (3.15%) | 0.003±0.001a 163.857±24.220a (4.56%) | 0.002±0.001a 54.156±5.802c (1.64%) | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_02 | 槲皮素-3-O-葡萄糖醛酸苷 | 黄酮醇 | 705.296±59.981ab | 726.203±15.629a | 645.872±30.336b | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_98 | 金丝桃苷 | 84.123±16.962ab | 100.957±22.073a | 52.459±10.554b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_57 | 芦丁 | 72.699±16.037ab | 86.735±11.412a | 51.383±3.789b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_115 | 槲皮苷 | 42.880±9.875a | 39.482±4.102ab | 29.499±1.936b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_197 | 异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 | 35.671±4.306b | 65.029±19.704a | 19.015±4.202b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_52 | 堪非醇3-新橙皮糖苷 | 5.296±1.359a | 5.693±0.679a | 2.181±0.177b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_119 | 紫云英苷 | 4.158±0.833ab | 6.389±2.894a | 1.958±1.081b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_194 | 槲皮素-7-O-β-D-葡萄糖苷 | 1.165±0.196ab | 1.420±0.329a | 0.878±0.168b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_138 | Baimaside | 0.840±0.196b | 1.627±0.336a | 0.317±0.068c | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_54 | 异鼠李素-3-O-新橙皮苷 | 0.486±0.020a | 0.618±0.124a | 0.205±0.040b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_23 | 槲皮素 | 0.326±0.043b | 0.537±0.090a | 0.285±0.018b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_178 | 杨梅素 | 0.193±0.025b | 0.516±0.169a | 0.124±0.064b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_92 | 杨梅素 | 0.167±0.044b | 0.518±0.199a | 0.063±0.018b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_175 | Afzelin | 0.117±0.050a | 0.134±0.035a | 0.037±0.023b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_58 | 异鼠李素 | 0.092±0.010b | 0.207±0.041a | 0.066±0.003b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_188 | 西伯利亚落叶松黄酮 | 0.000±0.000b | 0.058±0.007a | 0.000±0.000b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_123 | 2'-O-没食子酰基金丝桃苷 总含量 | 0.000±0.000a 953.342±39.099 ab (29.40%) | 0.14±0.024a 1036.137±62.291a (28.84%) | 0.000±0.000a 804.342±39.099b (24.32%) | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_153 | Glycitin | 异黄酮 | 0.614±0.143a | 0.691±0.070a | 0.726±0.065a | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_73 | Genistin | 0.220±0.039a | 0.246±0.095a | 0.147±0.034a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_96 | 毛蕊异黄酮苷 | 0.005±0.005a 0.839±0.185a (0.03%) | 0.000±0.000a 0.937±0.028a (0.03%) | 0.000±0.000a 0.873±0.035a (0.03%) | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_122 | 7-Hydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one | 酚酸类 | 0.396±0.116a | 0.302±0.085a | 0.395±0.050a | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_79 | 女贞苷 | 0.052±0.012a | 0.045±0.010a | 0.031±0.013a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_35 | 丁香醛 总含量 | 0.000±0.000a 0.448±0.124a (0.01%) | 0.000±0.000a 0.347±0.077a (0.01%) | 0.153±0.266a 0.580±0.236a (0.02%) | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_157 | 异芒果苷 | 口山酮 | 0.024±0.004a (0.00%) | 0.021±0.001a (0.00%) | 0.021±0.001a (0.00%) | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_102 | 茶黄素 | - | 27.176±3.262b (0.84%) | 49.820±1.176a (1.39%) | 48.822±5.892a (1.48%) | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_154 | 黄酮碳糖苷 | - | 0.007±0.002a (0.00%) | 0.003±0.001b (0.00%) | 0.009±0.001a (0.00%) | |||||||||||
表 4 不同地面覆盖方式下葡萄果皮黄酮代谢物组分和含量变化
Tab.4 Components and contents of flavonoid metabolites of grape peel by different mulch type(mg/kg)
| 代谢物ID Metabolite ID | 物质 Compound | 二级代谢产物 Class Ⅱ metabolite | 清耕Q (对照,CK) Clean tillage | 园艺地布 Horticultural ground cloth | 生草栽培 Sod-culture | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoid_145 | 原花青素B2 | 花青素 | 113.161±5.062a (3.489%) | 121.677±14.285a (3.387%) | 76.123±7.106b (2.302%) | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_65 | 查耳酮 | 17.546±1.872a | 18.213±2.625a | 15.875±0.745a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_191 | 柚皮素查尔酮 | 0.198±0.058b | 0.345±0.048a | 0.186±0.049b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_202 | 0.703±0.117a | 0.626±0.097a | 0.624±0.016a | |||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_22 | 新橙皮甙二氢查尔酮 | 0.023±0.017ab | 0.039±0.015a | 0.004±0.002b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_31 | 柚皮苷二氢查尔酮 | 0.010±0.004a | 0.011±0.002a | 0.006±0.002a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_177 | 总含量 | 0.008±0.001b 18.848±1.946a (0.57%) | 0.018±0.004a 19.253±2.706a (0.54%) | 0.005±0.001b 16.700±0.683a (0.51%) | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_195 | 没食子儿茶素(-) | 黄烷醇类 | 718.783±77.192b | 792.625±48.743ab | 903.325±68.297a | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_147 | (-)-表儿茶素 | 397.187±41.006a | 455.475±48.453a | 383.830±17.308a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_55 | (-)-儿茶素 | 385.300±6.333a | 328.490±16.378b | 404.035±10.757a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_84 | (-)-Epigallocatechin | 248.105±37.000c | 303.825±4.475b | 393.096±23.182a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_150 | 儿茶素没食子酸酯(-) | 9.069±1.240b | 10.132±0.997b | 12.403±0.370a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_80 | 没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(-) 总含量 | 6.282±1.771b 1 764.726±137.344b (54.41%) | 7.469±0.628b 1 898.014±115.200ab (52.83%) | 10.787±1.140a 2 107.475±103.044a (63.73%) | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_176 | 柚皮素7-O-葡萄糖苷 | 二氢黄酮 | 2.280±0.397a | 2.186±0.387a | 1.484±0.028b | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_126 | Eriodictyol | 0.184±0.026b | 0.263±0.046a | 0.140±0.020b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_78 | 圣草次甙 | 0.043±0.005ab | 0.047±0.014a | 0.026±0.006b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_108 | Pinocembrin | 0.026±0.022a 2.533±0.715a (0.08%) | 0.008±0.001a 2.503±0.631a (0.07%) | 0.016±0.009b 1.665±0.024b (0.05%) | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_01 | 落新妇苷 | 二氢黄酮醇 | 232.382±48.012ab | 262.966±16.701a | 176.495±16.215b | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_117 | 黄杞苷 | 24.027±6.243b | 33.018±2.330a | 16.988±1.595b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_56 | 花旗松素 | 2.236±0.037a | 2.327±0.048a | 1.735±0.226b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_40 | 二氢杨梅素 | 1.369±0.254a | 1.607±0.221a | 0.668±0.070b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_139 | 二氢山奈酚 | 0.240±0.034a | 0.251±0.055a | 0.208±0.019a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_04 | 异水飞蓟宾 总含量 | 0.008±0.001b 260.262±54.785ab (8.03%) | 0.011±0.002a 300.181±18.845a (8.36%) | 0.000±0.000c 196.094±17.889b (5.93%) | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_161 | 地奥司明 | 黄酮 | 82.793±9.443b | 135.293±20.719a | 43.813±5.059c | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_42 | Nicotiflorin | 13.405±2.472b | 20.647±2.846a | 6.015±0.631c | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_118 | 水仙苷 | 2.515±0.464bA | 4.043±0.852a | 1.741±0.480b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_90 | 木犀草苷 | 2.121±0.035a | 1.932±0.411a | 1.790±0.241a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_203 | 柠檬黄素 | 0.928±0.105b | 1.658±0.296a | 0.576±0.179b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_165 | 高车前苷 | 0.217±0.017a | 0.201±0.026a | 0.157±0.014b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_160 | 芹菜素7-葡萄糖苷 | 0.048±0.006a | 0.039±0.016ab | 0.014±0.014b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_187 | Tricetin | 0.025±0.007a | 0.032±0.006a | 0.037±0.012a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_50 | 木犀草素 | 0.007±0.002a | 0.008±0.001a | 0.009±0.004a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_61 | Chrysin | 0.007±0.013a | 0.000±0.000a | 0.001±0.001a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_06 | 香叶木素 总含量 | 0.002±0.001a 102.069±12.266b (3.15%) | 0.003±0.001a 163.857±24.220a (4.56%) | 0.002±0.001a 54.156±5.802c (1.64%) | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_02 | 槲皮素-3-O-葡萄糖醛酸苷 | 黄酮醇 | 705.296±59.981ab | 726.203±15.629a | 645.872±30.336b | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_98 | 金丝桃苷 | 84.123±16.962ab | 100.957±22.073a | 52.459±10.554b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_57 | 芦丁 | 72.699±16.037ab | 86.735±11.412a | 51.383±3.789b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_115 | 槲皮苷 | 42.880±9.875a | 39.482±4.102ab | 29.499±1.936b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_197 | 异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 | 35.671±4.306b | 65.029±19.704a | 19.015±4.202b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_52 | 堪非醇3-新橙皮糖苷 | 5.296±1.359a | 5.693±0.679a | 2.181±0.177b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_119 | 紫云英苷 | 4.158±0.833ab | 6.389±2.894a | 1.958±1.081b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_194 | 槲皮素-7-O-β-D-葡萄糖苷 | 1.165±0.196ab | 1.420±0.329a | 0.878±0.168b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_138 | Baimaside | 0.840±0.196b | 1.627±0.336a | 0.317±0.068c | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_54 | 异鼠李素-3-O-新橙皮苷 | 0.486±0.020a | 0.618±0.124a | 0.205±0.040b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_23 | 槲皮素 | 0.326±0.043b | 0.537±0.090a | 0.285±0.018b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_178 | 杨梅素 | 0.193±0.025b | 0.516±0.169a | 0.124±0.064b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_92 | 杨梅素 | 0.167±0.044b | 0.518±0.199a | 0.063±0.018b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_175 | Afzelin | 0.117±0.050a | 0.134±0.035a | 0.037±0.023b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_58 | 异鼠李素 | 0.092±0.010b | 0.207±0.041a | 0.066±0.003b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_188 | 西伯利亚落叶松黄酮 | 0.000±0.000b | 0.058±0.007a | 0.000±0.000b | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_123 | 2'-O-没食子酰基金丝桃苷 总含量 | 0.000±0.000a 953.342±39.099 ab (29.40%) | 0.14±0.024a 1036.137±62.291a (28.84%) | 0.000±0.000a 804.342±39.099b (24.32%) | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_153 | Glycitin | 异黄酮 | 0.614±0.143a | 0.691±0.070a | 0.726±0.065a | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_73 | Genistin | 0.220±0.039a | 0.246±0.095a | 0.147±0.034a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_96 | 毛蕊异黄酮苷 | 0.005±0.005a 0.839±0.185a (0.03%) | 0.000±0.000a 0.937±0.028a (0.03%) | 0.000±0.000a 0.873±0.035a (0.03%) | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_122 | 7-Hydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one | 酚酸类 | 0.396±0.116a | 0.302±0.085a | 0.395±0.050a | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_79 | 女贞苷 | 0.052±0.012a | 0.045±0.010a | 0.031±0.013a | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_35 | 丁香醛 总含量 | 0.000±0.000a 0.448±0.124a (0.01%) | 0.000±0.000a 0.347±0.077a (0.01%) | 0.153±0.266a 0.580±0.236a (0.02%) | ||||||||||||
| Flavonoid_157 | 异芒果苷 | 口山酮 | 0.024±0.004a (0.00%) | 0.021±0.001a (0.00%) | 0.021±0.001a (0.00%) | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_102 | 茶黄素 | - | 27.176±3.262b (0.84%) | 49.820±1.176a (1.39%) | 48.822±5.892a (1.48%) | |||||||||||
| Flavonoid_154 | 黄酮碳糖苷 | - | 0.007±0.002a (0.00%) | 0.003±0.001b (0.00%) | 0.009±0.001a (0.00%) | |||||||||||
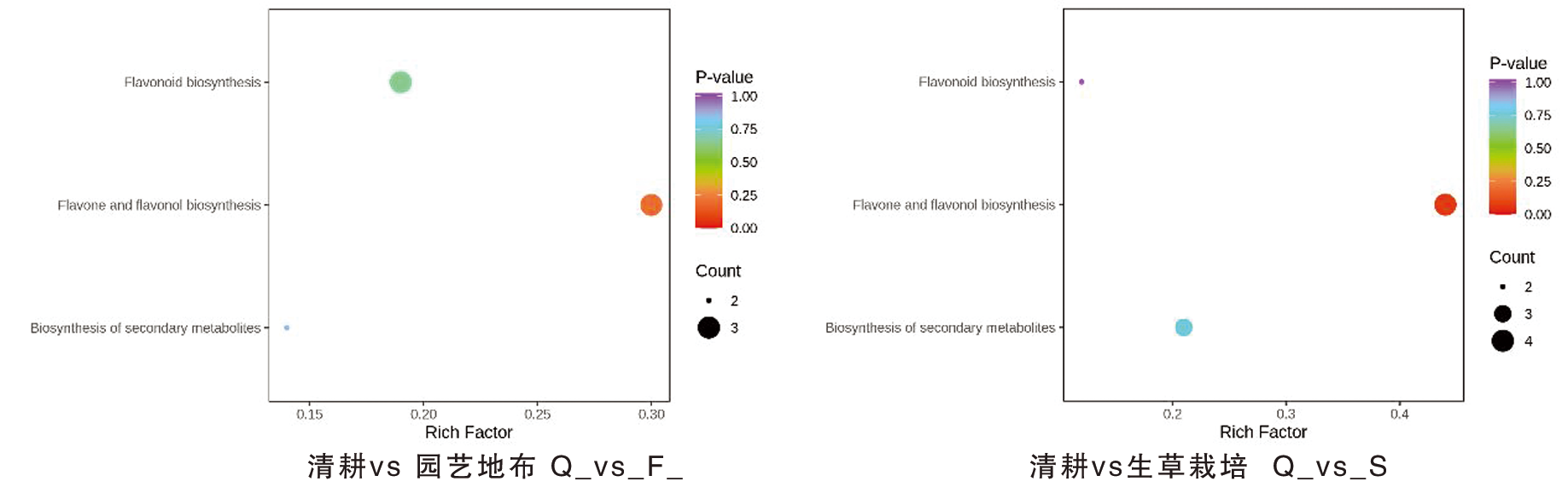
图5 不同地面覆盖方式下葡萄果皮差异代谢物KEGG富集图 注(Note):纵坐标表示每个通路对应的Rich factor,纵坐标为通路名称,点的颜色为P value,越红表示富集越显著。点的大小代表富集到的差异代谢物的个数多少(The ordinate represents the Rich factor corresponding to each pathway,the ordinate represents the pathway name,and the color of the point is P value. The redder indicates the more significant enrichment. The size of the dot represents the number of enriched differential metabolites);类黄酮生物合成(Flavonoid biosynthesis); 黄酮和黄烷醇代谢物生物合成(Flavone and flavonol biosynthesis); 次级代谢物生物合成(Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites)
Fig.5 KEGG enrichment map of differential metabolites of grape peel by different mulch type
| 序号 No. | 清耕vs园艺地布Q_vs_F Clean tillage vs Horticultural ground cloth Q_vs_F | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物合成途径 Biosynthesis | 名称 Name | 缩写 Abbreviations | KEGG注释到 unigene数量 KEGG notes the number of unigene | 备注 Note | |
| 1 | 类黄酮代谢生物合成 | 反式肉桂酸-4-单加氧酶 | CYP73A(C4H) | 1 | 上调 |
| 2 | 查尔酮合成酶 | CHS | 6 | 上调 | |
| 3 | 黄酮-3-脱氢酶 | F3H | 6 | 上调 | |
| 4 | 无色花色素还原酶 | LAR | 3 | 上调 | |
| 5 | 莽草酸羟基肉桂酰基转移酶 | HCT | 4 | 上调和下调 | |
| 6 | 黄酮醇合成酶 | FLS | 4 | 上调和下调 | |
| 7 | 黄烷酮-7-氧-葡萄糖苷 2″-氧-β-L-鼠李糖基转移酶 | C12RT1 | 2 | 下调 | |
| 8 | 黄酮和黄酮醇生物合成 | 黄烷酮-7-氧-葡萄糖苷 2″-氧-β-L-鼠李糖基转移酶 | C12RT1 | 2 | 下调 |
| 序号 No. | 清耕vs生草栽培Q_vs_S Clean tillage vs Sod-culture Q_vs_S | ||||
| 1 | 类黄酮代谢生物合成 | 查尔酮合成酶 | CHS | 6 | 下调 |
| 2 | 黄酮-3-脱氢酶 | F3H | 6 | 下调 | |
| 3 | 类黄酮3',5'异构酶 | CYP75A(F3',5'H) | 8 | 下调 | |
| 4 | 黄酮醇合成酶 | FLS | 3 | 下调 | |
| 5 | 无色花色素还原酶 | LAR | 3 | 下调 | |
| 6 | 黄酮和黄酮醇生物合成 | 类黄酮3',5'异构酶 | CYP75A(F3',5'H) | 3 | 下调 |
表5 新郁葡萄果皮黄酮生物合成途径中候选基因
Tab.5 Candidate gene involved in flavonoid biosynthesis pathway in Xinyu grape peel
| 序号 No. | 清耕vs园艺地布Q_vs_F Clean tillage vs Horticultural ground cloth Q_vs_F | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物合成途径 Biosynthesis | 名称 Name | 缩写 Abbreviations | KEGG注释到 unigene数量 KEGG notes the number of unigene | 备注 Note | |
| 1 | 类黄酮代谢生物合成 | 反式肉桂酸-4-单加氧酶 | CYP73A(C4H) | 1 | 上调 |
| 2 | 查尔酮合成酶 | CHS | 6 | 上调 | |
| 3 | 黄酮-3-脱氢酶 | F3H | 6 | 上调 | |
| 4 | 无色花色素还原酶 | LAR | 3 | 上调 | |
| 5 | 莽草酸羟基肉桂酰基转移酶 | HCT | 4 | 上调和下调 | |
| 6 | 黄酮醇合成酶 | FLS | 4 | 上调和下调 | |
| 7 | 黄烷酮-7-氧-葡萄糖苷 2″-氧-β-L-鼠李糖基转移酶 | C12RT1 | 2 | 下调 | |
| 8 | 黄酮和黄酮醇生物合成 | 黄烷酮-7-氧-葡萄糖苷 2″-氧-β-L-鼠李糖基转移酶 | C12RT1 | 2 | 下调 |
| 序号 No. | 清耕vs生草栽培Q_vs_S Clean tillage vs Sod-culture Q_vs_S | ||||
| 1 | 类黄酮代谢生物合成 | 查尔酮合成酶 | CHS | 6 | 下调 |
| 2 | 黄酮-3-脱氢酶 | F3H | 6 | 下调 | |
| 3 | 类黄酮3',5'异构酶 | CYP75A(F3',5'H) | 8 | 下调 | |
| 4 | 黄酮醇合成酶 | FLS | 3 | 下调 | |
| 5 | 无色花色素还原酶 | LAR | 3 | 下调 | |
| 6 | 黄酮和黄酮醇生物合成 | 类黄酮3',5'异构酶 | CYP75A(F3',5'H) | 3 | 下调 |
| [1] | 骆强伟, 孙锋, 蔡军社, 等. 葡萄新品种新郁[J]. 园艺学报, 2007, 34(3):797. |
| LUO Qiangwei, SUN Feng, CAI Junshe, et al. A new grape variety Xinyu[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2007, 34(3):797. | |
| [2] |
Morimoto M, Tanimoto K, Nakano S, et al. Insect antifeedant activity of flavones and chromones against Spodoptcra litura[J]. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 2003, 51(2):389-393.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
张波, 韩舜愈, 马腾臻, 等. 红葡萄酒中花色苷衍生物结构研究进展[J]. 食品科学, 2018, 39(5):284-295.
DOI |
|
ZHANG Bo, HAN Shunyu, MA Tengzhen, et al. Progress in understanding structures of anthocyanins derivatives in red wines[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(5):284-295.
DOI |
|
| [4] |
Cook N C, Samman S. Flavonoids-Chemistry,metabolism,cardioprotective effects,and dietary sources[J]. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 1996, 7(2):66-76.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Springob K, Nakajima J I, Yamazaki M, et al. Recent advances in the biosynthesis and accumulation of anthocyanins[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2003, 20(3):288-303..
DOI PMID |
| [6] | 赵德英. 梨园树盘覆盖的土壤生态效应及树体生理响应研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2013. |
| ZHAO Deying. Study on the soil ecological effects and physiological response in different ground cover pear tree[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2013. | |
| [7] |
罗玲, 钟奇, 王进, 等. 不同覆盖材料对避雨栽培葡萄园土壤微生物特征及葡萄生长与品质的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2021, 35(2):471-480.
DOI |
|
LUO Ling, ZHONG Qi, WANG Jin, et al. Influence of Different Mulching Materials on Soil Microbe and Grape Growth in Rai-Shelter Vineyard[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 35(2):471-480.
DOI |
|
| [8] | 刘思, 王志磊, 张军翔. 葡萄行内覆盖对园区微域生态环境及果实品质的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(6):73-79,88. |
| LIU Si, WANG Zhilei, ZHANG Junxiang. Effects of within-row mulching on soil microsites in vineyard and fruit quality[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(6):73-79,88. | |
| [9] | 侯婷, 闫鹏科, 庞群虎, 等. 行内覆盖对果园土壤特性及酿酒葡萄产量和品质的影响[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2019, 53(6):869-875. |
| HOU Ting, YAN Pengke, PANG Qunhu, et al. Effects of intra-row coverage on orchard soil features and wine grape yield and quality[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 2019, 53(6):869 - 875. | |
| [10] | 王锐, 闫鹏科, 马婷慧, 等. 行内生草对土壤微环境和酿酒葡萄品质的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2020, 38(3):195-203. |
| WANG Rui, YAN Pengke, MA Tinghui, et al. Effects of intra-row planted grass on soil microenvironment and wine grape quality[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2020, 38(3):195-203. | |
| [11] |
Rai A, Saito K, Yamazaki M. Integrated omics analysis of specialized metabolism in medicinal plants[J]. The Plant Journal, 2017, 90(4):764-787.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | 张少平, 邱珊莲, 张帅, 等. 紫背天葵叶片中花青素种类及合成调控基因转录组分析[J]. 西北植物学报, 2019, 39(5):808-816. |
| ZHANG Shaoping, QIU Shanlian, ZHANG Shuai, et al. Transcriptome analysis of anthocyanidins and their synthesis regulatory genes in Gynura bicolor leaves[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2019, 39(5):808-816. | |
| [13] |
卢素文, 郑暄昂, 王佳洋, 等. 葡萄类黄酮代谢研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(12):2506-2524.
DOI |
|
LU Suwen, ZHENG Xuanang, WANG Jiayang, et al. Research progress on the metabolism of flavonoids in grape[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(12):2506-2524.
DOI |
|
| [14] | 刘伟, 王俊燚, 李萌, 等. 基于转录组测序的银杏类黄酮生物合成关键基因表达分析[J]. 中草药, 2018, 49(23):5633-5639. |
| LIU Wei, WANG Junyi, LI Meng, et al. Transcriptome sequencing analysis of gene expression of flavonoid biosynthesis in Ginkgo biloba[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2018, 49(23):5633-5639. | |
| [15] | 姚运法, 张少平, 练冬梅, 等. 黄秋葵花和果荚转录组测序及类黄酮代谢差异表达分析[J]. 西北植物学报, 2018, 38(11):2000-2009. |
| YAO Yunfa, ZHANG Shaoping, LIAN Dongmei, et al. Transcriptome sequencing and differential expression analysis of flavonoid metabolism in flowers and fruits of Okra[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2018, 38(11):2000-2009. | |
| [16] | 陈为凯. 一年两收栽培模式下葡萄果实靶向代谢组和转录组研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2018. |
| CHEN Weikai. Study of targeted metabolome and transcriptome in grape berries grown under double cropping viticulture system[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| [17] |
Petrussa E, Braidot E, Zancani M, et al. Plant flavonoids-biosynthesis,transport and involvement in stress responses[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2013, 14(7):14950-14973.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Gouot J C, Smith J P, Holzapfel B P, et al. Grape berry flavonoids:A review of their biochemical responses to high and extreme high temperature[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2019, 70(2):397-423.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ØM Andersen, Markham K R, ØM Andersen, et al. Flavonoids. Chemistry,biochemistry and application[J]. Pesticide Science, 2006, 7(3):223-224.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Williams Christine A, Grayer Renée J. Anthocyanins and other flavonoids[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2004, 21(4):539-573.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Iwashina T. The structure and distribution of the flavonoids in plant[J]. Journal of Plant Research, 2000, 113:287-299.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
赵婷, 吴佳颖, 陈黄曌, 等. 延迟采收对酿酒葡萄类黄酮物质的影响[J]. 食品科学, 2019, 40(14):229-235.
DOI |
|
ZHAO Ting, WU Jiaying, CHEN Huangzhao, et al. Influence of Delayed Harvest on Flavonoids Compounds of Vitis vinifera Grape[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(14):229-235.
DOI |
|
| [23] |
Nilgün, Göktürk, Baydar, et al. Total phenolic contents and antibacterial activities of grape(Vitis vinifera L.) extracts[J]. Food Control, 2004, 15(5):335-339.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Hu J G, Bai S J, Zhao R H, et al. Effects of black geotextile much and grass mulch on the microclimate,fruit quality and anthocyanin components of ‘Xinyu’ table grape[J]. New Zealand Journal of Crop and Horticultural Science, 2022,1-18. |
| [25] |
Wang Y, Gao X, Li H, et al. Microclimate changes caused by black inter-row mulch decreased flavonoids concentrations in grapes and wines under semi-arid climate[J]. Food Chemistry, 2021, 361:130064.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Rienth M, Vigneron N, Darriet P, et al. Grape berry secondary metabolites and their modulation by abiotic factors in a climate change scenario-a review[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021,643258. |
| [27] |
Forkmann G. Flavonoids as flower pigments:the formation of natural spectrum and its extension by genetic engineering[J]. Plant Breeding, 1991, 106(1):1-26.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Pelletier M K, Murrell J R, Shirley B W. Characterization of flavonol synthase and leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase genes in Arabidopsis(further evidence for differential regulation of early and late genes[J]. Plant Physiology, 1997, 113(4):1437-1445.
PMID |
| [29] |
Quattrocchio F, Wing J F, Leppen H T C, et al. Regulatory genes controlling anthocyanin pigmentation are functionally conserved among plant species and have distinct sets of garget genes[J]. The Plant Cell, 1993, 5(11):1497-1512.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Kubasek W L, Shirley B W, Mckillop A, et al. Regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis genes in germinating Arabidopsis seedlings[J]. Plant Cell, 1992, 4(10):1229-1236.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Pelletier M K, Shirley B W. Analysis of flavanone 3-hydroxylase in Arabidopsis seedling(Coordinate regulation with chalcone synthase and chalcone isomerase)[J]. Plant Physiology, 1996, 111(1):339-345.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
戴思兰, 洪艳. 基于花青素合成和成色机理的观赏植物花色改良分子育种[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(3):529-542.
DOI |
|
DAI Silan, HONG Yan. Molecular breeding for flower colors modification on ornamental plants based on the mechanism of anthocyanins biosynthesis and coloration[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(3):529-542.
DOI |
|
| [33] | Das K, Roychoudhury A. Reactive oxygen species(ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2014, 2:53. |
| [34] |
Gaiotti F, Pastore C, Fillippetti I, et al. Low night temperature at veraison enhances the accumulation of anthocyanins in Corvina grapes(Vitis vinifera L.)[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1):8719.
DOI |
| [35] | Mori K, Goto-Yamamoto N, Kitayama M, et al. Effect of high temperature on anthocyanin composition and transcription of flavonoid hydroxylase genes in ‘Pinot noir’ grapes(Vitis vinifera). The Journal of Horticulture Science and Biotechnology, 2007, 82(2):199-206. |
| [1] | 鞠乐, 齐军仓, 牛银亭, 石培春, 宋瑞娇, 宋凌宇, 阴志刚, 陈培育, 强学兰. 基于RNA-seq的大麦苗期抗旱相关基因的挖掘与分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(5): 1077-1084. |
| [2] | 户金鸽, 白世践, 陈光, 蔡军社. 不同地面覆盖方式对酿酒葡萄品种马瑟兰果实品质的影响及综合评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(5): 1131-1139. |
| [3] | 林青, 时红玲, 秦新政, 李月, 王子涵, 高雁, 曾军, 王浩中, 娄恺, 霍向东. 基于非靶向代谢组学分析两种酵母培养物的成分差异[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(5): 1218-1226. |
| [4] | 何婉洁, 孟涵颖, 支梦婷, 陈静. 双斑长跗萤叶甲雌虫、雄虫触角转录组及差异表达基因分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 984-995. |
| [5] | 陈沛, 鲍军秀, 王斐, 汤寿伍, 刘海峰, 李鸿彬. 响应面优化超声提取绿色棉纤维总黄酮[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(3): 576-583. |
| [6] | 朱夏芬, 何伟, 罗文芳, 周军辉, 李克梅, 许建军. 基于防御酶与代谢组学分析贝莱斯芽孢杆菌JTB8-2诱导番茄拮抗瓜列当机制[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(10): 2396-2407. |
| [7] | 束佳敏, 郭元印, 卫丁一, 刘浩然, 依斯马依力, 黄磊, 何子涵, 姚刚, 戴小华. 野山杏总黄酮对LPS诱导鸡肝炎的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 2066-2073. |
| [8] | 韦伟, 单守明, 徐文娣, 李光宗. 山葡萄‘双优’组织培养生根期愈伤组织的转录组分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1451-1459. |
| [9] | 李硕, 王娟, 尼格尔热依·亚迪卡尔, 朱金芳, 冯作山, 帕尔哈提·艾尼瓦尔. 不同品种杏果实不同发育期功能性成分变化规律[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(5): 1200-1207. |
| [10] | 宋金迪, 刘君, 孙玉芳, 优丽图孜·乃比, 陈宝强, 颉兵兵. 铜胁迫下的西瓜食酸菌转录组分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(2): 389-398. |
| [11] | 张仕琦, 李晓斌, 张文杰, 韩明, 王世昌, 郑文祥, 欧阳文, 祁居中, 杨开伦. 基于LC/MS的伊犁马3 600 m速度赛赛前、赛后血浆代谢组学差异变化[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(2): 501-510. |
| [12] | 王威, 徐乐, 樊艳星, 王帆, 马艳明, 唐中华. 鹰嘴豆种子代谢产物的GC-MS分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(12): 2962-2972. |
| [13] | 兖攀, 王久照, 姜继元, 陈奇凌. 不同地面覆盖材料对绿洲苹果园土壤环境的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(7): 1690-1696. |
| [14] | 金科旭, 戴小华, 谷虹霏, 束佳敏, 王天琪, 海婷玉. 大孔树脂纯化野山杏总黄酮工艺[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(4): 900-907. |
| [15] | 杨永, 范蓉, 张学军, 李寐华, 凌悦铭, 张红, 杨文莉, 姜雪, 张永兵, 伊鸿平. 厚皮甜瓜心部果肉蔗糖含量QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(10): 2446-2455. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 70
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 329
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||