

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (8): 2034-2042.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.08.024
• Plant Protection · Facility Agriculture · Animal Husbandry Veterinarian · Agricultural Eeconomy • Previous Articles Next Articles
LAI Chengxia1( ), YANG Yanlong1, LI Chunping1, Mayila Yusuyin1, WANG Yan2, YANG Dong3, YANG Ni1, GE Fengwei4, WANG Penglong1, MA Jun1(
), YANG Yanlong1, LI Chunping1, Mayila Yusuyin1, WANG Yan2, YANG Dong3, YANG Ni1, GE Fengwei4, WANG Penglong1, MA Jun1( )
)
Received:2024-01-28
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-09-19
Correspondence author:
MA Jun
Supported by:
赖成霞1( ), 杨延龙1, 李春平1, 玛依拉·玉素音1, 王燕2, 杨栋3, 阳妮1, 葛风伟4, 汪鹏龙1, 马君1(
), 杨延龙1, 李春平1, 玛依拉·玉素音1, 王燕2, 杨栋3, 阳妮1, 葛风伟4, 汪鹏龙1, 马君1( )
)
通讯作者:
马君
作者简介:赖成霞(1972-),女,新疆乌鲁木齐人,副研究员,研究方向为棉花抗逆分子育种,(E-mail)lchxia2001@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LAI Chengxia, YANG Yanlong, LI Chunping, Mayila Yusuyin, WANG Yan, YANG Dong, YANG Ni, GE Fengwei, WANG Penglong, MA Jun. Biological characteristics and chemical control of defoliating cotton Verticillium wilt[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 2034-2042.
赖成霞, 杨延龙, 李春平, 玛依拉·玉素音, 王燕, 杨栋, 阳妮, 葛风伟, 汪鹏龙, 马君. 落叶型棉花黄萎病的生物学特征及药剂防治分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 2034-2042.
| 温度 Temperature (℃) | 试验点 Test point | 菌系 Microflora | 菌落颜色 Colony color | 生长速率 Growth rate (cm/d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.064±0.01e |
| Vd-2 | 白色 | 0.123±0.006c | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色 | 0.143±0.008b | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色 | 0.124±0.005c | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.100±0.008d | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.140±0.007b | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.143±0.006b | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.160±0.006a | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色 | 0.139±0.008b | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.123±0.006c | ||
| 15 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.205±0.01e |
| Vd-2 | 白色 | 0.256±0.004c | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色 | 0.208±0.005e | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色 | 0.260±0.01c | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.203±0.007e | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.267±0.008b | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.289±0.008a | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.268±0.05b | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色 | 0.270±0.006b | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.245±0.005d | ||
| 20 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.307±0.008d |
| Vd-2 | 白色 | 0.362±0.009b | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色 | 0.272±0.005f | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色 | 0.296±0.014e | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.325±0.01c | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.303±0.007de | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.362±0.007b | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.370±0.011ab | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色 | 0.373±0.013a | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.323±0.004c | ||
| 25 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.377±0.01e |
| Vd-2 | 白色 | 0.406±0.008bc | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色 | 0.324±0.008f | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色 | 0.393±0.01d | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.374±0.009e | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.400±0.01cd | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.411±0.01b | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.426±0.005a | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色 | 0.410±0.011b | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.294±0.01g | ||
| 30 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.250±0.01a |
| Vd-2 | 白色 | 0.098±0.007e | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色 | 0.066±0.004g | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色 | 0.216±0.003b | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.251±0.008a | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.146±0.01c | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.100±0.006e | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.084±0.005f | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色 | 0.135±0.009d | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.086±0.003f |
Tab.1 Changes of different temperatures on mycelial growth rate of Verticillium dahliae on cotton in 14 days
| 温度 Temperature (℃) | 试验点 Test point | 菌系 Microflora | 菌落颜色 Colony color | 生长速率 Growth rate (cm/d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.064±0.01e |
| Vd-2 | 白色 | 0.123±0.006c | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色 | 0.143±0.008b | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色 | 0.124±0.005c | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.100±0.008d | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.140±0.007b | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.143±0.006b | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.160±0.006a | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色 | 0.139±0.008b | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.123±0.006c | ||
| 15 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.205±0.01e |
| Vd-2 | 白色 | 0.256±0.004c | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色 | 0.208±0.005e | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色 | 0.260±0.01c | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.203±0.007e | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.267±0.008b | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.289±0.008a | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.268±0.05b | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色 | 0.270±0.006b | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.245±0.005d | ||
| 20 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.307±0.008d |
| Vd-2 | 白色 | 0.362±0.009b | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色 | 0.272±0.005f | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色 | 0.296±0.014e | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.325±0.01c | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.303±0.007de | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.362±0.007b | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.370±0.011ab | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色 | 0.373±0.013a | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.323±0.004c | ||
| 25 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.377±0.01e |
| Vd-2 | 白色 | 0.406±0.008bc | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色 | 0.324±0.008f | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色 | 0.393±0.01d | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.374±0.009e | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.400±0.01cd | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.411±0.01b | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.426±0.005a | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色 | 0.410±0.011b | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.294±0.01g | ||
| 30 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.250±0.01a |
| Vd-2 | 白色 | 0.098±0.007e | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色 | 0.066±0.004g | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色 | 0.216±0.003b | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.251±0.008a | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.146±0.01c | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.100±0.006e | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.084±0.005f | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色 | 0.135±0.009d | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.086±0.003f |

Fig.1 Changes of growth rate of pathogens under different ions for 12 days Note:Different lowercase letters indicated significant difference among different ions application amounts of different treatments at 0.05 level
| 酸碱度 pH值 | 试验点 Test point | 菌系 Microflora | 菌落颜色 Colony color | 生长速率 Growth rate (cm/d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.361±0.008c |
| Vd-2 | 白色 | 0.302±0.008f | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色 | 0.384±0.01b | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色 | 0.331±0.008e | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.246±0.009h | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.342±0.009d | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.337±0.006de | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.258±0.005g | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色 | 0.406±0.007a | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.245±0.008h | ||
| 6 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.361±0.01c |
| Vd-2 | 白色 | 0.338±0.008f | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色 | 0.350±0.01de | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色 | 0.355±0.01cd | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.296±0.009g | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.345±0.006ef | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.351±0.008de | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.402±0.011a | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.391±0.008b | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.255±0.009h | ||
| 7 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.330±0.006d |
| Vd-2 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.325±0.008d | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.316±0.01e | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色 | 0.356±0.007c | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.269±0.01f | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.327±0.01d | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.331±0.004d | |
| Vc-2 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.358±0.013c | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色 | 0.400±0.007a | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.372±0.006b | ||
| 8 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.316±0.006cd |
| Vd-2 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.319±0.014cd | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.321±0.007c | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.312±0.011de | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.233±0.004f | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.305±0.01e | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.314±0.008cd | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.352±0.007b | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.374±0.006a | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.348±0.007b | ||
| 9 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.301±0.01e |
| Vd-2 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.273±0.007g | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.309±0.007d | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.297±0.007e | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.202±0.008h | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.323±0.008bc | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.281±0.012f | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.332±0.006a | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.317±0.01c | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.329±0.009ab |
Tab.2 Changes of different pH on mycelial growth rate of Verticillium dahliae
| 酸碱度 pH值 | 试验点 Test point | 菌系 Microflora | 菌落颜色 Colony color | 生长速率 Growth rate (cm/d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.361±0.008c |
| Vd-2 | 白色 | 0.302±0.008f | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色 | 0.384±0.01b | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色 | 0.331±0.008e | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.246±0.009h | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.342±0.009d | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.337±0.006de | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.258±0.005g | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色 | 0.406±0.007a | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.245±0.008h | ||
| 6 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.361±0.01c |
| Vd-2 | 白色 | 0.338±0.008f | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色 | 0.350±0.01de | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色 | 0.355±0.01cd | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.296±0.009g | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.345±0.006ef | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.351±0.008de | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.402±0.011a | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.391±0.008b | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.255±0.009h | ||
| 7 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.330±0.006d |
| Vd-2 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.325±0.008d | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.316±0.01e | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色 | 0.356±0.007c | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.269±0.01f | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.327±0.01d | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.331±0.004d | |
| Vc-2 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.358±0.013c | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色 | 0.400±0.007a | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.372±0.006b | ||
| 8 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.316±0.006cd |
| Vd-2 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.319±0.014cd | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.321±0.007c | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.312±0.011de | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.233±0.004f | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.305±0.01e | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色 | 0.314±0.008cd | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.352±0.007b | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.374±0.006a | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.348±0.007b | ||
| 9 | 沙湾市 Shawan City | Vd-1 | 白色 | 0.301±0.01e |
| Vd-2 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.273±0.007g | ||
| Vd-3 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.309±0.007d | ||
| Vd-4 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.297±0.007e | ||
| Vd-5 | 白色 | 0.202±0.008h | ||
| Vd-6 | 白色 | 0.323±0.008bc | ||
| 昌吉市 Changji City | Vc-1 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.281±0.012f | |
| Vc-2 | 白色 | 0.332±0.006a | ||
| Vc-3 | 白色,微菌核 | 0.317±0.01c | ||
| Vc-4 | 白色 | 0.329±0.009ab |
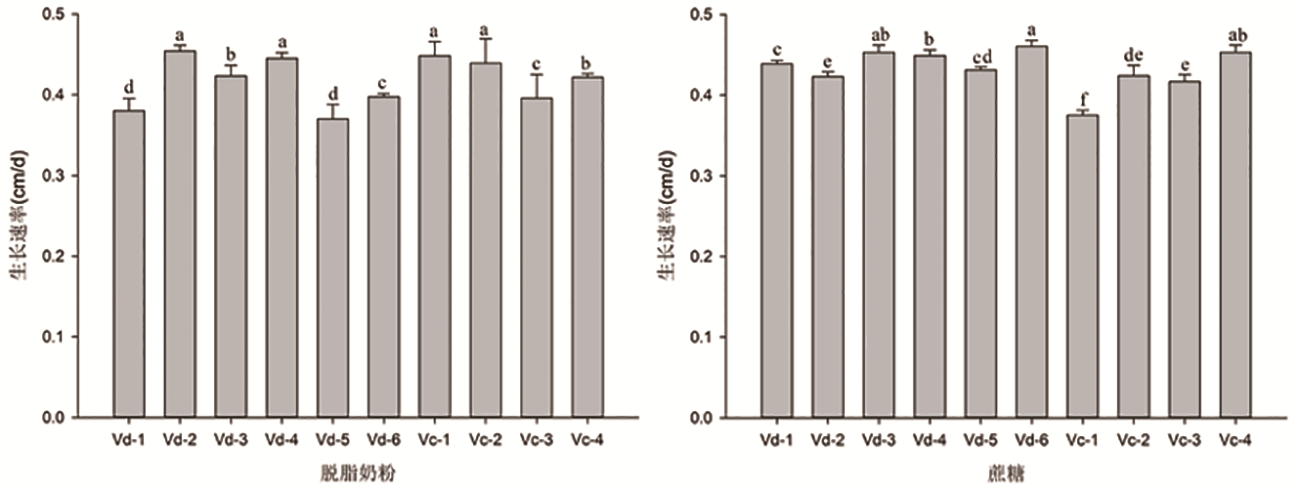
Fig.2 Growth rate of pathogens under different carbon sources for 12 days Note:Different lowercase letters indicated significant difference among different carbon source application amounts of different treatments at 0.05 level
| [1] | 张绪振, 张树琴, 陈吉棣, 等. 我国棉花黄萎病菌“种”的鉴定[J] 植物病理学报, 1981,(3): 15-20,67-68. |
| ZHANG Xuzhen, ZHANG shuqin, CHEN jili, et al. The Fungal Type Identification of Vercillium Dahilae in China[J] Chinese Plant Pathology, 1981,(3): 15-20,67-68. | |
| [2] | 商文静, 陈婷, 白应文, 等. 大丽轮枝菌微菌核的萌发条件及致死温度[J]. 菌物学报, 2013, 32(6): 986-992. |
| SHANG Wenjing, CHEN Ting, BAI Yingwen, et al. Germination Conditions and Lethal Temperature of Microsclerotium of Verticillium Dahliae[J]. Mycosystema, 2013, 32(6): 986-992. | |
| [3] | 商文静, 魏峰, 冯小军, 等. 棉田大丽轮枝菌微菌核的空间分布及其抽样技术[J] 西北农业学报, 2014, 23(4): 192-197. |
| SHANG Wenjing, WEI Feng, FENG Xiaojun, et al. Spatial Distribution and Sampling Techniques of Verticillium Dahliae Sclerotia in Cotton Field[J] Acta Agriculture Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2014, 23(4): 192-197. | |
| [4] |
张梦恬, 裴娟, 李国, 等. 新疆石河子地区棉花黄萎病菌分离鉴定及其致病力分析. 生物技术通报, 2018, 34(6): 73-78
DOI |
|
ZHANG Mengtian, PEI Juan, LI Guo, et al. Identification and Pathogenicity Analysis of Cotton Verticillium Wilt from Shihezi Region of Xinjiang[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2018, 34(6): 73-78
DOI |
|
| [5] | 陈志荣, 赵小强, 孙琦, 等. 不同寄主大丽轮枝菌培养性状的比较及致病力分化的分析. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 36(4): 457-466 |
| CHEN Zhirong, ZHAO Xiaoqiang, SUN QI, et al. Cultural Characteristics and Pathogenicity Differ entiation among Strains of Verticillium Dahliae Isolated from Different Host Plants[J], Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science), 2018, 36(4): 457-466 | |
| [6] | 刘海洋, 王伟, 张仁福, 等. 北疆棉花黄萎病发病率调查及土壤中黄萎病菌微菌核数量与种群类型分析[J]. 植物保护, 2023, 49(4): 276-283,292. |
| LIU Haiyang, WANG Wei, ZHANG Renfu, et al. Investigation the incidencerate of Verticillium wilt and analysis on the number of microsclerotia and the population type of Verticillium Dahliae in soil of northern Xin jiang[J]. Plant Protection, 2023, 49(4): 276-283,292. | |
| [7] |
刘廷利, 惠慧, 阚家亮, 等. 新疆北部棉花黄萎病菌培养特性、致病型、致病性分化及ISSR遗传变异研究[J]. 棉花学报, 2017, 29 (6): 541-549.
DOI |
| LIU Tingli, XI Hui, KAN Jialiang, et al. The Monitoring of Cultural Characteristics, Pathotype, Pathogenicity Differentiation and ISSR Genetic Variation of Verticillium Dahliae Isolates from Cotton in Northern Xinjiang[J]. Cotton Science, 2017, 29(6):541-549 | |
| [8] | 段维军, 李国英, 张莉, 等. 新疆棉花黄萎病菌致病性分化监测研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2004, (5): 324-328. |
| DUAN Weijun, LI Guoying, ZHANG Li, et al. The Monitor of Pathogenic Differentiation of Verticillium.Dahliae fromCotton in Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2004, (5): 324-328. | |
| [9] | 张莉, 马慧宁, 陈文霞, 等. 石河子地区棉花黄萎病菌致病型监测研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2007,(16): 4879-4880, 4882. |
| ZHANG Li, MA Huining, CHEN Wenxia, et al. Monitoring Study on Pathotype of Verticillium Dahliae of Cotton in Shihezi Region[J]. Journal of Anhui Agri.Sci. 2007, 35(16):4879-4880, 4882 | |
| [10] | 韩宏伟, 刘培源, 高峰, 等. 新疆北部棉区黄萎病菌种群致病性分化及变异[J]. 植物保护学报, 2011, 38(2): 121-126. |
| HAN Hongwei, LIU Peiyuan, GAO Feng, et al. The Pathogenicity Differentiation and Variability of Verticillium Dahliae from Cotton in Northern Xinjiang[J]. Plant Protection, 2011, 38(2): 121-126 | |
| [11] |
袁洪波, 艾尼江, 赵建军, 等. 棉花黄萎病菌致病力分化与ISSR遗传变异分析[J]. 华北农学报, 2013, 28(5): 84-89.
DOI |
| YUAN Hongbo, Ainijiang, ZHAO Jianjun, et al. Pathogenicity Differentiation and ISSR Genetic Variation Analysis of Verticillium Dahliae Isolates from Cotton in Shihezi, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2013, 28(5): 84-89. | |
| [12] |
赖成霞, 玛依拉·玉素音, 石必显, 等. 助剂激健在防治棉花黄萎病中的效果[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58 (12): 2220-2227.
DOI |
|
LAI Chengxia, Mayila Yusuyin, SHI Bixian, et al. Application Study on the Adjuvant Jijian as Synergist for Cotton Verticillium Disease Control[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58 (12): 2220-2227.
DOI |
|
| [13] | 张栋海, 蔡志平, 魏俊梅, 等. 不同枯草芽孢杆菌制剂防治棉花黄萎病药效试验[J]. 新疆农垦科技, 2014, 37 (7): 29-31. |
| ZHANG Donghai, CAI Zhiping, WEI Junmei, et al. Efficacy Test of Different Preparations of Bacillus Subtilis to Control Cotton Verticillium Wilt[J], Xin Jiang Farm Research of Science and Technology, 2014, 37 (7): 29-31. | |
| [14] | 石磊, 吕宁, 李全胜, 等. 生物农药随水滴施防治棉花黄萎病用量筛选研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 2019, 32 (4): 829-836. |
| SHI Lei, LYU Ning, LI Quangsheng, et al. Amount Screening of Different Biological Agents Application through Drip Irrigation to Prevent Cotton Vertillium wilt[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 32 (4): 829-836. | |
| [15] | 李素英, 刘冬青, 牛赡光, 等. 生物防治菌与多菌灵混用防治棉花黄萎病的效应研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2004, 12(1): 119-121. |
| LI Suying, LIU Dongqing, NIU Zhanguang, et al. Studies on the control of verticillium wilt of cotton with the mixtures of biological agents and carbendazi[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2004, 12(1): 119-121 | |
| [16] | 吕宁, 周光海, 陈云, 等. 滴施生物药剂对棉花生长、黄萎病防治及土壤微生物数量的影响[J] 西北农业学报, 2018, 27 (7): 1056-1064. |
| LYU Ning, ZHOU Guanghai, CHEN Yun, et al. Effects of biological agents on cotton growth, verticillium wilt control and soil microbial population[J]. ACTA Agriculturae Borealiioccidentalis sinica, 2018, 27 (7): 1056-1064 | |
| [17] |
戴宝生, 吕锐玲, 李蔚. 4种药剂防治棉花黄萎病研究[J] 中国棉花, 2010, 37(8): 15-16.
DOI |
|
DAI Baosheng, LYU Ruiling, LI Wei. Control Study of Four Fungicides against Cotton Verticillium Wilt[J]. China Cotton, 2010, 37(8): 15-16.
DOI |
|
| [18] |
曹小蕾, 姚兆群, 彭金凤, 等. 防治棉花黄萎病的最优菌/药组合筛选[J] 中国棉花, 2016, 43(1): 19-23.
DOI |
|
CAO Xiaolei, YAO Zhaoqun, PENG Jingfeng, et al. Screening of the Optimal Bacterial / Drug Combination against Cotton Verticillium Wilt[J]. China Cotton, 2016, 43(1): 19-23.
DOI |
| [1] | MA Baihuan, ZHAO Qiang, XIE Jia, XU Kaiyue, REN Ruofei, SONG Xinghu. Effects of biopharmaceutical mixture on the control and growth of cotton Verticillium wilt [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1748-1756. |
| [2] | WANG Li, ZHOU Xiaoyun, YAN Rong, ZHANG Jungao, LI Jin, LIANG Jing, GONG Jingyun, DU Yu, MA Deying, LEI Bin. Pathogen identification and biological characteristics analysis of wheat snow rot caused by Microdochium nivale [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(5): 1201-1208. |
| [3] | YAN Rong, ZHOU Xiaoyun, ZHANG Jungao, WANG Li, LI Jin, LIANG Jing, GONG Jingyun, DU Yu, LI Kemei, LEI Bin. Identification and biological characterization of the root rot pathogen of wheat in Xinjiang caused by Bipolaris sorokiniana [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(5): 1209-1217. |
| [4] | WEI Yang, CHEN Guoxiang, Adili Sattar, Mahamatopiti Tusun, TIAN Guangyu. Indoor toxicity determination and field efficacy trials of several pesticides against Grapholita molesta in walnut production areas of Hotan County [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(3): 665-671. |
| [5] | LIU Feng, Zulipiye Anwaier, LI Kemei, Tuolunbate Biyahong. Identification of new pathogens of alfalfa anthracnose (Colletotrichum liriopes) and preliminary study on biological characteristics [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(3): 690-698. |
| [6] | OUYANG Danhua, ZHAO Kang, SONG Dongbo, LIU Ziqing, GUO Wangzhen, LIU Yan, GU Aixing, Azhatiguli Maimaitituer, Alikaerjiang Amaier. Identification and comprehensive analysis of Verticillium wilt resistance in 35 cotton strains [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(1): 9-18. |
| [7] | XU Lijuan, CHEN Yong, WANG Zeyu, WANG Bo, Ainijiang Ersiman, GUO Rui, LI Kemei, SONG Suqin. Isolation, identification and biological characteristics of potato scab pathogen in Baicheng, Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2258-2265. |
| [8] | YANG Ni, Mayila Yusuyin, YANG Yanlong, LI Chunping, ZHANG Dawei, XU Haijiang, LAI Chengxia. Comparative analysis of plant volatiles from the Verticillium-Infected withered spot and etiolated leaves in cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 1975-1986. |
| [9] | SONG Danbo, ZHANG Guoxin, WANG Quan, LIU Baojun, HUANG Tao, HAN Hongwei, BAI Jianyu, GUO Qingyuan. Study on the biological characteristics of the pathogen of bacterial perforation of alternaria alternata in Xinjiang and the screening of laboratory agents [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1515-1522. |
| [10] | ZHANG Guoxin, SONG Danbo, LIU Baojun, WANG Quan, BAI Jianyu, GUO Qingyuan. Biological characteristics and screening of fungicides of Xanthoceras sorbifolium bunge root rot in the lab [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1523-1530. |
| [11] | CHENG Lihua, YANG Honglan, MA Qingqian, SHI Ying, ZHANG Dawei, Alisher A. Abdullaev, ZHANG Daoyuan. Physiological identification and analysis of Verticillium wilt resistance of 10 foreign cotton germplasm resources [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(4): 992-1002. |
| [12] | MA Qingqian, YANG Honglan, WEI Xin, ZHANG Dawei, Alisher A Abdullaev, CHENG Lihua, ZHANG Daoyuan. Identification and Screen from Eighteen Foreign Cotton Germplasm on Agronomy and Verticillium Resistance [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(2): 286-294. |
| [13] | WANG Haitao, LIU Cunjing, TANG Liyuan, ZHANG Sujun, CAI Xiao, LI Xinghe, MA Wenna, HAN Junwei, ZHANG Xiangyun, ZHANG Jianhong. The influence of different planting densities on agronomic traits, yield and quality of machine-picked cotton varieties [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(11): 2638-2645. |
| [14] | LIN Xinzhang, LEI Jin, REN Zichao, ZHANG Jie, LIANG Bingqin, WANG Bingpeng, WANG Weibing. Study on physical parameters and biological characteristics of Xinjiang seabuckthorn fruit after frozen storage [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(10): 2479-2485. |
| [15] | RONG Hua, ZHANG Luhui, LIU Long, ZHENG Tongtong, LEI Bin, GUO Qingyuan. Study on Biological properties of Verticillium and Virulence Comparison of 16 Fungicides [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(8): 1984-1992. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 27
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 113
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||