

新疆农业科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (1): 86-94.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2022.01.011
• 作物遗传育种·分子遗传学·耕作栽培·种质资源 • 上一篇 下一篇
王仙1( ), 聂石辉1, 向莉2, 张金汕3, 李鹏1,3, 方伏荣1(
), 聂石辉1, 向莉2, 张金汕3, 李鹏1,3, 方伏荣1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-01-02
出版日期:2022-01-20
发布日期:2022-02-18
通信作者:
方伏荣(1963-),男,广东惠来人,研究员,硕士,研究方向为大麦遗传育种与栽培,(E-mail) ffr118@sina.com作者简介:王仙(1984-),女,河北沧州人,副研究员,硕士,研究方向为作物品质生理,(E-mail) 283215056@qq.com
基金资助:
WANG Xian1( ), NIE Shihui1, XIANG Li2, ZHANG Jinshan3, LI Peng1,3, FANG Furong1(
), NIE Shihui1, XIANG Li2, ZHANG Jinshan3, LI Peng1,3, FANG Furong1( )
)
Received:2021-01-02
Published:2022-01-20
Online:2022-02-18
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】研究干旱胁迫对中亚大麦农艺性状和品质的影响,为大麦耐旱育种以及干旱条件下提高产量与品质提供理论依据。【方法】以12个不同抗旱性的中亚大麦种质资源为研究对象,设3个水分处理,测定大麦株高、穗长、穗粒数、千粒重、产量、籽粒总黄酮含量和总多酚含量。【结果】干旱胁迫对测定的指标均有显著影响,其中(1)随着干旱胁迫增加,所有参试材料的株高、穗长、穗粒数、千粒重和产量均呈逐渐下降的趋势;(2)随着干旱胁迫加剧,吉引2013-7-DM-005、吉引2013-7-DM-045、吉引2013-7-DM-072、吉33、吉引2013-7-DM-088总黄酮含量显著升高,吉引2013-7-DM-71、吉引2013-7-DM-046、吉引2013-7-DM-051、吉2、吉35和哈3总黄酮含量先显著升高后降低;除吉引2013-7-DM-051总多酚含量先升高后显著减低,哈3总多酚含量先升高后略减低,其他10个中亚大麦籽粒总多酚含量均表现为显著升高。(3)总黄酮含量与参试大麦产量呈显著正相关,与总多酚含量、株高、穗长、穗粒数呈正相关,与千粒重呈负相关;总多酚含量与穗长和产量呈极显著负相关,与穗粒数呈正相关,与株高和千粒重呈负相关。【结论】干旱胁迫可不同程度的增加中亚大麦籽粒总黄酮和总多酚含量。
中图分类号:
王仙, 聂石辉, 向莉, 张金汕, 李鹏, 方伏荣. 干旱胁迫对中亚大麦农艺性状、产量和品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(1): 86-94.
WANG Xian, NIE Shihui, XIANG Li, ZHANG Jinshan, LI Peng, FANG Furong. Effects of Drought Stress on Agronomic Characters, Yield and Quality of Barley from Central Asia[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(1): 86-94.
| 编号Code | 原代码Original code | 名称Name | 特性Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | S2015-62/2016-62 | 吉引2013-7-DM-005 | 春性、二棱、皮大麦 |
| C2 | S2015-96/2016-96 | 吉引2013-7-DM-045 | 春性、二棱、皮大麦 |
| C3 | S2015-118/2016-118 | 吉引2013-7-DM-071 | 春性、四棱、皮大麦 |
| C4 | S2015-119/2016-119 | 吉引2013-7-DM-072 | 春性、二棱、皮大麦 |
| C5 | S2015-33/2016-33 | 吉33 | 春性、四棱、皮大麦 |
| C6 | S2015-97/2016-97 | 吉引2013-7-DM-046 | 春性、二棱、皮大麦 |
| C7 | S2015-102/2016-102 | 吉引2013-7-DM-051 | 春性、二棱、皮大麦 |
| C8 | S2015-131/2016-131 | 吉引2013-7-DM-086 | 春性、四棱、皮大麦 |
| C9 | S2015-133/2016-133 | 吉引2013-7-DM-088 | 春性、四棱、皮大麦 |
| C10 | S2015-2/2016-2 | 吉2 | 春性、二棱、皮大麦 |
| C11 | S2015-35/2016-35 | 吉35 | 春性、四棱、皮大麦 |
| C12 | S2015-50/2016-50 | 哈3 | 半冬性、二棱、皮大麦 |
表1 12份供试材料
Table 1 12 test materials
| 编号Code | 原代码Original code | 名称Name | 特性Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | S2015-62/2016-62 | 吉引2013-7-DM-005 | 春性、二棱、皮大麦 |
| C2 | S2015-96/2016-96 | 吉引2013-7-DM-045 | 春性、二棱、皮大麦 |
| C3 | S2015-118/2016-118 | 吉引2013-7-DM-071 | 春性、四棱、皮大麦 |
| C4 | S2015-119/2016-119 | 吉引2013-7-DM-072 | 春性、二棱、皮大麦 |
| C5 | S2015-33/2016-33 | 吉33 | 春性、四棱、皮大麦 |
| C6 | S2015-97/2016-97 | 吉引2013-7-DM-046 | 春性、二棱、皮大麦 |
| C7 | S2015-102/2016-102 | 吉引2013-7-DM-051 | 春性、二棱、皮大麦 |
| C8 | S2015-131/2016-131 | 吉引2013-7-DM-086 | 春性、四棱、皮大麦 |
| C9 | S2015-133/2016-133 | 吉引2013-7-DM-088 | 春性、四棱、皮大麦 |
| C10 | S2015-2/2016-2 | 吉2 | 春性、二棱、皮大麦 |
| C11 | S2015-35/2016-35 | 吉35 | 春性、四棱、皮大麦 |
| C12 | S2015-50/2016-50 | 哈3 | 半冬性、二棱、皮大麦 |
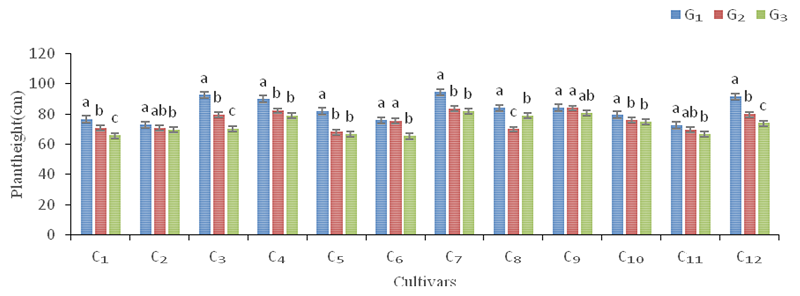
图1 干旱胁迫下不同大麦品种株高变化 注:不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)
Fig.1 Effect of drought stress on t'he plant height of different barley varieties Note: Different lowercase letters on the figure indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05)
| 品种 Variety | 穗长 Spike length(cm) | 穗粒数(个) Spike grain number | 千粒重 Thousand-grain weight(g) | 产量 Yield(kg/667m2) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | G2 | G3 | G1 | G2 | G3 | G1 | G2 | G3 | G1 | G2 | G3 | |
| C1 | 8.40a | 8.2 | 8.10b | 22.20a | 21.80a | 19.20b | 55.00a | 50.10b | 40.00c | 314.78a | 290.54b | 87.50c |
| C2 | 9.10a | 7.80b | 7.40b | 21.70b | 21.00b | 26.00a | 58.00a | 55.0 | 49.00b | 165.97a | 134.67b | 45.84c |
| C3 | 8.10b | 8.50a | 7.50c | 51.50b | 58.00a | 46.70c | 38.00a | 37.00a | 30.0 | 417.41a | 358.35b | 87.50c |
| C4 | 9.40a | 8.30b | 7.90c | 23.50a | 21.00b | 18.20c | 70.30a | 64.00b | 56.00c | 339.48a | 262.51b | 50.00c |
| C5 | 7.50a | 7.20b | 6.30c | 47.20a | 42.40b | 47.30a | 45.2 | 44.00a | 30.00b | 274.29a | 237.71b | 75.00c |
| C6 | 8.60a | 8.30a | 7.50c | 19.20b | 21.50a | 20.7 | 63.80a | 48.00b | 36.00c | 306.76a | 206.48b | 62.50c |
| C7 | 8.40a | 8.30a | 8.20a | 21.80a | 19.80c | 20.50b | 63.20a | 61.00a | 55.00b | 318.05a | 268.32b | 100.01c |
| C8 | 8.80a | 7.90b | 6.90c | 20.30b | 22.80a | 20.00b | 50.20a | 45.70b | 45.00b | 320.53a | 317.06a | 54.17c |
| C9 | 9.10a | 7.70b | 6.80c | 49.80b | 62.00a | 39.00c | 42.30a | 36.00b | 33.00b | 256.40a | 210.30b | 62.50c |
| C10 | 9.30a | 9.30a | 7.90b | 23.40a | 20.8 | 21.70b | 55.50a | 42.20b | 40.00b | 283.87a | 220.17b | 108.34c |
| C11 | 7.0 | 7.20a | 5.80b | 43.0 | 49.40a | 45.80b | 42.40a | 38.10b | 32.00c | 239.66a | 176.36b | 120.84c |
| C12 | 8.90a | 8.20b | 7.80c | 22.00b | 25.60a | 22.60b | 43.35a | 38.20b | 35.00b | 331.75a | 315.43a | 91.67c |
表2 不同干旱处理下各大麦品种产量变化
Table 2 Effects of different drought treatments on the yield of Barley Varieties
| 品种 Variety | 穗长 Spike length(cm) | 穗粒数(个) Spike grain number | 千粒重 Thousand-grain weight(g) | 产量 Yield(kg/667m2) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | G2 | G3 | G1 | G2 | G3 | G1 | G2 | G3 | G1 | G2 | G3 | |
| C1 | 8.40a | 8.2 | 8.10b | 22.20a | 21.80a | 19.20b | 55.00a | 50.10b | 40.00c | 314.78a | 290.54b | 87.50c |
| C2 | 9.10a | 7.80b | 7.40b | 21.70b | 21.00b | 26.00a | 58.00a | 55.0 | 49.00b | 165.97a | 134.67b | 45.84c |
| C3 | 8.10b | 8.50a | 7.50c | 51.50b | 58.00a | 46.70c | 38.00a | 37.00a | 30.0 | 417.41a | 358.35b | 87.50c |
| C4 | 9.40a | 8.30b | 7.90c | 23.50a | 21.00b | 18.20c | 70.30a | 64.00b | 56.00c | 339.48a | 262.51b | 50.00c |
| C5 | 7.50a | 7.20b | 6.30c | 47.20a | 42.40b | 47.30a | 45.2 | 44.00a | 30.00b | 274.29a | 237.71b | 75.00c |
| C6 | 8.60a | 8.30a | 7.50c | 19.20b | 21.50a | 20.7 | 63.80a | 48.00b | 36.00c | 306.76a | 206.48b | 62.50c |
| C7 | 8.40a | 8.30a | 8.20a | 21.80a | 19.80c | 20.50b | 63.20a | 61.00a | 55.00b | 318.05a | 268.32b | 100.01c |
| C8 | 8.80a | 7.90b | 6.90c | 20.30b | 22.80a | 20.00b | 50.20a | 45.70b | 45.00b | 320.53a | 317.06a | 54.17c |
| C9 | 9.10a | 7.70b | 6.80c | 49.80b | 62.00a | 39.00c | 42.30a | 36.00b | 33.00b | 256.40a | 210.30b | 62.50c |
| C10 | 9.30a | 9.30a | 7.90b | 23.40a | 20.8 | 21.70b | 55.50a | 42.20b | 40.00b | 283.87a | 220.17b | 108.34c |
| C11 | 7.0 | 7.20a | 5.80b | 43.0 | 49.40a | 45.80b | 42.40a | 38.10b | 32.00c | 239.66a | 176.36b | 120.84c |
| C12 | 8.90a | 8.20b | 7.80c | 22.00b | 25.60a | 22.60b | 43.35a | 38.20b | 35.00b | 331.75a | 315.43a | 91.67c |
| 项目 Item | 均方Mean square | F值F-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总黄酮含量 Total flavone content | 总多酚含量 Total polyphenol content | 总黄酮含量 Total flavone content | 总多酚含量 Total polyphenol content | |
| 灌水量Irrigation amount(G) | 127.398 5 | 0.362 7 | 13.622 8** | 21.759 1** |
| 品种Varieties(C) | 32.666 4 | 0.146 1 | 3.493** | 8.761 8** |
| G×C | 9.351 8 | 0.016 7 | 247.306 8** | 649.415 6** |
| 总误差Total error | 0.0378 | 0 | ||
表3 干旱胁迫下12个品种籽粒总黄酮和总多酚含量的方差
Table 3 Variance analysis of total flavonoids andpolyphenols contents in grains of 12 varieties under drought stress
| 项目 Item | 均方Mean square | F值F-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总黄酮含量 Total flavone content | 总多酚含量 Total polyphenol content | 总黄酮含量 Total flavone content | 总多酚含量 Total polyphenol content | |
| 灌水量Irrigation amount(G) | 127.398 5 | 0.362 7 | 13.622 8** | 21.759 1** |
| 品种Varieties(C) | 32.666 4 | 0.146 1 | 3.493** | 8.761 8** |
| G×C | 9.351 8 | 0.016 7 | 247.306 8** | 649.415 6** |
| 总误差Total error | 0.0378 | 0 | ||
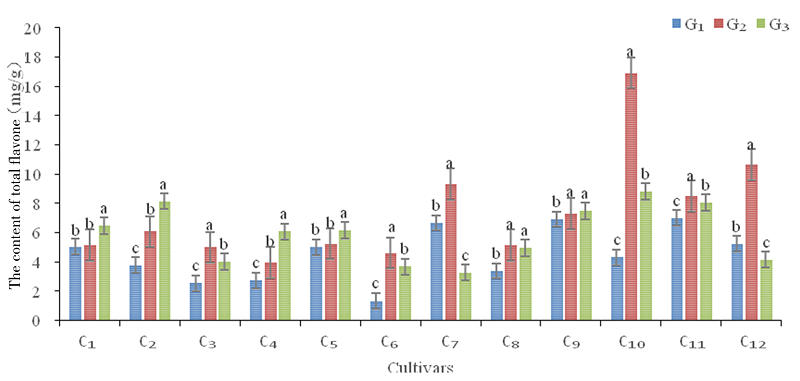
图2 干旱胁迫下大麦籽粒总黄酮含量变化 注:不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)
Fig.2 Effect of drought stress on the content of total flavone of different malting barley Note: Different lowercase letters on the figure indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05)
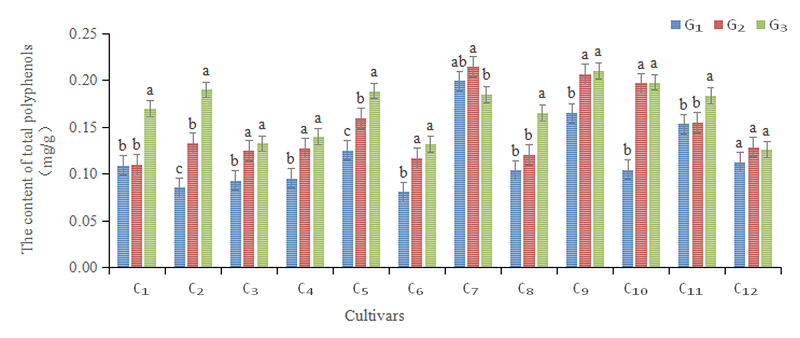
图3 干旱胁迫下大麦籽粒总多酚含量变化 注:不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)
Fig.3 Effect of drought stress on the content of total polyphenols of different malting barley Note: Different lowercase letters on the figure indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05)
| 指标 Index | 总黄酮含量 Total flavone content | 总多酚含量 Total polyphenol content | 株高 Plant height | 穗长 Spike length | 穗粒数 Spike grain number | 千粒重 Thousand-grain weight | 产量 Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总黄酮含量 Total flavone content | 1 | ||||||
| 总多酚含量 Total polyphenol content | 0.29 | 1 | |||||
| 株高 Plant height | 0.18 | -0.08 | 1 | ||||
| 穗长 Spike length | 0.28 | -0.44** | 0.51** | 1 | |||
| 穗粒数 Spike grain number | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.06 | -0.31 | 1 | ||
| 千粒重 Thousand-grain weight | -0.01 | -0.3 | 0.39* | 0.58** | -0.53** | 1 | |
| 产量 Yield | 0.34* | -0.48** | 0.57** | 0.56** | 0.17 | 0.35* | 1 |
表4 供试中亚大麦材料各指标的相关性
Table 4 Correlation of each index of all indexes in tested barley from Central Asian
| 指标 Index | 总黄酮含量 Total flavone content | 总多酚含量 Total polyphenol content | 株高 Plant height | 穗长 Spike length | 穗粒数 Spike grain number | 千粒重 Thousand-grain weight | 产量 Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总黄酮含量 Total flavone content | 1 | ||||||
| 总多酚含量 Total polyphenol content | 0.29 | 1 | |||||
| 株高 Plant height | 0.18 | -0.08 | 1 | ||||
| 穗长 Spike length | 0.28 | -0.44** | 0.51** | 1 | |||
| 穗粒数 Spike grain number | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.06 | -0.31 | 1 | ||
| 千粒重 Thousand-grain weight | -0.01 | -0.3 | 0.39* | 0.58** | -0.53** | 1 | |
| 产量 Yield | 0.34* | -0.48** | 0.57** | 0.56** | 0.17 | 0.35* | 1 |
| [1] |
Nirupama G, Hossain M B, Rai D K, et al. A review of extraction and analysis of bioactives in oat and barley and scope for use of novel food processing technologies[J]. Molecules, 2015, 20(6):10884-10909.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 叶梅荣, 刘爱荣, 陈利明, 等. 大豆异黄酮对干旱胁迫下油菜幼苗生长的影响[J]. 云南植物研究, 2008, 30(3):351-354. |
| YE Meirong, LIU Airong, CHEN Liming, et al. Effects of soybean isoflavones on rape seedlings under drought stress[J]. Acta Botani Yunnanica, 2008, 30(3):351-354. | |
| [3] | 胡庆辉. 盐与干旱胁迫诱导烤烟叶片细胞程序性死亡及多酚含量变化的研究[D]. 北京:中国农业科学院, 2012. |
| HU Qinghui. The Study of programmed cell death and polyphenols contents changes of fluecured tobacco leaves induced by salt and drought stress[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2012. | |
| [4] | Zahir A, Abbasi B H, Adil M, et al. Synergistic Effects of Drought Stress and Photoperiods on Phenology and Secondary Metabolism of Silybummarianum[J]. Applied Biochemistry & Biotechnology, 2014, 174(2):693-707. |
| [5] | 金梦. 干旱胁迫对黄瓜幼苗次生代谢物质含量及相关酶活性的影响[D]. 合肥:安徽农业大学, 2017. |
| JIN Meng. Drought Stress of The Seedlings of Cucumber Secondary Metabolism Substance Content and Related Enzyme Activity[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| [6] | 綦文涛, 陈文若, 陈银基, 等. 大麦功能活性物质含量与抗氧化活性的关系[J]. 中国食品学报, 2018, 11(18):232-239. |
| QI Weitao, CHEN Wenruo, CHEN Yinji, et al. An exploration of the correlation between the contents of functional active substances in barley and their antioxidant capacity[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2018, 11(18):232-239. | |
| [7] | 杨涛, 闵康, 曾亚文, 等. 青稞和普通大麦全谷物功能成分差异分析[J]. 西南农业学报, 2015, 28(6):2360-2362. |
| YANG Tao, MIN Kang, ZENG Yawen, et al. Difference analysis of functional components of whole grains between hull-less barley and normal barley[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 28(6):2360-2362. | |
| [8] | 胡新颖, 陶玉欣, 李兴国, 等. 大麦多酚抗氧化及抑菌活性的研究[J]. 农产品加工, 2020, (9):1671-9646. |
| HU Xinying, TAO Yuxin, LI Xingguo, et al. Antioxidant and antibacterial activity of barley polyphenols[J]. Farm Products Processing, 2020(9):1671-9646. | |
| [9] | 杨涛, 曾亚文, 萧凤回, 等. 药用大麦及其活性物质研究进展[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2007, 27(6):1154-1158. |
| YANG Tao, ZENG Yawen, XIAO Fenghui, et al. Research progress on medicinal barley and its active substance[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2007, 27(6):1154-1158. | |
| [10] | Daryanto S, Wang L X, Jacinthe P A. Global synjournal of drought effects on maize and wheat production[J]. PloS One, 2016, 11(5):pone.0156362. |
| [11] | Kadam N N, Xiao G, Melgar R J, et al. Agronomic and physiological responses to high temperature, drought, and elevated CO2 interactions in cereals[J]. Advances in Agronomy, 2014, 127:111-156. |
| [12] | 肖亚, 杜娟, 杨晓梦, 等. 中国西南与 ICARDA 大麦品种类型间籽粒功能成分含量分析[J]. 西南农业学报, 2017, 30(8):1700-1707. |
| XIAO Ya, DU Juan, YANG Xiaomeng, et al. Analysis of functional ingredients in barley grains from different gions between southwest China and ICARDA[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 30(8):1700-1707. | |
| [13] | 普晓英, 赵大伟, 曾亚文, 等. 大麦农艺性状分析及籽粒黄酮含量的测定[J]. 西南农业学报, 2013, 26(6):2204-2207. |
| PU Xiaoying, ZHAO Dawei, ZENG Yawen, et al. Analysis of agronomic characters of barley And determination of total flavone contents in grains[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 26(6):2204-2207. | |
| [14] | 张金汕, 董庆国, 陈勇, 等. 中亚大麦种质资源的农艺性状及抗旱性研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2015, 52(6):1152-1158. |
| ZHANG Jinshan, DONG Qingguo, CHEN Yong, et al. The introduction of barley germplasm resources of Central Asia agronomic traits and the analysis of drought resistance[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 52(6):1152-1158. | |
| [15] | 王仙, 王祥军, 曹连莆, 等. 大麦籽粒总黄酮超声辅助提取工艺的优化[J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 28(2):152-157. |
| WANG Xian, WANG Xiangjun, CAO Liaopu, et al. Optimization of the ultrasound-assisted extraction of total favonoids from barley ( Hordeumvulgare L.)[J]. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science Ed.), 2010, 28(2):152-157. | |
| [16] | 徐宏化, 程慧, 王正加, 等. 美国山核桃总多酚与总黄酮含量及抗氧化活性[J]. 核农学报, 2016, 30(1) : 0072-0078. |
| XU Honghua, CHENG Hui, WANG Zhengjia, et al. The study of total polyphenols,total flavonoids and antioxidant capacity in pecan[Caryaillinoinensis ( Wangenh.) K.Koch]Kernels[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 30(1):0072-0078. | |
| [17] | 李慧兵. 国外大麦种质资源的适应性评价及其利用[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2011. |
| LI Huibing. Evaluation of the adaptability of imported barley germaplasm[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2011. | |
| [18] | 蔡康锋. 大麦根系细胞离子平衡对干旱的响应及其生理机制研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2020. |
| CAI Kangfeng. Studies on response of root cellular ion homeostasis to drought and its physiological mechanisms in barley[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2020. | |
| [19] | 冉生斌, 蔡立群. 干旱胁迫对不同基因型啤酒大麦品种(系)生长发育的影响[J]. 甘肃农业科技, 2017, (5):28-33. |
| RAN Shengbin, CAI Liqun, Effects of drought stress on growth and development of different genotypes of malting barley cultivars(Lines)[J]. Gansu Agricultural Sciences and Technology, 2017 (5):28-33. | |
| [20] | 范敏, 金黎平, 黄三文, 等. 干旱胁迫对马铃薯类黄酮和类胡萝卜素合成关键酶基因表达的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2008, 35(4) :535-542. |
| FAN Min, JIN Liping, HUANG Sanwen, et al. Effects of Drought on gene expressions of key enzymes in carotenoid and flavonoid biosynjournal in potato[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2008, 35(4):535-542. | |
| [21] | 谭茂玲, 廖爽, 万燕, 等. 干旱胁迫对苦荞麦农艺性状、产量和品质的影响[J]. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 40(10):88-93.) |
| TAN Maoling, LIAO Shuang, WAN Yan, et al. On effects of drought stress on agronomic traits, yield and quality of Tartary buckwheat[J]. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Natural Science Ed.), 2015, 40(10):88-93. | |
| [22] | Iris A, luigi P, Ruiz K B, et al. New Insight into Quality under Salinity: Changes in Proteomic and Amino Acid Profiles, Phenolic Content, and Anotioxidant Activity of Protein Extracts[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7. |
| [23] | 岳凯. 不同品系藜麦抗旱性及种子主要次生物质的研究[D]. 兰州:甘肃农业大学, 2018. |
| YUE Kai. Study on Drought Resistance and Main Secondary Metabolites in Seeds of Different Species Quinoa[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| [24] | 刘松. 极端干旱环境下植物体内多酚类物质含量及其对逆境的响应研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2007. |
| LIU Song. Study on plant phenolic compound content and their response to hyperarid extreme environment[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2007. | |
| [25] |
Massimo B, Monica L, Alessandra G, et al. Hull-less barley pearling fractions: Nutritional properties and their effect on the functional and technological quality in bread making[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2015, 65(1) : 48-56.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 刘敏洁, 刘文辉, 张永超, 等. 聚乙二醇模拟干旱胁迫对老芒麦幼苗生长及次生代谢部分产物的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2020, 28(5):1355-1362. |
| LIU Minjie, LIU Wenhui, ZHANG Yongchao, et al. Effects of Drought Stresses Simulated by PEG on Growth and Secondary Metabolites in Elymussibiricus[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(5):1355-1362. |
| [1] | 张泽华, 叶含春, 王振华, 李文昊, 李海强, 刘健. 等氮配施脲酶抑制剂对滴灌棉花生长发育和产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2103-2111. |
| [2] | 陈瑞杰, 罗林毅, 阮向阳, 冶军. 腐植酸对滴灌棉田土壤养分和棉花产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2112-2121. |
| [3] | 黄铂轩, 李鹏程, 郑苍松, 孙淼, 邵晶晶, 冯卫娜, 庞朝友, 徐文修, 董合林. 不同氮素抑制剂对棉花生长发育、氮素利用与产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2122-2131. |
| [4] | 曾婉盈, 耿洪伟, 程宇坤, 李思忠, 钱松廷, 高卫时, 张立明. 甜菜品系叶丛快速生长期抗旱性综合评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2140-2151. |
| [5] | 张鸟, 王卉, 冯国郡, 再吐尼古丽·库尔班. 不同粒用高粱品种产量和农艺性状及品质的差异性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2160-2167. |
| [6] | 阿热孜姑·吐逊, 高杰. 干旱胁迫和播种密度对洋葱小鳞茎生理特性及产出鳞茎个数的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2211-2222. |
| [7] | 陈芳, 李字辉, 孙孝贵, 张庭军. 不同剂量的微生物菌剂对加工番茄产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2285-2289. |
| [8] | 张承洁, 胡浩然, 段松江, 吴一帆, 张巨松. 氮肥与密度互作对海岛棉生长发育及产量和品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1821-1830. |
| [9] | 候丽丽, 王伟, 崔新菊, 周大伟. 有机无机肥配施对冬小麦产量和土壤养分及酶活性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1845-1852. |
| [10] | 陈芳, 李字辉, 王兵跃, 孙孝贵, 张庭军. 微生物菌剂对冬小麦生长发育及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1853-1860. |
| [11] | 袁莹莹, 赵经华, 迪力穆拉提·司马义, 杨庭瑞. 基于apriori算法对盆栽春小麦生理指标及产量的分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1861-1871. |
| [12] | 牛婷婷, 马明生, 张军高. 秸秆还田和覆膜对旱作雨养农田土壤理化性质及春玉米产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1896-1906. |
| [13] | 赵敏华, 宋秉曦, 张宇鹏, 高志红, 朱勇勇, 陈晓远. 旱作条件下氮肥减施对水稻产量及氮肥偏生产力的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1907-1915. |
| [14] | 李锁丞, 柳延涛, 董红业, 孙振博, 李紫薇, 张春媛, 王开勇, 李强, 杨明凤. 不同施钾量对滴灌花生光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1926-1936. |
| [15] | 张彩虹, 王国强, 姜鲁艳, 刘涛, 德贤明. 低能耗组装式深冬生产型日光温室环境因子变化及番茄性状分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 2043-2053. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 71
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 777
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||