

新疆农业科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (2): 474-484.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2022.02.026
顾美英1( ), 徐万里2(
), 徐万里2( ), 马凯3, 欧提库尔·玛合木提1, 张志东1, 朱静1, 唐琦勇1, 楚敏1, 张丽娟1
), 马凯3, 欧提库尔·玛合木提1, 张志东1, 朱静1, 唐琦勇1, 楚敏1, 张丽娟1
收稿日期:2021-02-10
出版日期:2022-02-20
发布日期:2022-03-22
通信作者:
徐万里(1971- ),男,陕西宝鸡人,研究员,研究方向为土壤环境与生态,(E-mail) 363954019@qq.com作者简介:顾美英(1974- ),女,江苏无锡人,研究员,研究方向为土壤微生物生态,(E-mail) gmyxj2008@163.com
基金资助:
GU Meiying1( ), XU Wanli2(
), XU Wanli2( ), MA Kai3, Otkur Mahmut1, ZHANG Zhidong1, ZHU Jing1, TANG Qiyong1, CHU Min1, ZHANG Lijuan1
), MA Kai3, Otkur Mahmut1, ZHANG Zhidong1, ZHU Jing1, TANG Qiyong1, CHU Min1, ZHANG Lijuan1
Received:2021-02-10
Published:2022-02-20
Online:2022-03-22
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】 评价新疆南疆不同定植年限核桃土壤微生物生态,为分析核桃园土壤退化问题及研究区域土壤微生物生态健康的研究提供参考。【方法】 采用时空互代法,以叶城地区核桃树为研究对象,分析土壤理化性质、微生物数量和土壤酶活性等微生物生态特征在时间(5、8~10、15、20~25 年的定植年限)和空间(0~20 cm和20~40 cm土层)上的变化规律,并采用主成分-聚类分析进行评价。【结果】 随着核桃定植年限的延长,0~20 cm和20~40 cm土壤pH总体呈酸化趋势。土壤总盐和除速效磷外的其余养分含量有明显表聚现象,全氮和有机质含量呈先降低后升高趋势。土壤可培养细菌、放线菌和真菌数量也存在表聚现象,随着核桃定植年限延长,土壤细菌数量呈先升高后降低趋势,放线菌和真菌数量有增长趋势。脲酶和蔗糖酶活性均随土层深度的增加总体降低,但不同定植年限没有明显的变化规律。0~20 cm土壤微生物生态综合得分排名为核桃定植15年>20~25年>8~10年>5年;20~40 cm土壤为核桃定植20~25年>8~10年>15年>5年。【结论】 5年定植的核桃土壤微生物生态条件最差;0~20 cm表层定植15年、20~40 cm亚表层定植20~25年核桃土壤微生物生态条件最好。
中图分类号:
顾美英, 徐万里, 马凯, 欧提库尔·玛合木提, 张志东, 朱静, 唐琦勇, 楚敏, 张丽娟. 基于主成分-聚类分析评价不同定植年限核桃土壤微生物生态[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(2): 474-484.
GU Meiying, XU Wanli, MA Kai, Otkur Mahmut, ZHANG Zhidong, ZHU Jing, TANG Qiyong, CHU Min, ZHANG Lijuan. Soil Microbial Ecological Evaluation of Walnut with Different Planting Years Based on Principal Component-Cluster Analysis[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(2): 474-484.
| 样品 Sample | pH | 总盐 Total salt (g/kg) | 全氮 Total N (g/kg) | 有机质 OM (g/kg) | 速效氮 Available N (mg/kg) | 速效磷 Available P (mg/kg) | 速效钾 Available K (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a-1 | 8.47±0.03a | 1.50±0.01b | 0.88±0.03a | 12.34±0.15ab | 70.50±0.85b | 5.50±0.53c | 80.00±2.03d |
| b-1 | 8.53±0.04a | 2.00±0.00a | 0.45±0.01b | 8.78±0.23c | 66.00±1.02b | 9.40±0.19b | 117.00±5.34c |
| c-1 | 8.39±0.01a | 1.40±0.01b | 0.75±0.05a | 14.04±0.31a | 99.00±0.73a | 12.80±0.69a | 203.00±7.69a |
| d-1 | 8.41±0.02a | 0.90±0.01c | 1.00±0.02a | 14.51±0.09a | 72.00±0.89b | 6.60±0.71c | 165.00±6.03b |
| a-2 | 8.26±0.01b | 1.40±0.00a | 0.45±0.01a | 7.01±0.18b | 49.50±1.12b | 7.60±0.32b | 82.00±5.47b |
| b-2 | 8.53±0.03a | 1.30±0.01a | 0.38±0.04b | 7.00±0.44b | 189.00±2.36a | 14.80±0.58a | 59.00±2.18c |
| c-2 | 8.49±0.03a | 1.40±0.02a | 0.43±0.01a | 7.65±0.27b | 49.50±0.99b | 12.40±0.81a | 130.00±8.92a |
| d-2 | 8.41±0.02a | 1.30±0.00a | 0.56±0.03a | 9.75±0.14a | 52.50±0.84b | 6.70±0.43b | 136.00±7.05a |
表1 不同定植年限下核桃土壤理化性质变化
Table 1 Effect of different planting years on soil physical and chemical properties in walnut
| 样品 Sample | pH | 总盐 Total salt (g/kg) | 全氮 Total N (g/kg) | 有机质 OM (g/kg) | 速效氮 Available N (mg/kg) | 速效磷 Available P (mg/kg) | 速效钾 Available K (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a-1 | 8.47±0.03a | 1.50±0.01b | 0.88±0.03a | 12.34±0.15ab | 70.50±0.85b | 5.50±0.53c | 80.00±2.03d |
| b-1 | 8.53±0.04a | 2.00±0.00a | 0.45±0.01b | 8.78±0.23c | 66.00±1.02b | 9.40±0.19b | 117.00±5.34c |
| c-1 | 8.39±0.01a | 1.40±0.01b | 0.75±0.05a | 14.04±0.31a | 99.00±0.73a | 12.80±0.69a | 203.00±7.69a |
| d-1 | 8.41±0.02a | 0.90±0.01c | 1.00±0.02a | 14.51±0.09a | 72.00±0.89b | 6.60±0.71c | 165.00±6.03b |
| a-2 | 8.26±0.01b | 1.40±0.00a | 0.45±0.01a | 7.01±0.18b | 49.50±1.12b | 7.60±0.32b | 82.00±5.47b |
| b-2 | 8.53±0.03a | 1.30±0.01a | 0.38±0.04b | 7.00±0.44b | 189.00±2.36a | 14.80±0.58a | 59.00±2.18c |
| c-2 | 8.49±0.03a | 1.40±0.02a | 0.43±0.01a | 7.65±0.27b | 49.50±0.99b | 12.40±0.81a | 130.00±8.92a |
| d-2 | 8.41±0.02a | 1.30±0.00a | 0.56±0.03a | 9.75±0.14a | 52.50±0.84b | 6.70±0.43b | 136.00±7.05a |
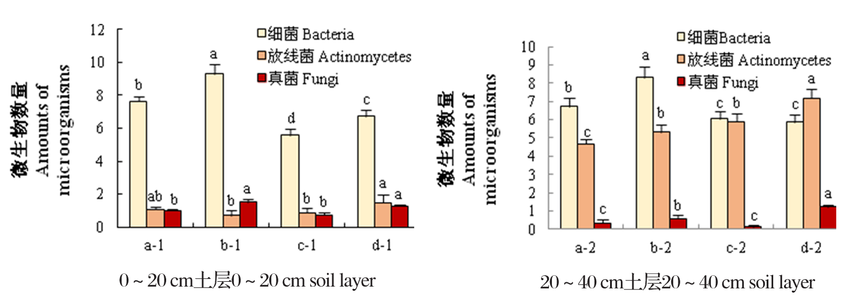
图1 不同定植年限下核桃土壤微生物数量变化 注(Note):细菌Bacteria ( 107 CFU/g,放线菌 Actinomycetes(106CFU/g,真菌 Fungi (104CFU/g)
Fig.1 Effect of different planting years on soil microorganism quantities in walnut
| 土层 Soil layer | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | pH | 总盐 Total salt | 全氮 Total N | 有机质 OM | 速效氮 Available N | 速效磷 Available P | 速效钾 Available K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~20 cm | Bacteria | 0.982** | 0.711 | -0.628 | -0.921** | -0.841* | -0.362 | -0.744 |
| Actinomycetes | -0.521 | -0.916** | 0.906** | 0.709 | -0.173 | -0.608 | 0.103 | |
| Fungi | 0.720 | 0.315 | -0.398 | -0.655 | -0.849* | -0.383 | -0.415 | |
| Urease | 0.683 | 0.228 | 0.038 | -0.455 | -0.898* | -0.878* | -0.956** | |
| Invertase | -0.546 | -0.174 | -0.160 | 0.311 | 0.732 | 0.860* | 0.955** | |
| 20~40 cm | Bacteria | 0.336 | -0.361 | -0.734 | -0.658 | 0.937** | 0.680 | -0.935** |
| Actinomycetes | 0.326 | -0.526 | 0.740 | 0.948** | -0.255 | -0.304 | 0.774 | |
| Fungi | 0.023 | -0.824* | 0.747 | 0.814* | 0.055 | -0.456 | 0.256 | |
| Urease | 0.475 | -0.784 | 0.598 | 0.856* | 0.081 | -0.121 | 0.507 | |
| Invertase | -0.831* | 0.426 | -0.134 | -0.515 | -0.124 | -0.361 | -0.546 |
表2 土壤微生物生态因子间的相关性
Table 2 Pearson correlation coefficients among soil microbial ecology
| 土层 Soil layer | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | pH | 总盐 Total salt | 全氮 Total N | 有机质 OM | 速效氮 Available N | 速效磷 Available P | 速效钾 Available K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~20 cm | Bacteria | 0.982** | 0.711 | -0.628 | -0.921** | -0.841* | -0.362 | -0.744 |
| Actinomycetes | -0.521 | -0.916** | 0.906** | 0.709 | -0.173 | -0.608 | 0.103 | |
| Fungi | 0.720 | 0.315 | -0.398 | -0.655 | -0.849* | -0.383 | -0.415 | |
| Urease | 0.683 | 0.228 | 0.038 | -0.455 | -0.898* | -0.878* | -0.956** | |
| Invertase | -0.546 | -0.174 | -0.160 | 0.311 | 0.732 | 0.860* | 0.955** | |
| 20~40 cm | Bacteria | 0.336 | -0.361 | -0.734 | -0.658 | 0.937** | 0.680 | -0.935** |
| Actinomycetes | 0.326 | -0.526 | 0.740 | 0.948** | -0.255 | -0.304 | 0.774 | |
| Fungi | 0.023 | -0.824* | 0.747 | 0.814* | 0.055 | -0.456 | 0.256 | |
| Urease | 0.475 | -0.784 | 0.598 | 0.856* | 0.081 | -0.121 | 0.507 | |
| Invertase | -0.831* | 0.426 | -0.134 | -0.515 | -0.124 | -0.361 | -0.546 |
| 土层 Soil layer | 因子 Factor | 因子载荷Factor loadings | 特征向量Eigenvectors of matrix | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | ||
| 0~20 cm | Bacteria | -0.977** | 0.119 | 0.174 | -0.370 | 0.060 | 0.171 |
| Actinomycetes | 0.336 | -0.890* | 0.307 | 0.127 | -0.446 | 0.301 | |
| Fungi | -0.741 | -0.052 | 0.670 | -0.280 | -0.026 | 0.655 | |
| pH | -0.975** | 0.223 | 0.015 | -0.369 | 0.112 | 0.015 | |
| Total salt | -0.685 | 0.690 | -0.233 | -0.259 | 0.346 | -0.228 | |
| Total N | 0.524 | -0.848* | -0.081 | 0.198 | -0.425 | -0.079 | |
| OM | 0.875 | -0.483 | -0.048 | 0.331 | -0.242 | -0.047 | |
| Available N | 0.862* | 0.422 | -0.282 | 0.326 | 0.212 | -0.276 | |
| Available P | 0.483 | 0.875* | 0.029 | 0.183 | 0.439 | 0.029 | |
| Available K | 0.868* | 0.338 | 0.365 | 0.328 | 0.169 | 0.357 | |
| Urease | -0.827* | -0.541 | -0.152 | -0.313 | -0.271 | -0.149 | |
| Invertase | 0.700 | 0.582 | 0.414 | 0.265 | 0.292 | 0.405 | |
| 20~40 cm | Bacteria | -0.735 | 0.567 | 0.373 | -0.295 | 0.284 | 0.275 |
| Actinomycetes | 0.940** | 0.313 | -0.133 | 0.378 | 0.157 | -0.099 | |
| Fungi | 0.748 | 0.340 | 0.570 | 0.301 | 0.171 | 0.421 | |
| pH | -0.014 | 0.883* | -0.469 | -0.006 | 0.443 | -0.347 | |
| Total salt | -0.367 | -0.788 | -0.494 | -0.148 | -0.395 | -0.365 | |
| Total N | 0.919** | -0.283 | 0.273 | 0.369 | -0.142 | 0.202 | |
| OM | 0.994** | 0.076 | 0.078 | 0.399 | 0.038 | 0.058 | |
| Available N | -0.505 | 0.819* | 0.271 | -0.203 | 0.411 | 0.200 | |
| Available P | -0.608 | 0.681 | -0.409 | -0.244 | 0.341 | -0.302 | |
| Available K | 0.833* | -0.243 | -0.497 | 0.335 | -0.122 | -0.368 | |
| Urease | 0.812* | 0.581 | 0.056 | 0.326 | 0.291 | 0.042 | |
| Invertase | -0.512 | -0.652 | 0.559 | -0.206 | -0.327 | 0.413 | |
表3 因子载荷与特征向量
Table 3 Factor loadings and eigenvectors of matrix
| 土层 Soil layer | 因子 Factor | 因子载荷Factor loadings | 特征向量Eigenvectors of matrix | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | ||
| 0~20 cm | Bacteria | -0.977** | 0.119 | 0.174 | -0.370 | 0.060 | 0.171 |
| Actinomycetes | 0.336 | -0.890* | 0.307 | 0.127 | -0.446 | 0.301 | |
| Fungi | -0.741 | -0.052 | 0.670 | -0.280 | -0.026 | 0.655 | |
| pH | -0.975** | 0.223 | 0.015 | -0.369 | 0.112 | 0.015 | |
| Total salt | -0.685 | 0.690 | -0.233 | -0.259 | 0.346 | -0.228 | |
| Total N | 0.524 | -0.848* | -0.081 | 0.198 | -0.425 | -0.079 | |
| OM | 0.875 | -0.483 | -0.048 | 0.331 | -0.242 | -0.047 | |
| Available N | 0.862* | 0.422 | -0.282 | 0.326 | 0.212 | -0.276 | |
| Available P | 0.483 | 0.875* | 0.029 | 0.183 | 0.439 | 0.029 | |
| Available K | 0.868* | 0.338 | 0.365 | 0.328 | 0.169 | 0.357 | |
| Urease | -0.827* | -0.541 | -0.152 | -0.313 | -0.271 | -0.149 | |
| Invertase | 0.700 | 0.582 | 0.414 | 0.265 | 0.292 | 0.405 | |
| 20~40 cm | Bacteria | -0.735 | 0.567 | 0.373 | -0.295 | 0.284 | 0.275 |
| Actinomycetes | 0.940** | 0.313 | -0.133 | 0.378 | 0.157 | -0.099 | |
| Fungi | 0.748 | 0.340 | 0.570 | 0.301 | 0.171 | 0.421 | |
| pH | -0.014 | 0.883* | -0.469 | -0.006 | 0.443 | -0.347 | |
| Total salt | -0.367 | -0.788 | -0.494 | -0.148 | -0.395 | -0.365 | |
| Total N | 0.919** | -0.283 | 0.273 | 0.369 | -0.142 | 0.202 | |
| OM | 0.994** | 0.076 | 0.078 | 0.399 | 0.038 | 0.058 | |
| Available N | -0.505 | 0.819* | 0.271 | -0.203 | 0.411 | 0.200 | |
| Available P | -0.608 | 0.681 | -0.409 | -0.244 | 0.341 | -0.302 | |
| Available K | 0.833* | -0.243 | -0.497 | 0.335 | -0.122 | -0.368 | |
| Urease | 0.812* | 0.581 | 0.056 | 0.326 | 0.291 | 0.042 | |
| Invertase | -0.512 | -0.652 | 0.559 | -0.206 | -0.327 | 0.413 | |
| 土层 Soil layer | 样品 Sample | 第一主成分(F1) The primary principal component | 第二主成分(F2) The secondary principal component | 第三主成分(F3) The third principal component | 综合得分 Integrative value | 排名Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~20 cm | a-1 | -0.792 | -0.498 | -0.106 | -1.396 | 4 |
| b-1 | -1.673 | 0.576 | 0.049 | -1.048 | 3 | |
| c-1 | 1.785 | 0.565 | -0.037 | 2.313 | 1 | |
| d-1 | 0.68 | -0.643 | 0.094 | 0.131 | 2 | |
| 20~40 cm | a-2 | -0.781 | -0.803 | 0.131 | -1.453 | 4 |
| b-2 | -1.005 | 0.805 | 0.081 | -0.119 | 2 | |
| c-2 | -0.036 | -0.1 | -0.307 | -0.443 | 3 | |
| d-2 | 1.823 | 0.098 | 0.095 | 2.016 | 1 |
表4 不同定植年限核桃土壤在PC1、PC2和PC3上的综合得分
Fig.4 Comprehensive scores of walnut soil on PC1、PC2 and PC3 with different planting years
| 土层 Soil layer | 样品 Sample | 第一主成分(F1) The primary principal component | 第二主成分(F2) The secondary principal component | 第三主成分(F3) The third principal component | 综合得分 Integrative value | 排名Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~20 cm | a-1 | -0.792 | -0.498 | -0.106 | -1.396 | 4 |
| b-1 | -1.673 | 0.576 | 0.049 | -1.048 | 3 | |
| c-1 | 1.785 | 0.565 | -0.037 | 2.313 | 1 | |
| d-1 | 0.68 | -0.643 | 0.094 | 0.131 | 2 | |
| 20~40 cm | a-2 | -0.781 | -0.803 | 0.131 | -1.453 | 4 |
| b-2 | -1.005 | 0.805 | 0.081 | -0.119 | 2 | |
| c-2 | -0.036 | -0.1 | -0.307 | -0.443 | 3 | |
| d-2 | 1.823 | 0.098 | 0.095 | 2.016 | 1 |
| [1] | 宋岩, 王小红, 张锐, 等. 新疆核桃品种间品质差异比较[J]. 中国粮油学报, 2019, 34(8):91-97. |
| SONG Yan, WANG Xiaohong, ZHANG Yue, et al. Comparison of quality differences among varieties of walnut from Xinjiang[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2019, 34(8):91-97. | |
| [2] |
黄建, 张玉玲, 冯耀祖, 等. 南疆不同树龄核桃树根系质量空间变化特征分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(9):1684-1690.
DOI |
| HUANG Jian, ZHANG Yuling, FENG Yaozu, et al. Spatial variability analysis of root mass of different age walnut trees in Southern Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(9):1684-1690. | |
| [3] |
李曦光, 刘平, 王蕾, 等. 基于3S技术分析经济林资源时空分布[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(9):1733-1742.
DOI |
| LI Xiguang, LIU Ping, WANG Lei, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution research on economic forest resources in Yecheng County, Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(9):1733-1742. | |
| [4] | 李源, 马文强, 朱占江, 等. 新疆核桃产业发展现状及对策建议[J]. 农学学报, 2019, 9(7):80-86. |
| LI Yuan, MA Wenqiang, ZHU Zhanjiang, et al. Xinjiang walnut industry: the development status and countermeasures[J]. Journal of Agriculture, 2019, 9(7):80-86. | |
| [5] | 马丽. 豫东不同树龄梨园土壤微生物生态特征[J]. 河南农业科学, 2018, 47(1):37-42. |
| MA Li. Soil microbial ecological characteristics of pear orchard with different ages in Eastern Henan province[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 47(1):37-42. | |
| [6] |
Zhao W, Qi X J, Lyu J W, et al. Characterization of microbial community structure in rhizosphere soils of Cowskin Azalea (Rhododendron aureum Georgi) on northern slope of Changbai Mountains, China[J]. Chinese Geographical Science, 2016, 26(1):78-89.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 马红叶, 张文娥, 潘学军, 等. 胡桃科植物的化感作用及其应用前景综述[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(20):57-63, 74. |
| MA Hongye, ZHANG Wene, PAN Xuejun, et al. Walnut allelopathy and its application prospects: a review[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(20):57-63, 74. | |
| [8] | 李鸣. 配施肥对核桃物候、生长及产量的影响[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2015. |
| LI Ming. Effects of organic manure on phenophase, growth, and yield of walnut[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2015. | |
| [9] | 李娇, 蒋先敏, 尹华军, 等. 不同林龄云杉人工林的根系分泌物与土壤微生物[J]. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(2):325-332. |
| LI Jiao, JIANG Xianmin, YIN Huajun, et al. Root exudates and soil microbes in three Picea asperata plantations with different stand ages[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(2):325-332. | |
| [10] | 张雅倩, 黄蕊, 左林芝, 等. 海南岛不同林龄木麻黄凋落物内外细菌多样性及其化感潜力[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(7):2185-2194. |
| ZHANG Yaqian, HUANG Rui, ZUO Linzhi, et al. Diversity of bacteria and allelopathic potential of their metabolites in differently aged Casuarina equisetifolia litter[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(7):2185-2194. | |
| [11] | 徐志霞, 李小容, 蔡莲子, 等. 海南不同林龄木麻黄海防林土壤微生物群落组成与酶活性的动态分析[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(10):24-34. |
| XU Zhixia, LI Xiaorong, CAI Lianzi, et al. Analysis of soil microbial community and enzyme activity of Casuarina equisetifolia plantations at different stand ages in Hainan[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Ed.), 2018, 46(10):24-34. | |
| [12] | 朱海云, 马瑜, 柯杨, 等. 不同种植年限猕猴桃园土壤微生物功能多样性研究[J]. 微生物学杂志, 2019, 39(5):64-72. |
| ZHU Haiyun, MA Yu, KE Yang, et al. Functional diversities of soil microbial community in kiwifruit orchards of different planting years.[J]. Journal of Microbiology, 2019, 39(5):64-72. | |
| [13] | 郭睿, 王士华, 赵应勇. 不同种植年限对大叶女贞土壤生态环境的影响[J]. 西部林业科学, 2019, 48(6):86-92. |
| GUO Rui, WANG Shihua, ZHAO Yingyong. Effects of planting years on the soil environment of Ligustrum compactum[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2019, 48(6):86-92. | |
| [14] | Zhang J, Zhao Y, Xin Y. Changes in and evaluation of surface soil quality in Populus×xiaohei shelterbelts in midwestern Heilongjiang province, China[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 2020,(1):1-13. |
| [15] | 李志军, 唐光木, 孙霞, 等. 种植年限对新疆南部果园土壤养分变化的影响[J]. 天津农业科学, 2016, 22(5):15-20. |
| LI Zhijun, TANG Guangmu, SUN Xia, et al. Effect of planting years on soil nutrient changes in southern Xinjiang orchard[J]. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 22(5):15-20. | |
| [16] | 余晓. 土壤微生物性质及植物营养生理状况与山核桃干腐病的关系及其调控措施[D]. 杭州:浙江农林大学, 2017. |
| YU Xiao. The relationship between soil microbial communities, plant nutrition, physiological characters and Carya cathayensis canker disease and soil regulation[D]. Hang zhou: Zhejiang A&F University, 2017. | |
| [17] | Firdous S, Begum S, Yasmin A. Assessment of soil quality parameters using multivariate analysis in the Rawal Lake watershed[J]. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 2016, 188(9):533. |
| [18] |
李青军, 耿庆龙, 赖宁, 等. 核桃土壤养分评价及其与核桃产量的相关性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(5):826-833.
DOI |
| LI Qingjun, GENG Qinglong, LAI Ning, et al. Evaluation of walnut soil nutrients and the correlation with its yield[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(5):826-833. | |
| [19] | 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京, 中国农业科技出版社, 2000. |
| LU Rukun. Analytical methods for soil and agricultural chemistry[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000. | |
| [20] | 姚槐应, 黄昌勇. 土壤微生物生态学及其实验技术[M]. 北京, 科学出版社, 2006. |
| YAO Huaiying, HUANG Changyong. Edaphon ecology and experimental technology [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006. | |
| [21] | Chandra P, Enespa . Soil-microbes-plants: interactions and ecological diversity[M]. Plant Microbe Interface, 2019:145-176. |
| [22] | 王平安, 任旭明, 薄夫京, 等. 关帝山不同林龄华北落叶松人工林土壤化学计量特征及土壤理化性质分析[J]. 山西农业科学, 2020, 48(6):956-963. |
| WANG Ping'an, REN Xuming, BO Fujing, et al. Analysis on soil stoichiometric characteristics and soil physicochemical properties oflarix principis-rupprechtii plantations in different forest ages in Guandi Mountain[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(6):956-963. | |
| [23] | 阿迪力·吾彼尔, 袁素芬, 赵万羽. 准噶尔盆地新建防护林对林下土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 干旱区地理, 2007, (3):420-425. |
| ADIL Gopur, YUAN Sufen, ZHAO Wanyu. Effects of newly-constructed shelterbelt on soil physical and chemical properties in Junggar basin, Xinjiang[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2007, (3):420-425. | |
| [24] | Devi S, Soni R. Relevance of microbial diversity in implicating soil restoration and health management[M]. Soil Health Restoration and Management, 2019, 161-202. |
| [25] | 李歆博, 林伟杰, 李湘君, 等. 琯溪蜜柚园土壤酸化特征研究[J]. 经济林研究, 2020, 38(1):169-176. |
| LI Xinbo, LIN Weijie, LI Xiangjun, et al. Research on soil acidification characteristics of Guanxi pomelo orchards[J]. Non-wood Forest Research, 2020, 38(1):169-176. | |
| [26] | 雷泽勇, 白津宁, 周凤艳, 等. 辽宁章古台地区不同年龄樟子松固沙林对土壤pH值的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(11):3264-3272. |
| LEI Zeyong, BAI Jinning, ZHOU Fengyan, et al. Effects of Pinus sylvestris var.mongolica sand-fixation plantations with different ages on soil pH in Zhanggutai, Liaoning Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(11):3264-3272. | |
| [27] | 热依拉·木民, 玉米提·哈力克, 塔依尔江·艾山, 等. 基于分形维数的不同林龄新疆杨对土壤理化特性的影响分析[J]. 土壤通报, 2018, 49(2):313-319. |
| Reyila Mumin, Umut Halik, Tayierjiang Aishan, et al. Influence of different aged Populus alba var. pyramidalis on soil physicochemical properties based on fractal dimension[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2018, 49(2):313-319. | |
| [28] | 白晓霞, 艾海舰. 榆林沙地樟子松人工林土壤养分变化特征[J]. 西部林业科学, 2020, 49(3):80-85. |
| BAI Xiaoxia, AI Haijian. Soil nutrients variability of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantations in desertificated land of Yulin[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2020, 49(3):80-85. | |
| [29] |
Telesnina V M, Semenyuk O V, Bogatyrev L G . Features of forest litters in conjunction with ground cover in the forest ecosystems of Moscow oblast (based on the example of the Chashnikovo Educational-Experimental Soil-Ecological Center)[J]. Moscow University Soil Science Bulletin, 2017, 72(4):151-160.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 黄晶淼, 刘国鑫, 刘佩杭, 等. 不同种植年限苹果园根际土壤养分、pH及微生物的相关性[J]. 山西农业科学, 2020, 48(8):1263-1266. |
| HUANG Jingmiao, LIU Guoxin, LIU Peihang, et al. Correlation of nutrient, pH and microorganism in rhizosphere soil of apple orchard with different cultivation years[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(8):1263-1266. | |
| [31] | 杨满元, 杨宁, 吴磊, 等. 亚热带地区5种土地利用模式土壤微生物生态特性的比较[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2019, 54(4):124-130, 141. |
| YANG Manyuan, YANG Ning, WU Lei, et al. Comparison of ecological characteristics of microorganism under five land use patterns in subtropical region[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2019, 54(4):124-130, 141. | |
| [32] | 俞慎, 何振立, 陈国潮, 等. 不同树龄茶树根层土壤化学特性及其对微生物区系和数量的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2003, (3):433-439. |
| YU Shen, HE Zhenli, CHEN Guochao, et al. Soil chemical characteristics and their impacts on soil microflora in the root layer of tea plants with different cultivating ages[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2003, (3):433-439. | |
| [33] | 费裕翀, 路锦, 刘丽, 等. 铝胁迫对不同林分土壤中杉木幼苗根际土壤酶活性和微生物的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2020, 48(1):74-79. |
| FEI Yuchong, LU Jin, LIU Li, et al. Effects of Al stress on enzyme activity and microorganism in rhizosphere soil of Cunninghamia lanceolate in different stand soil[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2020, 48(1):74-79. | |
| [34] | 于德良, 雷泽勇, 赵国军, 等. 土壤酶活性对沙地樟子松人工林衰退的响应[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(1):97-105. |
| YU Deliang, LEI Zeyong, ZHAO Guojun, et al. Response of soil enzyme activity to the decline of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantations on sand land[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(1):97-105. | |
| [35] | 范媛媛, 李懿, 李启迪. 不同林龄油松土壤微生物、酶活性和养分特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(6):58-64. |
| FAN Yuanyuan, LI Yi, LI Qidi. Microbe, enzymatic activity and nutrient contents of soils in different stand ages of Pinus tabuliformis[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 26(6):58-64. |
| [1] | 帕孜丽耶·艾合麦提, 王新勇, 周燕, 宋彬, 玉苏甫·阿不力提甫. 微生物菌剂对核桃叶片生理及光合特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2299-2306. |
| [2] | 亚森·吐尔迪, 马天宇, 图尔迪麦麦提·努尔麦麦提, 阿地力·沙塔尔. 苹果蠹蛾和梨小食心虫迷向丝在核桃园中的使用模式[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1757-1765. |
| [3] | 周光辉, 陈凤, 孙守霞, 吕威, 朴涵琪, 郝金莲, 张述斌, 陈虹. 水肥耦合对核桃光合特性及产量和品质的效应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(5): 1151-1159. |
| [4] | 刘钧庆, 梁国成, 张欣, 王庆勇, 赵经华. 调亏灌溉对滴灌核桃树根系空间分布特征的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(5): 1160-1171. |
| [5] | 马合木提·阿不来提, 木合塔尔·扎热, 米热古力·外力, 哈地尔·依沙克. 核桃叶缘焦枯病与其养分含量的相关性回归分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 945-953. |
| [6] | 王文窈, 施万斌, 芦屹, 图尔荪托合提·阿卜杜拉, 叶尔胜·哈尔肯, 马荣. 两种助剂在核桃腐烂病化学防控中的减药增效分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(3): 672-680. |
| [7] | 欧源, 罗莎莎, 王如月, 孙雅丽, 虎海防. 盐胁迫对美国黑核桃幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 393-401. |
| [8] | 叶晓琴, 曹小艳, 阿地力·沙塔尔. 苹果蠹蛾生物学特性及其幼虫对核桃果实的为害习性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 434-440. |
| [9] | 文霞, 郭发城, 高桂珍. 集团外猎物种类及猎物密度对七星瓢虫集团内捕食作用的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 441-447. |
| [10] | 李慧, 毕莹, 王新宇, 雷雅馨, 张琪, 黄帅, 热扎·库忘德克, 王静. 核桃青皮多酚调控对哈密瓜采后活性氧代谢水平及腐烂率的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(12): 2966-2975. |
| [11] | 赵莎莎, 王世伟, 张翠芳, 郝洪龙, 郭桐, 杨先安, 杨雯洁. 核桃焦叶病与矿质元素关系分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2750-2760. |
| [12] | 王苹, 孔娜, 潘俨, 孙席平, 徐斌, 张婷. ClO2熏蒸处理对湿鲜核桃贮藏效果的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1940-1949. |
| [13] | 徐静, 石书兵, 秦小钢, 朱军. 核桃林间作西红花对其土壤微生物数量的动态变化[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 2022-2027. |
| [14] | 付强, 王琴, 徐彩芹, 牛俊丽, 牛建新, 王建友. 黑核桃组培中消毒及防止褐化最适浓度分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1499-1505. |
| [15] | 孙席平, 孔娜, 许铭强, 王苹, 徐斌, 张婷. 低压静磁场处理对鲜食核桃解冻效果及货架期品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1506-1514. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 48
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 192
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||