

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (6): 1423-1432.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.06.015
• Microbes·Horticultural Special Local Products·Storage and Preservation Processing • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Peiqi1( ), SUN Qingpei1, WANG Zhihui2, QIN Xinzheng2(
), SUN Qingpei1, WANG Zhihui2, QIN Xinzheng2( ), FAN Yonghong1(
), FAN Yonghong1( )
)
Received:2022-09-29
Online:2023-06-20
Published:2023-06-20
Correspondence author:
QIN Xinzheng(1977-), male, native place: Shihezi, Xinjiang. Associate researcher. Research field: Environmental microbiology, (E-mail) qinxinzheng@163.com; FAN Yonghong(1974-), female, native place: Jinning, Gansu. Professor. Research field: Environmental microbiology, (E-mail) yhfanzyb2004@163.com
Supported by:
李佩琪1( ), 孙庆培1, 王志慧2, 秦新政2(
), 孙庆培1, 王志慧2, 秦新政2( ), 樊永红1(
), 樊永红1( )
)
通讯作者:
秦新政(1977-),新疆石河子人,副研究员,硕士,研究方向为环境微生物学,(E-mail) qinxinzheng@163.com; 樊永红(1974-),女,甘肃静宁人,教授,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为环境微生物学,(E-mail) yhfanzyb2004@163.com
作者简介:李佩琪(1997-),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为环境微生物学,(E-mail)2394767902@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LI Peiqi, SUN Qingpei, WANG Zhihui, QIN Xinzheng, FAN Yonghong. Correlation analysis of lignin degradation and enzyme activity changes in solid fermentation of cotton stalks[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1423-1432.
李佩琪, 孙庆培, 王志慧, 秦新政, 樊永红. 棉秆固体发酵中木质素降解与酶活性变化的关联分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1423-1432.
| 固体发酵时期 Solid fermentation period | 失重率 Weight loss rate (%) | 纤维素含量 Cellulose content (%) | 半纤维素含量 Hemicellulose content (%) | 木质素含量 Lignin content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 初始 Initial stage | 0.00a | 29.32±1.81a | 15.17±0.71a | 31.51±0.98a |
| 升温期 Warming period | 5.86±1.05b | 28.47±1.49a | 13.30±0.67b | 31.45±0.88a |
| 高温期 High temperature period | 6.42±0.9b | 28.36±0.87a | 11.48±0.16c | 30.60±1.19ab |
| 熟化期 Maturation period | 29.30±0.75c | 21.27±0.38b | 8.42±0.15d | 27.52±1.25ab |
| 末期 Final stage | 35.59±1.55d | 18.18±0.82c | 7.75±0.34d | 25.38±0.98b |
Tab.1 Contents of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin in solid fermented cotton straw
| 固体发酵时期 Solid fermentation period | 失重率 Weight loss rate (%) | 纤维素含量 Cellulose content (%) | 半纤维素含量 Hemicellulose content (%) | 木质素含量 Lignin content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 初始 Initial stage | 0.00a | 29.32±1.81a | 15.17±0.71a | 31.51±0.98a |
| 升温期 Warming period | 5.86±1.05b | 28.47±1.49a | 13.30±0.67b | 31.45±0.88a |
| 高温期 High temperature period | 6.42±0.9b | 28.36±0.87a | 11.48±0.16c | 30.60±1.19ab |
| 熟化期 Maturation period | 29.30±0.75c | 21.27±0.38b | 8.42±0.15d | 27.52±1.25ab |
| 末期 Final stage | 35.59±1.55d | 18.18±0.82c | 7.75±0.34d | 25.38±0.98b |
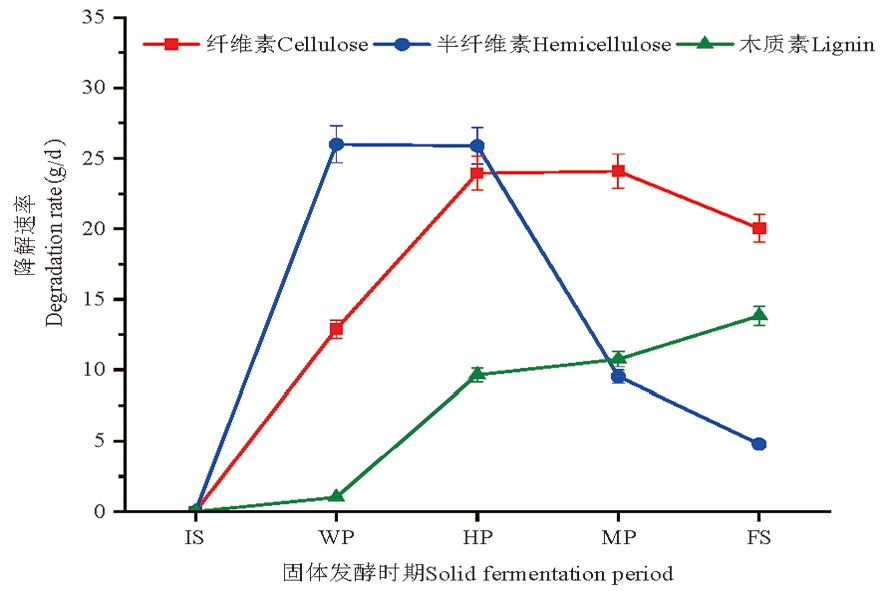
Fig.2 Change of lignocellulose degradation rate during cotton stalk fermentation Note: IS: Initial stage;WP:Warming period:HP:High temperature period;MP:Maturation period;FS:Final stage, the same as below
| 指标 Index | 发酵温度 Fermentation temperature | Lac活性 Lac activity | LiP活性 LiP activity | MnP活 MnP activity | 木质素 降解速率 Lignin degradation rate | 纤维素降解速 Cellulose degradation rate | 半纤维素 降解速率 Hemicellulose degradation rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 发酵温度 Fermentation temperature | 1 | ||||||
| Lac活性Lac activity | -0.461 | 1 | |||||
| LiP活性LiP activity | -0.29 | 0.848** | 1 | ||||
| MnP活性MnP activity | -0.281 | 0.888** | 0.908** | 1 | |||
| 木质素降解速率 Lignin degradation rate | -0.088 | 0.611** | 0.698** | 0.695** | 1 | ||
| 纤维素降解速率 Cellulose degradation rate | 0.344 | 0.467* | 0.477* | 0.617** | 0.666** | 1 | |
| 半纤维素降解速率 Hemicellulose degradation rate | 0.919** | -0.363 | -0.205 | -0.164 | -0.049 | 0.403 | 1 |
Tab.2 Correlation analysis between lignin degradation enzyme activity and lignin degradation
| 指标 Index | 发酵温度 Fermentation temperature | Lac活性 Lac activity | LiP活性 LiP activity | MnP活 MnP activity | 木质素 降解速率 Lignin degradation rate | 纤维素降解速 Cellulose degradation rate | 半纤维素 降解速率 Hemicellulose degradation rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 发酵温度 Fermentation temperature | 1 | ||||||
| Lac活性Lac activity | -0.461 | 1 | |||||
| LiP活性LiP activity | -0.29 | 0.848** | 1 | ||||
| MnP活性MnP activity | -0.281 | 0.888** | 0.908** | 1 | |||
| 木质素降解速率 Lignin degradation rate | -0.088 | 0.611** | 0.698** | 0.695** | 1 | ||
| 纤维素降解速率 Cellulose degradation rate | 0.344 | 0.467* | 0.477* | 0.617** | 0.666** | 1 | |
| 半纤维素降解速率 Hemicellulose degradation rate | 0.919** | -0.363 | -0.205 | -0.164 | -0.049 | 0.403 | 1 |
| 成分 Components | 初始特征值 Initial eigenvalue | 提取平方和载入 Extraction sums of squared loadings | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 方差贡献率 Variance contribution rate (%) | 累积方差贡献率 Cumulative variance contribution rate (%) | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 方差贡献率 Variance contribution rate (%) | 累积方差贡献率 Cumulative variance contribution rate (%) | |
| 1 | 6.259 | 62.591 | 62.591 | 6.259 | 62.591 | 62.591 |
| 2 | 2.280 | 22.800 | 85.391 | 2.280 | 22.800 | 85.391 |
| 3 | 0.501 | 5.013 | 90.404 | |||
| 4 | 0.369 | 3.687 | 94.091 | |||
| 5 | 0.276 | 2.760 | 96.851 | |||
| 6 | 0.110 | 1.101 | 97.952 | |||
| 7 | 0.087 | 0.874 | 98.826 | |||
| 8 | 0.073 | 0.730 | 99.555 | |||
| 9 | 0.035 | 0.352 | 99.907 | |||
| 10 | 0.009 | 0.093 | 100.000 | |||
Tab.3 Interpretation of total variance
| 成分 Components | 初始特征值 Initial eigenvalue | 提取平方和载入 Extraction sums of squared loadings | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 方差贡献率 Variance contribution rate (%) | 累积方差贡献率 Cumulative variance contribution rate (%) | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 方差贡献率 Variance contribution rate (%) | 累积方差贡献率 Cumulative variance contribution rate (%) | |
| 1 | 6.259 | 62.591 | 62.591 | 6.259 | 62.591 | 62.591 |
| 2 | 2.280 | 22.800 | 85.391 | 2.280 | 22.800 | 85.391 |
| 3 | 0.501 | 5.013 | 90.404 | |||
| 4 | 0.369 | 3.687 | 94.091 | |||
| 5 | 0.276 | 2.760 | 96.851 | |||
| 6 | 0.110 | 1.101 | 97.952 | |||
| 7 | 0.087 | 0.874 | 98.826 | |||
| 8 | 0.073 | 0.730 | 99.555 | |||
| 9 | 0.035 | 0.352 | 99.907 | |||
| 10 | 0.009 | 0.093 | 100.000 | |||
| 指标 Index | 成分 Components | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |
| 纤维素含量Cellulose content | -0.959 | 0.145 |
| 锰过氧化物酶活性Manganese peroxidase activity | 0.957 | 0.070 |
| 半纤维素含量Hemicellulose content | -0.955 | -0.187 |
| 木质素过氧化物酶活性Lignin peroxidases activity | 0.931 | -0.155 |
| 漆酶活性Laccase activity | 0.909 | 0.007 |
| 木质素降解速率Lignin degradation rate | 0.790 | 0.260 |
| 木质素含量Lignin content | -0.775 | 0.026 |
| 半纤维素降解速率Hemicellulose degradation rate | -0.278 | 0.918 |
| 温度Temperature | -0.362 | 0.898 |
| 纤维素降解速率Cellulose degradation rate | 0.621 | 0.690 |
Tab.4 Principal component factor loading matrix
| 指标 Index | 成分 Components | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |
| 纤维素含量Cellulose content | -0.959 | 0.145 |
| 锰过氧化物酶活性Manganese peroxidase activity | 0.957 | 0.070 |
| 半纤维素含量Hemicellulose content | -0.955 | -0.187 |
| 木质素过氧化物酶活性Lignin peroxidases activity | 0.931 | -0.155 |
| 漆酶活性Laccase activity | 0.909 | 0.007 |
| 木质素降解速率Lignin degradation rate | 0.790 | 0.260 |
| 木质素含量Lignin content | -0.775 | 0.026 |
| 半纤维素降解速率Hemicellulose degradation rate | -0.278 | 0.918 |
| 温度Temperature | -0.362 | 0.898 |
| 纤维素降解速率Cellulose degradation rate | 0.621 | 0.690 |
| [1] | 中华人民共和国国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴[J]. 北京:中国统计出版社, 2021. |
| National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook[J]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2021. | |
| [2] | 班婷, 郭兆峰, 马艳, 等. 新疆棉秸秆综合利用现状及基质化利用发展前景[J]. 农业工程, 2019, 9(10):59-65. |
| BAN Tin, GUO Zhaofeng, MA Yan, et al. Comprehensive utilization present situation and culture medium utilization prospects of cotton straw in Xinjiang[J]. Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 9(10):59-65. | |
| [3] | 刘艳慧, 王双磊, 李金埔, 等. 棉花秸秆还田对土壤速效养分及微生物特性的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(7):1037-1046. |
|
LIU Yanhui, WANG Shuanglei, LI Jinpu, et al. Effects of cotton straw returning on soil available nutrients and microbial characteristics[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(7):1037-1046.
DOI URL |
|
| [4] |
Perez J, Munoz D J, Rubia D L T, et al. Biodegradation and biological trearments of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin: an overview[J]. International Microbiology, 2002, 5(2):53-63.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Mei J, Shen X, Gang L, et al. A novel lignin degradation bacteria-Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SL-7 used to degrade straw lignin efficiently[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 310:123445.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
杨朝元, 刘国涛, 李伟雨, 等. 堆肥化过程木质素降解和腐殖质形成的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(2):148-154.
DOI |
|
YANG Chaoyuan, LIU Guotao, LI Weiyu, et al. Research on lignin degradation and humus formation during composting[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(2):148-154.
DOI |
|
| [7] | Gonzalo D, Gonzalo C C. Bacterial enzymes involved in lignin degradation[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2016,(236):110-119. |
| [8] | Falade A O, Nwodo U U, Iweriebor B C, et al. Lignin peroxidase functionalities and prospective applications[J]. Microbiology Open, 2017, 6(1):1-14. |
| [9] | 米兴旺, 王学强, 何萌, 等. 不同农业废弃物发酵复配番茄栽培基质研究[J]. 农业科技与信息, 2021,(4):24-27, 30. |
| MI Xingwang, WANG Xueqiang, HE Meng, et al. Study on tomato culture substrate mixed with fermentation of different agricultural wastes[J]. Agricultural Science- technology and Information, 2021,(4):24-27, 30. | |
| [10] | 李林, 郭红艳, 孙晓杰, 等. 利用大豆秸杆和玉米秸秆栽培灵芝[J]. 食用菌学报, 2021, 28(4):15-19. |
| LI Lin, GUO Hongyan, SUN Xiaojie, et al. Cultivation of ganoderma lucidum with soybean and corn straw[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2021, 28(4):15-19. | |
| [11] | You H X, Yu L Z. Rganic substrate application in vegetable seedling raising in China[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology, 2017, 18(2):353-356. |
| [12] | 李洪涛, 王涵, 臧翔云, 等. 堆肥过程中纤维素酶活与纤维素降解相关研究[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2016, 47(6):33-40. |
| LI Hongtao, WANG Han, ZANG Xiangyun, et al. Correlation study on cellulose activities and lignocelluloses degradation during composting[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2016, 47(6):33-40. | |
| [13] | Liu H, Zhang L, Sun Y, et al. Degradation of lignocelluloses in straw using AC-1, a thermophilic composite microbial system[J]. PeerJ 9, 2021, 9(12364):1-13. |
| [14] | Kausar H, Ismail M R, Saud H M, et al. Use of lignocellulolytic mi-crobial consortium and pH amendment on composting efficacy of rice straw[J]. Com-post Sci. Util, 2013, (21):121-133. |
| [15] | Jorge M, Carlos M M, Luis O, et al. Influence of saprophytic fungi and inorganic additives on enzyme activities and chemical properties of the biodegradation process of wheat straw for the production of organo-mineral amendments[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 255(10922):1-10. |
| [16] | Oates N C, Abood A, Schirmacher A M, et al. A multi-omics approach to lignocellulolytic enzyme discovery reveals a new ligninase activity from Parascedosporium putredinis NO1[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2021, 118(18):1-10. |
| [17] | 赵清泉, 池玉杰, 张健, 等. 偏肿革裥菌降解木质素关键基因挖掘[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2019, 47(6):79-83. |
| ZHAO Qingquan, CHI Yujie, ZHANG Jian, et al. Key Genes of Lignin Degradation by Lenzites gibbosa[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2019, 47(6):79-83. | |
| [18] |
陈建军, 刘梁涛, 曹香林. 黄孢原毛平革菌漆酶基因lac1680的克隆、表达及产酶研究[J]. 生物技术通报, 2018,(4):214-220.
DOI |
|
CHEN Jianjun, LIU Liangtao, CAO Xianglin. Cloning, Expression and enzyme production of laccase gene lac1680 in Phanerochaete chrysosporium[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2018,(4):214-220.
DOI |
|
| [19] | Kuppuraj S P, Venkidasamy B, Selvaraj D, et al. Comprehensive in silico and gene expression profiles of MnP family genes in Phanerochaete chrysosporium towards lignin biodegradation[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2021, (157):1-10. |
| [20] | 徐龙乾, 文湘华, 丁杭军. 木质素过氧化物酶在球型介孔材料上的固定化特性研究[J]. 环境科学, 2010, 31(10):2493-2499. |
| XU Longqian, WEN Xianghua, DING Hangjun. Immobilization of Lignin Peroxidase on Spherical Mesoporous Material[J]. Environmental Science, 2010, 31(10):2493-2499. | |
| [21] |
Li X, Zheng Y. Lignin-enzyme interaction: Mechanism, mitigation approach, modeling, and research prospects[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2017, 35(4):466-489.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | NY-T34942019.农业生物质原料纤维素、 半纤维素、木质素测定[S]. |
| NY-T34942019 Agricultural biomass raw materials- Determination of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin[S]. | |
| [23] | Wariishi H, Vallis K, Gold M H. Manganese(I1) Oxidation by Manganese Peroxidase from the Basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1992, 267(33):23689-23695. |
| [24] | John G, Holt, Noel R, et al. Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology (9th Ed.)[M]. USA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1994. |
| [25] | Tien M, Kirk T K, Lignin peroxidase of Phanerochaete Cherysosporium[J]. Meth Enzymology, 1988,(161):238-249. |
| [26] | 蔡涵冰, 冯雯雯, 董永华, 等. 畜禽粪便和桃树枝工业化堆肥过程中微生物群演替及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(2):997-1003. |
| CAI Hanbing, FENG Wenwen, DONG Yonghua, et al. Microbial community succession in industrial composting with livestock manure and peach branches and relations with environmental factors[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(2):997-1003. | |
| [27] | Zhang X M, Zhu Y, Li J L, et al. Exploring dynamics and associations of dominant lignocellulose degraders in tomato stalk composting[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, (294):1-12. |
| [28] |
Kang J, Yuan Z Z, Feng L, et al. Microbial succession law during the composting process of various livestock and poultry manures[J]. Journal of Biobased Materials and Bioenergy, 2019, 13(5):732-738.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Zhu N, Zhu Y Y, Kan Z X, et al. Effects of two-stage microbial inoculation on organic carbon turnover and fungal community succession during co-composting of cattle manure and rice straw[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021,(341):1-8. |
| [30] | Tha B, Xw A, Lz B, et al. Effects of inoculating with lignocellulose-degrading consortium on cellulose degrading genes and fungal community during co-composting of spent mushroom substrate with swine manure[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019,(291):121876. |
| [31] | Wei Y Q, Wu D, Wei D, et al. Improved lignocellulose-degrading performance during straw composting from diverse sources with actinomycetes inoculation by regulating the key enzyme activities[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, (271):66-74. |
| [32] | Ezzariai A, Hafidi M, Khadra A, et al. Human and veterinary antibiotics during composting of sludge or manure: Global perspectives on persistence, degradation, and resistance genes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, (359):465-481. |
| [33] | 王景, 陈曦, 魏俊岭. 水稻秸秆和玉米秸秆在好气和厌氧条件下的腐解规律[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2017, 34(1):59-65. |
| WANG Jing, CHEN Xi, WEI Junling. Decomposition of rice straw and corn straw under aerobic and anaerobic conditions[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2017, 34(1):59-65. | |
| [34] | Munster J M, Daly P, Delmas S, et al. The role of carbon starvation in the induction of enzymes that degrade plant-derived carbohydrates in Aspergillus Niger[J]. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 2014, (72):34-47. |
| [35] | Bohacz J, Korniłłowicz K T. Changes in enzymatic activity in composts containing chicken feathers[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2009, (100):3604-3612. |
| [36] |
Strom P F. Effect of temperature on bacterial species diversity in thermophilic solid-waste composting[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1985, 50(4):899-905.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Goyal S, Dhull S K, Kapoor K K. Chemical and biological changes during composting of different organic wastes and assessment of compost maturity[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2005, 96(14):1584-1591.
PMID |
| [38] | Bohacz J. Lignocellulose-degrading enzymes, free-radical transformations during composting of lignocellulosic waste and biothermal phases in small-scale reactors[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017,(580):744-754. |
| [39] | Volchatova I V, Belovezhets L A, Medvedeva S A. Microbiological and biochemical investigation of succession in lignin-containing compost piles[J]. Microbiology, 2002,(71):467-470. |
| [40] | Chefetz B, Kerem Z, Chen Y, et al. Isolation and partial characterization of laccase from a thermophilic composted municipal solid waste[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 1998,(30):1091-1098. |
| [41] | 杨晔. 木质素降解酶研究进展[J]. 农业工程, 2014, 4(4):48-51. |
| YANG Ye. Review on lignin degradation enzyme[J]. Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 4(4):48-51. | |
| [42] | 赵秀云, 赵昕宇, 杨津津, 等. 堆肥过程中木质素的降解机理及影响因素研究进展[J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(6):128-136. |
| ZHAO Xiuyun, ZHAO Xinyu, YANG Jinjin, et al. Research progress on lignin degradation mechanism and influencing factors during composting[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2021, 39(6):128-136. | |
| [43] | Zeng G, Yu M, Chen Y, et al. Effects of inoculation with Phaneroachete chrysosporiumat various time points on enzyme activities during agricultural waste composting[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010,(101):222-227. |
| [44] | Mikiashvili N, Wasser S P, Nevo E, et al. Effects of carbon and nitrogen sources on Pleurotus ostreatus ligninolytic enzyme activity[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2006,(22):999-1002. |
| [45] | D'Agostini E C, D'Agostini M T R, Silveira D V J, et al. Low carbon/nitrogen ratio increases laccase produc-tion from basidiomycetes in solid substrate cultivation[J]. Scientia Agricola (Piracicaba, Braz.), 2011, 68(3): 295-300. |
| [1] | ZENG Wanying, GENG Hongwei, CHENG Yukun, LI Sizhong, QIAN Songting, GAO Weishi, ZHANG Liming. Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance during the rapid growth stage of sugar beet cultivars [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2140-2151. |
| [2] | HU Huabing, SUN Linlin, LIU Jianxiong, HE Biwei, LIU Xun, HUAN Tin, LI Youfang. Correlation analysis of sugar accumulation and temperature in sugar beet under drip irrigation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1916-1925. |
| [3] | YE Pingyi, LONG Yilei, TANG Yanping, DU Xiao, AN Mengjie, TAO Zhixin, LIANG Farui, AI Xiantao, HU Shoulin. Identification and evaluation of fruit branch angle and machine-picked agronomic traits in Gossypium hirsutum L. [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1318-1327. |
| [4] | Mahemuti Abulaiti, Muhetaer zhare, Mireguli Waili, Hadier Yishake. Correlation and regression analysis between leaf margin scorch diseases and leaf nutrient content of walnut [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 945-953. |
| [5] | LI Xiaojuan, ZHAO Wenju, GA Sang, DENG Changrong, ZHAO Mengliang, REN Yanjing. Analysis of turnip nutrient at different altitudes [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(3): 652-664. |
| [6] | WANG Jijiao, PAN Yue, WANG Shiwei, HAN Zhengwei, MA Yong, HU Haifang, WANG Baoqing. Canonical correlation analysis of soil nutrients and the quality of Beibinghong grape juice [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(2): 355-364. |
| [7] | YANG Cunming, ZHANG Xiaoxue, ZHANG Menghua, ZHAO Zhiwen, LI Fengjie, HUANG Xixia, LI Jie, Aizimaiti Awuti, HE Junmin, LI Xue, LI Tingting, TANG Li, ZHANG Wenjing, TIAN Yuezhen, TIAN Kechuan. Analysis of correlation and difference of target traits in fine wool sheep breeding [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(2): 514-520. |
| [8] | MA Yuejun, TAN Zhanming, CHENG Yunxia, WU Hui, ZHANG Qiaoqiao, DU Jiageng, WANG Qi, CUI Hewei, MA Xing. Effects of different matrix ratios and anvil combinations on cucumber growth and development [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2635-2647. |
| [9] | OUYANG Danhua, ZHAO Kang, SONG Dongbo, LIU Ziqing, GUO Wangzhen, LIU Yan, GU Aixing, Azhatiguli Maimaitituer, Alikaerjiang Amaier. Identification and comprehensive analysis of Verticillium wilt resistance in 35 cotton strains [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(1): 9-18. |
| [10] | WANG Peng, ZHENG Kai, ZHAO Jieyin, GAO Wenju, LONG Yilei, CHEN Quanjia, QU Yanying. Evaluation and index screening of heat resistance of Gossypium hirsutum germplasm resources [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2081-2090. |
| [11] | ZHAO Lianjia, LI Gan, XU Lin, YAN Guorong, LIU Ning, WANG Fan, DENG Chaohong, Abudukeyoumu Abudurezike, WANG Cong, WANG Wei. Analysis of the main characters of soybean varieties in Xinjiang and their correlation with yield [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(7): 1663-1670. |
| [12] | HUANG Qiannan, Maerheba Aisibaier, ZOU Hui, WANG Cairong, Ailimaimaiti Kuerban, SUN Na, LEI Junjie. Genetic diversity of main agronomic traits in Xinjiang winter wheat germplasm resources [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(5): 1050-1058. |
| [13] | SANG Zhiwei, LIANG Yajun, GONG Zhaolong, ZHENG Juyun, WANG Junduo, LI Xueyuan, CHEN Quanjia. Analysis of mechanical harvesting characters of germplasm resources of different upland cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(5): 1088-1098. |
| [14] | LU Tao, ZENG Qingtao, ZHANG Wen, WANG Wenbo, WANG Zhengyang, YANG Rui, SUN Yuyan. Comprehensive evaluation of cotton yield and quality by principal component analysis and grey correlation analysis [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(5): 1099-1109. |
| [15] | LI Shuo, WANG Juan, Nigary Yadikar, ZHU Jinfang, FENG Zuoshan, Parhat Ainiwaer. Functional components changes of different apricot cultivars in different development stages [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(5): 1200-1207. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 65
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 281
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||