

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (5): 1041-1049.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.05.001
• Special volume for green, yield increasing, quality improving and eficiencyimproving technologies for major grain crops in Xinjiang • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Yanhong1( ), HOU Tianyu1, BA Yinhua1, ZHAO Caiyue1, LYU Yuping2, Buhalikeimu Abunzi1, ZHAO Zhiqiang1, LI Dong2, DU Xiaojing2, YUAN Jie1, WANG Fengbin2(
), HOU Tianyu1, BA Yinhua1, ZHAO Caiyue1, LYU Yuping2, Buhalikeimu Abunzi1, ZHAO Zhiqiang1, LI Dong2, DU Xiaojing2, YUAN Jie1, WANG Fengbin2( )
)
Received:2022-09-05
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-05-22
Correspondence author:
WANG Fengbin (1968-), male, born in Jiangxi Province, master degree, researcher, engaged in rice genetic breeding and cultivation technology, (E-mail)Supported by:
张燕红1( ), 侯天钰1, 巴音花1, 赵彩月1, 吕玉平2, 布哈丽且木·阿不力孜1, 赵志强1, 李冬2, 杜孝敬2, 袁杰1, 王奉斌2(
), 侯天钰1, 巴音花1, 赵彩月1, 吕玉平2, 布哈丽且木·阿不力孜1, 赵志强1, 李冬2, 杜孝敬2, 袁杰1, 王奉斌2( )
)
通讯作者:
王奉斌(1968-),男,江西人,研究员,硕士,研究方向为水稻遗传育种及栽培,(E-mail)作者简介:张燕红(1982-),女,甘肃武威人,副研究员,研究方向为水稻遗传育种,(E-mail)zhangyanhong9527@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHANG Yanhong, HOU Tianyu, BA Yinhua, ZHAO Caiyue, LYU Yuping, Buhalikeimu Abunzi, ZHAO Zhiqiang, LI Dong, DU Xiaojing, YUAN Jie, WANG Fengbin. Identification and evaluation of salt tolerance of rice recombinant inbred lines at bud and seedling stages[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(5): 1041-1049.
张燕红, 侯天钰, 巴音花, 赵彩月, 吕玉平, 布哈丽且木·阿不力孜, 赵志强, 李冬, 杜孝敬, 袁杰, 王奉斌. 水稻重组自交系群体芽期和苗期耐盐性鉴定与评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(5): 1041-1049.
| 评价级别 Rating | 耐盐指数 Salt tolerant coefficient | 耐盐性 Salt tolerant ability |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ≤20 | 高耐 |
| 3 | 20.1~40.0 | 耐盐 |
| 5 | 40.1~60.0 | 中 |
| 7 | 60.1~80.0 | 敏感 |
| 9 | 80.1~100.0 | 高敏 |
Tab.1 Salt tolerance evaluation criteria of rice during germination
| 评价级别 Rating | 耐盐指数 Salt tolerant coefficient | 耐盐性 Salt tolerant ability |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ≤20 | 高耐 |
| 3 | 20.1~40.0 | 耐盐 |
| 5 | 40.1~60.0 | 中 |
| 7 | 60.1~80.0 | 敏感 |
| 9 | 80.1~100.0 | 高敏 |
| 评价级别 Rating | 盐害症状 Symptoms of salt damage | 耐盐性 Salt tolerant ability |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 生长分蘖基本正常,叶片无受害症状 | 高耐 |
| 3 | 生长分蘖近正常,但叶尖或上部叶片1 /2发 白或卷曲;或生长分蘖受抑制,有些叶片卷曲 | 耐盐 |
| 5 | 生长分蘖严重抑制,多数叶片卷曲, 仅少数叶片伸长 | 中 |
| 7 | 生长分蘖停止,多数叶片干枯 | 敏感 |
| 9 | 植株死亡或接近死亡 | 高敏 |
Tab.2 Salt tolerance evaluation criteria at seedling stage of rice
| 评价级别 Rating | 盐害症状 Symptoms of salt damage | 耐盐性 Salt tolerant ability |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 生长分蘖基本正常,叶片无受害症状 | 高耐 |
| 3 | 生长分蘖近正常,但叶尖或上部叶片1 /2发 白或卷曲;或生长分蘖受抑制,有些叶片卷曲 | 耐盐 |
| 5 | 生长分蘖严重抑制,多数叶片卷曲, 仅少数叶片伸长 | 中 |
| 7 | 生长分蘖停止,多数叶片干枯 | 敏感 |
| 9 | 植株死亡或接近死亡 | 高敏 |
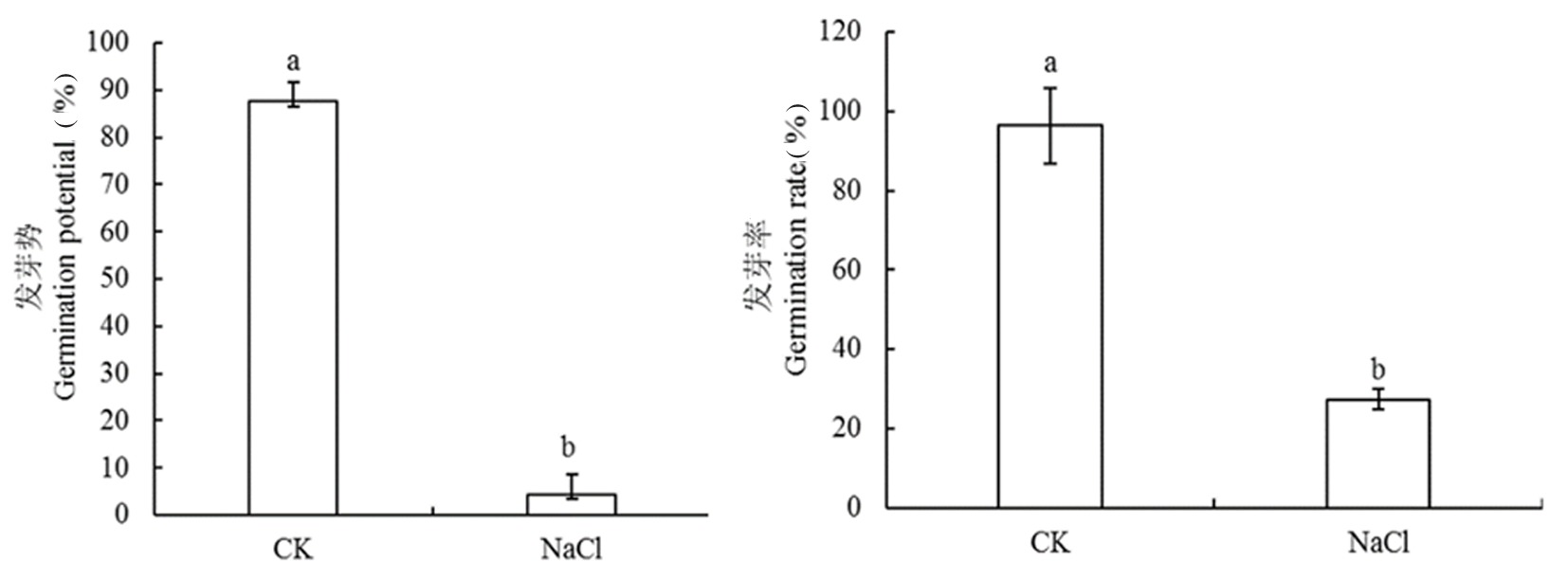
Fig.1 Comparison of germination potential and germination rate of population materials under different treatments Note: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in the same material under different treatments (P<0.05), the same as below
| 性状 Trait | 处理 Treatment | 平均值 Mean | 最大值 Max | 最小值 Min | 极差 Range | 标准差 SD | 变异系数 CV(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 发芽势 Germination potential (%) | CK | 87.9 | 99.2 | 31.4 | 67.8 | 10.5 | 11.9 |
| NaCl | 4.5 | 66.3 | 0.0 | 66.3 | 7.5 | 169.2 | |
| 相对发芽势 Relative germination potential(%) | 4.9 | 68.5 | 0.0 | 68.5 | 8.0 | 163.8 | |
| 发芽率 Germination rate (%) | CK | 96.8 | 99.4 | 82.2 | 17.2 | 3.1 | 3.2 |
| NaCl | 27.4 | 92.2 | 0.0 | 92.2 | 19.4 | 70.8 | |
| 相对发芽率 Relative germination rate(%) | 28.2 | 93.1 | 0.0 | 93.1 | 19.8 | 70.3 | |
| 发芽势相对盐害率 Germination potential relative salt damage rate(%) | 73.9 | 100.0 | 32.0 | 68.0 | 8.0 | 16.7 | |
| 发芽率相对盐害率 Germination rate relative to salt damage rate(%) | 48.1 | 98.3 | 21.3 | 78.7 | 18.2 | 24.7 |
Tab.3 Seedling stage traits of 219 rice population materials under salt stress
| 性状 Trait | 处理 Treatment | 平均值 Mean | 最大值 Max | 最小值 Min | 极差 Range | 标准差 SD | 变异系数 CV(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 发芽势 Germination potential (%) | CK | 87.9 | 99.2 | 31.4 | 67.8 | 10.5 | 11.9 |
| NaCl | 4.5 | 66.3 | 0.0 | 66.3 | 7.5 | 169.2 | |
| 相对发芽势 Relative germination potential(%) | 4.9 | 68.5 | 0.0 | 68.5 | 8.0 | 163.8 | |
| 发芽率 Germination rate (%) | CK | 96.8 | 99.4 | 82.2 | 17.2 | 3.1 | 3.2 |
| NaCl | 27.4 | 92.2 | 0.0 | 92.2 | 19.4 | 70.8 | |
| 相对发芽率 Relative germination rate(%) | 28.2 | 93.1 | 0.0 | 93.1 | 19.8 | 70.3 | |
| 发芽势相对盐害率 Germination potential relative salt damage rate(%) | 73.9 | 100.0 | 32.0 | 68.0 | 8.0 | 16.7 | |
| 发芽率相对盐害率 Germination rate relative to salt damage rate(%) | 48.1 | 98.3 | 21.3 | 78.7 | 18.2 | 24.7 |
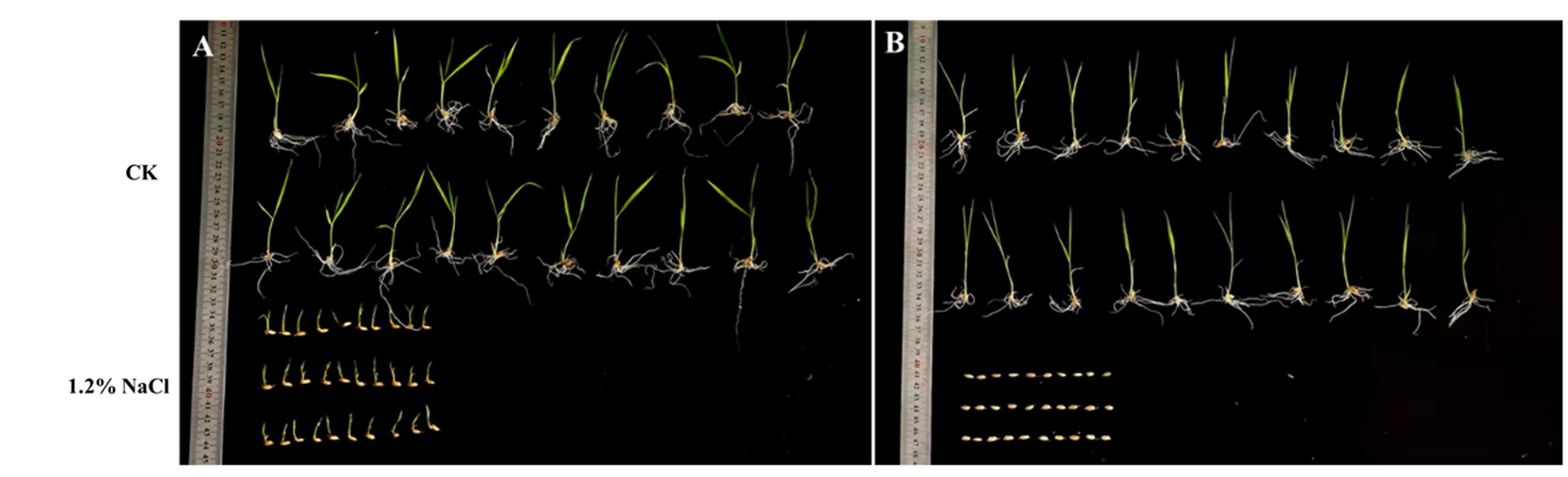
Fig.4 Comparison of growth conditions of salt-tolerant and sensitive materials under different treatments Note:A: salt-resistant material, B: sensitive material, the same as below
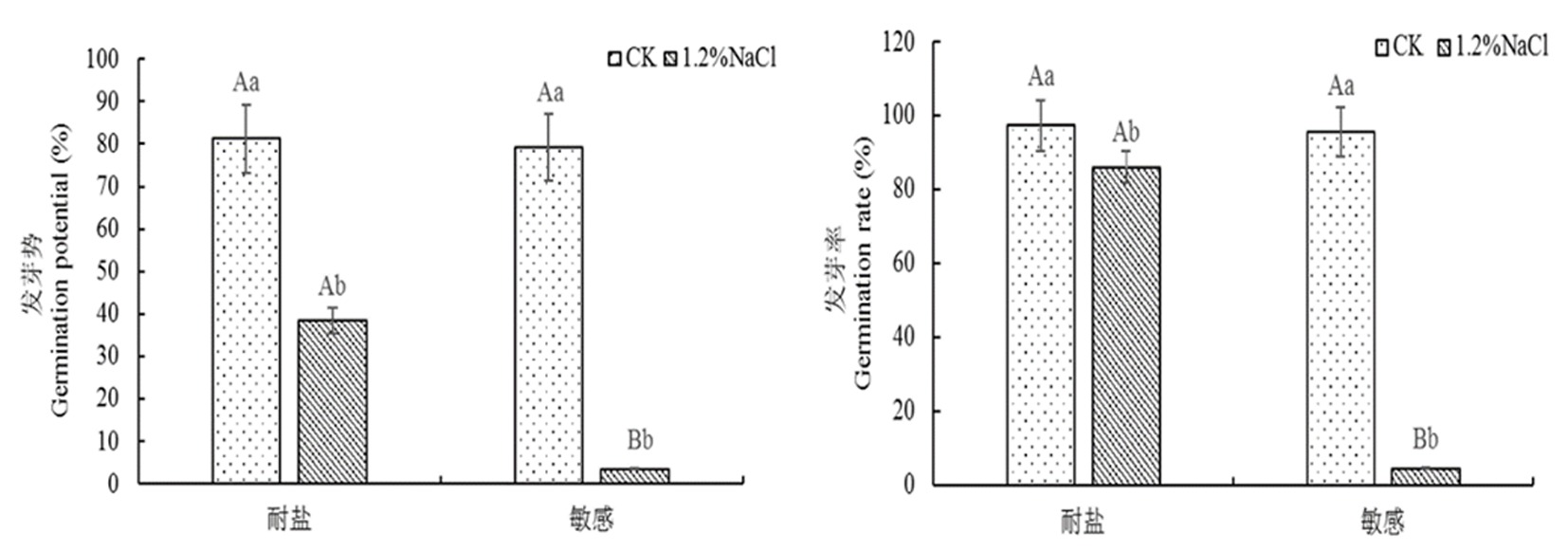
Fig.5 Comparison of germination potential and germination rate of different salt-tolerant materials under salt stress Note: The same uppercase letter means significant difference between different materials under the same treatment, and different lowercase letter means significant difference between the same materials under different treatment (P<0.05), the same as below
| [1] | 赵可夫, 范海. 盐生植物及其对盐渍生境的适应生理[M]. 北京: 科学技术出版社, 2005. |
| ZHAO Kefu, FAN Hai. Halophytes and Their Adaptive Physiology to Saline Habitat[M]. Beijing: Science and Technology Press, 2005. | |
| [2] |
宋志平, 陈家宽, 赵耀. 水稻驯化与长江文明[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(4): 346-356.
DOI |
|
SONG Zhiping, CHEN Jiakuan, ZHAO Yao. Rice domestication and Yangtze River Civilization[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2018, 26(4): 346-356.
DOI |
|
| [3] | 邵华伟, 孙九胜, 胡伟, 等. 新疆盐碱地分布特点和成因及改良利用技术研究进展[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2014,(11):160-164. |
| SHAO Huawei, SUN Jiusheng, HU Wei, et al. Research progress on distribution characteristics, causes and improved utilization technology of saline-alkali land in Xinjiang[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2014,(11):160-164. | |
| [4] | 方先文, 汤陵华, 王艳平. 耐盐水稻种质资源的筛选[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2004, 5(3):295-298. |
| FANG Xianwen, TANG Linhua, WANG Yanping. Screening of salt-tolerant rice Germplasm resources[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2004, 5(3):295-298. | |
| [5] |
WANG Z F, WANG J F, BAO Y M, et al. Quantitative trait loci controlling rice seed germination under salt stress[J]. Euphytica, 2011, 178(3): 297-307.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
肖文斐, 马华升, 陈文岳, 等. 籼稻耐盐性与稻米品质性状的关联分析[J]. 核农学报, 2013, 27(12): 1938-1947.
DOI |
| XIAO Wenfei, MA Huasheng, CHEN Wenyue, et al. Correlation analysis of salt tolerance and rice quality characters in indica rice[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agriculture, 2013, 27(12): 1938-1947. | |
| [7] | 谢留杰, 段敏, 潘晓飚, 等. 不同类型水稻品系苗期和全生育期耐盐性鉴定与分析[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2015, 37(3):404-410. |
| XIE Liujie, DUAN Min, PAN Xiaobiao, et al. Identification and analysis of salt tolerance of different rice strains at seedling stage and whole growth stage[J]. Journal of Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2015, 37(3): 404-410. | |
| [8] |
WANG Z F, WANG J F, BAO Y M, et al. Inheritance of rice seed germination ability under salt stress[J]. Rice Science, 2010, 17(2): 105-110.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
CHEN D F, LI Y L, FANG T, et al. Specific roles of tocopherols and tocotrienols in seed longevity and germination tolerance to abiotic stress in transgenic rice[J]. Plant Science, 2016, 244: 31-39.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | 夏秀忠, 张宗琼, 杨行海, 等. 广西地方稻种资源核心种质的耐盐性鉴定评价[J]. 南方农业学报, 2017, 48(6): 979-984. |
| XIA Xiuzhong, ZHANG Zongqiong, YANG Xinhai, et al. Identification and evaluation of salt tolerance of core germplasm of local rice seed resources in Guangxi[J]. Journal of Southern Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 48(6): 979-984. | |
| [11] |
田蕾, 陈亚萍, 刘俊, 等. 粳稻种质资源芽期耐盐性综合评价与筛选. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(6): 631-642.
DOI |
|
TIAN Lei, CHEN Yaping, LIU Jun, et al. Comprehensive evaluation and screening of salt tolerance at bud stage of japonica rice germplasm resources[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(6): 631-642.
DOI |
|
| [12] |
Khan M.A., Abdullah Z. Salinity-sodicity induced changes in reproductive physiology of rice (Oryza sativa) under dense soil conditions[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2003, 49(2): 145-157.
DOI URL |
| [13] | LEE S Y, AHN J H, CHA Y S, et al. Mapping QTLs related to salinity tolerance of rice at the young seedling stage[J]. Plant Breeding, 2007. |
| [14] | 张燕红, 袁杰, 王奉斌. 不同新疆水稻品种种子发芽耐盐性的比较[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2009, 15(3): 102-103. |
| ZHANG Yanhong, YUAN Jie, WANG Fengbin. Comparison of seed germination salt tolerance of different Xinjiang rice varieties[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2009, 15(3): 102-103. | |
| [15] | 赵红, 徐芬芬, 熊安琪, 等. 不同种类盐胁迫对水稻种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 分子植物育种, 2021, 19(17): 5842-5847. |
| ZHAO Hong, XU Fenfen, XIONG Anqi, et al. Effects of different kinds of salt stress on seed germination and seedling growth of rice[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(17): 5842-5847. | |
| [16] | 朱丽伟, 曹栋栋, 付玉营, 等. 可溶性寡糖和小分子的热激蛋白与杂交水稻种子成熟过程中发芽能力及种子活力相关[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(5): 714-724. |
| ZHU Liwei, CAO Dongdong, FU Yuying, et al. Soluble oligo saccharides and small molecular heat shock proteins were associated with germination ability and seed vigor during the maturation of hybrid rice seeds[J]. Crops, 2016, 42(5): 714-724. | |
| [17] | 鱼小军, 肖红, 徐长林, 等. 扁蓿豆和苜蓿种子萌发期抗旱性和耐盐性比较[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2015, 16(2): 405-410. |
| YU Xiaojun, XIAO Hong, XU Changlin, et al. Comparison of drought resistance and salt tolerance of seeds of Ruthenica ruthenica and alfalfa during germination[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2015, 16(2): 405-410. | |
| [18] | 李振, 廖同庆, 冯青春. 基于图像处理技术的黄瓜种子活力指数检测系统设计[J]. 种子, 2015, 34(6): 111-115. |
| LI Zhen, LIAO Tongqin, FENG Qinchun. Design of cucumber seed vigor index detection system based on image processing technology[J]. Seed, 2015, 34(6): 111-115. | |
| [19] | 郑崇珂, 张治振, 周冠华, 等. 不同水稻品种发芽期耐盐性评价[J]. 山东农业科学, 2018, 50(10):38-42. |
| ZHENG Chongke, ZHANG Zhizhen, ZHOU Guanhua, et al. Evaluation of salt tolerance of different rice varieties at germination stage[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 50(10):38-42. | |
| [20] | 郭望模, 傅亚萍, 孙宗修, 等. 盐胁迫下不同水稻种质形态指标与耐盐性的相关分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2003, 4(3): 245-251. |
| GUO Wangmo, FU Yaping, SUN Zongxiu, et al. Correlation analysis of morphological indexes and salt tolerance of different rice germplasm under salt stress[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2003, 4(3): 245-251. | |
| [21] |
肖文斐, 马华升, 陈文岳, 等. 籼稻耐盐性与稻米品质性状的关联分析[J]. 核农学报, 2013, 27(12): 1938-1947.
DOI |
| XIAO Wenfei, MA Hhuasheng, CHEN Wenyue, et al. Association analysis between salt tolerance and rice quality in indica rice[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agronomy, 2013, 27(12): 1938-1947. | |
| [22] | 贾宝艳, 周婵婵, 孙晓雪, 等. 辽宁省水稻种质资源的耐盐性鉴定评价[J]. 作物杂志, 2013, 4: 57-62. |
| JIA Baoyan, ZHOU Chanchan, SUN Xiaoxue, et al. Evaluation of salt tolerance of rice germplasm resources in Liaoning Province[J]. Crops Journal, 2013, 4: 57-62. | |
| [23] | 崔江慧, 谢登磊, 常金华. 高粱材料耐盐性综合评价方法的初步建立与验证[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2012, 13(1): 35-41. |
| CUI Jianghui, XIE Denglei, CHANG Jinhua. Preliminary establishment and verification of a comprehensive evaluation method for salt tolerance of sorghum materials[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2012, 13(1): 35-41. | |
| [24] | 张治振, 李稳, 周起先, 等. 不同水稻品种幼苗期耐盐性评价[J]. 作物杂志, 2020, (3): 92-101. |
| ZHANG Zhizhen, Li Wen, ZHOU Qixian, et al. Evaluation of salt tolerance of different rice varieties at seedling stage[J]. Crops, 2020, (3): 92-101. | |
| [25] | 刘佳音, 邵晓宇, 邹丹丹, 等. 水稻耐盐碱鉴定方法及评价指标研究进展[J]. 杂交水稻, 2019, 34(6): 1-6. |
| LIU Jiayin, SHAO Xiaoyu, ZOU Dandan, et al. Research progress on methods and evaluation indexes of salt and alkali tolerance of rice[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2019, 34(6): 1-6. | |
| [26] |
吴家富, 杨博文, 向珣朝, 等. 不同水稻种质在不同生育期耐盐鉴定的差异[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(1): 77-88.
DOI |
|
WU Jiafu, YANG Bowen, XIANG Xunchao, et al. Differences in salt tolerance of different rice germplasm at different growth stages[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2017, 52(1): 77-88.
DOI URL |
|
| [27] | 马帅国, 田蓉蓉, 胡慧, 等. 粳稻种质资源苗期耐盐性综合评价与筛选[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2020, 21(5): 1089-1101. |
| MA Shuaiguo, TIAN Rongrong, HU Hui, et al. Comprehensive evaluation and screening of salt tolerance of japonica rice germplasm resources at seedling stage[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2020, 21(5): 1099-1101. |
| [1] | WANG Chao, XU Wenxiu, LI Pengcheng, ZHENG Cangsong, SUN Miao, FENG Weina, SHAO Jingjing, DONG Helin. Response of cotton seedling growth and development to soil available potassium levels [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2132-2139. |
| [2] | ZENG Wanying, GENG Hongwei, CHENG Yukun, LI Sizhong, QIAN Songting, GAO Weishi, ZHANG Liming. Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance during the rapid growth stage of sugar beet cultivars [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2140-2151. |
| [3] | ZHANG Fan, CHEN Xiaolu, WANG Jie, HOU Xianfei, JIA Donghai, GU Yuanguo, MIAO Haocui, LI Qiang. Effects of mixed salt stress on seed germination and seedling growth of peanut seed [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2168-2182. |
| [4] | LIU Jing, DU Mingchuan, ZHANG Wenting, BAO Haijuan, JING Meiling, DU Wenhua. Screening of triticale germplasm in different areas of Qinghai [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2183-2190. |
| [5] | CHEN Yong, ZHOU Lei, SUI Chun, LIN Caixia. The characteristics of 32 cultivated germplasms of Isatis tinctoria Linnaeus in Xinjiang production area [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2307-2314. |
| [6] | DONG Zhiduo, XU Fei, FU Qiuping, HUANG Jian, QI Tong, MENG Ajing, FU Yanbo, Kaisaier Kuerban. Effects of different types of salt and alkali stress on cotton seed germination [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1831-1844. |
| [7] | ZHAO Minhua, SONG Bingxi, ZHANG Yupeng, GAO Zhihong, ZHU Yongyong, CHEN Xiaoyuan. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer reduction on rice yield and nitrogen partial factor productivity under dry farming conditions [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1907-1915. |
| [8] | LIU Huijie, WANG Junhao, GONG Zhaolong, LIANG Yajun, WANG Junduo, LI Xueyuan, ZHENG Juyun, WANG Jichuan. Identification of salt tolerance of 197 upland cotton varieties at germination stage [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1574-1581. |
| [9] | YAO Qing, WANG Jiehua, Xiernayi Abudula, Dilimulati Tulahong, CUI Hongliang. Physiological responses of different quinoa varieties during seedling stage under low temperature stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1597-1604. |
| [10] | Abudukadier Kurban, PAN Jinghai, CHEN Youqiang, LIU Huajun, DONG Xinjiu, BAI Xiaoshan, LI Sizhong, GAO Weishi, LI Xiaohui. Comprehensive evaluation of adaptability of late sowing sugar-beet varieties based on yield correlation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1368-1377. |
| [11] | YANG Junyan, YAN Miao, WU Haibo, YANG Wenli, WANG Haojie, MAO Jiancai, ZHAI Wenqiang, LI Junhua. The impact of high temperature on different thick -skinned melon varieties and comprehensive evaluation of its heat resistance [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1386-1396. |
| [12] | ZHU Tao, Lei Qingyuan, MA Liang. Effects of water and nitrogen on growth, yield and water and nitrogen utilization efficiency of resown Maize and verification of scheme optimization model [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 835-844. |
| [13] | QIAN Tao, WU Lili, LI Lei, Anniwaer Kuerban, DING Ruifeng. Control effect of pyroxasulfone mixed with pendimethalin on broadleaf weeds in cotton filed and its safety evaluation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 861-868. |
| [14] | ZHANG Jiatuo, SONG Zhanteng, Maerhaba Paerhati, LI Jing, WANG Hui, ZHANG Ruili, ZHU Jingrong. Nutritional quality analysis and comprehensive evaluation of different chamagu(Brassica rapa L.) varieties [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 926-936. |
| [15] | KANG Mintai, DU Xiaojing, ZHANG Yanhong, CHEN Yuhuan, WEN Xiaorong, TANG Fusen, ZHAO Zhiqiang, YUAN Jie, WANG Fengbin. Salt tolerance screening and fertility performance of rice varieties in saline areas of Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(3): 591-598. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 110
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 210
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||