

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (8): 1983-1992.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.08.019
奚瑞1,2( ), 陈怡佳1,2, 李宁2, 余庆辉2, 王强2(
), 陈怡佳1,2, 李宁2, 余庆辉2, 王强2( ), 秦勇1(
), 秦勇1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-02-05
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-09-19
通信作者:
秦勇(1962-),男,甘肃人,教授,博士,硕士生/博士生导师,研究方向为蔬菜栽培与生理,(E-mail)352167610@qq.com;作者简介:奚瑞(1999-),女,吉林人,硕士研究生,研究方向为蔬菜栽培生理与逆境胁迫,(E-mail)Tsuki_re@163.com
基金资助:
XI Rui1,2( ), CHEN Yijia1,2, LI Ning2, YU Qinghui2, WANG Qiang2(
), CHEN Yijia1,2, LI Ning2, YU Qinghui2, WANG Qiang2( ), QIN Yong1(
), QIN Yong1( )
)
Received:2024-02-05
Published:2024-08-20
Online:2024-09-19
Correspondence author:
QIN Yong(1962-),male,from Gansu, professor, Ph.D, Ph.D supervisor, research direction: Vegetable cultivation and physiology,(E-mail)352167610@qq.com;Supported by:摘要:
【目的】研究盐胁迫下不同浓度2,4-表芸苔素内酯(2,4-Epibrassinolide,EBR)处理对番茄种子萌发特性和关键酶活性的影响,筛选影响番茄种子萌发及生长发育效果的最佳浓度,为外源EBR的科学应用提供理论依据。【方法】以盐敏感型‘M82’和耐盐型‘IL-7-5-5’番茄种子为材料,在50 mmol/L的NaCl处理下,添加0.01、0.1和0.5 μmol/L的外源EBR,测定番茄种子在萌发过程中的发芽率、发芽势等形态指标,分析抗氧化酶活性和渗透调节物质含量的变化。【结果】外源EBR处理后的‘M82’和‘IL-7-5-5’种子的发芽势较盐胁迫处理均提高了10%~30%以上,种子活力指数均提高了100~200以上,并且随着EBR浓度升高,2个番茄品种的发芽率、发芽势均呈下降的趋势。0.01 μmol/L EBR处理的‘M82’种子胚芽长和鲜重较盐胁迫下分别增加了94.26%和135.71%;0.1 μmol/L EBR处理的‘IL-7-5-5’胚芽长和鲜重较盐胁迫分别增加了32.48%和14.52%。幼芽体内MDA和SOD、CAT、POD活性显著提升,可溶性蛋白、可溶性糖等渗透调节物质含量显著增加,但不同EBR浓度、不同番茄品种之间的生理指标变化存在明显差异。【结论】外源EBR可以增强在盐胁迫条件下番茄种子萌发过程中调节渗透的能力,增强体内抗氧化系统的活性,膜脂过氧化产物的积累减少,促进番茄种子萌发和生长发育,提高番茄种子萌发期的耐盐性。盐胁迫下0.01 μmol/L的EBR处理对‘M82’的缓解效果最佳,0.1 μmol/L对‘IL-7-5-5’的缓解效果最佳。
中图分类号:
奚瑞, 陈怡佳, 李宁, 余庆辉, 王强, 秦勇. 外源2, 4-表芸苔素内酯对盐胁迫下不同盐敏感型番茄种子萌发的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1983-1992.
XI Rui, CHEN Yijia, LI Ning, YU Qinghui, WANG Qiang, QIN Yong. Effects of exogenous 2, 4-epibrassinolide on seed germination of different salt-sensitive tomatoes under salt stress[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1983-1992.
| 处理 Treatments | 胚根长 Radicle length(cm) | 胚芽长 Plumule length(cm) | 鲜重 Fresh weight(g) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘M82’ | ‘IL-7-5-5’ | ‘M82’ | ‘IL-7-5-5’ | ‘M82’ | ‘IL-7-5-5’ | |
| CK | 8.683±1.441a | 5.986±1.515b | 2.792±0.640a | 2.979±0.529b | 0.028±0.004b | 0.036±0.007b |
| T1 | 1.778±1.153b | 9.533±1.111a | 1.656±0.235b | 2.617±0.194b | 0.028±0.008b | 0.062±0.013a |
| T2 | 7.233±1.309a | 1.150±0.235c | 3.217±0.214a | 4.233±0.423a | 0.066±0.009a | 0.075±0.014a |
| T3 | 2.670±1.434b | 4.567±0.973b | 2.670±0.721a | 3.467±0.398ab | 0.058±0.038a | 0.071±0.010a |
| T4 | 0.983±0.360b | 4.500±1.028b | 3.233±0.163a | 3.817±0.417a | 0.059±0.006a | 0.071±0.007a |
表1 外源EBR对盐胁迫下番茄种子生物量的变化
Tab.1 Changes of Different concentrations of exogenous EBR on biomass of tomato seeds under salt stress
| 处理 Treatments | 胚根长 Radicle length(cm) | 胚芽长 Plumule length(cm) | 鲜重 Fresh weight(g) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘M82’ | ‘IL-7-5-5’ | ‘M82’ | ‘IL-7-5-5’ | ‘M82’ | ‘IL-7-5-5’ | |
| CK | 8.683±1.441a | 5.986±1.515b | 2.792±0.640a | 2.979±0.529b | 0.028±0.004b | 0.036±0.007b |
| T1 | 1.778±1.153b | 9.533±1.111a | 1.656±0.235b | 2.617±0.194b | 0.028±0.008b | 0.062±0.013a |
| T2 | 7.233±1.309a | 1.150±0.235c | 3.217±0.214a | 4.233±0.423a | 0.066±0.009a | 0.075±0.014a |
| T3 | 2.670±1.434b | 4.567±0.973b | 2.670±0.721a | 3.467±0.398ab | 0.058±0.038a | 0.071±0.010a |
| T4 | 0.983±0.360b | 4.500±1.028b | 3.233±0.163a | 3.817±0.417a | 0.059±0.006a | 0.071±0.007a |
| 处理 Treatments | 盐害指数 Salt damage index(%) | 盐害级别 Salt damage level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘M82’ | ‘IL-7-5-5’ | ‘M82’ | ‘IL-7-5-5’ | |
| T1 | 31.08 | 0.6 | 2 | 1 |
| T2 | 10.31 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| T3 | 12.06 | 3.80 | 1 | 1 |
| T4 | 13.10 | 4.43 | 1 | 1 |
表2 外源EBR下不同番茄品种盐害指数和盐害级别的变化
Tab.2 Changes of exogenous EBR on salt damage index and salt damage grade of different tomato varieties
| 处理 Treatments | 盐害指数 Salt damage index(%) | 盐害级别 Salt damage level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘M82’ | ‘IL-7-5-5’ | ‘M82’ | ‘IL-7-5-5’ | |
| T1 | 31.08 | 0.6 | 2 | 1 |
| T2 | 10.31 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| T3 | 12.06 | 3.80 | 1 | 1 |
| T4 | 13.10 | 4.43 | 1 | 1 |
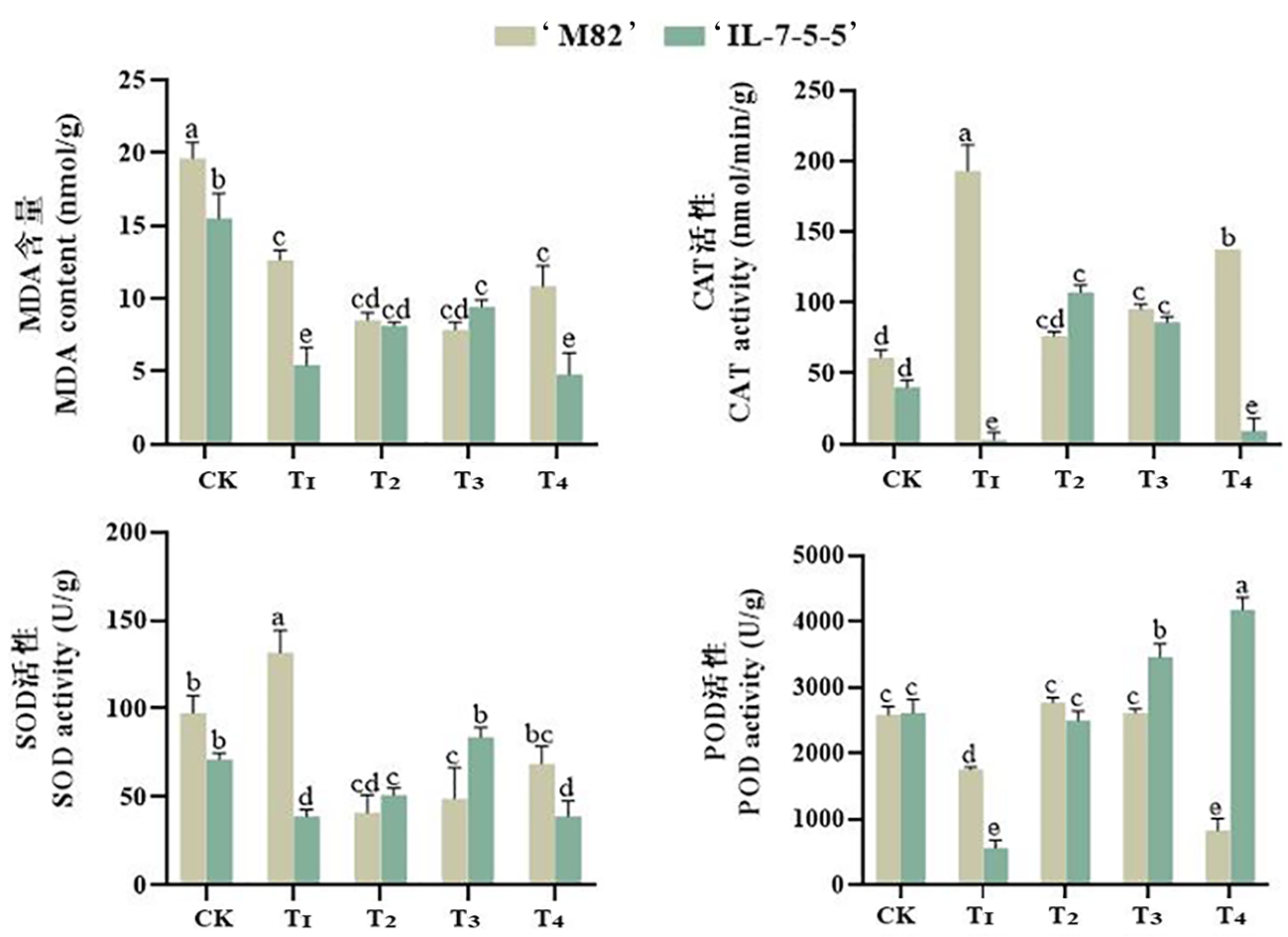
图3 外源EBR对NaCl胁迫下番茄幼芽体内MDA含量和抗氧化酶活性的变化
Fig.3 Changes of exogenous EBR on MDA content and antioxidant enzyme activity in tomato sprouts under salt stress
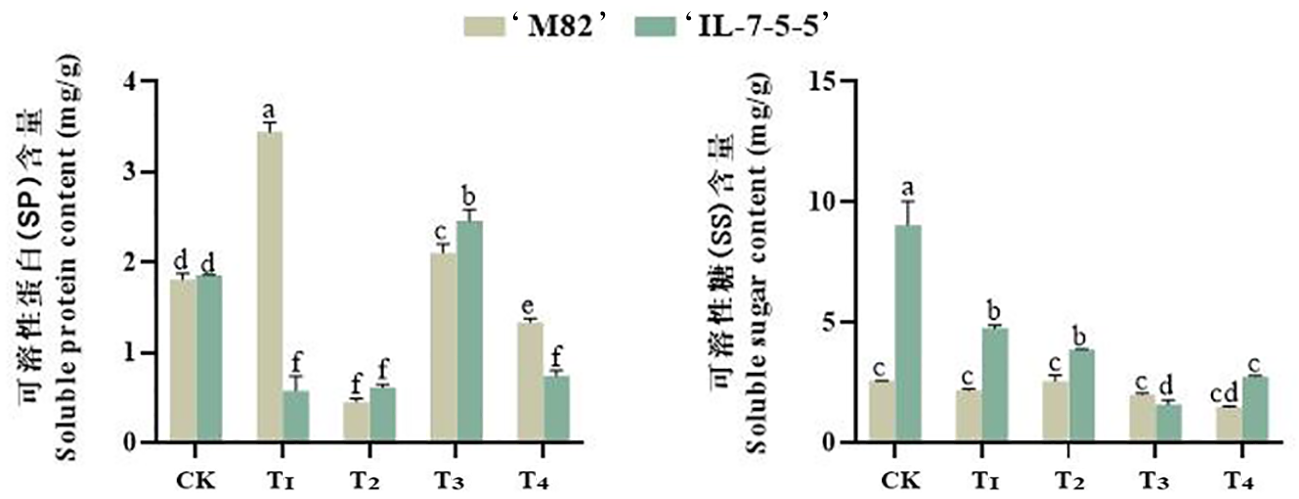
图4 外源EBR对NaCl胁迫下番茄幼芽体内可溶性糖和可溶性蛋白含量的变化
Fig.4 Changes of exogenous EBR on soluble sugar and soluble protein contents in tomato sprouts under NaCl stress
| 番茄品种 参数 Tomato varieties paramter | ‘M82’ | ‘IL-7-5-5’ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 提取成分 Extracted component | 提取成分 Extracted component | |||
| PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | |
| POD/CK | -4.516 74 | 0.023 612 | -3.315 34 | -0.123 07 |
| POD/T1 | -2.818 11 | 0.024 878 | -0.153 94 | 0.154 382 |
| POD/T2 | -4.898 28 | 0.009 012 | -3.138 23 | -0.105 94 |
| POD/T3 | -4.573 49 | 0.028 571 | -4.630 61 | 0.241 061 |
| POD/T4 | -0.905 18 | -0.258 95 | -5.738 05 | -0.079 96 |
| SOD/CK | 0.592 356 | 0.023 681 | 0.606 218 | 0.001 529 |
| SOD/T1 | 0.522 783 | 0.010 684 | 0.656 309 | -0.000 25 |
| SOD/T2 | 0.708 62 | 0.019 055 | 0.637 441 | -0.000 25 |
| SOD/T3 | 0.692 586 | -0.019 39 | 0.587 064 | -0.01 |
| SOD/T4 | 0.652 105 | 0.013 944 | 0.656 031 | -0.011 14 |
| CAT/CK | 0.667 488 | 0.009 894 | 0.653 886 | -0.008 24 |
| CAT/T1 | 0.397 363 | 0.004 979 | 0.711 403 | -0.009 52 |
| CAT/T2 | 0.597 567 | 0.012 894 | 0.550 948 | 0.003 602 |
| CAT/T3 | 0.510 239 | 0.006 908 | 0.583 378 | -0.004 14 |
| CAT/T4 | 0.510 239 | 0.011 432 | 0.701 728 | 0.001 578 |
| MAD/CK | 0.753 945 | 0.005 247 | 0.690 946 | -0.002 92 |
| MAD/T1 | 0.767 382 | 0.005 167 | 0.708 154 | -0.003 18 |
| MAD/T2 | 0.775 85 | 0.004 66 | 0.703 684 | -0.002 98 |
| MAD/T3 | 0.777 252 | 0.004 999 | 0.701 834 | -0.002 94 |
| MAD/T4 | 0.769 486 | 0.005 383 | 0.709 295 | -0.004 88 |
| SP/CK | 0.789 429 | 0.005 378 | 0.713 289 | -0.003 37 |
| SP/T1 | 0.786 07 | 0.005 546 | 0.715 262 | -0.003 18 |
| SP/T2 | 0.792 213 | 0.005 314 | 0.715 209 | -0.003 43 |
| SP/T3 | 0.788 82 | 0.005 336 | 0.712 359 | -0.003 42 |
| SP/T4 | 0.790 397 | 0.005 366 | 0.715 003 | -0.003 43 |
| SS/CK | 0.787 845 | 0.005 372 | 0.702 173 | -0.002 07 |
| SS/T1 | 0.788 676 | 0.005 395 | 0.708 79 | -0.003 5 |
| SS/T2 | 0.787 871 | 0.004 966 | 0.710 174 | -0.003 38 |
| SS/T3 | 0.789 014 | 0.005 402 | 0.713 701 | -0.003 62 |
| SS/T4 | 0.790 074 | 0.005 263 | 0.711 894 | -0.003 34 |
表3 参考矩阵
Tab.3 Reference matrix
| 番茄品种 参数 Tomato varieties paramter | ‘M82’ | ‘IL-7-5-5’ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 提取成分 Extracted component | 提取成分 Extracted component | |||
| PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | |
| POD/CK | -4.516 74 | 0.023 612 | -3.315 34 | -0.123 07 |
| POD/T1 | -2.818 11 | 0.024 878 | -0.153 94 | 0.154 382 |
| POD/T2 | -4.898 28 | 0.009 012 | -3.138 23 | -0.105 94 |
| POD/T3 | -4.573 49 | 0.028 571 | -4.630 61 | 0.241 061 |
| POD/T4 | -0.905 18 | -0.258 95 | -5.738 05 | -0.079 96 |
| SOD/CK | 0.592 356 | 0.023 681 | 0.606 218 | 0.001 529 |
| SOD/T1 | 0.522 783 | 0.010 684 | 0.656 309 | -0.000 25 |
| SOD/T2 | 0.708 62 | 0.019 055 | 0.637 441 | -0.000 25 |
| SOD/T3 | 0.692 586 | -0.019 39 | 0.587 064 | -0.01 |
| SOD/T4 | 0.652 105 | 0.013 944 | 0.656 031 | -0.011 14 |
| CAT/CK | 0.667 488 | 0.009 894 | 0.653 886 | -0.008 24 |
| CAT/T1 | 0.397 363 | 0.004 979 | 0.711 403 | -0.009 52 |
| CAT/T2 | 0.597 567 | 0.012 894 | 0.550 948 | 0.003 602 |
| CAT/T3 | 0.510 239 | 0.006 908 | 0.583 378 | -0.004 14 |
| CAT/T4 | 0.510 239 | 0.011 432 | 0.701 728 | 0.001 578 |
| MAD/CK | 0.753 945 | 0.005 247 | 0.690 946 | -0.002 92 |
| MAD/T1 | 0.767 382 | 0.005 167 | 0.708 154 | -0.003 18 |
| MAD/T2 | 0.775 85 | 0.004 66 | 0.703 684 | -0.002 98 |
| MAD/T3 | 0.777 252 | 0.004 999 | 0.701 834 | -0.002 94 |
| MAD/T4 | 0.769 486 | 0.005 383 | 0.709 295 | -0.004 88 |
| SP/CK | 0.789 429 | 0.005 378 | 0.713 289 | -0.003 37 |
| SP/T1 | 0.786 07 | 0.005 546 | 0.715 262 | -0.003 18 |
| SP/T2 | 0.792 213 | 0.005 314 | 0.715 209 | -0.003 43 |
| SP/T3 | 0.788 82 | 0.005 336 | 0.712 359 | -0.003 42 |
| SP/T4 | 0.790 397 | 0.005 366 | 0.715 003 | -0.003 43 |
| SS/CK | 0.787 845 | 0.005 372 | 0.702 173 | -0.002 07 |
| SS/T1 | 0.788 676 | 0.005 395 | 0.708 79 | -0.003 5 |
| SS/T2 | 0.787 871 | 0.004 966 | 0.710 174 | -0.003 38 |
| SS/T3 | 0.789 014 | 0.005 402 | 0.713 701 | -0.003 62 |
| SS/T4 | 0.790 074 | 0.005 263 | 0.711 894 | -0.003 34 |
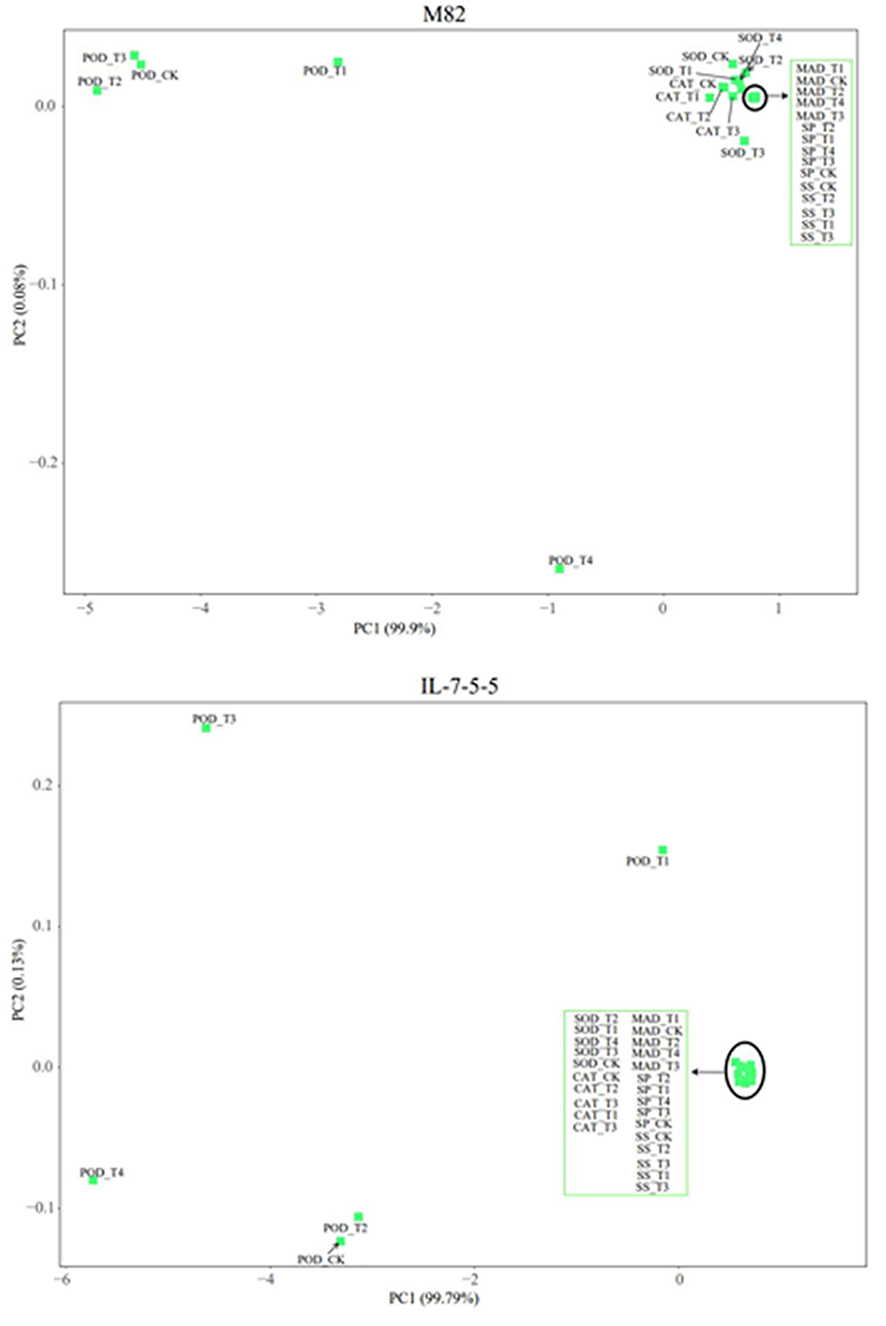
图5 不同浓度外源EBR对盐胁迫下番茄发芽参数的主成分变异
Fig.5 Principal component variation of tomato germination parameters under salt stress with different concentrations of exogenous EBR
| [1] |
罗子敬, 孙宇涵, 卢楠, 等. 杨树耐盐机制及转基因研究进展[J]. 核农学报, 2017, 31(3): 482-492.
DOI |
|
LUO Zijing, SUN Yuhan, LU Nan, et al. Research advances on salt-tolerance mechanism and genetic transformation of poplar[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 31(3): 482-492.
DOI |
|
| [2] | 刘振斌, 任东涛. 应对土壤盐渍化日益增加的农作物育种策略分析[J]. 中国农业信息, 2016,(16): 6-7. |
| LIU Zhenbin, REN Dongtao. Analysis of crop breeding strategy to deal with the increasing soil salinization[J]. China Agricultural Information, 2016,(16): 6-7. | |
| [3] | Zelm E V, Zhang Y, Testerink C. Research advances on salt-tolerance mechanism and genetic transformation of poplar[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2020, 71 (1): 403-433. |
| [4] | 毛恋, 芦建国, 江海燕. 植物响应盐碱胁迫的机制[J]. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(10): 3441-3448. |
| MAO Lian, LU Jianguo, JIANG Haiyan. Mechanisms of plant responses to salt-alkali stress[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(10): 3441-3448. | |
| [5] | 王学征, 李秋红, 吴凤芝. NaCl胁迫下栽培型番茄Na+、K+吸收、分配和转运特性[J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(7): 1423-1432. |
| WANG Xuezheng, LI Qiuhong, WU Fengzhi. Study on the characteristics of absorption, distribution and selective transport of Na+ and K+ in tomato plants under salt stress[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(7): 1423-1432. | |
| [6] | 李换丽. 硅对番茄幼苗抗盐性的影响及机理初探[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2015. |
| LI Huanli. The Effect And Mechanism of Exogenous Silicon on Salt Resistance of Tomato Seedlings[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2015. | |
| [7] |
Siddiqui M H, Mohammad F, Khan M M A, et al. Cumulative effect of nitrogen and sulphur on Brassica juncea L. genotypes under NaCl stress[J]. Protoplasma, 2012, 249(1): 139-153.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Singh M. Plant tolerance mechanism against salt stress: the nutrient management approach[J]. Biochemistry & Pharmacology: Open Access, 2014, 3(5): 165-178. |
| [9] | Taïbi K, Taïbi F, Ait Abderrahim L, et al. Effect of salt stress on growth, chlorophyll content, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defence systems in Phaseolus vulgaris L[J]. South African Journal of Botany, 2016, (105): 306-312. |
| [10] | 王晚霞, 高立杨, 张瑞, 等. 2, 4-表油菜素内酯对盐碱胁迫下垂丝海棠光合及生理特性的影响[J]. 果树学报, 2021, 38(9): 1479-1490. |
| WANG Wanxia, GAO Liyang, ZHANG Rui, et al. Effects of 2, 4 epbrassinolide on photosynthetic and physiological characteristics of Malusa halliana under saline-alkali stress[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2021, 38(9): 1479-1490. | |
| [11] | Fujioka S, Yokota T. Biosynthesis and metabolism of brassinosteroids[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2003, (54): 137-164. |
| [12] | 郭慧琴, 任卫波, 李平, 等. 2, 4-表油菜素内酯和赤霉素互作对羊草种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2014, 31(6): 1097-1103. |
| GUO Huiqin, REN Weibo, LI Ping, et al. Effect of epi-brassinosteroid and Gibberellin on seed germination and seedling growth of Leymus chinensis[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2014, 31(6): 1097-1103. | |
| [13] | Shu S, Tang Y Y, Yuan Y H, et al. The role of 24-epibrassinolide in the regulation of photosynthetic characteristics and nitrogen metabolism of tomato seedlings under a combined low temperature and weak light stress[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2016, (107): 344-353. |
| [14] |
Bajguz A, Hayat S. Effects of brassinosteroids on the plant responses to environmental stresses[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2009, 47(1): 1-8.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | Li J, Yang P, Kang J G, et al. Transcriptome analysis of pepper (Capsicum annuum) revealed a role of 24-epibrassinolide in response to chilling[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, (7): 1281. |
| [16] |
Oh E, Zhu J Y, Wang Z Y. Interaction between BZR1 and PIF4 integrates brassinosteroid and environmental responses[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2012, 14(8): 802-809.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | 杨爽. 钾介导番茄耐盐机理的研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2020. |
| YANG Shuang. Study on the Mechanism of Potassium-mediated Tomato Salt Tolerance[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| [18] | 施雨. 褪黑素对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子萌发及幼苗生长生理特性的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2022. |
| SHI Yu. Effects of Melatonin on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Alfalfa under Salt Stress[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2022. | |
| [19] | 李彦, 张英鹏, 孙明, 等. 盐分胁迫对植物的影响及植物耐盐机理研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2008, 24(1): 258-265. |
| LI Yan, ZHANG Yingpeng, SUN Ming, et al. Research advance in the effects of salt stress on plant and the mechanism of plant resistance[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2008, 24(1): 258-265. | |
| [20] | 侯会云. 油菜素内酯对盐胁迫下水稻种子萌发的影响[J]. 热带农业科学, 2020, 40(7): 1-6. |
| HOU Huiyun. Effects of brassinolide on seed germination of rice under salt stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2020, 40(7): 1-6. | |
| [21] | 舒思晨, 王娟, 王柏柯, 等. 外源MeJA和BR对番茄种子萌发及幼根生长的影响[J]. 农业工程, 2022, 12(3): 138-143. |
| SHU Sichen, WANG Juan, WANG Boke, et al. Effects of exogenous MeJA and BR on tomato seed germination and root growth[J]. Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 12(3): 138-143. | |
| [22] | 王丹, 刘亚西, 周扬, 等. 油菜素内酯对盐胁迫下黑麦草种子萌发及幼苗生长的生理调控作用[J]. 草业科学, 2021, 38(6): 1110-1118. |
| WANG Dan, LIU Yaxi, ZHOU Yang, et al. Physiological regulation of brassinosteroids on seed germination and seedling growth in Lolium perenne in response to salt stress[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(6): 1110-1118. | |
| [23] | 于明艳. 不同外源性试剂对盐胁迫下黄瓜种子萌发的影响[J]. 农业科技与装备, 2019,(2): 27-29. |
| YU Mingyan. Effects of different exogenous reagents on seed germination of Cucumis sativus L[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology and Equipment, 2019,(2): 27-29. | |
| [24] | Zhang S, Hu J, Zhang Y, et al. Seed priming with brassinolide improves lucerne (Medicago sativa L.) seed germination and seedling growth in relation to physiological changes under salinity stress[J]. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 2007, 58(8): 811-815. |
| [25] | CHENG C, HAN H, DING D, et al. Effects of Natural Brassinolide on Seed Germination and Hypocotyl Elongation of Beans[J]. Agricultural Biotechnology, 2015, 4(5): 26-28. |
| [26] | Larré C F, de Moraes D M, Lopes N F. Qualidade fisiológica de sementes de arroz tratadas com solução Salina e 24-epibrassinolídeo[J]. Revista Brasileira De Sementes, 2011, 33(1): 86-94. |
| [27] | Tanveer M, Shahzad B, Sharma A, et al. 24-Epibrassinolide; an active brassinolide and its role in salt stress tolerance in plants: a review[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2018, (130): 69-79. |
| [28] | 纪秀娥, 史留功, 胡春红, 等. 油菜素内酯对小麦、玉米种子萌发的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2014, 42(9): 88-89. |
| JI Xiue, SHI Liugong, HU Chunhong, et al. Effect of brassinolide on seed germination of wheat and maize[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 42(9): 88-89. | |
| [29] | Hu Y Q, Xia S T, Su Y, et al. Brassinolide increases potato root growth in vitro in a dose-dependent way and alleviates salinity stress[J]. BioMed Research International, 2016, 2016: 8231873. |
| [30] | 赵旭庆, 徐珊珊, 李强, 等. 盐胁迫下24-表油菜素内酯浸种对黑果枸杞种子萌发的影响[J]. 林业科技通讯, 2021,(3): 59-61. |
| ZHAO Xuqing, XU Shanshan, LI Qiang, et al. Effects of EBR immersion on seed germination of Lycium ruthenicum under salt stress[J]. Forest Science and Technology, 2021,(3): 59-61. | |
| [31] | Kaur H, Sirhindi G, Bhardwaj R, et al. 28-homobrassinolide regulates antioxidant enzyme activities and gene expression in response to salt- and temperature-induced oxidative stress in Brassica juncea[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 8735. |
| [32] | 杨文文, 刘媛, 聂书明. 外源油菜素内酯对盐胁迫下番茄种子萌发的影响[J]. 园艺与种苗, 2022, 42(11): 43-46. |
| YANG Wenwen, LIU Yuan, NIE Shuming. Effect of exogenous brassinosteroids on germination of tomato seeds under salt stress[J]. Horticulture & Seed, 2022, 42(11): 43-46. | |
| [33] | Zhang S, Hu J, Zhang Y, et al. Seed priming with brassinolide improves lucerne (Medicago sativa L.) seed germination and seedling growth in relation to physiological changes under salinity stress[J]. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 2007, 58(8): 811. |
| [34] | Arora N, Bhardwaj R, Sharma P, et al. Effects of 28-homobrassinolide on growth, lipid peroxidation and antioxidative enzyme activities in seedlings of Zea mays L. under salinity stress[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2008, 30(6): 833-839. |
| [35] | Wu W L, Zhang Q, Ervin E H, et al. Physiological mechanism of enhancing salt stress tolerance of perennial ryegrass by 24-epibrassinolide[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, (8): 1017. |
| [36] |
高景慧, 母养秀, 张越利, 等. 外源NO对渗透胁迫下多年生黑麦草幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2011, 19(4): 625-630.
DOI |
|
GAO Jinghui, MU Yangxiu, ZHANG Yueli, et al. Effects of exogenous nitric oxide on the growth and physiological characteristics of perennial ryegrass seedlings under osmotic stress[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2011, 19(4): 625-630.
DOI |
|
| [37] |
闫慧萍, 彭云玲, 赵小强, 等. 外源24-表油菜素内酯对逆境胁迫下玉米种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2016, 30(5): 988-996.
DOI |
|
YAN Huiping, PENG Yunling, ZHAO Xiaoqiang, et al. Effect of exogenous 24-epibrassinolide on seed germination and seedling growth of maize under different stress[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 30(5): 988-996.
DOI |
|
| [38] | 寇江涛. 外源2, 4-表油菜素内酯对盐胁迫下燕麦种子萌发抑制的缓解效应[J]. 草业科学, 2020, 37(5): 916-925. |
| KOU Jiangtao. Mitigating effect of exogenous 2, 4-epibrassinolide on the inhibition of oat seed germination under salt stress[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(5): 916-925. |
| [1] | 巩雪花, 王小武, 付开赟, 贾尊尊, 吐尔逊·阿合买提, 乔小燕, 叶晓琴, 郭文超, 丁新华. 新疆绿洲灌区玉米田杂草种子库及环境因子对杂草种子萌发的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 49-59. |
| [2] | 张帆, 陈晓露, 王洁, 侯献飞, 贾东海, 顾元国, 苗昊翠, 李强. 混合盐碱胁迫对花生种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2168-2182. |
| [3] | 徐毛毛, 高杰, 李君明, 李鑫, 刘磊, 潘峰. 20个番茄商业品种群体的多样性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2191-2196. |
| [4] | 田海燕, 张占琴, 颉建辉, 王建江, 杨相昆. 加工番茄果实番茄红素与主要品质性状的关系[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2197-2202. |
| [5] | 田超, 李玉姗, 马越, 宋羽. 不同浓度苦豆子浸提液对连作番茄生长及土壤肥力的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2203-2210. |
| [6] | 陈芳, 李字辉, 孙孝贵, 张庭军. 不同剂量的微生物菌剂对加工番茄产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2285-2289. |
| [7] | 董志多, 徐菲, 付秋萍, 黄建, 祁通, 孟阿静, 付彦博, 开赛尔·库尔班. 不同类型盐碱胁迫对棉花种子萌发的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1831-1844. |
| [8] | 张彩虹, 王国强, 姜鲁艳, 刘涛, 德贤明. 低能耗组装式深冬生产型日光温室环境因子变化及番茄性状分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 2043-2053. |
| [9] | 张福林, 李宁, 刘宇翔, 陈怡佳, 余庆辉, 闫会转. 外源2,4-表油菜素内酯及褪黑素对樱桃番茄果实品质和果皮形态结构的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1738-1747. |
| [10] | 杨君妍, 闫淼, 吴海波, 杨文莉, 王豪杰, 毛建才, 翟文强, 李俊华. 高温对不同厚皮甜瓜品种种子萌发的影响及其耐热性综合评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1386-1396. |
| [11] | 阮向阳, 蒲敏, 肖乐乐, 罗林毅, 陈瑞杰, 李然, 陈国永, 冶军. 镁肥施用策略对加工番茄产量和品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 916-925. |
| [12] | 欧源, 罗莎莎, 王如月, 孙雅丽, 虎海防. 盐胁迫对美国黑核桃幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 393-401. |
| [13] | 李春雨, 谭占明, 程云霞, 高源, 马全会, 李志国, 马兴. 水肥耦合对沙培番茄叶绿素含量以及光合特性日变化的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(12): 3006-3013. |
| [14] | 李亚莉, 哈丽哈什·依巴提, 唐亚莉, 段婧婧, 李青军. 氮磷减施与钾协同共效对加工番茄产量和养分吸收的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(12): 3014-3019. |
| [15] | 周小云, 张军高, 梁晶, 龚静云, 周广威, 张少民, 雷斌. 低温和水分胁迫条件下萎锈灵对棉花种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(12): 3051-3060. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 36
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 124
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||