

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (12): 3051-3060.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.12.020
周小云( ), 张军高, 梁晶, 龚静云, 周广威, 张少民, 雷斌(
), 张军高, 梁晶, 龚静云, 周广威, 张少民, 雷斌( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-07
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2025-01-16
通信作者:
雷斌(1973-),男,四川巴中人,研究员,博士,研究方向为农药研制及作物化控,(E-mail)leib668@xaas.ac.cn作者简介:周小云(1977-),男,重庆人,研究员,博士,研究方向为作物化控与生物技术,(E-mail)xiaoyunzhou77@126.com
基金资助:
ZHOU Xiaoyun( ), ZHANG Jungao, LIANG Jing, GONG Jingyun, ZHOU Guangwei, ZHANG Shaomin, LEI Bin(
), ZHANG Jungao, LIANG Jing, GONG Jingyun, ZHOU Guangwei, ZHANG Shaomin, LEI Bin( )
)
Received:2024-05-07
Published:2024-12-20
Online:2025-01-16
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】 研究低温与水分胁迫条件下萎锈灵对棉花种子发芽和幼苗形态建成的影响。【方法】 以萎锈灵包衣棉种为材料,利用人工气候箱结合盆栽沙土持水量控制模拟田间低温和水分环境,分析萎锈灵对棉花种子萌发指标、幼苗形态指标和生理生化特性的影响。【结果】 与常温条件相比,低温胁迫处理降低棉花种子的发芽率,降低21.95%;与低温胁迫相比,萎锈灵处理增加棉花种子的发芽率,增加14.06%;与正常水分条件相比,干旱胁迫处理降低棉花种子发芽率,降低29.41%;与干旱胁迫相比,萎锈灵处理增加棉花种子的发芽率,增加11.67%。低温使棉苗的株高、根长显著减小,棉苗地上部的生物量积累减少。在低温水分共同处理下,未包衣处理的丙二醛含量和细胞膜相对透性增大,而萎锈灵包衣棉苗最高分别降低14.71%和24.14%。水分胁迫下渗透调节物质以可溶性糖为主,低温下以可溶性蛋白为主,萎锈灵包衣棉苗低温水分共同处理下两者含量均最高,分别为15.56%和20.14%。低温水分胁迫条件下,萎锈灵包衣棉苗抗氧化酶活性均最大,抗氧化酶相关基因的表达也更高。【结论】 低温和水分胁迫抑制了棉花萌发和生长,导致叶片的氧化伤害。棉苗启动了活性氧清除机制来抵抗氧化损伤。萎锈灵能够通过改变渗透调节物质含量,增强抗氧化酶活性,抑制膜质过氧化,从而增强棉苗的抗低温和干旱迫能力。
中图分类号:
周小云, 张军高, 梁晶, 龚静云, 周广威, 张少民, 雷斌. 低温和水分胁迫条件下萎锈灵对棉花种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(12): 3051-3060.
ZHOU Xiaoyun, ZHANG Jungao, LIANG Jing, GONG Jingyun, ZHOU Guangwei, ZHANG Shaomin, LEI Bin. Effects of the carboxin from seed coating formulation on the cotton seed germination and seedling agronomic characteristics under water and temperature stress[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(12): 3051-3060.
| 基因 Gene | 上游引物(5'-3') Forwardprimer | 下游引物(5'-3') Reverseprimer |
|---|---|---|
| Gh18s | TTGGACTTAGGGTGGGT | TGGTOGGCATOGTTTA |
| GhSOD(Cu/Zn) | GTCAACAGGACCTCACTTC | ATGTATTACTCCGCTCACC |
| GhPOD | TGCTCAAATGGGTCTCAGTG | GGCAAATGTTGTTGGCTTC |
| GhCAT | CCTGCCATTGTGGTTCCT | TCGTTCTTGCCTGTCTGC |
表1 试验中所用到的引物
Tab.1 Primers from this experiment
| 基因 Gene | 上游引物(5'-3') Forwardprimer | 下游引物(5'-3') Reverseprimer |
|---|---|---|
| Gh18s | TTGGACTTAGGGTGGGT | TGGTOGGCATOGTTTA |
| GhSOD(Cu/Zn) | GTCAACAGGACCTCACTTC | ATGTATTACTCCGCTCACC |
| GhPOD | TGCTCAAATGGGTCTCAGTG | GGCAAATGTTGTTGGCTTC |
| GhCAT | CCTGCCATTGTGGTTCCT | TCGTTCTTGCCTGTCTGC |
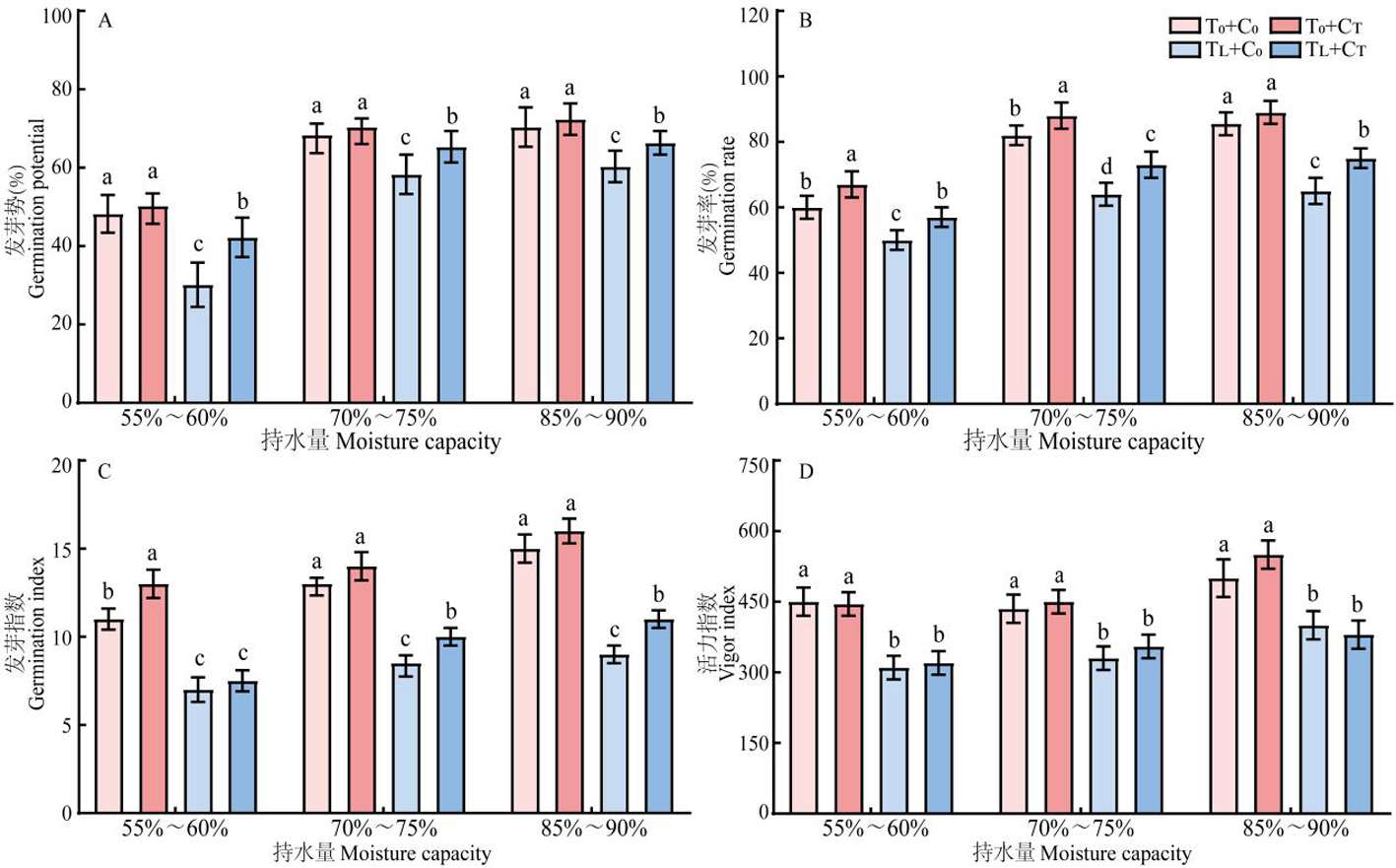
图1 棉种萌发特征的比较 注:C0+T0:未包衣与常温处理,C0+TT:未包衣与低温处理,CT+T0:包衣与常温处理,CT+TT:包衣与低温处理。短线表示标准差,小写字母表示各处理在P<0.05水平上的差异显著性,下同
Fig.1 Comparison of germination characteristics of cotton seeds Notes: C0+T0: Uncoated and room temperature treatment, C0+TT: Uncoated and low temperature treatment, CT+T0 : Coated and room temperature treatment, CT+TT : Coated and low temperature treatment.The bar is mean standard deviation.Lowercase letters indicate the significant difference among treatments at 0.05 level,the same as below
| 指标 Indexes | M | C | T | T×M | T×C | C×M | T×C×M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 发芽势 Germination potential | 10.51** | 98.02*** | 35.52*** | 0.34 | 1.21 | 0.34 | 3.95 |
| 发芽率 Germination rate | 37.23** | 118.60*** | 152.40*** | 0.02 | 3.69* | 0.54 | 1.63 |
| 发芽指数 Germination index | 38.55*** | 70.93*** | 506.60*** | 0.15 | 2.86 | 3.16 | 1.02 |
| 活力指数 Vigor index | 1.71 | 24.77*** | 164.50*** | 0.30 | 1.39 | 2.08 | 0.62 |
表2 持水量、包衣、温度及其互作效应对棉花种子萌发指标影响的方差
Tab.2 Variance analysis of the effects of temperature, water content, coating and their interactions on cotton seed germination indexes
| 指标 Indexes | M | C | T | T×M | T×C | C×M | T×C×M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 发芽势 Germination potential | 10.51** | 98.02*** | 35.52*** | 0.34 | 1.21 | 0.34 | 3.95 |
| 发芽率 Germination rate | 37.23** | 118.60*** | 152.40*** | 0.02 | 3.69* | 0.54 | 1.63 |
| 发芽指数 Germination index | 38.55*** | 70.93*** | 506.60*** | 0.15 | 2.86 | 3.16 | 1.02 |
| 活力指数 Vigor index | 1.71 | 24.77*** | 164.50*** | 0.30 | 1.39 | 2.08 | 0.62 |
| 指标Indexes | M | T | C | T×M | T×C | C×M | T×C×M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 胚轴长Hypocotyl length | 121.00*** | 289.00*** | 259.30*** | 1.01 | 19.00*** | 1.14 | 25.00*** |
| 胚根长Radicle length | 49.00*** | 400.00*** | 34.75*** | 0.25 | 3.25 | 0.75 | 9.00** |
| 胚轴粗Hypocotyl diameter | 6.25* | 0.69 | 7.02** | 1.62 | 2.08 | 0.08 | 3.78 |
| 须根Fibrous root | 0.83 | 176.1*** | 3.48* | 0.07 | 0.97 | 0.12 | 1.00 |
| 鲜重Fresh weight | 0.03 | 101.4*** | 242.20*** | 1.42 | 0.6 | 0.19 | 1.39 |
| 干重Dry weight | 0.02 | 42.11*** | 53.66*** | 0.19 | 0.36 | 1.48 | 0.01 |
表3 持水量、包衣、温度及其互作效应对棉花幼苗农艺性状指标影响的方差
Tab.3 Variance analysis of the effects of temperature, water content, coating and their interactions on agronomic traits of cotton seedlings
| 指标Indexes | M | T | C | T×M | T×C | C×M | T×C×M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 胚轴长Hypocotyl length | 121.00*** | 289.00*** | 259.30*** | 1.01 | 19.00*** | 1.14 | 25.00*** |
| 胚根长Radicle length | 49.00*** | 400.00*** | 34.75*** | 0.25 | 3.25 | 0.75 | 9.00** |
| 胚轴粗Hypocotyl diameter | 6.25* | 0.69 | 7.02** | 1.62 | 2.08 | 0.08 | 3.78 |
| 须根Fibrous root | 0.83 | 176.1*** | 3.48* | 0.07 | 0.97 | 0.12 | 1.00 |
| 鲜重Fresh weight | 0.03 | 101.4*** | 242.20*** | 1.42 | 0.6 | 0.19 | 1.39 |
| 干重Dry weight | 0.02 | 42.11*** | 53.66*** | 0.19 | 0.36 | 1.48 | 0.01 |
| 指标Indexes | M | C | T | T×M | T×C | C×M | T×C×M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干重 Dry weight | 0.02 | 53.66*** | 42.11*** | 0.19 | 0.36 | 1.48 | 0.01 |
| 细胞膜相对透性 Cell membrane permeability | 0.88 | 50.57*** | 47.63*** | 0.2 | 0.12 | 4.32 | 8.75** |
| 丙二醛含量 Malondialdehyde content | 0.04 | 3.27 | 11.96** | 0.29 | 23.13*** | 0.29 | 1.03 |
| 可溶性糖含量 Soluble sugar content | 4.82* | 0.07 | 9.91** | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 2.13 |
| 可溶性蛋白含量 Soluble protein content | 25.91* | 3.21 | 16.17*** | 2.08 | 0.39 | 0.17 | 3.30 |
| SOD酶活性 SOD activity | 2.74 | 12.67*** | 1.58 | 1.67 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.15 |
| POD酶活性 POD activity | 2.19 | 43.70*** | 344.1*** | 0.30 | 1.94 | 0.86 | 8.80** |
| CAT酶活性 CAT activity | 4.92* | 22.26*** | 86.22*** | 2.64 | 0.06 | 0.49 | 1.01 |
| GhSOD相对表达量 Relative expression of GhSOD | 5.83* | 16.80*** | 92.85*** | 0.10 | 3.45* | 1.26 | 2.21 |
| GhPOD相对表达量 Relative expression of GhPOD | 12.01*** | 15.86*** | 72.33*** | 1.08 | 0.90 | 1.51 | 1.11 |
| GhCAT相对表达量 Relative expression of GhCAT | 1.59 | 13.59*** | 44.62*** | 0.33 | 1.16 | 0.33 | 0.69 |
表4 持水量、包衣、温度及其互作效应对棉花幼苗生理生化指标影响的方差
Tab.4 Variance analysis of the effects of temperature, water content, coating and their interactions on physiological and biochemical indexes of cotton seedlings
| 指标Indexes | M | C | T | T×M | T×C | C×M | T×C×M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干重 Dry weight | 0.02 | 53.66*** | 42.11*** | 0.19 | 0.36 | 1.48 | 0.01 |
| 细胞膜相对透性 Cell membrane permeability | 0.88 | 50.57*** | 47.63*** | 0.2 | 0.12 | 4.32 | 8.75** |
| 丙二醛含量 Malondialdehyde content | 0.04 | 3.27 | 11.96** | 0.29 | 23.13*** | 0.29 | 1.03 |
| 可溶性糖含量 Soluble sugar content | 4.82* | 0.07 | 9.91** | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 2.13 |
| 可溶性蛋白含量 Soluble protein content | 25.91* | 3.21 | 16.17*** | 2.08 | 0.39 | 0.17 | 3.30 |
| SOD酶活性 SOD activity | 2.74 | 12.67*** | 1.58 | 1.67 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.15 |
| POD酶活性 POD activity | 2.19 | 43.70*** | 344.1*** | 0.30 | 1.94 | 0.86 | 8.80** |
| CAT酶活性 CAT activity | 4.92* | 22.26*** | 86.22*** | 2.64 | 0.06 | 0.49 | 1.01 |
| GhSOD相对表达量 Relative expression of GhSOD | 5.83* | 16.80*** | 92.85*** | 0.10 | 3.45* | 1.26 | 2.21 |
| GhPOD相对表达量 Relative expression of GhPOD | 12.01*** | 15.86*** | 72.33*** | 1.08 | 0.90 | 1.51 | 1.11 |
| GhCAT相对表达量 Relative expression of GhCAT | 1.59 | 13.59*** | 44.62*** | 0.33 | 1.16 | 0.33 | 0.69 |
| [1] | Li W, Zhao S S, Chen Y, et al. State of China’s climate in 2020[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2021, 14(4): 100048. |
| [2] |
徐敏, 李憬霖, 叶福民, 等. 温湿度对棉花种子萌发的影响研究[J]. 农学学报, 2022, 12(10): 10-14, 20.
DOI |
|
XU Min, LI Jinglin, YE Fumin, et al. Effects of temperature and humidity on cotton seed germination[J]. Journal of Agriculture, 2022, 12(10): 10-14, 20.
DOI |
|
| [3] | 叶尔克江·霍依哈孜, 阿吉古丽·沙依提, 买买提艾力·买买提依明, 等. 新疆气温季节变化时空分布特征研究[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2022, 61(15): 25-33, 41. |
| Yeerkejiang Huoyihazi, Ajiguli Shayiti, Maimaitiaili Maimaitiyiming, et al. Study on temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of seasonal variation of air temperature in Xinjiang[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 61(15): 25-33, 41. | |
| [4] |
李茂春, 练文明, 毛树春, 等. 2021年春季气候变化对新疆棉花生长影响及中期管理建议——以阿拉尔垦区为例[J]. 中国棉花, 2021, 48(6): 45-46.
DOI |
|
LI Maochun, LIAN Wenming, MAO Shuchun, et al. Effect of climate change in spring of 2021 on cotton growth in Xinjiang and medium term management suggestions: based on the Aral reclamation area[J]. China Cotton, 2021, 48(6): 45-46.
DOI |
|
| [5] | 韩松, 吉庆勋, 杨曼利, 等. 添加抗寒剂对包衣棉花种子萌芽及其耐冷性的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(4): 78-81. |
| HAN Song, JI Qingxun, YANG Manli, et al. Effects of cold-resistant agent on germination and chilling tolerance of coated cotton seeds under low temperature stress[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(4): 78-81. | |
| [6] | 雷斌, 李进, 段留生, 等. 种衣剂对低温处理下棉花胚根及幼苗外部形态和超微结构的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 2017, 38(4): 248-256. |
| LEI Bin, LI Jin, DUAN Liusheng, et al. Effect of seed coating agents on external morphology and ultrastructure of cotton radicles and seedlings under low temperature treatments[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2017, 38(4): 248-256. | |
| [7] | 毛玉帅, 段亚冰, 周明国. 琥珀酸脱氢酶抑制剂类杀菌剂抗性研究进展[J]. 农药学学报, 2022, 24(5): 937-948. |
| MAO Yushuai, DUAN Yabing, ZHOU Mingguo. Research progress of the resistance to succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors[J]. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science, 2022, 24(5): 937-948. | |
| [8] | 彭军. 萎锈灵的合成研究[J]. 山东化工, 2021, 50(8): 27-28, 31. |
| PENG Jun. Study on the synthesis of carboxin[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2021, 50(8): 27-28, 31. | |
| [9] | Lee W S, Hahn H G, Nam K D. Synthesis of dihydro-1, 4-oxathiins by rearrangement of 1, 3-oxathiolane sulfoxides[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1986, 51(14): 2789-2795. |
| [10] | Cecchini G, Schrder I, Gunsalus R P, et al. Succinate dehydrogenase and fumarate reductase from Escherichia coli[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2002, 1553(1/2): 140-157. |
| [11] | 徐永哲, 上官小来, 岑江杰, 等. 萎锈灵原药的毒性研究[J]. 浙江化工, 2004, 35(12): 11-12. |
| XU Yongzhe, SHANGGUAN Xiaolai, CEN Jiangjie, et al. Study on the toxicity of carboxin[J]. Zhejiang Chemical Industry, 2004, 35(12): 11-12. | |
| [12] | 周小云, 刘梦丽, 李进, 等. 萎锈灵包衣对低温胁迫下棉种萌发特性的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 2020, 41(8): 495-505. |
| ZHOU Xiaoyun, LIU Mengli, LI Jin, et al. Effects of the carboxin from seed coating formulation on the cotton seed germination characteristics under low temperature stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2020, 41(8): 495-505. | |
| [13] |
周小云, 李进, 张军高, 等. 萎锈灵杀菌剂对提高棉花耐低温冷害胁迫能力的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(4): 705-712.
DOI |
|
ZHOU Xiaoyun, LI Jin, ZHANG Jungao, et al. Effects of the carboxin fungicide on the chilling stress of cotton seedlings[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(4): 705-712.
DOI |
|
| [14] | Al-Beldawi A S, Jawad A, Sheik-Raddy H M. Rhizoctonia seedling disease of hemp and its control[J]. Crop Protection, 1982, 1(1): 111-113. |
| [15] |
肖怀娟, 李娟起, 王吉庆, 等. 亚低温与干旱胁迫对番茄植株水分传输和形态解剖结构的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(8): 2630-2636.
DOI |
|
XIAO Huaijuan, LI Juanqi, WANG Jiqing, et al. Effects of sub-low temperature and drought stress on water transport and morphological anatomy of tomato plant[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(8): 2630-2636.
DOI |
|
| [16] | 高荣岐, 张春庆. 种子生物学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2009. |
| GAO Rongqi, ZHANG Chunqing. Seed biology[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2009. | |
| [17] | Shen Q, Zhang S P, Liu S D, et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis provides insights into the seed germination in cotton in response to chilling stress[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(6): 2067. |
| [18] | 田又升, 王志军, 于航, 等. 干旱胁迫对不同抗旱性棉花品种抗氧化酶活性及基因表达的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2015, 35(12): 2483-2490. |
| TIAN Yousheng, WANG Zhijun, YU Hang, et al. Response of antioxidant enzyme activities and gene expression in different drought resistance cotton varieties under drought stress[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2015, 35(12): 2483-2490. | |
| [19] |
Rajjou L, Duval M, Gallardo K, et al. Seed germination and vigor[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2012, 63: 507-533.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
吉状状, 谭韵, 黄众基, 等. 基于海藻酸的包衣剂对甜玉米种子活力、抗氧化酶系统和产量的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2023, 37(11): 2297-2304.
DOI |
|
JI Zhuangzhuang, TAN Yun, HUANG Zhongji, et al. Effects of seed coating agent based on alginic acid on seed vigor, antioxidant enzyme system and yield of sweet corn[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 37(11): 2297-2304.
DOI |
|
| [21] | 李防洲, 冶军, 侯振安. 外源调节剂包衣对低温胁迫下棉花种子萌发及幼苗耐寒性的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2017, 35(1): 192-197. |
| LI Fangzhou, YE Jun, HOU Zhenan. Effects of seed film coating with exogenous regulating substances on cotton germination rate and cold tolerance of seedlings[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2017, 35(1): 192-197. | |
| [22] | 王雅玲, 杨代斌, 袁会珠, 等. 低温胁迫下戊唑醇和苯醚甲环唑种子包衣对玉米种子出苗和幼苗的影响[J]. 农药学学报, 2009, 11(1): 59-64. |
| WANG Yaling, YANG Daibin, YUAN Huizhu, et al. Effects of seed-coating tebuconazole and difenoconazole on emergence of maize seeds and response of seedlings at chilling stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science, 2009, 11(1): 59-64. | |
| [23] | Chang K F, Conner R L, Hwang S F, et al. Effects of seed treatments and inoculum density of Fusarium avenaceum and Rhizoctonia solani on seedling blight and root rot of faba bean[J]. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 2014, 94(4): 693-700. |
| [24] |
李淑叶, 马慧娟, 张思平, 等. 外源24-表油菜素内酯对低温胁迫下棉花幼苗光合生理的影响[J]. 棉花学报, 2018, 30(3): 252-260.
DOI |
| LI Shuye, MA Huijuan, ZHANG Siping, et al. Effects of exogenous 24-epibrassinolide on photosynthetic physiology of cotton-seedlings under low temperature[J]. Cotton Science, 2018, 30(3): 252-260. | |
| [25] |
孔春艳, 赵静, 徐照丽, 等. 抗氧化系统参与水杨酸诱导烟草幼苗抗冷性提高的生化机制[J]. 热带作物学报, 2023, 44(1): 154-166.
DOI |
|
KONG Chunyan, ZHAO Jing, XU Zhaoli, et al. Involvement of antioxidant system in salicylic acid induced-chilling resistance and biochemical mechanism in tobacco(Nicotiana tabacum L.) seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2023, 44(1): 154-166.
DOI |
|
| [26] |
郑子漂, 徐海江, 崔建平, 等. 水分胁迫对陆地棉生长发育的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(8): 1821-1830.
DOI |
|
ZHENG Zipiao, XU Haijiang, CUI Jianping, et al. Effects of water stress on growth and development in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(8): 1821-1830.
DOI |
| [1] | 巩雪花, 王小武, 付开赟, 贾尊尊, 吐尔逊·阿合买提, 乔小燕, 叶晓琴, 郭文超, 丁新华. 新疆绿洲灌区玉米田杂草种子库及环境因子对杂草种子萌发的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 49-59. |
| [2] | 张帆, 陈晓露, 王洁, 侯献飞, 贾东海, 顾元国, 苗昊翠, 李强. 混合盐碱胁迫对花生种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2168-2182. |
| [3] | 乔雅洁, 付慧鑫, 乔雪, 孟新涛, 张婷, 潘俨. 不同贮藏温度条件下鲜牛肉品质的变化规律[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2323-2329. |
| [4] | 董志多, 徐菲, 付秋萍, 黄建, 祁通, 孟阿静, 付彦博, 开赛尔·库尔班. 不同类型盐碱胁迫对棉花种子萌发的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1831-1844. |
| [5] | 袁莹莹, 赵经华, 迪力穆拉提·司马义, 杨庭瑞. 基于apriori算法对盆栽春小麦生理指标及产量的分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1861-1871. |
| [6] | 胡华兵, 孙琳琳, 刘建雄, 贺碧微, 刘珣, 郇町, 李有芳. 滴灌甜菜糖分积累与温度的相关性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1916-1925. |
| [7] | 奚瑞, 陈怡佳, 李宁, 余庆辉, 王强, 秦勇. 外源2, 4-表芸苔素内酯对盐胁迫下不同盐敏感型番茄种子萌发的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1983-1992. |
| [8] | 付鑫法, 吕廷波, 王久龙, 李港强, 宋仁友, 刘一凡. 春灌定额对棉田水温盐分布及棉花苗期生长发育的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1336-1344. |
| [9] | 杨君妍, 闫淼, 吴海波, 杨文莉, 王豪杰, 毛建才, 翟文强, 李俊华. 高温对不同厚皮甜瓜品种种子萌发的影响及其耐热性综合评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1386-1396. |
| [10] | 党旭伟, 林馨园, 贺正, 陈燕, 慈宝霞, 马学花, 郭晨荔, 贺亚星, 刘扬, 马富裕. 基于无人机热红外遥感图像提取滴灌棉花冠层温度及精度评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(3): 565-575. |
| [11] | 常笑康, 曾亚琦, 孟军, 王建文, 张亚昂, 李林玲, 邓海峰, 郑文祥, 姚新奎, 周静. 耐力运动对伊犁马血液生理指标的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(3): 742-748. |
| [12] | 马云龙, 谢辉, 张雯, 朱学慧, 王艳蒙, 麦斯乐, 张佳喜. 温度对绿色葡萄干色泽及干燥特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 345-354. |
| [13] | 卢红琴, 白云岗, 柴仲平, 卢震林, 刘洪波, 郑明, 肖军. 拱棚环境下“干播湿出”棉田保苗技术效果评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(12): 2872-2882. |
| [14] | 廖彩云, 马贵, 周炎炎, 丁家富, 周悦, 毕可心, 孙蓉, 李有花. 微塑料作用下锌对玉米种子萌发与生长影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2713-2721. |
| [15] | 党新晨, 沈忠义, 屈冬林, 宋于洋. 不同农艺措施对霞多丽葡萄叶幕微气候的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(10): 2427-2433. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 18
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 64
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||